SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Structure of the Russian Population during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Organization and Formation of a Volunteer Cohort
2.2. Antibody Analysis Methodology
2.3. Statistical Analyses
2.4. General Features of Collective Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in the Russian Population
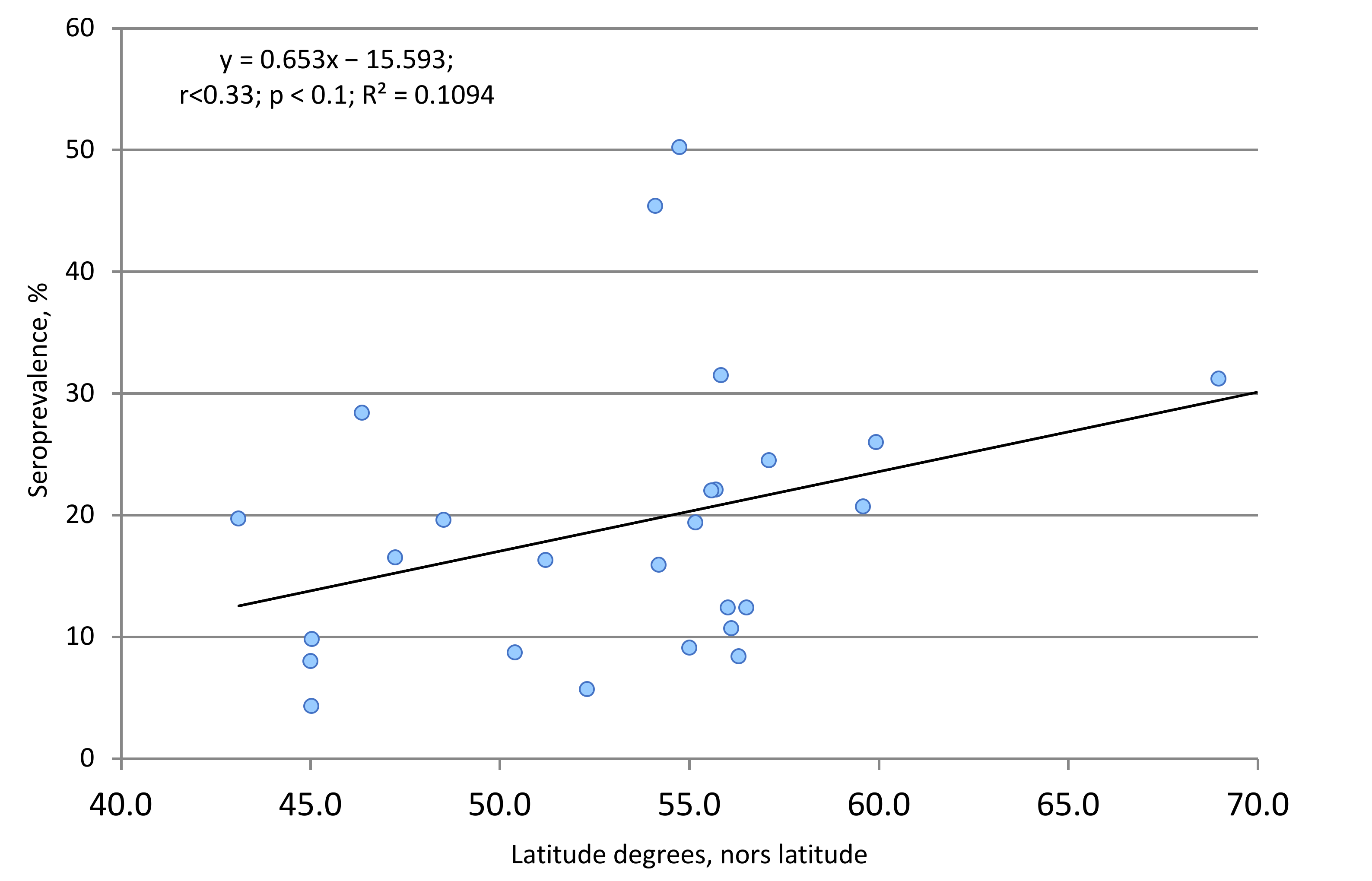
2.5. Territorial and Climatic Features of Collective Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in the Russian Population
2.6. Three-Phase Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 Seropositivity
2.7. Seroprevalence among COVID-19 Convalescents and Contacts
2.8. Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smirnov, V.S.; Zarubaev, V.V.; Petlenko, S.V. Biology of Pathogens and Control. of Ibfluenza and Acute Respiratory Viral Infections; Hyppokrates Publishing: Saint-Petersburg, Russia, 2020; p. 336. ISBN 978-5-8232-0643-3. [Google Scholar]
- Perico, L.; Benigni, A.; Casiraghi, F.; Ng, L.F.P.; Renia, L.; Remuzzi, G. Immunity, endothelial injury and complement-induced coagulopathy in COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 17, 46–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Elrashdy, F.; Aljadawi, A.; Ali, S.M.; Khan, R.H.; Redwan, E.M. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection reaches the human nervous system: How? J. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 99, 750–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, I.; Limonta, D.; Mahal, L.K.; Hobman, T.C. Endothelium Infection and Dysregulation by SARS-CoV-2: Evidence and Caveats in COVID-19. Viruses 2021, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujari, R.; Thommana, M.V.; Mercedes, B.R.; Serwat, A. Therapeutic Options for COVID-19: A Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e10480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Suárez., V.J.; Hormeño-Holgado, A.; Jiménez, M.; Benitez-Agudelo, J.C.; Navarro-Jiménez, E.; Perez-Palencia, N.; Maestre-Serrano, R.; Laborde-Cárdenas, C.C.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Dynamics of Population Immunity Due to the Herd Effect in the COVID-19 Pandemic. Vaccines 2020, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randolph, H.E.; Barreiro, L.B. Herd Immunity: Understanding COVID-19. Immunity 2020, 52, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vabret, N.; Britton, G.J.; Gruber, C.; Hegd, S.; Kim, J.; Kuksin, M.; Levantovsky., R.; Malle, L.; Moreira, A.; Park, M.D.; et al. The Sinai Immunology Review Project. Immunology of COVID-19: Current state of the science. Immunity 2020, 52, 910–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami, A.; Sepidarkish, M.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Riahi, S.M.; Shiadeh, M.N.; Esfandyari, S.; Mokdad, A.H.; Hotez, P.J.; Gasser, R.B. SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 27, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balicer, R.D.; Ohana, R. Israel’s COVID-19 endgame. Science 2021, 37, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignesh, R.; Shankar, E.M.; Velu, V.; Thyagarajan, S.P. Is Herd Immunity Against SARS-CoV-2 a Silver Lining? Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 586781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanat, F.; Stadlbauer, D.; Strohmeier, S.; Nguyen, T.H.O.; Chromikova, V.; McMahon, M.; Jiang., K.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Jurczyszak, D.; Polanco, J.; et al. A serological assay to detect SARS-CoV-2 seroconversion in humans. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1033–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttiatt, V.S.; Abraham, P.R.; Menon, R.P.; Vaidya, P.C.; Rahi, M. Coronavirus disease 2019 in children: Clinical & epidemiological implications. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 152, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Ren, L.; Yang, J.; Guo, L.; Feng, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, X.; Leng, Z.; Tong., X.; Zhou, W.; et al. Seroprevalence and humoral immune durability of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in Wuhan, China: A longitudinal, population-level, cross-sectional study. Lancet 2021, 397, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapha, H.J.; Routledge, I.; Takahashi, S.; Choisy, M.; Cummings, D.; Grenfell, B.C.; Metcalf, J.E.; Mina, M.; Barraquer, I.R. Seroepidemiologic Study Designs for Determining SARS-COV-2 Transmission and Immunity. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Protocol for a Population-Based Age-Stratified Sero-Epidemiological Study of COVID-19 Infection in Humans. Version 2.0.. 2020. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/332188/WHO-2019-nCoV-Seroepidemiology-2020.2-rus.pdf (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Popova, A.Y.; Andreeva, E.E.; Babura, E.A.; Balakhonov, S.V.; Bashketova, N.S.; Bulanov, M.V.; Valeullina, N.N.; Goryaev, D.V.; Detkovskaya, N.N.; Ezhlova, E.B.; et al. Features of developing SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein population-based seroprevalence during the first wave of the COVID-19 epidemic in the Russian Federation. Russ. J. Infect. Immun. [Infektsiya I Immun.] 2021, 11, 297–323. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Istorik, O.A.; Mosevich, O.S.; Lyalina, L.V.; Smirnov, V.S.; Cherny, M.A.; Balabysheva, N.S.; Loginova, I.S.; et al. Assessment of the Herd Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 among the Population of the Leningrad Region during the COVID-19 Epidemic. Probl. Part. Danger. Infect. [Probl. Osob. Opasnykh Infektsii] 2020, 3, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Bashketova, N.S.; Fridman, R.K.; Lyalina, L.V.; Smirnov, V.S.; Chkhindzheriya, I.G.; Grechaninova, T.A.; Agapov, K.A.; et al. Herd Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 among the Population in Saint-Petersburg during the COVID-19 Epidemic. Probl. Osob. Opasnykh Infektsii [Probl. Part. Danger. Infect.] 2020, 3, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agresti, A.; Coull, B.A. Approximate Is Better than "Exact" for Interval Estimation of Binomial Proportions. Am. Stat. 1998, 52, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzhibovsky, A.M. Confidence intervals for frequencies and beats. Hum. Ecol. 2008, 5, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Popova, A.Y.; Andreeva, E.E.; Babura, E.A.; Balakhonov, S.V.; Bashketova, N.S.; Bulanov, M.V.; Valeullina, N.N.; Goryaev, D.V.; Detkovskaya, N.N.; Ezhlova, E.B. Peculiarities of seroprevalence to nucleocapsid SARS-CoV-2 in children during the 2020 COVID-19 epidemic. Pediatric 2021, 100, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Balakhonov, S.V.; Chesnokova, M.V.; Dubrovina, V.I.; Lyalina, L.V.; Smirnov, V.S.; Trukhina, A.G.; Perezhogin, A.N.; et al. Experience in Studying Seroprevalence to SARS-CoV-2 Virus in the Population of the Irkutsk Region during COVID-19 Outbreak. Probl. Part. Danger. Infect. [Probl. Osob. Opasnykh Infektsii] 2020, 3, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Melnikova, A.A.; Stepanova, T.F.; Sharukho, G.V.; Letyushev, A.N.; Folmer, A.Y.; Shepotkova, A.A.; Lyalina, L.V.; Smirnov, V.S.; et al. Distribution of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence among residents of the Tyumen Region during the COVID-19 epidemic period. J. Microbiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. {Zhurnal Mikrobiol. Èpidemiologii I Immunobiol.] 