Co-Infection of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) and White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in the Wild Crustaceans of Andaman and Nicobar Archipelago, India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Samples
2.2. DNA Isolation and PCR Amplification of Target Viruses
2.3. Sequencing of PCR Products and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.4. Histopathological Analysis
2.5. Analysis of Data
3. Results
3.1. Co-Infection of IHHNV and WSSV in Wild Shrimps
3.2. Co-Infection of IHHNV and WSSV in Wild Crabs
3.3. Analysis of Odds Ratio
3.4. Sequence Analysis of IHHNV and WSSV
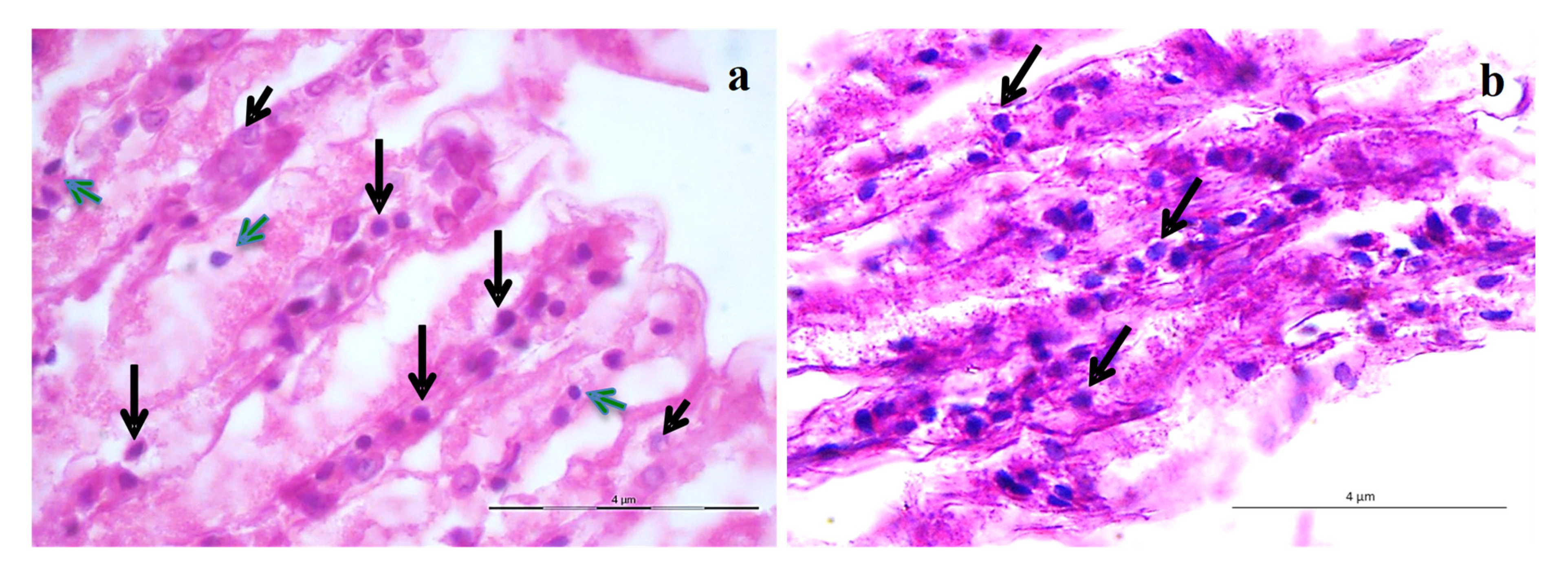
3.5. Histopathology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thitamadee, S.; Prachumwat, A.; Srisala, J.; Jaroenlak, P.; Salachan, P.V.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Flegel, T.W.; Itsathitphaisarn, O. Review of current disease threats for cultivated penaeid shrimp in Asia. Aquaculture 2016, 452, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M. Strategies for the Control of Viral Diseases of Shrimp in the Americas. Fish Pathol. 1998, 33, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lightner, D.V. A Handbook of Shrimp Pathology and Diagnostic Procedures for Diseases of Cultured Penaeid Shrimp; World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Flegel, T.; Fegan, D.F. Strategies for preventing the spread of fish and shellfish diseases. Fish. Sci. 2002, 68, 776–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otta, S.K.; Arulraj, R.; Ezhil Praveena, P.; Manivel, R.; Panigrahi, A.; Bhuvaneswari, T.; Ravichandran, P.; Jithendran, K.P.; Ponniah, A.G. Association of dual viral infection with mortality of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in culture ponds in India. Virusdisease 2014, 25, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lightner, D. The penaeid shrimp viral pandemics due to IHHNV, WSSV, TSV and YHV: History in the Americas and current status. In Proceedings of the 32nd Joint UJNR Aquaculture Panel Symposium, Davis and Santa Barbara, CA, USA, January 2003; pp. 17–20. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/228580878_The_penaeid_shrimp_viral_pandemics_due_to_IHHNV_WSSV_TSV_and_YHV_history_in_the_Americas_and_current_status (accessed on 20 January 2003).
