Emodin from Aloe Inhibits Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus via Toll-Like Receptor 3 Activation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Virus and Virus Preparation
2.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis of Ae
2.3. CCK-8 Assay
2.4. PRRSV Infection and Drugs Treatment In Vitro
2.5. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Time Course Analysis of Emodin Anti-PRRSV
2.8. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.9. Direct Virion Inactivation Activity of Emodin Analysis
2.10. Activation of Signal Transduction Pathways by Emodin after PRRSV Infection
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
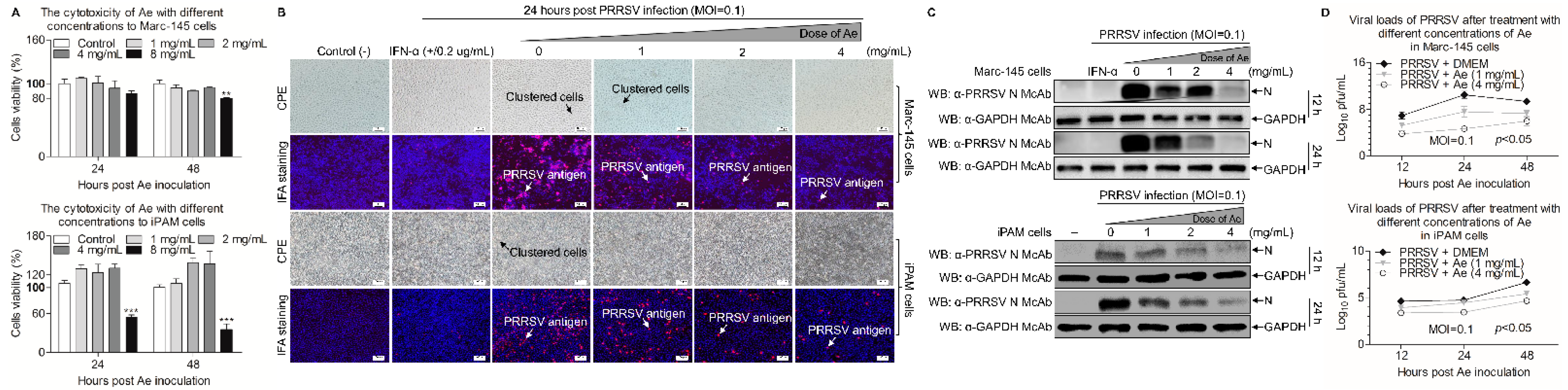
3.1. Ae Inhibits PRRSV Infection In Vitro
3.2. Emodin from Ae Inhibits PRRSV Infection In Vitro
3.3. Emodin Acts at Whole Stages the Replication Cycle of PRRSV
3.4. Viricidal Effect of Emodin on PRRSV Viral Particles
3.5. Emodin Stimulation of TLR3 Activation Might Contribute to Its Anti-PRRSV Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dea, S.; Gagnon, C.A.; Mardassi, H.; Prizadeh, B.; Rogan, D. Current knowledge on the structural proteins of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 659–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.; Ren, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Feng, W.H. Cryptoporus volvatus extract inhibits porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firth, A.E.; Zevenhoven-Dobbe, J.C.; Wills, N.M.; Go, Y.Y.; Balasuriya, U.B.R.; Atkins, J.F.; Snijder, E.J.; Posthuma, C.C. Discovery of a small arterivirus gene that overlaps the GP5 coding sequence and is important for virus production. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, E.J.; Meulenberg, J.J. The molecular biology of arteriviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 961–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.R.; Griggs, T.F.; Gnanandarajah, J.; Murtaugh, M.P. Novel structural protein in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus encoded by an alternative ORF5 present in all arteriviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Gao, L.; Si, J.; Sun, Y.; Liu, J.; Cao, L.; Feng, W.H. Inhibition of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus replication by flavaspidic acid AB. Antiviral Res. 2013, 97, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossow, K.D. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome. Vet. Pathol. 1998, 35, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Zeng, S.; Zou, C.; Zhang, H.; Peng, O.; Xue, C.; Cao, Y. Porcine TRIM21 RING-finger E3 ubiquitin ligase is essential for anti-PRRSV activity. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 256, 109043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Y.; Wu, C.; Gu, G.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhou, E.M. Improved vaccine against PRRSV: Current progress and future perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Bo, K.; Wang, X.; Tang, B.; Yang, B.; Jiang, W.; Jiang, P. Emergence of a highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in the Mid-Eastern region of China. Vet. J. 2007, 174, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreman, S.; McCaffrey, J.; Popma-de Graaf, D.J.; Nauwynck, H.; Savelkoul, H.F.J.; Moore, A.; Rebel, J.M.J.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N. Toll-like receptor agonists as adjuvants for inactivated porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) vaccine. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2019, 212, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Kang, I.; Kim, S.; Park, S.J.; Park, K.H.; Oh, T.; Yang, S.; Chae, C. A modified-live porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV)-1 vaccine protects late-term pregnancy gilts against heterologous PRRSV-1 but not PRRSV-2 challenge. Transbound Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, J.L.; Zuniga, S.; Becares, M.; Sola, I.; Ceriani, J.E.; Juanola, S.; Plana, J.; Enjuanes, L. Vectored vaccines to protect against PRRSV. Virus Res. 2010, 154, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; O’Connell, C.M.; Costa, A.; Pan, Y.; Smyth, J.A.; Verardi, P.H.; Burgess, D.J.; Van Kruiningen, H.J.; Garmendia, A.E. A PRRSV GP5-mosaic vaccine: Protection of pigs from challenge and ex vivo detection of IFNgamma responses against several genotype 2 strains. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0208801. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, T.; Kim, H.; Hwan, K.; Jiwoon, P.; Ikjae, J.; Siyeon, K.; Chanhee, Y.; Chae, C. Effectiveness of a commercial porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) subunit vaccine against heterologous PRRSV-1 and PRRSV-2 challenge in late-term pregnant gilts. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2019, 83, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Wang, M.; Zhu, Z.; He, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.; Shi, X.; Tang, T.; Yu, P.; Zeng, J.; et al. Highly efficient generation of pigs harboring a partial deletion of the CD163 SRCR5 domain, which are fully resistant to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 2 infection. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, E.; Wang, D.; Fang, L.; Ma, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, H.; Li, K.; Xiao, S. Suppression of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus proliferation by glycyrrhizin. Antiviral Res. 2015, 120, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, C. Antiviral mechanism of tea polyphenols against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Pathogens 2021, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.L. Natural products in drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, F.; Moshaverinia, M.; Motamedifar, M.; Alyaseri, M. Assessment of anti HSV-1 activity of aloe vera gel extract: An in vitro study. J. Dent. 2016, 17, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dziewulska, D.; Stenzel, T.; Śmiałek, M.; Tykałowski, B.; Koncicki, A. An evaluation of the impact of aloe vera and licorice extracts on the course of experimental pigeon paramyxovirus type 1 infection in pigeons. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansukh, E.; Gopal, J.; Paul, D.; Muthu, M.; Kim, D.-H.; Oh, J.-W.; Chun, S. Ultrasound mediated accelerated Anti-influenza activity of aloe vera. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, L.-J.; Huang, T.; Ying, J.-Q.; Li, J. The pharmacology, toxicology and therapeutic potential of anthraquinone derivative emodin. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 18, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zheng, N.; Liang, J.; Wang, Q.; Zu, X.; Wang, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, R.; Guo, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Emodin resists to cyprinid herpesvirus 3 replication via the pathways of Nrf2/Keap1-ARE and NF-kappaB in the ornamental koi carp (Cyprinus carpio haematopterus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 246, 109023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, J.; Cheng, L.B.; Huang, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Ji, J.Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Zhao, L. Effect of emodin on coxsackievirus B3m-mediated encephalitis in hand, foot, and mouth disease by inhibiting toll-like receptor 3 pathway in vitro and in vivo. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.M.; Ye, Q.; Xin, Y.; Hanson, P.; Shen, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, F. Emodin inhibits coxsackievirus B3 replication via multiple signalling cascades leading to suppression of translation. Biochem. J. 2015, 473, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wei, F.; Chen, L.J.; Xiong, H.R.; Liu, Y.Y.; Luo, F.; Hou, W.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Z.Q. In vitro and in vivo studies of the inhibitory effects of emodin isolated from Polygonum cuspidatum on Coxsakievirus B(4). Molecules 2013, 18, 11842–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batista, M.N.; Braga, A.C.S.; Campos, G.R.F.; Souza, M.M.; Matos, R.P.A.; Lopes, T.Z.; Candido, N.M.; Lima, M.L.D.; Machado, F.C.; Andrade, S.T.Q.; et al. Natural products isolated from oriental medicinal herbs inactivate zika virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, T.; Zhang, L.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, F.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yu, J.H. Rheum emodin inhibits enterovirus 71 viral replication and affects the host cell cycle environment. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yiu, C.