The Over-40-Years-Epidemic of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
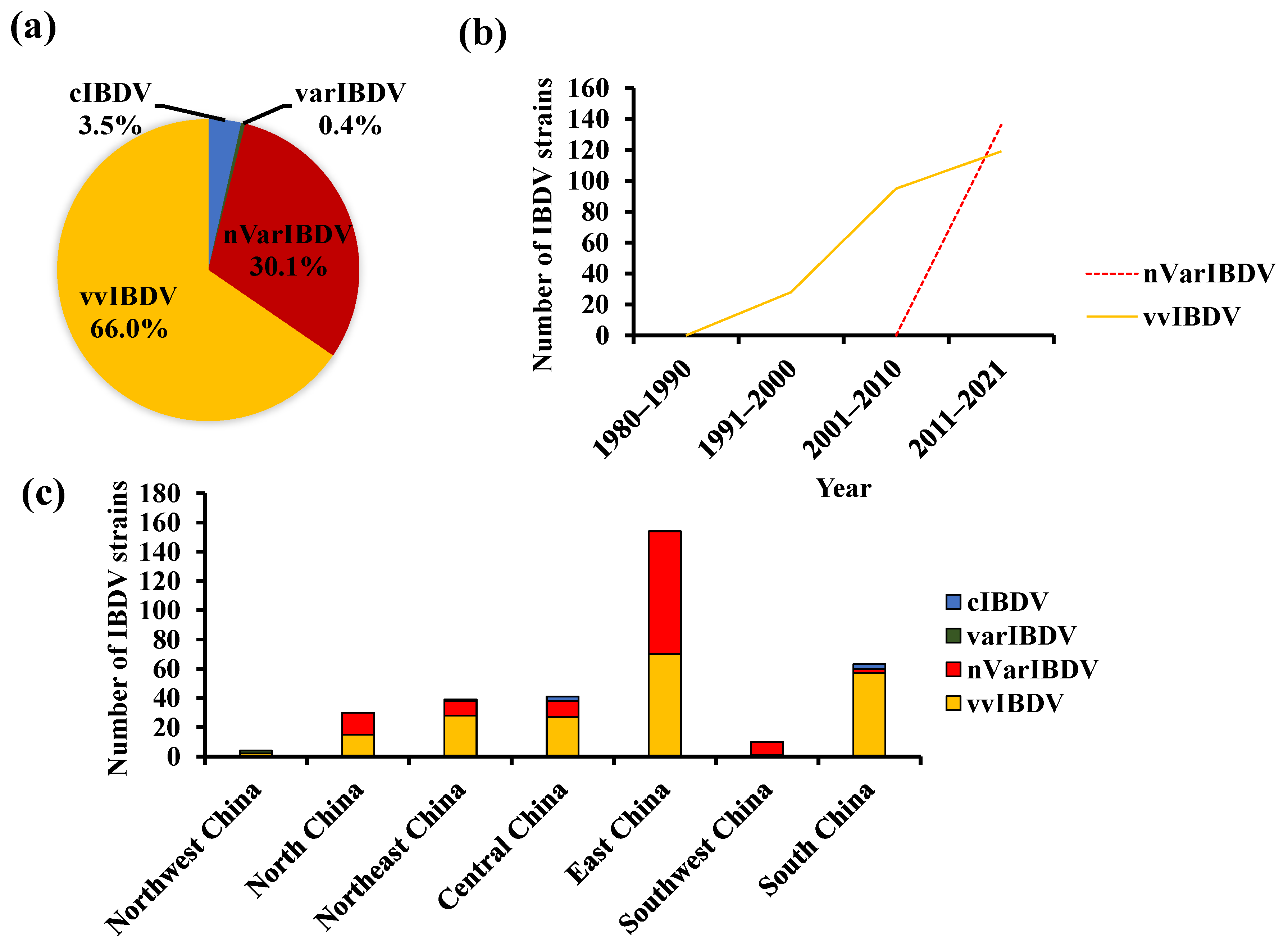
2. The Coexistence of Various Strains of IBDV in China
3. Genotype Classification of IBDV
4. The Persistently Circulating vvIBDV
5. The Newly Emerging nVarIBDV
6. The Segment Reassortment and Gene Recombination among Circulating Strains
7. Immune Prevention and Control of IBDV
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cosgrove, A.S. An Apparently New Disease of Chickens: Avian Nephrosis. Avian Dis. 1962, 6, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettle, N.; Stuart, J.C.; Wyeth, P.J. Outbreak of virulent infectious bursal disease in East Anglia. Vet. Rec. 1989, 125, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, J.; Rossini, L.; Eterradossi, N.; Toquin, M.D.; Gardin, Y. European-like pathogenic infectious bursal disease viruses in Brazil. Vet. Rec. 1999, 145, 203–204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, F.; Chen, L.; Wang, S. Isolation of pathogen of infectious bursal disease in Beijing area. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 1982, 8, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, Y. A study on infectious bursal disease of the chicken in Guangdong area. J. South China Agric. Univ. 1985, 1, 46–61. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Wu, Z. Isolation and preliminary identification of a supervirulent strain of infectious bursal disease virus. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 1991, 6, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, L.; Wu, T.; Hussain, A.; Gao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. Novel variant strains of infectious bursal disease virus isolated in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 230, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, O.; Suwanruengsri, M.; Araki, K.; Izzati, U.Z.; Pornthummawat, A.; Nueangphuet, P.; Fuke, N.; Hirai, T.; Jackwood, D.J.; Yamaguchi, R. Bursa atrophy at 28 days old caused by variant infectious bursal disease virus has a negative economic impact on broiler farms in Japan. Avian Pathol. 2021, 50, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thai, T.N.; Jang, I.; Kim, H.A.; Kim, H.S.; Kwon, Y.K.; Kim, H.R. Characterization of antigenic variant infectious bursal disease virus strains identified in South Korea. Avian Pathol. 2021, 50, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xue, J.; Ruan, S.; Zhang, G. Phylogenetic analyses and pathogenicity of a variant infectious bursal disease virus strain isolated in China. Virus Res. 2020, 276, 197833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, H.B.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Omar, A.R.; Ideris, A. Genetic Diversity of Recent Infectious Bursal Disease Viruses Isolated From Vaccinated Poultry Flocks in Malaysia. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 643976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliyu, H.B.; Hamisu, T.M.; Hair Bejo, M.; Omar, A.R.; Ideris, A. Comparative Pathogenicity of Malaysian Variant and Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Viruses in Chickens. Avian Pathol. 2022, 51, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, T.N.; Yoo, D.S.; Jang, I.; Kwon, Y.K.; Kim, H.R. Dynamics of the Emerging Genogroup of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Infection in Broiler Farms in South Korea: A Nationwide Study. Viruses 2022, 14, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.D.; Skinner, M.A. Coding Sequences of Both Genome Segments of a European “very Virulent” Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Virus Res. 1996, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, S.; Lejal, N.; Huet, J.; Delmas, B. Active Residues and Viral Substrate Cleavage Sites of the Protease of the Birnavirus Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2057–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackwood, D.J. Advances in Vaccine Research against Economically Important Viral Diseases of Food