Multiple Occurrences of a 168-Nucleotide Deletion in SARS-CoV-2 ORF8, Unnoticed by Standard Amplicon Sequencing and Variant Calling Pipelines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR Assays
2.2. Nanopore Sequencing
2.3. Illumina Sequencing
2.4. Sanger Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatic and Data Analysis
2.6. Phylogenetic and ORF8 Deletion Analyses
2.7. Structural Computational Analysis of ORF8
3. Results
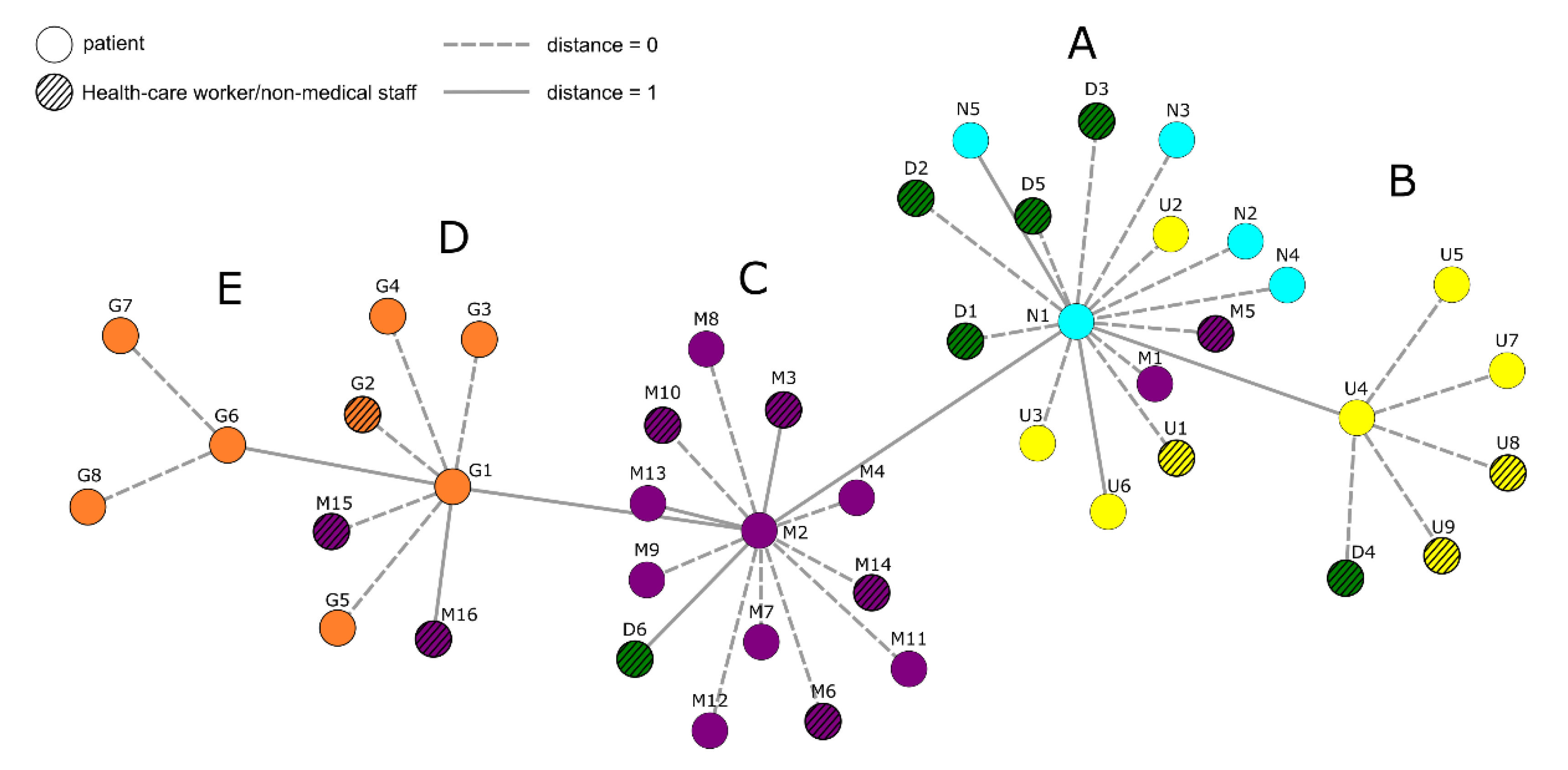
3.1. Nanopore Long-Read Amplicon Sequencing Identified a Large Deletion in ORF8 in an Infection Chain from a Local Hospital
3.2. The Same 168 Bases Long Deletion Has Occurred Independently throughout Europe