2020, 97, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Noskov, A.K.; Kovalev, E.V.; Karpushchenko, G.V.; Lyalina, L.V.; Smirnov, V.S.; Chemisova, O.S.; Trishina, A.V.; et al. Assessment of Population Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 Virus in the Rostov Region. Probl. Part. Danger. Infect. [Probl. Osob. Opasnykh Infektsii] 2020, 4, 117–124. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Babura, E.A.; Mikheenko, O.P.; Lyalina, L.V.; Smirnov, V.S.; Molchanova, J.R.; Gorbatova, Y.V.; Kharitonova, M.N.; et al. Population immunity to SARS-CoV-2 of the population of the Kaliningrad region during the epidemic season of COVID-19. J. Infectology [Zhurnal Infektologii] 2020, 12, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Yezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Andreeva, E.E.; Kombarova, S.Y.; Lyalina, L.V.; Smirnov, V.S.; Aleshkin, A.V.; Kobzeva, Y.V.; Ignatova, E.N.; et al. Collective immunity to SARS-CoV-2 of Moscow residents during the COVID-19 epidemic period. Infekc. Bolezn. [Infect. Dis.] 2020, 18, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Mikailova, O.M.; Kombarova, S.Y.; Kostina, M.A.; Aлёшкин, A.B.; Лялина, Л.B.; Cмирнoв, B.C.; Гвазава, K.P.; et al. The structure of seroprevalence to the SARS-CoV-2 virus among residents of the Moscow Region during the period of epidemic incidence of COVID-19. Infekc. Bolezn. [Infect. Dis.] 2020, 18, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Kutyrev, V.V.; Kozhanova., O.I.; Cherkasskaya, T.S.; Lyalina, V.I.; Smirnov, V.S.; Bugorkova, S.A.; Portenko, S.A.; et al. Characteristics of the Herd Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in Residents of the Saratov Region under COVID-19 Epidemic. Probl. Part. Danger. Infect. [Probl. Osob. Opasnykh Infektsii] 2020, 4, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Trotsenko, O.E.; Zaitseva, T.A.; Lyalina, L.V.; Garbuz, Y.A.; Smirnov, V.S.; Lomonosova, V.I.; Balakhontseva, L.A.; et al. The seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 among residents of the Khabarovsk Krai during the COVID-19 epidemic. J. Microbiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. [Zhurnal Mikrobiol. Èpidemiologii I Immunobiol.] 2021, 98, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Danilova, T.E.; Bulanov, M.V.; Lyalina, L.V.; Smirnov, V.S.; Totolyan, A.A. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence among the population of the Vladimir Region during the COVID-19 epidemic. Epidemiology and infectious diseases. Curr. Items 2021, 11, 29–35. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Lukicheva, L.A.; Nikitina, L.I.; Lyalina, L.V.; Smirnov, V.S.; Koltsov, N.S.; Ermakova, M.V.; Kubashev, A.K.; et al. Humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 among the population of Murmansk region amid COVID-19 epidemic. HIV Infect. Immunosuppr. 