Polydnavirus Innexins Disrupt Host Cellular Encapsulation and Larval Maturation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. Recombinant Virus Generation and Injection
2.3. Immunoassays
2.4. Caterpillar Survival and Development
2.5. Hemocyte Count Determination and Vmem Measurement
2.6. Ex Vivo Encapsulation Assay
2.7. Statistical Analyses and Figures
3. Results
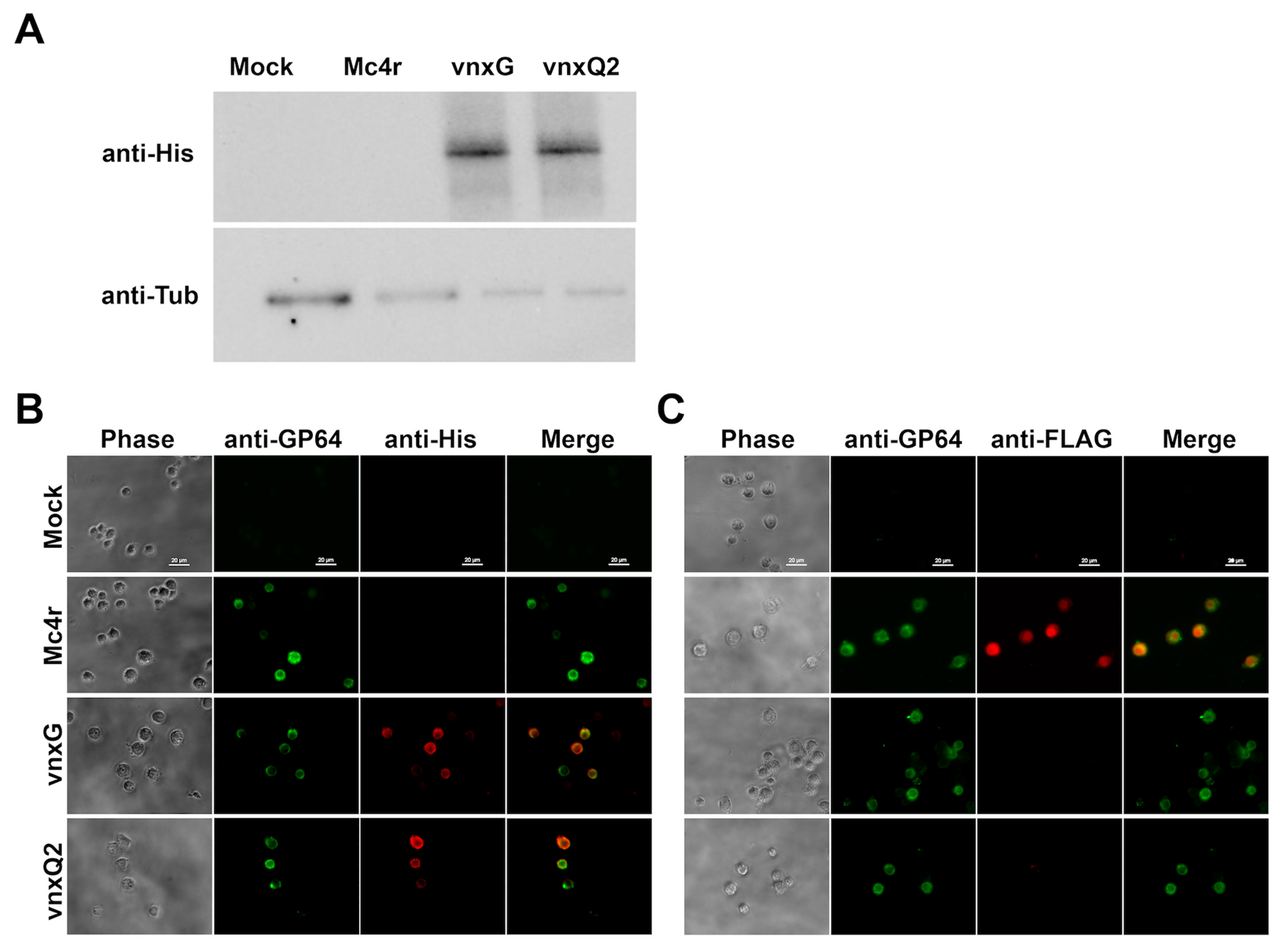
3.1. In Vivo Recombinant Protein Expression
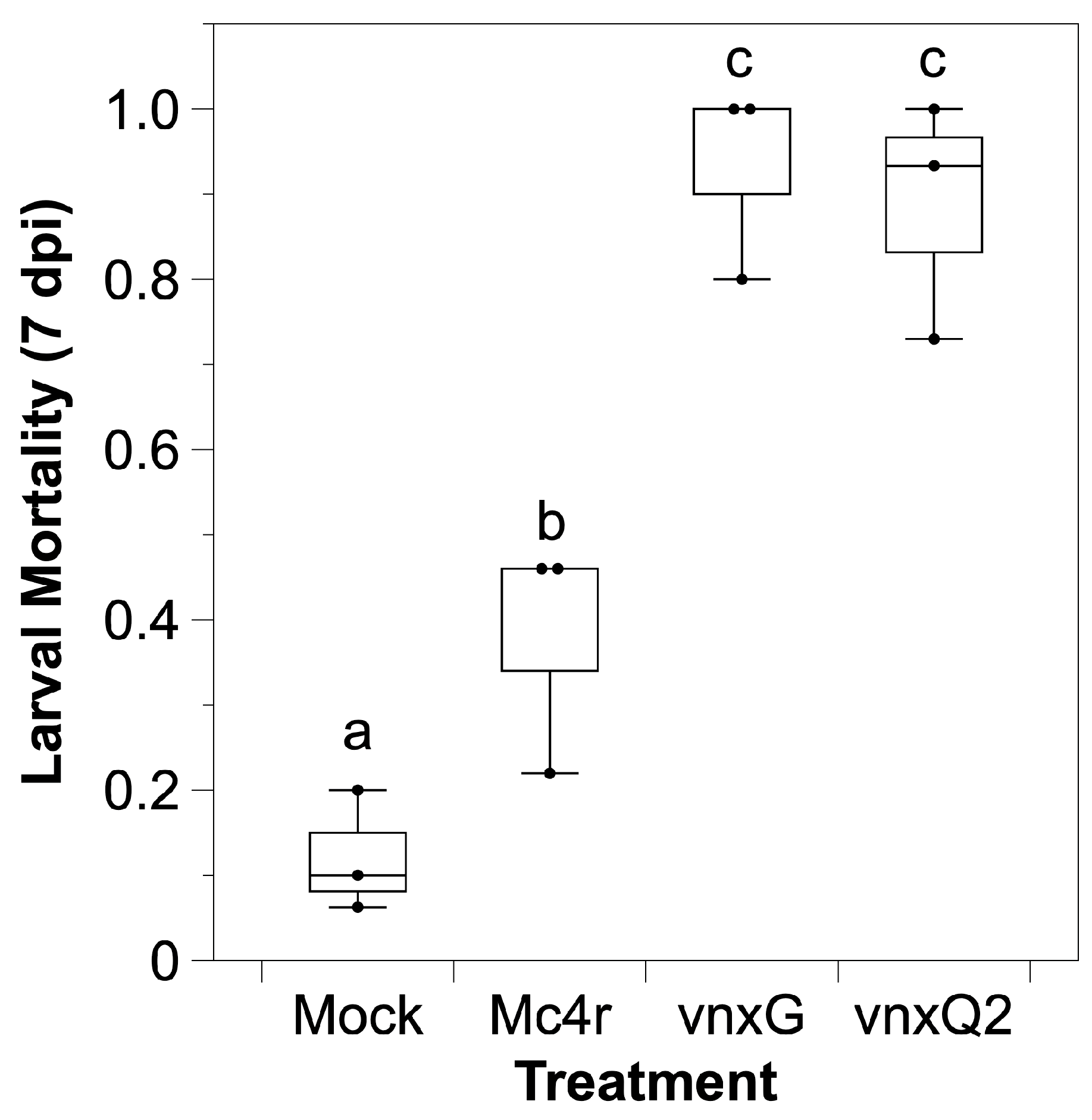
3.2. Infection with Vinnexin-Recombinant Baculoviruses Increases Caterpillar Mortality
3.3. Infection with Vinnexin-Recombinant Baculoviruses Slows Development of Host Larvae
3.4. Vinnexin Expression Has No Effect on Total Hemocyte Count (THC)
3.5. Vinnexin Expression Depolarizes Hemocyte Cell Membrane
3.6. Vinnexin Expression Disrupts Hemocyte Encapsulation Function
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drezen, J.-M.; Leobold, M.; Bezier, A.; Huguet, E.; Volkoff, A.-N.; Herniou, E.A. Endogenous viruses of parasitic wasps: Variations on a common theme. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 25, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, M.R.; Burke, G.R. Polydnaviruses: Nature’s Genetic Engineers. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2014, 1, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.; Turnbull, M.W. Manipulations of host cell physiology by polydnaviruses. In Recent Advances in Insect Physiology, Toxicology, and Molecular Biology; Liu, N., Ed.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2008; pp. 93–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.-Q.; Shi, M.; Huang, J.-H.; Chen, X.-X. Parasitoid polydnaviruses and immune interaction with secondary hosts. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2018, 83, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theilmann, D.A.; Summers, M.D. Identification and comparison of Campoletis sonorensis virus transcripts expressed from four genomic segments in the insect hosts Campoletis sonorensis and Heliothis virescens. Virology 1988, 167, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, J.A.; Webb, B.A. Polydnavirus Genes and Genomes: Emerging Gene Families and New Insights into Polydnavirus Replication. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2004, 49, 431–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, M.W.; Webb, B.A. Perspectives on polydnavirus origins and evolution. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2002, 58, 203–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupas, S.; Turnbull, M.W.; Webb, B.A. Diversifying selection in a parasitoid’s symbiotic virus among genes involved in inhibiting host immunity. Immunogen 2003, 55, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Webb, B.A.; Summers, M.D. Structure and evolutionary implications of a “cysteine-rich” Campoletis sonorensis polydnavirus gene family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 3765–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gueguen, G.; Kalamarz, M.E.; Ramroop, J.; Uribe, J.; Govind, S. Polydnaviral Ankyrin Proteins Aid Parasitic Wasp Survival by Coordinate and Selective Inhibition of Hematopoietic and Immune NF-kappa B Signaling in Insect Hosts. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Webb, B.A. Apparent functional role for a cysteine-rich polydnavirus protein in suppression of the insect cellular immune response. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 7482–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Djoumad, A.; Dallaire, F.; Lucarotti, C.J.; Cusson, M. Characterization of the polydnaviral ‘T. ostrale virus’ (TrV) gene family: TrV1 expression inhibits in vitro cell proliferation. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, W.; Kim, Y. A viral histone H4 encoded by Cotesia plutellae bracovirus inhibits haemocyte-spreading behaviour of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoetkiattikul, H.; Beck, M.H.; Strand, M.R. Inhibitor ΚB-like proteins from a polydnavirus inhibit NF-ΚB activation and suppress the insect immune response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11426–11431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Turnbull, M.W.; Martin, S.B.; Webb, B.A. Quantitative analysis of hemocyte morphological abnormalities associated with Campoletis sonorensis parasitization. J. Insect. Sci. 2004, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.H.; Strand, M.R.; Vinson, S.B. Changes in differential haemocyte count and in vitro behaviour of plasmatocytes from host Heliothis virescens caused by Campoletis sonorensis polydnavirus. J. Insect Physiol. 1987, 33, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, D.H.; Vinson, S.B. Interference with function of plasmatocytes of Heliothis virescens in vivo by calyx fluid of the parasitoid Campoletis sonorensis. Cell Tissue Res. 1988, 251, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, M.W.; Volkoff, A.-N.; Webb, B.A.; Phelan, P. Functional gap junction genes are encoded by insect viruses. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, R491–R492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, D.K.; Turnbull, M.W. Recent findings in evolution and function of insect innexins. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marziano, N.K.; Hasegawa, D.K.; Phelan, P.; Turnbull, M.W. Functional Interactions between Polydnavirus and Host Cellular Innexins. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 10222–10229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Turnbull, M.W. Virus innexin expression in insect cells disrupts cell membrane potential and pH. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchill, D.; Coodin, S.; Shivers, R.R.; Caveney, S. Rapid de novo formation of gap junctions between insect hemocytes in vitro: A freeze-fracture, dye- transfer and patch-clamp study. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 104, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Turnbull, M.W. Characterization of Nonjunctional Hemichannels in Caterpillar Cells. J. Insect Sci. 2011, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pang, Z.; Li, M.; Yu, D.; Yan, Z.; Liu, X.; Ji, X.