The Performance of Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein for Detecting Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Influenced by Antiviral Therapy and Serum Aspartate Aminotransferase: A Study in a Large Cohort of Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients Selection
2.2. Study Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Factors Independently Associated with Abnormally Elevated AFP (>1× ULN) in Non-HCC and Early-Stage HCC Patients
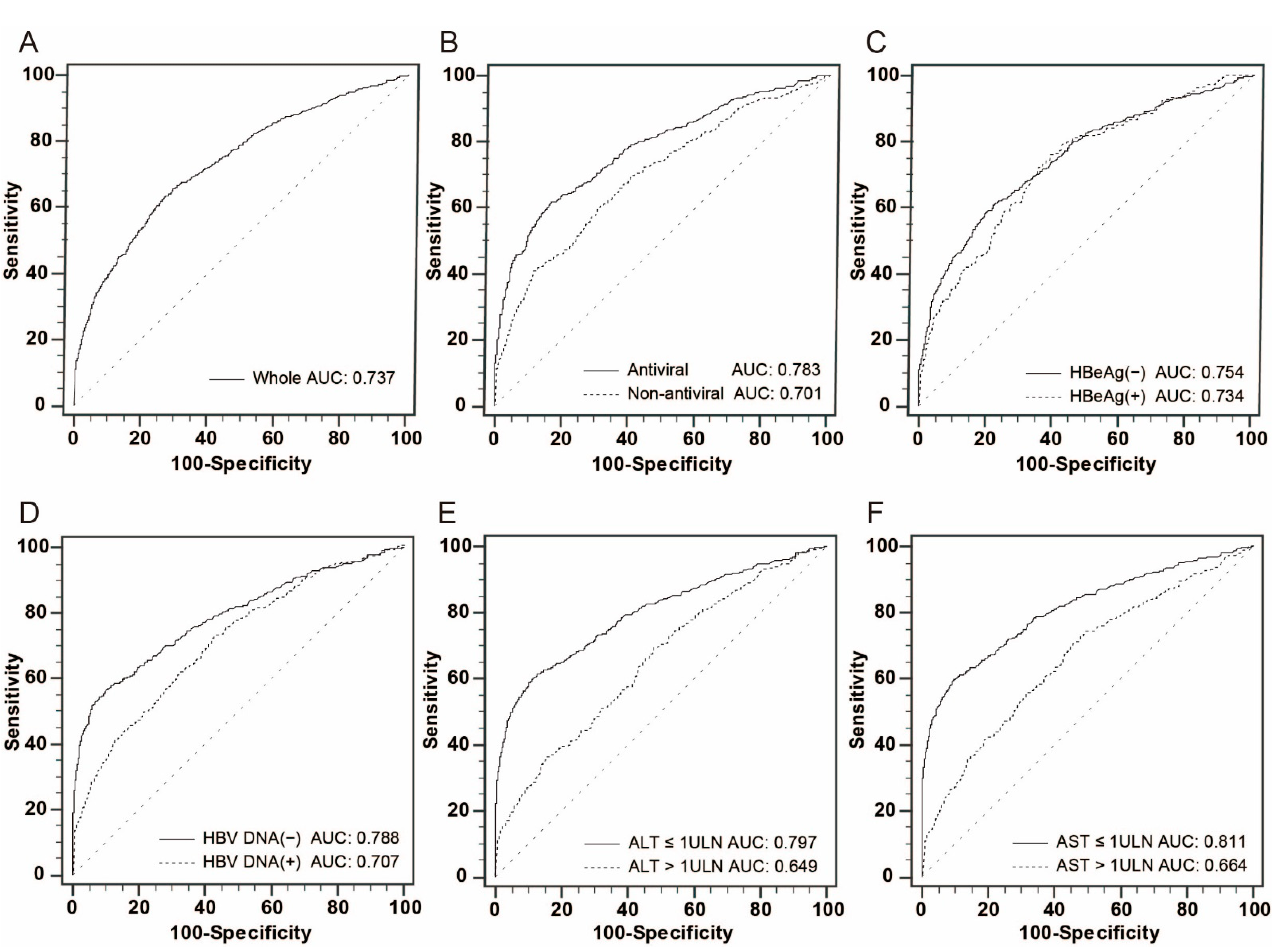
3.3. Performance of Serum AFP in Discriminating Early-Stage HCC in Different Subgroups
3.4. Better Performance of Serum AFP in Discriminating Early-Stage HCC at the Subgroup of AST ≤ 1× ULN Both in Antiviral and Non-Antiviral Groups
3.5. The Influence of Antiviral Therapy and Serum AST on the Cut-Off Values of Serum AFP in Discriminating Early-Stage HCC
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFP | alpha-fetoprotein |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| CHB | chronic hepatitis B |
| HBeAg | hepatitis B e antigen |
| NAs | nucleos(t)ide analogues |
| SD | standard deviation |
| IQR | inter quartile range |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| TBIL | total bilirubin |
| ROC curve | receiver operating characteristic curve |
| AUC | area under the ROC curve |
| OR | odds ratio |
| CI | confidence interval |
| LR+ | positive likelihood ratio |
| LR− | negative likelihood ratio |
| ULN | upper limit of normal |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omata, M.; Cheng, A.L.; Kokudo, N.; Kudo, M.; Lee, J.M.; Jia, J.; Tateishi, R.; Han, K.H.; Chawla, Y.K.; Shiina, S.; et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A 2017 update. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 317–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.D.; Roberts, L.R. Hepatocellular carcinoma: A global view. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, M.; Melin, A.A.; Douaiher, J.; Lin, C.; Zhen, W.K.; Hussain, S.M.; Geschwind, J.F.; Doyle, M.B.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Are, C. A Review and Update of Treatment Options and Controversies in the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2016, 263, 1112–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Sterling, R.K.; Everhart, J.E.; Wright, E.C.; Hoefs, J.C.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Morgan, T.R.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, W.M.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; et al. Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin and alpha-fetoprotein as biomarkers for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heimbach, J.K.; Kulik, L.M.; Finn, R.S.; Sirlin, C.B.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Zhu, A.X.; Murad, M.H.; Marrero, J.A. AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 358–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mittal, S.; Kanwal, F.; Ying, J.; Chung, R.; Sada, Y.H.; Temple, S.; Davila, J.A.; El-Serag, H.B. Effectiveness of surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma in clinical practice: A United States cohort. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanwal, F.; Singal, A.G. Surveillance for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Best Practice and Future Direction. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loglio, A.; Iavarone, M.; Facchetti, F.; Di Paolo, D.; Perbellini, R.; Lunghi, G.; Ceriotti, F.; Galli, C.; Sandri, M.T.; Vigano, M.; et al. The combination of PIVKA-II and AFP improves the detection accuracy for HCC in HBV caucasian cirrhotics on long-term oral therapy. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1987–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Alpha-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis: The demise of a brilliant star. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Sherman, M. Why Won’t the Alpha-fetoprotein Test Go Gentle into the Good Night? Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Sterling, R.K.; Chung, R.T.; Everhart, J.E.; Dienstag, J.L.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Wright, E.C.; Everson, G.T.; Lindsay, K.L.; Lok, A.S.; et al. Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in patients with advanced hepatitis C: Results from the HALT-C Trial. J. Hepatol. 2005, 43, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Kim, W.R. Surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atiq, O.; Tiro, J.; Yopp, A.C.; Muffler, A.; Marrero, J.A.; Parikh, N.D.; Murphy, C.; McCallister, K.; Singal, A.G. An assessment of benefits and harms of hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Liu, S.; Long, H.; Zhang, S.; Yan, X.; Yao, M.; Zhou, J.; Gong, J.; Wang, J.; Wen, X.; et al. Reappraisal of the diagnostic value of alpha-fetoprotein for surveillance of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of antiviral therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 2021, 28, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.; Duan, Z.; Kramer, J.; Davila, J.A.; Tyson, G.L.; El-Serag, H.B. Determinants of serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in hepatitis C-infected patients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.D.; Dai, J.; Singal, A.G.; Gopal, P.; Addissie, B.D.; Nguyen, M.H.; Befeler, A.S.; Reddy, K.R.; Schwartz, M.; Harnois, D.M.; et al. Improved Performance of Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosis in HCV Cirrhosis with Normal Alanine Transaminase. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2017, 26, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ministry of Health of the People’s Republic of China. Updated standards for the diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2012, 20, 419–426. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Medical Administration; National Health and Family Planning Comission of the People’s Republic of China. Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (V2017). Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2017, 25, 886–895. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Regalia, E.; Doci, R.; Andreola, S.; Pulvirenti, A.; Bozzetti, F.; Montalto, F.; Ammatuna, M.; Morabito, A.; Gennari, L. Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzartzeva, K.; Obi, J.; Rich, N.E.; Parikh, N.D.; Marrero, J.A.; Yopp, A.; Waljee, A.K.; Singal, A.G. Surveillance Imaging and Alpha Fetoprotein for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1706–1718.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trevisani, F.; Garuti, F.; Neri, A. Alpha-fetoprotein for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Transplant Selection. Semin. Liver Dis. 2019, 39, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.W.; Hwang, S.J.; Luo, J.C.; Lai, C.R.; Tsay, S.H.; Li, C.P.; Wu, J.C.; Chang, F.Y.; Lee, S.D. Clinical, virologic, and pathologic significance of elevated serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2001, 32, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.M.; Huang, P.T.; Tsai, M.H.; Lin, L.F.; Liu, C.C.; Ho, K.S.; Siauw, C.P.; Chao, P.L.; Tung, J.N. Predictors of alpha-fetoprotein elevation in patients with chronic hepatitis C, but not hepatocellular carcinoma, and its normalization after pegylated interferon alfa 2a-ribavirin combination therapy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.Q.; Kyulo, N.L.; Lim, N.; Elhazin, B.; Hillebrand, D.J.; Bock, T. Clinical significance of elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in patients with chronic hepatitis C, but not hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.S.; Cheng, K.S.; Lai, Y.C.; Wu, C.H.; Chen, T.K.; Lee, C.L.; Chen, D.S. Decreasing serum alpha-fetoprotein levels in predicting poor prognosis of acute hepatic failure in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 37, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakisaka, K.; Kataoka, K.; Onodera, M.; Suzuki, A.; Endo, K.; Tatemichi, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Ishida, K.; Takikawa, Y. Alpha-fetoprotein: A biomarker for the recruitment of progenitor cells in the liver in patients with acute liver injury or failure. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, E12–E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Li, H.; Jiang, W.; Hou, W.; McNutt, M.A.; Lu, F.; Li, G. Alpha fetoprotein mediates HBx induced carcinogenesis in the hepatocyte cytoplasm. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1818–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.L.; Chuang, W.L.; Chen, S.C.; Dai, C.Y.; Hou, C.; Wang, J.H.; Lu, S.N.; Huang, J.F.; Lin, Z.Y.; Hsieh, M.Y.; et al. Changing prevalence of hepatitis C virus genotypes: Molecular epidemiology and clinical implications in the hepatitis C virus hyperendemic areas and a tertiary referral center in Taiwan. J. Med. Virol. 