- Lo, G.C.-F. White spot disease. In Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals; Office International des Epizooties (OIE): Paris, France, 2006; pp. 379–391. [Google Scholar]
- Lightner, D.; Redman, R. Shrimp diseases and current diagnostic methods. Aquaculture 1998, 164, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorelli, S.R.; Overstreet, R.M.; Jovonovich, J.A. First report of viral pathogens WSSV and IHHNV in Argentine crustaceans. Bull. Mar. Sci. 2010, 86, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- OIE Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals. Available online: https://www.oie.int/en/what-we-do/standards/codes-and-manuals/aquatic-manual-online-access/ (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Yang, B.; Song, X.-L.; Huang, J.; Shi, C.-Y.; Liu, Q.-H.; Liu, L. A single-step multiplex PCR for simultaneous detection of white spot syndrome virus and infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis virus in penaeid shrimp. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, M.A. A summary of taxonomic changes recently approved by ICTV. Arch. Virol. 2002, 147, 1655–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegel, T.W. Detection of major penaeid shrimp viruses in Asia, a historical perspective with emphasis on Thailand. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somboonna, N.; Mangkalanan, S.; Udompetcharaporn, A.; Krittanai, C.; Sritunyalucksana, K.; Flegel, T. Mud crab susceptibility to disease from white spot syndrome virus is species-dependent. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magbanua, F.O.; Natividad, K.T.; Migo, V.P.; Alfafara, C.G.; de la Peña, F.O.; Miranda, R.O.; Albaladejo, J.D.; Nadala, E.C.; Loh, P.C.; Mahilum-Tapay, L. White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in cultured Penaeus monodon in the Philippines. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2000, 42, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chayaburakul, K.; Nash, G.; Pratanpipat, P.; Sriurairatana, S.; Withyachumnarnkul, B. Multiple pathogens found in growth-retarded black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon cultivated in Thailand. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2004, 60, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flegel, T.W.; Nielsen, L.; Thamavit, V.; Kongtim, S.; Pasharawipas, T. Presence of multiple viruses in non-diseased, cultivated shrimp at harvest. Aquaculture 2004, 240, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesha, K.R.; Dass, B.K.M.; Naik, B.M.; Venugopal, M.N.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I. High prevalence of dual and triple viral infections in black tiger shrimp ponds in India. Aquaculture 2006, 258, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, H.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Z.-L. Molecular detection of three shrimp viruses and genetic variation of white spot syndrome virus in Hainan Province, China, in 2007. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Z. Prevalence of three shrimp viruses in Zhejiang Province in 2008. Virol. Sin. 2011, 26, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamizhvanan, S.; Sivakumar, S.; Kumar, S.S.; Kumar, D.V.; Suryakodi, S.; Balaji, K.; Rajkumar, T.; Vimal, S.; Majeed, S.A.; Taju, G.; et al. Multiple infections caused by white spot syndrome virus and Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei in pond-reared Penaeus vannamei in India and multiplex PCR for their simultaneous detection. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira-Lopes, M.A.; Vieira-Girão, P.R.N.; da Cruz Freire, J.E.; Rocha, Í.R.C.B.; Costa, F.H.F.; Rádis-Baptista, G. Natural co-infection with infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) and infectious myonecrosis virus (IMNV) in Litopenaeus vannamei in Brazil. Aquaculture 2011, 312, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, L.S.; Batista, C.R.; Nornberg, B.F.S.; Mayer, F.Q.; Seixas, F.K.; Romano, L.A.; Marins, L.F.; Abreu, P.C. Natural occurrence of White spot syndrome virus and Infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus in Neohelice granulata crab. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2013, 114, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, S.; Biswas, G.; Ghoshal, T.K. Occurrence of pathogenic shrimp viruses in selected wild crab species of Sunderban, India. Indian J. Fish. 2016, 63, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anshary, H.; Sriwulan; Sukenda, S.; Baxa, D.V. Multiple viral pathogens occurrence in tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon) broodstock from Sulawesi coastal waters. AACL Bioflux 2017, 10, 936–950. [Google Scholar]
