Changes in Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Subclasses over Time and in Association with Disease Severity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cohort Description
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Methodology
2.4. Quantitative Assessment of Anti-N Protein IgG
2.5. Quantitative Assessment of Anti-S Protein IgG
2.6. Analysis by Subclass
2.7. Quantitative Assessment by Anti-N Protein IgG Subclass
2.8. ELISA Readings
2.9. Statistical Analysis and Visualization
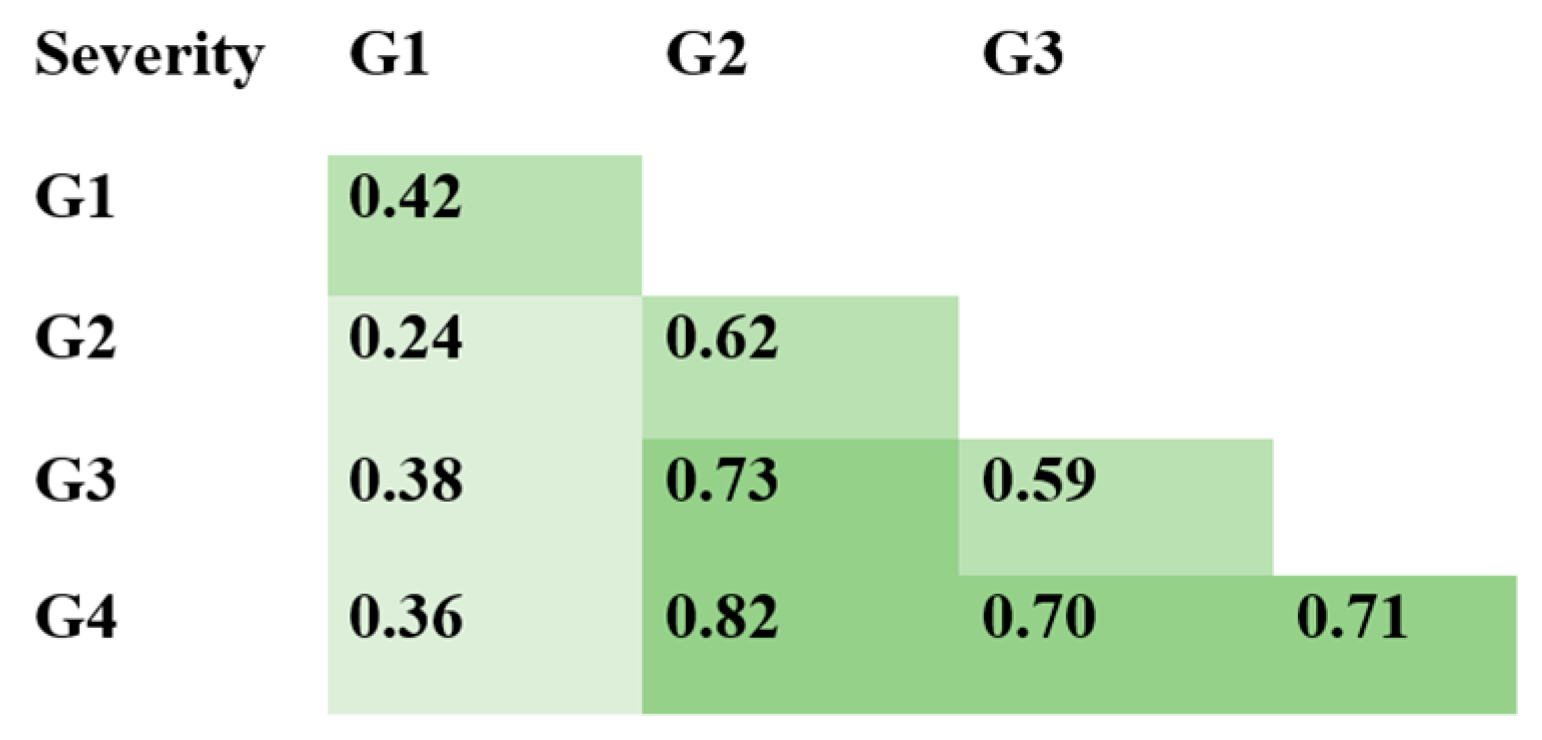
3. Results
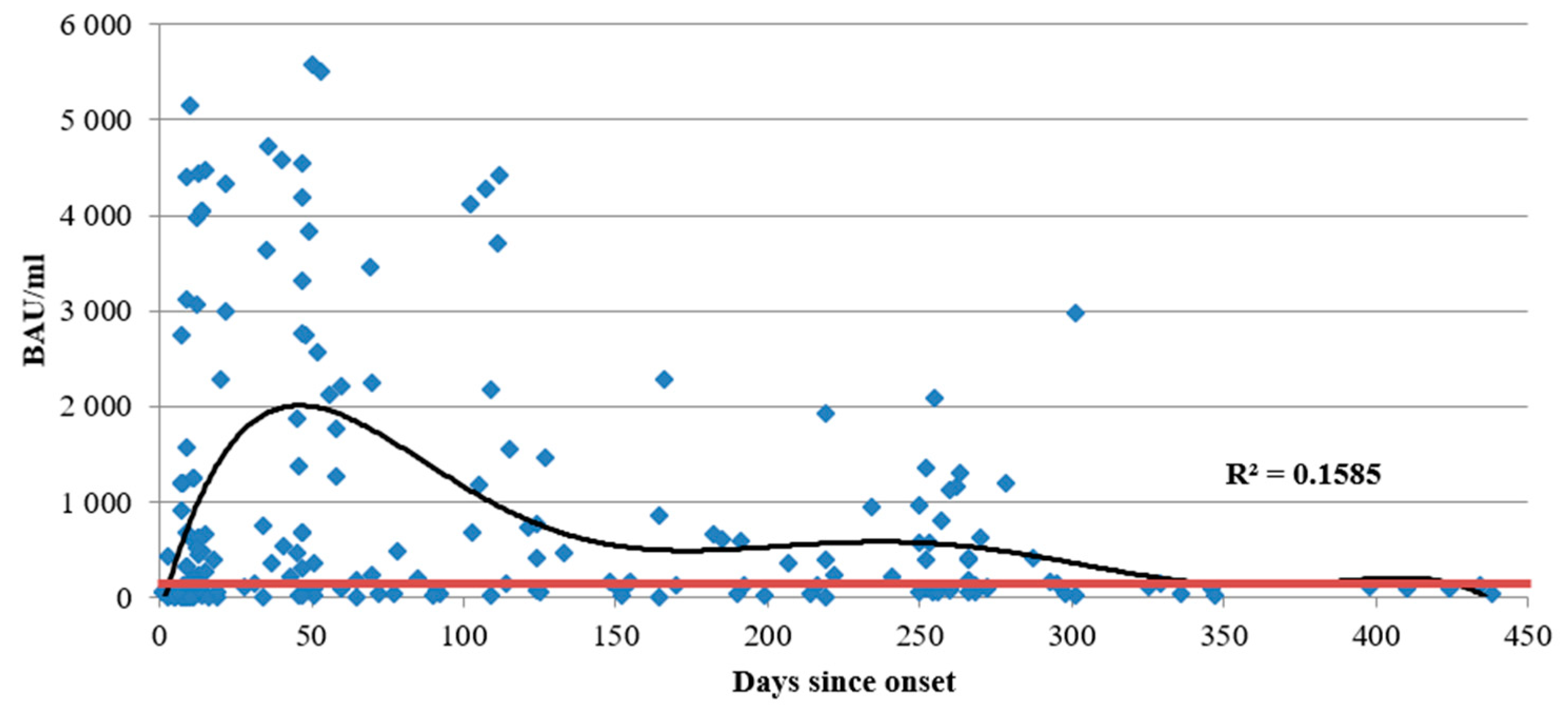
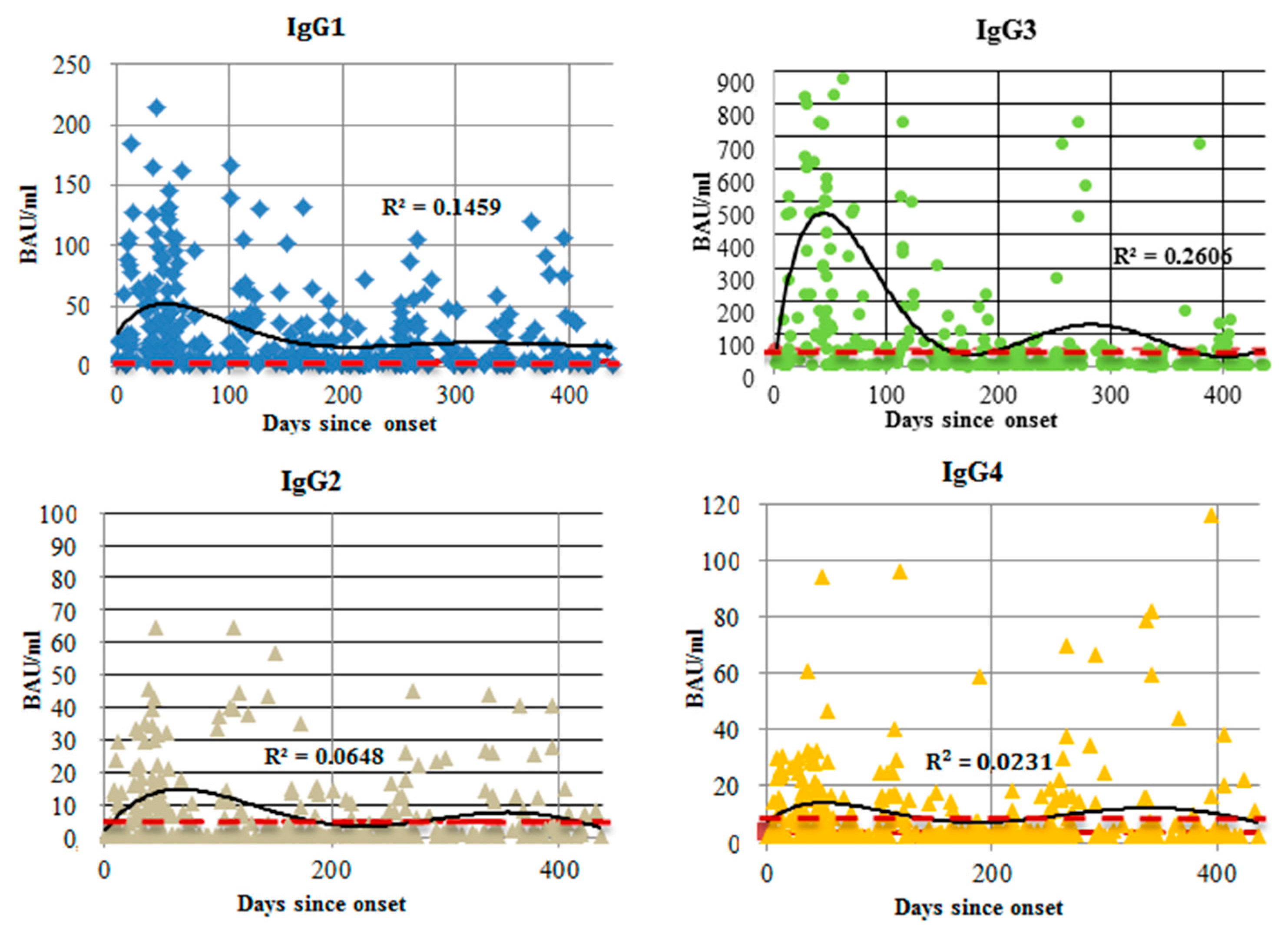
3.1. Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 N Protein
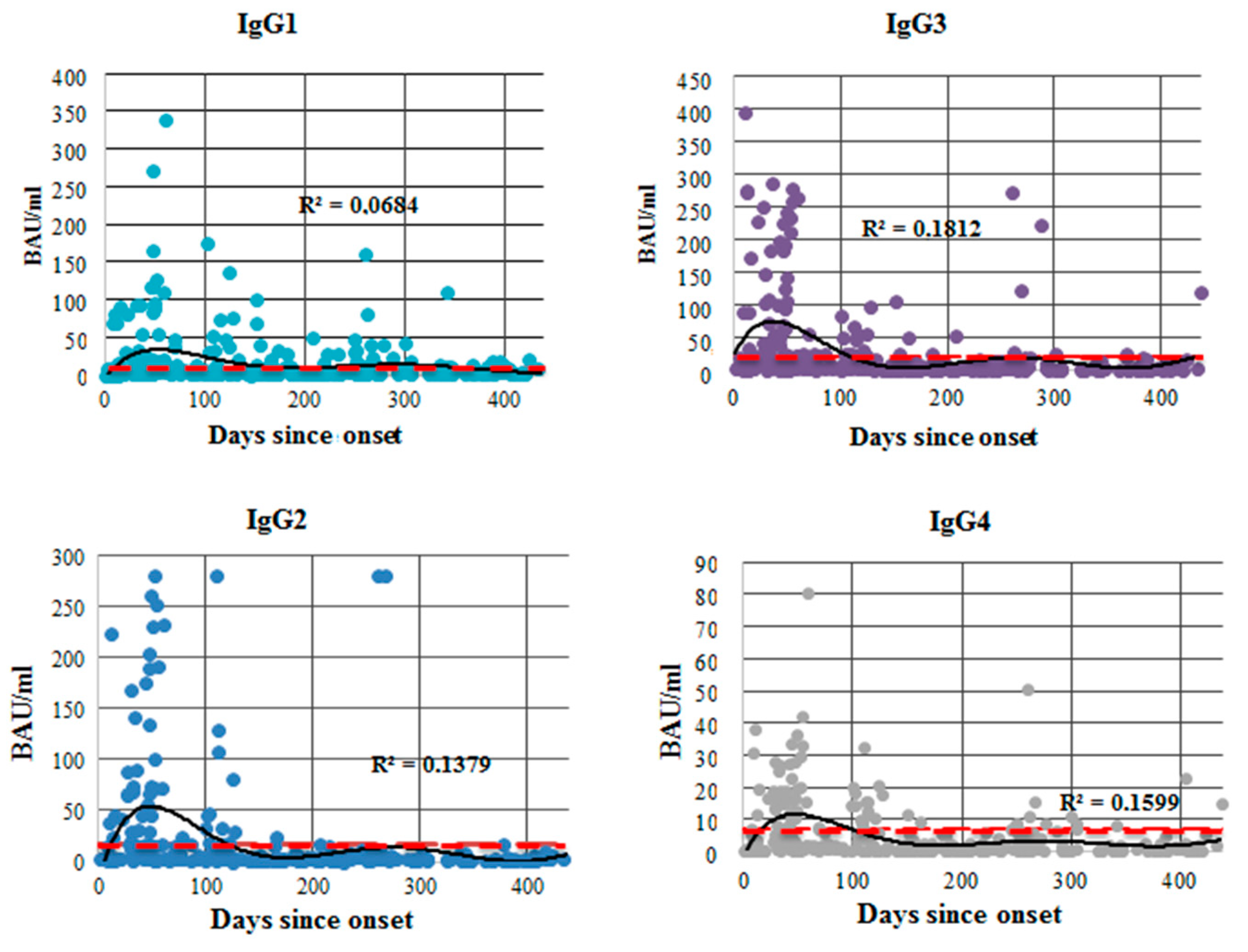
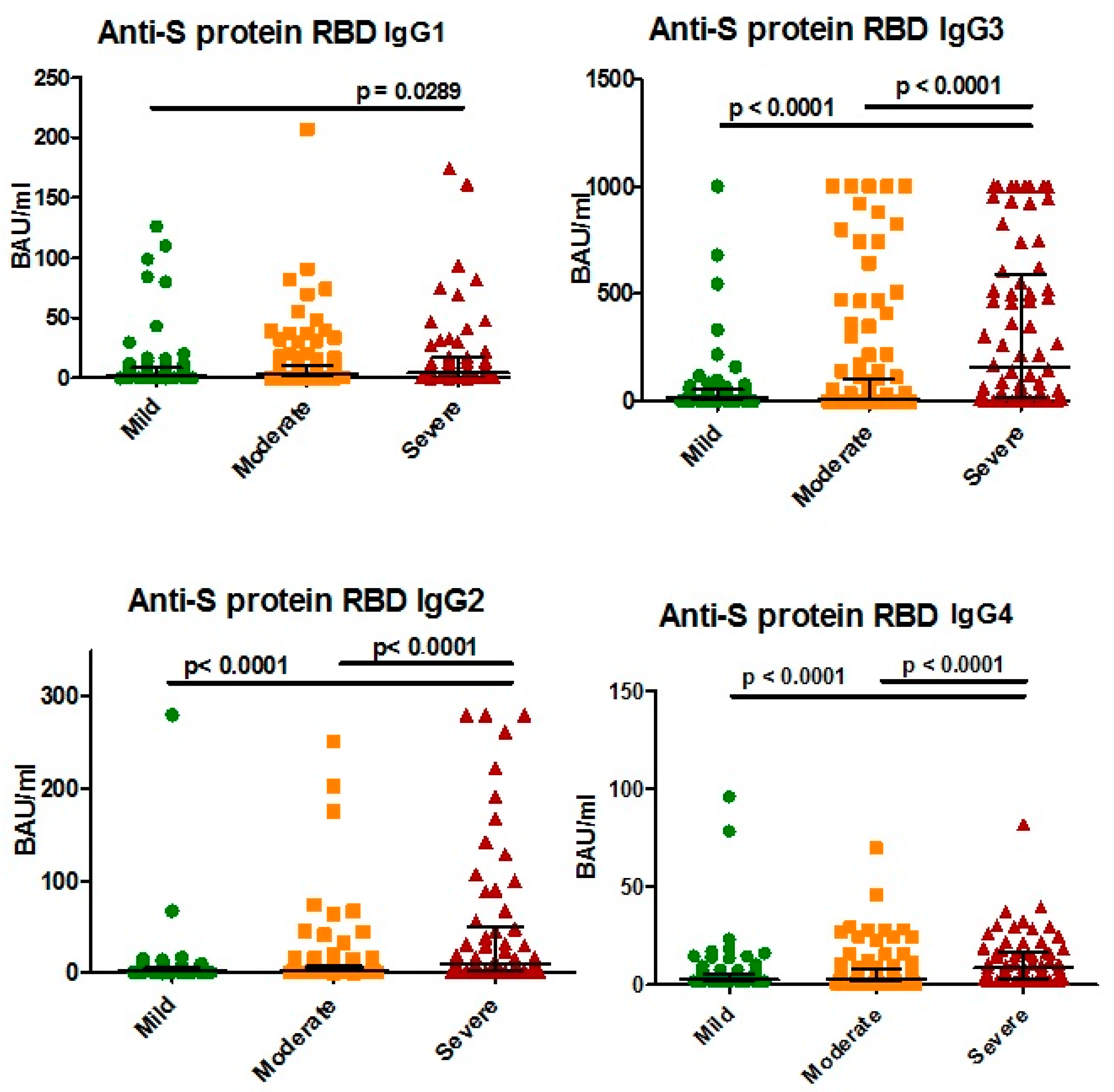
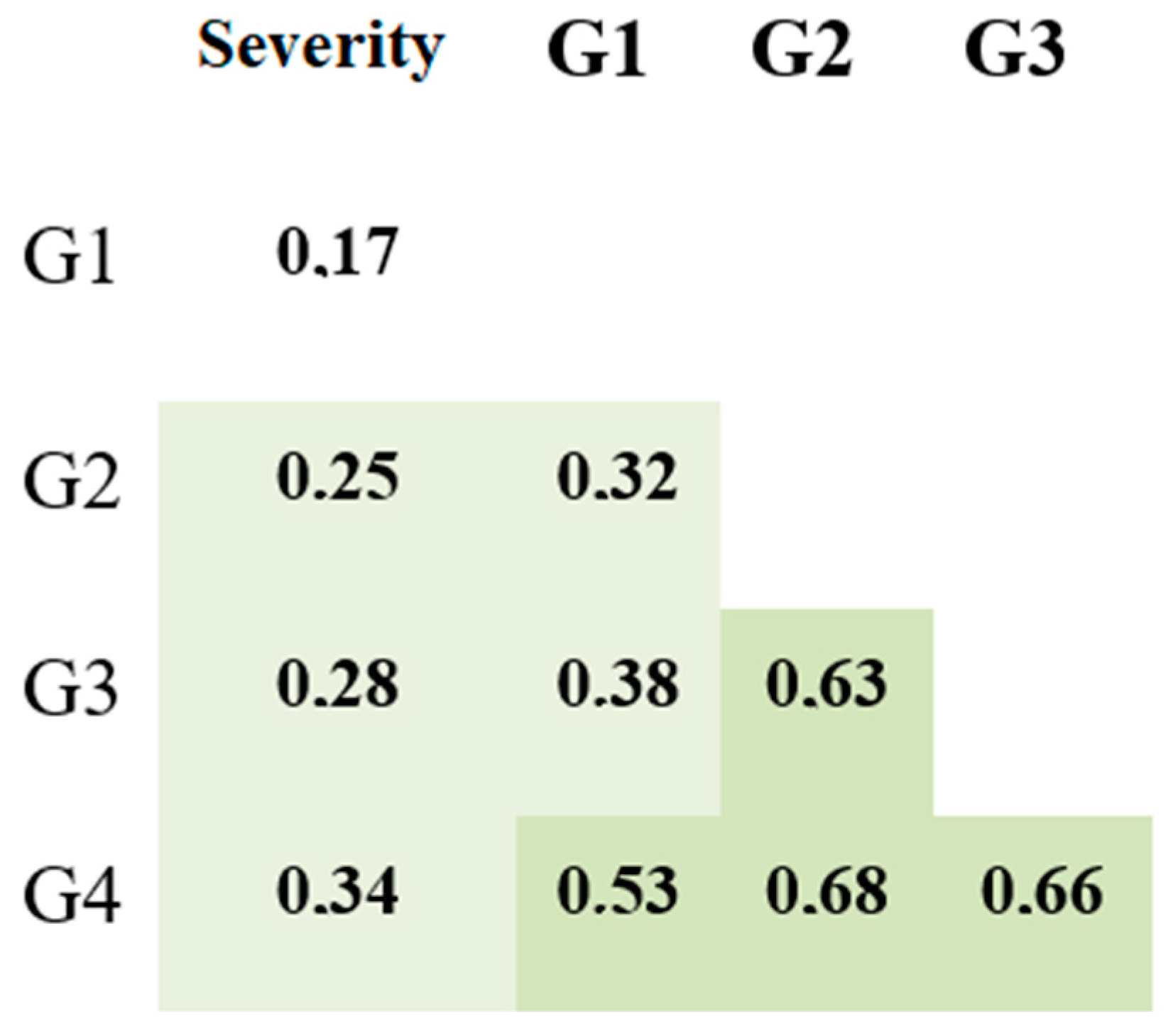
3.2. Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 S Protein
4. Discussion
4.1. Total Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Assessment
4.2. Anti-N Protein IgG Subclasses
4.3. Anti-S Protein IgG Subclasses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, F.; Zhao, S.; Yu, B.; Chen, Y.-M.; Wang, W.; Song, Z.-G.; Hu, Y.; Tao, Z.-W.; Tian, J.-H.; Pei, Y.-Y.; et al. A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China. Nature 2020, 579, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 29 March 2022).
- Struyf, T.; Deeks, J.J.; Dinnes, J.; Takwoingi, Y.; Davenport, C.; Leeflang, M.M.; Spijker, R.; Hooft, L.; Emperador, D.; Dittrich, S.; et al. Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19 disease. Cochrane COVID-19, Diagnostic Test Accuracy Group. