Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Japanese Immigrants and Descendants: The Need to Strengthen Preventive and Control Measures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
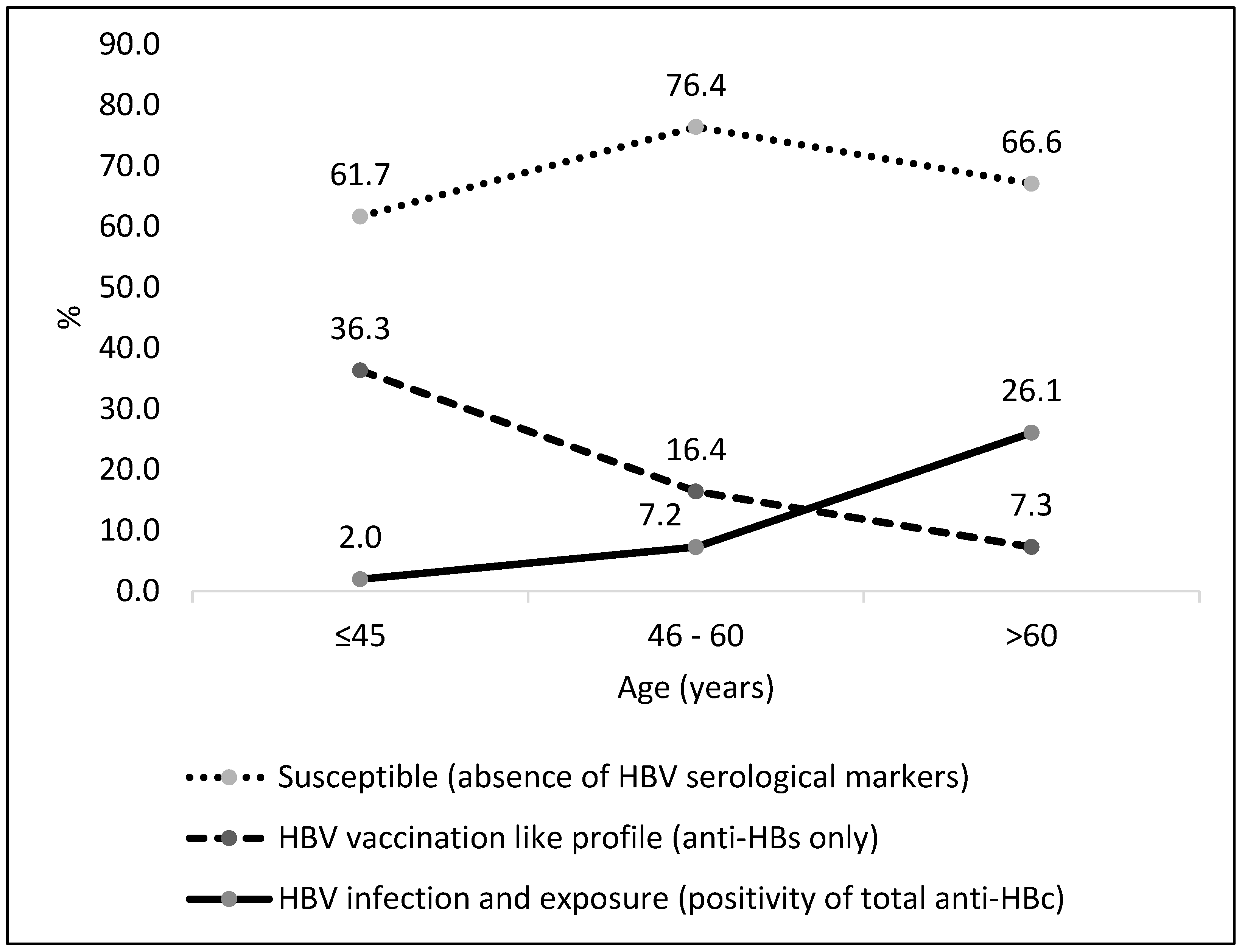
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Hepatitis B. Key Facts. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 22 August 2021).
