Collection of Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production and Purification of SARS-CoV-2 Recombinant Proteins and Antibodies
2.2. Immunization and Generation of Hybridomas
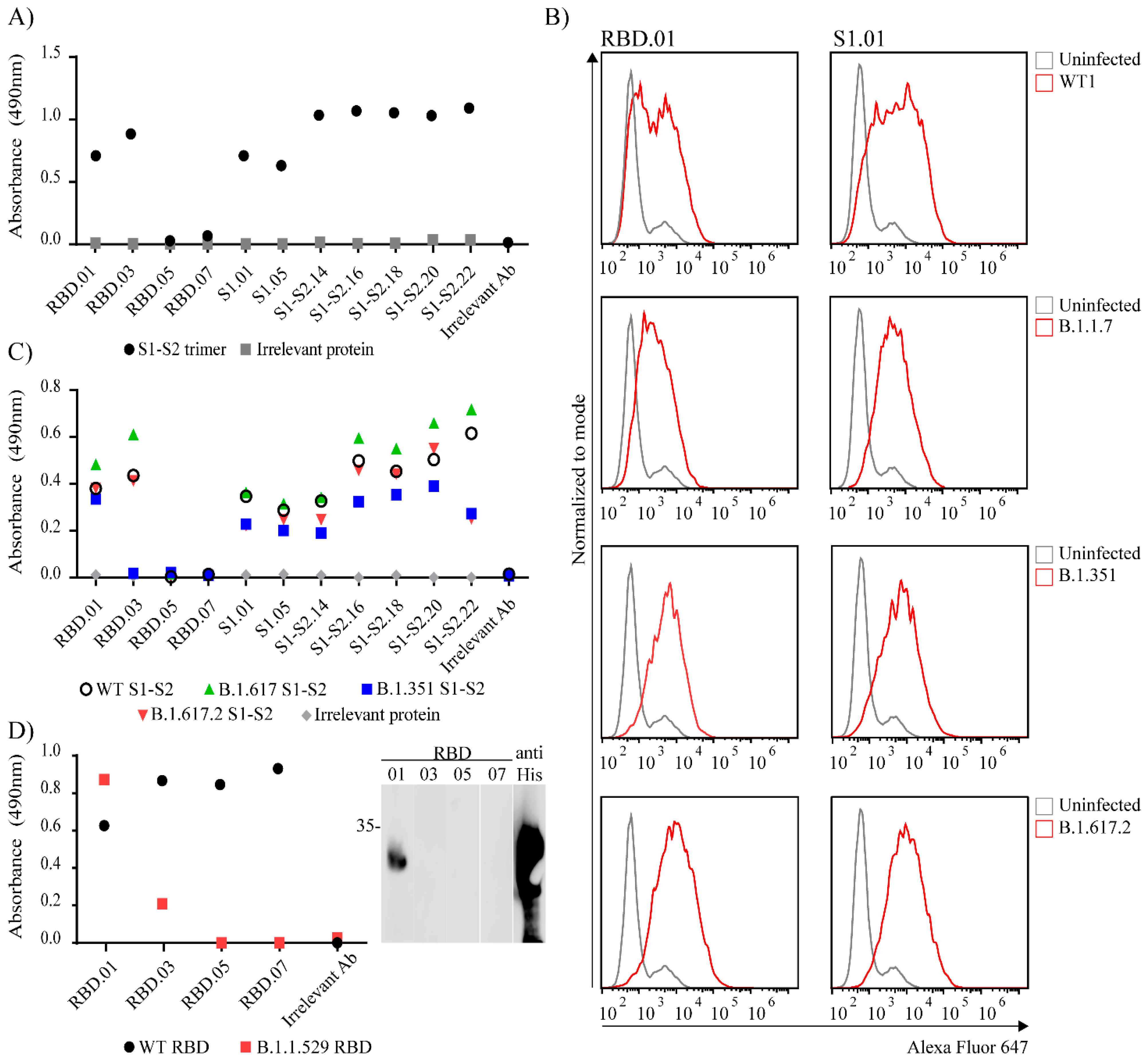
2.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.4. Viruses
2.5. Flow Cytometry and Immunofluorescence
2.6. Western Blot
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.-L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Niu, P.; Yang, B.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Song, H.; Huang, B.; Zhu, N.; et al. Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus origins and receptor binding. Lancet 2020, 395, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.-L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, M.; Ruggiero, A.; Squeglia, F.; Maga, G.; Berisio, R. A Structural View of SARS-CoV-2 RNA Replication Machinery: RNA Synthesis, Proofreading and Final Capping. Cells 2020, 9, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Tzou, P.L.; Nouhin, J.; Gupta, R.K.; de Oliveira, T.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Fera, D.; Shafer, R.W. The biological and clinical significance of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 22, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadlbauer, D.; Amanat, F.; Chromikova, V.; Jiang, K.; Strohmeier, S.; Arunkumar, G.A.; Tan, J.; Bhavsar, D.; Capuano, C.; Kirkpatrick, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Seroconversion in Humans: A Detailed Protocol for a Serological Assay, Antigen Production, and Test Setup. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2020, 57, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korn, J.; Schackermann, D.; Kirmann, T.; Bertoglio, F.; Steinke, S.; Heisig, J.; Ruschig, M.; Rojas, G.; Langreder, N.; Wenzel, E.V.; et al. Baculovirus-free insect cell expression system for high yield antibody and antigen production. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashorn, P.; Krohn, K. Washing of ELISA plates with running tap water. J. Immunol. Methods 1986, 88, 141–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rnjak, D.; Ravlić, S.; Šola, A.M.; Halassy, B.; Šemnički, J.; Šuperba, M.; Hećimović, A.; Kurolt, I.C.; Kurtović, T.; Mačak Šafranko, Ž.; et al. COVID-19 convalescent plasma as long-term therapy in immunodeficient patients? Transfus. Clin. Biol. 2021, 28, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, M.Z.; Eschke, K.; Hoffmann, M.; Grashoff, M.; Abassi, L.; Kim, Y.; Brunotte, L.; Ludwig, S.; Kröger, A.; Klawonn, F.; et al. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Adaptation to Available Cellular Proteases. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaouat, A.E.; Achdout, H.; Kol, I.; Berhani, O.; Roi, G.; Vitner, E.B.; Melamed, S.; Politi, B.; Zahavy, E.; Brizic, I.