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 7, CD013665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fields, B.K.K.; Demirjian, N.L.; Dadgar, H.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 312–320. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, Y.; Fong, S.; Poh, C.; Carissimo, G.; Yeo, N.K.; Amrun, S.N.; Goh, Y.S.; Lim, J.; Xu, W.; Chee, R.S.; et al. Asymptomatic COVID-19: Disease tolerance with efficient anti-viral immunity against SARS-CoV-2. EMBO Mol. Med. 2021, 13, e14045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.-X.; Liu, B.-Z.; Deng, H.-J.; Wu, G.-C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.-K.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.-F.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.F.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sho, B.; Abe, K.T.; Zuo, M.; Jamal, A.J.; Rathod, B.; Wang, J.H.; Li, Z.; Chao, G.; Rojas, O.L.; Bang, Y.M.; et al. Persistence of serum and saliva antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 spike antigens in COVID-19 patients. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eabe5511. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.; Gong, Y.; Mai, Y.; Li, B.; Zhu, X.; Wan, X.; Xie, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. Clinical and antibody characteristics reveal diverse signatures of severe and non-severe SARS-CoV-2 patients. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa Bastos, M.; Tavaziva, G.; Abidi, S.K.; Campbell, J.R.; Haraoui, L.; Johnston, J.C.; Haraoui, L.P.; Johnston, J.C.; Lan, Z.; Law, S.