Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Cat with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case History
2.2. Diagnostic Investigation
2.3. SARS-CoV-2 and Feline Respiratory Pathogen PCRs
2.4. Virus Isolation and Titrations
2.5. In Situ Hybridization
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.8. Whole Genome Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
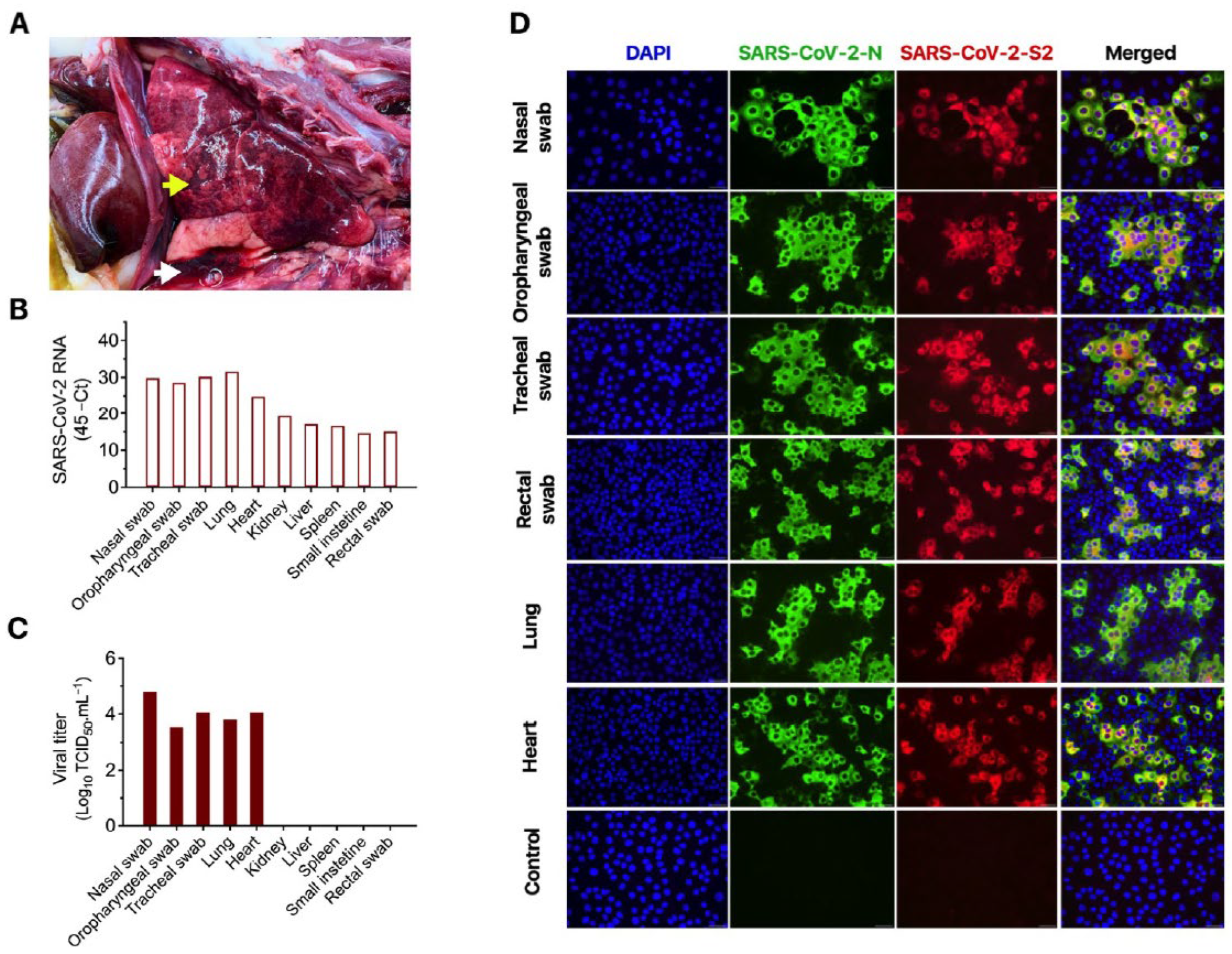
3.1. Clinical Description and Pathological Observations
3.2. Molecular, Bacteriological and Virological Diagnostic Investigation
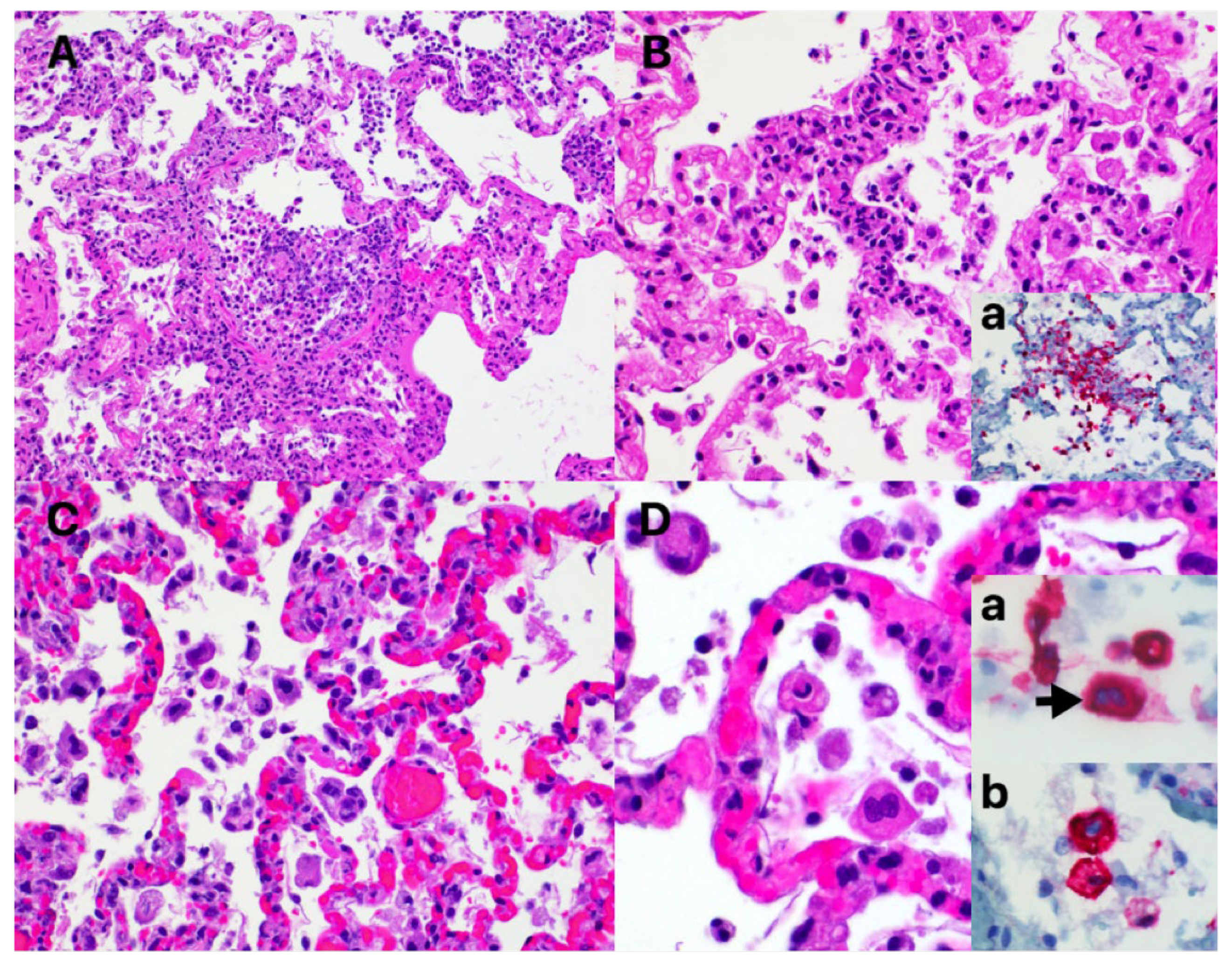
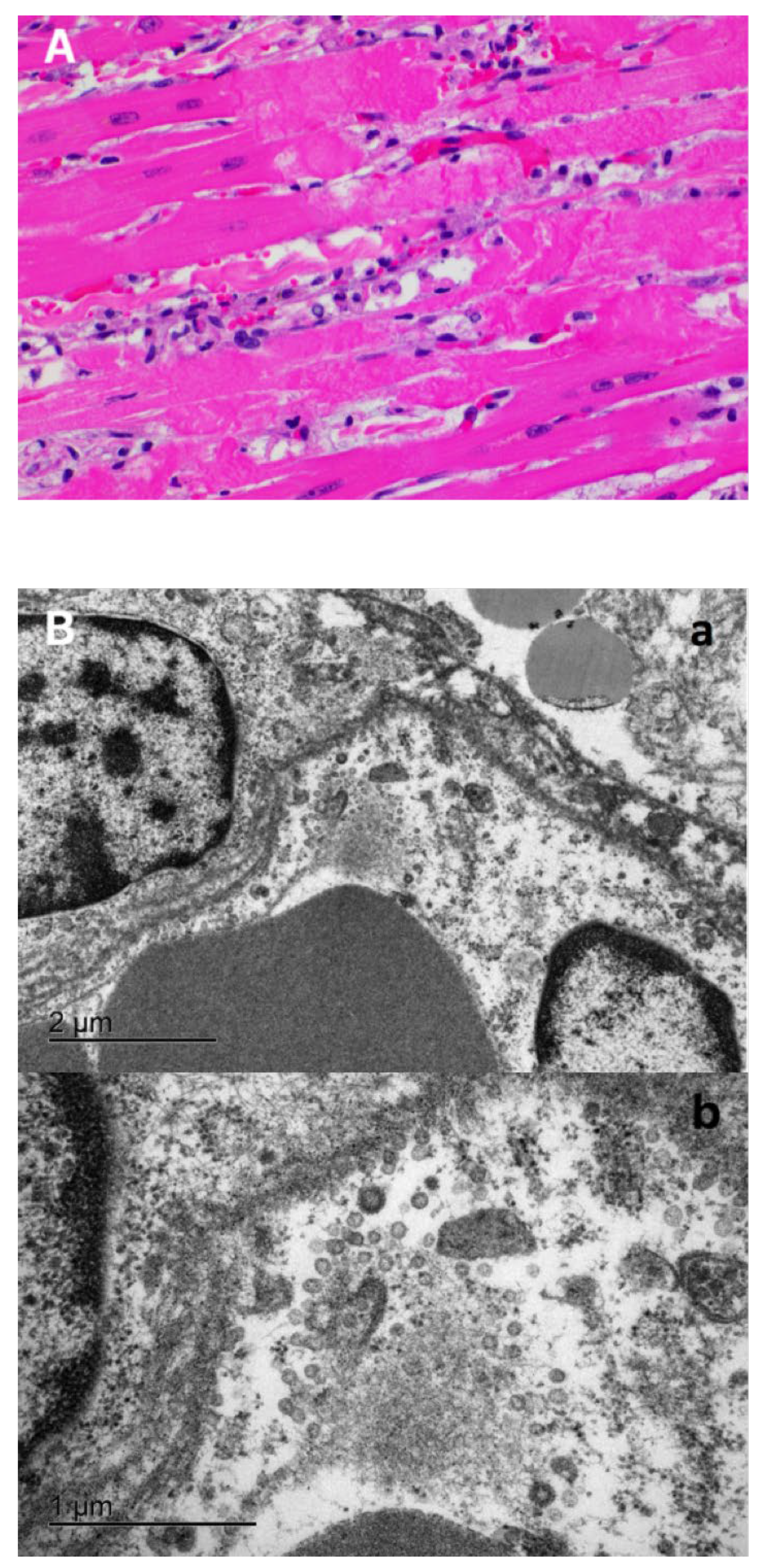
3.3. Characteristic COVID-19 Lesions Observed in Lung and Heart of the Affected Cat