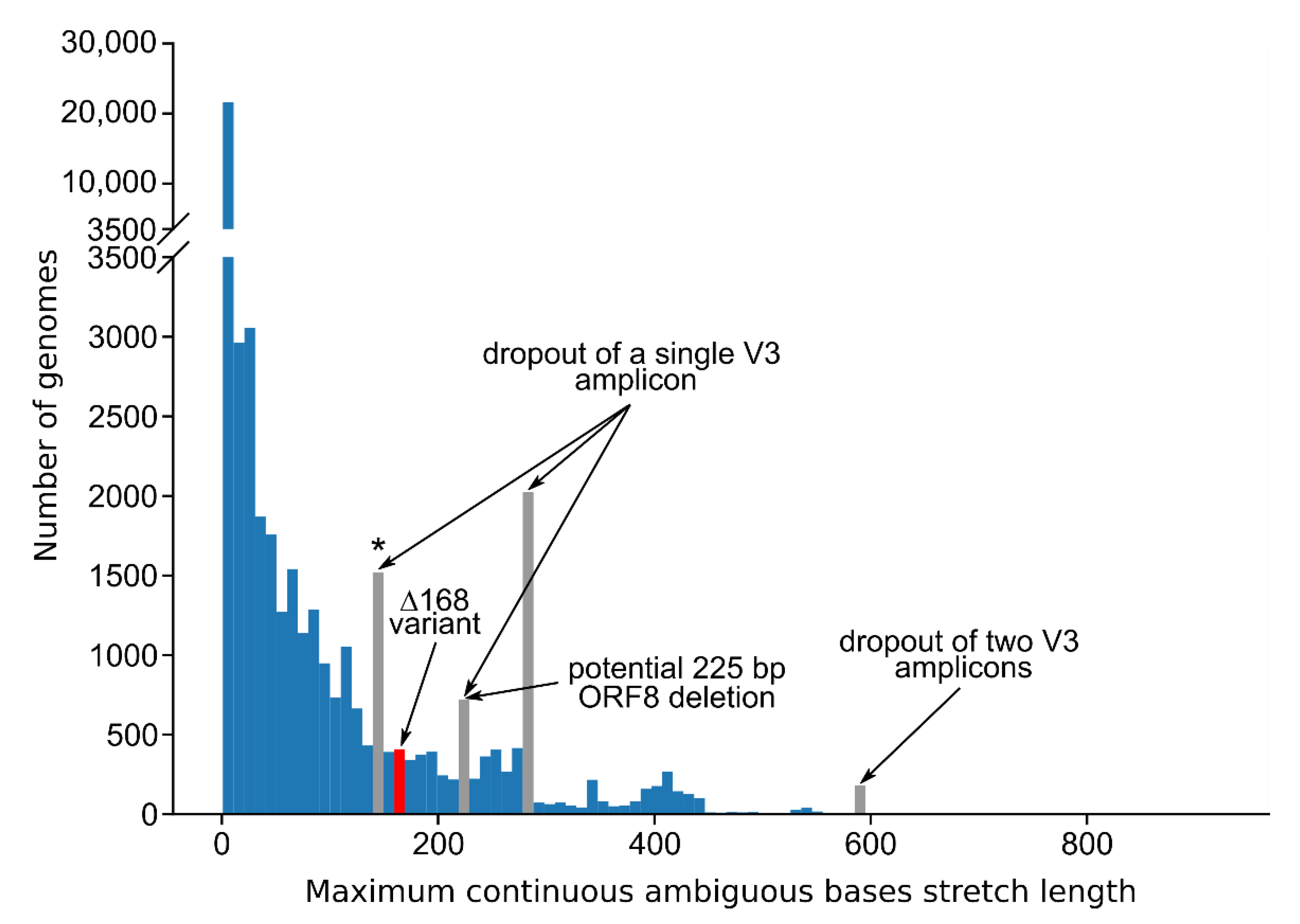
3.3. Standard Amplicon Sequencing and Variant Calling Pipelines Potentially Hide Other Large Deletions
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.F.W.; Kok, K.H.; Zhu, Z.; Chu, H.; To, K.K.W.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.Y. Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, E.; Du, H.; Gardner, L. An interactive web-based dashboard to track COVID-19 in real time. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Genomic Sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 A. A Guide to Implementation for Maximum Impact on Public Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240018440 (accessed on 29 March 2021).