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of serological tests for COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 370, m2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chansaenroj, J.; Yorsaeng, R.; Posuwan, N.; Puenpa, J.; Yong, P. Long-term specific IgG response to SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein in recovered COVID-19 patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidarsson, G.; Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T. IgG subclasses and allotypes: From structure to effector functions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chvatal-Medina, M.; Mendez-Cortina, Y.; Patiño, P.J.; Velilla, P.A.; Rugeles, M.T. Antibody Responses in COVID-19: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 633184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, K.; Yang, H.; Liu, B.; Pang, X.; Du, J.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Jing, X.; Chen, J.; Deng, S.; et al. Antibodies Can Last for More Than 1 Year After SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Follow-Up Study from Survivors of COVID-19. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 684864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löfström, E.; Eringfält, A.; Kötz, A.; Wickbom, F.; Tham, J.; Lingman, M.; Nygren, J.M.; Undén, J. Dynamics of IgG-avidity and antibody levels after COVID-19. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 144, 104986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marklund, E.; Leach, S.; Axelsson, H.; Nystrm, K.; Norder, H.; Bemark, M.; Angeletti, D.; Lundgren, A.; Nilsson, S.; Andersson, L.M. Correction: Serum-IgG responses to SARS-CoV-2 after mild and severe COVID-19 infection and analysis of IgG non-responders. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glück, V.; Grobecker, S.; Tydykov, L.; Salzberger, B.; Peterhoff, D. SARS-CoV-2-directed antibodies persist for more than six months in a cohort with mild to moderate COVID-19. Infection 2021, 49, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspersen, K.A.; Greve, T.; Nielsen, K.J.; Jespersen, S.; Mikkelsen, S.; Vestergaard, J.M.; Redder, J.D.; Tolstrup, M.; Thomsen, M.K.; Møller, H.J.; et al. Symptoms reported by SARS-CoV-2 seropositive and seronegative healthcare and administrative employees in Denmark from May to August 2020. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 109, 17–23, PMCID:PMC8193970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popova, A.Y.; Smirnov, V.S.; Andreeva, E.E.; Babura, E.A.; Balakhonov, S.V.; Bashketova, N.S.; Bugorkova, S.A.; Bulanov, M.V.; Valeullina, N.N.; Vetrov, V.V.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence Structure of the Russian Population during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Viruses 2021, 13, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lustig, Y.; Mendelson, E.; Mandelboim, M.; Biber, A.; Levin, E.G.; Cohen, C.; Regev-Yochay, G.; Schwartz, E. Existence of immunological memory response in true sero-negative individuals post COVID-19 molecular diagnosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, ciac196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, Z.Q.; Anderson, J.; Mazarakis, N.; Neeland, M.; Higgins, R.A.; Rautenbacher, K.; Dohle, K.; Nguyen, J.; Overmars, I.; Donato, C.; et al. Comparison of Seroconversion in Children and Adults with Mild COVID-19. JAMA Netw. Open. 2022, 5, e221313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, X.; Gao, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, H.; Hu, Y.; Liu, E.