Norovirus Infection in Young Nicaraguan Children Induces Durable and Genotype-Specific Antibody Immunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Specimen Collection
2.3. Norovirus Detection in AGE Stools
2.4. Norovirus Detection in Monthly Collected Stools
2.5. Nucleotide Sequencing
2.6. Virus-like Particle (VLP) Production
2.7. Antibody Blockade of VLP Binding Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genetic Diversity of Norovirus in Children < 2 Years of Age in the Nicaraguan Birth Cohort
3.2. Norovirus Antibody Response and Pre-Existing Antibodies
3.3. Monotypic and Multitypic Seroconversion in Children Experiencing the First Norovirus AGE Episode before 18 Months of Life
3.4. Correlation between Ab Blockade Seroconversion and Norovirus Genotyping
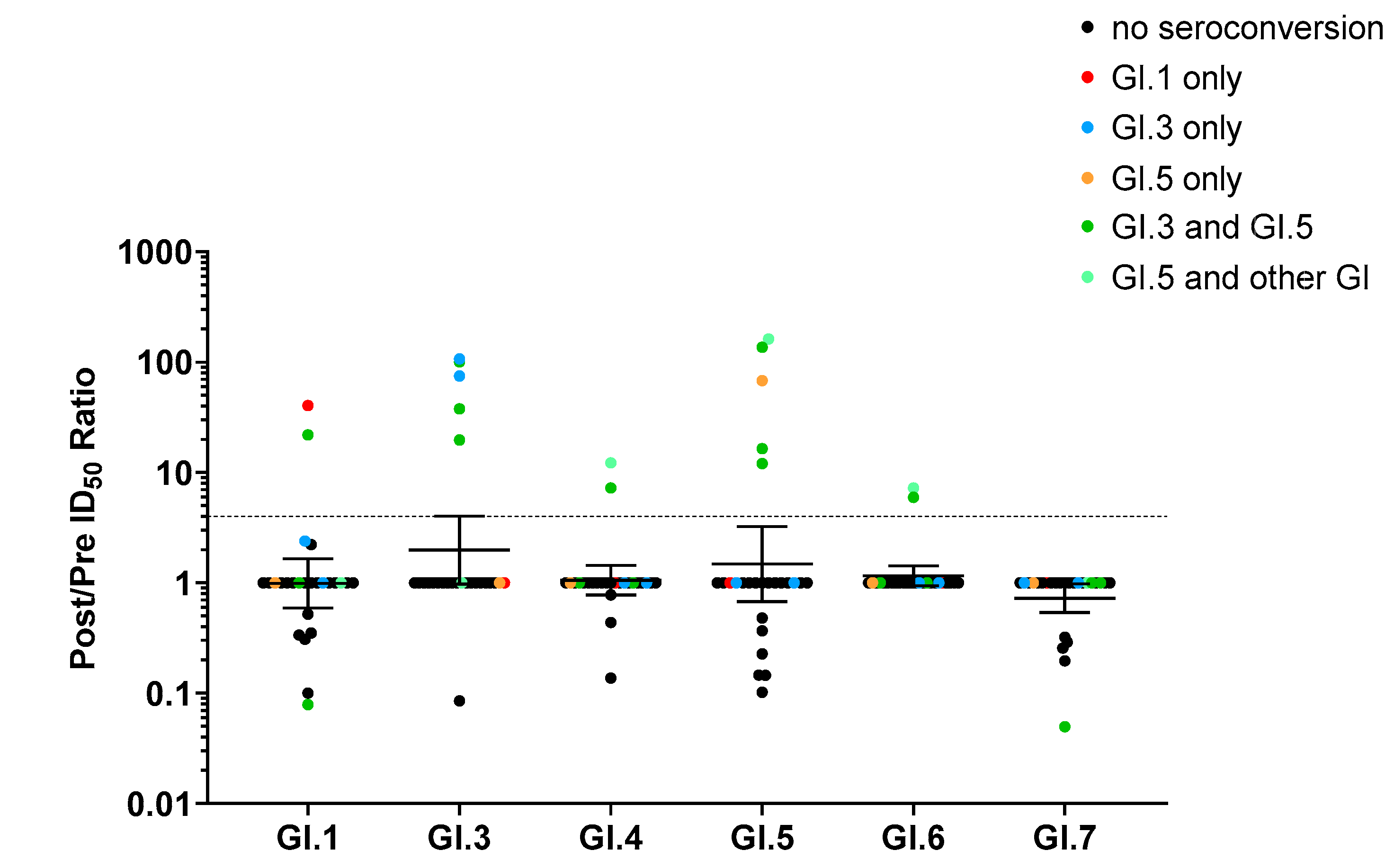
3.5. Blockade Ab Response Was Genotype-Specific but Not Variant-Specific
3.6. Asymptomatic Norovirus Infections in Children with Multitypic Blockade Ab Response
3.7. Duration of Norovirus Blockade Ab Titer after First AGE Episode
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.M.; Hall, A.J.; Robinson, A.E.; Verhoef, L.; Premkumar, P.; Parashar, U.D.; Koopmans, M.; Lopman, B.A. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mans, J. Norovirus infections and disease in lower-middleand low-income countries, 1997–2018. Viruses 2019, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Hong, X.; Wu, A.; Jiang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Gao, J.; Xue, L.; Kou, X. Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of acute gastroenteritis from 1997 to 2021: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 161 Pt A, 105259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, G.T.; Phan, K.; Teng, I.; Pu, J.; Watanabe, T. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis in developing countries. Medicine 2017, 96, e8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.L.; A Lopman, B.; Payne, D.C.; Vinjé, J. Corrigendum to: Birth Cohort Studies Assessing Norovirus Infection and Immunity in Young Children: A Review. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopman, B.; Steele, D.; Kirkwood, C.D.; Parashar, U.D. The Vast and Varied Global Burden of Norovirus: Prospects for Prevention and Control. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1001999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapikian, A.Z.; Wyatt, R.G.; Dolin, R.; Thornhill, T.S.; Kalica, A.R.; Chanock, R.M. Visualization by Immune Electron Microscopy of a 27-nm Particle Associated with Acute Infectious Nonbacterial Gastroenteritis. J. Virol. 1972, 10, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Estes, M.K. Sequence and Genomic Organization of Norwalk Virus. Virology 1993, 195, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.V.; Hardy, M.E.; Dokland, T.; Bella, J.; Rossmann, M.G.; Estes, M.K. X-ray crystallographic structure of the Norwalk virus capsid. Science 1999, 286, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Xia, M.; Cao, S.; Huang, P.; Farkas, T.; Meller, J.; Hegde, R.S.; Li, X.; Rao, Z.; Jiang, X. Elucidation of strain-specific interaction of a GII-4 norovirus with HBGA receptors by site-directed mutagenesis study. Virology 2008, 379, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Huang, P.; Meller, J.; Zhong, W.; Farkas, T.; Jiang, X. Mutations within the P2 domain of norovirus capsid affect binding to human histo-blood group antigens: Evidence for a binding pocket. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12562–12571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruvoën-Clouet, N.; Belliot, G.; Le Pendu, J. Noroviruses and histo-blood groups: The impact of common host genetic polymorphisms on virus transmission and evolution. Rev. Med. Virol. 2013, 23, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Pendu, J.; Ruvoën-Clouet, N. Fondness for sugars of enteric viruses confronts them with human glycans genetic diversity. Hum. Genet. 2020, 139, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordgren, J.; Svensson, L. Genetic Susceptibility to Human Norovirus Infection: An Update. Viruses 2019, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, P.; De Graaf, M.; Parra, G.I.; Chan, M.C.-W.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Wang, Q.; White, P.A.; Katayama, K.; Vennema, H.; et al. Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.L.; Bonifacio, J.; Bucardo, F.; Buesa, J.; Bruggink, L.; Chan, M.C.-W.; Fumian, T.M.; Giri, S.; Gonzalez, M.D.; Hewitt, J.; et al. Global Trends in Norovirus Genotype Distribution among Children with Acute Gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebenga, J.J.; Vennema, H.; Zheng, D.-P.; Vinjé, J.; Lee, B.E.; Pang, X.; Ho, E.C.M.; Lim, W.; Choudekar, A.; Broor, S.; et al. Norovirus Illness Is a Global Problem: Emergence and Spread of Norovirus GII.4 Variants, 2001–2007. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Donaldson, E.F.; LoBue, A.D.; Cannon, J.L.; Zheng, D.-P.; Vinje, J.; Baric, R.S. Mechanisms of GII.4 Norovirus Persistence in Human Populations. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, R.A.; Eden, J.S.; Rawlinson, W.D.; White, P.A. Rapid evolution of pandemic noroviruses of the GII.4 lineage. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, M.; van Beek, J.; Vennema, H.; Podkolzin, A.T.; Hewitt, J.; Bucardo, F.; Templeton, K.; Mans, J.; Nordgren, J.; Reuter, G.; et al. Emergence of a novel GII.17 norovirus—End of the GII.4 era? Euro Surveill. Bull. Eur. Mal. Transm. = Eur. Commun. Dis. Bull. 2015, 20, 21178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.C.-W.; Hu, Y.; Chen, H.; Podkolzin, A.T.; Zaytseva, E.V.; Komano, J.; Sakon, N.; Poovorawan, Y.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Thanusuwannasak, T.; et al. Global Spread of Norovirus GII.17 Kawasaki 308, 2014–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmar, R.L.; Ramani, S.; Estes, M.K. Human noroviruses: Recent advances in a 50-year history. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford-Siltz, L.A.; Tohma, K.; Parra, G.I. Understanding the relationship between norovirus diversity and immunity. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, G.I.; Squires, R.B.; Karangwa, C.K.; Johnson, J.A.; Lepore, C.J.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Green, K.Y. Static and Evolving Norovirus Genotypes: Implications for Epidemiology and Immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Beltramello, M.; Donaldson, E.F.; Corti, D.; Swanstrom, J.; Debbink, K.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Baric, R.S. Immunogenetic Mechanisms Driving Norovirus GII.4 Antigenic Variation. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Beltramello, M.; Swanstrom, J.; Jones, T.A.; Corti, D.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Baric, R.S. Serum Immunoglobulin A Cross-Strain Blockade of Human Noroviruses. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, ofv084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.; Moe, C.; LePendu, J.; Frelinger, J.A.; Treanor, J.; Baric, R.S. Cellular and Humoral Immunity following Snow Mountain Virus Challenge. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 2900–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Ferris, M.T.; Mullan, C.; Ferreira, J.; Debbink, K.; Swanstrom, J.; Richardson, C.; Goodwin, R.R.; Baehner, F.; Mendelman, P.M.; et al. Broad Blockade Antibody Responses in Human Volunteers after Immunization with a Multivalent Norovirus VLP Candidate Vaccine: Immunological Analyses from a Phase I Clinical Trial. PLoS Med. 2015, 12, e1001807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, G.I.; Bok, K.; Taylor, R.; Haynes, J.R.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Richardson, C.; Green, K.Y. Immunogenicity and specificity of norovirus Consensus GII.4 virus-like particles in monovalent and bivalent vaccine formulations. Vaccine 2012, 30, 3580–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettayebi, K.; Crawford, S.E.; Murakami, K.; Broughman, J.R.; Karandikar, U.; Tenge, V.; Neill, F.H.; Blutt, S.E.; Zeng, X.-L.; Qu, L.; et al. Replication of human noroviruses in stem cell-derived human enteroids. Science 2016, 353, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeck, A.; Kavanagh, O.; Estes, M.K.; Opekun, A.R.; Gilger, M.A.; Graham, D.Y.; Atmar, R.L. Serological Correlate of Protection against Norovirus-Induced Gastroenteritis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malm, M.; Uusi-Kerttula, H.; Vesikari, T.; Blazevic, V. High Serum Levels of Norovirus Genotype-Specific Blocking Antibodies Correlate with Protection from Infection in Children. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1755–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmar, R.L.; Ettayebi, K.; Ayyar, B.V.; Neill, F.H.; Braun, R.P.; Ramani, S.; Estes, M.K. Comparison of Microneutralization and Histo-Blood Group Antigen–Blocking Assays for Functional Norovirus Antibody Detection. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; McDaniel, J.R.; Changela, A.; Verardi, R.; Kerr, S.A.; Costantini, V.; Brewer-Jensen, P.D.; Mallory, M.L.; Voss, W.N.; Boutz, D.R.; et al. Sera Antibody Repertoire Analyses Reveal Mechanisms of Broad and Pandemic Strain Neutralizing Responses after Human Norovirus Vaccination. Immunity 2019, 50, 1530–1541.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanstrom, J.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Donaldson, E.F.; Yount, B.; Baric, R.S. Characterization of Blockade Antibody Responses in GII.2.1976 Snow Mountain Virus-Infected Subjects. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazevic, V.; Malm, M.; Honkanen, H.; Knip, M.; Hyöty, H.; Vesikari, T. Development and maturation of norovirus antibodies in childhood. Microbes Infect. 2016, 18, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielot, N.A.; González, F.; Reyes, Y.; Zepeda, O.; Blette, B.; Paniagua, M.; Toval-Ruiz, C.; Diez-Valcarce, M.; Hudgens, M.G.; Gutiérrez, L.; et al. Risk Factors and Clinical Profile of Sapovirus-associated Acute Gastroenteritis in Early Childhood: A Nicaraguan Birth Cohort Study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2021, 40, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trujillo, A.A.; McCaustland, K.A.; Zheng, D.