Escalated (Dependent) Oxycodone Self-Administration Is Associated with Cognitive Impairment and Transcriptional Evidence of Neurodegeneration in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Transgenic Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Intravenous Catheterization
2.3. Drugs
2.4. Oxycodone Self-Administration
2.5. Novel Object Recognition Test
2.6. Total RNA Isolation and RNA-Sequencing
2.7. Gene Expression Profiling and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
2.8. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction Validation
3. Results
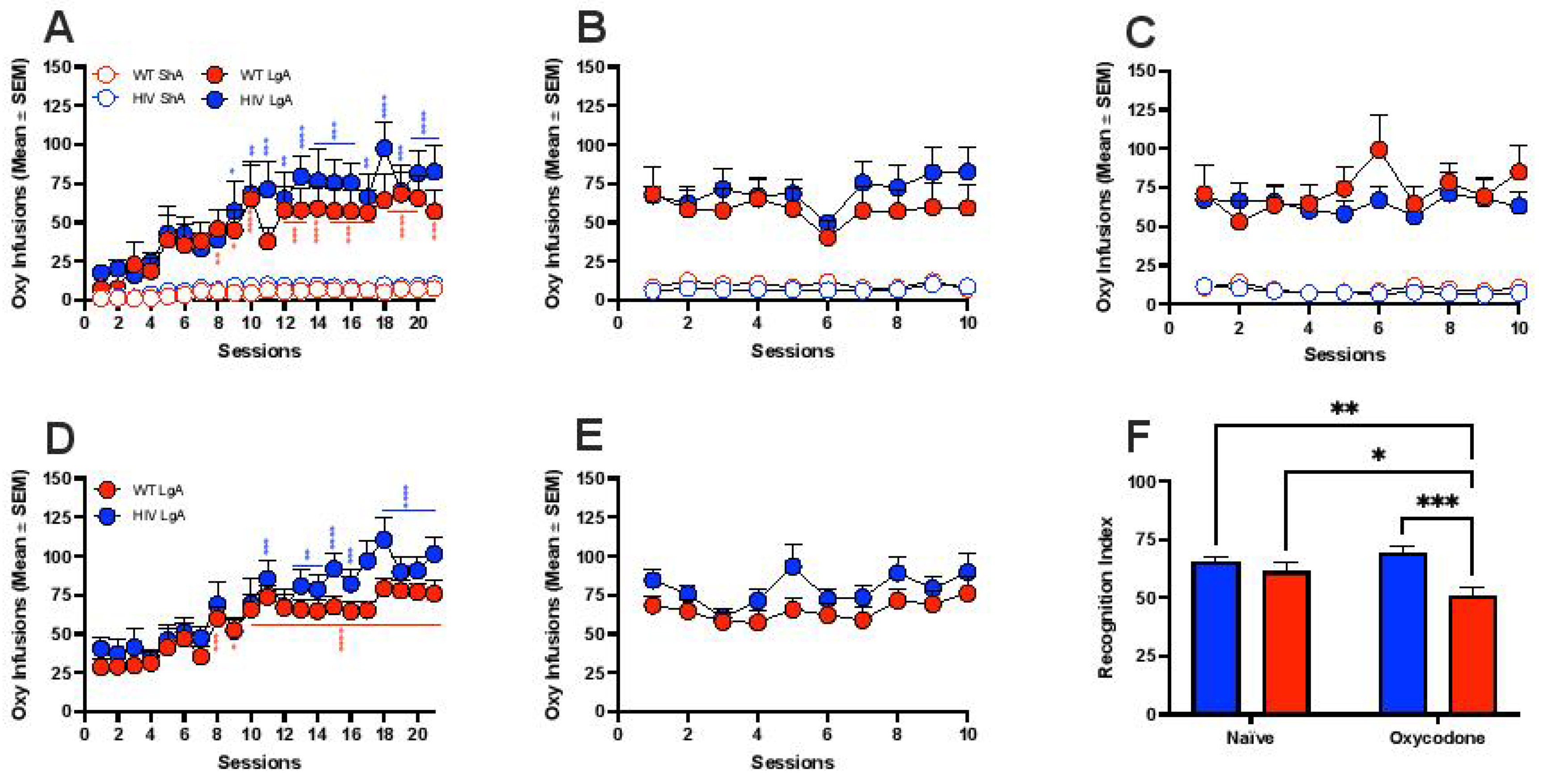
3.1. Oxycodone Self-Administration in HIV Transgenic Rats
3.2. Gene Expression Profiling in the mPFC in HIV Tg and WT Rats That Self-Administered Oxycodone under Nondependent (ShA) and Dependent (LgA) Conditions


3.3. Transcriptional Evidence of Increases in Neuroinflammation, Neuronal Injury, and Neurodegeneration in HIV Tg Rats with a History of Oxycodone Self-Administration
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nath, A. Human immunodeficiency virus-associated neurocognitive disorder: Pathophysiology in relation to drug addiction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1187, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodkin, K.; Shapshak, P.; Metsch, L.R.; McCoy, C.B.; Crandall, K.A.; Kumar, M.; Fujimura, R.K.; McCoy, V.; Zhang, B.T.; Reyblat, S.; et al. Cocaine abuse and HIV-1 infection: Epidemiology and neuropathogenesis. J. Neuroimmunol. 1998, 83, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, E.G.; Burnam, M.A.; Longshore, D.; Fleishman, J.A.; Sherbourne, C.D.; London, A.S.; Turner, B.J.; Eggan, F.; Beckman, R.; Vitiello, B.; et al. Psychiatric Disorders and Drug Use among Human Immunodeficiency Virus–Infected Adults in the United States. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2001, 58, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, F.H.; Bing, E.G.; Fleishman, J.A.; London, A.S.; Caetano, R.; Burnam, M.A.; Longshore, D.; Morton, S.C.; Orlando, M.; Shapiro, M. The prevalence of alcohol consumption and heavy drinking among people with HIV in the United States: Results from the HIV Cost and Services Utilization Study. J. Stud. Alcohol 2002, 63, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, G.M.; Cheever, L.W.; Chaisson, R.E.; Moore, R.D. Detrimental effects of continued illicit drug use on the treatment of HIV-1 infection. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 2001, 27, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, G.M.; Gebo, K.A.; Chaisson, R.E.; Moore, R.D. Longitudinal assessment of the effects of drug and alcohol abuse on HIV-1 treatment outcomes in an urban clinic. AIDS 2002, 16, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, G.M.; Griswold, M.; Gebo, K.A.; Keruly, J.; Chaisson, R.E.; Moore, R.D. Illicit Drug Use and HIV-1 Disease Progression: A Longitudinal Study in the Era of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volkow, N.D.; Wang, G.-J.; Fowler, J.S.; Telang, F.; Jayne, M.; Wong, C. Stimulant-Induced Enhanced Sexual Desire as a Potential Contributing Factor in HIV Transmission. Am. J. Psychiatry 2007, 164, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, K.E.; Galai, N.; Safaeian, M.; Strathdee, S.A.; Celentano, D.D.; Vlahov, D. Temporal trends in the incidence of human immunodeficiency virus infection and risk behavior among injection drug users in Baltimore, Maryland, 1988–1998. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 156, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, J.C.; Woods, S.P.; Matt, G.E.; Meyer, R.A.; Heaton, R.K.; Atkinson, J.H.; Grant, I. Neurocognitive Effects of Methamphetamine: A Critical Review and Meta-analysis. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2007, 17, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chana, G.; Everall, I.P.; Crews, L.; Langford, D.; Adame, A.; Grant, I.; Cherner, M.; Lazzaretto, D.; Heaton, R.; Ellis, R.; et al. Cognitive deficits and degeneration of interneurons in HIV+ methamphetamine users. Neurology 2006, 67, 1486–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.L.; Krasnova, I.N. Interactions of HIV and methamphetamine: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of toxicity potentiation. Neurotox. Res. 2007, 12, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; McLellan, T.A. Curtailing diversion and abuse of opioid analgesics without jeopardizing pain treatment. JAMA 2011, 305, 1346–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Volkow, N.D.; Compton, W.M.; McCance-Katz, E.F. Reported Heroin Use, Use Disorder, and Injection among Adults in the United States, 2002–2018. JAMA 2020, 323, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventuneac, A.; Hecht, G.; Forcht, E.; Duah, B.A.; Tarar, S.; Langenbach, B.; Gates, J.; Cain, D.; Rendina, H.J.; Aberg, J.A.; et al. Chronic High Risk Prescription Opioid Use among Persons with HIV. Front. Sociol. 