Genetic Reassortment between Endemic and Introduced Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodaviruses in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MrNV Discovery and Genome Annotation
2.2. Estimation of Transcript Abundance
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Screening for Invertebrate Sequences in Fish Metagenomes
3. Results
3.1. Composition of Metatranscriptomes and Identification of Macrobrachium australiense
3.2. Presence of MrNV and XSV
3.3. Genome Organization
3.4. MrNV Nucleotide Similarity between Northern and Southern Rivers of the MDB
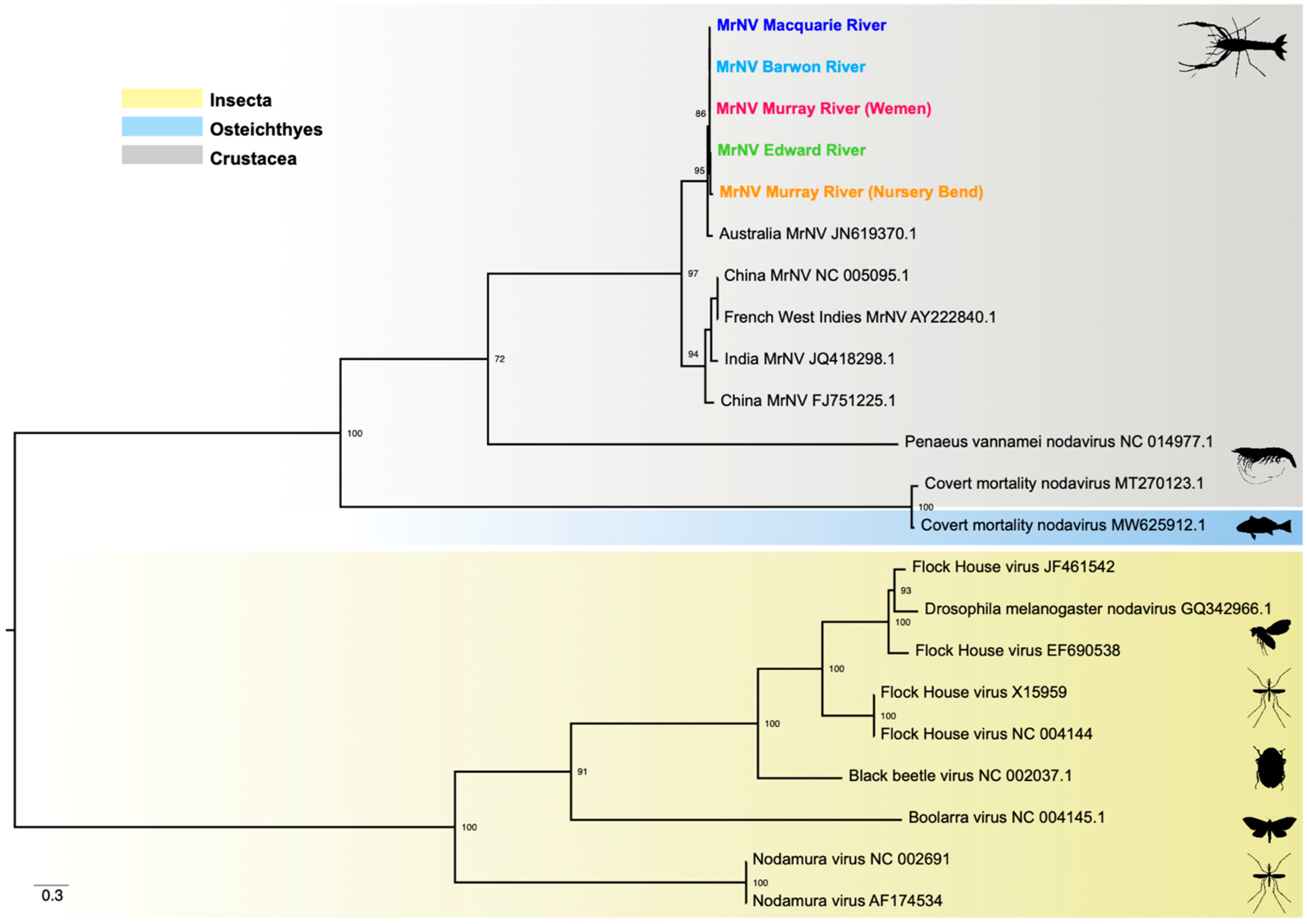
3.5. Phylogenetic Relationships
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation. Available online: https://www.fao.org/documents/card/en/c/cc0461en (accessed on 9 August 2022).