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Luo, K. Two Innexins of Spodoptera litura Influences Hemichannel and Gap Junction Functions in Cellular Immune Responses. Arch Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 90, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerwald, R.J. Inverted gap and other cell junctions in cockroach hemocyte capsules: A thin section and freeze-fracture study. Tissue Cell 1975, 7, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, D.K.; Erickson, S.L.; Hersh, B.M.; Turnbull, M.W. Virus Innexins induce alterations in insect cell and tissue function. J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 98, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strand, M.R.; Johnson, J.A.; Culin, J.D. Developmental Interactions between the Parasitoid Microplitis demolitor (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and Its Host Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Ann. Ѐntomol. Soc. Am. 1988, 81, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, D.R.; Miller, L.K.; Luckow, V.A. Baculovirus Expression Vectors: A Laboratory Manual; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994; p. 347. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, A.M.; Kim, Y. Parasitism by Cotesia plutellae alters the hemocyte population and immunological function of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. J. Insect Physiol. 2006, 52, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, D.K.; Zhang, P.; Turnbull, M.W. Intracellular dynamics of polydnavirus innexin homologues. Insect Mol. Biol. 2020, 29, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.L.; Friedman, R. Genome-wide survey for genes horizontally transferred from cellular organisms to baculoviruses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clavijo, G.; Dorémus, T.; Ravallec, M.; Mannucci, M.-A.; Jouan, V.; Volkoff, A.-N.; Darboux, I. Multigenic Families in Ichnovirus: A Tissue and Host Specificity Study through Expression Analysis of Vankyrins from Hyposoter didymator Ichnovirus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, L.; Soldevila, A.I.; Webb, B.A. Relationships between polydnavirus gene expression and host range of the parasitoid wasp Campoletis sonorensis. J. Insect Physiol. 2000, 46, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorémus, T.; Cousserans, F.; Gyapay, G.; Jouan, V.; Milano, P.; Wajnberg, E.; Darboux, I.; Cônsoli, F.L.; Volkoff, A.-N. Extensive Transcription Analysis of the Hyposoter didymator Ichnovirus Genome in Permissive and Non-Permissive Lepidopteran Host Species. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.I.; Kwon, M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y. Parasitism and survival rate of Diadegma fenestrale (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) and DfIV gene expression patterns in two lepidopteran hosts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 459, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.-P.; Zhang, J.-H.; Wang, C.-Z. Cloning and characterization of two Campoletis chlorideae ichnovirus vankyrin genes expressed in parasitized host Helicoverpa armigera. J. Insect Physiol. 