The Evolving Faces of the SARS-CoV-2 Genome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SARS-CoV-2 Genome Data and Preprocessing
2.2. Mutation Coding, SOM Training and Genome Portrayal
2.3. Spot Detection, Pattern Types (PATs) and Diversity Analysis
2.4. Extension SOM (xSOM)
2.5. SARS-CoV-2 oposSOM Browser and Epidemiological Numbers
3. Results
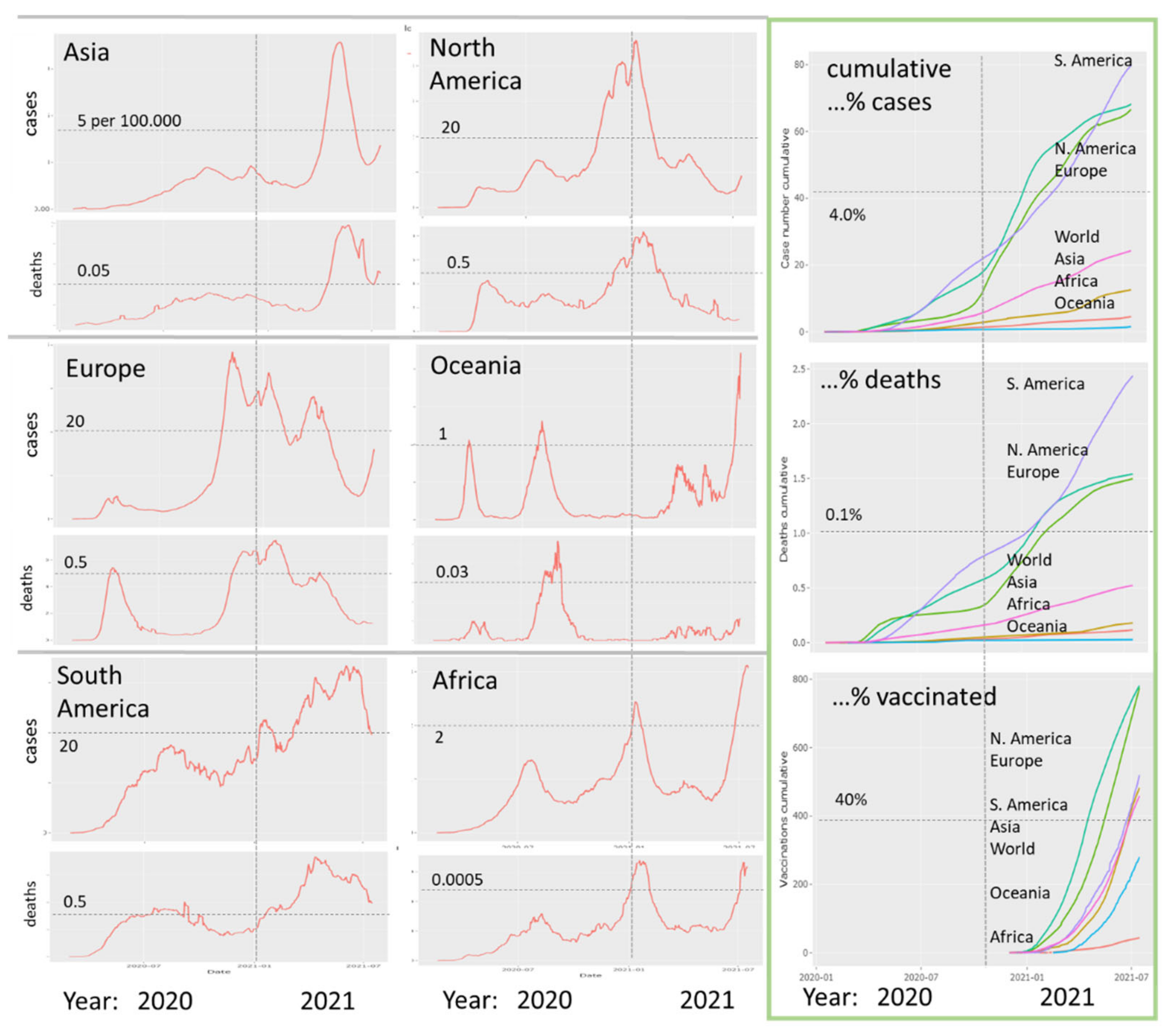
3.1. The Pandemic until Summer 2021: Waves of Incidence and Variants

3.2. COVID-19 in Time and Space
3.3. SOM Portrayal of the SARS-CoV-2 Mutational Patterns
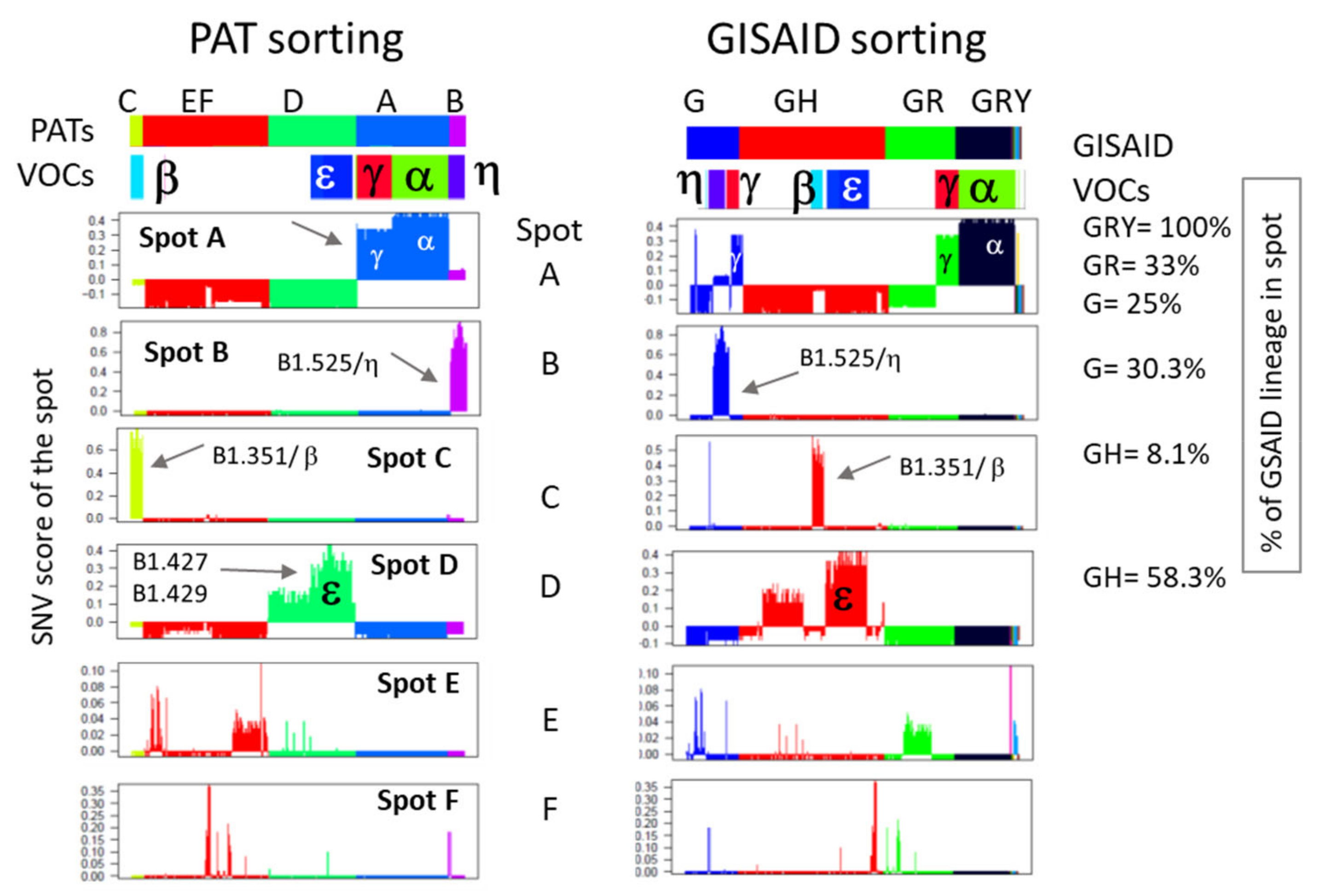
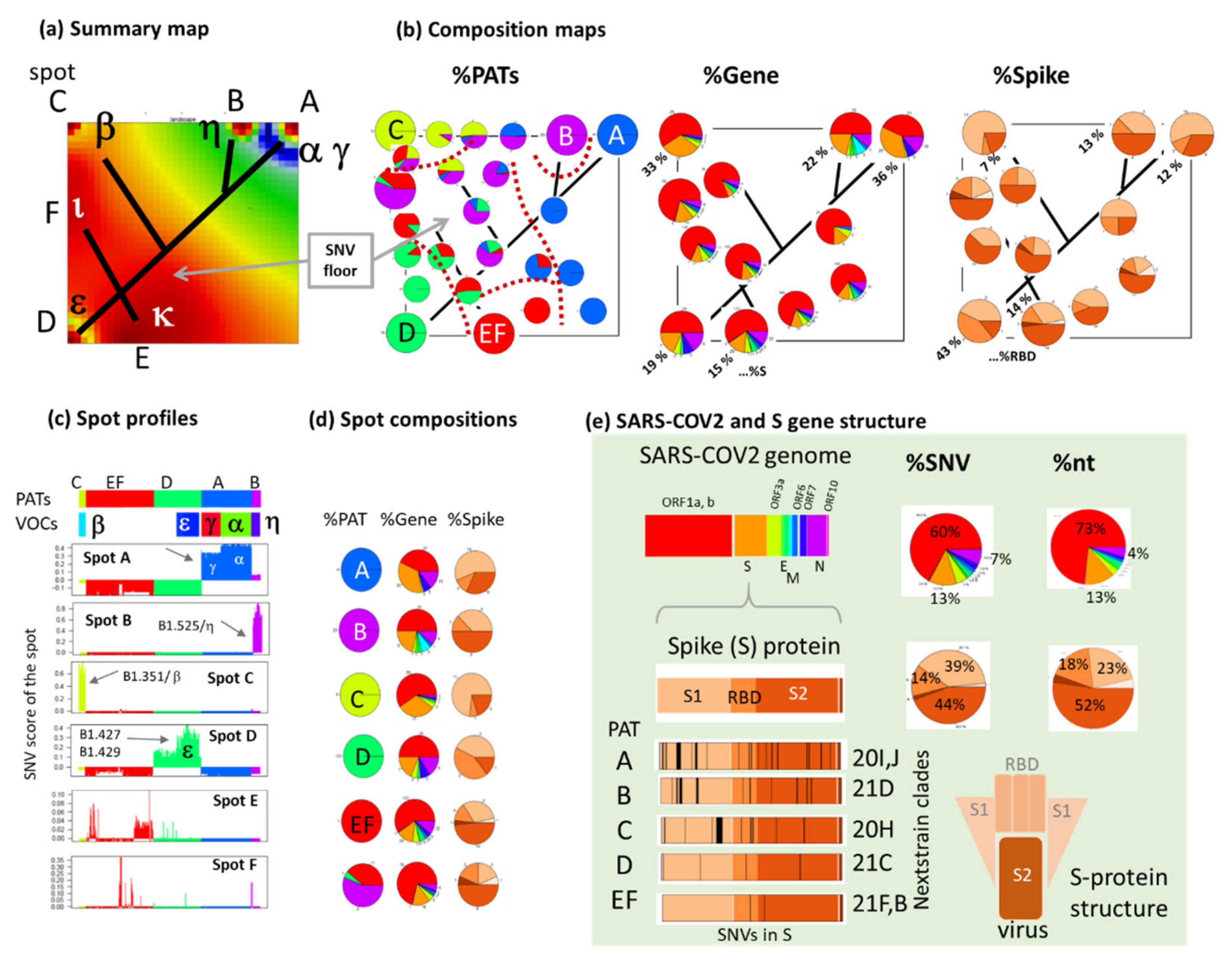
3.4. Relation to the SARS-CoV-2 Genome: Spots and SNV-Floor
3.5. Cartography of the Mutational Landscape
3.6. SNV Mapping of the SARS-CoV-2 Genes
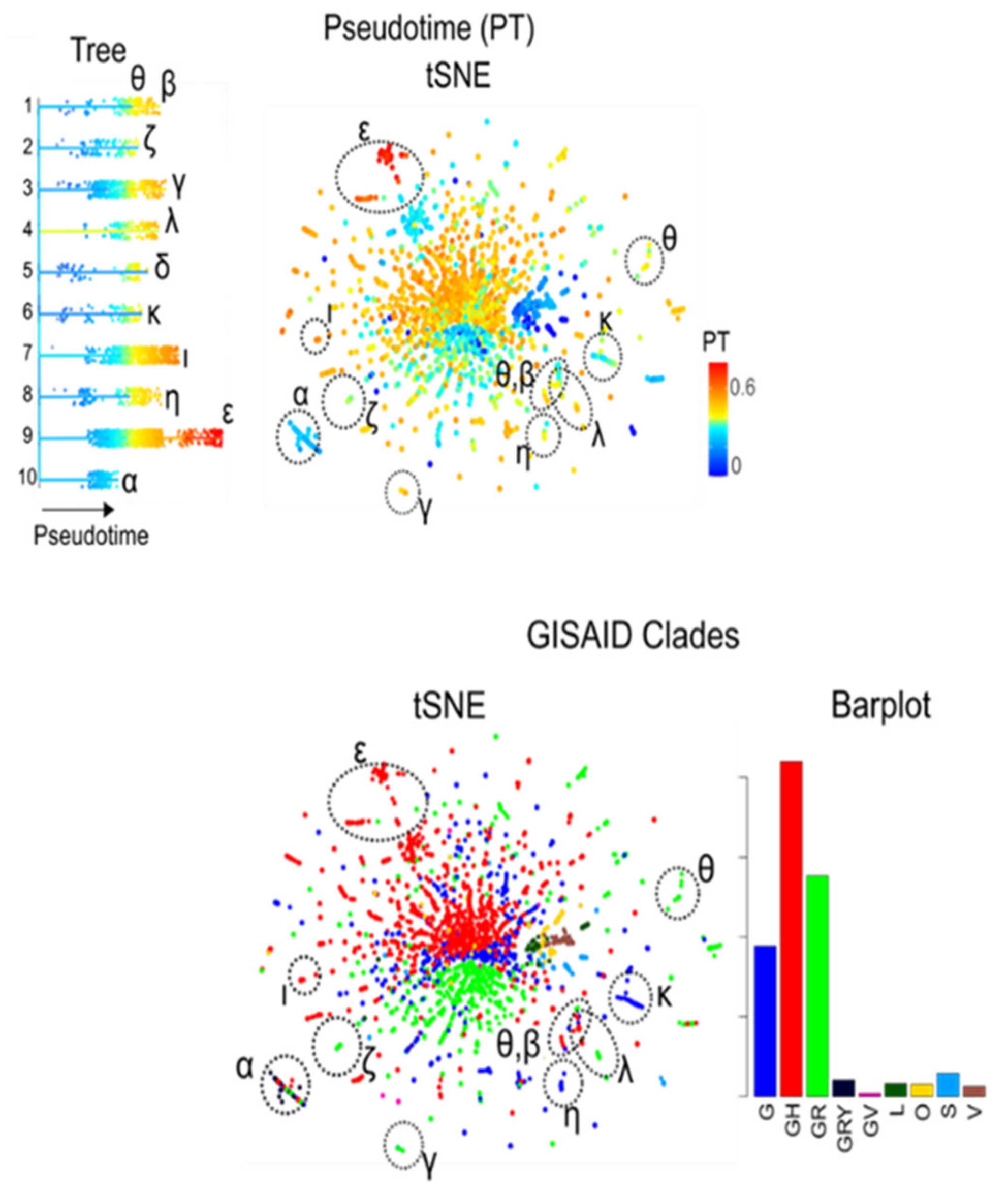
3.7. Development SARS-CoV-2 in Variant and SNV Space
3.8. Pseudotime Describes Development of the Virus Genomes
3.9. Extending the Data: xSOM
4. Discussion
4.1. Trade-Offs Shaping the Diversity and Evolution of SARS-CoV-2

4.2. Cartography of the Virus Genomes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Additional Tables
| WHO a | PANGO-LINE | GI-SAID | Next-Strain | PAT | Portrait Standard and Coastline Style |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variants of Concern (VOCs) | |||||
| alpha ‘British’ variant | B.1.1.1.7 | GRY | 20I | A | 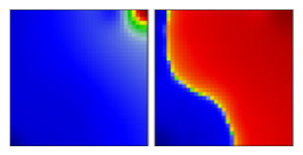 |
| beta ‘South African’ variant | B.1.351 | GH | 20H | C | 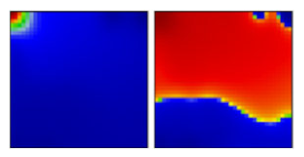 |
| gamma ‘Brasilian’ variant | P1 | GR | 20J | A |  |
| delta b ‘Indian’ variant | B1.617.2 | G | 21A | EF | 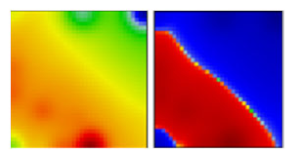 |
| Variants of Interest (VOIs) | |||||
| lambda b | C37 | GR | 21G | B |  |
| eta | B.1.525 | G | 21D | B | 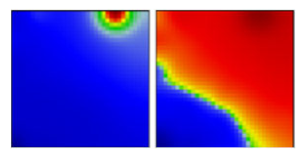 |
| iota | B.1.526 | GH | 21F | EF |  |
| kappa | B.1.617.1 | G | 21B | EF | 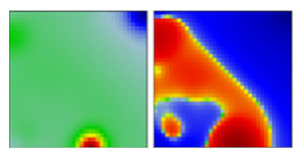 |
| Others | |||||
| epsilon | B.1.427, B.1.429 | GH | 21C | D |  |
| zeta b | P2 | GR | 20B | EF | 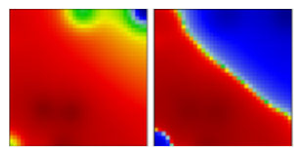 |
| Theta b | P3 | GR | 21E | EF | 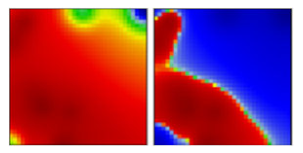 |
| A | S | 19B | EF | 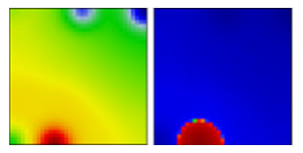 | |
| A.1 | S | 19B | EF |  | |
| B | L | 19A | EF | 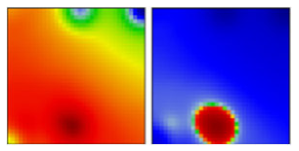 | |
| B.1 | G/GH | 20A | EF | 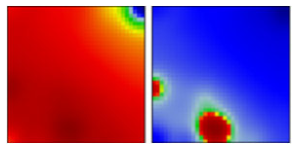 | |
| B.1.1 | GR | 20B | EF | 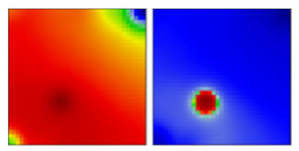 | |
| B.1.1.136 | GR | 20D | EF |  | |
| B.1.1.186 | GR | 20D | EF |  | |
| B.1.1.205 | GR | 20B | EF | 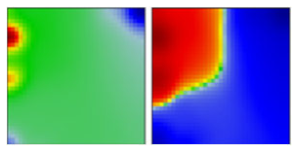 | |
| B.1.1.228 | GR | 20B | EF |  | |
| B.1.1.231 | GR | 20B | EF | 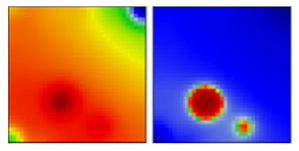 | |
| B.1.1.316 | GR | 20B | EF |  | |
| B.1.1.434 | GR | 20B | EF |  | |