- Stentiford, G.D.; Neil, D.M.; Peeler, E.J.; Shields, J.D.; Small, H.J.; Flegel, T.W.; Vlak, J.M.; Jones, B.; Morado, F.; Moss, S.; et al. Disease will limit future food supply from the global crustacean fishery and aquaculture sectors. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.; Yu, Y.-B.; Choi, J.-H.; Jo, A.H.; Hong, S.-M.; Kang, J.-C.; Kim, J.-H. Viral Shrimp Diseases Listed by the OIE: A Review. Viruses 2022, 14, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.L.; Gabrielsen, M.; Beh, P.L.; Kueh, C.L.; Thong, Q.X.; Streetley, J.; Tan, W.S.; Bhella, D. Structure of the Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus: A new genus within the Nodaviridae? PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e3000038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, K.F.; Tan, W.S.; Ong, L.K.; Zainal Abidin, S.A.; Othman, I.; Tey, B.T.; Lee, R.F.S. The Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus: A detailed review of structure, infectivity, host immunity, diagnosis and prevention. Rev. Aquc. 2021, 13, 2117–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahul Hameed, A.S.; Ninawe, A.S.; Nakai, T.; Chi, S.C.; Johnson, K.L.; Ictv Report, C. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Sarthroviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1563–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakijkosol, O.; La Fauce, K.; Owens, L. Experimental infection of redclaw crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) with Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus, the aetiological agent of white tail disease. Aquaculture 2011, 319, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, M.; Sahul Hameed, A.S. Experimental transmission of Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV) and extra small virus (XSV) in Macrobrachium malcolmsonii and Macrobrachium