Animals: Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 206, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letzel, T.; Coulibaly, F.; Rey, F.A.; Delmas, B.; Jagt, E.; van Loon, A.A.M.W.; Mundt, E. Molecular and Structural Bases for the Antigenicity of VP2 of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 12827–12835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qi, X.; Gao, H.; Gao, Y.; Qin, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, X. Naturally Occurring Mutations at Residues 253 and 284 in VP2 Contribute to the Cell Tropism and Virulence of Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Antivir. Res. 2009, 84, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L.; Wu, G.; Qin, L.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; et al. Mutations of Residues 249 and 256 in VP2 Are Involved in the Replication and Virulence of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escaffre, O.; Le Nouën, C.; Amelot, M.; Ambroggio, X.; Ogden, K.M.; Guionie, O.; Toquin, D.; Müller, H.; Islam, M.R.; Eterradossi, N. Both Genome Segments Contribute to the Pathogenicity of Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2767–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Li, K.; Qi, X.; Gao, H.; Gao, Y.; Qin, L.; Wang, Y.; Shen, N.; Kong, X.; Wang, X. Triplet Amino Acids Located at Positions 145/146/147 of the RNA Polymerase of Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Contribute to Viral Virulence. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 888–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ye, C. Rapid Generation of Attenuated Infectious Bursal Disease Virus from Dual-Promoter Plasmids by Reduction of Viral Ribonucleoprotein Activity. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01569-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikuła, A.; Śmietanka, K.; Perez, L.J. Emergence and expansion of novel pathogenic reassortant strains of infectious bursal disease virus causing acute outbreaks of the disease in Europe. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1739–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.C.; Yeung, W.S.; Law, M.; Bi, Y.Z.; Leung, F.C.; Lim, B.L. Molecular Characterization of Seven Chinese Isolates of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus: Classical, Very Virulent, and Variant Strains. Avian Dis. 1998, 42, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Niu, X.; Huang, M.; Gao, Y.; Liu, A.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Pan, Q.; et al. Genotyping and Molecular Characterization of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Identified in Important Poultry-Raising Areas of China During 2019 and 2020. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 759861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackwood, D.H.; Saif, Y.M. Antigenic Diversity of Infectious Bursal Disease Viruses. Avian Dis. 1987, 31, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackwood, D.J. Molecular Epidemiologic Evidence of Homologous Recombination in Infectious Bursal Disease Viruses. Avian Dis. 2012, 56, 574–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.; Tomás, G.; Marandino, A.; Iraola, G.; Maya, L.; Mattion, N.; Hernández, D.; Villegas, P.; Banda, A.; Panzera, Y.; et al. Genetic Characterization of South American Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Reveals the Existence of a Distinct Worldwide-Spread Genetic Lineage. Avian Pathol. J. WVPA 2015, 44, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupini, C.; Giovanardi, D.; Pesente, P.; Bonci, M.; Felice, V.; Rossi, G.; Morandini, E.; Cecchinato, M.; Catelli, E. A Molecular Epidemiology Study Based on VP2 Gene Sequences Reveals That a New Genotype of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Is Dominantly Prevalent in Italy. Avian Pathol. J. WVPA 2016, 45, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michel, L.O.; Jackwood, D.J. Classification of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus into Genogroups. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3661–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, L.; Jiang, N.