| B.1.1.519 | GR | 20B | EF | 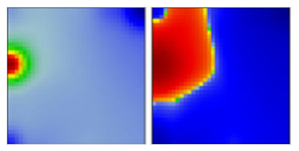 | |
| B.1.110 | GH | 20A | EF | 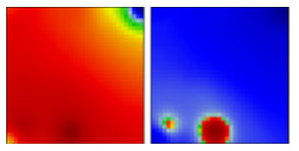 | |
| B.1.139 | G | 20A | EF | 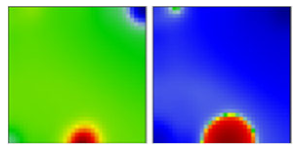 | |
| B.1.2 | GH | 20C | EF | 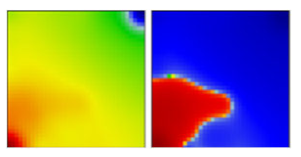 | |
| B.1.234 | G | 20A | EF | 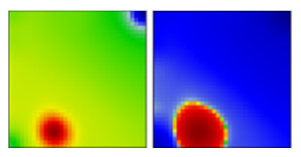 | |
| B.1.274 | GH | 20A | EF | 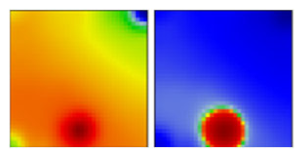 | |
| B.1.298 | GH | 20A | EF |  | |
| B.1.305 | GH | 20C | EF |  | |
| B.1.360 | GH | 20C | EF | 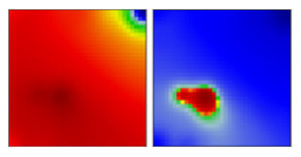 | |
| B.1.400 | G | - | EF |  | |
| B.1.517 | GH | - | EF |  | |
| B.1.595 | GH | - | D/EF | 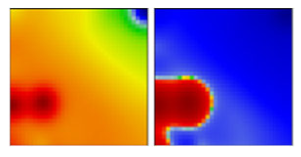 | |
| B.19 | L | 19A | EF |  | |
| B.46 | L | 19A | EF | 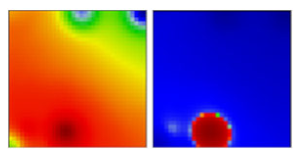 | |
| C.26 | GR | 20D | EF | 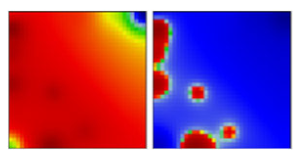 | |
| C.35 | GR | EF | 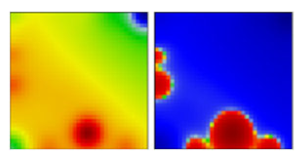 | ||
| D.2 | GR | EF |  | ||
| W.1 | GV | EF | 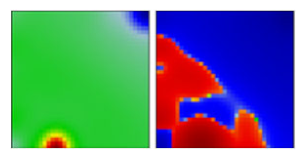 | ||
| Spot | Enriched Lineages | Number of SNVs | SNV in the Spot a |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Alpha, gamma | 72 | Orf1ab: 733, 913, 2110, 2749, 3267, 3828, 5388, 5648, 5986, 6319, 6613, 6954, 11288, 11289, 11290, 11291, 11292, 11293, 11294, 11295, 11296, 12778, 13860, 14120, 14676, 15279, 16176, 17259, 17615 S: 21614, 21621, 21638, 21765, 21766, 21767, 21768, 21769, 21770, 21974, 21991, 21992, 21993, 22132, 22812, 23012, 23063, 23271, 23525, 23604, 23709, 24506, 24642, 24914, 25088 Orf3a: 26149 Orf8: 27972 28048 28095 28111 28167 N: 28280 28281 28282 28512 28877 28878 28881 28882 28883 28977 Intergenic: 28271, 29834 |
| B | eta | 37 | Orf1ab: 1498, 1594, 1807, 2659, 5869, 6285, 8031, 8323, 8593, 9565, 12540, 14407, 18171, 18646, 19684, 20724 S: 21717, 21762, 21764, 22879, 23593, 24224, 24472, 24748 Orf3a:25613 E: 26305 M: 26767 Orf6: 27205, 27206, 27207 Orf7a: 27425 N: 28278, 28279, 28308, 28699 Intergenic: 12, 29543 |
| C | beta | 33 | Orf1ab: 661, 2692, 2830, 3966, 5100, 5230, 8043, 10323, 13620, 17999, 18525, 19524 S: 21801, 22206, 22281, 22282, 22283, 22284, 22285, 22286, 22287, 22288, 22289, 22813, 23664, 24415 Orf3a: 25904, 26158 E: 26456 Orf8: 28253 Intergenic: 174, 29743, 29754 |
| D | epsilon | 46 | Orf1ab: 1059, 2395, 2597, 3817, 8083, 8257, 8895, 8947, 9738, 9991, 10319 10641, 10831, 12100, 12878, 13019, 13713, 14805, 16394, 17014, 18424, 19515, 21304 S: 21600, 22018, 22335, 22597, 22917, 23126, 23155, 24349 Orf3a: 25563, 25907 M: 26681 Orf8: 27964, 27987, 28087, 28191 N: 28472, 28869, 28887, 28975, 29362, 29402 Intergenic: 27890, 28272 |