2001, 65, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Lin, S.T.; Kuo, C.L.; Nien, C.K. Clinical significance of elevated alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in chronic hepatitis C without hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology 2008, 55, 1423–1427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, G.L.; Chan, H.L.; Tse, Y.K.; Chan, H.Y.; Tse, C.H.; Lo, A.O.; Wong, V.W. On-treatment alpha-fetoprotein is a specific tumor marker for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B receiving entecavir. Hepatology 2014, 59, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, T.; Tateishi, R.; Kondo, M.; Nakagomi, R.; Fujiwara, N.; Sato, M.; Uchino, K.; Enooku, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Asaoka, Y.; et al. Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein Has High Specificity for the Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Hepatitis C Virus Eradication in Patients. Medicine 2015, 94, e901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Non-HCC | Early-Stage HCC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Antiviral (n = 1803) | Antiviral (n = 1877) | p-Value | Non-Antiviral (n = 342) | Antiviral (n = 379) | p-Value | |
| Age (year) | 42.58 ± 12.78 | 46.07 ± 11.44 | <0.001 | 53.59 ± 10.29 | 52.73 ± 10.11 | 0.260 |
| Male, n (%) | 1337 (74.2) | 1375 (73.3) | 0.536 | 282 (82.5) | 311 (82.1) | 0.889 |
| HBeAg (+/−) | 845/958 | 579/1298 | <0.001 | 104/238 | 104/275 | 0.380 |
| HBV DNA (+/−) | 1540/263 | 333/1544 | <0.001 | 268/74 | 75/304 | <0.001 |
| Cirrhosis (+/−) | 793/1010 | 1069/808 | <0.001 | 293/49 | 350/29 | 0.004 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 60 [30, 301] | 25 [18, 36] | <0.001 | 38 [25, 57] | 29 [21, 42] | <0.001 |
| ALT > 1× ULN *, n (%) | 1123 (62.3) | 337 (18.0) | <0.001 | 149 (43.6) | 105 (27.7) | <0.001 |
| AST (IU/L) | 58 [31, 176] | 28 [22, 40] | <0.001 | 39 [28, 64] | 31 [24, 45] | <0.001 |
| AST > 1× ULN *, n (%) | 1156 (64.1) | 486 (25.9) | <0.001 | 163 (47.7) | 121 (31.9) | <0.001 |
| TBIL (μmol/L) | 21.2 [13.5, 44.8] | 15.3 [11.2, 23.2] | <0.001 | 17.7 [12.0, 26.6] | 16.4 [12.0, 24.4] | 0.221 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 39.3 [33.0, 43.8] | 41.5 [36.0, 45.2] | <0.001 | 38.0 [33.2, 41.0] | 40.0 [35.0, 43.0] | <0.001 |
| Platelet (×109/L) | 149 [91, 202] | 136 [78, 191] | <0.001 | 113 [72, 170] | 107 [71, 154] | 0.055 |
| Tumor size (cm) | - | - | - | 2.86 ± 1.16 | 2.51 ± 1.10 | <0.001 |
| Number of tumors (1/2–3) | - | - | - | 314/28 | 342/37 | 0.461 |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 5.58 [2.61, 25.4] | 2.68 [1.75, 4.60] | <0.001 | 29.2 [5.38, 275.1] | 12.1 [3.57, 125.5] | <0.001 |
| AFP > 1× ULN *, n (%) | 672 (37.3) | 213 (11.4) | <0.001 | 228 (66.7) | 203 (53.6) | <0.001 |
| Non-HCC | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (year) | 0.996 (0.990, 1.002) | 0.239 | - | - |
| Gender (M) | 1.287 (1.077, 1.538) | 0.005 | - | - |
| HBeAg (+) | 2.226 (1.909, 2.595) | <0.001 | 1.353 (1.115, 1.641) | 0.002 |
| HBV DNA (+) | 7.486 (6.170, 9.083) | <0.001 | 2.860 (2.164, 3.780) | <0.001 |
| Cirrhosis (+) | 1.581 (1.356, 1.842) | <0.001 | 1.456 (1.151, 1.841) | 0.002 |
| ALT > 1× ULN | 7.972 (6.695, 9.492) | <0.001 | 2.051 (1.585, 2.656) | <0.001 |
