Complexity of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection in South African HIV-Exposed Infants with Pneumonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Specimens
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction and HCMV and HIV Testing
2.3. High-Throughput DNA Sequencing
2.4. Sequencing Data Analysis, Strain Composition, Genome Assembly, and Compartmentalization
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Specimen Data
3.2. Quality Assessment of Sequencing Libraries, and Strain Enumeration
3.3. HCMV Genomes Assembled
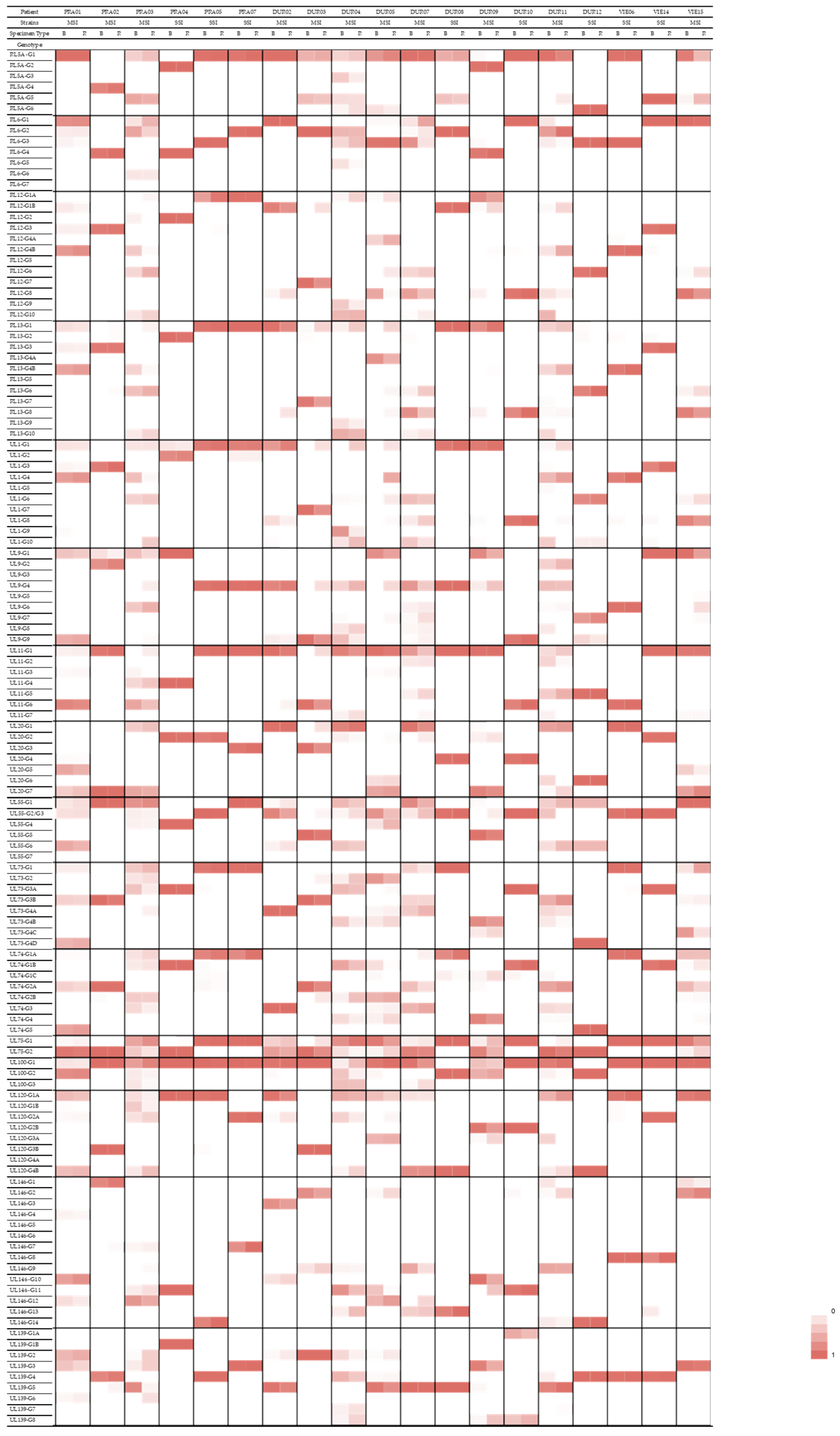
3.4. Analysis of Genotype and Variant Differences between the Cohorts
3.5. Compartmentalization of Genotypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mocarski, E.S. Cytomegaloviruses. In Fields Virology; Knipe, D.M., Ed.; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; Volume 2, pp. 2702–2772. [Google Scholar]
- Manicklal, S.; van Niekerk, A.M.; Kroon, S.M.; Hutto, C.; Novak, Z.; Pati, S.K.; Chowdhury, N.; Hsiao, N.Y.; Boppana, S.B. Birth prevalence of congenital cytomegalovirus among infants of HIV-infected women on prenatal antiretroviral prophylaxis in South Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mwaanza, N.; Chilukutu, L.; Tembo, J.; Kabwe, M.; Musonda, K.; Kapasa, M.; Chabala, C.; Sinyangwe, S.; Mwaba, P.; Zumla, A.; et al. High rates of congenital cytomegalovirus infection linked with maternal HIV infection among neonatal admissions at a large referral center in sub-Saharan Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manicklal, S.; Emery, V.C.; Lazzarotto, T.; Boppana, S.B.; Gupta, R.K. The “silent” global burden of congenital cytomegalovirus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaye, S.; Miles, D.; Antoine, P.; Burny, W.; Ojuola, B.; Kaye, P.; Rowland-Jones, S.; Whittle, H.; van der Sande, M.; Marchant, A. Virological and immunological correlates of mother-to-child transmission of cytomegalovirus in The Gambia. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, B.A.; John-Stewart, G.; Atkinson, C.; Nduati, R.; Asbjornsdottir, K.; Boeckh, M.; Overbaugh, J.; Emery, V.; Slyker, J.A. Vertical Cytomegalovirus Transmission From HIV-Infected Women Randomized to Formula-Feed or Breastfeed Their Infants. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Knight, M.A.; Nduati, E.; Hassan, A.S.; Nkumama, I.; Etyang, T.J.; Hajj, N.J.; Gambo, F.; Odera, D.; Berkley, J.A.; Rowland-Jones, S.L.; et al. Cytomegalovirus viraemia is associated with poor growth and T-cell activation with an increased burden in HIV-exposed uninfected infants. Aids 2017, 31, 1809–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filteau, S.; Rowland-Jones, S. Cytomegalovirus Infection May Contribute to the Reduced Immune Function, Growth, Development, and Health of HIV-Exposed, Uninfected African Children. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gompels, U.A.; Larke, N.; Sanz-Ramos, M.; Bates, M.; Musonda, K.; Manno, D.; Siame, J.; Monze, M.; Filteau, S.; Group, C.S. Human cytomegalovirus infant infection adversely affects growth and development in maternally HIV-exposed and unexposed infants in Zambia. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronborg, H.L.; Jespersen, S.; Honge, B.L.; Jensen-Fangel, S.; Wejse, C. Review of cytomegalovirus coinfection in HIV-infected individuals in Africa. Rev. Med. Virol. 