rude. Aquac. Int. 2014, 23, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, M.; Nazeer Basha, A.; Sarathi, M.; Rosa Idalia, H.H.; Sri Widada, J.; Bonami, J.R.; Sahul Hameed, A.S. Studies on the occurrence of white tail disease (WTD) caused by MrNV and XSV in hatchery-reared post-larvae of Penaeus indicus and P. monodon. Aquaculture 2009, 292, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakaran, R.; Haribabu, P.; Rajesh Kumar, S.; Sarathi, M.; Ishaq Ahmed, V.P.; Sarath Babu, V.; Venkatesan, C.; Sahul Hameed, A.S. Natural aquatic insect carriers of Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV) and extra small virus (XSV). Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 79, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arcier, J.M.; Herman, F.; Lightner, D.V.; Redman, R.M.; Mari, J.; Bonami, J.R. A viral disease associated with mortalities in hatchery-reared postlarvae of the giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Dis. Aquat. Org. 1999, 38, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cao, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, L.; Xie, Y.; Cambournac, I.; Bonami, J.R. Extra small virus-like particles (XSV) and nodavirus associated with whitish muscle disease in the giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. J. Fish Dis. 2003, 26, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahul Hameed, A.S.; Yoganandhan, K.; Sri Widada, J.; Bonami, J.R. Studies on the occurrence of Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus and extra small virus-like particles associated with white tail disease of M. rosenbergii in India by RT-PCR detection. Aquaculture 2004, 238, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.S.; Chang, J.S.; Wen, C.M.; Shih, H.H.; Chen, S.N. Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus infection in M. rosenbergii (de Man) with white tail disease cultured in Taiwan. J. Fish Dis. 2008, 31, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoganandhan, K.; Leartvibhas, M.; Sriwongpuk, S.; Limsuwan, C. White tail disease of the giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii in Thailand. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2006, 69, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saedi, T.A.; Moeini, H.; Tan, W.S.; Yusoff, K.; Daud, H.M.; Chu, K.B.; Tan, S.G.; Bhassu, S. Detection and phylogenetic profiling of nodavirus associated with white tail disease in Malaysian Macrobrachium rosenbergii de Man. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 5785–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakijkosol, O.; Burgess, G.; La Fauce, K.; Owens, L. The complete sequence of the Australia recognizate of Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus which causes white tail disease. Aquaculture 2012, 366–367, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, L.; La Fauce, K.; Juntunen, K.; Hayakijkosol, O.; Chaoshu, Z. Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus disease (white tail disease) in Australia. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 85, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, V.A.; Mifsud, J.C.O.; Gilligan, D.; Williamson, J.E.; Holmes, E.C.; Geoghegan, J.L. Metagenomic sequencing reveals a lack of virus exchange between native and invasive freshwater fish across the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De novo transcript sequence reconstruction from RNA-seq using the Trinity platform for reference generation and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Thierer, T.; Ashton, B.; Meintjes, P.; Drummond, A.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Silla-Martinez, J.M.; Gabaldon, T. trimAl: A tool for automated alignment trimming in large-scale phylogenetic analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clausen, P.T.L.C.