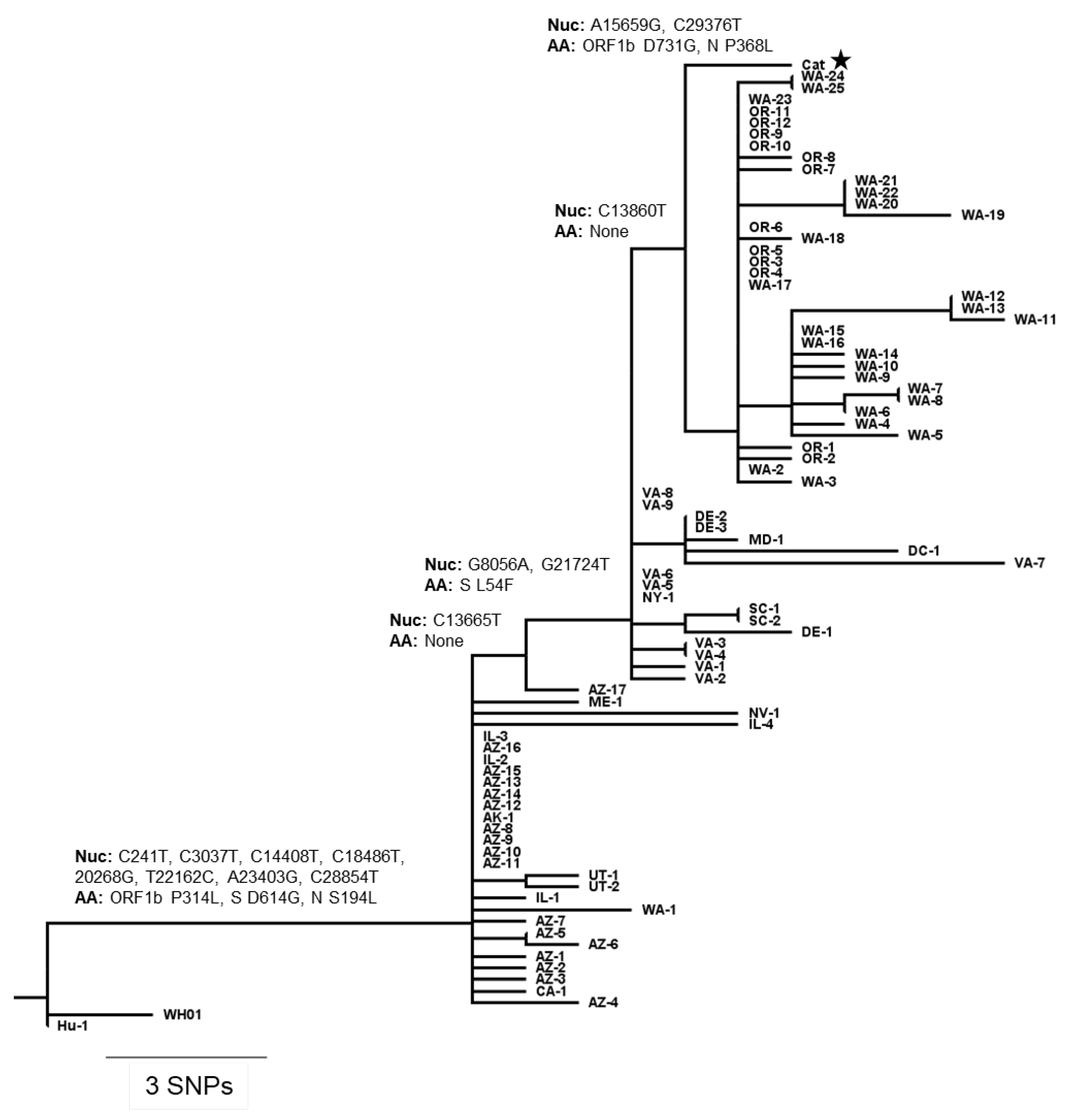
3.4. Comparative Genomic Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, S.; Perlman, S. CHAPTER 28-Coronaviridae. In Fields Virol, 6th ed.; UMass Medical School: Worcester, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, R.L.; Baric, R.S. Recombination, Reservoirs, and the Modular Spike: Mechanisms of Coronavirus Cross-Species Transmission. J. Virol. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murakami, S.; Kitamura, T.; Suzuki, J.; Sato, R.; Aoi, T.; Fujii, M.; Matsugo, H.; Kamiki, H.; Ishida, H.; Takenaka-Uema, A.; et al. Detection and Characterization of Bat Sarbecovirus Phylogenetically Related to SARS-CoV-2, Japan. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Luk, H.K.H.; Wong, A.C.P.; Li, K.S.M.; Zhu, L.; He, Z.; Fung, J.; Chan, T.T.Y.; Fung, K.S.C.; Woo, P.C.Y. Possible Bat Origin of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 1542–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sit, T.H.C.; Brackman, C.J.; Ip, S.M.; Tam, K.W.S.; Law, P.Y.T.; To, E.M.W.; Yu, V.Y.T.; Sims, L.D.; Tsang, D.N.C.; Chu, D.K.W.; et al. Infection of dogs with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oreshkova, N.; Molenaar, R.J.; Vreman, S.; Harders, F.; Oude Munnink, B.B.; Van Der Honing, R.W.H.; Gerhards, N.; Tolsma, P.; Bouwstra, R.; Sikkema, R.S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in farmed minks, the Netherlands, April and May 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAloose, D.; Laverack, M.; Wang, L.; Killian, M.L.; Caserta, L.C.; Yuan, F.; Mitchell, P.K.; Queen, K.; Mauldin, M.R.; Cronk, B.D.; et al. From people to panthera: Natural sars-cov-2 infection in tigers and lions at the bronx zoo. MBio 2020, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, N.; April, M.; Dvm, A.N.; Smith, D.; Ghai, R.R.; Wallace, R.M.; Torchetti, M.K.; Loiacono, C. First Reported Cases of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Companion Animals—New York, March–April 2020. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2020, 69, 710–713. [Google Scholar]
- Gortázar, C.; Barroso-Arévalo, S.; Ferreras-Colino, E.; Isla, J.; de la Fuente, G.; Rivera, B.; Domínguez, L.; de la Fuente, J.; Sánchez-Vizcaíno, J.M. Natural SARS-CoV-2 infection in kept ferrets, Spain. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriner, S.A.; Ellis, J.W.; Root, J.J.; Roug, A.; Stopak, S.R.; Wiscomb, G.W.; Zierenberg, J.R.; Ip, H.S.; Torchetti, M.K.; DeLiberto, T.J. SARS-CoV-2 exposure in escaped mink, Utah, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 988–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA APHIS|Confirmation of COVID-19 in a Snow Leopard at a Kentucky Zoo. Available online: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/aphis/newsroom/stakeholder-info/sa_by_date/sa-2020/sa-12/ky-snow-leopard-covid (accessed on 1 April 2021).