2017, 27, e1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slyker, J.A.; Lohman-Payne, B.L.; Rowland-Jones, S.L.; Otieno, P.; Maleche-Obimbo, E.; Richardson, B.; Farquhar, C.; Mbori-Ngacha, D.; Emery, V.C.; John-Stewart, G.C. The detection of cytomegalovirus DNA in maternal plasma is associated with mortality in HIV-1-infected women and their infants. AIDS 2009, 23, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Itzikowitz, R.; Young, B.; Machoki, S.M.; Hsiao, N.Y.; Pillay, K.; Alexander, A. Surgical manifestations of gastrointestinal cytomegalovirus infection in children: Clinical audit and literature review. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2015, 50, 1874–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goussard, P.; Kling, S.; Gie, R.P.; Nel, E.D.; Heyns, L.; Rossouw, G.J.; Janson, J.T. CMV pneumonia in HIV-infected ventilated infants. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2010, 45, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampoli, M.; Morrow, B.; Hsiao, N.Y.; Whitelaw, A.; Zar, H.J. Prevalence and outcome of cytomegalovirus-associated pneumonia in relation to human immunodeficiency virus infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, M.; Shibemba, A.; Mudenda, V.; Chimoga, C.; Tembo, J.; Kabwe, M.; Chilufya, M.; Hoelscher, M.; Maeurer, M.; Sinyangwe, S.; et al. Burden of respiratory tract infections at post mortem in Zambian children. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeena, P.M.; Govender, K.; Parboosing, R.; Adhikari, M. The significance of cytomegalovirus in children with pneumonia admitted for mechanical ventilation. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2017, 21, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.; Reeves, M. Pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus in the immunocompromised host. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 759–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govender, K.; Msomi, N.; Moodley, P.; Parboosing, R. Cytomegalovirus pneumonia of infants in Africa: A narrative literature review. Future Microbiol. 2021, 16, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puchhammer-Stöckl, E.; Görzer, I. Human cytomegalovirus: An enormous variety of strains and their possible clinical significance in the human host. Future Virol. 2011, 6, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arav-Boger, R. Strain Variation and Disease Severity in Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: In Search of a Viral Marker. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 29, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renzette, N.; Gibson, L.; Jensen, J.D.; Kowalik, T.F. Human cytomegalovirus intrahost evolution-a new avenue for understanding and controlling herpesvirus infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 8, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer-Konig, U.; Vogelberg, C.; Bongarts, A.; Kampa, D.; Delbruck, R.; Wolff-Vorbeck, G.; Kirste, G.; Haberland, M.; Hufert, F.T.; von Laer, D. Glycoprotein B genotype correlates with cell tropism in vivo of human cytomegalovirus infection. J. Med. Virol. 1998, 55, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Slyker, J.A.; Roy, S.; Bryant, J.; Atkinson, C.; Cudini, J.; Farquhar, C.; Griffiths, P.; Kiarie, J.; Morfopoulou, S.; et al. Mixed cytomegalovirus genotypes in HIV-positive mothers show compartmentalization and distinct patterns of transmission to infants. eLife 2020, 9, e63199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slyker, J.; Farquhar, C.; Atkinson, C.; Asbjornsdottir, K.; Roxby, A.; Drake, A.; Kiarie, J.; Wald, A.; Boeckh, M.; Richardson, B.; et al. Compartmentalized cytomegalovirus replication and transmission in the setting of maternal HIV-1 infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coaquette, A.; Bourgeois, A.; Dirand, C.; Varin, A.; Chen, W.; Herbein, G. Mixed cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B genotypes in immunocompromised patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 39, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Govender, K.; Jeena, P.; Parboosing, R. Clinical utility of bronchoalveolar lavage cytomegalovirus viral loads in the diagnosis of cytomegalovirus pneumonitis in infants. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bates, M.; Monze, M.; Bima, H.; Kapambwe, M.; Kasolo, F.C.; Gompels, U.A.; CIGNIS Study Group. High human cytomegalovirus loads and diverse linked variable genotypes in both HIV-1 infected and exposed, but uninfected, children in Africa. Virology 2008, 382, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.Y.; Valencia, S.M.; Pfeifer, S.P.; Jensen, J.D.; Kowalik, T.F.; Permar, S.R. Common Polymorphisms in the Glycoproteins of Human Cytomegalovirus and Associated Strain-Specific Immunity. Viruses 2021, 13, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, E.; Wilkie, G.S.; Linnenweber-Held, S.; Dhingra, A.; Suarez, N.M.; Schmidt, J.J.; Kay-Fedorov, P.C.; Mischak-Weissinger, E.; Heim, A.; Schwarz, A.; et al. Characterization of Human Cytomegalovirus Genome Diversity in Immunocompromised Hosts by Whole-Genome Sequencing Directly From Clinical Specimens. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1673–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, N.M.; Musonda, K.G.; Escriva, E.; Njenga, M.; Agbueze, A.; Camiolo, S.; Davison, A.J.; Gompels, U.A. Multiple-Strain Infections of Human Cytomegalovirus With High Genomic Diversity Are Common in Breast Milk From Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Women in Zambia. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalser, J.; Adler, B.; Mach, M.; Kropff, B.; Puchhammer-Stockl, E.; Gorzer, I. Differences in Growth Properties among Two Human Cytomegalovirus Glycoprotein O Genotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Kimura, H.; Iida, K.; Saito, Y.; Tsuge, I.; Yoshimi, A.; Matsuyama, T.; Morishima, T. Quantitative analysis of cytomegalovirus load using a real-time PCR assay. J. Med. Virol. 2000, 60, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, N.M.; Wilkie, G.S.; Hage, E.; Camiolo, S.; Holton, M.; Hughes, J.; Maabar, M.; Vattipally, S.B.; Dhingra, A.; Gompels, U.A.; et al. Human Cytomegalovirus Genomes Sequenced Directly From Clinical Material: Variation, Multiple-Strain Infection, Recombination, and Gene Loss. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camiolo, S.; Suarez, N.M.; Chalka, A.; Venturini, C.; Breuer, J.; Davison, A.J. GRACy: A tool for analysing human cytomegalovirus sequence data. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veaa099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, G.G.; Dutilh, B.E.; Matthews, T.D.; Elkins, K.; Schmieder, R.; Dinsdale, E.A.; Edwards, R.A. Combining de novo and reference-guided assembly with scaffold_builder. Source Code Biol. Med. 2013, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milne, I.; Stephen, G.; Bayer, M.; Cock, P.J.; Pritchard, L.; Cardle, L.; Shaw, P.D.; Marshall, D. Using Tablet for visual exploration of second-generation sequencing data. Brief. Bioinform. 