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Rapid and precise alignment of raw reads against redundant databases with KMA. BMC Bioinform. 2018, 19, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcelino, V.R.; Clausen, P.T.L.C.; Buchmann, J.P.; Wille, M.; Iredell, J.R.; Meyer, W.; Lund, O.; Sorrell, T.C.; Holmes, E.C. CCMetagen: Comprehensive and accurate identification of eukaryotes and prokaryotes in metagenomic data. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahola, T.; Karlin, D.G. Sequence analysis reveals a conserved extension in the capping enzyme of the alphavirus supergroup, and a homologous domain in nodaviruses. Biol. Direct 2015, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geoghegan, J.L.; Di Giallonardo, F.; Wille, M.; Ortiz-Baez, A.S.; Costa, V.A.; Ghaly, T.; Mifsud, J.C.O.; Turnbull, O.M.H.; Bellwood, D.R.; Williamson, J.E.; et al. Virome composition in marine fish revealed by meta-transcriptomics. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, V.A.; Bellwood, D.R.; Mifsud, J.C.O.; Geoghegan, J.L.; Holmes, E.C.; Harvey, E. Limited Cross-Species Virus Transmission in a Spatially Restricted Coral Reef Fish Community. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, N.P.; Austin, C.M. Phylogeography of the widespread Australian freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium australiense (Decapoda, Palaemonidae). J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, S.M.; Nelson, M.I.; Turner, P.E.; Patton, J.T. Reassortment in segmented RNA viruses: Mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijaykrishna, D.; Mukerji, R.; Smith, G.J.D. RNA Virus Reassortment: An Evolutionary Mechanism for Host Jumps and Immune Evasion. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olveira, J.G.; Souto, S.; Dopazo, C.P.; Thiery, R.; Barja, J.L.; Bandin, I. Comparative analysis of both genomic segments of betanodaviruses isolated from epizootic outbreaks in farmed fish species provides evidence for genetic reassortment. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 2940–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toffan, A.; Pascoli, F.; Pretto, T.; Panzarin, V.; Abbadi, M.; Buratin, A.; Quartesan, R.; Gijón, D.; Padrós, F. Viral nervous necrosis in gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) caused by reassortant betanodavirus RGNNV/SJNNV: An emerging threat for Mediterranean aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gangnonngiw, W.; Bunnontae, M.; Phiwsaiya, K.; Senapin, S.; Dhar, A.K. In experimental challenge with infectious clones of Macrobrachium rosenbergii nodavirus (MrNV) and extra small virus (XSV), MrNV alone can cause mortality in freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii). Virology 2020, 540, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
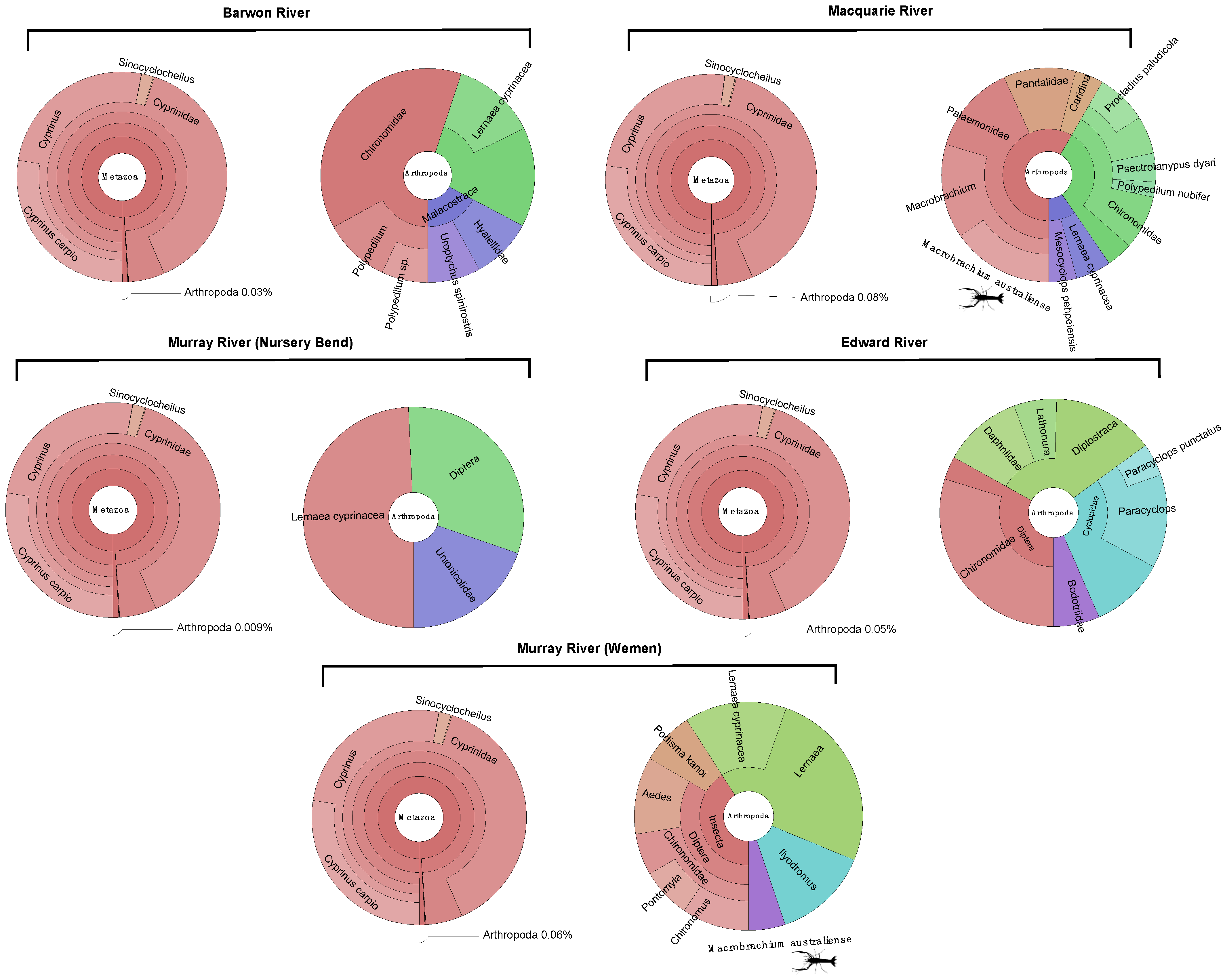
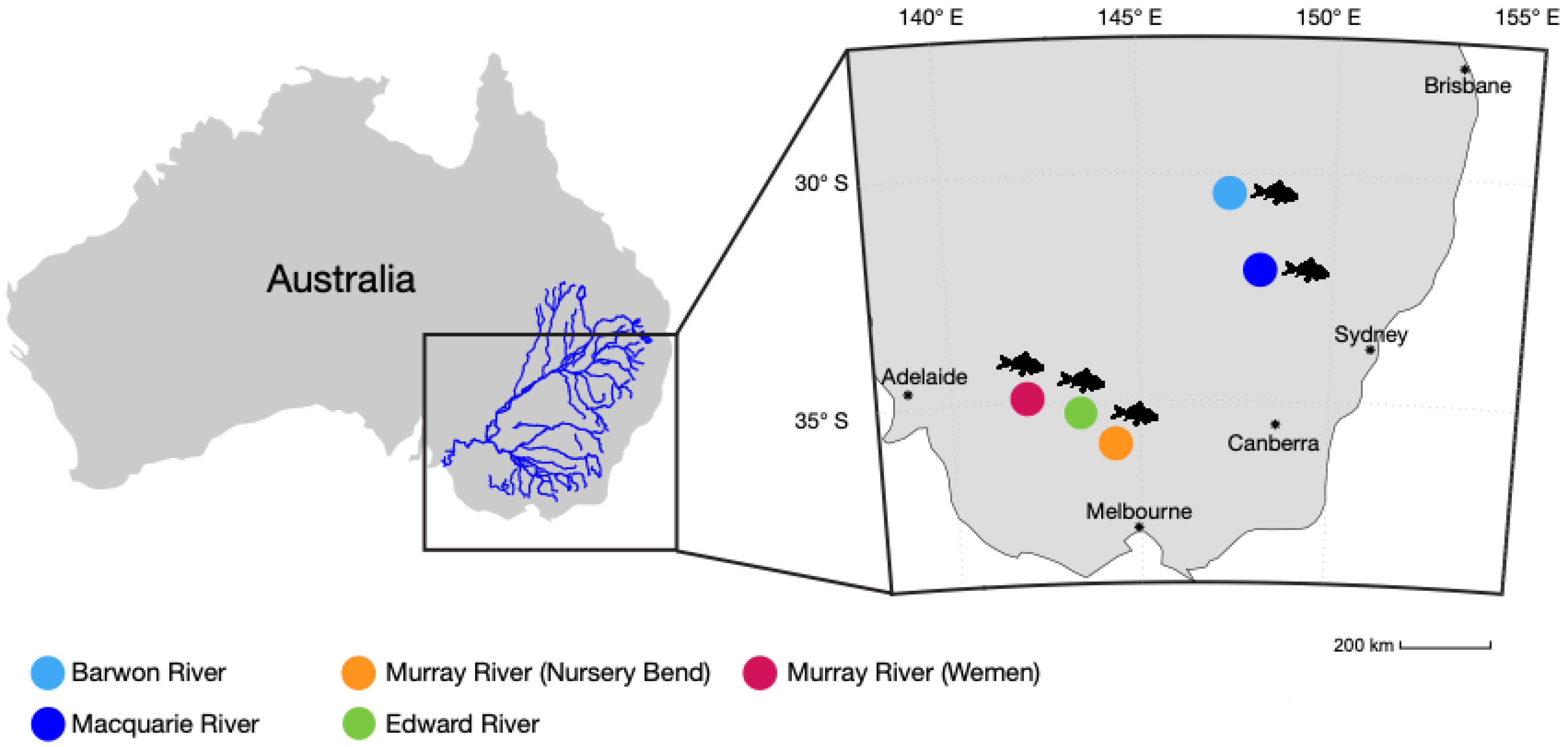
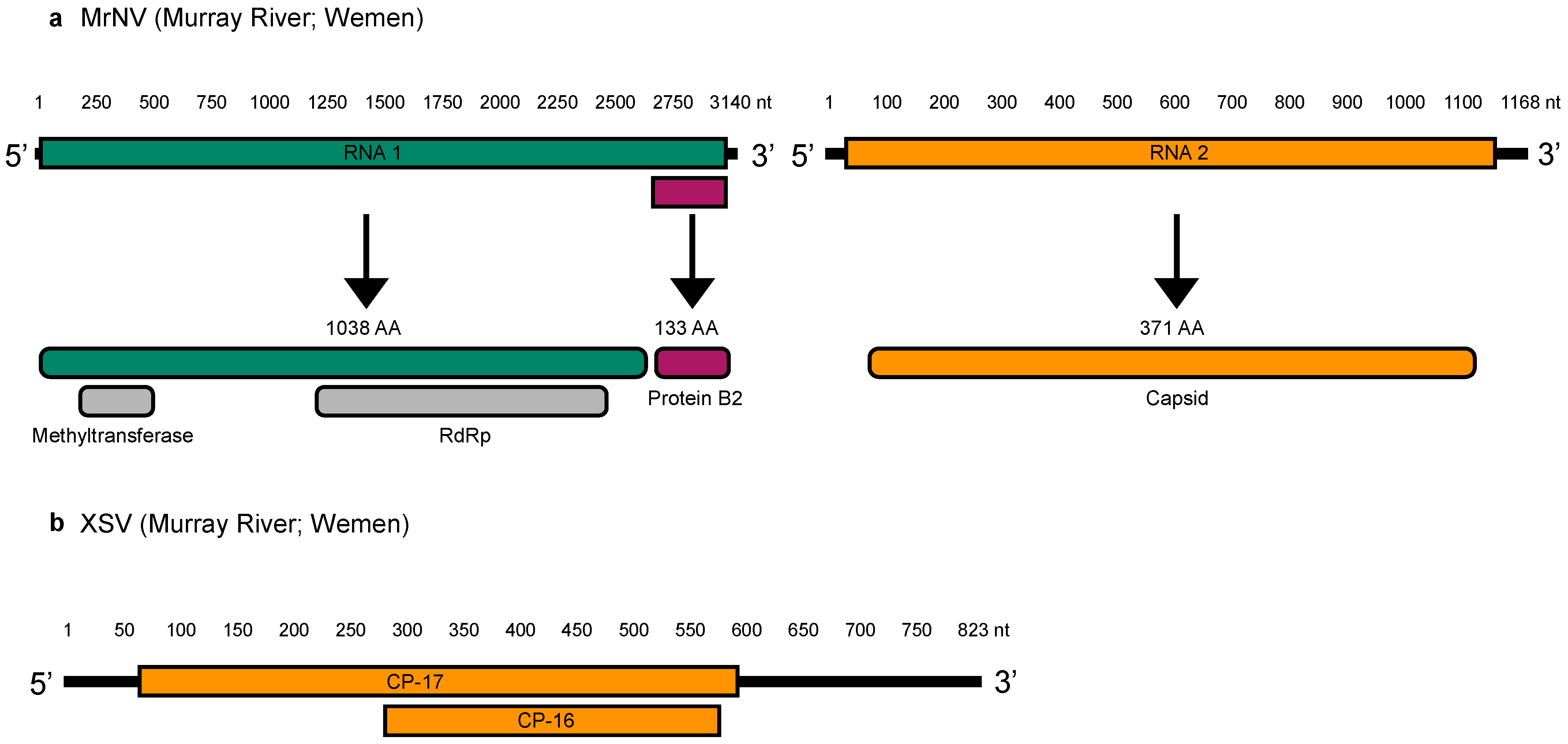
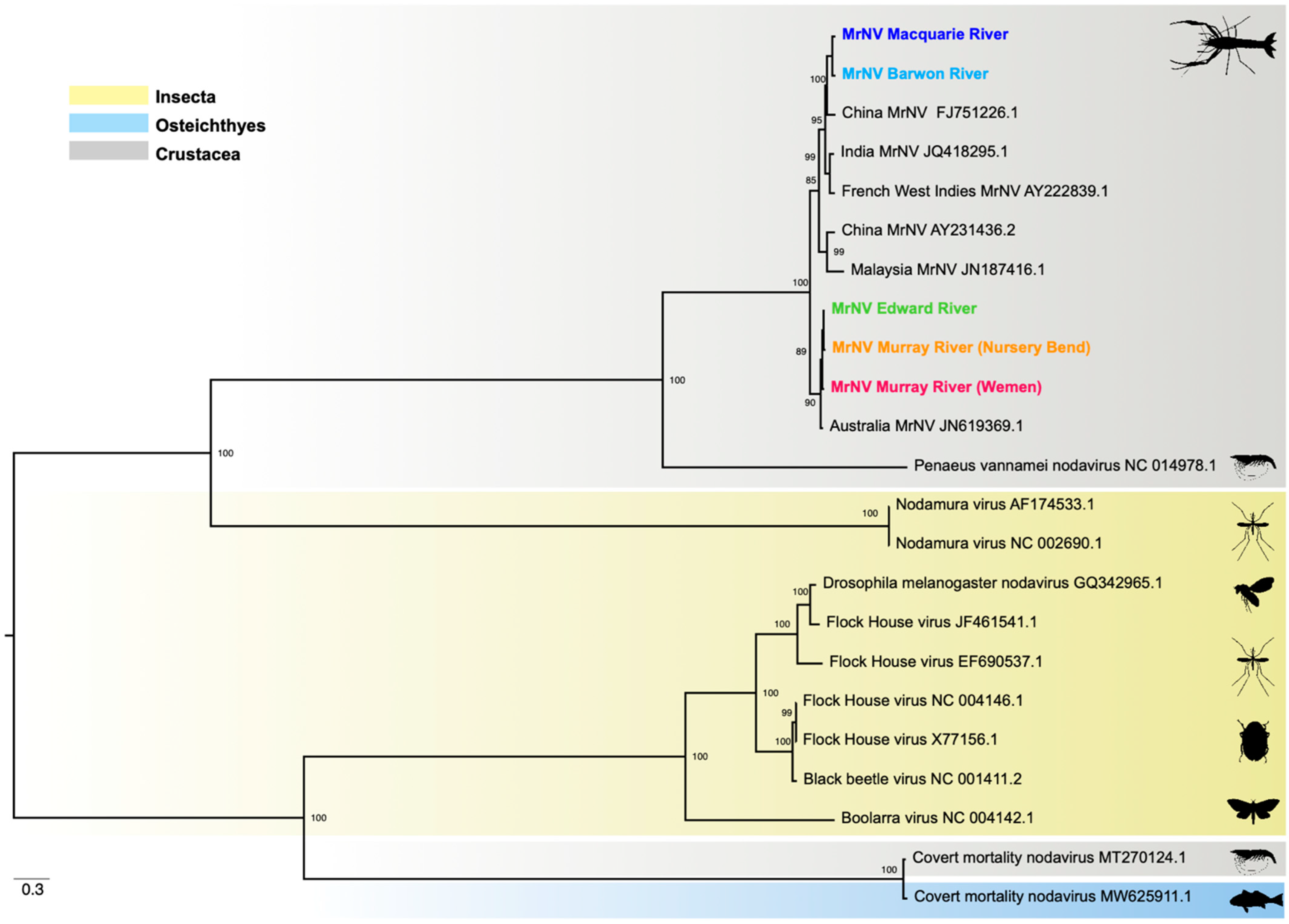
| Virus | Site/NCBI SRA Accession | Coordinates | Gene | Length (nt) | Standardised Abundance (%) | Closest Relative (GenBank) | Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MrNV | Barwon River/SRX10098043 | 29°58′26.8″ S 148°06′45.5″ E | RdRp | 3126 | 0.052 | China MrNV (FJ751226.1) | 98.1 |
| Capsid | 1116 | 0.022 | Australia MrNV (JN619370) | 98.8 | |||
| MrNV | Macquarie River/SRX10098050 | 31°59′10.7″ S 148°12′37.8″ E | RdRp | 3126 | 0.003 | China MrNV (FJ751226.1) | 98 |
| Capsid | 1116 | 0.002 | Australia MrNV (JN619370) | 98.8 | |||
| MrNV | Murray River (Nursery Bend)/SRX10098058 | 35°45′58.0″ S 144°20′55.0″ E | RdRp | 3126 | 0.001 | Australia MrNV (JN619369) | 99.1 |
