COVID-19 Pandemic: Influence of Schools, Age Groups, and Virus Variants in Italy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Influence of School Activity on Health System
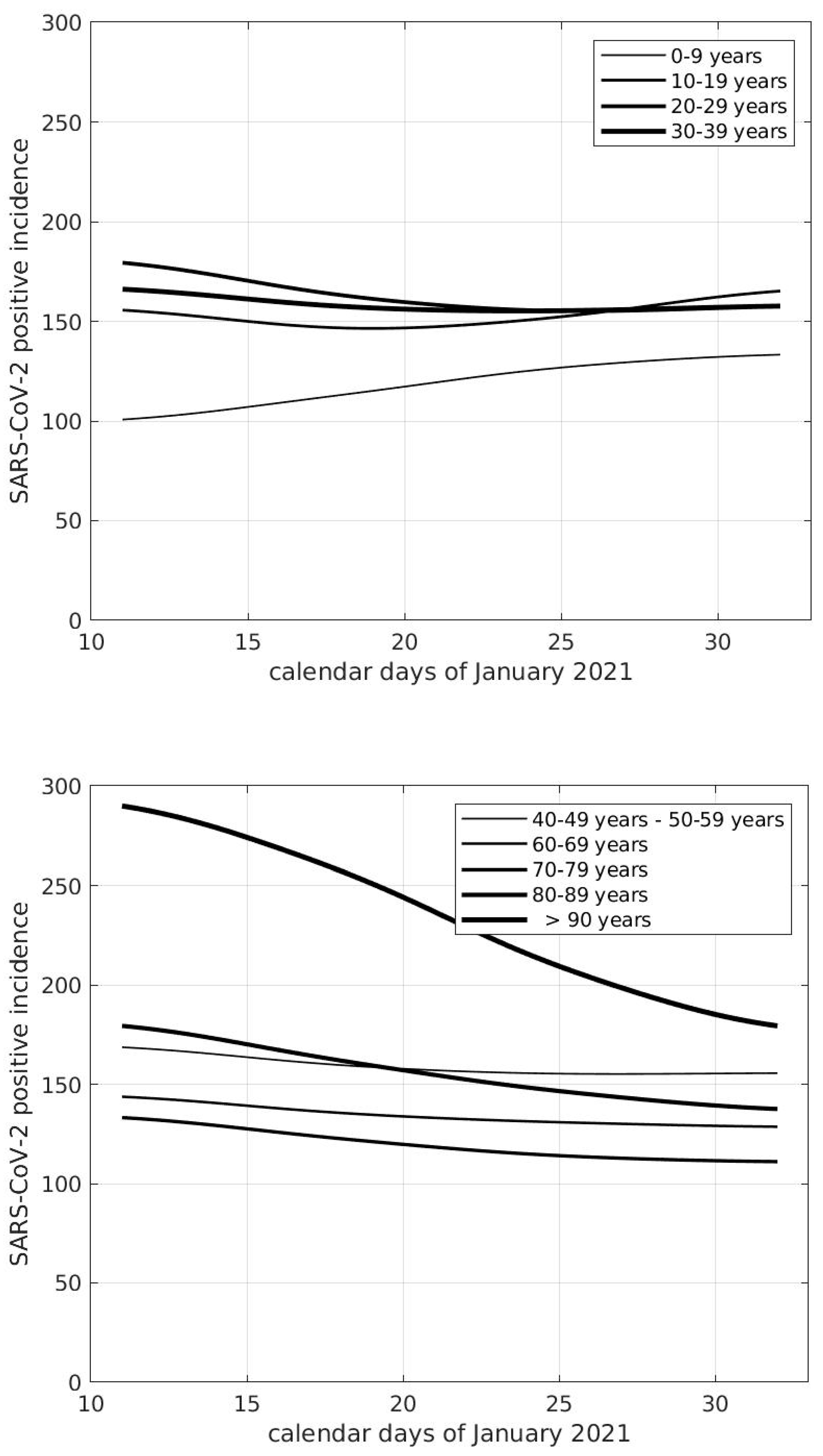
4. Age Groups and Epidemic Diffusion
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Snape, M.D.; Viner, R.M. COVID-19 in children and young people. Science 2020, 370, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. Coronavirus infections in children including COVID-19: An overview of the epidemiology, clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and prevention options in children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2020, 39, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, A.; Chorath, K.; Moreira, A.; Evans, M.; Burmeister-Morton, F.; Burmeister, F.; Naqvi, R.; Petershack, M.; Moreira, A. COVID-19 in 7780 pediatric patients: A systematic review. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 24, 100433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viner, R.M.; Mytton, O.T.; Bonell, C. Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection among children and adolescents compared with adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, N.G.; Klepac, P.; Liu, Y.; Prem, K.; Jit, M.; Pearson, C.A.B.; Quilty, B.J.; Kucharski, A.J.; Gibbs, H.; Clifford, S.; et al. Age-Dependent Effects in the Transmission and Control of COVID-19 Epidemics. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippich, M.; Holthaus, L.; Assfalg, R. A public health antibody screening indicates a 6-fold higher SARS-CoV-2 exposure rate than reported cases in children. Med 2021, 2, 149–163.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedeli, U.; Porreca, A.; Colicchia, M.; Schievano, E.; Artibani, W.; Biasio, L.R.; Palù, G. Intravescical instillation of Calmette-Guérin bacillus and COVID-19 risk. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2021, 17, 416–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.W.; Faulkner, N.; Cornish, G.H. Preexisting and de novo humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in humans. Science 2020, 370, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, H.; Morton, C.E.; Bacon, S.; McDonald, H.I.; Minassian, C.; Brown, J.P.; Rentsch, C.T.; Mathur, R.; Schultze, A.; DeVito, N.J.; et al. Association between living with children and outcomes from covid-19: OpenSAFELY cohort study of 12 million adults in England. BMJ 2021, 372, n628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Hanley, J.P.; Nowak, S.; Bates, J.H.T.; Hébert-Dufresne, L. Modeling the impact of school reopening on SARS-CoV-2 transmission using contact structure data from Shanghai. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viner, R.M.; Russell, S.J.; Croker, H.; Packer, J.; Ward, J.; Stansfield, C.; Mytton, O.; Bonell, C.; Booy, R. School closure and management practices during coronavirus outbreaks including COVID-19: A rapid systematic review. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Choe, Y.J.; Park, O.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kim, J.; Kweon, S.; Woo, Y.; Gwack, J.; Kim, S.S.; et al. Contact Tracing during Coronavirus Disease Outbreak, South Korea, 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2465–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heald-Sargent, T.; Muller, W.J.; Zheng, X.; Rippe, J.; Patel, A.B.; Kociolek, L.K. Age-related differences in nasopharyngeal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) levels in patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szablewski, C.M.; Chang, K.T.; Brown, M.M. SARS-CoV-2 transmission and infection among attendees of an overnight camp-Georgia, June 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein-Zamir, C.; Abramson, N.; Shoob, H. A large COVID-19 outbreak in a high school 10 days after schools’ reopening, Israel, May 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Campbell, H.; Kulkarni, D.; Harpur, A.; Nundy, M.; Wang, X.; Nair, H. The temporal association of introducing and lifting non-pharmaceutical interventions with the time-varying reproduction number (R) of SARS-CoV-2: A modelling study across 131 countries. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauner, J.M.; Mindermann, S.; Sharma, M.; Johnston, D.; Salvatier, J.; Gavenčiak, T.; Stephenson, A.B.; Leech, G.; Altman, G.; Mikulik, V.; et al. Inferring the effectiveness of government interventions against COVID-19. Science 2021, 371, eabd9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, G.; Palù, G. COVID-19 and School Activities in Italy. Viruses 2020, 12, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://alessandroferrettiblog.files.wordpress.com/2020/12/dati-contagi-scuola.pdf (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Eubanks, R.L. Nonparametric Regression and Spline Smoothing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Olivieri, A.; Palù, G.; Sebastiani, G. COVID-19 cumulative incidence, intensive care, and mortality in Italian regions compared to selected European countries. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 102, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRosa, E.; Djuric, O.; Cassinadri, M.; Cilloni, S.; Bisaccia, E.; Vicentini, M.; Venturelli, F.; Rossi, P.G.; Pezzotti, P.; Bedeschi, E.; et al. Secondary transmission of COVID-19 in preschool and school settings in northern Italy after their reopening in September 2020: A population-based study. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.; Ainslie, K.E.C.; Eales, O.; Walters, C.E.; Wang, H. High prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 swab positivity and in-creasing R number in England during October 2020: REACT-1 round 6 interim report. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandini, S.; Rainisio, M.; Iannuzzo, M.L.; Bellerba, F.; Cecconi, F.; Scorrano, L. A cross-sectional and prospective cohort study of the role of schools in the SARS-CoV-2 second wave in Italy. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 5, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevalenza Della Variante VOC2020/12/01, Lineage B.1.1.7 in Italia. Studio di Prevalenza 4-5 Febbraio 2021, Istituto Superiore di Sanità. 2021. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/coronavirus/sars-cov-2-sorveglianza-dati (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Epidemia COVID-19, Aggiornamento Nazionale 31 Marzo 2021, Published 2 April 2021, Istituto Superiore di Sanità. Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/coronavirus/sars-cov-2-sorveglianza-dati (accessed on 28 June 2021).
- Davies, N.G.; Abbott, S.; Barnard, R.C.; Jarvis, C.I.; Kucharski, A.J.; Munday, J.D.; Pearson, C.A.B.; Russell, T.W.; Tully, D.C.; Washburne, A.D.; et al. Estimated transmissibility and impact of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England. Science 2021, 372, eabg3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hippich, M.; Sifft, P.; Zapardiel-Gonzalo, J.; Böhmer, M.M.; Lampasona, V.; Bonifacio, E.; Ziegler, A.-G. A public health antibody screening indicates a marked increase of SARS-CoV-2 exposure rate in children during the second wave. Med 2021, 2, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sebastiani, G.; Palù, G. COVID-19 Pandemic: Influence of Schools, Age Groups, and Virus Variants in Italy. Viruses 2021, 13, 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071269
Sebastiani G, Palù G. COVID-19 Pandemic: Influence of Schools, Age Groups, and Virus Variants in Italy. Viruses. 2021; 13(7):1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071269
Chicago/Turabian StyleSebastiani, Giovanni, and Giorgio Palù. 2021. "COVID-19 Pandemic: Influence of Schools, Age Groups, and Virus Variants in Italy" Viruses 13, no. 7: 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071269
APA StyleSebastiani, G., & Palù, G. (2021). COVID-19 Pandemic: Influence of Schools, Age Groups, and Virus Variants in Italy. Viruses, 13(7), 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071269