| E | kappa | 207 | Orf1ab: 445, 490, 1157, 1163, 1578, 1624, 1812, 2227, 2244, 2258, 2488, 2937, 2973, 3114, 3177, 3355, 3564, 3768, 3896, 3951, 3952, 3953, 3984, 4002, 4158, 4303, 5140, 5144, 5974, 6033, 6070, 6317, 6320, 6403, 6441, 6502, 6543, 6606, 6618, 7113, 7540, 7819, 7833, 7945, 7960, 8140, 8149, 8662, 8782, 9204, 9430, 9805, 9875, 9996, 10078, 10332, 10456, 10717, 10741, 11008, 11077, 11453, 11575, 11830, 11866, 12116, 13059, 13094, 13216, 13354, 14187, 14241, 14316, 14808, 14980, 15102, 15327, 15594, 16647, 16728, 17140, 17463, 17642, 17676, 17747, 17858, 18060, 18543, 18555, 18568, 18736, 18981, 19072, 19215, 19422, 19735, 19816, 19983, 20016, 20091, 20268, 20437, 20629, 21077, 21099, 21255, 21390, 21516 S: 21622, 21644, 21773, 21844, 21850, 21986, 22101, 22227, 22326, 22480, 22591, 22852, 22992, 23120, 23401, 23457, 23577, 23608, 23624, 24026, 24034, 24076, 24337, 24370, 24727, 24766, 24771, 24852, 25266 Orf3a: 25459, 25514, 25515, 25710, 25714, 25757, 25785, 25793, 25922, 26072, 26162 E: 26326 M: 26607, 26669, 26690, 26729, 26801, 26882, 27024, 27059, 27110 Orf6: 27213, 27281 Orf7a: 27483, 27579, 27600, 27635, 27679 Orf7b: 27812 Orf8: 27923, 27944, 27957, 28077, 28144 N: 28520, 28657, 28690, 28774, 28854, 28880, 28884, 28885, 28886, 28888, 28889, 28891, 28894, 28896, 28932, 28961, 29095, 29266, 29384, 29412, 29445, 29527 Orf10: 29645 Intergenic: 13, 19, 80, 173, 180, 201, 205, 221, 29546, 29692, 29700, 29710, 29803 |
| F | iota | 111 | Orf1ab: 565, 686, 687, 688, 689, 690, 691, 692, 693, 694, 1132, 2644, 2683, 2867, 2945, 3140, 3745, 4456, 6015, 6101, 6379, 6479, 6751, 7201, 8809, 8890, 9152, 9190, 9289, 9654, 9867, 10029, 10567, 10705, 10775, 10954, 11117, 11203, 11653, 12043, 12789, 14210, 16396, 16500, 16569, 16859, 17748, 18452, 18647, 19068, 19839, 20262, 20592, 21306 S: 21575, 21642, 21846, 22320, 22957, 22995, 23047, 23248, 23695, 23731, 23756, 24095, 24432, 24799, 24933, 25340 Orf3a: 25517, 25587, 25844, 25948, 25968 M: 26700 Orf7a: 27534, 27630, 27739 Orf8: 27925 N: 28311, 28531, 28706, 28879, 29197, 29311 Orf10: 29566 Intergenic: 140, 203, 222, 29738, 29739, 29740, 29741, 29742, 29744, 29745, 29746, 29747, 29748, 29749, 29750, 29751, 29752, 29753, 29755, 29756, 29757, 29758, 29759, 29760 |
Appendix B. Additional Figures










References
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Peacock, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, E. The coronavirus is mutating—Does it matter? Nature 2020, 585, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, E. Coronavirus variants get Greek names—But will scientists use them? Nature 2021, 594, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Lam, E.C.; Denis, K.S.; Nitido, A.D.; Garcia, Z.H.; Hauser, B.M.; Feldman, J.; Pavlovic, M.N.; Gregory, D.J.; Poznansky, M.C.; et al. Multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants escape neutralization by vaccine-induced humoral immunity. Cell 2021, 184, 2372–2383.