The Post-Acute Phase of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Two Macaque Species Is Associated with Signs of Ongoing Virus Replication and Pathology in Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Tissues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics and Biosafety Statement
2.2. Animals
2.3. Virus
2.4. Experimental Infections and Post-Exposure Study Follow-Up
2.5. Biochemistry and Hematology
2.6. Detection of Viral RNA in Swabs, Blood, and Tissue
2.7. Imaging
2.7.1. PET-CT
2.7.2. Gated-CT
2.8. Cytokine and Chemokine Analysis
2.9. Serology
2.10. Necropsy and Histological Analysis
2.11. Immunohistochemistry
3. Results
3.1. Infection of Macaques with SARS-CoV-2
3.2. Body Temperature, Activity, Clinical Symptoms, and Blood Parameters after SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3.3. Humoral Immune Response to SARS-CoV-2 Infection
3.4. Cytokine and Chemokine Measurements in Sera of Infected Macaques
3.5. Development of Lung Lesions and Lymph Node Activation during SARS-CoV2 Infection
3.6. Gross Pathology
3.7. Wide-Spread Presence of Viral RNA in Post-Mortem Tissue Samples, and Evidence of Active Virus Replication in the Respiratory Tract of Infected Macaques
3.8. Histopathology
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Whetton, A.D.; Preston, G.W.; Abubeker, S.; Geifman, N. Proteomics and Informatics for Understanding Phases and Identifying Biomarkers in COVID-19 Disease. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 4219–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polak, S.B.; Van Gool, I.C.; Cohen, D.; von der Thusen, J.H.; van Paassen, J. A systematic review of pathological findings in COVID-19: A pathophysiological timeline and possible mechanisms of disease progression. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 2128–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwee, T.C.; Kwee, R.M. Chest CT in COVID-19: What the Radiologist Needs to Know. Radiographics 2020, 40, 1848–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Lu, L.; Cao, W.; Li, T. Hypothesis for potential pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection-a review of immune changes in patients with viral pneumonia. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oronsky, B.; Larson, C.; Hammond, T.C.; Oronsky, A.; Kesari, S.; Lybeck, M.; Reid, T.R. A Review of Persistent Post-COVID Syndrome (PPCS). Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollini, M.; Morbelli, S.; Ciccarelli, M.; Cecconi, M.; Aghemo, A.; Morelli, P.; Chiola, S.; Gelardi, F.; Chiti, A. Long COVID hallmarks on [18F]FDG-PET/CT: A case-control study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudre, C.H.; Murray, B.; Varsavsky, T.; Graham, M.S.; Penfold, R.S.; Bowyer, R.C.; Pujol, J.C.; Klaser, K.; Antonelli, M.; Canas, L.S.; et al. Attributes and predictors of long COVID. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 626–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandian, A.; Sehgal, K.; Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; McGroder, C.; Stevens, J.S.; Cook, J.R.; Nordvig, A.S.; Shalev, D.; Sehrawat, T.S.; et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat. Med. 2021, 7862, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, S.J.; Pitchford, S.C.; Amison, R.T.; Carrington, R.; Robaina Cabrera, C.L.; Magnen, M.; Looney, M.R.; Gray, E.; Page, C.P. Animal models of mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 pathology. