Cytolytic Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Viruses Expressing STLV-1 Receptor Specifically Eliminate STLV-1 Env-Expressing Cells in an HTLV-1 Surrogate Model In Vitro
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Construction of Plasmids
2.3. Recoveries of rVSVs
2.4. Preparation of Non-G-Complemented rVSV Stocks
2.5. Immunofluorescence Test
2.6. Titration of rVSVs
2.7. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.8. Cell-Killing Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Construction and Generation of VSV Recombinants Expressing STLV-1 Receptor
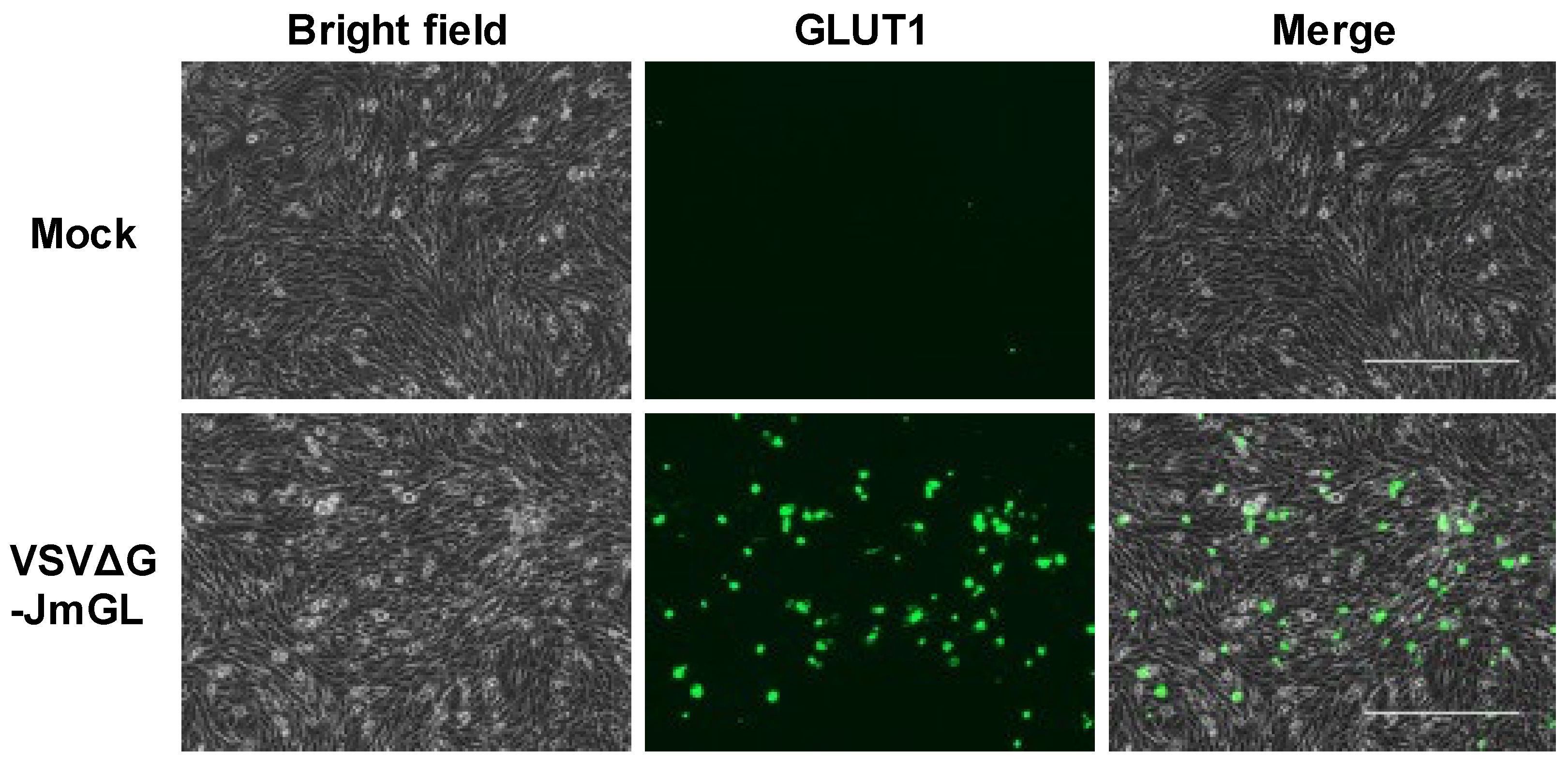
3.2. Cell Surface Expression of the STLV-1 Receptor Molecule Encoded in the rVSV Genome
3.3. Specific Infection of STLV-1 Env-Expressing Cells by rVSV Carrying the JM GLUT1
3.4. Elimination of STLV-1 Env-Expressing Cells by Infection with VSVΔG-JmGL-AcGFP
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gessain, A.; Barin, F.; Vernant, J.C.; Gout, O.; Maurs, L.; Calender, A.; De Thé, G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet 1985, 2, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, S.; Uemura, Y.; Fujishita, M.; Kitagawa, T.; Yamashita, M.; Imamura, J.; Ohtsuki, Y.; Taguchi, H.; Miyoshi, I. Isolation of HTLV-I from cerebrospinal fluid of a patient with myelopathy. Lancet 1986, 2, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takatsuki, K.; Yoshimura, K.; Shirao, M.; Nakashima, S.; Mori, S.; Araki, S.; Miyata, N. HTLV-I uveitis: A distinct clinical entity caused by HTLV-I. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1992, 83, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osame, M.; Usuku, K.; Izumo, S.; Ijichi, N.; Amitani, H.; Igata, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Tara, M. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet 1986, 1, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, T.; Yodoi, J.; Sagawa, K.; Takatsuki, K.; Uchino, H. Adult T-cell leukemia: Clinical and hematologic features of 16 cases. Blood 1977, 50, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, M.; Miyoshi, I.; Hinuma, Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2031–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moriuchi, H.; Masuzaki, H.; Doi, H.; Katamine, S. Mother-to-child transmission of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2013, 32, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poiesz, B.J.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Gazdar, A.F.; Bunn, P.A.; Minna, J.D.; Gallo, R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7415–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tezuka, K.; Fuchi, N.; Okuma, K.; Tsukiyama, T.; Miura, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Nagata, A.; Komatsu, N.; Hasegawa, H.; Sasaki, D.; et al. HTLV-1 targets human placental trophoblasts in seropositive pregnant women. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 6171–6186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessain, A.; Cassar, O. Epidemiological Aspects and World Distribution of HTLV-1 Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willems, L.; Hasegawa, H.; Accolla, R.; Bangham, C.; Bazarbachi, A.; Bertazzoni, U.; Carneiro-Proietti, A.B.; Cheng, H.; Chieco-Bianchi, L.; Ciminale, V.; et al. Reducing the global burden of HTLV-1 infection: An agenda for research and action. Antiviral. Res. 2017, 137, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satake, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tadokoro, K. Current prevalence of HTLV-1 in Japan as determined by screening of blood donors. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satake, M.; Iwanaga, M.; Sagara, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Okuma, K.; Hamaguchi, I. Incidence of human T-lymphotropic virus 1 infection in adolescent and adult blood donors in Japan: A nationwide retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, C.R.; Araujo, A.; Yamano, Y.; Taylor, G.P. HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bangham, C.R.; Ratner, L. How does HTLV-1 cause adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma (ATL)? Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 14, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bangham, C.R.M.; Matsuoka, M. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1: Parasitism and pathogenesis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwanaga, M.; Watanabe, T.; Yamaguchi, K. Adult T-cell leukemia: A review of epidemiological evidence. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamano, Y.; Sato, T. Clinical pathophysiology of human T-lymphotropic virus-type 1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hishizawa, M.; Kanda, J.; Utsunomiya, A.; Taniguchi, S.; Eto, T.; Moriuchi, Y.; Tanosaki, R.; Kawano, F.; Miyazaki, Y.; Masuda, M.; et al. Transplantation of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cells for adult T-cell leukemia: A nationwide retrospective study. Blood 2010, 116, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, K.; Utsunomiya, A.; Tobinai, K.; Tsukasaki, K.; Uike, N.; Uozumi, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamada, Y.; Hanada, S.; Tamura, K.; et al. Phase I study of KW-0761, a defucosylated humanized anti-CCR4 antibody, in relapsed patients with adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma and peripheral T-cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.B.; Taylor, G.P. Treatment of adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma: Is the virus a target? Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 28, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsunomiya, A.; Choi, I.; Chihara, D.; Seto, M. Recent advances in the treatment of adult T-cell leukemia-lymphomas. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukasaki, K.; Utsunomiya, A.; Fukuda, H.; Shibata, T.; Fukushima, T.; Takatsuka, Y.; Ikeda, S.; Masuda, M.; Nagoshi, H.; Ueda, R.; et al. VCAP-AMP-VECP compared with biweekly CHOP for adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma: Japan Clinical Oncology Group Study JCOG9801. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 5458–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, J.; Hishizawa, M.; Utsunomiya, A.; Taniguchi, S.; Eto, T.; Moriuchi, Y.; Tanosaki, R.; Kawano, F.; Miyazaki, Y.; Masuda, M.; et al. Impact of graft-versus-host disease on outcomes after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for adult T-cell leukemia: A retrospective cohort study. Blood 2012, 119, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tezuka, K.; Okuma, K.; Kuramitsu, M.; Matsuoka, S.; Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Hamaguchi, I. Control of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1 (HTLV-1) Infection by Eliminating Envelope Protein-Positive Cells with Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Viruses Encoding HTLV-1 Primary Receptor. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01885-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaddy, D.F.; Lyles, D.S. Vesicular stomatitis viruses expressing wild-type or mutant M proteins activate apoptosis through distinct pathways. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 4170–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawson, N.D.; Stillman, E.A.; Whitt, M.A.; Rose, J.K. Recombinant vesicular stomatitis viruses from DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4477–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnell, M.J.; Buonocore, L.; Whitt, M.A.; Rose, J.K. The minimal conserved transcription stop-start signal promotes stable expression of a foreign gene in vesicular stomatitis virus. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 2318–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghez, D.; Lepelletier, Y.; Lambert, S.; Fourneau, J.M.; Blot, V.; Janvier, S.; Arnulf, B.; van Endert, P.M.; Heveker, N.; Pique, C.; et al. Neuropilin-1 is involved in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 entry. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 6844–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, K.S.; Petrow-Sadowski, C.; Bertolette, D.C.; Huang, Y.; Ruscetti, F.W. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate attachment and entry of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 virions into CD4+ T cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12692–12702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manel, N.; Kim, F.J.; Kinet, S.; Taylor, N.; Sitbon, M.; Battini, J.L. The ubiquitous glucose transporter GLUT-1 is a receptor for HTLV. Cell 2003, 115, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuoka, M.; Jeang, K.T. Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular transformation. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daenke, S.; Booth, S. Molecular mechanisms affecting HTLV type 1-dependent fusion at the cell membrane: Implications for inhibiting viral transmission. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2000, 16, 1731–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayami, M.; Komuro, A.; Nozawa, K.; Shotake, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Ishida, T.; Honjo, S.; Hinuma, Y. Prevalence of antibody to adult T-cell leukemia virus-associated antigens (ATLA) in Japanese monkeys and other non-human primates. Int. J. Cancer 1984, 33, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jégado, B.; Kashanchi, F.; Dutartre, H.; Mahieux, R. STLV-1 as a model for studying HTLV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2019, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.G.; Wong-Stall, F.; Gallo, R.C. Novel viral sequences related to human T-cell leukemia virus in T cells of a seropositive baboon. Science 1984, 223, 1195–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, M.P.; Saksena, N.K.; Dube, D.K.; Yanagihara, R.; Poiesz, B.J. Evolutionary insights on the origin of human T-cell lymphoma/leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) derived from sequence analysis of a new HTLV-I variant from Papua New Guinea. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 2556–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watanabe, T.; Seiki, M.; Tsujimoto, H.; Miyoshi, I.; Hayami, M.; Yoshida, M. Sequence homology of the simian retrovirus genome with human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Virology 1985, 144, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, R.; Yasunaga, J.I.; Miura, M.; Sugata, K.; Saito, A.; Akari, H.; Ueno, T.; Takenouchi, N.; Fujisawa, J.I.; Koh, K.R.; et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infects multiple lineage hematopoietic cells in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Yasunaga, J.I.; Washizaki, A.; Seki, Y.; Kuramitsu, M.; Tan, W.K.; Hu, A.; Okuma, K.; Hamaguchi, I.; Mizukami, T.; et al. Frequent horizontal and mother-to-child transmission may contribute to high prevalence of STLV-1 infection in Japanese macaques. Retrovirology 2020, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuma, K.; Boritz, E.; Walker, J.; Sarkar, A.; Alexander, L.; Rose, J.K. Recombinant vesicular stomatitis viruses encoding simian immunodeficiency virus receptors target infected cells and control infection. Virology 2006, 346, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schnell, M.J.; Johnson, J.E.; Buonocore, L.; Rose, J.K. Construction of a novel virus that targets HIV-1-infected cells and controls HIV-1 infection. Cell 1997, 90, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Kodama, A.; Fujii, H.; Hasegawa, A.; Kannagi, M.; Ansari, A.A.; Saito, M. Elimination of human T cell leukemia virus type-1-infected cells by neutralizing and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity-inducing antibodies against human t cell leukemia virus type-1 envelope gp46. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2014, 30, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.; Zeng, L.; Shiraki, H.; Shida, H.; Tozawa, H. Identification of a neutralization epitope on the envelope gp46 antigen of human T cell leukemia virus type I and induction of neutralizing antibody by peptide immunization. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 354–360. [Google Scholar]