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; Cui, H.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, Y.-P.; et al. An improved scheme for infectious bursal disease virus genotype classification based on both genome-segments A and B. J. Integr. Agr. 2021, 20, 1372–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.R.; Nooruzzaman, M.; Rahman, T.; Mumu, T.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Eterradossi, N.; Müller, H. A Unified Genotypic Classification of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Based on Both Genome Segments. Avian Pathol. J. WVPA 2021, 50, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, M. Sequence analysis of the VP2 hyperirable region of nine infectious bursal disease viruses from Mainland China. Avian Dis. 1998, 42, 762–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Xiong, Z.; Yang, L.; Guan, D.; Yang, X.; Wei, P. Molecular Epidemiology Studies on Partial Sequences of Both Genome Segments Reveal That Reassortant Infectious Bursal Disease Viruses Were Dominantly Prevalent in Southern China during 2000–2012. Arch. Virol. 2014, 159, 3279–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Z.; Chen, F.; Ji, J.; Qin, J.; Li, H.; Lu, J.; Xue, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Molecular Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Infectious Bursal Disease Viruses Isolated from Chicken in South China in 2011. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2013, 45, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Yu, W.; Wu, G.; Ren, J.; Cao, S.; Zhao, J.; Meng, F.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z. Isolation and identification of infectious bursal disease virus in chickens in Shanxi Province. China Prog. Vet. Med. 2016, 37, 70–74. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, X.; Qin, L.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Lu, Z.; Wang, N.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Genetic Analysis of the VP2 hypervariable region of thirty-six infectious bursal disease virus Isolates in China. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 16, 1565–1569. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, X.; Gao, H.; Fu, C.; Wei, P. Changes in VP2 Gene during the Attenuation of Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Strain Gx Isolated in China. Avian Dis. 2004, 48, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Fu, C. Direct evidence of reassortment and mutant spectrum analysis of a very virulent infectious bursal disease virus. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Gao, L.; Qin, L.; Deng, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, L.; Yu, F.; Ren, X.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; et al. Genomic sequencing and characterization of a very virulent strain of infectious bursal disease virus isolated in China. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 12, 1950–1953. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, R.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Huang, G.M.; Zhang, M.F. Sequence and phylogenetic analysis of a chinese very virulent infectious bursal disease virus. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 1725–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Fan, L.; Niu, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, M.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; et al. Identification and Pathogenicity Evaluation of a Novel Reassortant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (Genotype A2dB3). Viruses 2021, 13, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Deng, Q.; Chen, R.; Chen, J.; Huang, T.; Wei, T.; Mo, M.; et al. The Emerging Naturally Reassortant Strain of IBDV (Genotype A2dB3) Having Segment A from Chinese Novel Variant Strain and Segment B from HLJ 0504-like Very Virulent Strain Showed Enhanced Pathogenicity to Three-Yellow Chickens. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e566–e579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Wu, T.; Li, H.; Fan, L.; Li, K.