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4851–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCray, P.B., Jr.; Pewe, L.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Hickey, M.; Manzel, L.; Shi, L.; Netland, J.; Jia, H.P.; Halabi, C.; Sigmund, C.D.; et al. Lethal infection of K18-hACE2 mice infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lutz, C.; Maher, L.; Lee, C.; Kang, W. COVID-19 preclinical models: Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 transgenic mice. Hum. Genom. 2020, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Felipe, L.; Vercruysse, T.; Sharma, S.; Ma, J.; Lemmens, V.; Van Looveren, D.; Arkalagud Javarappa, M.P.; Boudewijns, R.; Malengier-Devlies, B.; Liesenborghs, L.; et al. A single-dose live-attenuated YF17D-vectored SARS-CoV-2 vaccine candidate. Nature 2021, 590, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudewijns, R.; Thibaut, H.J.; Kaptein, S.J.F.; Li, R.; Vergote, V.; Seldeslachts, L.; Van Weyenbergh, J.; De Keyzer, C.; Bervoets, L.; Sharma, S.; et al. STAT2 signaling restricts viral dissemination but drives severe pneumonia in SARS-CoV-2 infected hamsters. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.I.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, E.H.; Park, S.J.; Yu, K.M.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, S.; Casel, M.A.B.; et al. Infection and Rapid Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Ferrets. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 704–709.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, M.; Kok, A.; de Meulder, D.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Lamers, M.M.; Okba, N.M.A.; van Fentener Vlissingen, M.; Rockx, B.; Haagmans, B.L.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 is transmitted via contact and via the air between ferrets. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Thao, T.T.N.; Hoffmann, D.; Taddeo, A.; Ebert, N.; Labroussaa, F.; Pohlmann, A.; King, J.; Steiner, S.; Kelly, J.N.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike D614G change enhances replication and transmission. Nature 2021, 592, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, R.D.; Schmitz, K.S.; Bovier, F.T.; Predella, C.; Khao, J.; Noack, D.; Haagmans, B.L.; Herfst, S.; Stearns, K.N.; Drew-Bear, J.; et al. Intranasal fusion inhibitory lipopeptide prevents direct-contact SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets. Science 2021, 371, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matute-Bello, G.; Frevert, C.W.; Martin, T.R. Animal models of acute lung injury. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2008, 295, L379–L399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Estes, J.D.; Wong, S.W.; Brenchley, J.M. Nonhuman primate models of human viral infections. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.R.; Bao, L.L. The battle against SARS and MERS coronaviruses: Reservoirs and Animal Models. Anim. Model Exp. Med. 2018, 1, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutton, T.C.; Subbarao, K. Development of animal models against emerging coronaviruses: From SARS to MERS coronavirus. Virology 2015, 479–480, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, W.; Yang, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, J.; Kuang, D.; Yang, M.; Yang, J.; Ma, C.; et al. Comparison of nonhuman