| AST > 1× ULN | 11.491 (9.425, 14.011) | <0.001 | 2.655 (2.015, 3.499) | <0.001 |
| TBIL (μmol/L) | 1.014 (1.012, 1.015) | <0.001 | 1.006 (1.004, 1.007) | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 0.908 (0.898, 0.918) | <0.001 | 0.960 (0.945, 0.976) | <0.001 |
| Platelet (×109/L) | 0.996 (0.995, 0.997) | <0.001 | - | - |
| Antiviral therapy (+) | 0.215 (0.181, 0.256) | <0.001 | 0.772 (0.601, 0.993) | 0.044 |
| Early-Stage HCC | Univariate | Multivariate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p-Value | OR (95%CI) | p-Value | |
| Age (year) | 0.997 (0.983, 1.012) | 0.713 | - | - |
| Gender (M) | 0.546 (0.361, 0.828) | 0.004 | 0.549 (0.358, 0.842) | 0.006 |
| HBeAg (+) | 1.668 (1.187, 2.343) | 0.003 | 1.535 (1.080, 2.182) | 0.017 |
| HBV DNA(+) | 1.880 (1.388, 2.546) | <0.001 | - | - |
| Cirrhosis (+) | 1.562 (0.975, 2.502) | 0.064 | - | - |
| ALT > 1× ULN | 1.556 (1.132, 2.139) | 0.007 | - | - |
| AST > 1× ULN | 2.238 (1.628, 3.075) | <0.001 | 1.780 (1.262, 2.510) | 0.001 |
| TBIL (μmol/L) | 1.010 (1.003, 1.017) | 0.006 | - | - |
| Albumin (g/L) | 0.976 (0.952, 1.000) | 0.055 | - | - |
| Platelet (×109/L) | 0.998 (0.996, 1.001) | 0.134 | - | - |
| Tumor size (cm) | 1.038 (0.911, 1.183) | 0.577 | - | - |
| Number of tumors (2–3/1) | 1.253 (0.736, 2.133) | 0.405 | - | - |
| Antiviral therapy (+) | 0.577 (0.426, 0.780) | <0.001 | 0.632 (0.463, 0.865) | 0.004 |
| Subgroups of Non-Antiviral Therapy (n = 2145) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | AUC (95%CI) | Cut-Off | Se (%) | Sp (%) | LR+ | LR− | p-Value |
| HBeAg | 0.976 | ||||||
| − | 0.720 (0.682, 0.758) | 6.90 | 68.07 | 65.45 | 1.97 | 0.49 | - |
| + | 0.719 (0.665, 0.773) | 10.14 | 77.88 | 54.56 | 1.71 | 0.41 | - |
| HBV DNA | 0.091 | ||||||
| − | 0.767 (0.698, 0.836) | 10.45 | 56.76 | 87.83 | 4.66 | 0.49 | - |
| + | 0.700 (0.665, 0.736) | 87.40 | 43.28 | 86.62 | 3.24 | 0.65 | - |
| ALT | <0.001 | ||||||
| ≤1× ULN | 0.788 (0.747, 0.829) | 15.11 | 59.59 | 88.97 | 5.40 | 0.45 | - |
| >1× ULN | 0.667 (0.619, 0.715) | 87.40 | 44.30 | 82.99 | 2.60 | 0.67 | - |
| AST | <0.001 | ||||||
| ≤1× ULN | 0.813 (0.773, 0.854) | 6.90 | 64.80 | 85.94 | 4.61 | 0.41 | - |
| >1× ULN | 0.669 (0.621, 0.716) | 87.40 | 44.79 | 82.35 | 2.54 | 0.67 | - |
| Subgroups of Antiviral Therapy (n = 2256) | |||||||
| Variables | AUC (95%CI) | Cut-Off | Se (%) | Sp (%) | LR+ | LR− | p-Value |
| HBeAg | 0.525 | ||||||
| − | 0.780 (0.746, 0.813) | 7.02 | 55.64 | 88.06 | 4.66 | 0.50 | - |
| + | 0.801 (0.752, 0.850) | 6.39 | 74.04 | 79.97 | 3.70 | 0.32 | - |
| HBV DNA | 0.307 | ||||||
| − | 0.791 (0.759, 0.822) | 7.04 | 55.92 | 90.93 | 6.17 | 0.48 | - |
| + | 0.748 (0.689, 0.808) | 6.40 | 78.67 | 62.16 | 2.08 | 0.34 | - |
| ALT | 0.001 | ||||||
| ≤1× ULN | 0.796 (0.763, 0.829) | 7.32 | 56.57 | 91.82 | 6.91 | 0.47 | - |
| >1× ULN | 0.682 (0.624, 0.739) | 6.10 | 71.43 | 60.24 | 1.80 | 0.47 | - |
| AST | 0.002 | ||||||
| ≤1× ULN | 0.806 (0.773, 0.839) | 6.56 | 56.20 | 92.52 | 7.52 | 0.47 | - |
| >1× ULN | 0.711 (0.657, 0.764) | 10.80 | 62.81 | 73.66 | 2.38 | 0.50 | - |