- Tyson, J.R.; James, P.; Stoddart, D.; Sparks, N.; Wickenhagen, A.; Hall, G.; Choi, J.H.; Lapointe, H.; Kamelian, K.; Smith, A.D.; et al. Improvements to the ARTIC multiplex PCR method for SARS-CoV-2 genome sequencing using nanopore. Biorxiv Prepr. Serv. Biol. 2020, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charre, C.; Ginevra, C.; Sabatier, M.; Regue, H.; Destras, G.; Brun, S.; Burfin, G.; Scholtes, C.; Morfin, F.; Valette, M.; et al. Evaluation of NGS-based approaches for SARS-CoV-2 whole genome characterisation. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Ding, R.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Duan, G. Extended ORF8 gene region is valuable in the epidemiological investigation of severe acute respiratory syndrome-similar coronavirus. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Luo, B.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, F.; Yang, T.; Yu, F.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; et al. The ORF8 protein of SARS-CoV-2 mediates immune evasion through potently downregulating MHC-I. Biorxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Liao, C.H.; Wang, Q.; Tan, Y.J.; Luo, R.; Qiu, Y.; Ge, X.Y. The ORF6, ORF8 and nucleocapsid proteins of SARS-CoV-2 inhibit type I interferon signaling pathway. Virus Res. 2020, 286, 198074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinzula, L. Lost in deletion: The enigmatic ORF8 protein of SARS-CoV-2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 538, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F. Evolutionary dynamics of the SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 accessory gene. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 85, 104525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.C.F.; Anderson, D.E.; Young, B.E.; Linster, M.; Zhu, F.; Jayakumar, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Kalimuddin, S.; Low, J.G.H.; Tan, C.W.; et al. Discovery and genomic characterization of a 382-nucleotide deletion in ORF7B and orf8 during the early evolution of SARS-CoV-2. MBio 2020, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, B.E.; Fong, S.W.; Chan, Y.H.; Mak, T.M.; Ang, L.W.; Anderson, D.E.; Lee, C.Y.P.; Amrun, S.N.; Lee, B.; Goh, Y.S.; et al. Effects of a major deletion in the SARS-CoV-2 genome on the severity of infection and the inflammatory response: An observational cohort study. Lancet 2020, 396, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muth, D.; Corman, V.M.; Roth, H.; Binger, T.; Dijkman, R.; Gottula, L.T.; Gloza-Rausch, F.; Balboni, A.; Battilani, M.; Rihtarič, D.; et al. Attenuation of replication by a 29 nucleotide deletion in SARS-coronavirus acquired during the early stages of human-to-human transmission. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freed, N.E.; Vlková, M.; Faisal, M.B.; Silander, O.K. Rapid and Inexpensive Whole-Genome Sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 using 1200 bp Tiled Amplicons and Oxford Nanopore Rapid Barcoding. Biol. Methods Protoc. 2020, 5, bpaa014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covid-, T.; Consortium, G.U. An integrated national scale SARS-CoV-2 genomic surveillance network. Lancet Microbe 2020, 1, e99–e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libin, P.J.K.; Deforche, K.; Abecasis, A.B.; Theys, K. VIRULIGN: Fast codon-correct alignment and annotation of viral genomes. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1763–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šošić, M.; Šikić, M. Edlib: A C/C ++ library for fast, exact sequence alignment using edit distance. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 1394–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, A.A.; Schult, D.A.; Swart, P.J. Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function using NetworkX. In Proceedings of the 7th Python in Science Conference (SciPy 2008), Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–24 August 2008; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Franz, M.; Lopes, C.T.; Huck, G.; Dong, Y.; Sumer, O.; Bader, G.D. Cytoscape.js: A graph theory library for visualisation and analysis. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huddleston, J.; Hadfield, J.; Sibley, T.; Lee, J.; Fay, K.; Ilcisin, M.; Harkins, E.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.; Hodcroft, E. Augur: A bioinformatics toolkit for phylogenetic analyses of human pathogens. J. Open Source Softw. 2021, 6, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; Sagulenko, P.; Bedford, T.; Neher, R.A. NextStrain: Real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, S.K.; Berman, H.M.; Bhikadiya, C.; Bi, C.; Chen, L.; Di Costanzo, L.; Christie, C.; Duarte, J.M.; Dutta, S.; Feng, Z.; et al. Protein Data Bank: The single global archive for 3D macromolecular structure data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D520–D528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casañal, A.; Lohkamp, B.; Emsley, P. Current developments in Coot for macromolecular model building of Electron Cryo-microscopy and Crystallographic Data. Protein Sci. 2020, 29, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schrödinger, L.; DeLano, W. PyMOL. 2020. Available online: http://www.pymol.org/pymol (accessed on 10 July 2021).