primates identified the suitable model for COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Singh, R.S.; Sarma, P.; Batra, G.; Joshi, R.; Kaur, H.; Sharma, A.R.; Prakash, A.; Medhi, B. A Comprehensive Review of Animal Models for Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV. Virol. Sin. 2020, 35, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.C.; Ricks, K.M.; Jay, A.; Raymond, J.L.; Rossi, F.; Zeng, X.; Scruggs, J.; Dyer, D.; Frick, O.; Koehler, J.W.; et al. Development of a coronavirus disease 2019 nonhuman primate model using airborne exposure. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolsey, C.; Borisevich, V.; Prasad, A.N.; Agans, K.N.; Deer, D.J.; Dobias, N.S.; Heymann, J.C.; Foster, S.L.; Levine, C.B.; Medina, L.; et al. Establishment of an African green monkey model for COVID-19 and protection against re-infection. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munster, V.J.; Feldmann, F.; Williamson, B.N.; van Doremalen, N.; Perez-Perez, L.; Schulz, J.; Meade-White, K.; Okumura, A.; Callison, J.; Brumbaugh, B.; et al. Respiratory disease in rhesus macaques inoculated with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 585, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockx, B.; Kuiken, T.; Herfst, S.; Bestebroer, T.; Lamers, M.M.; Oude Munnink, B.B.; de Meulder, D.; van Amerongen, G.; van den Brand, J.; Okba, N.M.A.; et al. Comparative pathogenesis of COVID-19, MERS, and SARS in a nonhuman primate model. Science 2020, 368, 1012–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brining, D.L.; Mattoon, J.S.; Kercher, L.; LaCasse, R.A.; Safronetz, D.; Feldmann, H.; Parnell, M.J. Thoracic radiography as a refinement methodology for the study of H1N1 influenza in cynomologus macaques (Macaca fascicularis). Comp. Med. 2010, 60, 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brunink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Muller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological assessment of hospitalized patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stammes, M.A.; Bakker, J.; Vervenne, R.A.W.; Zijlmans, D.G.M.; van Geest, L.; Vierboom, M.P.M.; Langermans, J.A.M.; Verreck, F.A.W. Recommendations for Standardizing Thorax PET–CT in Non-Human Primates by Recent Experience from Macaque Studies. Animals 2021, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finch, C.L.; Crozier, I.; Lee, J.H.; Byrum, R.; Cooper, T.K.; Liang, J.; Sharer, K.; Solomon, J.; Sayre, P.J.; Kocher, G.; et al. Characteristic and quantifiable COVID-19-like abnormalities in CT- and PET/CT-imaged lungs of SARS-CoV-2-infected crab-eating macaques (Macaca fascicularis). bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Ye, T.; Sun, P.; Gui, S.; Liang, B.; Li, L.; Zheng, D.; Wang, J.; Hesketh, R.L.; Yang, L.; et al. Time Course of Lung Changes at Chest CT during Recovery from Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Radiology 2020, 295, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maaskant, A.; Meijer, L.; Bakker, J.; van Geest, L.; Zijlmans, D.G.M.; Langermans, J.A.M.; Verschoor, E.J.; Stammes, M.A. Bronchoalveolar lavage affects thorax computed tomography of healthy and SARS-CoV-2 infected rhesus macaques bioRxiv. PloS ONE 2021, 16, e0252941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, A.C.R.; Venteo, A.; Fresco-Taboada, A.; Tapia, I.; Monedero, A.; Lopez, L.; Jebbink, M.F.; Perez-Ramirez, E.; Jimenez-Clavero, M.A.; Almonacid, M.; et al. Two serological approaches for detection of antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in different scenarios: A screening tool and a point-of-care test. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 98, 115167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagotto, G.; Mercado, N.B.; Martinez, D.R.; Hou, Y.J.; Nkolola, J.P.; Carnahan, R.H.; Crowe, J.E., Jr.; Baric, R.S.; Barouch, D.H. Comparison of Subgenomic and Total RNA in SARS-CoV-2 Challenged Rhesus Macaques. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02370-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. C-reactive protein levels in the early stage of COVID-19. Med. Mal. Infect. 2020, 50, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Reis, T. Kidney involvement in COVID-19 and rationale for extracorporeal therapies. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ronco, C.; Reis, T.; Husain-Syed, F. Management of acute kidney injury in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Luo, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Dong, L.; Li, J.; Yao, Y.; Ge, S.; Xu, G. Kidney disease is associated with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiezia, L.; Boscolo, A.; Poletto, F.; Cerruti, L.; Tiberio, I.; Campello, E.; Navalesi, P.; Simioni, P. COVID-19-Related Severe Hypercoagulability in Patients Admitted to Intensive Care Unit for Acute Respiratory Failure. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 998–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.M.; Levy, J.H. COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation. Blood 2020, 135, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, A.; Palasti, P.; Vereb, D.; Bozsik, B.; Palko, A.; Kincses, Z.T. The sensitivity and specificity of chest CT in the diagnosis of COVID-19. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2819–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glazer, G.M.; Gross, B.H.; Quint, L.E.; Francis, I.R.; Bookstein, F.L.; Orringer, M.B. Normal mediastinal lymph nodes: Number and size according to American Thoracic Society mapping. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1985, 144, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, U.M.; Abokor, A.A.; Edwards, J.M.; Waigi, E.W.; Royfman, R.S.; Hasan, S.A.; Smedlund, K.B.; Hardy, A.M.G.; Chakravarti, R.; Koch, L.G. SARS-CoV-2, ACE2 expression, and systemic organ invasion. Physiol. Genom. 2021, 53, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walitt, B.; Bartrum, E. A clinical primer for the expected and potential post-COVID-19 syndromes. Pain Rep. 2021, 6, e887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, A.; Liu, J.; Martinot, A.J.; McMahan, K.; Mercado, N.B.; Peter, L.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Yu, J.; Maliga, Z.; Nekorchuk, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection protects against rechallenge in rhesus macaques. Science 2020, 369, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, B.N.; Feldmann, F.; Schwarz, B.; Meade-White, K.; Porter, D.P.; Schulz, J.; van Doremalen, N.; Leighton, I.; Yinda, C.K.; Perez-Perez, L.; et al. Clinical benefit of remdesivir in rhesus macaques infected with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 585, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, E.; Rasmussen, A.L.; Falzarano, D.; Bushmaker, T.; Feldmann, F.; Brining, D.L.; Fischer, E.R.; Martellaro, C.; Okumura, A.; Chang, J.; et al. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) causes transient lower respiratory tract infection in rhesus macaques. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16598–16603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coperchini, F.; Chiovato, L.; Croce, L.; Magri, F.; Rotondi, M. The cytokine storm in COVID-19: An overview of the involvement of the chemokine/chemokine-receptor system. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartman, A.L.; Nambulli, S.; McMillen, C.M.; White, A.G.; Tilston-Lunel, N.L.; Albe, J.R.; Cottle, E.; Dunn, M.D.; Frye, L.J.; Gilliland, T.H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of African green monkeys results in mild respiratory disease discernible by PET/CT imaging and shedding of infectious virus from both respiratory and gastrointestinal tracts. PLoS Pathog 2020, 16, e1008903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.; Kay, F.U.; Abbara, S.; Bhalla, S.; Chung, J.H.; Chung, M.; Henry, T.S.; Kanne, J.P.; Kligerman, S.; Ko, J.P.; et al. Radiological Society of North America Expert Consensus Statement on Reporting Chest CT Findings Related to COVID-19. Endorsed by the Society of Thoracic Radiology, the American College of Radiology, and RSNA-Secondary Publication. J. Thorac. Imaging 2020, 35, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Liu, S. CT and COVID-19: Chinese experience and recommendations concerning detection, staging and follow-up. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 5214–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, R.V.; Vaccari, M.; Doyle-Meyers, L.A.; Roy, C.J.; Russell-Lodrigue, K.; Fahlberg, M.; Monjure, C.J.; Beddingfield, B.; Plante, K.S.; Plante, J.A.; et al. Acute Respiratory Distress in Aged, SARS-CoV-2-Infected African Green Monkeys but Not Rhesus Macaques. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Singh, B.; Ganatra, S.R.; Gazi, M.; Cole, J.; Thippeshappa, R.; Alfson, K.J.; Clemmons, E.; Gonzalez, O.; Escobedo, R.; et al. Responses to acute infection with SARS-CoV-2 in the lungs of rhesus macaques, baboons and marmosets. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Tostanoski, L.H.; Peter, L.; Mercado, N.B.; McMahan, K.; Mahrokhian, S.H.; Nkolola, J.P.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Chandrashekar, A.; et al. DNA vaccine protection against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques. Science 2020, 369, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercado, N.B.; Zahn, R.; Wegmann, F.; Loos, C.; Chandrashekar, A.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Peter, L.; McMahan, K.; Tostanoski, L.H.; et al. Single-shot Ad26 vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques. Nature 2020, 383, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.J.L. Persistent SARS-2 infections contribute to long COVID-19. Med. Hypotheses 2021, 149, 110538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.D.; Harris, C.; Cain, J.K.; Hummer, C.; Goyal, H.; Perisetti, A. Pulmonary and Extra-Pulmonary Clinical Manifestations of COVID-19. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, O.P.; Bhandari, P.; Raut, A.; Kacimi, S.E.O.; Huy, N.T. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Comprehensive Review of Clinical Presentation. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 582932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