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wei, D.; et al. Characterization of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 2227–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, G.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B.; He, J.; Yin, S.; Huang, J.; Fan, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG levels in relation to disease severity of COVID-19. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xu, Q.; Yang, B.; Li, J.; Dong, R.; Da, J.; Ye, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhuou, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. IgG antibody titers against SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein correlate with the severity of COVID-19 patients. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitani, A.; Horie, T.; Yokoyama, R.; Nakano, Y.; Hamada, K.; Inoue, Y.; Saito, M.; Ishii, T.; Sunohara, M.; Takahashi, R.; et al. Interpretations of SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG antibody titers in the seroepidemiological study of asymptomatic healthy volunteers. J. Infect. Chemother. 2022, 28, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, J.L.; Ehrbar, D.J.; Hunt, D.T.; Girardin, R.C.; Dupuis, A.P., 2nd; Payne, A.F.; Sowizral, M.; Varney, S.; Kulas, K.E.; Demarest, V.L.; et al. Serological analysis reveals an imbalanced IgG subclass composition associated with COVID-19 disease severity. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrante, A.; Beard, L.J.; Feldman, R.G. IgG subclass distribution of antibodies to bacterial and viral antigens. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1990, 9 (Suppl. S8), S16–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelsen, T.E.; Naess, L.M.; Aase, A. Human IgG3 is decreased and IgG1, IgG2 and IgG4 are unchanged in molecular size by mild reduction and reoxidation without any major change in effector functions. Mol. Immunol. 1993, 30, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, K.H.; Strelets, L.; Michaelsen, T.E. Flexibility of human IgG subclasses. J. Immunol. 1997, 159, 3372–3382. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Jia, T.; Chen, J.; Zeng, S.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, X.; Lei, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, W.; et al. The Characterization of Disease Severity Associated IgG Subclasses Response in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 632814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tong, X.; Li, Y.; Gu, B.; Yan, J.; Liu, Y.; Shen, H.; Huang, R.; Wu, C. A comprehensive, longitudinal analysis of humoral responses specific to four recombinant antigens of SARS-CoV-2 in severe and non-severe COVID-19 patients. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.D.; da Costa, H.H.M.; Correa, V.A.; Lima, A.K.d.S.; Lindoso, J.A.L.; De Gaspari, E.; Hong, M.A.; Cunha-Junior, J.P.; Prudencio, C.R. Assessment of avidity related to IgG subclasses in SARS-CoV-2 Brazilian infected patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, H.P.; Rane, P.S.; Shrivastava, S.; Palkar, S.; Lalwani, S.; Mishra, A.C.; Arankalle, V.A. Antibody (IgA, IgG, and IgG Subtype) Responses to SARS-CoV-2 in Severe and Nonsevere COVID-19 Patients. Viral. Immunol. 2021, 34, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| COVID-19 Patients and Convalescents | Healthy Donors for Cut-Off Estimation | |