- Flower, T.G.; Buffalo, C.Z.; Hooy, R.M.; Allaire, M.; Ren, X.; Hurley, J.H. Structure of SARS-cov-2 ORF8, a rapidly evolving immune evasion protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2021785118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usón, I.; Pohl, E.; Schneider, T.R.; Dauter, Z.; Schmidt, A.; Fritz, H.J.; Sheldrick, G.M. 1.7 Å Structure of the stabilized REI(v) mutant T39K. Application of local NCS restraints. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1999, 55, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edge, P.; Bansal, V. Longshot enables accurate variant calling in diploid genomes from single-molecule long read sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loman, N.J.; Quick, J.; Simpson, J.T. A complete bacterial genome assembled de novo using only nanopore sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagulenko, P.; Puller, V.; Neher, R.A. TreeTime: Maximum-likelihood phylodynamic analysis. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vex042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.I.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hassan, S.S.; Kodakandla, V.; Redwan, E.M.; Lundstrom, K.; Choudhury, P.P.; Mohamed, T.; El-Aziz, A.; Takayama, K.; Kandimalla, R.; Lal, A.; et al. An Issue of Concern: Unique Truncated ORF8 Protein Variants of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brandt, D.; Simunovic, M.; Busche, T.; Haak, M.; Belmann, P.; Jünemann, S.; Schulz, T.; Klages, L.J.; Vinke, S.; Beckstette, M.; et al. Multiple Occurrences of a 168-Nucleotide Deletion in SARS-CoV-2 ORF8, Unnoticed by Standard Amplicon Sequencing and Variant Calling Pipelines. Viruses 2021, 13, 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091870
Brandt D, Simunovic M, Busche T, Haak M, Belmann P, Jünemann S, Schulz T, Klages LJ, Vinke S, Beckstette M, et al. Multiple Occurrences of a 168-Nucleotide Deletion in SARS-CoV-2 ORF8, Unnoticed by Standard Amplicon Sequencing and Variant Calling Pipelines. Viruses. 2021; 13(9):1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091870
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrandt, David, Marina Simunovic, Tobias Busche, Markus Haak, Peter Belmann, Sebastian Jünemann, Tizian Schulz, Levin Joe Klages, Svenja Vinke, Michael Beckstette, and et al. 2021. "Multiple Occurrences of a 168-Nucleotide Deletion in SARS-CoV-2 ORF8, Unnoticed by Standard Amplicon Sequencing and Variant Calling Pipelines" Viruses 13, no. 9: 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091870
APA StyleBrandt, D., Simunovic, M., Busche, T., Haak, M., Belmann, P., Jünemann, S., Schulz, T., Klages, L. J., Vinke, S., Beckstette, M., Pohl, E., Scherer, C., Sczyrba, A., & Kalinowski, J. (2021). Multiple Occurrences of a 168-Nucleotide Deletion in SARS-CoV-2 ORF8, Unnoticed by Standard Amplicon Sequencing and Variant Calling Pipelines. Viruses, 13(9), 1870. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13091870