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; Cui, H.; et al. Pathogenic Characterization and Full Length Genome Sequence of a Reassortant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Newly Isolated in Pakistan. Virol. Sin. 2019, 34, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.K.; Pandey, V.C.; Pal, J.K. Evidence of Genetic Drift and Reassortment in Infectious Bursal Disease Virus and Emergence of Outbreaks in Poultry Farms in India. Virusdisease 2016, 27, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nooruzzaman, M.; Hossain, I.; Rahman, M.M.; Uddin, A.J.; Mustari, A.; Parvin, R.; Chowdhury, E.H.; Islam, M.R. Comparative Pathogenicity of Infectious Bursal Disease Viruses of Three Different Genotypes. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 169, 105641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nouën, C.L.; Rivallan, G.; Toquin, D.; Darlu, P.; Morin, Y.; Beven, V.; de Boisseson, C.; Cazaban, C.; Comte, S.; Gardin, Y.; et al. Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus: Reduced Pathogenicity in a Rare Natural Segment-B-Reassorted Isolate. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbohun, O.; Owoade, A.; Oluwayelu, D.; Olayemi, F. Serological survey of infectious bursal diseases virus antibodies in cattle egrets, pigeons and Nigerian laughing doves. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2000, 3, 191–192. [Google Scholar]
- Jackwood, D.J.; Gough, R.E.; Sommer, S.E. Nucleotide and Amino Acid Sequence Analysis of a Birnavirus Isolated from Penguins. Vet. Rec. 2005, 156, 550–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, S.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Y.; Bi, Y.; Huang, J.; Guan, S.; Dai, C.; Huang, B.; Zeng, J. Isolation of serotype I virus subtype strains of infectious bursal disease in chickens. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 1991, 5, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; He, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Shi, J.; Chen, R.; Chen, J.; Xiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, G.; et al. Analysis of the Global Origin, Evolution and Transmission Dynamics of the Emerging Novel Variant IBDV (A2dB1b): The Accumulation of Critical Aa-Residue Mutations and Commercial Trade Contributes to the Emergence and Transmission of Novel Variants. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e2832–e2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, B.; Wang, C.; Luo, Z.; Shao, G. Commercial Vaccines Used in China Do Not Protect against a Novel Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Variant Isolated in Fujian. Vet. Rec. 2022, e1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Chen, M.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Cui, H.; Pan, Q.; Liu, C.; et al. Novel Variant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Suppresses Newcastle Disease Vaccination in Broiler and Layer Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 6542–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Hussain, A.; Jiang, N.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; Cui, H.; et al. Novel Variants of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Can Severely Damage the Bursa of Fabricius of Immunized Chickens. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 240, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Sun, L.; Tu, K.; Teng, Q.; Xue, J.; Zhang, G. Experimental Co-Infection of Variant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus and Fowl Adenovirus Serotype 4 Increases Mortality and Reduces Immune Response in Chickens. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Gao, Y.; Niu, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, M.; Bao, K.; Liu, A.; Wang, S.; et al. Residues 318 and 323 in Capsid Protein Are Involved in Immune Circumvention of the Atypical Epizootic Infection of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 909252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, N.; Chen, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, K.; Qi, X.; et al. Naturally Occurring Reassortant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Northern China. Virus Res. 2015, 203, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, P.; Yan, Y.; Hua, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, Y. Sequence and Analysis of Genomic Segment A and B of Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Isolated from China. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2003, 50, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Jang, I.; Shin, S.; Lee, H.; Choi, K. Genome Sequence of a Novel Reassortant and Very Virulent Strain of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00730-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, P.; Senthilkumar, T.M.A.; Parthiban, M.; Thangavelu, A.; Gowri, A.M.; Palanisammi, A.; Kumanan, K. Complete Genome Sequence Analysis of a Naturally Reassorted Infectious Bursal Disease Virus from India. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00709-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pikuła, A.; Lisowska, A.; Jasik, A.; Śmietanka, K. Identification and Assessment of Virulence of a Natural Reassortant of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Vet. Res. 2018, 49, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nwagbo, I.O.; Shittu, I.; Nwosuh, C.I.; Ezeifeka, G.O.; Odibo, F.J.C.; Michel, L.O.; Jackwood, D.J. Molecular Characterization of Field Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Isolates from Nigeria. Vet. World 2016, 9, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasanga, C.J.; Yamaguchi, T.; Munang’andu, H.M.; Ohya, K.; Fukushi, H. Genomic Sequence of an Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Isolate from Zambia: Classical Attenuated Segment B Reassortment in Nature with Existing Very Virulent Segment A. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, P.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Cui, B.; Chen, H. Genomic Sequence Analysis of a New Reassortant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus from Commercial Broiler Flocks in Central China. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 1973–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Yu, X.; Zheng, J.; Chu, W.; Xu, H.; Yu, X.; Yu, L. Reassortant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Isolated in China. Virus Res. 2008, 131, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, L.; Jiang, N.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Liu, C.; Cui, H.; et al. Naturally Occurring Homologous Recombination between Novel Variant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus and Intermediate Vaccine Strain. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 245, 108700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrao, F.; Rauw, F.; Lambrecht, B.; van den Berg, T. Infectious Bursal Disease: A Complex Host–Pathogen Interaction. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 41, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Cui, H.; Pan, Q.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A Reassortment Vaccine Candidate of the Novel Variant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 251, 108905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, N.; Fan, L.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Gao, Y.; Niu, X.; Zhang, W.; Cui, H.; Liu, A.; et al. Development of a Viral-Like Particle Candidate Vaccine Against Novel Variant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Vaccines 2021, 9, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Kuang, H.; Guo, H.; Cai, L.; Chu, D.; Wang, X.; Hu, J.; Rong, J. Development of a Recombinant VP2 Vaccine for the Prevention of Novel Variant Strains of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Avian Pathol. J. WVPA 2020, 49, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Phenotype | Genotype | Reference Strain | GenBank No. (A, B) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classic strains | A1B1 | YL052 China | DQ656521, KC968889 |