- Hamano, K.; Maeno, Y.; Klomkling, S.; Aue-Umneoy, D.; Tsutsui, I. Presence of viral pathogens amongst wild Penaeus monodon in Thailand. Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. JARQ 2017, 51, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orosco, F.; Lluisma, A. Prevalence, diversity and co-occurrence of the white spot syndrome virus, monodon baculovirus and Penaeus stylirostris densovirus in wild populations of Penaeus monodon in the Philippines. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2017, 125, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norizan, N.; Harrison, F.S.; Hassan, M.; Musa, N.; Musa, N.; Wahid, M.E.A.; Zainathan, S.C. First detection of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in wild mud crab Scylla spp. (de haan, 1883) from setiu wetlands, Malaysia. Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 41, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Martínez, J.G.; Aguirre-Guzmán, G.; Mejía-Ruíz, H. White Spot Syndrome Virus in cultured shrimp: A review. Aquac. Res. 2007, 38, 1339–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotob, M.H.; Menanteau-Ledouble, S.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of co-infections on fish: A review. Vet. Res. 2017, 47, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kotob, M.H.; Gorgoglione, B.; Kumar, G.; Abdelzaher, M.; Saleh, M.; El-Matbouli, M. The impact of Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae and Myxobolus cerebralis co-infections on pathology in rainbow trout. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.F.; Durand, S.V.; White, B.L.; Redman, R.M.; Mohney, L.L.; Lightner, D.V. Induced resistance to white spot syndrome virus infection in Penaeus stylirostris through pre-infection with infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus—A preliminary study. Aquaculture 2003, 216, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotob, M.H.; Kumar, G.; Saleh, M.; Gorgoglione, B.; Abdelzaher, M.; El-Matbouli, M. Differential modulation of host immune genes in the kidney and cranium of the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in response to Tetracapsuloides bryosalmonae and Myxobolus cerebralis co-infections. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Escobedo-Bonilla, C.M.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Wille, M.; Sorgeloos, P.; Pensaert, M.B.; Nauwynck, H.J. A review on the morphology, molecular characterization, morphogenesis and pathogenesis of white spot syndrome virus. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 31, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightner, D.V. Biosecurity in shrimp farming: Pathogen exclusion through use of SPF stock and routine surveillance. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2005, 36, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Yin, Z.-X.; Ai, H.-S.; Huang, X.-D.; Li, S.-D.; Weng, S.-P.; He, J.-G. Characterization of WSSV resistance in selected families of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2011, 311, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shome, R.; Shome, B.; Soundararajan, R. Studies on luminous Vibrio harveyi isolated from Penaeus monodon larvae reared in hatcheries in Andamans. Indian J. Fish. 1999, 46, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.S.; Krishnan, P.; Makesh, M.; Chaudhari, A.; Purushothaman, C.; Rajendran, K. Natural host-range and experimental transmission of Laem-Singh virus (LSNV). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 96, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sethi, S.N.; Mahendran, V.; Nivas, K.; Krishnan, P.; Damroy, S.; Ram, N.; Sethi, S. Detection of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in brood stock of tiger shrimp, Penaeus monodon and other crustaceans of Andaman waters. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 40, 403–406. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan, K.; Kumar, P.P.; Praveenraj, J.; Baruah, A.; Sivaramakrishnan, T.; Kumar, T.S.; Kumar, S.P.; Sankar, R.K.; Roy, S.D. Investigation and confirmation of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) infection in wild caught penaeid shrimps of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. Virusdisease 2017, 28, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanan, K.; Kumar, P.P.; Baruah, A.; Praveenraj, J.; Kumar, T.S.; Kumar, S.P.; Sivaramakrishnan, T.; Anuraj, A.; Angel, J.R.J.; Sankar, R.K.; et al. IHHNV infection from the wild Shrimps of Andaman and Nicobar islands, India. Curr. Sci. 2017, 113, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Navarro, S.; Lightner, D. PCR assay for discriminating between infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) and virus-related sequences in the genome of Penaeus monodon. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2007, 74, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, T.; Yamano, K.; Nakano, H.; Momoyama, K.; Hiraoka, M.; Inouye, K. Detection of Penaeid Rod-shaped DNA Virus (PRDV) by PCR. Fish Pathol. 1996, 31, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.A.; Lightner, D.V. A Handbook of Normal Penaeid Shrimp Histology; World Aquaculture Society: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, T.S.; Vidya, R.; Kumar, S.; Alavandi, S.V.; Vijayan, K.K. Zoea-2 syndrome of Penaeus vannamei in shrimp hatcheries. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Mohan, C.V. Viral disease emergence in shrimp aquaculture: Origins, impact and the effectiveness of health management strategies. Rev. Aquac. 2009, 1, 125–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, P.; Pradeep, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I. Detection of viruses in Penaeus monodon from India showing signs of slow growth syndrome. Aquaculture 2009, 289, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Shan, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, T.; Teng, G.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; Tang, K.F.J.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, X. White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) prevalence in wild crustaceans in the Bohai Sea. Aquaculture 2021, 542, 736810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otta, S.; Shubha, G.; Joseph, B.; Chakraborty, A.; Karunasagar, I.; Karunasagar, I. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in cultured and wild crustaceans in India. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 38, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joseph, T.C.; James, R.; Rajan, L.A.; Surendran, P.K.; Lalitha, K.V. White spot syndrome virus infection: Threat to crustacean biodiversity in Vembanad lake, India. Biotechnol. Rep. 2015, 7, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalli, L.S.; Romano, L.A.; Marins, L.F.; Abreu, P.C. First report of White spot syndrome virus in farmed and wild penaeid shrimp from lagoa dos patos estuary, southern brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2011, 42, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Pérez, A.; Zamora-Briseño, J.A.; Vega, J.A.P.; Mena-Loria, R.J.D.D.; Coronado-Molina, D.; Hernández-López, J.; Angelica-López-Téllez, N.; Rodríguez-Canul, R. Presence of infectious hypodermal and haematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) in native shrimps from Southern Mexico. Open J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 07, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morales-Covarrubias, M.S.; Nunan, L.M.; Lightner, D.V.; Mota-Urbina, J.C.; Garza-Aguirre, M.C.; Chávez-Sánchez, M.C. Prevalence of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosisvirus (IHHNV) in wild adult blue shrimp Penaeus stylirostris from the Northern Gulf of California, Mexico. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1999, 11, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunan, L.M.; Arce, S.M.; Staha, R.J.; Lightner, D.V. Prevalence of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) and white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in Litopenaeus vannamei in the Pacific Ocean off the Coast of Panama. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2001, 32, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantoja, C.R.; Lightner, D.V.; Holtschmit, K.H. Prevalence and geographic distribution of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) in wild blue shrimp Penaeus stylirostris from the Gulf of California, Mexico. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1999, 11, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motte, E.; Yugcha, E.; Luzardo, J.; Castro, F.; Leclercq, G.; Rodríguez, J.; Miranda, P.; Borja, O.; Serrano, J.; Terreros, M.; et al. Prevention of IHHNV vertical transmission in the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 2003, 219, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-Y.; Yang, N.; Hou, Z.-H.; Wang, J.-J.; Li, T.; Chang, L.-R.; Fang, Y.; Yan, D.-C. Research progress on hosts and carriers, prevalence, virulence of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV). J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2021, 183, 107556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightner, D.V.; Bell, T.A.; Redman, R.M. A review of the known hosts, geographic range and current diagnostic procedures for the virus diseases of cultured penaeid shrimp. In Advances in Tropical Aquaculture; AQUACOP, IFREMER: Tahiti, French Polynesia, 1989; Volume 9, pp. 113–126. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Lo, C.; Chiu, Y.; Chang, C.; Kou, G. Natural and experimental infection of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in benthic larvae of mud crab Scylla serrata. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2000, 40, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.A.; Lightner, D.V. IHHN virus: Infectivity and pathogenicity studies in Penaeus stylirostris and Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 1984, 38, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, J.M. Viruses, biosecurity and specific pathogen-free stocks in shrimp aquaculture. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 13, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Covarrubias, M.S.; Chavez-Sanchez, C. Histopathological studies on wild broodstock of white shrimp Penaeus vannamei in the platanitos area, adjacent to San Blas, Nayarit, Mexico. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1999, 30, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, K.V.; Vijayan, K.K.; Santiago, T.C.; Krol, R.M. Experimental host range and histopathology of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) infection in shrimp, prawns, crabs and lobsters from India. J. Fish Dis. 1999, 22, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, L.S.; Marins, L.F.; Abreu, P.C. Evaluation of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in wild shrimp after a major outbreak in shrimp farms at Laguna, Southern Brazil. Atlântica Rio Gd. 2008, 30, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Braz, R.D.F.D.S.; da Silva, C.P.R.D.O.; Reis, L.G.; Martins, P.C.C.; de Sales, M.P.; Meissner, R.V. Prevalence of infectious hypodermal and hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHHNV) in Penaeus vannamei cultured in Northeastern Brazil. Aquaculture 2009, 288, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| District Wise Landing Centres | Number of Samples Collected and Found Positive for IHHNV (I), WSSV (W) and Both (B) | Total Number of Samples and Positive Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District | Landing Centre | P. monodon | P. merguiensis | P. indicus | P. penicillatus | |
