Features of Audio-Vestibular Deficit and 3D-FLAIR Temporal Bone MRI in Patients with Herpes Zoster Oticus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. MRI
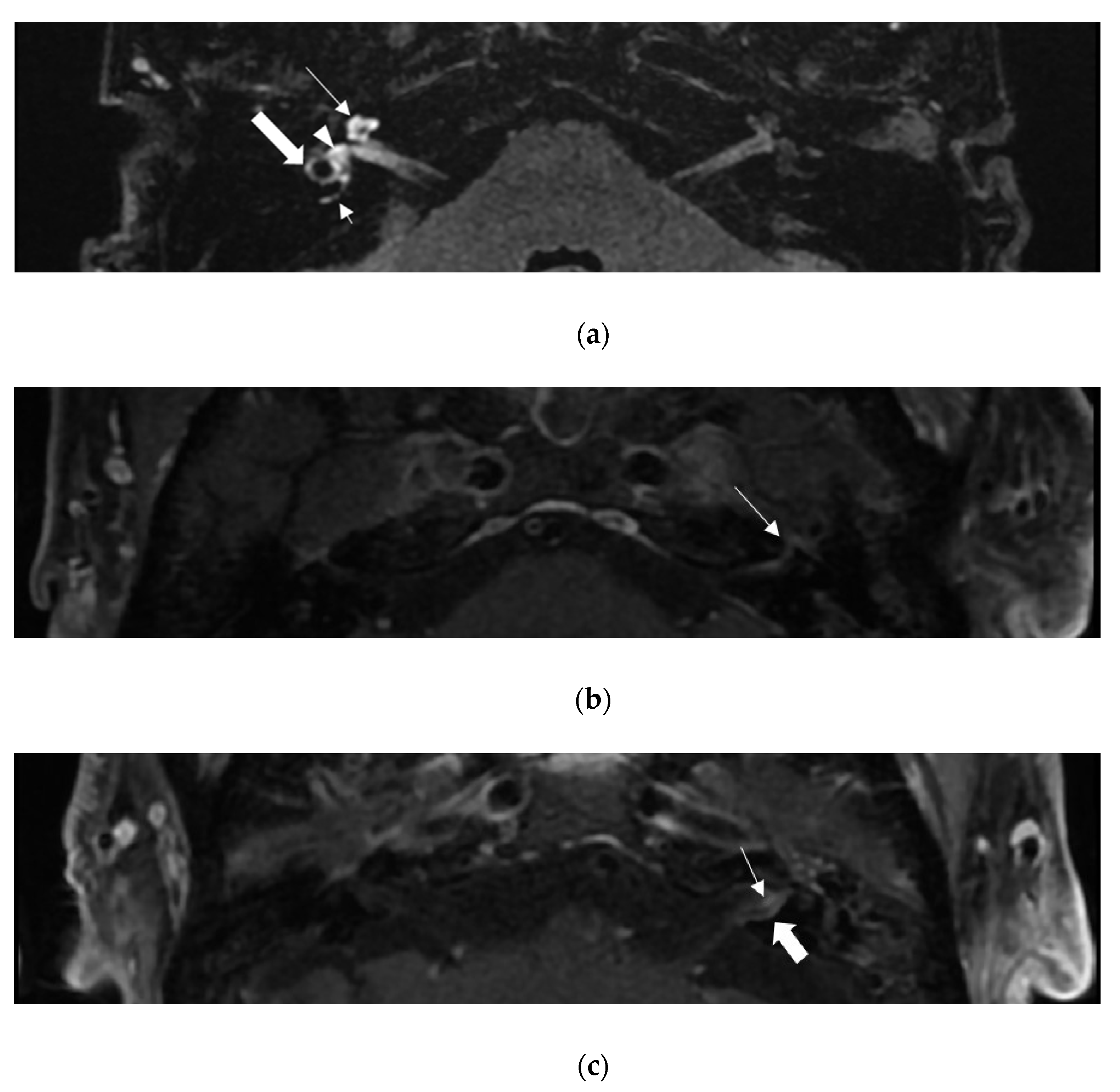
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van de Steene, V.; Kuhweide, R.; Vlaminck, S.; Casselman, J. Varicella-zoster virus DNA level and facial paralysis in Ramsay Hunt syndrome. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Belg. 2004, 113, 700–705. [Google Scholar]
- Sivapathasingam, V.; Bakshi, S.S. Ramsay Hunt Syndrome. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 135, e125–e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.H.; Kim, B.R.; Shin, J.E.; Kim, C.H. Clinical manifestations in patients with herpes zoster oticus. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 1739–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Choi, H.; Shin, J.E. Characteristics of hearing loss in patients with herpes zoster oticus. Medicine 2016, 95, e5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Choi, J.W.; Han, K.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Shin, J.E. Direction-fixed and Direction-changing Positional Nystagmus in Ramsay Hunt Syndrome. Otol. Neurotol. 2018, 39, e209–e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Jeong, K.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, Y.W.; Shin, J.E. Vibration- and hyperventilation-induced nystagmus in patients with Ramsay Hunt syndrome with vertigo. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 152, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.H.; Shin, J.E.; Kim, C.H. Mastoid effusion on temporal bone MRI in patients with Bell’s palsy and Ramsay Hunt syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.W.; Nahm, H.; Shin, J.E.; Kim, C.H. Atypical clinical manifestations of herpes zoster oticus: Diagnostic usefulness of magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neurovirol. 2019, 25, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, B.; Noh, H.; Jeong, H.; Shin, J.E.; Kim, C.H. Nystagmus in Ramsay Hunt syndrome with or without dizziness. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Kang, S.I.; Kim, Y.H. A case of ramsay hunt syndrome with cranial polyneuropathy. Korean J. Audiol. 2012, 16, 80–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Li, Z. Acute myelitis with multicranial neuritis caused by Varicella zoster virus: A case report. BMC Neurol 2022, 22, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gohel, A.; Vengalil, S.; Mundlamuri, R.C.; Nalini, A.; Kulanthaivelu, K.; Yadav, R. Ramsay Hunt Syndrome Leading to the Brainstem and Cerebellar Involvement: A Case Report of a Rare Co-occurrence. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2022, 25, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthapadmanabhan, S.; Soodin, D.; Sritharan, N.; Sivapathasingam, V. Ramsay Hunt syndrome with multiple cranial neuropathy: A literature review. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 2239–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ani, R.M. Ramsay Hunt Syndrome With Cranial Polyneuropathy and Delayed Facial Nerve Palsy: A Case Report. Cureus 2022, 14, e27434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, X. Ramsay Hunt syndrome affecting the vagus nerve with epiglottic ulcers as the first manifestation: A case report. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520952276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhweide, R.; Van de Steene, V.; Vlaminck, S.; Casselman, J.W. Ramsay Hunt syndrome: Pathophysiology of cochleovestibular symptoms. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2002, 116, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozeki, H.; Iwasaki, S.; Ushio, M.; Takeuchi, N.; Murofushi, T. The lesion site of vestibular dysfunction in Ramsay Hunt syndrome: A study by click and galvanic VEMP. J. Vestib. Res. 2006, 16, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, D.L.; Czervionke, L.F.; Millen, S.J. MR findings in the Ramsay Hunt syndrome. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 1988, 9, 609. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, H.; Toda, N.; Takahashi, M.; Azuma, T.; Nakamura, K.; Takao, S.; Harada, M.; Takeda, N. Vestibular and cochlear neuritis in patients with Ramsay Hunt syndrome: A Gd-enhanced MRI study. Acta Otolaryngol 2013, 133, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, L.; Tien, R.; Engström, M.; Thuomas, K.A. Gd-DPTA enhanced MRI in Bell’s palsy and herpes zoster oticus: An overview and implications for future studies. Acta Otolaryngol. 1995, 115, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackmann, D.E.; House, J. Facial nerve grading system. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1985, 93, 146–147. [Google Scholar]
- Jongkees, L.B.; Maas, J.P.; Philipszoon, A.J. Clinical nystagmography: A detailed study of electronystagmography in 341 patients with vertigo. Pract. Otorhinolaryngol. 1962, 24, 65–93. [Google Scholar]
- Aviel, A.; Marshak, G. Ramsay Hunt syndrome: A cranial polyneuropathy. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 1982, 3, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakata, T.; Inagaki, A.; Sekiya, S.; Murakami, S. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of facial nerve swelling in patients with severe Ramsay Hunt syndrome. Auris Nasus Larynx 2019, 46, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuya, J.; Kuya, K.; Shinohara, Y.; Kunimoto, Y.; Yazama, H.; Ogawa, T.; Takeuchi, H. Usefulness of High-Resolution 3D Multi-Sequences for Peripheral Facial Palsy: Differentiation Between Bell’s Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome. Otol. Neurotol. 2017, 38, 1523–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berrettini, S.; Seccia, V.; Fortunato, S.; Forli, F.; Bruschini, L.; Piaggi, P.; Canapicchi, R. Analysis of the 3-dimensional fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery (3D-FLAIR) sequence in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2013, 139, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugiura, M.; Naganawa, S.; Nakata, S.; Kojima, S.; Nakashima, T. 3D-FLAIR MRI findings in a patient with Ramsay Hunt syndrome. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007, 127, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, S.; Mizuno, T.; Naganawa, S.; Sugiura, M.; Yoshida, T.; Teranishi, M.; Sone, M.; Nakashima, T. 3D-FLAIR MRI in facial nerve paralysis with and without audio-vestibular disorder. Acta Otolaryngol. 2010, 130, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patient No. | Sex/Age | Lesion Side | Vestibulo-Cochlear Symptom | FNP | CP (%) | Decreased vHIT Gain | cVEMP | Hearing Loss | PTA (Speech Frequency/High Frequency) | CE-3D-T1WI | Post-Contrast 3D-FLAIR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 * | M/39 | R | - | − | Rt 30 † | − | 11/27 | - | - | ||
| 2 | M/42 | L | Dizz EF Tinn | + | Lt 43 | - | A ‡ | + | 16/30 | VII | C V |
| 3 | F/22 | R | Dizz EF HL | + | Lt 7 | - | A | + | 23/20 | - | - |
| 4 | M/47 | L | Dizz | + | Lt 68 | - | A | + | 30/97 | VII | C V LSCC PSCC |
| 5 | F/66 | R | Dizz HL | + | Rt 100 | LSCC | A | + § | 40/60 | VII | C V LSCC PSCC |
| 6 | F/44 | R | Dizz | − | Rt 31 | - | A | − | 20/22 | - | C V LSCC PSCC |
| 7 | F/46 | R | - | + | Lt 1 | - | N ‖ | − | 13/37 | VII | - |
| 8 | F/59 | L | - | + | Rt 13 | - | N | − | 15/17 | VII | - |
| 9 | M/76 | L | Dizz | + | Lt 82 | PSCC LSCC | A | + | 61/77 | VIII | C V LSCC PSCC |
| 10 | F/35 | R | Dizz EF HL | + | Rt 48 | - | A | + | 18/30 | VII VIII | C V LSCC PSCC |
| 11 | M/71 | L | EF HL | − | Lt 21 | - | A | + | 95/85 | - | V |
| 12 | F/60 | R | Dizz HL | − | Rt 100 | PSCC LSCC | N | + | 71/92 | VII | C V LSCC PSCC |
| 13 | M/89 | L | - | − | Lt 20 | LSCC | A | − | 71/so | VII | C V LSCC PSCC |
| 14 | M/64 | R | Dizz EF HL Tinn | − | Rt 63 | - | A | + | 33/42 | - | - |
| 15 | F/60 | L | Dizz | + | Lt 64 | LSCC | N | + | 21/37 | VII VIII | C V LSCC |
| 16 | M/19 | L | Dizz | + | Lt 24 | - | N | − | 15/12 | VII VIII | C V LSCC PSCC |
| 17 | M/57 | R | Dizz | − | Rt 92 | PSCC LSCC | N | + | 80/so | VII VIII | C V LSCC PSCC |
| 18 | F/55 | R | Dizz | + | Rt 34 | - | N | + | 21/42 | VII | C V LSCC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, C.-H. Features of Audio-Vestibular Deficit and 3D-FLAIR Temporal Bone MRI in Patients with Herpes Zoster Oticus. Viruses 2022, 14, 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112568
Lee J, Choi JW, Kim C-H. Features of Audio-Vestibular Deficit and 3D-FLAIR Temporal Bone MRI in Patients with Herpes Zoster Oticus. Viruses. 2022; 14(11):2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112568
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jiyeon, Jin Woo Choi, and Chang-Hee Kim. 2022. "Features of Audio-Vestibular Deficit and 3D-FLAIR Temporal Bone MRI in Patients with Herpes Zoster Oticus" Viruses 14, no. 11: 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112568
APA StyleLee, J., Choi, J. W., & Kim, C.-H. (2022). Features of Audio-Vestibular Deficit and 3D-FLAIR Temporal Bone MRI in Patients with Herpes Zoster Oticus. Viruses, 14(11), 2568. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14112568