| Non-Antiviral Group (n = 2145) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFP, ng/mL | AST ≤ 1× ULN | AST > 1× ULN | ||||||
| Se (%) | Sp (%) | LR+ | LR− | Se (%) | Sp (%) | LR+ | LR− | |
| ULN | 58.10 | 88.87 | 5.22 | 0.47 | 76.07 | 48.10 | 1.47 | 0.50 |
| 20 | 50.84 | 94.90 | 9.97 | 0.52 | 61.35 | 60.21 | 1.54 | 0.64 |
| 100 | 34.64 | 99.07 | 37.35 | 0.66 | 41.72 | 83.74 | 2.57 | 0.70 |
| 200 | 25.14 | 99.38 | 40.66 | 0.75 | 31.90 | 89.97 | 3.18 | 0.76 |
| 400 | 16.76 | 99.69 | 54.22 | 0.83 | 19.02 | 95.42 | 4.15 | 0.85 |
| Antiviral Group (n = 2256) | ||||||||
| AFP, ng/mL | AST ≤ 1× ULN | AST > 1× ULN | ||||||
| Se (%) | Sp (%) | LR+ | LR− | Se (%) | Sp (%) | LR+ | LR− | |
| ULN | 48.45 | 95.26 | 10.21 | 0.54 | 64.46 | 69.75 | 2.13 | 0.51 |
| 20 | 41.09 | 98.63 | 30.08 | 0.60 | 50.41 | 81.07 | 2.66 | 0.61 |
| 100 | 27.91 | 99.86 | 194.09 | 0.72 | 26.45 | 93.00 | 3.78 | 0.79 |
| 200 | 22.48 | 99.93 | 312.71 | 0.78 | 15.70 | 95.88 | 3.82 | 0.88 |
| 400 | 15.89 | 100 | - | 0.84 | 12.40 | 97.94 | 6.02 | 0.89 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhang, S.; Gong, J.; Nan, Y.; Hu, B.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; et al. The Performance of Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein for Detecting Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Influenced by Antiviral Therapy and Serum Aspartate Aminotransferase: A Study in a Large Cohort of Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Patients. Viruses 2022, 14, 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081669
Qian X, Liu Y, Wu F, Zhang S, Gong J, Nan Y, Hu B, Chen J, Zhao J, Chen X, et al. The Performance of Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein for Detecting Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Influenced by Antiviral Therapy and Serum Aspartate Aminotransferase: A Study in a Large Cohort of Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Patients. Viruses. 2022; 14(8):1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081669
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Xiangjun, Yanna Liu, Fengping Wu, Siyu Zhang, Jiao Gong, Yuemin Nan, Bo Hu, Junhui Chen, Jingmin Zhao, Xiangmei Chen, and et al. 2022. "The Performance of Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein for Detecting Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Influenced by Antiviral Therapy and Serum Aspartate Aminotransferase: A Study in a Large Cohort of Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Patients" Viruses 14, no. 8: 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081669
APA StyleQian, X., Liu, Y., Wu, F., Zhang, S., Gong, J., Nan, Y., Hu, B., Chen, J., Zhao, J., Chen, X., Pan, W., Dang, S., & Lu, F. (2022). The Performance of Serum Alpha-Fetoprotein for Detecting Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Influenced by Antiviral Therapy and Serum Aspartate Aminotransferase: A Study in a Large Cohort of Hepatitis B Virus-Infected Patients. Viruses, 14(8), 1669. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14081669








