SARS-CoV-2 Infection Modulates ACE2 Function and Subsequent Inflammatory Responses in Swabs and Plasma of COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Samples
2.2. ACE2 Enzymatic Assay
2.3. SARS-CoV-2 PCR Detection and Viral Load Quantification
2.4. Quantitative RT-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.5. IL6 Plasma Levels
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
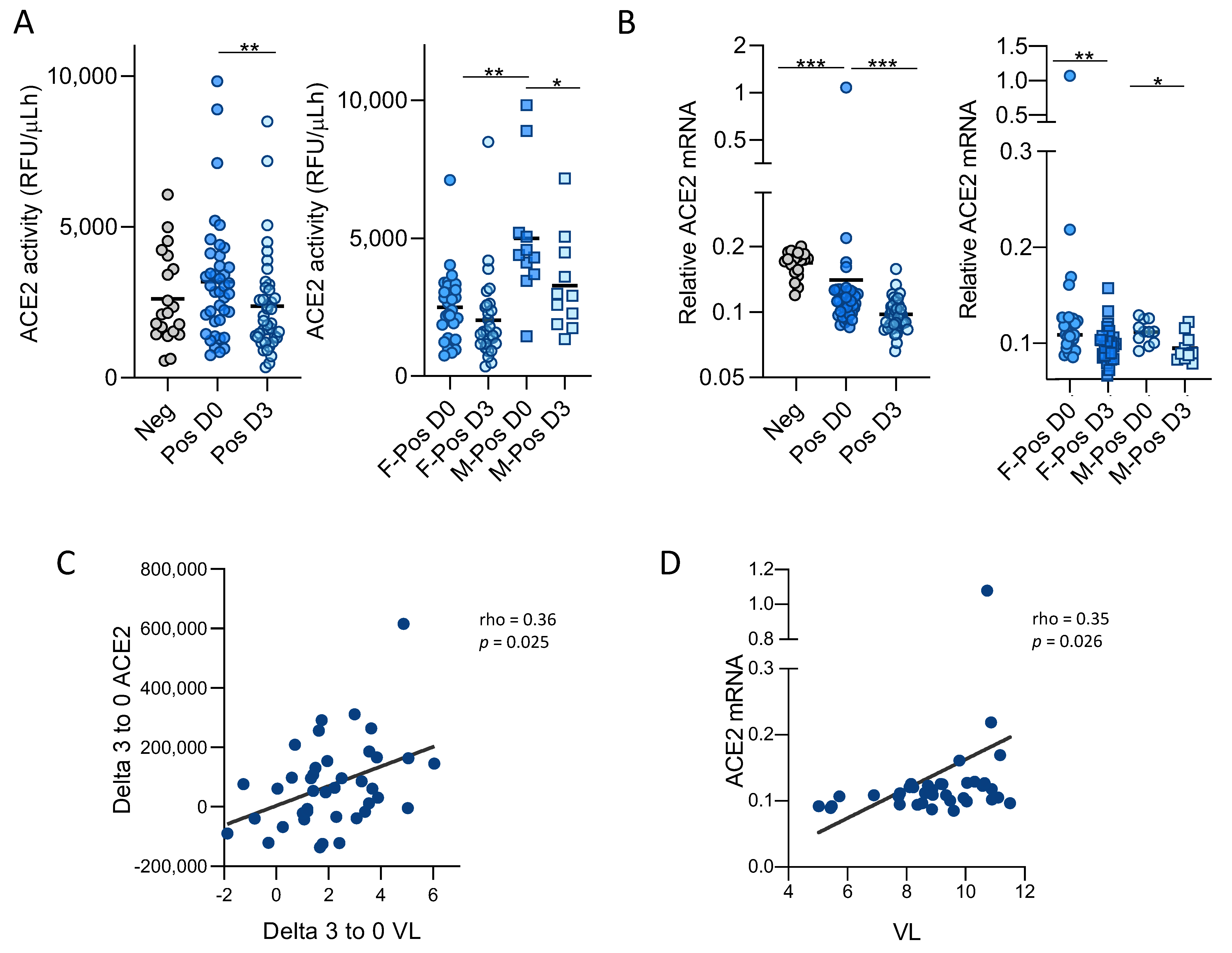
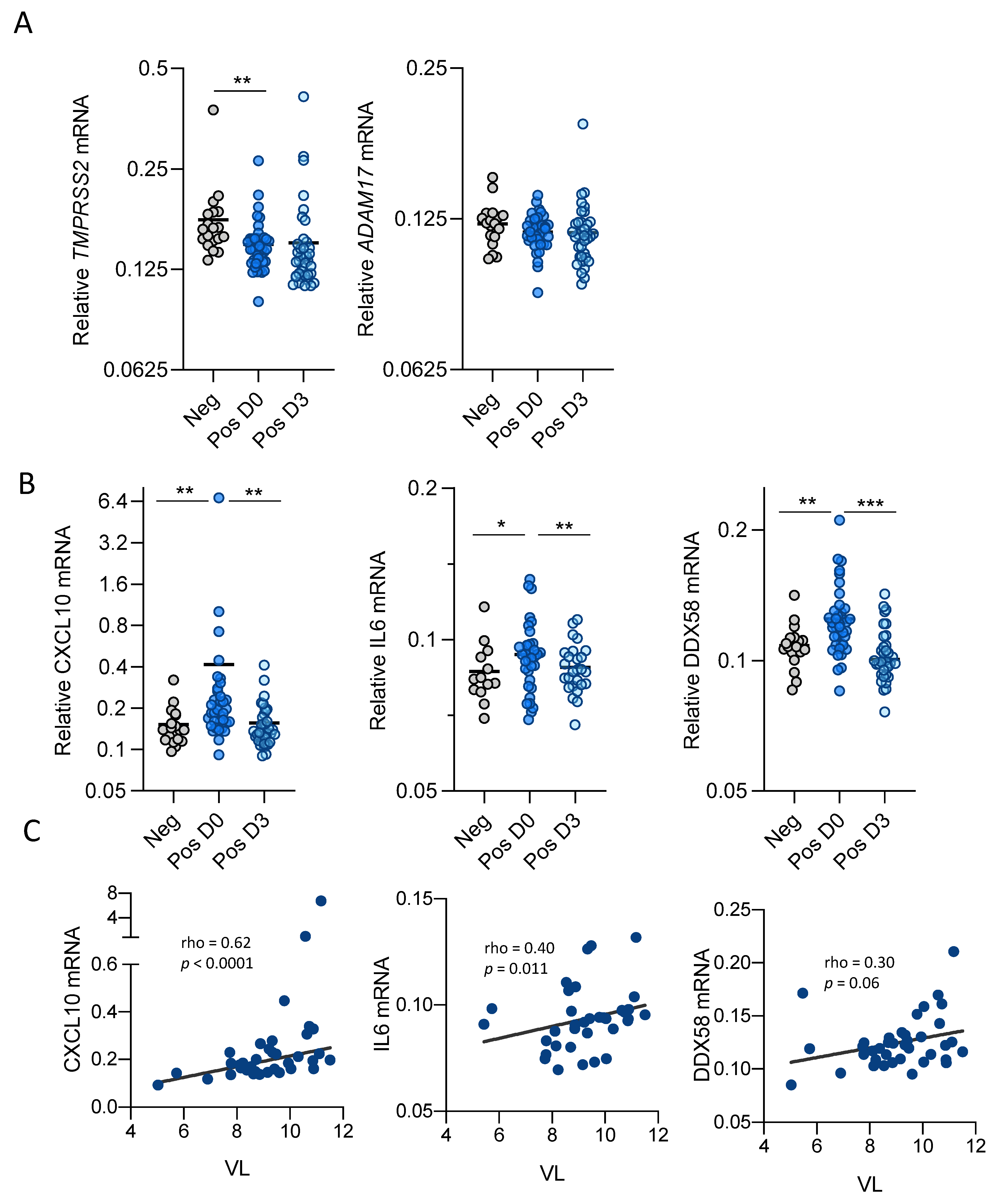
3.1. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Modulates ACE2 Function and Expression in Upper Respiratory Tract
3.2. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Modulates Inflammatory Cytokine Expression in Upper Respiratory Track
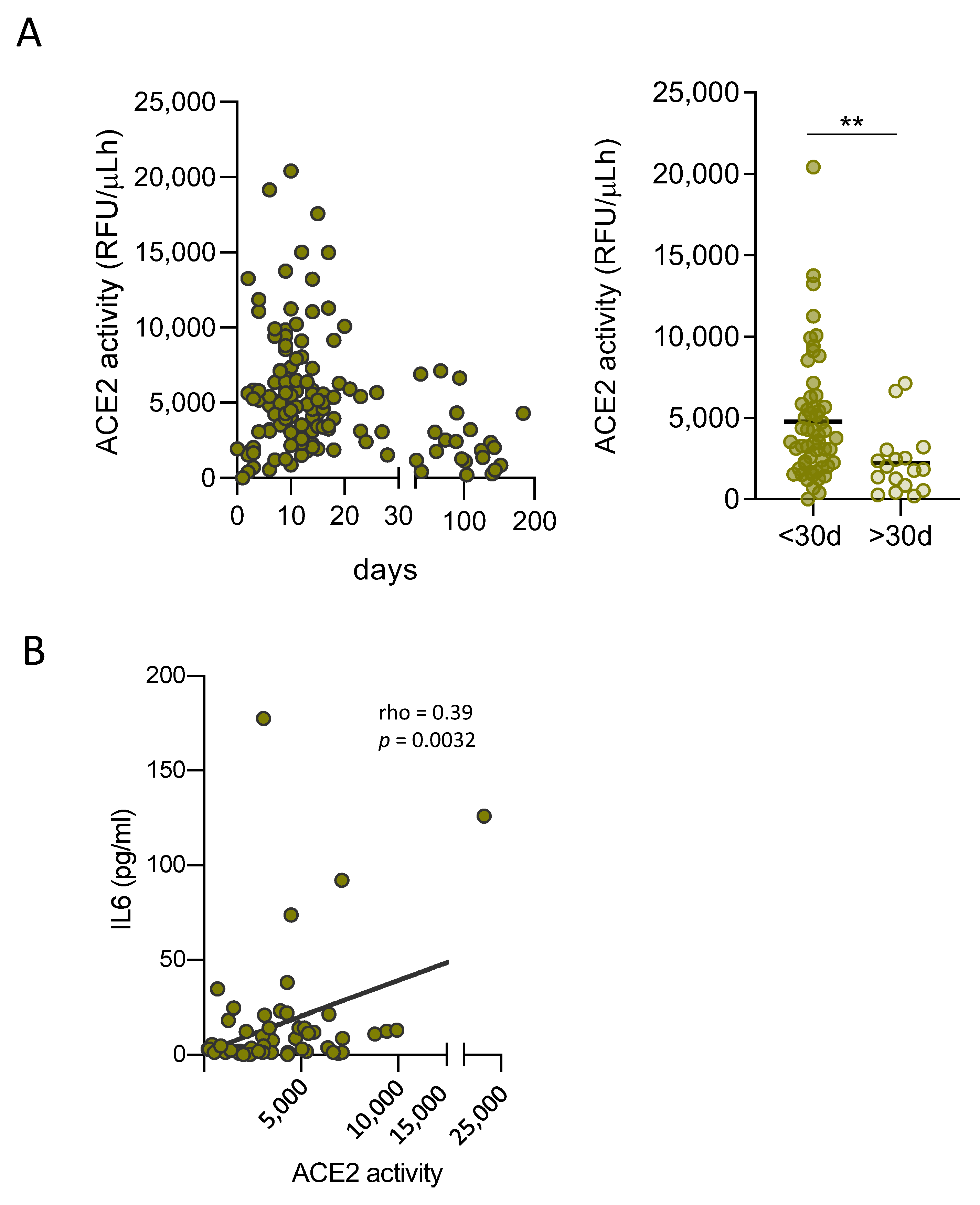
3.3. Soluble ACE2 Is Transiently Elevated in Plasma of SARS-CoV-2 Infected Patients and Correlates with Inflammation Markers
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- COVID-19 Situation Update Worldwide, as of 15 October 2020. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/geographical-distribution-2019-ncov-cases (accessed on 16 October 2020).