2013, 14, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marti-Carreras, J.; Maes, P. Human cytomegalovirus genomics and transcriptomics through the lens of next-generation sequencing: Revision and future challenges. Virus Genes 2019, 55, 138–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musonda, K.G.; Nyonda, M.; Filteau, S.; Kasonka, L.; Monze, M.; Gompels, U.A. Increased Cytomegalovirus Secretion and Risks of Infant Infection by Breastfeeding Duration From Maternal Human Immunodeficiency Virus Positive Compared to Negative Mothers in Sub-Saharan Africa. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2016, 5, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sowmya, P.; Madhavan, H.N. Analysis of mixed infections by multiple genotypes of human cytomegalovirus in immunocompromised patients. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.J.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Jahn, G.; Xiong, H.R.; Yang, Z.Q.; Liu, Y.Y. Human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein polymorphisms and increasing viral load in AIDS patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shikhagaie, M.; Merce-Maldonado, E.; Isern, E.; Muntasell, A.; Alba, M.M.; Lopez-Botet, M.; Hengel, H.; Angulo, A. The human cytomegalovirus-specific UL1 gene encodes a late-phase glycoprotein incorporated in the virion envelope. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4091–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.J.; Park, A.; Kang, S.; Lee, E.; Lee, T.A.; Ra, E.A.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Park, B. Human cytomegalovirus-encoded US9 targets MAVS and STING signaling to evade type I interferon immune responses. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ourahmane, A.; Cui, X.; He, L.; Catron, M.; Dittmer, D.P.; Al Qaffasaa, A.; Schleiss, M.R.; Hertel, L.; McVoy, M.A. Inclusion of Antibodies to Cell Culture Media Preserves the Integrity of Genes Encoding RL13 and the Pentameric Complex Components During Fibroblast Passage of Human Cytomegalovirus. Viruses 2019, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, C.C.; Kamil, J.P. Pathogen at the Gates: Human Cytomegalovirus Entry and Cell Tropism. Viruses 2018, 10, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabanova, A.; Marcandalli, J.; Zhou, T.; Bianchi, S.; Baxa, U.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Lilleri, D.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Foglierini, M.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, B.M.; et al. Platelet-derived growth factor-alpha receptor is the cellular receptor for human cytomegalovirus gHgLgO trimer. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endale, M.; Ahlfeld, S.; Bao, E.; Chen, X.; Green, J.; Bess, Z.; Weirauch, M.T.; Xu, Y.; Perl, A.K. Temporal, spatial, and phenotypical changes of PDGFRalpha expressing fibroblasts during late lung development. Dev. Biol. 2017, 425, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouveia, L.; Betsholtz, C.; Andrae, J. Expression analysis of platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and its ligands in the developing mouse lung. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bons, E.; Regoes, R.R. Virus dynamics and phyloanatomy: Merging population dynamic and phylogenetic approaches. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 285, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, N.M.; Blyth, E.; Li, K.; Ganzenmueller, T.; Camiolo, S.; Avdic, S.; Withers, B.; Linnenweber-Held, S.; Gwinner, W.; Dhingra, A.; et al. Whole-Genome Approach to Assessing Human Cytomegalovirus Dynamics in Transplant Patients Undergoing Antiviral Therapy. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNAIDS FACT SHEET. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/UNAIDS_FactSheet_en.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2022).