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Yang, T.H.; Chang, C.J.; Yeh, D.B.; Chen, Y.J.; Lin, T.P. Inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus lytic cycle by an ethyl acetate subfraction separated from Polygonum cuspidatum root and its major component, emodin. Molecules 2014, 19, 1258–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.; Wang, K.; Yu, W.; Sun, B.; Schwarz, W. Emodin inhibits current through SARS-associated coronavirus 3a protein. Antiviral Res. 2011, 90, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.R.; Luo, J.; Hou, W.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Z.Q. The effect of emodin, an anthraquinone derivative extracted from the roots of Rheum tanguticum, against herpes simplex virus in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiang, C.Y.; Ho, T.Y. Emodin is a novel alkaline nuclease inhibitor that suppresses herpes simplex virus type 1 yields in cell cultures. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dang, S.S.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chen, Y.R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.F.; Yuan, L.C.; Cheng, Y.A. Inhibition of the replication of hepatitis B virus in vitro by emodin. Med. Sci. Monit. 2006, 12, BR302–BR306. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, T.Y.; Wu, S.L.; Chen, J.C.; Li, C.C.; Hsiang, C.Y. Emodin blocks the SARS coronavirus spike protein and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 interaction. Antiviral Res. 2007, 74, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent end points. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1937, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- Quinting, B.; Robert, B.; Letellier, C.; Boxus, M.; Kerkhofs, P.; Schynts, F.; Collard, A. Development of a 1-step enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the rapid diagnosis of bovine respiratory syncytial virus in postmortem specimens. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2007, 19, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Bian, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhong, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Liu, Z. Huai hua san alleviates dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis and modulates colonic microbiota. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Peng, P.; Liu, Y.; Huang, M.; Ma, Y.; Xue, C.; Cao, Y. Aloe extract inhibits porcine epidemic diarrhea virus in vitro and in vivo. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 249, 108849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhong, H.; Huang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Du, Y.; Chen, L.; Xue, C.; Cao, Y. Porcine deltacoronavirus induces TLR3, IL-12, IFN-alpha, IFN-beta and PKR mRNA expression in infected Peyer’s patches in vivo. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 228, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Zheng, M.; Lv, H.; Guo, K.; Zhang, Y. Tissue expression of Toll-like receptors 2, 3, 4 and 7 in swine in response to the Shimen strain of classical swine fever virus. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7122–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, W.; Wu, J.J.; Deng, X.Y.; Cao, Z.; Yu, X.L.; Wang, C.B.; Zhao, T.Z.; Chen, N.H.; Hu, H.H.; Bin, W.; et al. Molecular mutations associated with the in vitro passage of virulent porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Virus Genes 2009, 38, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruansit, W.; Charerntantanakul, W. Oral supplementation of quercetin in PRRSV-1 modified-live virus vaccinated pigs in response to HP-PRRSV-2 challenge. Vaccine 2020, 38, 3570–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Y.; Ross, C.R.; Rowland, R.R.; Blecha, F. Toll-like receptor 3 activation decreases porcine arterivirus infection. Viral Immunol. 2008, 21, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muresan, X.M.; Bouchal, J.; Culig, Z.; Soucek, K. Toll-like receptor 3 in solid cancer and therapy resistance. Cancers 2020, 12, 3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Batista, L.; Dee, S.; Halbur, P.; Murtaugh, M.P. The level of virus-specific T-cell and macrophage recruitment in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection in pigs is independent of virus load. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5923–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hakobyan, A.; Arabyan, E.; Avetisyan, A.; Abroyan, L.; Hakobyan, L.; Zakaryan, H. Apigenin inhibits African swine fever virus infection in vitro. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 3445–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manigandan, T.; Elumalai, M.; Cholan, P.; Kaur, R.P.; Mangaiyarkarasi, S. Benefits of Aloe vera in dentistry. J. Pharmacy Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarshan, R.; Amsigeri, R.G.; Vijayabala, G.S. Aloe vera in dentistry. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, 01–02. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.G.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, Y.H.; Oh, Y.C.; Lee, B.; Moon, K.M.; Cho, W.K.; Ma, J.Y. Aloe vera and its components inhibit influenza a virus-induced autophagy and replication. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2019, 47, 1307–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.T.; Hung, C.Y.; Hseih, Y.C.; Chang, C.S.; Velu, A.B.; He, Y.C.; Huang, Y.L.; Chen, T.A.; Chen, T.C.; Lin, C.Y.; et al. Effect of aloin on viral neuraminidase and hemagglutinin-specific T cell immunity in acute influenza. Phytomedicine 2019, 64, 152904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Bedoui, Y.; Giry, C.; Gasque, P.; Guiraud, P.; Selambarom, J. Quercetin can reduce viral RNA level of O’nyong-nyong virus and resulting innate immune cytokine responses in cultured human synovial fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, N.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Su, G.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, F.; Liang, D.; Liu, B.; et al. Emodin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis in mice by inhibiting activation of NF-kappaB and MAPKs signal pathways. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 705, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leen, D.; Nidya, S.G.; Ali, T.; Gilles, Q.; Boris, P.; Mathy, F.; Kai, D.; Dirk, J.; Piet, H.; Felio, B. Mutations in the chikungunya virus non-structural proteins cause resistance to favipiravir (T-705), a broad-spectrum antiviral. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 10, 2770–2784. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjuan, R.; Nebot, M.R.; Chirico, N.; Mansky, L.M.; Belshaw, R. Viral mutation rates. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 9733–9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sydiskis, R.J.; Owen, D.G.; Lohr, J.L.; Rosler, K.H.; Blomster, R.N. Inactivation of enveloped viruses by anthraquinones extracted from plants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1991, 35, 2463–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Bai, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, P. Toll-like receptor ligands enhance the protective effects of vaccination against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in swine. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 164, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Fu, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, H.; Zheng, S.J. gga-miR-155 enhances type I interferon expression and suppresses infectious burse disease virus replication via targeting SOCS1 and TANK. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Z.; Huang, M.; Xia, Y.; Peng, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, X.; Xue, C.; Cao, Y. Emodin from Aloe Inhibits Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus via Toll-Like Receptor 3 Activation. Viruses 2021, 13, 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071243
Xu Z, Huang M, Xia Y, Peng P, Zhang Y, Zheng S, Wang X, Xue C, Cao Y. Emodin from Aloe Inhibits Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus via Toll-Like Receptor 3 Activation. Viruses. 2021; 13(7):1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071243
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Zhichao, Meiyan Huang, Yongbo Xia, Peng Peng, Yun Zhang, Shumei Zheng, Xiaowei Wang, Chunyi Xue, and Yongchang Cao. 2021. "Emodin from Aloe Inhibits Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus via Toll-Like Receptor 3 Activation" Viruses 13, no. 7: 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071243
APA StyleXu, Z., Huang, M., Xia, Y., Peng, P., Zhang, Y., Zheng, S., Wang, X., Xue, C., & Cao, Y. (2021). Emodin from Aloe Inhibits Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus via Toll-Like Receptor 3 Activation. Viruses, 13(7), 1243. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071243