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, M.L.; Alonso-Palomares, L.; Bustamante, A.; Gaggero, A.; Paredes, F.; Cortés, C.P.; Valiente-Echeverría, F.; Soto-Rifo, R. Infectivity and immune escape of the new SARS-CoV-2 variant of interest Lambda. medRxiv 2021, 2021.06.28.21259673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. Nextstrain: Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial. Genomic sequencing in pandemics. Lancet 2021, 397, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxmen, A. One million coronavirus sequences: Popular genome site hits mega milestone. Nature 2021, 593, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbe, S.; Buckland-Merrett, G. Data, disease and diplomacy: GISAID’s innovative contribution to global health. Glob. Chall. 2017, 1, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morris, C.P.; Luo, C.H.; Amadi, A.; Schwartz, M.; Gallagher, N.; Ray, S.C.; Pekosz, A.; Mostafa, H.H. An update on SARS-CoV-2 diversity in the United States National Capital Region: Evolution of novel and variants of concern. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, ciab636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodcroft, E.B.; de Maio, N.; Lanfear, R.; MacCannell, D.R.; Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Stamatakis, A.; Goldman, N.; Dessimoz, C. Want to track pandemic variants faster? Fix the bioinformatics bottleneck. Nature 2021, 591, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willscher, E.; Hopp, L.; Kreuz, M.; Schmidt, M.; Hakobyan, S.; Arakelyan, A.; Hentschel, B.; Jones, D.; Pfister, S.; Loeffler, M.; et al. High-resolution cartography of the transcriptome and methylome landscapes of diffuse gliomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Hopp, L.; Arakelyan, A.; Kirsten, H.; Engel, C.; Wirkner, K.; Krohn, K.; Burkhardt, R.; Thiery, J.; Loeffler, M.; et al. The Human Blood Transcriptome in a Large Population Cohort and Its Relation to Aging and Health. Front. Big Data 2020, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Kreuz, M.; Hopp, L.; Arakelyan, A.; Haake, A.; Cogliatti, S.B.; Feller, A.C.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Lenze, D.; Möller, P.; et al. A modular transcriptome map of mature B cell lymphomas. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wirth, H.; Löffler, M.; von Bergen, M.; Binder, H. Expression cartography of human tissues using self organizing maps. Nat. Preceed. 2011, 12, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Binder, H. Developmental scRNAseq trajectories in gene- and cell-state space—The flatworm example. Genes 2020, 11, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoghosyan, M.; Hakobyan, S.; Hovhannisyan, A.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Binder, H.; Arakelyan, A. Population levels assessment of the distribution of disease-associated variants with emphasis on Armenians—A machine learning approach. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nikoghosyan, M.; Schmidt, M.; Margaryan, K.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Arakelyan, A.; Binder, H. SOMmelier—Intuitive visualization of the topology of grapevine genome landscapes using artificial neural networks. Genes 2020, 11, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A.; Holmes, E.C.; O’Toole, Á.; Hill, V.; McCrone, J.T.; Ruis, C.; du Plessis, L.; Pybus, O.G. A dynamic nomenclature proposal for SARS-CoV-2 lineages to assist genomic epidemiology. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, P.; Buathong, R.; Phuygun, S.; Thanadachakul, T.; Parnmen, S.; Wongboot, W.; Waicharoen, S.; Wacharapluesadee, S.; Uttayamakul, S.; Vachiraphan, A.; et al. Early transmission patterns of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in travellers from Wuhan to Thailand, January 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löffler-Wirth, H.; Kalcher, M.; Binder, H. OposSOM: R-package for high-dimensional portraying of genome-wide expression landscapes on bioconductor: Fig. 1. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3225–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, H.; von Bergen, M.; Binder, H. Mining SOM expression portraits: Feature selection and integrating concepts of molecular function. BioData Min. 2012, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopp, L.; Wirth, H.; Fasold, M.; Binder, H. Portraying the expression landscapes of cancer subtypes: A glioblastoma multiforme and prostate cancer case study. Syst. Biomed. 2013, 1, 99–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.A.; Wang, Y.; Riesenfeld, S.; Shekhar, K.; Regev, A.; Schier, A.F. Single-cell reconstruction of developmental trajectories during zebrafish embryogenesis. Science 2018, 360, eaar3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunz, M.; Löffler-Wirth, H.; Dannemann, M.; Willscher, E.; Doose, G.; Kelso, J.; Kottek, T.; Nickel, B.; Hopp, L.; Landsberg, J.; et al. RNA-seq analysis identifies different transcriptomic types and developmental trajectories of primary melanomas. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6136–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avetyan, D.; Hakobyan, S.; Nikoghosyan, M.; Khachatryan, G.; Sirunyan, T.; Muradyan, N.; Zakharyan, R.; Chavushyan, A.; Ghazaryan, H.; Melkonyan, A.; et al. Molecular genetic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 lineages in Armenia. medRxiv 2021, 2021.06.19.21259172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Reikowski, J.; Hakobyan, S.; Wagner, J.; Binder, H. OposSOM-browser: An interactive tool to explore omics data landscapes in health science. BMC Bioinform. 