Serological Evidence of Exposure to Saint Louis Encephalitis and West Nile Viruses in Horses of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.1.1. Seroprevalence Study
Sample Size
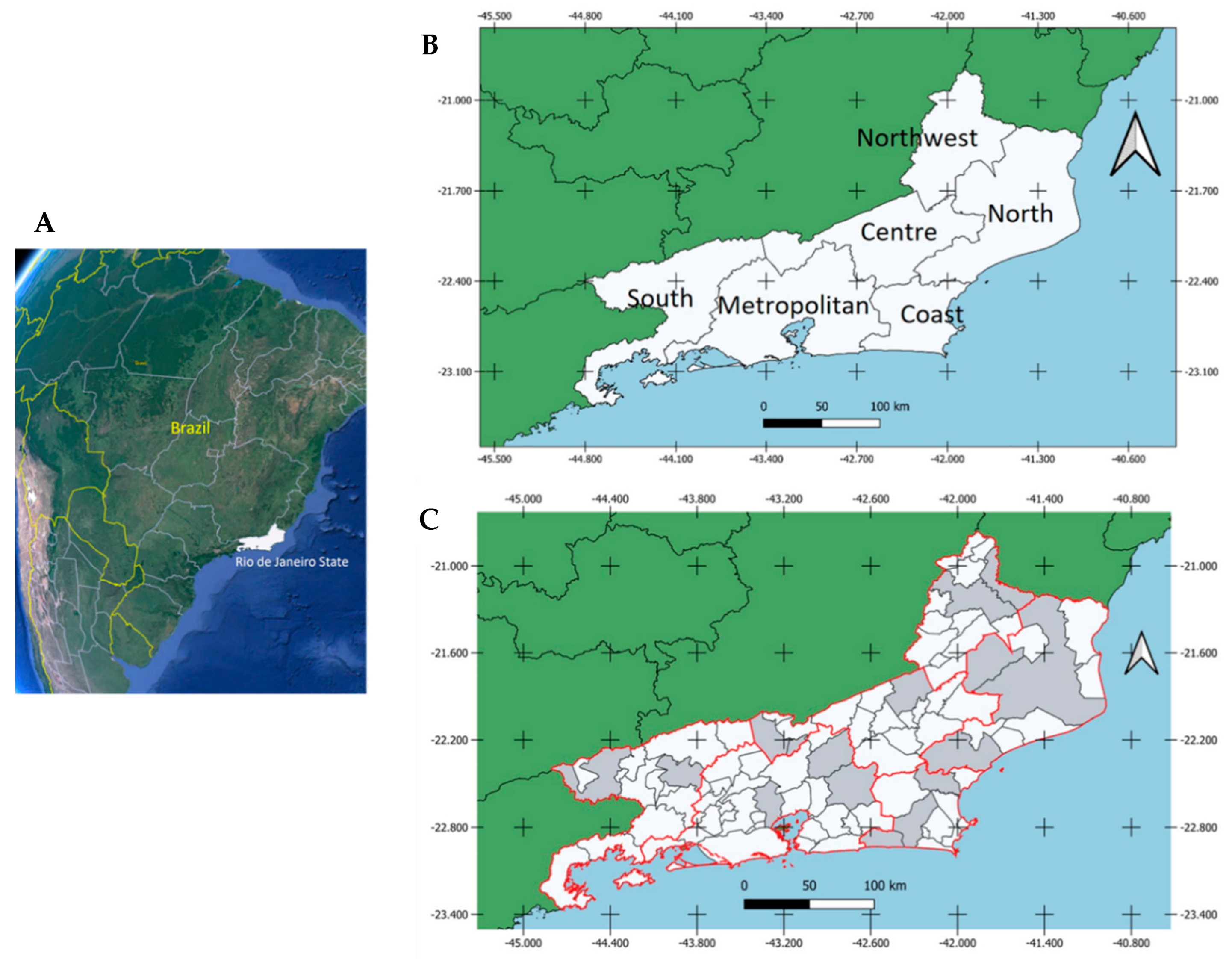
Study Area
Horse Categories
2.1.2. Horses with Neurological Disorder
2.2. Laboratory Tests
2.2.1. Plaque Reduction Neutralization Test (PRNT90)
2.2.2. Horses with Neurological Disorder
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sampling and Zootechnical Features
3.2. PRNT90 Results
Results by Geographic Location, Sex, Activities and Age Group
3.3. Real-Time Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pfeffer, M.; Dobler, G. Emergence of zoonotic arboviruses by animal trade and migration. Parasit. Vectors 2010, 3, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casals, J. Viruses: The versatile parasites; the arthropod-borne group of animal viruses. Trans. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1957, 19, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P.; Becher, P.; Bukh, J.; Gould, E.A.; Meyers, G.; Monath, T.; Muerhoff, S.; Pletnev, A.; Rico-Hesse, R.; Smith, D.B.; et al. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Flaviviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travassos da Rosa, A.P.A.; Travassos da Rosa, J.F.S.; Pinheiro, F.P.; Vasconcelos, P. Arboviroses. In Doenças Infecc. e Parasitárias—Enfoque Amaz.; Leão, R.N.Q., Ed.; CEJUP; UEPA; Instituto Evandro Chagas: Belém, Brazil, 1997; pp. 207–225. [Google Scholar]
- Lima-Camara, T.N. Emerging arboviruses and public health challenges in Brazil. Rev. Saude Publica 2016, 50, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz, A.; Coffey, L.L.; Burkett-Cadena, N.; Day, J.F. Reemergence of St. Louis Encephalitis Virus in the Americas. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2150–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komar, N. West Nile virus: Epidemiology and ecology in North America. Adv. Virus Res. 2003, 61, 185–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Jorge, L.A.; Siconelli, M.J.L.; Ribeiro, B.D.S.; Moraes, F.M.; Moraes, J.B.; Agostinho, M.R.; Klein, T.M.; Floriano, V.G.; Fonseca, B.A.L.D. West Nile virus infections are here! Are we prepared to face another flavivirus epidemic? Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2019, 52, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Barrett, A.D. Transmission cycles, host range, evolution, and emergence of arboviral disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, L.R.; Hayes, E.B. West Nile virus in the Americas. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 92, 1307–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Reisen, W.K. Present and future arboviral threats. Antivir. Res. 2010, 85, 328–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Gao, X.; Gould, E.A. Factors responsible for the emergence of arboviruses; strategies, challenges, and limitations for their control. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2015, 4, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saegerman, C.; Alba-Casals, A.; García-Bocanegra, I.; Dal Pozzo, F.; van Galen, G. Clinical Sentinel Surveillance of Equine West Nile Fever, Spain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, A.; Gillespie, T.R.; Hobelsberger, D.; Estrada, A.; Harper, J.M.; Miller, R.A.; Eckerle, I.; Müller, M.A.