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, X.; Chen, D.; Xia, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, T.; Ou, X.; Zhou, L.; Liu, J. Asymptomatic cases in a family cluster with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 410–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carsana, L.; Sonzogni, A.; Nasr, A.; Rossi, R.S.; Pellegrinelli, A.; Zerbi, P.; Rech, R.; Colombo, R.; Antinori, S.; Corbellino, M.; et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a series of COVID-19 cases from northern Italy: A two-centre descriptive study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.J.; Liang, W.H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.R.; Chen, Z.S.; Li, Y.M.; Liu, X.Q.; Chen, R.C.; Tang, C.L.; Wang, T.; et al. Comorbidity and its impact on 1,590 patients with COVID-19 in China: A nationwide analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donoghue, M.; Hsieh, F.; Baronas, E.; Godbout, K.; Gosselin, M.; Stagliano, N.; Donovan, M.; Woolf, B.; Robison, K.; Jeyaseelan, R.; et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tipnis, S.R.; Hooper, N.M.; Hyde, R.; Karran, E.; Christie, G.; Turner, A.J. A human homolog of angiotensin-converting enzyme: Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33238–33243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambert, D.W.; Clarke, N.E.; Turner, A.J. Not just angiotensinases: New roles for the angiotensin-converting enzymes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.-R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.-L.; et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rice, G.I.; Jones, A.L.; Grant, P.J.; Carter, A.M.; Turner, A.J.; Hooper, N.M. Circulating activities of angiotensin-converting enzyme, its homolog, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, and neprilysin in a family study. Hypertension 2006, 48, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciaglia, E.; Vecchione, C.; Puca, A.A. COVID-19 Infection and Circulating ACE2 Levels: Protective Role in Women and Children. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kragstrup, T.W.; Singh, H.S.; Grundberg, I.; Nielsen, A.L.L.; Rivellese, F.; Mehta, A.; Goldberg, M.B.; Filbin, M.R.; Qvist, P.; Bibby, B.M. Plasma ACE2 predicts outcome of COVID-19 in hospitalized patients. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.K.; Juno, J.A.; Lee, W.S.; Wragg, K.M.; Hogarth, P.M.; Kent, S.J.; Burrell, L.M. Plasma ACE2 activity is persistently elevated following SARS-CoV-2 infection: Implications for COVID-19 pathogenesis and consequences. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2003730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, B.; Fejes, Z.; Szentkereszty, Z.; Sütő, R.; Várkonyi, I.; Ajzner, É.; Kappelmayer, J.; Papp, Z.; Tóth, A.; Fagyas, M. A dramatic rise in serum ACE2 activity in a critically ill COVID-19 patient. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 103, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, D.; Guo, W.; Cao, Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Yu, H.; et al. Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, C.G.K.; Allon, S.J.; Nyquist, S.K.; Mbano, I.M.; Miao, V.N.; Tzouanas, C.N.; Cao, Y.; Yousif, A.S.; Bals, J.; Hauser, B.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Is an Interferon-Stimulated Gene in Human Airway Epithelial Cells and Is Detected in Specific Cell Subsets across Tissues. Cell 2020, 181, 1016–1035.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.M.; Wang, L.; Deng, J.; Wang, P.H. Increasing host cellular receptor—angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 expression by coronavirus may facilitate 2019-nCoV (or SARS-CoV-2) infection. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2693–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuba, K.; Imai, Y.; Rao, S.; Gao, H.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Huan, Y.; Yang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, W.; et al. A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 875–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Møller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1036–1045.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Péré, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, N.A.P.; Peddu, V.; Xie, H.; Shrestha, L.; Huang, M.L.; Mears, M.C.; Cajimat, M.N.; Bente, D.A.; Shi, P.Y.; Bovier, F.; et al. In vivo antiviral host transcriptional response to SARS-CoV-2 by viral load, sex, and age. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitjà, O.; Ubals, M.B.; Corbacho-Monné, M.B.; Alemany, A.B.; Tebe, C.; Tobias, A.; Peñafiel, J.; Ballana, E.; Pérez BM, C.A.; Admella, P.B.; et al. A Cluster-Randomized Trial of Hydroxychloroquine as Prevention of COVID-19 Transmission and 1 Disease 2. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler, M.J.; Riera, M.; Crespo, M.; Mir, M.; Márquez, E.; Pascual, M.J.; Puig, J.M.; Pascual, J. Circulating angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activity in kidney transplantation: A longitudinal pilot study. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2013, 121, c144–c150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguiano, L.; Riera, M.; Pascual, J.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Barrios, C.; Betriu, A.; Mojal, S.; Fernández, E.; Soler, M.J.; Faura, A.; et al. Circulating angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activity in patients with chronic kidney disease without previous history of cardiovascular disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Purushothaman, K.R.; Krishnan, P.; Purushothaman, M.; Wiley, J.; Alviar, C.L.; Ruiz, F.J.; Zubatov, Y.; Kini, A.S.; Sharma, S.K.; Fuster, V.; et al. Expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its end product angiotensin 1-7 is increased in diabetic atheroma: Implications for inflammation and neovascularization. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2013, 22, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epelman, S.; Shrestha, K.; Troughton, R.W.; Francis, G.S.; Sen, S.; Klein, A.L.; Wilson Tang, W.H. Soluble Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 in Human Heart Failure: Relation With Myocardial Function and Clinical Outcomes. J. Card. Fail. 2009, 15, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramchand, J.; Patel, S.K.; Kearney, L.G.; Matalanis, G.; Farouque, O.; Srivastava, P.M.; Burrell, L.M. Plasma ACE2 Activity Predicts Mortality in Aortic Stenosis and Is Associated With Severe Myocardial Fibrosis. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2020, 13, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguiano, L.; Riera, M.; Pascual, J.; Valdivielso, J.M.; Barrios, C.; Betriu, A.; Clotet, S.; Mojal, S.; Fernández, E.; Soler, M.J.; et al. Circulating angiotensin converting enzyme 2 activity as a biomarker of silent atherosclerosis in patients with chronic kidney disease. Atherosclerosis 2016, 253, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narula, S.; Yusuf, S.; Chong, M.; Ramasundarahettige, C.; Rangarajan, S.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; van Eikels, M.; Leineweber, K.; Wu, A.; Pigeyre, M.; et al. Plasma ACE2 and risk of death or cardiometabolic diseases: A case-cohort analysis. Lancet 2020, 396, 968–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.G.; Simpson, L.J.; Ferreira, A.M.; Rustagi, A.; Roque, J.; Asuni, A.; Ranganath, T.; Grant, P.M.; Subramanian, A.; Rosenberg-Hasson, Y.; et al. Cytokine profile in plasma of severe COVID-19 does not differ from ARDS and sepsis. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e140289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heurich, A.; Hofmann-Winkler, H.; Gierer, S.; Liepold, T.; Jahn, O.; Pohlmann, S. TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 Cleave ACE2 Differentially and Only Proteolysis by TMPRSS2 Augments Entry Driven by the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Protein. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambert, D.W.; Yarski, M.; Warner, F.J.; Thornhill, P.; Parkin, E.T.; Smith, A.I.; Hooper, N.M.; Turner, A.J. Tumor necrosis factor-α convertase (ADAM17) mediates regulated ectodomain shedding of the severe-acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (SARS-CoV) receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE2). J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30113–30119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Ayllón, M.-S.; Moreno-Pérez, O.; García-Arriaza, J.; Ramos-Rincón, J.-M.; Cortés-Gómez, M.-Á.; Brinkmalm, G.; Andrés, M.; León-Ramírez, J.-M.; Boix, V.; Gil, J.; et al. Plasma ACE2 species are differentially altered in COVID-19 patients. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Yogeswaran, S.; Muthumalage, T.; Rahman, I. Persistently Increased Systemic ACE2 Activity Is Associated With an Increased Inflammatory Response in Smokers With COVID-19. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 653045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Rao, S.; Huan, Y.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Yang, P.; Sarao, R.; Wada, T.; Leong-Poi, H.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure. Nature 2005, 436, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkman, R.; Jebbink, M.F.; Deijs, M.; Milewska, A.; Pyrc, K.; Buelow, E.; van der Bijl, A.; van der Hoek, L. Replication-dependent downregulation of cellular angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protein expression by human coronavirus NL63. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1924–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onabajo, O.O.; Banday, A.R.; Stanifer, M.L.; Yan, W.; Obajemu, A.; Santer, D.M.; Florez-Vargas, O.; Piontkivska, H.; Vargas, J.M.; Ring, T.J.; et al. Interferons and viruses induce a novel truncated ACE2 isoform and not the full-length SARS-CoV-2 receptor. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sama, I.E.; Ravera, A.; Santema, B.T.; Van Goor, H.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Rienstra, M.; Friedrich, A.W.; Samani, N.J.; Ng, L.L.; et al. Circulating plasma concentrations of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 inmen and women with heart failure and effects of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, B. The renin-angiotensin system: An integrated view of lung disease and coagulopathy in COVID-19 and therapeutic implications. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoufaly, A.; Poglitsch, M.; Aberle, J.H.; Hoepler, W.; Seitz, T.; Traugott, M.; Grieb, A.; Pawelka, E.; Laferl, H.; Wenisch, C.; et al. Human recombinant soluble ACE2 in severe COVID-19. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 1154–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, T.S.; Liu, D.X. Human Coronavirus: Host-Pathogen Interaction. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 73, 529–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Swab (n = 40) | Plasma (n = 75) | |
|---|---|---|
| Individual’s Characteristics | ||
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 42.1 (11.3) | 51.2 (14.6) |
| Sex (male), n (%) | 11 (27) | 44 (58) |
| Symptoms at baseline | ||
| Fever, N (%) | 27 (67.5) | 40 (53.3) |
| Cough, N (%) | 32 (80) | 49 (65.3) |
| Dyspnea, N (%) | 6 (15) | 30 (40) |
| Time from onset of symptoms to sample | ||
| Days, median (IQR) | 4 (3;6) | 12 (8;18) |
| LOG viral load (first sample) | ||
| RT-qPCR copies/mL, mean (SD) | 9 (1.6) | nd |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gutiérrez-Chamorro, L.; Riveira-Muñoz, E.; Barrios, C.; Palau, V.; Nevot, M.; Pedreño-López, S.; Senserrich, J.; Massanella, M.; Clotet, B.; Cabrera, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Modulates ACE2 Function and Subsequent Inflammatory Responses in Swabs and Plasma of COVID-19 Patients. Viruses 2021, 13, 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091715
Gutiérrez-Chamorro L, Riveira-Muñoz E, Barrios C, Palau V, Nevot M, Pedreño-López S, Senserrich J, Massanella M, Clotet B, Cabrera C, et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Modulates ACE2 Function and Subsequent Inflammatory Responses in Swabs and Plasma of COVID-19 Patients. Viruses. 2021; 13(9):1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091715
Chicago/Turabian StyleGutiérrez-Chamorro, Lucía, Eva Riveira-Muñoz, Clara Barrios, Vanesa Palau, Maria Nevot, Sònia Pedreño-López, Jordi Senserrich, Marta Massanella, Bonaventura Clotet, Cecilia Cabrera, and et al. 2021. "SARS-CoV-2 Infection Modulates ACE2 Function and Subsequent Inflammatory Responses in Swabs and Plasma of COVID-19 Patients" Viruses 13, no. 9: 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091715
APA StyleGutiérrez-Chamorro, L., Riveira-Muñoz, E., Barrios, C., Palau, V., Nevot, M., Pedreño-López, S., Senserrich, J., Massanella, M., Clotet, B., Cabrera, C., Mitjà, O., Crespo, M., Pascual, J., Riera, M., & Ballana, E. (2021). SARS-CoV-2 Infection Modulates ACE2 Function and Subsequent Inflammatory Responses in Swabs and Plasma of COVID-19 Patients. Viruses, 13(9), 1715. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091715