2020, 21, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Schmidt, M.; Binder, H. Covid-19 transmission trajectories—Monitoring the pandemic in the worldwide context. Viruses 2020, 12, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, S.M.; Elkhatib, W.F.; Khairalla, A.S.; Noreddin, A.M. Global dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 clades and their relation to COVID-19 epidemiology. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, N.; Majumder, P. Analysis of RNA sequences of 3636 SARS-CoV-2 collected from 55 countries reveals selective sweep of one virus type. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 151, 450–458. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, F.; Archer, B.; Laurenson-Schafer, H.; Jinnai, Y.; Konings, F.; Batra, N.; Pavlin, B.; Vandemaele, K.; van Kerkhove, M.D.; Jombart, T.; et al. Increased transmissibility and global spread of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern as at June 2021. Eurosurveillance 2021, 26, 2100509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, N.G.; Abbott, S.; Barnard, R.C.; Jarvis, C.I.; Kucharski, A.J.; Munday, J.D.; Pearson, C.A.; Russell, T.W.; Tully, D.C.; Washburne, A.D.; et al. Estimated transmissibility and impact of SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.1.7 in England. Science 2021, 372, eabg3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandoy, D.D.R.; Weimer, B.C. Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genomic epidemiology reveals disease transmission coupled to variant emergence and allelic variation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Deng, A.; Li, K.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Zou, L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Viral infection and transmission in a large well-traced outbreak caused by the Delta SARS-CoV-2 variant. medRxiv 2021, 2021.07.07.21260122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korber, B.; Fischer, W.M.; Gnanakaran, S.; Yoon, H.; Theiler, J.; Abfalterer, W.; Hengartner, N.; Giorgi, E.E.; Bhattacharya, T.; Foley, B.; et al. Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike: Evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus. Cell 2020, 182, 812–827.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molaei, S.; Dadkhah, M.; Asghariazar, V.; Karami, C.; Safarzadeh, E. The immune response and immune evasion characteristics in SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2: Vaccine design strategies. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 92, 107051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, M.; Bassi, J.; de Marco, A.; Chen, A.; Walls, A.C.; di Iulio, J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Navarro, M.J.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Saliba, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 immune evasion by the B.1.427/B.1.429 variant of concern. Science 2021, eabi7994. [Google Scholar]