- Sato, T.; Do, S.H.; Asao, T.; Akita, T.; Katayama, K.; Tatara, K.; Miyakawa, Y.; Tanaka, J. Estimating numbers of persons with persistent hepatitis B virus infection transmitted vertically and horizontally in the birth cohort during 1950–1985 in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2014, 44, E181–E188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rani, M.; Yang, B.; Nesbit, R. Hepatitis B control by 2012 in the WHO Western Pacific Region: Rationale and implications. Bull. World Health Organ. 2009, 87, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, H. Global Epidemiology of Viral Hepatitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 49, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, F.J.D. Distribution of hepatitis B infection in Brazil: The epidemiological situation at the beginning of the 21st century. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2016, 49, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, J.; Kajiyama, W.; Noguchi, A.; Ikematsu, H.; Nomura, H.; Nakashima, K.; Morofuji, M.; Kashiwagi, S. Marked Decrease of Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Children in Okinawa, Japan. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1990, 19, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, R.L.B.; Teles, S.A.; Reis, R.K.; Galvão, M.T.G.; Gir, E. Low completion rate of hepatitis B vaccination in female sex workers. Rev. Bras. Enferm. 2017, 70, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brasil, Ministério Da Saúde. Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde. Departamento de Condições Crônicas e Infecções Sexualmente Transmissíveis. Hepatite B. Available online: http://www.aids.gov.br/pt-br/publico-geral/hv/o-que-sao-hepatites/hepatite-b (accessed on 9 October 2020).
- Consulado Geral do Japão em São Paulo. Dados Gerais. Available online: emb-japan.go.jp (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Osaki, M.M. A Evolução da Assistência à saúde dos Imigrantes Japoneses no Brasil. Rev. Adm. Saúde 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prutsch, U. Migrantes na periferia: Indígenas, europeus e japoneses no Paraná durante as primeiras décadas do século XX. Hist. Ciênc. Saúde-Manguinhos 2014, 21, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bandeira, L.M.; Puga, M.A.M.; Weis-Torres, S.M.S.; Rezende, G.R.; Domingos, J.A.; Tanaka, T.S.O.; Cesar, G.A.; Nukui, Y.; Vicente, A.C.P.; Casseb, J.; et al. Human T-cell leucemia virus type 1 infection among Japanese immigrants and their descendants living in Southeast Brazil: A call for preventive and control responses. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes-Gouvêa, M.S.; Ferreira, A.C.; Teixeira, R.; Andrade, J.R.; Ferreira, A.S.; Barros, L.M.; Rezende, R.E.; Nastri, A.C.; Leite, A.G.; Piccoli, L.Z.; et al. HBV carrying drug-resistence mutations in chronically infected treatment-naive patients. Antivir. Ther. 2015, 20, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, T.A. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Suchard, M.A.; Lemey, P.; Baele, G.; Ayres, D.L.; Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. Bayesian phylogenetic and phylodynamic data integration using BEAST 1.10. Virus Evol. 2018, 4, vey016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosmer, D.W., Jr.; Lemeshow, S.; Sturdivant, R.X. Applied Logistic Regression, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Carrilho, F.J.; Ono-Nita, S.K.; Cardoso, R.A.; Cancado, E.L.R.