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Leendertz, F.H.; et al. Provenance and geographic spread of St. Louis encephalitis virus. mBio 2013, 4, e00322-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morales, M.A.; Barrandeguy, M.; Fabbri, C.; Garcia, J.B.; Vissani, A.; Trono, K.; Gutierrez, G.; Pigretti, S.; Menchaca, H.; Garrido, N.; et al. West Nile virus isolation from equines in Argentina. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 1559–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chancey, C.; Grinev, A.; Volkova, E.; Rios, M. The global ecology and epidemiology of West Nile virus. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 376230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webster, L.T.; Fite, G.L. A virus encountered in the study of material from cases of encephalitis in the St. Louis and Kansas City epidemics of 1933. Science 1933, 78, 463–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsden, L.L. St. Louis encephalitis in 1933; observations on epidemiological features. Public Health Rep. 1958, 73, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beltrán, F.J.; Bechara, Y.I.; Guido, G.G.; Cicuttin, G.L.; Beaudoin, J.B.; Gury Dohmen, F.E. Molecular detection of Saint Louis encephalitis virus in mosquitoes in Buenos Aires. Medicina (B Aires) 2014, 74, 433–436. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, A.N.; McLintock, J.; Francy, D.B. Isolation of St. Louis Encephalitis and Cache Valley Viruses from Saskatchewan Mosquitoes. Can. J. Public Health = Revue Canadienne de Sante Publique 1973, 64, 368–373. [Google Scholar]
- Causey, O.R.; Shope, R.E.; Theiler, M. Isolation of St. Louis encephalitis virus from arthropods in Pará, Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1964, 13, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Lopes, O.; de Abreu Sacchetta, L.; Coimbra, T.L.; Pereira, L.E. Isolation of St. Louis encephalitis virus in South Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1979, 28, 583–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, F.P.; LeDuc, J.W.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.; Leite, O.F. Isolation of St. Louis encephalitis virus from a patient in Belém, Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1981, 30, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocco, I.M.; Santos, C.L.; Bisordi, I.; Petrella, S.M.; Pereira, L.E.; Souza, R.P.; Coimbra, T.L.; Bessa, T.A.; Oshiro, F.M.; Lima, L.B.; et al. St. Louis encephalitis virus: First isolation from a human in São Paulo State, Brazil. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 2005, 47, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pinheiro, F.P.; Schatzmayr, H.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.A.; Homma, A.; Bensabath, G. Arbovirus antibodies in children of rural Guanabara, Brazil. Intervirology 1975, 5, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosa, R.; Costa, E.A.; Marques, R.E.; Oliveira, T.S.; Furtini, R.; Bomfim, M.R.; Teixeira, M.M.; Paixão, T.A.; Santos, R.L. Isolation of saint louis encephalitis virus from a horse with neurological disease in Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Tavares, F.N.; Costa, E.V.; Burlandy, F.M.; Murta, M.; Pellegrin, A.O.; Nogueira, M.F.; Silva, E.E. Serologic evidence of the recent circulation of Saint Louis encephalitis virus and high prevalence of equine encephalitis viruses in horses in the Nhecolândia sub-region in South Pantanal, Central-West Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2010, 105, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Campos, Z.; Juliano, R.; Velez, J.; Nogueira, R.M.R.; Komar, N. Serological