| Patient Code | Patient Location | Patient Diagnosis | Patient Age | HIV Status | Days Post-Transplant | Donor/Recipient HCMV Serostatus | Blood HCMV Load (Genome Copies/mL) | Respiratory HCMV Load (Genome Copies/mL) | Respiratory Specimen Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DUR01 | South Africa | HIV-exposed infants with HCMV pneumonia a | 4 months | Negative | N/A | N/A | 48,600 | 11,615 | NBBAL |
| DUR02 | South Africa | 2 months | Negative | N/A | N/A | 26,487 | 10,230 | NBBAL | |
| DUR03 | South Africa | 4 months | Negative | N/A | N/A | 80,676 | 981,721 | NBBAL | |
| DUR04 | South Africa | 4 months | Positive | N/A | N/A | 71,199 | 2,019,329 | NBBAL | |
| DUR05 | South Africa | 2 months | Negative | N/A | N/A | 34,263 | 181,278 | NBBAL | |
| DUR06 | South Africa | 7 months | Positive | N/A | N/A | 7363 | 58,320 | NBBAL | |
| DUR07 | South Africa | 3 months | Positive | N/A | N/A | 58,806 | 84,564 | NBBAL | |
| DUR08 | South Africa | 3 months | Positive | N/A | N/A | 8942 | 63,909 | NBBAL | |
| DUR09 | South Africa | 2 months | Negative | N/A | N/A | 49,572 | 24,276 | NBBAL | |
| DUR10 | South Africa | 7 months | Positive | N/A | N/A | 32,562 | 132,435 | NBBAL | |
| DUR11 | South Africa | 3 months | Positive | N/A | N/A | 35,721 | 2,964,599 | NBBAL | |
| DUR12 | South Africa | 5 months | Positive | N/A | N/A | 826,200 | 777,600 | NBBAL | |
| PRA01 | Czech Republic | AML | 52 years | Negative | N/A | N/A | 5,900,000 | 867,500 | BAL |
| PRA02 | Czech Republic | HSCT | 62 years | Negative | 67 | D−/R+ | 246,500 | 55,250 | BAL |
| PRA03 | Czech Republic | HSCT | 58 years | Negative | 62 | D+/R+ | 133,000 | 672,500 | ETA |
| PRA04 | Czech Republic | HSCT | 21 years | Negative | 227 | D−/R+ | 5,537,500 | 893,750 | BAL |
| PRA05 | Czech Republic | MDS | 21 years | Negative | N/A | N/A | 903,750 | 785,000 | ETA |
| PRA06 | Czech Republic | Hyper IgM syndrome | 8 months | Negative | N/A | N/A | 20,750 | 198,500 | ETA |
| PRA07 | Czech Republic | HSCT | 58 years | Negative | 252 | D−/R+ | 56,750 | 980,000 | BAL |
| VIE04 | Austria | COPD | 49 years | Negative | 183 | D+R+ | 6630 | 55,400 | BAL |
| VIE06 | Austria | Pulmonary hypertension | 32 years | Negative | 169 | D+/R− | 11,300 | 1620 | BAL |
| VIE08 | Austria | COPD | 46 years | Negative | 187 | D−/R+ | 3390 | 3650 | BAL |
| VIE13 | Austria | Pulmonary fibrosis | 50 years | Negative | 206 | D−/R+ | 24,800 | 101,000 | BAL |
| VIE14 | Austria | COPD | 52 years | Negative | 219 | D+R+ | 16,400 | 132,000 | BAL |
| VIE15 | Austria | Pulmonary fibrosis | 43 years | Negative | 167 | D−/R+ | 18,100 | 62,200 | BAL |
| VIE16 | Austria | COPD | 56 years | Negative | 456 | D+R+ | 12,300 | 2380 | BAL |
| VIE17 | Austria | Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency | 54 years | Negative | 55 | D+R− | 1310 | 28,900 | BAL |
| VIE21 | Austria | COPD | 57 years | Negative | 185 | D+R− | 1200 | 11,900 | BAL |