2021, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, R.; Stein, D.J.; Jelsma, J. Pain in people living with HIV/AIDS: A systematic review. J. Int. AIDS Soc. 2014, 17, 18719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miaskowski, C.; Penko, J.M.; Guzman, D.; Mattson, J.E.; Bangsberg, D.R.; Kushel, M.B. Occurrence and Characteristics of Chronic Pain in a Community-Based Cohort of Indigent Adults Living with HIV Infection. J. Pain 2011, 12, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merlin, J.S.; Long, D.; Becker, W.C.; Cachay, E.R.; Christopoulos, K.A.; Claborn, K.; Crane, H.M.; Edelman, E.J.; Harding, R.; Kertesz, S.G.; et al. Brief Report: The Association of Chronic Pain and Long-Term Opioid Therapy with HIV Treatment Outcomes. JAIDS J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2018, 79, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemons, A.; DeGroote, N.; Peréz, A.; Craw, J.; Nyaku, M.; Broz, D.; Mattson, C.L.; Beer, L. Opioid Misuse among HIV-Positive Adults in Medical Care: Results from the Medical Monitoring Project, 2009–2014. JAIDS J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2019, 80, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canan, C.E.; Chander, G.; Monroe, A.K.; Gebo, K.A.; Moore, R.D.; Agwu, A.L.; Alexander, G.C.; Lau, B.; For the HIV Research Network. High-Risk Prescription Opioid Use among People Living with HIV. JAIDS J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2018, 78, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canan, C.; Alexander, G.C.; Moore, R.; Murimi, I.; Chander, G.; Lau, B. Medicaid trends in prescription opioid and non-opioid use by HIV status. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 197, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, W.C.; Gordon, K.; Jennifer Edelman, E.; Kerns, R.D.; Crystal, S.; Dziura, J.D.; Fiellin, L.E.; Gordon, A.J.; Goulet, J.L.; Justice, A.C.; et al. Trends in Any and High-Dose Opioid Analgesic Receipt among Aging Patients with and without HIV. AIDS Behav. 2016, 20, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijayaraghavan, M.; Freitas, D.; Bangsberg, D.R.; Miaskowski, C.; Kushel, M.B. Non-medical use of non-opioid psychotherapeutic medications in a community-based cohort of HIV-infected indigent adults. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 143, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson-Papp, J.; Elliott, K.; Simpson, D.M.; Morgello, S.; Manhattan HIV Brain Bank. Problematic prescription opioid use in an HIV-infected cohort: The importance of universal toxicology testing. J. Acquir. Immune. Defic. Syndr. 2012, 61, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsao, J.C.I.; Plankey, M.W.; Young, M.A. Pain, psychological symptoms and prescription drug misuse in HIV: A literature review. J. Pain Manag. 2012, 5, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hartzler, B.; Dombrowski, J.C.; Crane, H.M.; Eron, J.J.; Geng, E.H.; Mathews, W.C.; Mayer, K.H.; Moore, R.D.; Mugavero, M.J.; Napravnik, S.; et al. Prevalence and Predictors of Substance Use Disorders among HIV Care Enrollees in the United States. AIDS Behav. 2016, 21, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelman, E.J.; Gordon, K.; Becker, W.C.; Goulet, J.L.; Skanderson, M.; Gaither, J.R.; Braden, J.B.; Gordon, A.J.; Kerns, R.D.; Justice, A.C.; et al. Receipt of Opioid Analgesics by HIV-Infected and Uninfected Patients. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2012, 28, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bose, J.; Hedden, S.; Lipari, R.; Park-Lee, E. Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. In Key Substance Use and Mental Health Indicators in the United States: Results from the 2017 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (HHS Publication No. SMA 18-5068, NSDUH Series H-53); Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration: Rockville, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tarasuk, J.; Ogunnaike-Cooke, S.; Archibald, C.; MacLean, R.; Bennett, R.; Kim, J.; Malloch, L. I-Track Principal Investigators Key findings from a national enhanced HIV surveillance system: 2010–2012. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2014, 40, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F.; Le Moal, M. Plasticity of reward neurocircuitry and the ’dark side’ of drug addiction. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1442–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F.; Ahmed, S.H.; Boutrel, B.; Chen, S.A.; Kenny, P.J.; Markou, A.; O’Dell, L.E.; Parsons, L.H.; Sanna, P.P. Neurobiological mechanisms in the transition from drug use to drug dependence. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2004, 27, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Guglielmo, G.; Kallupi, M.; Sedighim, S.; Newman, A.H.; George, O. Dopamine D3 Receptor Antagonism Reverses the Escalation of Oxycodone Self-administration and Decreases Withdrawal-Induced Hyperalgesia and Irritability-Like Behavior in Oxycodone-Dependent Heterogeneous Stock Rats. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wade, C.L.; Vendruscolo, L.F.; Schlosburg, J.E.; Hernandez, D.O.; Koob, G.F. Compulsive-Like Responding for Opioid Analgesics in Rats with Extended Access. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 40, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vendruscolo, L.F.; Schlosburg, J.E.; Misra, K.K.; Chen, S.A.; Greenwell, T.N.; Koob, G.F. Escalation patterns of varying periods of heroin access. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 98, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, S.H.; Walker, J.R.; Koob, G.F. Persistent Increase in the Motivation to Take Heroin in Rats with a History of Drug Escalation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2000, 22, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francesconi, W.; Berton, F.; Repunte-Canonigo, V.; Hagihara, K.; Thurbon, D.; Lekic, D.; Specio, S.E.; Greenwell, T.; Chen, S.A.; Rice, K.C.; et al. Protracted Withdrawal from Alcohol and Drugs of Abuse Impairs Long-Term Potentiation of Intrinsic Excitability in the Juxtacapsular Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 5389–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- George, O.; Koob, G.F.; Vendruscolo, L.F. Negative reinforcement via motivational withdrawal is the driving force behind the transition to addiction. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 3911–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reid, W.; Sadowska, M.; Denaro, F.; Rao, S.; Foulke, J., Jr.; Hayes, N.; Jones, O.; Doodnauth, D.; Davis, H.; Sill, A.; et al. An HIV-1 transgenic rat that develops HIV-related pathology and immunologic dysfunction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9271–9276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Royal, W., III; Zhang, L.; Guo, M.; Jones, O.; Davis, H.; Bryant, J.L. Immune activation, viral gene product expression and neurotoxicity in the HIV-1 transgenic rat. J. Neuroimmunol. 2012, 247, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Repunte-Canonigo, V.; Lefebvre, C.; George, O.; Kawamura, T.; Morales, M.; Koob, G.F.; Califano, A.; Masliah, E.; Sanna, P.P. Gene expression changes consistent with neuroAIDS and impaired working memory in HIV-1 transgenic rats. Mol. Neurodegener. 2014, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kallupi, M.; Carrette, L.L.G.; Kononoff, J.; Solberg Woods, L.C.; Palmer, A.A.; Schweitzer, P.; George, O.; de Guglielmo, G. Nociceptin attenuates the escalation of oxycodone self-administration by normalizing CeA-GABA transmission in highly addicted rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 2140–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimbrough, A.; Kononoff, J.; Simpson, S.; Kallupi, M.; Sedighim, S.; Palomino, K.; Conlisk, D.; Momper, J.D.; de Guglielmo, G.; George, O. Oxycodone self-administration and withdrawal behaviors in male and female Wistar rats. Psychopharmacology 2020, 237, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ipser, J.C.; Brown, G.G.; Bischoff-Grethe, A.; Connolly, C.G.; Ellis, R.J.; Heaton, R.K.; Grant, I. Translational Methamphetamine AIDS Research Center (TMARC) Group HIV Infection Is Associated with Attenuated Frontostriatal Intrinsic Connectivity: A Preliminary Study. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2015, 21, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Volkow, N.D.; Morales, M. The Brain on Drugs: From Reward to Addiction. Cell 2015, 162, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plessis, S.D.; Vink, M.; Joska, J.A.; Koutsilieri, E.; Stein, D.J.; Emsley, R. HIV infection and the fronto-striatal system: A systematic review and meta-analysis of fMRI studies. AIDS 2014, 28, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feil, J.; Sheppard, D.; Fitzgerald, P.B.; Yücel, M.; Lubman, D.I.; Bradshaw, J.L. Addiction, compulsive drug seeking, and the role of frontostriatal mechanisms in regulating inhibitory control. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2010, 35, 248–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koob, G.F.; Volkow, N.D. Neurobiology of addiction: A neurocircuitry analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2016, 3, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.H.; Lutjens, R.; van der Stap, L.D.; Lekic, D.; Romano-Spica, V.; Morales, M.; Koob, G.F.; Repunte-Canonigo, V.; Sanna, P.P. Gene expression evidence for remodeling of lateral hypothalamic circuitry in cocaine addiction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11533–11538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Repunte-Canonigo, V.; Kawamura, T.; Lefebvre, C.; Shin, W.; Howell, L.L.; Hemby, S.E.; Harvey, B.K.; Califano, A.; Morales, M.; et al. Hypothalamic proteoglycan syndecan-3 is a novel cocaine addiction resilience factor. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Repunte-Canonigo, V.; Chen, J.; Lefebvre, C.; Kawamura, T.; Kreifeldt, M.; Basson, O.; Roberts, A.J.; Sanna, P.P. MeCP2 regulates ethanol sensitivity and intake. Addict. Biol. 2013, 19, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Repunte-Canonigo, V.; Berton, F.; Cottone, P.; Reifel-Miller, A.; Roberts, A.J.; Morales, M.; Francesconi, W.; Sanna, P.P. A potential role for adiponectin receptor 2 (AdipoR2) in the regulation of alcohol intake. Brain Res. 2010, 1339, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Repunte-Canonigo, V.; Lutjens, R.; van der Stap, L.D.; Sanna, P.P. Increased expression of protein kinase A inhibitor α (PKI-α) and decreased PKA-regulated genes in chronic intermittent alcohol exposure. Brain Res. 2007, 1138, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Repunte-Canonigo, V.; Shin, W.; Vendruscolo, L.F.; Lefebvre, C.; Van Der Stap, L.; Kawamura, T.; Schlosburg, J.E.; Alvarez, M.; Koob, G.F.; Califano, A.; et al. Identifying candidate drivers of alcohol dependence-induced excessive drinking by assembly and interrogation of brain-specific regulatory networks. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Repunte-Canonigo, V.; van der Stap, L.D.; Chen, J.; Sabino, V.; Wagner, U.; Zorrilla, E.P.; Schumann, G.; Roberts, A.J.; Sanna, P.P. Genome-wide gene expression analysis identifies K-ras as a regulator of alcohol intake. Brain Res. 2010, 1339, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caine, S.B.; Koob, G.F. Modulation of Cocaine Self-Administration in the Rat Through D-3 Dopamine Receptors. Science 1993, 260, 1814–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Guglielmo, G.; Cippitelli, A.; Somaini, L.; Gerra, G.; Li, H.; Stopponi, S.; Ubaldi, M.; Kallupi, M.; Ciccocioppo, R. Pregabalin reduces cocaine self-administration and relapse to cocaine seeking in the rat. Addict. Biol. 2012, 18, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, Y.; Zorman, B.; Sumazin, P.; Sanna, P.P.; Repunte-Canonigo, V. Epitranscriptomics: Correlation of N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation and pathway dysregulation in the hippocampus of HIV transgenic rats. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0203566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antunes, M.; Biala, G. The novel object recognition memory: Neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn. Process. 2012, 13, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.J.; Stackman, R.W., Jr. Assessing rodent hippocampal involvement in the novel object recognition task. A review. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 285, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorzetto, M.; Datturi, F.; Divizia, L.; Pistono, C.; Campo, I.; De Silvestri, A.; Cuccia, M.; Ricevuti, G. Complement C4A and C4B Gene Copy Number Study in Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Curr. Alzheimer. Res. 2017, 14, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.; Grant, M.; Creese, A.J.; Mangialasche, F.; Cecchetti, R.; Cooper, H.J.; Mecocci, P.; Aldred, S. Plasma levels of complement 4a protein are increased in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer. Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2012, 26, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridas, V.; Shetty, P.; Sarathkumar, E.; Bargale, A.; Vishwanatha, J.; Patil, V.; Dinesh, U.S. Reciprocal regulation of pro-inflammatory Annexin A2 and anti-inflammatory Annexin A1 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2018, 46, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallacasagrande, V.; Hajjar, K.A. Annexin A2 in Inflammation and Host Defense. Cells 2020, 9, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, S.X.; Lok, J.; Whalen, M.; Dumont, A.S.; Wang, X. Recombinant annexin A2 inhibits peripheral leukocyte activation and brain infiltration after traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieker, J.; Zieker, D.; Jatzko, A.; Dietzsch, J.; Nieselt, K.; Schmitt, A.; Bertsch, T.; Fassbender, K.; Spanagel, R.; Northoff, H.; et al. Differential gene expression in peripheral blood of patients suffering from post-traumatic stress disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2007, 12, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pardo, M.; Cheng, Y.; Sitbon, Y.; Lowell, J.; Grieco, S.; Worthen, R.; Desse, S.; Barreda-Diaz, A. Insulin growth factor 2 (IGF2) as an emergent target in psychiatric and neurological disorders. Review. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 149, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, M.; Roh, J.D.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.S.; Han, H.M.; Yang, E.; Kang, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kang, R.; et al. SLC6A20 transporter: A novel regulator of brain glycine homeostasis and NMDAR function. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Morand, E.F. Targeting the side effects of steroid therapy in autoimmune diseases: The role of GILZ. Discov. Med. 2012, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Bonardi, C.M.; Heyne, H.O.; Fiannacca, M.; Fitzgerald, M.P.; Gardella, E.; Gunning, B.; Olofsson, K.; Lesca, G.; Verbeek, N.; Stamberger, H.; et al. KCNT1-related epilepsies and epileptic encephalopathies: Phenotypic and mutational spectrum. Brain 2021, 144, 3635–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Tian, X.; Lu, X.; Xu, D.; Guo, Y.; Dong, Z.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chen, C.; Yang, Y.; et al. TMEM25 modulates neuronal excitability and NMDA receptor subunit NR2B degradation. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 3864–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, W.F.; Bowlby, M.R.; Betty, M.; Cao, J.; Ling, H.-P.; Mendoza, G.; Hinson, J.W.; Mattsson, K.I.; Strassle, B.W.; Trimmer, J.S.; et al. Modulation of A-type potassium channels by a family of calcium sensors. Nature 2000, 403, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.K.; Chaboub, L.S.; Zhu, W.; Zollinger, D.; Rasband, M.; Fancy, S.P.; Deneen, B. Daam2-PIP5K Is a Regulatory Pathway for Wnt Signaling and Therapeutic Target for Remyelination in the CNS. Neuron 2015, 85, 1227–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeanneteau, F.; Guillin, O.; Diaz, J.; Griffon, N.; Sokoloff, P. GIPC Recruits GAIP (RGS19) To Attenuate Dopamine D2Receptor Signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 4926–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gold, N.B.; Li, D.; Chassevent, A.; Kaiser, F.J.; Parenti, I.; Strom, T.M.; Ramos, F.J.; Puisac, B.; Pie, J.; McWalter, K.; et al. Heterozygous de novo variants in CSNK1G1 are associated with syndromic developmental delay and autism spectrum disorder. Clin. Genet. 