Evidence of Widespread Circulation of West Nile Virus and Other Flaviviruses in Equines of the Pantanal, Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, S.G.; Oliva, O.P.; Araújo, F.A.A.; Martins, L.C.; Chiang, J.O.; Henriques, D.F.; da Silva, E.V.P.; Rodrigues, D.S.G.; Prazeres, A.S.C.; Tavares-Neto, J.; et al. Epidemiology of Saint Louis encephalitis virus in the Brazilian Amazon region and in the State of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil: Elevated prevalence of antibodies in horses. Rev. Pan-Amaz. Saúde 2010, 1, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, J.R.; Romeiro, M.F.; Souza, W.M.; Munhoz, T.D.; Borges, G.P.; Soares, O.A.; Campos, C.H.; Machado, R.Z.; Silva, M.L.; Faria, J.L.; et al. A Saint Louis encephalitis and Rocio virus serosurvey in Brazilian horses. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2014, 47, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbosa Costa, G.; Marinho, P.E.S.; Vilela, A.P.P.; Saraiva-Silva, A.T.; Crispim, A.P.C.; Borges, I.A.; Dutra, A.G.S.; Lobato, Z.I.P.; Dos Reis, J.K.P.; de Oliveira, D.B.; et al. Silent Circulation of the Saint Louis Encephalitis Virus among Humans and Equids, Southeast Brazil. Viruses 2019, 11, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Löwen Levy Chalhoub, F.; Maia de Queiroz-Júnior, E.; Holanda Duarte, B.; Eielson Pinheiro de Sá, M.; Cerqueira Lima, P.; Carneiro de Oliveira, A.; Medeiros Neves Casseb, L.; Leal das Chagas, L.; Antônio de Oliveira Monteiro, H.; Sebastião Alberto Santos Neves, M.; et al. West Nile Virus in the State of Ceará, Northeast Brazil. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.N.; Mosena, A.; Baumbach, L.F.; da Silva, M.S.; Canova, R.; Dos Santos, D.; Budaszewski, R.; de Oliveira, L.V.; Soane, M.M.; Saraiva, N.B.; et al. Serologic evidence of West Nile virus and Saint Louis encephalitis virus in horses from Southern Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Morales, M.A.; Levis, S.; Figueiredo, L.T.; Couto-Lima, D.; Campos, Z.; Nogueira, M.F.; da Silva, E.E.; Nogueira, R.M.; Schatzmayr, H.G. Neutralising antibodies for West Nile virus in horses from Brazilian Pantanal. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, M.A.; Romano, A.P.; Borba, A.S.; Silva, E.V.; Chiang, J.O.; Eulálio, K.D.; Azevedo, R.S.; Rodrigues, S.G.; Almeida-Neto, W.S.; Vasconcelos, P.F. West Nile Virus Encephalitis: The First Human Case Recorded in Brazil. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.S.G.; Matos, A.C.D.; da Cunha, M.A.C.R.; Rehfeld, I.S.; Galinari, G.C.F.; Marcelino, S.A.C.; Saraiva, L.H.G.; Martins, N.R.D.S.; Maranhão, R.P.A.; Lobato, Z.I.P.; et al. West Nile virus associated with equid encephalitis in Brazil, 2018. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martins, L.C.; Silva, E.; Casseb, L.; Silva, S.; Cruz, A.; Pantoja, J.; Medeiros, D.; Martins Filho, A.J.; Cruz, E.; Araújo, M.; et al. First isolation of West Nile virus in Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2019, 114, e180332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nota Técnica CEDESA n◦ 01/2019, 30 de agosto de 2019, Ocorrencia de Febre do Nilo Ocidental em Equino do Estado de Sao Paulo. Coordenadoria de Defesa Agropecuária, Secretaria de Agricultura e Abastecimento do Estado de São Paulo, Governo do Estado de São Paulo. Available online: https://www.defesa.agricultura.sp.gov.br/arquivos/sanidade-animal/nota-tecnica-febre-do-nilo-ocidental.pdf (accessed on 19 June 2022).