| South Andaman (SA) | Junglighat | 86 (I-17; W-2; B-23) | 28 (I-6; W-2; B-4) | 26 (I-6; W-3; B-2) | - | 140 (I-29; W-7; B-29) |
| Lohabarrack | 112 (I-19; W-8; B-22) | 24 (I-6; W-0; B-1) | - | - | 136 (I-25; W-8; B-23) | |
| Sub-total from SA | 198 (I-36; W-10; B-45) | 52 (I-12; W-2; B-5) | 26 (I-6; W-3; B-2) | - | 276 (I-54; W-15; B-52) | |
| North and Middle Andaman (NMA) | Durgapur | 51 (I-13; W-6; B-2) | 17 (I-2; W-1; B-0) | 61 (I-12; W-2; B-0) | - | 129 (I-27; W-9; B-2) |
| Kalighat | 11 (I-2; W-0; B-1) | - | - | 20 (I-1; W-1; B-1) | 31 (I-3; W-1; B-2) | |
| Mayabunder | 10 (I-4; W-0; B-1) | - | 16 (I-2; W-3; B-0) | - | 26 (I-6; W-3; B-1) | |
| Betapur | 95 (I-26; W-17; B-14) | 25 (I-3; W-0; B-1) | - | - | 120 (I-29; W-17; B-15) | |
| Sub-total from NMA | 167 (I-45; W-23; B-18) | 42 (I-5; W-1; B-1) | 77 (I-14; W-5; B-0) | 20 (I-1; W-1; B-1) | 306 (I-65; W-30; B-20) | |
| Nicobar (N) | Campbell Bay | 18 (I-3; W-1; B-9) | - | 7 (I-1; W-0; B-1) | - | 25 (I-4; W-1; B-10) |
| Sub-total from N | 18 (I-3; W-1; B-9) | - | 7 (I-1; W-0; B-1) | - | 25 (I-4; W-1; B-10) | |
| Grand total number of samples and positive samples from all the districts of Andaman and Nicobar Archipelago | 383 (I-84; W-34; B-72) | 94 (I-17; W-3; B-6) | 110 (I-21; W-8; B-3) | 20 (I-1; W-1; B-1) | 607 (I-123; W-46; B-82) | |
| District Wise Landing Centres | Number of Samples Collected and Found Positive for IHHNV (I), WSSV (W) and Both (B) | Total Number of Samples and Positive Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| District | Landing Centre | S. serrata | S. tranquebarica | P. pelagicus | P. reticulatus | |
| South Andaman (SA) | Guptapara | 12 (I-2; W-1; B-0) | 7 (I-1; W-1; B-0) | - | - | 19 (I-3; W-2; B-0) |
| Junglighat | - | - | 12 (I-1; W-1; B-1) | 4 (I-1; W-0; B-0) | 16 (I-2; W-1; B-1) | |
| Lohabarrack | 27 (I-3; W-3; B-1) | - | - | - | 27 (I-3; W-3; B-1) | |
| Sub-total from SA | 39 (I-5; W-4; B-1) | 7 (I-1; W-1; B-0) | 12 (I-1; W-1; B-1) | 4 (I-1; W-0; B-0) | 62 (I-8; W-6; B-2) | |
| North and Middle Andaman (NMA) | Durgapur | 17 (I-4; W-1; B-1) | - | - | - | 17 (I-4; W-1; B-1) |
| Rangat Bay | 8 (I-1; W-0; B-0) | - | - | - | 8 (I-1; W-0; B-0) | |
| Kadamtala | 6 (I-2; W-1; B-0) | - | - | - | 6 (I-2; W-1; B-0) | |
| Sub-total from NMA | 31 (I-7; W-2; B-1) | - | - | - | 31 (I-7; W-2; B-1) | |
| Nicobar (N) | Campbell Bay | 10 (I-2; W-1; B-1) | 2 (I-1; W-0; B-0) | - | - | 12 (I-3; W-1; B-1) |
| Car Nicobar | - | 5 (I-1; W-0; B-1) | - | - | 5 (I-1; W-0; B-1) | |
| Sub-total from N | 10 (I-2; W-1; B-1) | 7 (I-2; W-0; B-1) | - | - | 17 (I-4; W-1; B-2) | |
| Grand total number of samples and positive samples from all the districts of Andaman and Nicobar Archipelago | 80 (I-14; W-7; B-3) | 14 (I-3; W-1; B-1) | 12 (I-1; W-1; B-1) | 4 (I-1; W-0; B-0) | 110 (I-19; W-9; B-5) | |
| Shrimp/Crab Species | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | Z Statistics | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Shrimp species | |||||
| P. monodon | 4.87 | 3.01 | 7.88 | 6.439 | 0.0001 |
| P. merguiensis | 8 | 1.81 | 35.3 | 2.746 | 0.006 |
| P. indicus | 1.39 | 0.34 | 5.71 | 0.46 | 0.6455 |
| P. penicillatus | 17 | 0.55 | 523.79 | 1.62 | 0.1052 |
| Crab species | |||||
| S. serrata | 1.71 | 0.39 | 7.48 | 0.717 | 0.4735 |
| S. tranquebarica | 3 | 0.14 | 64.26 | 0.703 | 0.4823 |
| P. pelagicus | 9 | 0.28 | 285.52 | 1.246 | 0.2129 |
| P. reticulatus | 2.33 | 0.029 | 182.92 | 0.381 | 0.7034 |
| District Wise Landing Centres | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | Z Statistics | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Wild shrimps | |||||
| South Andaman (SA) | |||||
| Junglighat | 10.71 | 4.23 | 27.16 | 4.998 | 0.0001 |
| Lohabarrack | 9.2 | 3.66 | 23.12 | 4.721 | 0.0001 |
| Sub-total from SA | 9.95 | 5.18 | 19.11 | 6.9 | 0.0001 |
| North and Middle Andaman (NMA) | |||||
| Durgapur | 0.75 | 0.15 | 3.68 | 0.356 | 0.7218 |
| Kalighat | 16.67 | 1.14 | 243.72 | 2.056 | 0.0398 |
| Mayabunder | 0.89 | 0.08 | 10.3 | 0.094 | 0.9249 |
| Betapur | 1.8 | 0.79 | 4.09 | 1.391 | 0.1642 |
| Sub-total from NMA | 1.96 | 1.04 | 3.69 | 2.086 | 0.037 |
| Nicobar (N) | |||||