2021, 13, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, A.Y.; Ezhlova, E.B.; Mel’nikova, A.A.; Patyashina, M.A.; Sizova, E.P.; Yuzlibaeva, L.R.; Lyalina, L.V.; Smirnov, V.S.; Badamshina, G.G.; Goncharova, A.V.; et al. Distribution of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence among residents of the Republic of Tatarstan during the COVID-19 epidemic period. J. Microbiol. Epidemiol. Immunobiol. [Zhurnal Mikrobiol. Èpidemiologii I Immunobiologii] 2020, 97, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcombe, R.G. Two-sided confidence intervals for the single proportion: Comparison of seven methods. Stat. Med. 1998, 17, 857–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, N.; Simon, P.; Ebner, P.; Eichner, D.; Reynolds, J.; Bendavid, E.; Bhattacharya, J. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibodies Among Adults in Los Angeles County, California, on April 10–11, 2020. JAMA 2020, 323, 2425–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.S.; Costa, V.; Racine-Brzostek, S.E.; Acker, K.P.; Yee, J.; Chen, Z.; Karbaschi, M.; Zuk, R.; Rand, S.; Sukhu, A.; et al. Association of Age With SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response. JAMA Netw Open. 2021, 4, e214302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Li, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wei1, X. Distinct Characteristics of COVID-19 Infection in Children. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 619738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznik, B.I.; Khavinson, V.K.; Smirnov, V.S. Features of pathogenesis and COVID-19 course for the elderly and old age. Adv. Geront. 2020, 33, 1032–1042. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moderbacher, C.R.; Ramirez, S.I.; Dan, J.M.; Hastie, K.M.; Weiskopf, D.; Belanger, S.; Abbott, R.K.; Kim, C.; Choi, J.; Kato, Y.; et al. Antigen-Specific Adaptive Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in Acute COVID-19 and Associations with Age and Disease Severity. Cell 2020, 183, 996–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunyavanich, S.; Do, A.; Vicencio, A. Nasal Gene Expression of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 in Children and Adults. JAMA 2020, 323, 2427–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.W.; Faulkner, N.; Cornish, G.H.; Rosa, A.; Harvey, R.; Hussain, S.; Ulferts, R.; Earl, C.; Wrobel, A.; Benton, D.; et al. Pre-existing and de novo humoral immunity to SARS-CoV-2 in humans. BioRxiv 2020, 095414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiakolas, A.R.; Kramer, K.J.; Wrapp, D.; Richardson, S.I.; Schäfer, A.; Wall, S.; Wang, N.; Janowska, K.; Pilewski, K.A.; Venkat, R.; et al. Cross-reactive coronavirus antibodies with diverse epitope specificities and Fc effector functions. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.C.M.; Howard-Jones, A.R.; Hsu, P.; Palasanthiran, P.; Gray, P.E.; McMullan, B.J.; Britton, P.N.; Bartlett, A.W. SARS-CoV-2 in children: Spectrum of disease, transmission and immunopathological underpinnings. Pathol. 2020, 52, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hippich, M.; Holthaus, L.; Assfalg, R.; Zapardiel-Gonzalo, J.; Heigermoser, M.; Haupt, F.; Ewald, D.A.; Welzhofer, T.C. A Public Health Antibody Screening Indicates a 6-Fold Higher SARS-CoV-2 Exposure Rate than Reported Cases in Children. Med. 2021, 2, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, K.O.; Lai, F.; Wei, W.I.; Wong, S.Y.S.; Tang, J.W.T. Herd immunity—Estimating the level required to halt the COVID-19 epidemics in affected countries. J. Infect. 2020, 80, e32–e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanis, P.; Vraka, I.; Fragkou, D.; Bilali, A.; Kaitelidoua, D. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and associated factors in healthcare workers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hosp. Infect. 