- Costa, É.A.; Giovanetti, M.; Silva Catenacci, L.; Fonseca, V.; Aburjaile, F.F.; Chalhoub, F.L.L.; Xavier, J.; Campos de Melo Iani, F.; da Cunha e Silva Vieira, M.A.; Freitas Henriques, D.; et al. West Nile Virus in Brazil. Pathogens 2021, 10, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siconelli, M.J.L.; Jorge, D.M.M.; Castro-Jorge, L.A.; Fonseca-Júnior, A.A.; Nascimento, M.L.; Floriano, V.G.; Souza, F.R.; Queiroz- Júnior, E.M.; Camargos, M.F.; Costa, E.D.L.; et al. Evidence for current circulation of an ancient West Nile virus strain (NY99) in Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2021, 54, e0687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Segundo inquérito sorológico em aves migratórias e residentes do Parque Nacional da Lagoa do Peixe/RS para detecção do vírus da febre do Nilo ocidental e outros vírus. Bol. Eletrônico Epidemiológico 2004, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Melandri, V.; Guimarães, A.É.; Komar, N.; Nogueira, M.L.; Mondini, A.; Fernandez-Sesma, A.; Alencar, J.; Bosch, I. Serological detection of West Nile virus in horses and chicken from Pantanal, Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2012, 107, 1073–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ometto, T.; Durigon, E.L.; de Araujo, J.; Aprelon, R.; de Aguiar, D.M.; Cavalcante, G.T.; Melo, R.M.; Levi, J.E.; de Azevedo Júnior, S.M.; Petry, M.V.; et al. West Nile virus surveillance, Brazil, 2008–2010. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 107, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, L.T. The Brazilian flaviviruses. Microbes Infect. 2000, 2, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, L.T. Emergent arboviruses in Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2007, 40, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, M.L.P. Culicidae (Diptera) No Brasil: Relações Entre Diversidade, Distribuição E Enfermidades. Oecologia Aust. 2012, 16, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laporta, G.Z.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Ramos, D.G.; Sallum, M.A. Spatial distribution of arboviral mosquito vectors (Diptera, Culicidae) in Vale do Ribeira in the South-eastern Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Cad Saude Publica 2012, 28, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schatzmayr, H.; Nogueira, R.M.; Travassos da Rosa, A.P.A. An outbreak of dengue virus at Rio de Janeiro--1986. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 1986, 81, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valle, D.; Pimenta, D.N.; Aguiar, R. Zika, dengue and chikungunya: Challenges and issues. Epidemiol. Serv. Saude 2016, 25, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Périssé, A.R.S.; Souza-Santos, R.; Duarte, R.; Santos, F.; de Andrade, C.R.; Rodrigues, N.C.P.; Schramm, J.M.A.; da Silva, E.D.; Jacobson, L.D.S.V.; Lemos, M.C.F.; et al. Zika, dengue and chikungunya population prevalence in Rio de Janeiro city, Brazil, and the importance of seroprevalence studies to estimate the real number of infected individuals. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovanetti, M.; de Mendonça, M.C.L.; Fonseca, V.; Mares-Guia, M.A.; Fabri, A.; Xavier, J.; de Jesus, J.G.; Gräf, T.; Dos Santos Rodrigues, C.D.; Dos Santos, C.C.; et al. Yellow Fever Virus Reemergence and Spread in Southeast Brazil, 2016–2019. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01623-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEPERJ. Fundação Centro Estadual de Estatística, Pesquisa e Formação de Servidores Públicos do Rio de Janeiro. Divisão Regional Segundo as Mesorregiões, Microrregiões Geográficas e Municípios. Estado do Rio de Janeiro—Posição e Extensão 2016. Available online: http://www.fesp.rj.gov.br/ceep/info_territorios/posicao_extencao.html (accessed on 12 June 2022).