- Nemudryi, A.; Nemudraia, A.; Wiegand, T.; Nichols, J.; Snyder, D.T.; Hedges, J.F.; Cicha, C.; Lee, H.; Vanderwood, K.K.; Bimczok, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance identifies naturally occurring truncation of ORF7a that limits immune suppression. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungreis, I.; Sealfon, R.; Kellis, M. SARS-CoV-2 gene content and COVID-19 mutation impact by comparing 44 Sarbecovirus genomes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, V.; Ferreira, V.; Ierullo, M.; Ku, T.; Majchrzak-Kita, B.; Kulasingam, V.; Humar, A.; Kumar, D. Delayed interval BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19vaccination provides robust immunity. Res. Sq. Preprint 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Grimsby, J.; Pokharel, P.; Li, S.; Morse, M.; Lennon, N.J.; Livak, K.J.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Rinn, J.L. The dynamics and regulators of cell fate decisions are revealed by pseudotemporal ordering of single cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, C.-J.; Wang, Z.-X.; Xu, Y.; Hu, M.-X.; Chen, K.; Qin, G. Assessment of basic reproductive number for COVID-19 at global level: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e25837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.; Hanage, W.; Owusu-Boaitey, N.; Cochran, K.; Walsh, S.; Meyerowitz-Katz, G. Assessing the age specificity of infection fatality rates for COVID-19: Systematic review, meta-analysis, & public policy implications. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 1123–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupferschmidt, K. Do chronic infections breed dangerous new variants? Science 2021, 373, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, G.; Yuan, J.; Xiong, X.; Li, M. Mortality rate and characteristics of deaths following COVID-19 vaccination. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 670370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthukrishnan, J.; Vardhan, V.; Mangalesh, S.; Koley, M.; Shankar, S.; Yadav, A.K.; Khera, A. Vaccination status and COVID-19 related mortality: A hospital based cross sectional study. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2021, 77, S278–S282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, P.Y.; Ong, S.; Chiew, C.J.; Ang, L.W.; Chavatte, J.M.; Mak, T.M.; Cui, L.; Kalimuddin, S.; Chia, W.N.; Tan, C.W.; et al. Virological and serological kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant vaccine-breakthrough infections: A multi-center cohort study. medRxiv 2021, 2021.07.28.21261295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, N.; Mansoor, O.D.; Boyd, M.J.; Kvalsvig, A.; Baker, M.G. We