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Alves, V.A.F.; Silva, L.C. A prospective study of hepatitis B virus markers in patients with chronic HBV infection from Brazilian families of Western and Asian origin. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 1399–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kato, H.; Fujiwara, K.; Gish, R.G.; Sakugawa, H.; Yoshizawa, H.; Sugauchi, F.; Orito, E.; Ueda, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Kato, T.; et al. Classifying genotype F of hepatitis B virus into F1 and F2 subtypes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 6295–6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Neto, C.; Sabino, E.C.; Liu, J.; Blatyta, P.F.; Mendrone-Junior, A.; Salles, N.A.; Leão, S.C.; Wright, D.J.; Basques, F.V.; Ferreira, J.E.; et al. Prevalence of serologic markers for hepatitis B and C viruses in Brazilian blood donors and incidence and residual risk of transfusion transmission of hepatitis C virus. Transfusion 2013, 53, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lima, L.A.; Lago, B.V.; Weis-Torres, S.M.S.; Martins, R.M.B.; Cesar, G.A.; Bandeira, L.M.; Rezende, G.R.; Lindenberg, A.S.C.; Gomes, S.A.; Motta-Castro, A.R.C. Hepatitis B: Changes in epidemiological features of Afro-descendant communities in Central Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, A.; Hayashi, J.; Nakashima, K.; Ikematsu, H.; Hirata, M.; Kashiwagi, S. Decrease of Hepatitis A and B virus infection in the population of Okinawa, Japan. J. Infect. 1991, 23, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee. Guidelines for the Prevention, Care and Treatment of Persons with Chronic Hepatitis B Infection; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, C.; Shrier, I.; Marshall, L.; Cnossen, S.; Schwartzman, K.; Klein, M.B.; Schwarzer, G.; Greenaway, C. Seroprevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection and prior immunity in immigrants and refugees: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2012, 7, e0044611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottie, K.; Greenaway, C.; Feightner, J.; Welch, V.; Swinkels, H.; Rashid, M.; Narasiah, L.; Kirmayer, L.J.; Ueffing, E.; MacDonald, N.E.; et al. Evidence-based clinical guidelines for immigrants and refugees. CMAJ 2011, 183, E824–E925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinbaum, C.M.; Mast, E.E.; Ward, J.W. Recommendations for identification and public health management of persons with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2009, 49, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Burden of Disease Liver Cancer Collaboration. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, G.D.S.; Campos, D.; Ballalai, A.; Palhares, R.; da Silva, M.R.A.; Palhares, D.M.F.; Neto, B.F.; Barros, F.M.D.R.; Gil, R.A.; Chagas, A.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Patterns of Newly Diagnosed Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Brazil: The Need for Liver Disease Screening Programs Based on Real-World Data. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2021, 52, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paranaguá-Vezozzo, D.C.; Ono, S.K.; Alvarado-Mora, M.V.; Farias, A.Q.; Cunha-Silva, M.; França, J.I.; Alves, V.A.; Sherman, M.; Carrilho, F.J. Epidemiology of HCC in Brazil: Incidence and Risk Factors in a Ten-Year Cohort. Ann. Hepatol. 2014, 13, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Hepatitis D. Key Facts. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-d (accessed on 1 June 2021).