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain fusion protein efficiently neutralizes virus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoglio, F.; Meier, D.; Langreder, N.; Steinke, S.; Rand, U.; Simonelli, L.; Heine, P.A.; Ballmann, R.; Schneider, K.-T.; Roth, K.D.R.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing human recombinant antibodies selected from pre-pandemic healthy donors binding at RBD-ACE2 interface. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Feng, X.; Nie, L.; Tang, M.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, Y.; Swisher, S.K.; Srivastava, M.; Chen, J. Interactomes of SARS-CoV-2 and human coronaviruses reveal host factors potentially affecting pathogenesis. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e107776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boson, B.; Legros, V.; Zhou, B.; Siret, E.; Mathieu, C.; Cosset, F.-L.; Lavillette, D.; Denolly, S. The SARS-CoV-2 envelope and membrane proteins modulate maturation and retention of the spike protein, allowing assembly of virus-like particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, M.; Baek, K.; Kang, M.; Choi, J.-K.; Maharjan, S.; Akauliya, M.; Lee, Y.; et al. Production of SARS-CoV-2 N Protein-Specific Monoclonal Antibody and Its Application in an ELISA-Based Detection System and Targeting the Interaction Between the Spike C-Terminal Domain and N Protein. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilamowski, M.; Hammel, M.; Leite, W.; Zhang, Q.; Kim, Y.; Weiss, K.L.; Jedrzejczak, R.; Rosenberg, D.J.; Fan, Y.; Wower, J.; et al. Transient and stabilized complexes of Nsp7, Nsp8, and Nsp12 in SARS-CoV-2 replication. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 3152–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Liu, Y.; Lei, X.; Li, P.; Mi, D.; Ren, L.; Guo, L.; Guo, R.; Chen, T.; Hu, J.; et al. Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Sun, H.; Yu, H.; Li, S.; Zheng, Q.; Xia, N. Neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2: Current understanding, challenge and perspective. Antib. Ther. 2020, 3, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Harris, B.D.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Kobie, J.J.; Walter, M.R. Epitope Classification and RBD Binding Properties of Neutralizing Antibodies Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jang, S.; Kang, J.; Park, S.B.; Han, Y.W.; Nam, H.; Kim, M.; Lee, J.; Cho, K.J.; Kim, J.; et al. MG1141A as a Highly Potent Monoclonal Neutralizing Antibody Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 778829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaway, E. Heavily mutated Omicron variant puts scientists on alert. Nature 2021, 600, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhu, K.; Qin, B.; Olieric, V.; Wang, M.; Cui, S. Crystal structure of SARS-CoV-2 Orf9b in complex with human TOM70 suggests unusual virus-host interactions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Zhuang, M.W.; Deng, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, J.; Nan, M.L.; Zhang, X.J.; Gao, C.; Wang, P.H. SARS-CoV-2 ORF9b antagonizes type I and III interferons by targeting multiple components of the RIG-I/MDA-5-MAVS, TLR3-TRIF, and cGAS-STING signaling pathways. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 5376–5389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoni, R.; Krafcikova, P.; Baranowski, M.R.; Kowalska, J.; Boura, E.; Cahová, H. Substrate Specificity of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp10-Nsp16 Methyltransferase. Viruses 2021, 13, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapointe, C.P.; Grosely, R.; Johnson, A.G.; Wang, J.; Fernández, I.S.; Puglisi, J.D. Dynamic competition between SARS-CoV-2 NSP1 and mRNA on the human ribosome inhibits translation initiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2017715118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, K.; Karousis, E.D.; Jomaa, A.; Scaiola, A.; Echeverria, B.; Gurzeler, L.-A.; Leibundgut, M.; Thiel, V.; Mühlemann, O.; Ban, N. SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 binds the ribosomal mRNA channel to inhibit translation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2020, 27, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, C.; Swanson, S.E.; Negatu, S.G.; Dittmar, M.; Miller, J.; Ramage, H.R.; Cherry, S.; Jurado, K.A. SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins NSP1 and NSP13 inhibit interferon activation through distinct mechanisms. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.K.; Blanco, M.R.; Bruce, E.A.; Honson, D.D.; Chen, L.M.; Chow, A.; Bhat, P.; Ollikainen, N.; Quinodoz, S.A.; Loney, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Disrupts Splicing, Translation, and Protein Trafficking to Suppress Host Defenses. Cell 2020, 183, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipman, N.S.; Jackson, L.R.; Trudel, L.J.; Weis-Garcia, F. Monoclonal Versus Polyclonal Antibodies: Distinguishing Characteristics, Applications, and Information Resources. ILAR J. 2005, 46, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roncador, G.; Engel, P.; Maestre, L.; Anderson, A.P.; Cordell, J.L.; Cragg, M.S.; Šerbec, V.Č.; Jones, M.; Lisnic, V.J.; Kremer, L.; et al. The European antibody network’s practical guide to finding and validating suitable antibodies for research. mAbs 2016, 8, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Protein | Clone | Isotype | Western Blot * | IF | Flow Cytometry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleocapsid protein | N.01 | κ, IgG1 | + ** | + | + |
| N.03 | λ, IgG1 | + | - | + | |
| N.05 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | + | |
| N.07 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | - | |
| N.09 | λ, IgG1 | + ** | + | + | |
| N.11 | κ, IgG1 | + | + | + | |
| N.13 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | + | |
| Spike protein | RBD.01 | κ, IgG1 | - | - | + |
| RBD.03 | κ, IgG1 | + | + | - | |
| RBD.05 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | ND | |