- Takata, K.; Hirano, H.; Kasahara, M. Transport of glucose across the blood-tissue barriers. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1997, 172, 1–53. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Q.; Agrawal, L.; VanHorn-Ali, Z.; Alkhatib, G. Infection of CD4+ T lymphocytes by the human T cell leukemia virus type 1 is mediated by the glucose transporter GLUT-1: Evidence using antibodies specific to the receptor’s large extracellular domain. Virology 2006, 349, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manel, N.; Battini, J.L.; Sitbon, M. Human T cell leukemia virus envelope binding and virus entry are mediated by distinct domains of the glucose transporter GLUT1. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 29025–29029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okuma, K.; Fukagawa, K.; Kohma, T.; Takahama, Y.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Ito, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Buonocore, L.; Rose, J.K.; Hamaguchi, I. A recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus encoding CCR5-tropic HIV-1 receptors targets HIV-1-infected cells and controls HIV-1 infection. Microbes. Infect. 2017, 19, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruno, C.; Okuma, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Takahama, Y.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Hamaguchi, I.; Yamaguchi, K. A recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus encoding HIV-1 receptors and human OX40 ligand efficiently eliminates HIV-1-infected CD4-positive T cells expressing OX40. Hum. Immunol. 2011, 72, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, M.; Yasunaga, J.; Tanabe, J.; Sugata, K.; Zhao, T.; Ma, G.; Miyazato, P.; Ohshima, K.; Kaneko, A.; Watanabe, A.; et al. Characterization of simian T-cell leukemia virus type 1 in naturally infected Japanese macaques as a model of HTLV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugata, K.; Yasunaga, J.; Miura, M.; Akari, H.; Utsunomiya, A.; Nosaka, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Suzushima, H.; Koh, K.R.; Nakagawa, M.; et al. Enhancement of anti-STLV-1/HTLV-1 immune responses through multimodal effects of anti-CCR4 antibody. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buijs, P.R.; Verhagen, J.H.; van Eijck, C.H.; van den Hoogen, B.G. Oncolytic viruses: From bench to bedside with a focus on safety. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2015, 11, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hastie, E.; Grdzelishvili, V.Z. Vesicular stomatitis virus as a flexible platform for oncolytic virotherapy against cancer. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2529–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichty, B.D.; Power, A.T.; Stojdl, D.F.; Bell, J.C. Vesicular stomatitis virus: Re-inventing the bullet. Trends Mol. Med. 2004, 10, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldufsky, J.; Sivendran, S.; Harcharik, S.; Pan, M.; Bernardo, S.; Stern, R.H.; Friedlander, P.; Ruby, C.E.; Saenger, Y.; Kaufman, H.L. Oncolytic virus therapy for cancer. Oncolytic. Virother. 2013, 2, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Licata, J.M.; Harty, R.N. Rhabdoviruses and apoptosis. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 22, 451–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.; Buonocore, L.; Price, R.; Forman, J.; Rose, J.K. Attenuated vesicular stomatitis viruses as vaccine vectors. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 3723–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, K.S.; Lambert, S.; Bouttier, M.; Bénit, L.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Hermine, O.; Pique, C. Molecular aspects of HTLV-1 entry: Functional domains of the HTLV-1 surface subunit (SU) and their relationships to the entry receptors. Viruses 2011, 3, 794–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinet, S.; Swainson, L.; Lavanya, M.; Mongellaz, C.; Montel-Hagen, A.; Craveiro, M.; Manel, N.; Battini, J.L.; Sitbon, M.; Taylor, N. Isolated receptor binding domains of HTLV-1 and HTLV-2 envelopes bind Glut-1 on activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Retrovirology 2007, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, A.R.; Delamarre, L.; Preira, A.; Dokhélar, M.C. Analysis of functional conservation in the surface and transmembrane glycoprotein subunits of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and HTLV-2. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 7609–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geisbert, T.W.; Geisbert, J.B.; Leung, A.; Daddario-DiCaprio, K.M.; Hensley, L.E.; Grolla, A.; Feldmann, H. Single-injection vaccine protects nonhuman primates against infection with marburg virus and three species of ebola virus. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7296–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marzi, A.; Robertson, S.J.; Haddock, E.; Feldmann, F.; Hanley, P.W.; Scott, D.P.; Strong, J.E.; Kobinger, G.; Best, S.M.; Feldmann, H. EBOLA VACCINE. VSV-EBOV rapidly protects macaques against infection with the 2014/15 Ebola virus outbreak strain. Science 2015, 349, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rose, N.F.; Marx, P.A.; Luckay, A.; Nixon, D.F.; Moretto, W.J.; Donahoe, S.M.; Montefiori, D.; Roberts, A.; Buonocore, L.; Rose, J.K. An effective AIDS vaccine based on live attenuated vesicular stomatitis virus recombinants. Cell 2001, 106, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franchini, G.; Wong-Staal, F.; Gallo, R.C. Human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I) transcripts in fresh and cultured cells of patients with adult T-cell leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 6207–6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, T.; Shimoyama, M.; Tobinai, K.; Ito, M.; Ito, S.; Ikeda, S.; Tajima, K.; Shimotohno, K.; Sugimura, T. Detection of mRNA for the tax1/rex1 gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells of adult T-cell leukemia patients and viral carriers by using the polymerase chain reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5620–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Umadome, H.; Uchiyama, T.; Hori, T.; Tamori, S.; Motoi, T.; Araki, K.; Uchino, H. Close association between interleukin 2 receptor mRNA expression and human T cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type I viral RNA expression in short-term cultured leukemic cells from adult T cell leukemia patients. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 81, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Species | Accession No. | Description | Identity (Percentage) | Different Amino Acid Positions | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 49 | 55 | 183 | 195 | ||||
| Outside (ECL1) | Outside (ECL1) | Outside (ECL1) | TMhelix | ||||
| Homo sapiens | NP_006507.2 | Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 1 | - | V | S | K | I |
| Macaca fuscata | LC684847 | Macaca fuscata GLUT-1 (from Si-2 cells) | 488/492 (99%) | I | R | E | V |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seki, Y.; Kitamura, T.; Tezuka, K.; Murata, M.; Akari, H.; Hamaguchi, I.; Okuma, K. Cytolytic Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Viruses Expressing STLV-1 Receptor Specifically Eliminate STLV-1 Env-Expressing Cells in an HTLV-1 Surrogate Model In Vitro. Viruses 2022, 14, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040740
Seki Y, Kitamura T, Tezuka K, Murata M, Akari H, Hamaguchi I, Okuma K. Cytolytic Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Viruses Expressing STLV-1 Receptor Specifically Eliminate STLV-1 Env-Expressing Cells in an HTLV-1 Surrogate Model In Vitro. Viruses. 2022; 14(4):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040740
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeki, Yohei, Tomoya Kitamura, Kenta Tezuka, Megumi Murata, Hirofumi Akari, Isao Hamaguchi, and Kazu Okuma. 2022. "Cytolytic Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Viruses Expressing STLV-1 Receptor Specifically Eliminate STLV-1 Env-Expressing Cells in an HTLV-1 Surrogate Model In Vitro" Viruses 14, no. 4: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040740
APA StyleSeki, Y., Kitamura, T., Tezuka, K., Murata, M., Akari, H., Hamaguchi, I., & Okuma, K. (2022). Cytolytic Recombinant Vesicular Stomatitis Viruses Expressing STLV-1 Receptor Specifically Eliminate STLV-1 Env-Expressing Cells in an HTLV-1 Surrogate Model In Vitro. Viruses, 14(4), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14040740