- Sakugawa, H.; Nakasone, H.; Shokita, H.; Kawakami, Y.; Nakachi, N.; Adaniya, H.; Mizushima, T.; Nakayoshi, T.; Kinjo, F.; Saito, A.; et al. Seroepidemiological study on hepatitis delta virus infection in the Irabu Islands, Okinawa, Japan. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1997, 12, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, Y.; Moriyama, M.; Taira, M.; Hayashi, N.; Tanaka, N.; Okubo, H.; Sugitani, M.; Arakawa, Y. Molecular analysis of hepatitis D virus infection in Miyako Island, a small Japanese island. J. Viral Hepat. 2000, 7, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Nagayama, K.; Enomoto, N.; Chinzei, R.; Yamashiro, T.; Izumi, N.; Yatsuhashi, H.; Nakano, T.; Robertson, B.; Nakasone, H.; et al. Chronic hepatitis delta virus infection with genotype IIb variant is correlated with progressive liver disease. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 3275–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, B.V.; Mello, F.C.A.; Barros, T.M.; Mello, V.M.; Villar, L.M.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Pardini, M.I.M.C.; Lampe, E. Hepatitis D infection in Brazil: Prevalence and geographical distribution of anti-Delta antibody. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ximenes, R.A.A.; Figueiredo, G.M.; Cardoso, M.R.A.; Stein, A.T.; Moreira, R.C.; Coral, G.; Crespo, D.; Santos, A.A.; Montarroyos, U.R.; Braga, M.C.; et al. Population-Based Multicentric Survey of Hepatitis B Infection and Risk Factors in the North, South, and Southeast Regions of Brazil, 10–20 Years after the Beginning of Vaccination. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93, 1341–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos Weis-Torres, S.M.; Fitts, S.M.F.; Cardoso, W.M.; Junior, M.G.H.; Lima, L.A.; Bandeira, L.M.; Castro, V.O.L.; Carneiro, F.A.; Iglecias, L.M.M.; Cesar, G.A.; et al. High level of exposure to hepatitis B virus infection in a vulnerable population of a low endemic area: A challenge for vaccination coverage. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 90, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiya, A.S.; Levi, J.E.; de Almeida-Neto, C.; Witkin, S.S.; Ferreira, S.C.; Bassit, L.; Sabino, E.C.; Di-Lorenzo-Oliveira, C.; Salles, N.A.; Coutinho, A.S.; et al. Occult and active hepatitis B virus detection in donated blood in São Paulo, Brazil. Transfusion 2021, 61, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro Sant’Annaa, C.; Almeida, M.K.C.; Ferreira, P.; Oliveira, R.G.; Baraúna, A.R.F.; Gonçalvez, E.C.; Silva, A.M.; Pereira, C.S.; Martins, L.C. Prevalence of Occult Hepatitis B in a Population from the Brazilian Amazon Region. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontenele, A.M.; Gainer, J.B.; da Silva, E.; Silva, D.V.; Cruz Santos, M.D.; Salgado, J.V.; Salgado Filho, N.; Ferreira, A.S. Occult hepatites B among patients with chronic renal failure on hemodialysis from a capital city in northeast Brazil. Hemodial. Int. 2015, 19, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakugawa, H.; Ohwan, T.; Yamashiro, A.; Oyakawa, T.; Kadena, K.; Kinjo, F.; Saito, A. Natural Seroconversion from Hepatitis Be Antigen to Antibody Among Hepatitis B Virus Carriers in Okinawa Islands. J. Med. Virol. 1991, 34, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, S.; Hayashi, J.; Ikematsu, H.; Nomura, H.; Kusaba, T.; Shingu, T.; Hayashida, K.; Kaji, M. An Epidemiologic Study of Hepatitis B virus in Okinawa and Kyushu, Japan. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1983, 118, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, S.; Hayashi, J.; Nomura, H.; Kajiyama, W.; Ikematsu, H.; Noguchi, A. Changing Pattern of Intrafamilial Transmission of Hepatitis B Virus in Okinawa, Japan. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1988, 127, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, G.R.; Lago, B.V.; Puga, M.A.; Bandeira, L.M.; Pompilio, M.A.; Castro, V.O.L.; Tanaka, T.S.; Cesar, G.A.; Oliveira, S.M.V.L.; Yassuda, R.T.S.; et al. Prevalence, incidence and associated factors for HBV infection among male and female prisioners in Central Brazil: A multicenter study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 96, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, R.H.; Mbayed, V.A.; Pineiro, Y.L.F.G. Molecular epidemiology of hepatitis B virus in Latin America. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 34, S8–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Mora, M.V.; Santana, R.A.F.; Sitnik, R.; Ferreira, P.R.A.; Mangueira, C.L.P.; Carrilho, F.J.; Pinho, J.R.R. Full-length genomic sequence of hepatitis B virus genotype C2 isolated from a native Brazilian patient. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2011, 106, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunbul, M. Hepatitis B virus genotypes: Global distribution and clinical importance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5427–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramvis, A. Genotypes and Genetic Variability of Hepatitis B Virus. Intervirology 2014, 57, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norder, H.; Couroucé, A.M.; Coursaget, P.; Echevarria, J.M.; Lee, S.D.; Mushahwar, I.K.; Robertson. B., H.; Locarnini, S.; Magnius, L.O. Genetic diversity of hepatitis B virus strains derived worldwide: Genotypes, subgenotypes and HBsAg subtypes. Intervirology 2004, 47, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Yotsuyanagi, H.; Sugiyama, M.; Yatsuhashi, H.; Karino, Y.; Takikawa, Y.; Saito, T.; Arase, Y.; Imazeki, F.; Kurosaki, M.; et al. Geographic distribution and characteristics of genotype A hepatitis B virus infection in acute and chronic hepatitis B patients in Japan. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furusyo, N.; Nakashima, H.; Kashiwagi, K.; Kubo, N.; Hayashida, K.; Usuda, S.; Mishiro, S.; Kashiwagi, S.; Hayashi, J. Clinical Outcomes of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Genotypes B and C in Japanese Patients with Chronic HBV Infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 67, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ono-Nita, S.K.; Carrilho, F.J.; Cardoso, R.A.; Nita, M.E.; Silva, C. Searching for cjronic hepatitis B patients in a low prevalence área–role of racial origin. BMC Fam. Pract. 2004, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Clemente, C.M.; Carrilho, F.J.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Ono-Nita, S.K.; da Silva, L.C.; Moreira, R.C.; Lemos, M.F.; Mello, I.M.V.G.C. A phylogenetic study of hepatitis B virus chronically infected Brazilian patients od Western and Asian descent. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, B.V.; Espirito-Santo, M.P.; Costa, V.D.; Marques, V.A.; Villar, L.M.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; Lampe, E.; Mello, F.C.A. Genetic Diversity of the Hepatitis B Virus Subgenotypes in Brazil. Viruses 2019, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panduro, A.; Maldonado-Gonzalez, M.; Fierro, N.A.; Roman, S. Distribution of HBV genotypes F and H in Mexico and Central America. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, F.C.A.; Araujo, O.C.; Lago, B.V.; Motta-Castro, A.R.C.; Moraes, M.T.B.; Gomes, S.A.; Bello, G.; Araujo, N.M. Phylogeography and evolutionary history of hepatitis B virus genotype F in Brazil. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, S.R.; Santos, M.I.M.A.; Stocker, A.; Zarife, M.A.S.; Schinoni, M.I.; Parana, R.; Reis, M.G.; Silva, L.K. Genotyping of HBV and tracking of resistance mutations in treatment-naïve patients with chronic hepatitis B. Infect. Drug. Resist. 2017, 10, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | N a | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | ||