| RBD.07 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | ND | |
| S1.01 | κ, IgG1 | - | + | + | |
| S1.05 | κ, IgG1 | - | + | + | |
| S1-S2.14 | κ, IgG2a | +/- | ND | - | |
| S1-S2.15 | κ, IgG2a | ND | - | ND | |
| S1-S2.16 | κ, IgG2b | - | ND | - | |
| S1-S2.17 | κ, IgG2b | ND | + | ND | |
| S1-S2.18 | κ, IgG2b | +/- | ND | - | |
| S1-S2.19 | κ, IgG2b | ND | + | ND | |
| S1-S2.20 | κ, IgG2b | +/- | ND | - | |
| S1-S2.21 | κ, IgG2b | ND | + | ND | |
| S1-S2.22 | κ, IgG2b | + ** | + | - | |
| ORF3a | ORF3a.01 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | - |
| ORF3a.03 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | - | |
| ORF3a.05 | λ, IgG1 | - | - | - | |
| ORF3a.07 | λ, IgG1 | + | - | + | |
| ORF9b | ORF9b.01 | κ, IgG2b | + | - | - |
| ORF9b.03 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | - | |
| ORF9b.05 | κ, IgG1 | - | - | - | |
| ORF9b.07 | κ, IgG1 | + ** | + | - | |
| Nsp1 | Nsp1.01 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | - |
| Nsp1.03 | κ, IgG1 | + | ND | - | |
| Nsp7 | Nsp7.01 | κ, IgG2b | + | - | - |
| Nsp7.03 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | - | |
| Nsp8 | Nsp8.01 | κ, IgG1 | + | ND | - |
| Nsp8.03 | κ, IgG1 | + | ND | - | |
| Nsp9 | Nsp9.01 | κ, IgG1 | + | ND | - |
| Nsp10 | Nsp10.01 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | - |
| Nsp10.03 | κ, IgG1 | + | - | + | |
| Nsp16 | Nsp16.01 | κ, IgG2a | + | - | - |
| Nsp16.03 | κ, IgG2a | + | - | - | |
| Nsp16.05 | κ, IgG2a | + | - | - | |
| Nsp16.07 | κ, IgG1 | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pribanić Matešić, M.; Kučan Brlić, P.; Lenac Roviš, T.; Mačak Šafranko, Ž.; Chaouat, A.E.; Miklić, K.; Malić, S.; Ivanković, N.; Schubert, M.; Bertoglio, F.; et al. Collection of Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteins. Viruses 2022, 14, 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020443
Pribanić Matešić M, Kučan Brlić P, Lenac Roviš T, Mačak Šafranko Ž, Chaouat AE, Miklić K, Malić S, Ivanković N, Schubert M, Bertoglio F, et al. Collection of Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteins. Viruses. 2022; 14(2):443. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020443
Chicago/Turabian StylePribanić Matešić, Marina, Paola Kučan Brlić, Tihana Lenac Roviš, Željka Mačak Šafranko, Abigael Eva Chaouat, Karmela Miklić, Suzana Malić, Nina Ivanković, Maren Schubert, Federico Bertoglio, and et al. 2022. "Collection of Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteins" Viruses 14, no. 2: 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020443
APA StylePribanić Matešić, M., Kučan Brlić, P., Lenac Roviš, T., Mačak Šafranko, Ž., Chaouat, A. E., Miklić, K., Malić, S., Ivanković, N., Schubert, M., Bertoglio, F., Markotić, A., Mandelboim, O., Jonjić, S., & Brizić, I. (2022). Collection of Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Proteins. Viruses, 14(2), 443. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14020443