| FW2512 China | DQ656499, KC986359 | ||
| NN040124 China | DQ656502, KC968872 | ||
| IBD17JL01 China | MN604241, MN604242 | ||
| IBDV-GD19-15005 China | MW682890, MW863620 | ||
| Variant strains | A2aB1 | Variant E USA | AF133904, AF133905 |
| A2bB1 | 9109 USA | AY462027, AY459321 | |
| A2cB1 | GLS USA | AY368653, AY368654 | |
| Novel variant strains | A2dB1 | SHG19 China | MH879045, MH879092 |
| SHG120 China | MH879063, MH879110 | ||
| ZD-2018-1 China | MN485882, MN485883 | ||
| Gx-NNZ-11 China | JX134483, JX134484 | ||
| QZ191002 China | MZ066613, MZ066615 | ||
| vvIBDV | A3B2 | NN0704 China | FJ615511, KC968858 |
| YS07 China | FJ695138, FJ695139 | ||
| B-SD-RZ China | GQ166972, GQ166971 | ||
| SD10LY01 China | KF569803, KF569804 | ||
| HuB-1 China | KF569805, KF569804 | ||
| A3B3 | Gx China | AY444873, AY705393 | |
| S18 China | MK472711, MK472712 | ||
| QL China | JX682709, JX682710 | ||
| GL1001 China | KC968831, HQ452814 | ||
| HLJ0504 China | GQ166972, GQ451331 | ||
| Attenuated strains | A8B1 | Gt China | DQ403248, DQ403249 |
| BH15 China | DQ656498, KC968825 | ||
| JD1 China | AF321055, AY103464 | ||
| HuN0804 China | FJ615498, KC968842 | ||
| QX110603 China | KC918849, KC968876 |
| Genotype | Feature 1 | Reference Strain | GenBank No. (A, B) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A3B1 | vv-A/att-B | SH95 China | AY134874, AY134875 |
| 77.5% (31/40) | TSC-2(9) China | DQ656519, KC968881 | |
| BH11 China | DQ656497, KC968823 | ||
| NB1109 China | KC918838, KC968855 | ||
| JS0829 China | FJ615508, KC968853 | ||
| JS0822 China | FJ615507, KC968852 | ||
| JS0821 China | FJ615506, KC968851 | ||
| JS0819 China | FJ615505, KC968850 | ||
| JS0811 China | FJ615504, KC968849 | ||
| JS0809 China | FJ615502, KC968847 | ||
| GL0902 China | HQ452817, KC968830 | ||
| GL0901 China | HQ452816, KC968829 | ||
| NN0603 China | FJ615509, KC968856 | ||
| JS0806 China | FJ615501, KC968856 | ||
| HuN0802 China | FJ615496, KC968840 | ||
| HuN0801 China | FJ615495, KC968839 | ||
| WM1004 China | JQ260883, KC968883 | ||
| YN1162 China | JQ260876, KC968894 | ||
| YN1161 China | JQ260875, KC968894 | ||
| NN1166 China | JQ260874, KC968866 | ||
| NN1165 China | JQ260873, KC968865 | ||
| NN1164 China | JQ260872, KC968864 | ||
| YL051 China | DQ656506, KC968888 | ||
| IBDV-HN China | KT884486, KY948019 | ||
| IBDV-SD20-9103 China | MZ766382, MZ766407 | ||
| IBDV-SD20-9104 China | MZ766383, MZ766408 | ||
| IBDV-SD20-9102 China | MZ766381, MZ766406 | ||
| IBD13HeB01 China | KP676467, KP676468 | ||
| NN0704 China | FJ615511, KC968858 | ||
| NN1007 China | JQ260882, KC968860 | ||
| NN1005 China | JQ260881, KC968859 | ||
| A2dB3 | nVar-A/uniq-B | IBDV-JS19-14701 China | MW700332, MW700333 |
| 12.5% (5/40) | IBDV-JS19-14601 China | MW682905, MW863641 | |
| IBDV-GD1915010 China | MW682891, MW863621 | ||
| IBDV-SD19-9801 China | MW682907, MW863642 | ||
| IBDV-SD19-9804 China | MW682908, MW863643 | ||
| A8B2 | att-A/vv-B | ZJ2000 China | AF321056, DQ166818 |
| 10% (4/40) | TL2004 China | DQ088175, DQ118374 | |
| HN04 China | KC109816, KC109815 | ||
| YL160304 China | MZ066614, MZ066616 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Qi, X. The Over-40-Years-Epidemic of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in China. Viruses 2022, 14, 2253. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102253
Zhang W, Wang X, Gao Y, Qi X. The Over-40-Years-Epidemic of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in China. Viruses. 2022; 14(10):2253. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102253
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenying, Xiaomei Wang, Yulong Gao, and Xiaole Qi. 2022. "The Over-40-Years-Epidemic of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in China" Viruses 14, no. 10: 2253. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102253
APA StyleZhang, W., Wang, X., Gao, Y., & Qi, X. (2022). The Over-40-Years-Epidemic of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in China. Viruses, 14(10), 2253. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14102253