| ≤45 | 710 | 33.4 |
| 46–60 | 524 | 24.6 |
| ≥60 | 893 | 41.9 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 856 | 40.2 |
| Female | 1.271 | 59.8 |
| Formal education (years) a | ||
| Illiterate | 18 | 0.85 |
| 1–9 | 559 | 26.4 |
| 10–12 | 588 | 27.8 |
| >12 | 949 | 44.9 |
| Monthly household income * a | ||
| <1 | 121 | 6.5 |
| 1–3 | 565 | 28.7 |
| >3 | 1.281 | 65.1 |
| Marital status | ||
| Single | 544 | 25.6 |
| Married, divorced, or widowed | 1.583 | 74.4 |
| Recruitment site | ||
| Association A | 709 | 33.3 |
| Association B | 302 | 14.2 |
| Association C | 440 | 20.7 |
| Association D | 344 | 16.2 |
| Association E | 332 | 15.6 |
| Family heritage | ||
| Japanese immigrant | 316 | 14.9 |
| Japanese son/daughter | 1.007 | 47.3 |
| Grandson and great-grandson of Japanese immigrant | 750 | 35.3 |
| Non-Japanese descendant | 54 | 2.5 |
| Okinawan Descendant | ||
| No | 265 | 12.5 |
| Yes | 1.862 | 87.5 |
| History of residence in Japan | ||
| No | 1.305 | 61.4 |
| Yes | 822 | 38.7 |
| Blood transfusion | ||
| No | 1.982 | 93.2 |
| Yes | 145 | 6.8 |
| Surgery | ||
| No | 734 | 34.5 |
| Yes | 1.393 | 65.5 |
| History of Sexually transmitted infection a | ||
| No | 1.917 | 90.1 |
| Yes | 144 | 7.0 |
| Shared sharp objects | ||
| No | 1.263 | 59.4 |
| Yes | 864 | 40.6 |
| Accidental contact with blood of others | ||
| No | 2.061 | 96.9 |
| Yes | 66 | 3.1 |
| Regular use of condoms a | ||
| No | 1.576 | 83.7 |
| Yes | 308 | 16.3 |
| Born in São Paulo | ||
| No | 1.153 | 54.2 |
| Yes | 974 | 45.8 |
| Markers | n | % | 95% CI 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infected | |||
| HBsAg-positive | 22 | 1.1 | 0.68–1.56 |
| HBsAg only | 6 | 0.3 | 0.13–0.62 |
| HBsAg/anti-HBc | 16 | 0.8 | 0.46–1.22 |
| Anti-HBc positive | 262 | 12.3 | 11.10–13.93 |
| Anti-HBc only | 57 | 2.7 | 2.07–3.46 |
| Total anti-HBc/anti-HBs | 205 | 9.6 | 8.45–10.96 |
| Any HBV infection marker | 284 | 13.4 | 11.97–14.86 |
| Not susceptible, possibly vaccinated | |||
| Anti-HBs only | 409 | 19.2 | 17.61–20.96 |
| Not exposed, susceptible | 1434 | 67.4 | 65.40–69.40 |
| Factors/Variables | HBV Exposure a N (%) | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | Adjusted OR c (95%CI) | p-Value b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||||
| ≤45 | 14/452 | 3.1 | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| 46–60 | 37/438 | 8.4 | 2.88 (1.53–5.42) | 0.001 | 1.26 (0.62–2.57) | 0.526 |
| >60 | 233/828 | 28.1 | 12.25 (7.04–21.30) | 0.000 | 3.46 (1.70–7.04) | 0.001 |
| Gender | ||||||
| Female | 160/1006 | 15.9 | 1 | |||
| Male | 124/712 | 17.4 | 1.11 (0.86–1.44) | 0.406 | - | - |
| Marital status | ||||||
| Separated/divorced | 61/246 | 24.8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| Married | 202/1122 | 18.0 | 0.67 (0.48–0.92) | 0.015 | 1.01 (0.68–1.51) | 0.929 |
| Single | 21/350 | 6.0 | 0.15 (0.11–0.32) | 0.000 | 1.17 (0.56–2.44) | 0.674 |
| Recruitment site | ||||||
| Association A | 40/366 | 10.9 | 1 | - | 1 | - |
| Association B | 69/563 | 12.4 | 1.14 (0.75–1.72) | 0.539 | 1.40 (0.88–2.25) | 0.150 |