|---|---|---|
| Number of samples | 348 | 48 |
| Age (Me ± SD) | 62 ± 14 | 55 ± 18 |
| Sex differences | 45.11% female (n = 157) 54.89% male (n = 191) | 66.7% female (n = 32) 33.3% male (n = 16) |
| Antibody Concentration (BAU/mL) | |
|---|---|
| Calibrator 1 | 10.16 |
| Calibrator 2 | 5.08 |
| Calibrator 3 | 2.54 |
| Calibrator 4 | 1.27 |
| Calibrator 5 | 0.63 |
| Calibrator 6 | 0.31 |
| Calibrator 7 | 0.15 |
| Antibody Concentration (BAU/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG1 | IgG2 | IgG3 | IgG4 | |
| Calibrator 1 | 8.70 | 16.32 | 40.00 | 8.70 |
| Calibrator 2 | 4.35 | 8.16 | 20.00 | 4.35 |
| Calibrator 3 | 2.17 | 4.08 | 10.00 | 2.17 |
| Calibrator 4 | 1.09 | 2.04 | 5.00 | 1.09 |
| Calibrator 5 | 0.55 | 1.02 | 2.50 | 0.55 |
| Calibrator 6 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Antibody Concentration (BAU/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG1 | IgG2 | IgG3 | IgG4 | |
| 3.58 | 5.02 | 53.28 | 3.51 | |
| Antibody Concentration (BAU/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG1 | IgG2 | IgG3 | IgG4 | |
| Calibrator 1 | 340.00 | 500.00 | 395.00 | 385.00 |
| Calibrator 2 | 250.00 | 280.00 | 245.00 | 255.00 |
| Calibrator 3 | 95.00 | 100.00 | 115.00 | 100.00 |
| Calibrator 4 | 45.00 | 32.50 | 65.00 | 50.00 |
| Calibrator 5 | 20.00 | 12.50 | 35.00 | 20.00 |
| Calibrator 6 | 8.00 | 5.00 | 20.00 | 10.00 |
| Calibrator 7 | 3.30 | 2.25 | 10.00 | 5.00 |
| Calibrator 0 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Antibody Concentration (BAU/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG1 | IgG2 | IgG3 | IgG4 | |