2020, 98, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincheva-Tasheva, S.; Guil, A.F.N.; Homan, C.C.; Gecz, J.; Thomas, P.Q. Disrupted Excitatory Synaptic Contacts and Altered Neuronal Network Activity Underpins the Neurological Phenotype in PCDH19-Clustering Epilepsy (PCDH19-CE). Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 2005–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmoker, A.M.; Weinert, J.L.; Kellett, K.J.; Johnson, H.E.; Joy, R.M.; Weir, M.E.; Ebert, A.M.; Ballif, B.A. Dynamic multi-site phosphorylation by Fyn and Abl drives the interaction between CRKL and the novel scaffolding receptors DCBLD1 and DCBLD2. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 3963–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halperin, D.; Kadir, R.; Perez, Y.; Drabkin, M.; Yogev, Y.; Wormser, O.; Berman, E.M.; Eremenko, E.; Rotblat, B.; Shorer, Z.; et al. SEC31A mutation affects ER homeostasis, causing a neurological syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2018, 56, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, K.W.; van Beuningen, S.F.; Cunha-Ferreira, I.; Cloin, B.M.; van Battum, E.Y.; Will, L.; Schätzle, P.; Tas, R.P.; van Krugten, J.; Katrukha, E.A.; et al. Microtubule Minus-End Binding Protein CAMSAP2 Controls Axon Specification and Dendrite Development. Neuron 2014, 82, 1058–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brivio, P.; Sbrini, G.; Tarantini, L.; Parravicini, C.; Gruca, P.; Lason, M.; Litwa, E.; Favero, C.; Riva, M.; Eberini, I.; et al. Stress Modifies the Expression of Glucocorticoid-Responsive Genes by Acting at Epigenetic Levels in the Rat Prefrontal Cortex: Modulatory Activity of Lurasidone. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frodl, T.; Carballedo, A.; Hughes, M.M.; Saleh, K.; Fagan, A.J.; Skokauskas, N.; McLoughlin, D.; Meaney, J.F.; O’Keane, V.; Connor, T.J. Reduced expression of glucocorticoid-inducible genes GILZ and SGK-1: High IL-6 levels are associated with reduced hippocampal volumes in major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwon, O.C.; Song, J.J.; Yang, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Seok, M.J.; Hwang, I.; Yu, J.W.; Karmacharya, J.; Maeng, H.J.; et al. SGK1 inhibition in glia ameliorates pathologies and symptoms in Parkinson disease animal models. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e13076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahi, M.; Motoi, Y.; Shimonaka, S.; Ishida, Y.; Hioki, H.; Takanashi, M.; Ishiguro, K.; Imai, Y.; Hattori, N. High-fat diet-induced activation of SGK1 promotes Alzheimer’s disease-associated tau pathology. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 1693–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedito, A.B.; Lehtinen, M.; Massol, R.; Lopes, U.G.; Kirchhausen, T.; Rao, A.; Bonni, A. The Transcription Factor NFAT3 Mediates Neuronal Survival. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 2818–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vashishta, A.; Habas, A.; Pruunsild, P.; Zheng, J.J.; Timmusk, T.; Hetman, M. Nuclear factor of activated T-cells isoform c4 (NFATc4/NFAT3) as a mediator of antiapoptotic transcription in NMDA receptor-stimulated cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15331–15340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warwick, C.A.; Keyes, A.L.; Woodruff, T.M.; Usachev, Y.M. The complement cascade in the regulation of neuroinflammation, nociceptive sensitization, and pain. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, D.; Wolfarth, A.; Sanchez, C.; Pehrson, A.L. Frontal cortex dysfunction as a target for remediation in opiate use disorder: Role in cognitive dysfunction and disordered reward systems. Prog. Brain Res. 2018, 239, 179–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, F.; Arnsten, J.H.; Cunningham, C.O.; Coulehan, K.; Batchelder, A.; Brisbane, M.; Segal, K.; Rivera-Mindt, M. Neurocognitive, psychiatric, and substance use characteristics in opioid dependent adults. Addict. Behav. 2016, 60, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, V.J.; Rubin, L.H.; Martin, E.; Weber, K.M.; Cohen, M.H.; Golub, E.T.; Valcour, V.; Young, M.A.; Crystal, H.; Anastos, K.; et al. HIV and Recent Illicit Drug Use Interact to Affect Verbal Memory in Women. JAIDS J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2013, 63, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamargo, J.A.; Campa, A.; Martinez, S.S.; Li, T.; Sherman, K.E.; Zarini, G.; Meade, C.S.; Mandler, R.N.; Baum, M.K. Cognitive Impairment among People Who Use Heroin and Fentanyl: Findings from the Miami Adult Studies on HIV (MASH) Cohort. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2020, 53, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Thormeyer, E.M.; Paul, R.H. Drug Abuse and Hepatitis C Infection as Comorbid Features of HIV Associated Neurocognitive Disorder: Neurocognitive and Neuroimaging Features. Neuropsychol. Rev. 2009, 19, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, D.A.; Fellows, R.P.; Morgello, S.; Franklin, D.; Heaton, R.K.; Deutsch, R.; Atkinson, J.H.; Clifford, D.B.; Collier, A.C.; Marra, C.M.; et al. Neurocognitive Impact of Substance Use in HIV Infection. JAIDS J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2011, 58, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mundkur, M.L.; Rough, K.; Huybrechts, K.F.; Levin, R.; Gagne, J.J.; Desai, R.J.; Patorno, E.; Choudhry, N.K.; Bateman, B.T. Patterns of opioid initiation at first visits for pain in United States primary care settings. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2017, 27, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.A.; Kranzler, H.R.; Chang, K.-M.; Doubeni, C.A.; Gross, R. Long-term use of hydrocodone vs. oxycodone in primary care. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 205, 107524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remillard, D.; Kaye, A.D.; McAnally, H. Oxycodone’s Unparalleled Addictive Potential: Is it Time for a Moratorium? Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2019, 23, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibaly, C.; Alderete, J.A.; Liu, S.H.; Nasef, H.S.; Law, P.Y.; Evans, C.J.; Cahill, C.M. Oxycodone in the Opioid Epidemic: High ’Liking’, ’Wanting’, and Abuse Liability. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 41, 899–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Guglielmo, G.; Fu, Y.; Chen, J.; Larrosa, E.; Hoang, I.; Kawamura, T.; Lorrai, I.; Zorman, B.; Bryant, J.; George, O.; et al. Increases in compulsivity, inflammation, and neural injury in HIV transgenic rats with escalated methamphetamine self-administration under extended-access conditions. Brain Res. 2019, 1726, 146502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.A.; Brown, G.G. HIV-associated executive dysfunction in the era of modern antiretroviral therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2017, 40, 357–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harricharan, R.; Thaver, V.; Russell, V.A.; Daniels, W.M.U. Tat-induced histopathological alterations mediate hippocampus-associated behavioural impairments in rats. Behav. Brain Funct. 2015, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marks, W.D.; Paris, J.J.; Schier, C.J.; Denton, M.D.; Fitting, S.; McQuiston, A.R.; Knapp, P.E.; Hauser, K.F. HIV-1 Tat causes cognitive deficits and selective loss of parvalbumin, somatostatin, and neuronal nitric oxide synthase expressing hippocampal CA1 interneuron subpopulations. J. NeuroVirol. 2016, 22, 747–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowson, S.A.; Harrell, C.S.; Bekhbat, M.; Gangavelli, A.; Wu, M.J.; Kelly, S.D.; Reddy, R.; Neigh, G.N. Neuroinflammation and Behavior in HIV-1 Transgenic Rats Exposed to Chronic Adolescent Stress. Front. Psychiatry 2016, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Brabander, J.M.; de Bruin, J.P.; van Eden, C.G. Comparison of the effects of neonatal and adult medial prefrontal cortex lesions on food hoarding and spatial delayed alternation. Behav. Brain Res. 1991, 42, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnett, S.B.; Nathwani, F.; Brasted, P.J. Medial prefrontal and neostriatal lesions disrupt performance in an operant delayed alternation task in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 1999, 106, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jett, J.D.; Bulin, S.E.; Hatherall, L.C.; McCartney, C.M.; Morilak, D.A. Deficits in cognitive flexibility induced by chronic unpredictable stress are associated with impaired glutamate neurotransmission in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience 2017, 346, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gessi, S.; Borea, P.A.; Bencivenni, S.; Fazzi, D.; Varani, K.; Merighi, S. The activation of mu-opioid receptor potentiates LPS-induced NF-kB promoting an inflammatory phenotype in microglia. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 2813–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merighi, S.; Gessi, S.; Varani, K.; Fazzi, D.; Stefanelli, A.; Borea, P.A. Morphine mediates a proinflammatory phenotype via mu-opioid receptor-PKCvarepsilon-Akt-ERK1/2 signaling pathway in activated microglial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokhari, S.M.; Yao, H.; Bethel-Brown, C.; Fuwang, P.; Williams, R.; Dhillon, N.K.; Hegde, R.; Kumar, A.; Buch, S.J. Morphine enhances Tat-induced activation in murine microglia. J. NeuroVirol. 2009, 15, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Turchan-Cholewo, J.; Smart, E.J.; Geurin, T.; Chauhan, A.; Reid, R.; Xu, R.; Nath, A.; Knapp, P.E.; Hauser, K.F. Morphine causes rapid increases in glial activation and neuronal injury in the striatum of inducible HIV-1 tat transgenic mice. Glia 2008, 56, 1414–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapasi, A.A.; Gibbons, N.; Mattana, J.; Singhal, P.C. Morphine Stimulates Mesangial Cell TNF-α and Nitrite Production. Inflammation 2000, 24, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.C.; Gekker, G.; Sheng, W.S.; Hu, S.; Tsang, M.; Peterson, P.K. Priming effect of morphine on the production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by microglia: Implications in respiratory burst activity and human immunodeficiency virus-1 expression. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 269, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vallejo, R.; de Leon-Casasola, O.; Benyamin, R. Opioid therapy and immunosuppression: A review. Am. J. Ther. 2004, 11, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchi, S.; Moschetti, G.; Amodeo, G.; Sacerdote, P. Do All Opioid Drugs Share the Same Immunomodulatory Properties? A Review from Animal and Human Studies. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereshchenko, O.; Migliorati, G.; Bruscoli, S.; Riccardi, C. Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper: A Novel Anti-inflammatory Molecule. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vago, J.P.; Tavares, L.P.; Garcia, C.C.; Lima, K.M.; Perucci, L.O.; Vieira, E.L.; Nogueira, C.R.C.; Soriani, F.M.; Martins, J.O.; Silva, P.M.R.; et al. The Role and Effects of Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper in the Context of Inflammation Resolution. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 4940–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vago, J.P.; Galvão, I.; Negreiros-Lima, G.L.; Teixeira, L.C.; Lima, K.M.; Sugimoto, M.A.; Moreira, I.Z.; Jones, S.A.; Lang, T.; Riccardi, C.; et al. Glucocorticoid-induced leucine zipper modulates macrophage polarization and apoptotic cell clearance. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannarile, L.; Delfino, D.V.; Adorisio, S.; Riccardi, C.; Ayroldi, E. Implicating the Role of GILZ in Glucocorticoid Modulation of T-Cell Activation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, I.; Dejager, L.; Petta, I.; Vandevyver, S.; Puimège, L.; Mahieu, T.; Ballegeer, M.; Van Hauwermeiren, F.; Riccardi, C.; Vuylsteke, M.; et al. LPS resistance of SPRET/Ei mice is mediated by Gilz, encoded by the Tsc22d3 gene on the X chromosome. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salahuddin, M.; Mahdi, F.; Paris, J. HIV-1 Tat Dysregulates the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Stress Axis and Potentiates Oxycodone-Mediated Psychomotor and Anxiety-Like Behavior of Male Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Fitting, S.; Hahn, Y.K.; Welch, S.P.; El-Hage, N.; Hauser, K.F.; Knapp, P.E. Morphine potentiates neurodegenerative effects of HIV-1 Tat through actions at mu-opioid receptor-expressing glia. Brain 2011, 134 Pt 12, 3616–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitting, S.; Knapp, P.E.; Zou, S.; Marks, W.D.; Bowers, M.S.; Akbarali, H.I.; Hauser, K.F. Interactive HIV-1 Tat and morphine-induced synaptodendritic injury is triggered through focal disruptions in Na+ influx, mitochondrial instability, and Ca2+ overload. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 12850–12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupien, S.J.; Gillin, C.J.; Hauger, R.L. Working memory is more sensitive than declarative memory to the acute effects of corticosteroids: A dose-response study in humans. Behav. Neurosci. 1999, 113, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.H.; Sahakian, B.J.; Robbins, T.W.; Cowen, P.J. The effects of chronic administration of hydrocortisone on cognitive function in normal male volunteers. Psychopharmacology 1999, 145, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, A.Y.; Hodis, H.N.; Mack, W.J.; Mather, M. Estradiol Therapy After Menopause Mitigates Effects of Stress on Cortisol and Working Memory. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 4457–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehner, M.; Wisłowska-Stanek, A.; Skórzewska, A.; Płaźnik, A. Chronic restraint increases apoptosis in the hippocampus of rats with high responsiveness to fear stimuli. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 586, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellman, C.L. Dendritic reorganization in pyramidal neurons in medial prefrontal cortex after chronic corticosterone administration. J. Neurobiol. 2001, 49, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liston, C.; Miller, M.M.; Goldwater, D.S.; Radley, J.J.; Rocher, A.B.; Hof, P.R.; Morrison, J.H.; McEwen, B.S. Stress-induced alterations in prefrontal cortical dendritic morphology predict selective impairments in perceptual attentional set-shifting. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7870–7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, R.-J.; Aghajanian, G.K. Stress blunts serotonin- and hypocretin-evoked EPSCs in prefrontal cortex: Role of corticosterone-mediated apical dendritic atrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hains, A.B.; Vu, M.A.T.; Maciejewski, P.K.; van Dyck, C.H.; Gottron, M.; Arnsten, A.F.T. Inhibition of protein kinase C signaling protects prefrontal cortex dendritic spines and cognition from the effects of chronic stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17957–17962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gourley, S.L.; Swanson, A.M.; Koleske, A.J. Corticosteroid-Induced Neural Remodeling Predicts Behavioral Vulnerability and Resilience. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 3107–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McEwen, B.S.; Stellar, E. Stress and the individual. Mechanisms leading to disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 1993, 153, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, D.S.; McEwen, B. Allostasis, homeostats, and the nature of stress. Stress 2002, 5, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S. Sex, stress and the hippocampus: Allostasis, allostatic load and the aging process. Neurobiol. Aging 2002, 23, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S. From molecules to mind. Stress, individual differences, and the social environment. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 935, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolkowitz, O.M. Prospective controlled studies of the behavioral and biological effects of exogenous corticosteroids. Psychoneuroendocrinology 1994, 19, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, T.C.; Yau, J.L.; MacLullich, A.M.; Noble, J.; Deary, I.J.; Walker, B.R.; Seckl, J.R. 11Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase inhibition improves cognitive function in healthy elderly men and type 2 diabetics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6734–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wingenfeld, K.; Wolf, O.T. Effects of cortisol on cognition in major depressive disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder and borderline personality disorder—2014 Curt Richter Award Winner. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2015, 51, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, S.; Maatouk, L. Contribution of glucocorticoids and glucocorticoid receptors to the regulation of neurodegenerative processes. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 1175–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djamshidian, A.; Lees, A.J. Can stress trigger Parkinson’s disease? J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, G.; Tian, R.; Li, J.; Yuan, T.F. Chronic stress and Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Veldhuis, J.D.; Deuschle, M.; Standhardt, H.; Heuser, I. Twenty-four hour cortisol release profiles in patients with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease compared to normal controls: Ultradian secretory pulsatility and diurnal variation. Neurobiol. Aging 1997, 18, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarianni, E. Hypercortisolemia and Glucocorticoid Receptor-Signaling Insufficiency in Alzheimer’ s Disease Initiation and Development. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2013, 10, 714–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raboch, J.; Zvěřová, M.; Fišar, Z.; Jirák, R.; Kitzlerová, E.; Hroudová, J.; Raboch, J. Plasma cortisol in Alzheimer’s disease with or without depressive symptoms. Med. Sci. Monit. 2013, 19, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Popp, J.; Wolfsgruber, S.; Heuser, I.; Peters, O.; Hull, M.; Schroder, J.; Moller, H.J.; Lewczuk, P.; Schneider, A.; Jahn, H.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid cortisol and clinical disease progression in MCI and dementia of Alzheimer’s type. Neurobiol. Aging 2015, 36, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelfsema, F.; Van Heemst, D.; Iranmanesh, A.; Takahashi, P.; Yang, R.; Veldhuis, J.D. Impact of age, sex and body mass index on cortisol secretion in 143 healthy adults. Endocr. Connect. 2017, 6, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cook, S.C.; Wellman, C.L. Chronic stress alters dendritic morphology in rat medial prefrontal cortex. J. Neurobiol. 2004, 60, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, E.Y.; Wei, J.; Liu, W.; Zhong, P.; Li, X.; Yan, Z. Repeated Stress Causes Cognitive Impairment by Suppressing Glutamate Receptor Expression and Function in Prefrontal Cortex. Neuron 2012, 73, 962–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luczynski, P.; Moquin, L.; Gratton, A. Chronic stress alters the dendritic morphology of callosal neurons and the acute glutamate stress response in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Stress 2015, 18, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimba, A.; Ikuta, K. Control of immunity by glucocorticoids in health and disease. Semin. Immunopathol. 2020, 42, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Lorrai, I.; Zorman, B.; Mercatelli, D.; Shankula, C.; Marquez Gaytan, J.; Lefebvre, C.; de Guglielmo, G.; Kim, H.R.; Sumazin, P.; et al. Escalated (Dependent) Oxycodone Self-Administration Is Associated with Cognitive Impairment and Transcriptional Evidence of Neurodegeneration in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Transgenic Rats. Viruses 2022, 14, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040669
Fu Y, Lorrai I, Zorman B, Mercatelli D, Shankula C, Marquez Gaytan J, Lefebvre C, de Guglielmo G, Kim HR, Sumazin P, et al. Escalated (Dependent) Oxycodone Self-Administration Is Associated with Cognitive Impairment and Transcriptional Evidence of Neurodegeneration in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Transgenic Rats. Viruses. 2022; 14(4):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040669
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yu, Irene Lorrai, Barry Zorman, Daniele Mercatelli, Chase Shankula, Jorge Marquez Gaytan, Celine Lefebvre, Giordano de Guglielmo, Hyunjae Ryan Kim, Pavel Sumazin, and et al. 2022. "Escalated (Dependent) Oxycodone Self-Administration Is Associated with Cognitive Impairment and Transcriptional Evidence of Neurodegeneration in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Transgenic Rats" Viruses 14, no. 4: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040669
APA StyleFu, Y., Lorrai, I., Zorman, B., Mercatelli, D., Shankula, C., Marquez Gaytan, J., Lefebvre, C., de Guglielmo, G., Kim, H. R., Sumazin, P., Giorgi, F. M., Repunte-Canonigo, V., & Sanna, P. P. (2022). Escalated (Dependent) Oxycodone Self-Administration Is Associated with Cognitive Impairment and Transcriptional Evidence of Neurodegeneration in Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Transgenic Rats. Viruses, 14(4), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040669