| Association C | 41/237 | 17.3 | 1.70 (1.06–2.73) | 0.026 | 2.63 (1.53–4.51) | 0.000 |
| Association D | 74/269 | 27.5 | 3.10 (2.02–4.72) | 0.000 | 2.96 (1.82–4.81) | 0.000 |
| Association E | 60/283 | 21.2 | 2.19 (1.42–3.39) | 0.000 | 2.74 (1.66–4.51) | 0.000 |
| Family heritage b | ||||||
| Grandchild/great-grandchild of Japanese | 21/537 | 3.91 | 1 | 1 | 1 | - |
| Japanese son/daughter | 135/856 | 15.7 | 4.60 (2.86–7.38) | 0.000 | 2.39 (1.38–4.12) | 0.002 |
| Japanese immigrant | 127/287 | 44.2 | 19.50 (11.89–31.98) | 0.000 | 6.79 (3.45–13.38) | 0.000 |
| Okinawan descendant | ||||||
| No | 22/210 | 10.48 | 1 | - | ||
| Yes | 262/1508 | 17.3 | 1.79 (1.13–2.85) | 0.013 | 1.07 (0.62–1.85) | 0.802 |
| History of residence in Japan | ||||||
| No | 109/1017 | 10.7 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Yes | 175/701 | 24.9 | 2.77 (2.13–3.60) | 0.000 | 1.21 (0.81–1.80) | 0.339 |
| Education (years) b | ||||||
| >9 | 152/1172 | 12.9 | 1 | 1 | ||
| <9 | 130/534 | 24.3 | 2.16 (1.66–2.80) | 0.000 | 1.06 (0.74–1.53) | 0.742 |
| Income b | ||||||
| >3 minimum wage (0) | 138/998 | 13.8 | 1 | 1 | ||
| 1 to 3 minimum wages (2) | 104/483 | 21.5 | 1.71 (1.29–2.27) | 0.000 | 1.08 (0.76–1.54) | 0.660 |
| <1 minimum wage (3) | 22/109 | 20.2 | 1.57 (0.95–2.60) | 0.075 | 0.91 (0.51–1.62) | 0.760 |
| Piercing | ||||||
| No | 281/1663 | 16.90 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 3/55 | 5.45 | 0.28 (0.87–0.91) | 0.025 d | 0.50 (0.62–4.12) | 0.524 |
| History of surgery | ||||||
| No | 78/551 | 14.16 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 206/1167 | 17.65 | 1.29 (0.98–1.72) | 0.069 | 0.85 (0.59–1.19) | 0.347 |
| Tattooing | ||||||
| No | 271/1609 | 16.84 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 13/109 | 11.93 | 0.67 (0.37–1.21) | 0.184 | 0.78 (0.39–1.56) | 0.484 |
| Shared personal sharp objects | ||||||
| No | 187/1037 | 18.03 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Yes | 97/681 | 14.24 | 0.75 (0.57–0.98) | 0.039 | 1.02 (0.73–1.41) | 0.906 |
| Non-injectable drug usage | ||||||
| No | 281/1679 | 16.7 | 1 | |||
| Yes | 3/39 | 7.7 | 0.41 (0.13–1.35) | 0.145 | 0.39 (0.11–1.40) | 0.150 |
| Sexually transmitted infection (STI) b | ||||||
| No | 255/1546 | 16.49 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Yes | 29/124 | 23.39 | 1.54 (0.99–2.39) | 0.051 | 1.20 (0.71–2.04) | 0.495 |
| Condom use b | ||||||
| Always | 29/217 | 13.36 | 1 | |||
| Sometimes/never | 248/1332 | 18.62 | 0.67 (0.44–1.02) | 0.062 | 1.26 (0.75–2.11) | 0.382 |
| Anti-HTLV positivity | ||||||
| No | 252/1626 | 15.50 | ||||
| Yes | 32/92 | 34.78 | 2.90 (1.80–4.56) | 0.000 | 1.32 (0.78–2.24) | 0.297 |
| ID | Age (Years) | Recruitment Site | Gender | Serological Markers | HBV Viral Load (log) | HBV Subgenotype | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBeAg | Anti-HBe | Anti-HTLV | ||||||
| 49 a | 63 | A | M | Negative | Positive | Negative | <1.00 | NP |
| 481 a | 82 | B | M | Negative | Positive | Negative | 2.79 | B1 |
| 533 a | 73 | B | M | Negative | Positive | Positive | 2.07 | C2 |
| 815 b | 44 | B | M | Negative | Positive | Negative | 1.4 | NP |
| 836 a | 60 | B | F | Negative | Positive | Negative | 2.25 | B1 |
| 851 a | 66 | B | M | Negative | Positive | Negative | 1.98 | B1 |
| 1156 b | 69 | B | M | Negative | Positive | Negative | 1.57 | A1 |
| 1189 a | 58 | C | M | Negative | Positive | Negative | 3.32 | B1 |
| 1338 b | 77 | C | F | Negative | Positive | Positive | ND | NP |
| 1367 a | 56 | C | F | Negative | Positive | Negative | ND | NP |
| 1576 b | 71 | D | M | Negative | Negative | Negative | ND | NP |