-P.; Hadley, L.A.; Vaughn, G.; Adams, S.M.; Ando, T.; Glass, R.I.; Monroe, S.S. Use of TaqMan Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR for Rapid Detection, Quantification, and Typing of Norovirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, J.L.; Barclay, L.; Collins, N.R.; Wikswo, M.E.; Castro, C.J.; Magaña, L.C.; Gregoricus, N.; Marine, R.; Chhabra, P.; Vinjé, J. Genetic and Epidemiologic Trends of Norovirus Outbreaks in the United States from 2013 to 2016 Demonstrated Emergence of Novel GII.4 Recombinant Viruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2208–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, Y.; González, F.; Gutiérrez, L.; Blandón, P.; Centeno, E.; Zepeda, O.; Toval-Ruíz, C.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Baric, R.S.; Vielot, N.; et al. Secretor Status Strongly Influences the Incidence of Symptomatic Norovirus Infection in a Genotype-Dependent Manner in a Nicaraguan Birth Cohort. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 225, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, P.; Browne, H.; Huynh, T.; Diez-Valcarce, M.; Barclay, L.; Kosek, M.N.; Ahmed, T.; Lopez, M.R.; Pan, C.-Y.; Vinjé, J. Single-step RT-PCR assay for dual genotyping of GI and GII norovirus strains. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 134, 104689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Chhabra, P.; Diez-Valcarce, M.; Barclay, L.; Cannon, J.L.; Vinjé, J. Human Calicivirus Typing tool: A web-based tool for genotyping human norovirus and sapovirus sequences. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 134, 104718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnihothram, S.; Menachery, V.D.; Yount, B.L., Jr.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Scobey, T.; Whitmore, A.; Schäfer, A.; Heise, M.T.; Baric, R.S. Development of a Broadly Accessible Venezuelan Equine Encephalitis Virus Replicon Particle Vaccine Platform. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00027-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindesmith, L.C.; Donaldson, E.F.; Beltramello, M.; Pintus, S.; Corti, D.; Swanstrom, J.; Debbink, K.; Jones, T.A.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Baric, R.S. Particle Conformation Regulates Antibody Access to a Conserved GII.4 Norovirus Blockade Epitope. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8826–8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Yori, P.P.; Olortegui, M.P.; Caulfield, L.E.; Sack, D.A.; Fischer-Walker, C.; Black, R.E.; Kosek, M. An instrument for the assessment of diarrhoeal severity based on a longitudinal community-based study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e004816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, M.; Goel-Apaza, S.; Espetia, S.; Velasquez, D.; Cabrera, L.; Loli, S.; Crabtree, J.E.; Black, R.E.; Kosek, M.; Checkley, W.; et al. Multiple Norovirus Infections in a Birth Cohort in a Peruvian Periurban Community. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 58, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iritani, N.; Seto, T.; Hattori, H.; Natori, K.; Takeda, N.; Kubo, H.; Yamano, T.; Ayata, M.; Ogura, H.; Seto, Y. Humoral immune responses against norovirus infections of children. J. Med. Virol. 2007, 79, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, G.I.; Green, K.Y. Sequential Gastroenteritis Episodes Caused by 2 Norovirus Genotypes. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1016–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czako, R.; Atmar, R.L.; Opekun, A.R.; Gilger, M.A.; Graham, D.Y.; Estes, M.K. Experimental Human Infection with Norwalk Virus Elicits a Surrogate Neutralizing Antibody Response with Cross-Genogroup Activity. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2014, 22, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallory, M.L.; Lindesmith, L.C.; Graham, R.L.; Baric, R.S. GII.4 Human Norovirus: Surveying the Antigenic Landscape. Viruses 2019, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucardo, F. Understanding Asymptomatic Norovirus Infections. eClinicalMedicine 2018, 2–3, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, R.; Huang, Y.-T.; Liu, J.-W.; Sun, Y.; Sun, X.-F.; Han, H.-J.; Qin, X.-R.; Zhao, M.; Wang, L.-J.; Li, W.; et al. Global Prevalence of Asymptomatic Norovirus Infection: A Meta-analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2018, 2–3, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atmar, R.L.; Bernstein, D.I.; Harro, C.D.; Al-Ibrahim, M.S.; Chen, W.H.; Ferreira, J.; Estes, M.K.; Graham, D.Y.; Opekun, A.R.; Richardson, C.; et al. Norovirus Vaccine against Experimental Human Norwalk Virus Illness. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryder, R.W.; Singh, N.; Reeves, W.C.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Greenberg, H.B.; Sack, R.B. Evidence of Immunity Induced by Naturally Acquired Rotavirus and Norwalk Virus Infection on Two Remote Panamanian Islands. J. Infect. Dis. 1985, 151, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, V.; Morantz, E.K.; Browne, H.; Ettayebi, K.; Zeng, X.-L.; Atmar, R.L.; Estes, M.K.; Vinje, J. Human Norovirus Replication in Human Intestinal Enteroids as Model to Evaluate Virus Inactivation. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrino, T.A.; Schreiber, D.S.; Trier, J.S.; Kapikian, A.Z.; Blacklow, N.R. Clinical Immunity in Acute Gastroenteritis Caused by Norwalk Agent. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 297, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.C.; Mathewson, J.J.; Dupont, H.L.; Greenberg, H. Multiple-Challenge Study of Host Susceptibility to Norwalk Gastroenteritis in US Adults. J. Infect. Dis. 1990, 161, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunis, P.F.M.; Moe, C.L.; Liu, P.; Miller, S.E.; Lindesmith, L.; Baric, R.S.; Le Pendu, J.; Calderon, R.L. Norwalk virus: How infectious is it? J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hsiao, H.-M.; Jaykus, L.-A.; Moe, C. Quantification of Norwalk virus inocula: Comparison of endpoint titration and real-time reverse transcription-PCR methods. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, K.; Gambhir, M.; Leon, J.; Lopman, B. Duration of Immunity to Norovirus Gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1260–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Subject ID | Gender | Poverty Index * | Severity Score ** | Pre-Existing Blockade Antibodies † | Norovirus Genotype in Stools | GII Blockade Response ⋆ | GI Blockade Response ⋆ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 1 | 4 | GII.2, GI.1, GI.5 | GII.4 Sydney [P31] | GII.4 Sydney | - |
| 2 | F | 2 | 4 | - | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney | - |
| 3 | M | 1 | 7 | - | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney | - |
| 4 | F | 2 | 7 | - | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney | - |
| 5 | M | 2 | 9 | GII.12 | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney | - |
| 6 | M | 2 | 8 | GII.12, GI.1, GI.4, GI.5, GII.4 Den Haag, GI.7, GII.4 Sydney | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney | - |
| 7 | F | 2 | 9 | GI.4, GII.14 | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney | - |
| 8 | F | 1 | 8 | GII.2 | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney | - |
| 9 | M | 2 | 5 | GII.2 | GII.12 [P16] | GII.12 | - |
| 10 | M | 1 | 6 | GII.2, GI.3, GII.14, GI.1, GI.5, GII.4 Den Haag, GI.7, GII.4 Sydney, GII.3, GII.17, GI.4, GII.12 | GII.12 [P16] | GII.12 | - |
| 11 | M | 1 | 7 | GII.4 Den Haag, GII.4 Sydney, GII.2, GII.12, GI.5, GII.14, GI.1 | GII.12 [P16] | GII.12 | - |
| 12 | M | 1 | 4 | - | GI.3 [P3] | - | GI.3 |
| 13 | M | 1 | 8 | GII.17, GII.4 Sydney, GII.4 Den Haag | GI.5 [P4] | - | GI.3 |
| 14 | F | 2 | 3 | - | GI.5 [P4] | - | GI.5 |
| 15 | F | 1 | 3 | - | GII.4 Sydney [P31] | GII.4 Sydney, GII.12, GII.2, GII.3, GII.17 | - |
| 16 | M | 1 | 15 | - | GII.4 Sydney [P31] | GII.4 Sydney, GII.12, GII.2 | - |
| 17 | M | 1 | 8 | - | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney, GII.12, GII.2, GII.3 | - |
| 18 | M | 0 | 8 | GII.2, GI.5, GI.1, GII.3, GI.7, GII.4 Den Haag, GII.4 Sydney | GII.4 Sydney [P31] | GII.4 Sydney, GII.12 | - |
| 19 | M | 2 | 4 | - | GII.12 [P16] § | GII.4 Sydney, GII.12 | - |
| 20 | M | 2 | 3 | GI.1, GI.5, GI.7 | GII.12 [P16] | GII.4 Sydney, GII.12 | - |
| 21 | M | 1 | 5 | - | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney, GII.14, GII.2 | - |
| 22 | F | 0 | 5 | GII.2, GII.4 Den Haag | GI.3 [P3] | - | GI.3, GI.4, GI.5, GI.6 |
| 23 | M | 1 | 4 | GI.7, GI.1, GI.3, GI.5, GII.4 Den Haag | GI.5 [P4] | GII.12 | GI.3, GI.5 |
| 24 | M | 2 | 3 | GII.12 | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney | GI.3, GI.4, GI.5 |
| 25 | F | 2 | 7 | GII.12 | GII.4 Sydney [P16] | GII.4 Sydney, GII.3 | GI.1 |
| 26 | M | 2 | 4 | GII.2, GII.3 | GI.3 [P3] | GII.4 Sydney, GII.12 | GI.3, GI.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brewer-Jensen, P.D.; Reyes, Y.; Becker-Dreps, S.; González, F.; Mallory, M.L.; Gutiérrez, L.; Zepeda, O.; Centeno, E.; Vielot, N.; Diez-Valcarce, M.; et al. Norovirus Infection in Young Nicaraguan Children Induces Durable and Genotype-Specific Antibody Immunity. Viruses 2022, 14, 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092053
Brewer-Jensen PD, Reyes Y, Becker-Dreps S, González F, Mallory ML, Gutiérrez L, Zepeda O, Centeno E, Vielot N, Diez-Valcarce M, et al. Norovirus Infection in Young Nicaraguan Children Induces Durable and Genotype-Specific Antibody Immunity. Viruses. 2022; 14(9):2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092053
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrewer-Jensen, Paul D., Yaoska Reyes, Sylvia Becker-Dreps, Fredman González, Michael L. Mallory, Lester Gutiérrez, Omar Zepeda, Edwing Centeno, Nadja Vielot, Marta Diez-Valcarce, and et al. 2022. "Norovirus Infection in Young Nicaraguan Children Induces Durable and Genotype-Specific Antibody Immunity" Viruses 14, no. 9: 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092053
APA StyleBrewer-Jensen, P. D., Reyes, Y., Becker-Dreps, S., González, F., Mallory, M. L., Gutiérrez, L., Zepeda, O., Centeno, E., Vielot, N., Diez-Valcarce, M., Vinjé, J., Baric, R., Lindesmith, L. C., & Bucardo, F. (2022). Norovirus Infection in Young Nicaraguan Children Induces Durable and Genotype-Specific Antibody Immunity. Viruses, 14(9), 2053. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092053