2021, 108, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Azman, A.S.; Deng, X.; Sun, R.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, N.; Chen, X.; Lu, W.; Zhuang, T.; et al. Serological evidence of human infection with SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review and meta-analysis Lancet Glob. Health 2021, 9, e598–e609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triggle, C.R.; Bansal, D.; Ding, H.; Islam, M.M.; Farag, E.A.B.A.; Hadi, H.A.; Ali Sultan, A. A Comprehensive Review of Viral Characteristics, Transmission, Pathophysiology, Immune Response, and Management of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 as a Basis for Controlling the Pandemic. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 631139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Luo, Y.; Mao, L.; Wang, F.; Wu, S.; Sun, Z. Detection of IgM and IgG antibodies in patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2020, 9, e01136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.S.; Jones, F.K.; Nodoushani, A.; Kelly, M.; Becker, M.; Slater, D.; Mills, R.; Teng, E.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; et al. Dynamics and significance of the antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. medRxiv 2020, 20155374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialkowski, A.; Gernez, Y.; Arya, P.; Weinacht, K.G.; Kinane, T.B.; Yonker, L.M. Insight into the pediatric and adult dichotomy of COVID-19: Age-related differences in the immune response to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Pediatric Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 2556–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Reeves, D.B.; Cardozo-Ojeda, E.F.; Schiffer, J.T.; Mayeret, B.T. Viral load and contact heterogeneity predict SARS-CoV-2 transmission and super-spreading events. eLife 2021, 10, e63537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buitrago-Garcia, D.; Egli-Gany, D.; Counotte, M.J.; Hossmann, S.; Imeri, H.; Ipekci, A.M.; Salanti, G.; Low, N. Occurrence and transmission potential of asymptomatic and presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections: A living systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, T.H.; Pak, C.; Ock, M.; Lee, S.H.; Son, J.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Real Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection Might Be Rare: Importance of Careful Interviews and Follow-up. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2020, 35, e333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.-X.; Tang, X.-J.; Shi, Q.-L.; Li, Q.; Deng, H.-J.; Yuan, J.; Hu, J.-L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, F.-J.; et al. Clinical and immunological assessment of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1200–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshchehreh, M.; Wald-Dickler, N.; Holtom, P.; Butler-Wu, S.M. A needle in the haystack? Assessing the significance of envelope (E) gene-negative, nucleocapsid (N2) gene-positive SARS-CoV-2 detection by the Cepheid Xpert Xpress SARS-COV-2 assay. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 133, 104683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAndrews, K.M.; Dowlatshahi, D.P.; Dai, J.; Becker, L.M.; Hensel, J.; Snowden, L.M.; Leveille, J.M.; Brunner, M.R.; Holden, K.W.; Hopkins, N.S.; et al. Heterogeneous antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain and nucleocapsid with implications for COVID-19 immunity. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e142386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.A.; Mok, C.K.; Tsang, O.T.; Lv, H.; Ko, R.L.W.; Wu, N.C.; Yuan, M.; Leung, W.S.; Chan, J.M.C.; Chik, T.S.H.; et al. Serological assays for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), March 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020, 25, 2000421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Zhong, L.; Tan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lyu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, A.; Huang, L.; Long, Z.; Liu, N.-N.; et al. How to Understand “Herd Immunity” in COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 547314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, R.; Dub, T.; Andrianou, X.; Nohynek, H.; Wilder-Smith, A.; Pezzotti, P.; Fontanet, A. SARS-CoV-2 population-based seroprevalence studies in Europe: A scoping review. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, J.; Nie, S.; Li, H.; Kong, Y.; Liang, M.; Hou, J.; Huang, X.; Li, D.; Ma, T.; et al. Seroprevalence of immunoglobulin M and G antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in China. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1193–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeremijenko, A.; Chemaitelly, H.; Ayoub, H.H.; Alishaq, M.; Abou-Samra, A.-B.; Al Ajmi, J.A.A.A.; Al Ansari, N.A.A.; Al Kanaani, Z.; Al Khal, A.; Al Kuwari, E.; et al. Herd Immunity against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in 10 Communities, Qatar. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1343–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poustchi, H.; Darvishian, M.; Mohammadi, Z.; Shayanrad, A.; Delavari, A.; Bahadorimonfared, A.; Eslami, S.; Javanmard, S.H.; Shakiba, E.; Somi, M.H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 antibody seroprevalence in the general population and high-risk occupational groups across 18 cities in Iran: A population-based cross-sectional study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havers, F.P.; Reed, C.; Lim, T.; Montgomery, J.M.; Klena, J.D.; Hall, A.J.; Fry, A.M.; Cannon, D.L.; Chiang, C.-F.; Gibbons, A.; et al. Seroprevalence of Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in 10 Sites in the United States, March 23 May 12, 2020. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1576–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabino, E.C.; Buss, L.F.; Carvalho, M.P.S.; Prete, C.A.; Crispim, M.A.E.; Fraiji, N.A.; Pereira, R.H.M.; Parag, K.V.; Peixoto, P.d.S.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; et al. Resurgence of COVID-19 in Manaus, Brazil, despite high seroprevalence. Lancet 2021, 397, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gidding, H.F.; Machalek, D.A.; Hendry, A.J.; Quinn, H.E.; Vette, K.; Beard, F.H.; Shilling, H.S.; Hirani, R.; Gosbell, I.B.; Irving, D.O.; et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in Sydney after the first epidemic wave of 2020. Med. J. Aust. 2021, 214, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, M.; Rehman, A.; Ahmad, J.; Ahmed, S.; Khan, M.A.; Naveed, A.; Rajab, H.; Muhammad, F.; Naushad, W.; Aman, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2: Big seroprevalence data from Pakistan—Is herd immunity at hand? Infection 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsabouri, S.; Makis, A.; Kosmeri, C.; Siomou, E. Risk Factors for Severity in Children with Coronavirus Disease 2019. A Comprehensive Literature Review. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 68, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reicher, S.; Ratzon, R.; Ben-Sahar, S.; Hermoni-Alon, S.; Mossinson, D.; Shenhar, Y.; Friger, M.; Lustig, Y.; Alroy-Preis, S.; Anis, E.; et al. Nationwide seroprevalence of antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in Israel. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britton, T.; Ball, F.; Trapman, P. A mathematical model reveals the influence of population heterogeneity on herd immunity to SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











| Federal District(FD) | Number of Regions in the FD | Total number of Population Constituents | Characteristics of the Surveyed Regions in the FD | Characteristics of the Surveyed Cohorts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Surveyed Regions in the FD | Population Size of Surveyed Areas, Persons | Also in % | Number of volunteers | Number of Seropositive Persons | Seroprevalence, % (95% Confidence Interval, CI) | |||
| FEFD | 11 | 8,124,053 | 3 | 3,960,816 | 48.8 | 8295 | 2384 | 28.7 (27.8–29.7) * |
| NCFD | 7 | 9,967,301 | 1 | 2,792,796 | 28.0 | 2683 | 262 | 9.8 (8.6–11.0) * |
| UFD | 6 | 12,329,500 | 3 | 9,276,273 | 752 | 8584 | 1589 | 18.5 (17.6–19.4) |
| NWFD | 11 | 13,941,959 | 4 | 9,028,541 | 64.8 | 11,899 | 3800 | 31.9 (30.9–32.9) * |
| SbFD | 10 | 17,003,927 | 3 | 8,016,756 | 47.1 | 8165 | 748 | 9.2 (8.3–9.7) * |
| SFD | 8 | 16,482,488 | 4 | 12,764,789 | 77.4 | 11,632 | 1633 | 14.0 (13.4–14.7) * |
| VFD | 14 | 29,070,827 | 3 | 9,465,793 | 32.6 | 8982 | 1695 | 18.9 (17.9–19.8) |
| CFD | 18 | 39,250,960 | 5 | 24,706,022 | 63.9 | 13,964 | 2164 | 15.7 (15.1–16.5) * |
| Total | 85 | 146,171,015 | 26 | 80,011,786 | 54.8 | 74,158 | 14,275 | 19.2 (19.0–19.6) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Popova, A.Y.; Smirnov, V.S.; Andreeva, E.E.; Babura, E.A.; Balakhonov, S.V.; Bashketova, N.S.; Bugorkova, S.A.; Bulanov, M.V.; Valeullina, N.N.; Vetrov, V.V.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Structure of the Russian Population during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Viruses 2021, 13, 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081648
Popova AY, Smirnov VS, Andreeva EE, Babura EA, Balakhonov SV, Bashketova NS, Bugorkova SA, Bulanov MV, Valeullina NN, Vetrov VV, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Structure of the Russian Population during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Viruses. 2021; 13(8):1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081648
Chicago/Turabian StylePopova, Anna Y., Viacheslav S. Smirnov, Elena E. Andreeva, Elena A. Babura, Sergey V. Balakhonov, Natalia S. Bashketova, Svetlana A. Bugorkova, Maxim V. Bulanov, Natalia. N. Valeullina, Viacheslav. V. Vetrov, and et al. 2021. "SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Structure of the Russian Population during the COVID-19 Pandemic" Viruses 13, no. 8: 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081648
APA StylePopova, A. Y., Smirnov, V. S., Andreeva, E. E., Babura, E. A., Balakhonov, S. V., Bashketova, N. S., Bugorkova, S. A., Bulanov, M. V., Valeullina, N. N., Vetrov, V. V., Goryaev, D. V., Detkovskaya, T. N., Ezhlova, E. B., Zaitseva, N. N., Istorik, O. A., Kovalchuk, I. V., Kozlovskikh, D. N., Kombarova, S. Y., Kurganova, O. P., ... Totolian, A. A. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Structure of the Russian Population during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Viruses, 13(8), 1648. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081648