| 9.45 | 16.98 | 20.00 | 7.00 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korobova, Z.R.; Zueva, E.V.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Batsunov, O.K.; Liubimova, N.E.; Khamitova, I.V.; Kuznetsova, R.N.; Rubinstein, A.A.; Savin, T.V.; Stanevich, O.V.; et al. Changes in Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Subclasses over Time and in Association with Disease Severity. Viruses 2022, 14, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050941
Korobova ZR, Zueva EV, Arsentieva NA, Batsunov OK, Liubimova NE, Khamitova IV, Kuznetsova RN, Rubinstein AA, Savin TV, Stanevich OV, et al. Changes in Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Subclasses over Time and in Association with Disease Severity. Viruses. 2022; 14(5):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050941
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorobova, Zoia R., Elena V. Zueva, Natalia A. Arsentieva, Oleg K. Batsunov, Natalia E. Liubimova, Irina V. Khamitova, Raisa N. Kuznetsova, Artem A. Rubinstein, Tikhon V. Savin, Oksana V. Stanevich, and et al. 2022. "Changes in Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Subclasses over Time and in Association with Disease Severity" Viruses 14, no. 5: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050941
APA StyleKorobova, Z. R., Zueva, E. V., Arsentieva, N. A., Batsunov, O. K., Liubimova, N. E., Khamitova, I. V., Kuznetsova, R. N., Rubinstein, A. A., Savin, T. V., Stanevich, O. V., Kulikov, A. N., Pevtsov, D. E., & Totolian, A. A. (2022). Changes in Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG Subclasses over Time and in Association with Disease Severity. Viruses, 14(5), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14050941