| Campbell Bay | 25 | 2.36 | 264.8 | 2.673 | 0.0075 |
| Sub-total from N | 25 | 2.36 | 264.8 | 2.673 | 0.0075 |
| Wild crabs | |||||
| South Andaman (SA) | |||||
| Guptapara | 0.83 | 0.03 | 21.43 | 0.113 | 0.9098 |
| Junglighat | 6 | 0.26 | 140.05 | 1.115 | 0.2649 |
| Lohabarrack | 2.22 | 0.17 | 28.98 | 0.609 | 0.5422 |
| Sub-total from SA | 1.92 | 0.33 | 11.23 | 0.721 | 0.4707 |
| North and Middle Andaman (NMA) | |||||
| Durgapur | 2.75 | 0.14 | 55.17 | 0.661 | 0.5085 |
| Rangat Bay | 5 | 0.07 | 366.35 | 0.735 | 0.4626 |
| Kadamtala | 0.47 | 0.01 | 16.89 | 0.416 | 0.6772 |
| Sub-total from NMA | 1.5 | 0.12 | 19.18 | 0.312 | 0.7552 |
| Nicobar (N) | |||||
| Campbell Bay | 2.33 | 0.1 | 50.99 | 0.538 | 0.5903 |
| Car Nicobar | 7 | 0.17 | 291.36 | 1.023 | 0.3064 |
| Sub-total from N | 5 | 0.35 | 71.9 | 1.183 | 0.2367 |
| Name of the Crustacean Species | Name of the Viruses as Single/Co-Infection | Country | Year | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penaeus monodon | IHHNV, WSSV, MBV, HPV | Indonesia | 2014 | [25] |
| P. monodon | IHHNV, WSSV, YHV | Thailand | 2012–2013 | [26] |
| P. monodon | IHHNV, WSSV, MBV | Philippines | 2014–2015 | [27] |
| Scylla olivacea, S. tranquebarica and S. paramamosain | WSSV | Malaysia | 2015 | [28] |
| Euphausia pacifica, Leptochela gracilis, Latreutes anoplonyx, L. planirostris, Acetes chinensis, Crangon affinis, Palaemon graviera, Alpheus japonicus, A. distinguendus, Trachypenaeus curvirostris and Penaeus chinensis | WSSV | China | 2016–2018 | [50] |
| Uca spp. and Sesarma spp. Scylla serrata, Sesarma oceanica, Matuta planipes and Charybdis lucifera Parapenaeopsis stylifera, Penaeus monodon, P. indicus, Metapenaeus dobsoni, M. affinis, Heterocarpus woodmasoni, Scylla serrata, S. tranquebarica, Portunus sanguinolentus, P. pelagicus, Charybdis cruciata and Panulirus homarus | IHHNV, WSSV WSSV WSSV | India India India | 2014–2015 1999 2015 | [24] [51] [52] |
| Artemesia longinaris, Cyrtograpsus angulatus and Palaemon macrodactylus | IHHNV, WSSV | Argentina | 2003–2009 | [9] |
| Farfantepenaeus paulensis Neohelice granulata | WSSV IHHNV, WSSV | Brazil Brazil | 2008 2008 | [53] [23] |
| Penaeus notialis and P. brasiliensis P. stylirostris | IHHNV IHHNV | Mexico Mexico | 2016–2017 1996 | [54] [55] |
| L. vannamei | IHHNV, WSSV | Panama | 2000 | [56] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saravanan, K.; Praveenraj, J.; Kiruba-Sankar, R.; Devi, V.; Biswas, U.; Kumar, T.S.; Sudhagar, A.; El-Matbouli, M.; Kumar, G. Co-Infection of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) and White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in the Wild Crustaceans of Andaman and Nicobar Archipelago, India. Viruses 2021, 13, 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071378
Saravanan K, Praveenraj J, Kiruba-Sankar R, Devi V, Biswas U, Kumar TS, Sudhagar A, El-Matbouli M, Kumar G. Co-Infection of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) and White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in the Wild Crustaceans of Andaman and Nicobar Archipelago, India. Viruses. 2021; 13(7):1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071378
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaravanan, Kandasamy, Jayasimhan Praveenraj, Rajendran Kiruba-Sankar, Varsha Devi, Utpal Biswas, Thangaraj Sathish Kumar, Arun Sudhagar, Mansour El-Matbouli, and Gokhlesh Kumar. 2021. "Co-Infection of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) and White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in the Wild Crustaceans of Andaman and Nicobar Archipelago, India" Viruses 13, no. 7: 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071378
APA StyleSaravanan, K., Praveenraj, J., Kiruba-Sankar, R., Devi, V., Biswas, U., Kumar, T. S., Sudhagar, A., El-Matbouli, M., & Kumar, G. (2021). Co-Infection of Infectious Hypodermal and Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHHNV) and White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in the Wild Crustaceans of Andaman and Nicobar Archipelago, India. Viruses, 13(7), 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13071378