| Capsid | 1116 | 0.001 | Australia MrNV (JN619370) | 98.5 | |||
| MrNV | Murray River (Wemen)/ SRX10098067 | 34°45′55.6″ S 142°38′44.0″ E | RdRp | 3126 | 0.002 | Australia MrNV (JN619369) | 99.3 |
| Capsid | 1116 | 0.001 | Australia MrNV (JN619370) | 98.9 | |||
| XSV | Capsid | 525 | 6.3 × 10−5 | Thailand XSV (NC_043498) | 99 | ||
| MrNV | Murray River (Edward River)/SRX10098059 | 35°05′28.8″ S 144°00′36.4″ E | RdRp | 3126 | 0.009 | Australia MrNV (JN619369) | 99.2 |
| Capsid | 1116 | 0.004 | Australia MrNV (JN619370) | 98.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Costa, V.A.; Geoghegan, J.L.; Holmes, E.C.; Harvey, E. Genetic Reassortment between Endemic and Introduced Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodaviruses in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. Viruses 2022, 14, 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102186
Costa VA, Geoghegan JL, Holmes EC, Harvey E. Genetic Reassortment between Endemic and Introduced Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodaviruses in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. Viruses. 2022; 14(10):2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102186
Chicago/Turabian StyleCosta, Vincenzo A., Jemma L. Geoghegan, Edward C. Holmes, and Erin Harvey. 2022. "Genetic Reassortment between Endemic and Introduced Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodaviruses in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia" Viruses 14, no. 10: 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102186
APA StyleCosta, V. A., Geoghegan, J. L., Holmes, E. C., & Harvey, E. (2022). Genetic Reassortment between Endemic and Introduced Macrobrachium rosenbergii Nodaviruses in the Murray-Darling Basin, Australia. Viruses, 14(10), 2186. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102186