- ICMCBio/Instituto Chico Mendes. Relatório Anual de Rotas e Áreas de Concentração de aves migratórias no Brasil; CEMAVE; ICMBio Cabedelo: Cabedelo, PB, Brazil, 2016; p. 87.
- Rappole, J.H.; Derrickson, S.R.; Hubálek, Z. Migratory birds and spread of West Nile virus in the Western Hemisphere. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, F.L.L. Investigação da Circulação dos Vírus da Encefalite de Saint Louis e do Oeste do Nilo em Equinos do Estado do Rio de Janeiro. Master’s Thesis, Fundação Oswaldo Cruz, Instituto Oswaldo Cruz, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- OpenEpi—Toolkit Shell for Developing New Applications 2019. Available online: https://www.openepi.com/SampleSize/SSPropor.htm (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- IBGE. Censo Agropecuário Efetivo dos Rebanhos, por Tipo de Rebanho. @Ibgecomunica 2017. Available online: https://censoagro2017.ibge.gov.br// (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Komar, N. West Nile virus surveillance using sentinel birds. In: West Nile Virus: Detection, Surveillance, and Control. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 951, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kerst, A.J.; Nasci, R.S.; Godsey, M.S.; Mitchell, C.J.; Savage, H.M.; Komar, N.; Panella, N.A.; Allen, B.C.; Volpe, K.E. Rapid detection of west Nile virus from human clinical specimens, field-collected mosquitoes, and avian samples by a TaqMan reverse transcriptase-PCR assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 4066–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kerst, A.J. Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification assays for rapid detection of West Nile and St. Louis encephalitis viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 4506–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RStudio. 2021. Available online: https://www.rstudio.com/products/rstudio/older-versions/ (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Mondini, A.; Bronzoni, R.V.; Cardeal, I.L.; dos Santos, T.M.; Lázaro, E.; Nunes, S.H.; Silva, G.C.; Madrid, M.C.; Rahal, P.; Figueiredo, L.T.; et al. Simultaneous infection by DENV-3 and SLEV in Brazil. J. Clin. Virol. 2007, 40, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzian, A.C.; Mondini, A.; Bronzoni, R.V.; Drumond, B.P.; Ferro, B.P.; Cabrera, E.M.; Figueiredo, L.T.; Chiaravalloti-Neto, F.; Nogueira, M.L. Detection of Saint Louis encephalitis virus in dengue-suspected cases during a dengue 3 outbreak. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano-Lieber, N.S.; Iversson, L.B. Serological survey on arbovirus infection in residents of an ecological reserve. Rev Saude Publica 2000, 34, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Kenney, J.L.; Couto-Lima, D.; Campos, Z.M.; Schatzmayr, H.G.; Nogueira, R.M.; Brault, A.C.; Komar, N. Ilheus virus isolation in the Pantanal, west-central Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayeux, J.J.M.; Silva, A.S.G.; de Queiroz, G.A.; da Silva Santos, B.S.Á.; Rocha, M.N.; Rehfeld, I.S.; de Souza Franklin, L.F.; Valle, L.B.; Guedes, M.I.M.C.; Teixeira, R.B.C.; et al. Epidemiological surveillance of West Nile virus in the world and Brazil: Relevance of equine surveillance in the context of “one health”. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci. 2019, 56, e164335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrig, J.T.; Hombach, J.; Barrett, A.D. Guidelines for Plaque-Reduction Neutralization Testing of Human Antibodies to Dengue Viruses. Viral Immunol. 2008, 21, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, J.R.; Medeiros, L.C.; Reis, V.P.; Chávez, J.L.; Munhoz, T.D.; Borges, G.P.; Soares, O.A.; Campos, C.H.; Machado, R.Z.; Baldani, C.D.; et al. Serologic survey of West Nile virus in horses from Central-West, Northeast and Southeast Brazil. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisher, C.H.; Karabatsos, N.; Dalrymple, J.M.; Shope, R.E.; Porterfield, J.S.; Westaway, E.G.; Brandt, W.E. Relações antigênicas entre flavivírus conforme determinado por testes de neutralização cruzada com anti-soros policlonais. J. Gen. Virol. 1989, 70, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inouye, S.; Matsuno, S.; Tsurukubo, Y. “Original antigenic sin” phenomenon in experimental flavivirus infections of guinea pigs: Studies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Microbiol. Immunol. 1984, 28, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, M.M.; Kubiszeski, J.R.; Vieira, C.J.D.S.P.; Gusmao, A.F.; Pratis, T.S.; Colombo, T.E.; Thies, S.F.; do Carmo Araujo, F.; Zanelli, C.F.; Milhim, B.H.G.D.A.; et al. Detection of Saint Louis encephalitis virus in two Brazilian states. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, H.; Pereira, F.M.; Costa, E.A.; Fonseca, V.; Tosta, S.; Xavier, J.; Levy, F.; Oliveira, C.D.; Menezes, G.; Lima, J.; et al. Retrospective Investigation in Horses with Encephalitis Reveals Unnoticed Circulation of West Nile Virus in Brazil. Viruses 2022, 14, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, C.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; Desoutter, D.; Debergé, E.; Bichet, H.; Lowenski, S.; Dumarest, M.; Gonzalez, G.; Migné, C.; Vanhomwegen, J.; et al. Serological evidence of infection with dengue and Zika viruses in horses on French Pacific Islands. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorou, R. Zika virus, vectors, reservoirs, amplifying hosts, and their potential to spread worldwide: What we know and what we should investigate urgently. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burla, R.S.; Neto, R.S.; Werneck, L.G.; Maciel, C.P.; Silva, R.A.; Pessanha, H.M.; Oliveira, V.D.P.S. Analysis of socioeconomic and environmental constraints to implement forestry in the Northern and Northwestern areas of Rio de Janeiro State. BOAARL 2013, 6, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vianna, R.S.T. Inquéritos Soroepidemiológicos em Equinos da Região Sul do Brasil para Detecção de Anticorpos Anti-Flavivirus de Interesse em Saúde Pública. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal de Goiás, Goiânia, Brazil, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Juliano, R.S.; Campos, Z.; Velez, J.; Nogueira, R.M.; Komar, N. Neutralising antibodies for Mayaro virus in Pantanal, Brazil. Memórias Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2015, 110, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeffcott, L.B. Some practical aspects of the transfer of passive immunity to newborn foals. Equine Vet. J. 1974, 6, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Varella, R.B. Aspectos epidemiológicos da febre do Nilo Ocidental. Rev. Bras. Epidemiol. 2008, 11, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blitvich, B.J.; Bowen, R.A.; Marlenee, N.L.; Hall, R.A.; Bunning, M.L.; Beaty, B.J. Epitope-blocking enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for detection of West Nile virus antibodies in domestic mammals. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2676–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, R.M.S.J.; Straube, F.C.; Nascimento, J.L.X. Conservação de Aves Migratórias Neárticas no Brasil, 1st ed.; Segtowick, F., Ed.; Conservação Internacional: Belém, Brazil, 2011; p. 400. [Google Scholar]




| Regions | Municipalities | Properties | Horses Sampled Per Municipality | Total Horses Sampled Per Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metropolitan | Duque de Caxias Cachoeiras de Macacú Teresópolis | 1 3 2 | 17 54 43 | 114 |
| Northwest Fluminense | Bom Jesus do Itabapoana Itaperuna | 1 1 | 38 42 | 80 |
| North Fluminense | Campo dos Goytacazes São Fidelis Macaé | 1 2 1 | 6 24 46 | 76 |
| Coast | Araruama Saquarema Casimiro de Abreu | 1 1 1 | 22 30 24 | 76 |
| Centre Fluminense | Cantagalo Paraíba do Sul Areal | 1 1 1 | 20 16 13 | 49 |
| South Fluminense | Barra do Piraí Resende | 2 1 | 17 23 | 40 |