should not dismiss the possibility of eradicating COVID-19: Comparisons with smallpox and polio. BMJ Glob. Health 2021, 6, 006810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheepers, C.; Everatt, J.; Amoako, D.G.; Mnguni, A.; Ismail, A.; Mahlangu, B.; Wibmer, C.K.; Wilkinson, E.; Tegally, H.; San, J.E.; et al. The continuous evolution of SARS-CoV-2 in South Africa: A new lineage with rapid accumulation of mutations of concern and global detection. medRxiv 2021, 2021.08.20.21262342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, E.; Broberg, E.K.; Connor, T.; Hodcroft, E.B.; Komissarov, A.B.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; Melidou, A.; Neher, R.A.; O’Toole, Á.; Pereyaslov, D. Geographical and temporal distribution of SARS-CoV-2 clades in the WHO European Region, January to June 2020. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2001410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschenberger, M.; Hunszinger, V.; Sparrer, K.M.J. Implications of innate immunity in post-acute sequelae of non-persistent viral infections. Cells 2021, 10, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurkovetskiy, L.; Wang, X.; Pascal, K.E.; Tomkins-Tinch, C.; Nyalile, T.P.; Wang, Y.; Baum, A.; Diehl, W.E.; Dauphin, A.; Carbone, C.; et al. Structural and functional analysis of the D614G SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variant. Cell 2020, 183, 739–751.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazit, S.; Shlezinger, R.; Perez, G.; Lotan, R.; Peretz, A.; Ben-Tov, A.; Cohen, D.; Muhsen, K.; Chodick, G.; Patalon, T. Comparing SARS-CoV-2 natural immunity to vaccine-induced immunity: Reinfections versus breakthrough infections. medRxiv 2021, 2021.08.24.21262415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schmidt, M.; Arshad, M.; Bernhart, S.H.; Hakobyan, S.; Arakelyan, A.; Loeffler-Wirth, H.; Binder, H. The Evolving Faces of the SARS-CoV-2 Genome. Viruses 2021, 13, 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091764
Schmidt M, Arshad M, Bernhart SH, Hakobyan S, Arakelyan A, Loeffler-Wirth H, Binder H. The Evolving Faces of the SARS-CoV-2 Genome. Viruses. 2021; 13(9):1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091764
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchmidt, Maria, Mamoona Arshad, Stephan H. Bernhart, Siras Hakobyan, Arsen Arakelyan, Henry Loeffler-Wirth, and Hans Binder. 2021. "The Evolving Faces of the SARS-CoV-2 Genome" Viruses 13, no. 9: 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091764
APA StyleSchmidt, M., Arshad, M., Bernhart, S. H., Hakobyan, S., Arakelyan, A., Loeffler-Wirth, H., & Binder, H. (2021). The Evolving Faces of the SARS-CoV-2 Genome. Viruses, 13(9), 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091764