| 1592 a | 73 | D | F | Negative | Negative | Negative | ND | NP |
| 1596 b | 68 | D | M | Negative | Negative | Negative | ND | NP |
| 1621 a | 67 | D | M | NP | Positive | Positive | NP | NP |
| 1646 c | 47 | D | F | Negative | Negative | Negative | NP | NP |
| 1677 a | 67 | D | F | Negative | Positive | Negative | ND | NP |
| 1751 b | 64 | D | M | Negative | Negative | Negative | ND | NP |
| 1916 c | 39 | E | M | Negative | Negative | Negative | ND | NP |
| 1922 a | 64 | E | F | Negative | Positive | Negative | 2.53 | NP |
| 1960 b | 52 | E | F | Negative | Positive | Negative | 2.69 | F1b |
| 1974 a | 66 | E | F | Negative | Positive | Negative | 1.6 | NP |
| 2052 b | 75 | E | M | Negative | Positive | Negative | 2.12 | B1 |
| ID | Age (Years) | Recruitment Site | Gender | Serological Markers | HBV Viral Load (log) | Subgenotype | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HBeAg | Anti-HBe | ||||||
| 49 a | 63 | A | M | Negative | Positive | <1.00 | NP |
| 168 | 42 | A | M | NP | NP | <1.00 | NP |
| 317 | 70 | A | F | NP | NP | 1.66 | NP |
| 487 | 87 | B | F | NP | NP | <1.00 | NP |
| 815 b | 44 | B | M | Negative | Positive | 1.4 | NP |
| 935 | 72 | B | M | NP | NP | 1.02 | NP |
| 976 | 66 | B | M | NP | NP | <1.00 | NP |
| 1313 | 34 | C | F | NP | NP | <1.00 | NP |
| 1604 | 64 | D | F | NP | NP | 1.67 | NP |
| 1922 a | 64 | E | F | Negative | Positive | 2.53 | NP |
| 1974 a | 66 | E | F | Negative | Positive | 1.6 | NP |
| 2087 | 75 | E | F | NP | NP | <1.00 | NP |
| 2103 | 65 | E | M | NP | NP | <1.00 | NP |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demarchi, L.H.F.; Bandeira, L.M.; Taira, D.L.; Zardin, M.C.S.U.; Ibanhes, M.L.; Esposito, A.O.P.; De Arruda, L.D.C.; Gonçalves, C.C.M.; Weis-Torres, S.M.d.S.; Cesar, G.A.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Japanese Immigrants and Descendants: The Need to Strengthen Preventive and Control Measures. Viruses 2022, 14, 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14051085
Demarchi LHF, Bandeira LM, Taira DL, Zardin MCSU, Ibanhes ML, Esposito AOP, De Arruda LDC, Gonçalves CCM, Weis-Torres SMdS, Cesar GA, et al. Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Japanese Immigrants and Descendants: The Need to Strengthen Preventive and Control Measures. Viruses. 2022; 14(5):1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14051085
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemarchi, Luiz Henrique Ferraz, Larissa Melo Bandeira, Deborah Ledesma Taira, Marina Castilhos Souza Umaki Zardin, Mary Luizia Ibanhes, Ana Olivia Pascoto Esposito, Larissa Domingues Castilho De Arruda, Crhistinne Cavalheiro Maymone Gonçalves, Sabrina Moreira dos Santos Weis-Torres, Gabriela Alves Cesar, and et al. 2022. "Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Japanese Immigrants and Descendants: The Need to Strengthen Preventive and Control Measures" Viruses 14, no. 5: 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14051085
APA StyleDemarchi, L. H. F., Bandeira, L. M., Taira, D. L., Zardin, M. C. S. U., Ibanhes, M. L., Esposito, A. O. P., De Arruda, L. D. C., Gonçalves, C. C. M., Weis-Torres, S. M. d. S., Cesar, G. A., Da Cunha, R. V., Tanaka, T. S. O., Puga, M. A. M., De Rezende, G. R., Lopes, R. B., Uehara, S. N. d. O., Pinho, J. R. R., Carrilho, F. J., Gomes-Gouvêa, M. S., & Motta-Castro, A. R. C. (2022). Hepatitis B Virus Infection among Japanese Immigrants and Descendants: The Need to Strengthen Preventive and Control Measures. Viruses, 14(5), 1085. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14051085