| VIE24 | Austria | Bronchiectasis | 42 years | Negative | 176 | D+R+ | 35,800 | 134,000 | BAL |
| Gene Family/Function | Gene Locus | Genotype | Prevalence (%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV-Exposed Infants (South African Cohort) (n = 12 Patients) | Patients with HD and LT Recipients (Czech Republic and Austrian Cohorts) (n = 17 Patients) | ||||
| RL11 family of membrane glycoproteins | UL9 | G4 | 10 (83.3%) | 5 (29.4%) | 0.008 |
| G8 | 4 (33.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.021 | ||
| Glycoprotein B | UL55 | G2 | 8 (66.7%) | 2 (11.8%) | 0.005 |
| G5 | 4 (33.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.021 | ||
| Glycoprotein N | UL73 | G4B | 5 (41.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.007 |
| Glycoprotein O | UL74 | G4 | 5 (41.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.007 |
| Glycoprotein M | UL100 | G2 | 9 (75.0%) | 3 (17.6%) | 0.006 |
| Membrane glycoprotein | UL120 | G4B | 7 (58.3%) | 2 (11.8%) | 0.014 |
| Gene Family/Function | Gene | Genotype | Patients with a Predominance of This Genotype in the Respiratory Specimen |
|---|---|---|---|
| RL11 family of membrane glycoproteins | RL13 | G1 | PRA02, PRA03, DUR03, DUR04, DUR05, DUR09, DUR11 |
| UL1 | G1 | PRA03, DUR02, DUR03, DUR04, DUR05, DUR09, DUR11 | |
| UL9 | G4 | PRA03, DUR02, DUR03, DUR04, DUR05, DUR09 | |
| UL11 | G1 | PRA01, PRA02, PRA03, DUR03, DUR09, DUR11 | |
| Glycoprotein H | UL75 | G1 | PRA01, PRA03, DUR02, DUR03, DUR04, DUR07, DUR09, DUR11 |
| Glycoprotein M | UL100 | G1 | PRA02, PRA03, DUR02, DUR04, DUR05, DUR11, VIE15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Govender, K.; Parboosing, R.; Camiolo, S.; Hubáček, P.; Görzer, I.; Puchhammer-Stöckl, E.; Suárez, N.M. Complexity of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection in South African HIV-Exposed Infants with Pneumonia. Viruses 2022, 14, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050855
Govender K, Parboosing R, Camiolo S, Hubáček P, Görzer I, Puchhammer-Stöckl E, Suárez NM. Complexity of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection in South African HIV-Exposed Infants with Pneumonia. Viruses. 2022; 14(5):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050855
Chicago/Turabian StyleGovender, Kerusha, Raveen Parboosing, Salvatore Camiolo, Petr Hubáček, Irene Görzer, Elisabeth Puchhammer-Stöckl, and Nicolás M. Suárez. 2022. "Complexity of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection in South African HIV-Exposed Infants with Pneumonia" Viruses 14, no. 5: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050855
APA StyleGovender, K., Parboosing, R., Camiolo, S., Hubáček, P., Görzer, I., Puchhammer-Stöckl, E., & Suárez, N. M. (2022). Complexity of Human Cytomegalovirus Infection in South African HIV-Exposed Infants with Pneumonia. Viruses, 14(5), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050855