- Banerjee, A.; Pasea, L.; Harris, S.; Gonzalez-Izquierdo, A.; Torralbo, A.; Shallcross, L.; Noursadeghi, M.; Pillay, D.; Sebire, N.; Holmes, C.; et al. Estimating excess 1-year mortality associated with the COVID-19 pandemic according to underlying conditions and age: A population-based cohort study. Lancet 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Fan, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; He, T.; Wang, H.; Wan, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z. Cardiovascular Implications of Fatal Outcomes of Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inciardi, R.M.; Adamo, M.; Lupi, L.; Cani, D.S.; Di Pasquale, M.; Tomasoni, D.; Italia, L.; Zaccone, G.; Tedino, C.; Fabbricatore, D.; et al. Characteristics and outcomes of patients hospitalized for COVID-19 and cardiac disease in Northern Italy. Eur. Heart J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limongelli, G.; Limongelli, G.; Limongelli, G.; Limongelli, G.; Crotti, L.; Crotti, L.; Crotti, L.; Crotti, L. COVID-19 pandemia and inherited cardiomyopathies and channelopathies: A short term and long term perspective. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bos, J.M.; Hebl, V.B.; Oberg, A.L.; Sun, Z.; Herman, D.S.; Teekakirikul, P.; Seidman, J.G.; Seidman, C.E.; dos Remedios, C.G.; Maleszewski, J.J.; et al. Marked Up-Regulation of ACE2 in Hearts of Patients With Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Implications for SARS-CoV-2–Mediated COVID-19. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2020, 95, 1354–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, M.V.; Martins, M.; Falkenberg, S.; Buckley, A.; Caserta, L.C.; Mitchell, P.K.; Cassmann, E.D.; Rollins, A.; Zylich, N.C.; Renshaw, R.W.; et al. Susceptibility of white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) to SARS-CoV-2. J. Virol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, S.; Skaletsky, H. Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2000, 132, 365–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Coster, W.; D’hert, S.; Schultz, D.T.; Cruts, M.; Van Broeckhoven, C. NanoPack: Visualizing and processing long-read sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2018, 2666–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.-F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New Algorithms and Methods to Estimate Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies: Assessing the Performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, J.; Rahmann, S. Snakemake—A scalable bioinformatics workflow engine. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2520–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. Nextstrain: Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, E.I.; Elia, G.; Grassi, A.; Giordano, A.; Desario, C.; Medardo, M.; Smith, S.L.; Anderson, E.R.; Prince, T.; Patterson, G.T.; et al. Evidence of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 in cats and dogs from households in Italy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segalés, J.; Puig, M.; Rodon, J.; Avila-Nieto, C.; Carrillo, J.; Cantero, G.; Terrón, M.T.; Cruz, S.; Parera, M.; Noguera-Julián, M.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in a cat owned by a COVID-19-affected patient in Spain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 24790–24793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Events in Animals: OIE—World Organisation for Animal Health. Available online: https://www.oie.int/en/scientific-expertise/specific-information-and-recommendations/questions-and-answers-on-2019novel-coronavirus/events-in-animals/ (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- Shi, J.; Wen, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Huang, B.; Liu, R.; He, X.; Shuai, L.; Sun, Z.; et al. Susceptibility of ferrets, cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals to SARS-coronavirus 2. Science 2020, 368, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrashekar, A.; Liu, J.; Martino, A.J.; McMahan, K.; Mercad, N.B.; Peter, L.; Tostanosk, L.H.; Yu, J.; Maliga, Z.; Nekorchuk, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection protects against rechallenge in rhesus macaques. Science 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, V.J.; Feldmann, F.; Williamson, B.N.; van Doremalen, N.; Pérez-Pérez, L.; Schulz, J.; Meade-White, K.; Okumura, A.; Callison, J.; Brumbaugh, B.; et al. Respiratory disease in rhesus macaques inoculated with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 585, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, A.; Ghai, R.; Gary, J.; Ritter, J.; Carvallo, F.; Diel, D.G.; Martins, M.; Murphy, J.; Schroeder, B.; Brightbill, K.; et al. Determining the Role of Naturally Acquired SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Deaths of Ten Domestic Pets in the United States. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Trujillo, J.D.; Carossino, M.; Meekins, D.A.; Morozov, I.; Madden, D.W.; Indran, S.V.; Bold, D.; Balaraman, V.; Kwon, T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection, disease and transmission in domestic cats. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2322–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Carossino, M.; Morozov, I.; Trujillo, J.D.; Meekins, D.A.; Madden, D.W.; Cool, K.; Artiaga, B.L.; McDowell, C.; Bold, D.; et al. Experimental re-infected cats do not transmit SARS-CoV-2. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferasin, L.; Fritz, M.; Ferasin, H.; Legros, V.; Leroy, E.M. Myocarditis in naturally infected pets with the British variant of COVID-19. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, L.M.; Wan, L.; Xiang, T.X.; Le, A.; Liu, J.M.; Peiris, M.; Poon, L.L.M.; Zhang, W. Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorward, D.A.; Russell, C.D.; Um, I.H.; Elshani, M.; Armstrong, S.D.; Penrice-Randal, R.; Millar, T.; Lerpiniere, C.E.B.; Tagliavini, G.; Hartley, C.S.; et al. Tissue-specific immunopathology in fatal COVID-19. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edler, C.; Schröder, A.S.; Aepfelbacher, M.; Fitzek, A.; Heinemann, A.; Heinrich, F.; Klein, A.; Langenwalder, F.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Meißner, K.; et al. Dying with SARS-CoV-2 infection—an autopsy study of the first consecutive 80 cases in Hamburg, Germany. Int. J. Legal Med. 2020, 134, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borczuk, A.C.; Salvatore, S.P.; Seshan, S.V.; Patel, S.S.; Bussel, J.B.; Mostyka, M.; Elsoukkary, S.; He, B.; Del Vecchio, C.; Fortarezza, F.; et al. COVID-19 pulmonary pathology: A multi-institutional autopsy cohort from Italy and New York City. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2156–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, S.; Fiorentino, M.; De Palma, A.; Foschini, M.P.; Lazzarotto, T.; Gabrielli, L.; Viale, P.L.; Attard, L.; Riefolo, M.; D’Errico, A. Pathological post-mortem findings in lungs infected with SARS-CoV-2. J. Pathol. 2021, 253, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, S.E.; Akmatbekov, A.; Harbert, J.L.; Li, G.; Quincy Brown, J.; Vander Heide, R.S. Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in African American patients with COVID-19: An autopsy series from New Orleans. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martines, R.B.; Ritter, J.M.; Matkovic, E.; Gary, J.; Bollweg, B.C.; Bullock, H.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Silva-Flannery, L.; Seixas, J.N.; Reagan-Steiner, S.; et al. Pathology and pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 associated with fatal coronavirus disease, united states. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2005–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puelles, V.G.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Sperhake, J.P.; Wong, M.N.; Allweiss, L.; Chilla, S.; Heinemann, A.; Wanner, N.; Liu, S.; et al. Multiorgan and Renal Tropism of SARS-CoV-2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, P.; Liu, H.; Zhu, L.; et al. Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buja, L.M.; Wolf, D.; Zhao, B.; Akkanti, B.; McDonald, M.; Lelenwa, L.; Reilly, N.; Ottaviani, G.; Elghetany, M.T.; Trujillo, D.O.; et al. The emerging spectrum of cardiopulmonary pathology of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Report of 3 autopsies from Houston, Texas, and review of autopsy findings from other United States cities. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2020, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carvallo, F.R.; Martins, M.; Joshi, L.R.; Caserta, L.C.; Mitchell, P.K.; Cecere, T.; Hancock, S.; Goodrich, E.L.; Murphy, J.; Diel, D.G. Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Cat with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Viruses 2021, 13, 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081510
Carvallo FR, Martins M, Joshi LR, Caserta LC, Mitchell PK, Cecere T, Hancock S, Goodrich EL, Murphy J, Diel DG. Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Cat with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Viruses. 2021; 13(8):1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081510
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarvallo, Francisco R., Mathias Martins, Lok R. Joshi, Leonardo C. Caserta, Patrick K. Mitchell, Thomas Cecere, Sandy Hancock, Erin L. Goodrich, Julia Murphy, and Diego G. Diel. 2021. "Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Cat with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy" Viruses 13, no. 8: 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081510
APA StyleCarvallo, F. R., Martins, M., Joshi, L. R., Caserta, L. C., Mitchell, P. K., Cecere, T., Hancock, S., Goodrich, E. L., Murphy, J., & Diel, D. G. (2021). Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Cat with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Viruses, 13(8), 1510. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081510