| Total: | 16 | 21 | 435 | 435 |
| Type and Number of Collected Samples | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Municipalities | Properties | Cases | Fatal Cases | Contact Cases | CSF | CNS Tissues | Spinal Cord | Serum | Horses Sampled |
| Teresópolis | 2 | 13 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 23 | 23 |
| Saquarema | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 11 |
| Friburgo | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Duas Barras | 1 | 7 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 7 | 7 |
| Maricá | 1 | 3 | 2 | 22 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 25 | 25 |
| Rio de Janeiro | 1 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 06 | 07 | 30 | 11 | 42 | 5 | 06 | 06 | 72 | 72 |
| PRNT90 Final Result | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | WNV (%) | p-value | SLEV (%) | p-value | Undifferentiated flavivirus (%) | p-value | |
| Mesoregions | 0.39 | <0.001 | 0.42 | ||||
| Metropolitan | 114 (26.2) | 0 | 11 (9.6) | 6 (5.3) | |||
| Northwest Fluminense | 80 (18.4) | 2 (2.5) | 22 (27.5) | 8 (10.0) | |||
| North Fluminense | 76 (17.5) | 1 (1.3) | 23 (30.0) | 9 (11.8) | |||
| Coast | 76 (17.5) | 2 (2.6) | 18 (23.7) | 5 (6.6) | |||
| Centre Fluminense | 49 (11.3) | 0 | 15 (30.6) | 2 (4.1) | |||
| South Fluminense | 40 (9.2) | 0 | 0 | 2 (5.0) | |||
| Function | <0.001 | 0.21 | 0.66 | ||||
| Sport | 218 (50.1) | 0 | 37 (17.0) | 14 (6.4) | |||
| Recreation | 40 (9.2) | 0 | 8 (20.0) | 2 (5.0) | |||
| Reproduction | 175 (40.2) | 4 (2.3) | 44 (25.1) | 16 (9.1) | |||
| Work | 2 (0.5) | 1 (50.0) | 0 | 0 | |||
| Sex | 0.99 | 0.80 | 0.49 | ||||
| Female | 310 (71.3) | 4 (1.3) | 62 (20.0) | 25 (8.1) | |||
| Male | 125 (28.7) | 1 (0.8) | 27 (21.6) | 7 (5.6) | |||
| Age group | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.27 | ||||
| Group 1 | 7 (1.6) | 0 | 2 (28.6) | 0 | |||
| Group 2 | 63 (14.5) | 0 | 11 (17.5) | 2 (3.2) | |||
| Group 3 | 130 (29.9) | 0 | 20 (15.4) | 7 (5.4) | |||
| Group 4 | 141 (32.4) | 3 (2.1) | 34 (24.1) | 13 (9.2) | |||
| Group 5 | 94 (21.6) | 2 (2.1) | 22 (23.4) | 10 (10.6) | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chalhoub, F.L.L.; Horta, M.A.P.; Alcantara, L.C.J.; Morales, A.; dos Santos, L.M.B.; Guerra-Campos, V.; Rodrigues, C.D.S.; Santos, C.C.; Mares-Guia, M.A.M.; Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; et al. Serological Evidence of Exposure to Saint Louis Encephalitis and West Nile Viruses in Horses of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Viruses 2022, 14, 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112459
Chalhoub FLL, Horta MAP, Alcantara LCJ, Morales A, dos Santos LMB, Guerra-Campos V, Rodrigues CDS, Santos CC, Mares-Guia MAM, Pauvolid-Corrêa A, et al. Serological Evidence of Exposure to Saint Louis Encephalitis and West Nile Viruses in Horses of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Viruses. 2022; 14(11):2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112459
Chicago/Turabian StyleChalhoub, Flávia Löwen Levy, Marco Aurélio Pereira Horta, Luiz Carlos Junior Alcantara, Alejandra Morales, Lilha Maria Barbosa dos Santos, Vinícius Guerra-Campos, Cintia D. S. Rodrigues, Carolina C. Santos, Maria Angélica M. Mares-Guia, Alex Pauvolid-Corrêa, and et al. 2022. "Serological Evidence of Exposure to Saint Louis Encephalitis and West Nile Viruses in Horses of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil" Viruses 14, no. 11: 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112459
APA StyleChalhoub, F. L. L., Horta, M. A. P., Alcantara, L. C. J., Morales, A., dos Santos, L. M. B., Guerra-Campos, V., Rodrigues, C. D. S., Santos, C. C., Mares-Guia, M. A. M., Pauvolid-Corrêa, A., & de Filippis, A. M. B. (2022). Serological Evidence of Exposure to Saint Louis Encephalitis and West Nile Viruses in Horses of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Viruses, 14(11), 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112459