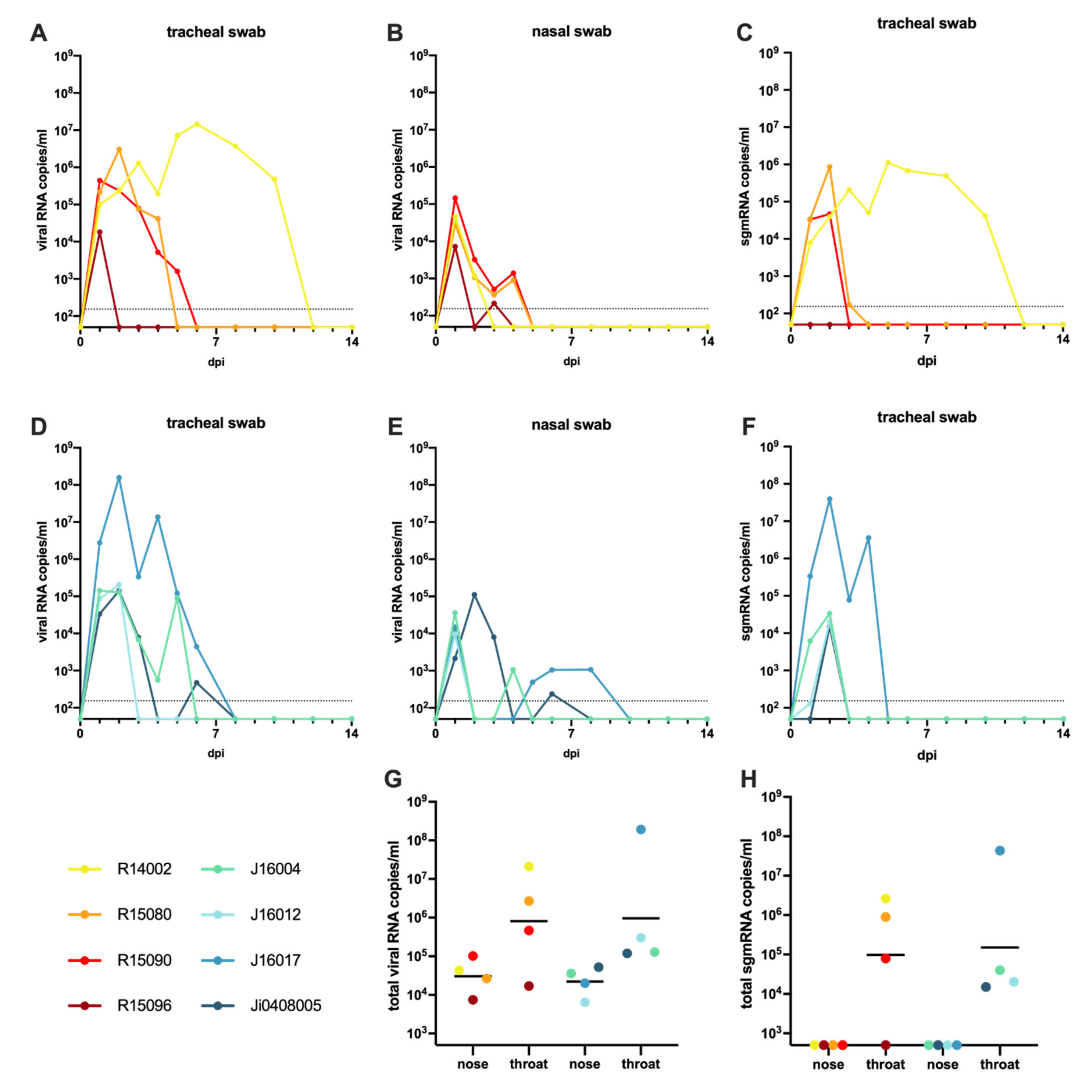






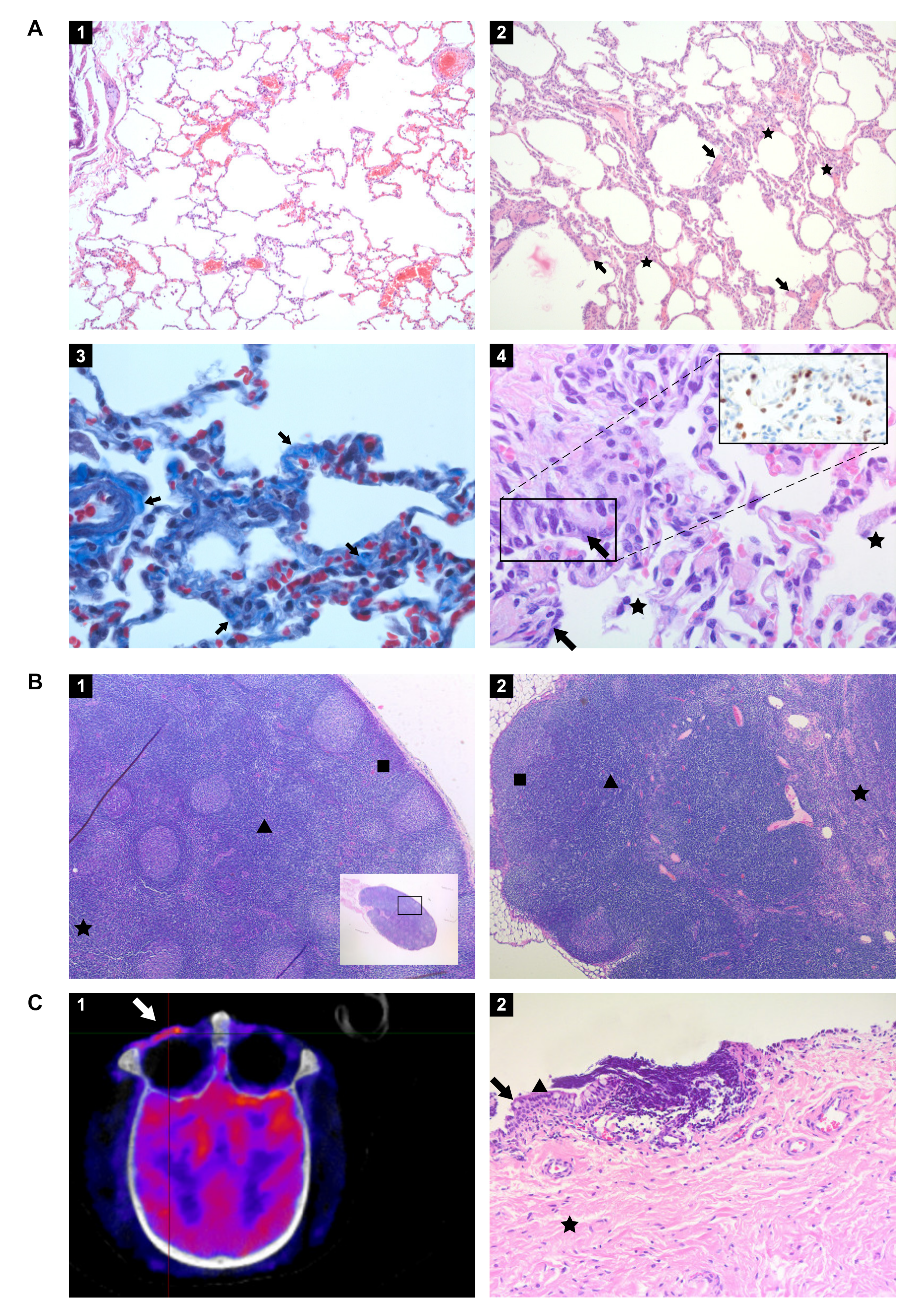
| Animals | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Days pi | R14002 | R15080 | R15090 | R15096 | J16004 | J16012 | J16017 | Ji408005 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 2 | 0 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 1.5 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4.5 | 0 | 0 | |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 4 | |
| 8 | 3.5 | 0 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 0 | 5 | 4.5 | 2 | |
| 10 | 1.75 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 3.5 | |
| 12 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1.5 | 0 | 0 | |
| 14 | 1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2 | |
| 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3.5 | 3 | 6.5 | 1.5 | 3.5 | |
| 22 | 2.5 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 6 | 0.5 | 2.5 | |
| 29/30 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4.5 | 0 | 5 | |
| 36/38 | nd | nd | nd | nd | 5 | 6.5 | 1.5 | 3 | |
| R14002 | J16012 | J16017 | Ji408005 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung, upper right lobe | - | - | - | 1.6 × 103 |
| Lung, accessory lobe | - | 1.52 × 104 | - | - |
| Lung, upper left lobe | 2.5 × 104 | - | - | - |
| Bronchus left | - | - | 1.27 × 105 | - |
| Bronchus right | - | - | 3.3 × 104 | - |
| Trachea | - | - | 1.84 × 104 | - |
| Left paratracheal LN | - | - | 4.22 × 104 | - |
| - | - | 8.4 × 104 | - | |
| Left hilar (bronchial) LN | 6.8 × 103 | 1.52 × 104 | 9.6 × 104 | - |
| - | - | 7.4 × 103 | - | |
| Subcarinal LN | - | 1.11 × 105 | 1.56 × 104 | - |
| Right hilar (bronchial) LN | - | 3.99 × 105 | 2.4 104 | 1.98 × 104 |
| - | - | - | 6.88 × 104 | |
| Right paratracheal LN | - | 1.34 × 105 | 1.26 × 104 | - |
| - | - | 9.2 × 103 | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Böszörményi, K.P.; Stammes, M.A.; Fagrouch, Z.C.; Kiemenyi-Kayere, G.; Niphuis, H.; Mortier, D.; van Driel, N.; Nieuwenhuis, I.; Vervenne, R.A.W.; Haaksma, T.; et al. The Post-Acute Phase of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Two Macaque Species Is Associated with Signs of Ongoing Virus Replication and Pathology in Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Tissues. Viruses 2021, 13, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081673
Böszörményi KP, Stammes MA, Fagrouch ZC, Kiemenyi-Kayere G, Niphuis H, Mortier D, van Driel N, Nieuwenhuis I, Vervenne RAW, Haaksma T, et al. The Post-Acute Phase of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Two Macaque Species Is Associated with Signs of Ongoing Virus Replication and Pathology in Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Tissues. Viruses. 2021; 13(8):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081673
Chicago/Turabian StyleBöszörményi, Kinga P., Marieke A. Stammes, Zahra C. Fagrouch, Gwendoline Kiemenyi-Kayere, Henk Niphuis, Daniella Mortier, Nikki van Driel, Ivonne Nieuwenhuis, Richard A. W. Vervenne, Tom Haaksma, and et al. 2021. "The Post-Acute Phase of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Two Macaque Species Is Associated with Signs of Ongoing Virus Replication and Pathology in Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Tissues" Viruses 13, no. 8: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13081673