2007, 53, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruijssers, A.; Strand, M.R. PTP-H2 and PTP-H3 from Microplitis demolitor Bracovirus Localize to Focal Adhesions and are Anti-Phagocytic in Insect Immune Cells. J. Virol. 2006, 81, 1209–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinson, S.B. Physiological interactions between the host genusHeliothis and its guild of parasitoids. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1990, 13, 63–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, K.S.; Webb, B.A. Polydnavirus infection inhibits translation of specific growth-associated host proteins. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 27, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dover, B.A.; Davies, D.H.; Vinson, S.B. Degeneration of last instar Heliothis virescens prothoracic glands by Campoletis sonorensis polydnavirus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1988, 51, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignesti, M.; Ferrara, R.; Romani, P.; Valzania, L.; Serafini, G.; Pennacchio, F.; Cavaliere, V.; Gargiulo, G. A polydnavirus-encoded ANK protein has a negative impact on steroidogenesis and development. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 95, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glazachev, Y.I.; Semenova, A.D.; Kryukova, N.A.; Slepneva, I.A.; Glupov, V.V. Express Method for Determination of Low Value of Trans-membrane Potential of Living Cells with Fluorescence Probe: Application on Haemocytes at Immune Responses. J. Fluoresc. 2012, 22, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, N.T.; Goecks, J.; Kacsoh, B.Z.; Mobley, J.A.; Bowersock, G.J.; Taylor, J.; Schlenke, T.A. Parasitoid wasp venom SERCA regulates Drosophila calcium levels and inhibits cellular immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9427–9432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grimstone, A.V.; Rotheram, S.; Salt, G. An electron-microscope study of capsule formation by insect blood cells. J. Cell Sci. 1967, 2, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.P. Gap Cell Junctions, Cell Adhesion Molecules, and Molecular Basis of Encapsulation. In Immmunology of Insects and Other Arthropods; Gupta, A.P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1991; pp. 133–167. [Google Scholar]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Turnbull, M. Polydnavirus Innexins Disrupt Host Cellular Encapsulation and Larval Maturation. Viruses 2021, 13, 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081621
Zhang P, Turnbull M. Polydnavirus Innexins Disrupt Host Cellular Encapsulation and Larval Maturation. Viruses. 2021; 13(8):1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081621
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Peng, and Matthew Turnbull. 2021. "Polydnavirus Innexins Disrupt Host Cellular Encapsulation and Larval Maturation" Viruses 13, no. 8: 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081621
APA StyleZhang, P., & Turnbull, M. (2021). Polydnavirus Innexins Disrupt Host Cellular Encapsulation and Larval Maturation. Viruses, 13(8), 1621. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081621





