Quantification of APOBEC3 Mutation Rates Affecting the VP1 Gene of BK Polyomavirus In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Amplification and Sequencing of VP1 Typing Region from Patient Samples
2.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.4. Cell Culture Model
3. Results
3.1. APOBEC3A/B Signatures Can Be Detected in Urine, Plasma, and Kidney Biopsy Samples
3.2. APOBEC3A/B Mutation Rate Varies between Patients, Whereas SBS89 Mutation Rate Varies between BKPyV Genotypes
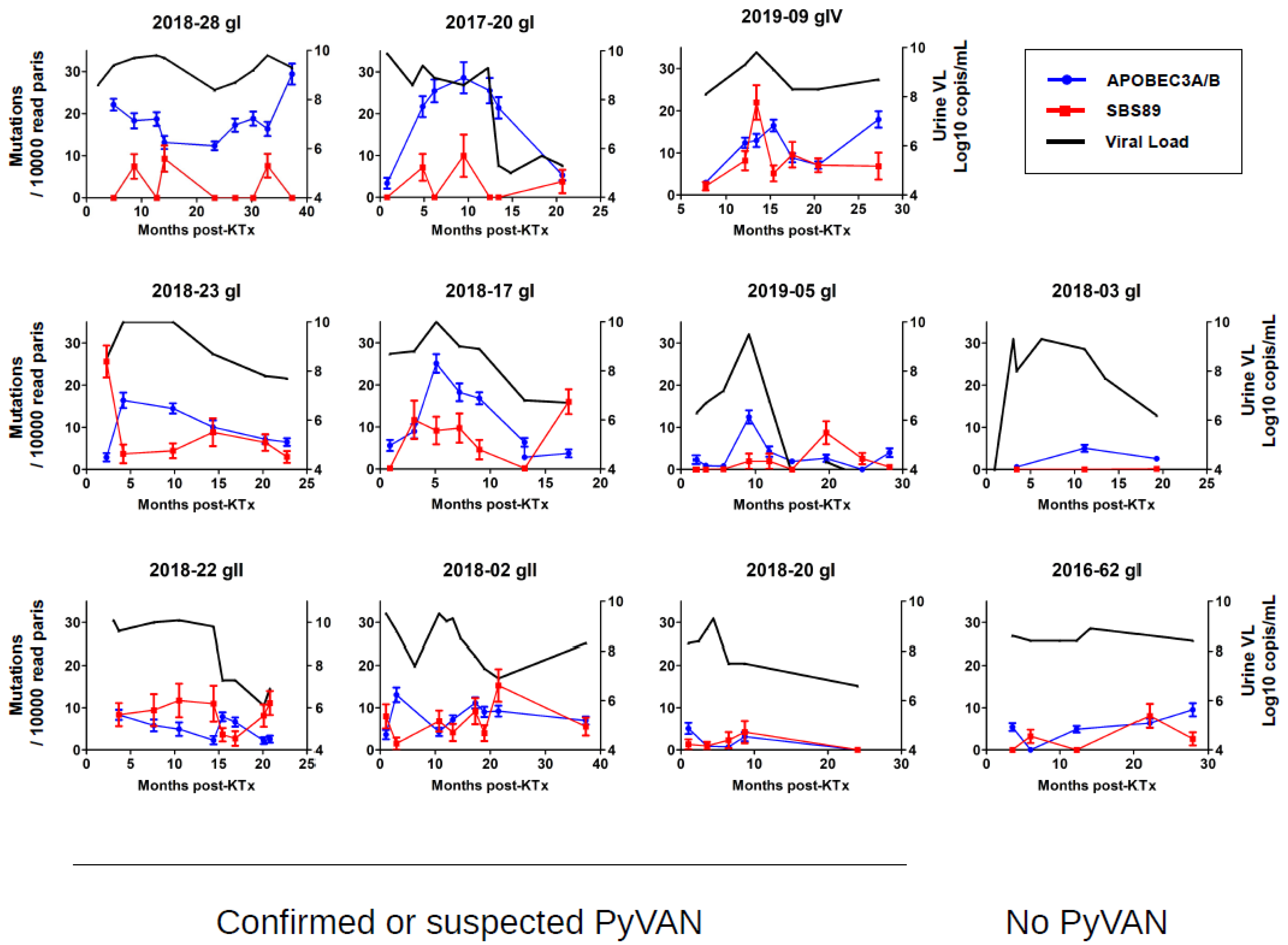
3.3. Longitudinal Variation in APOBEC3A/B and SBS89 Mutation Rates in Patients
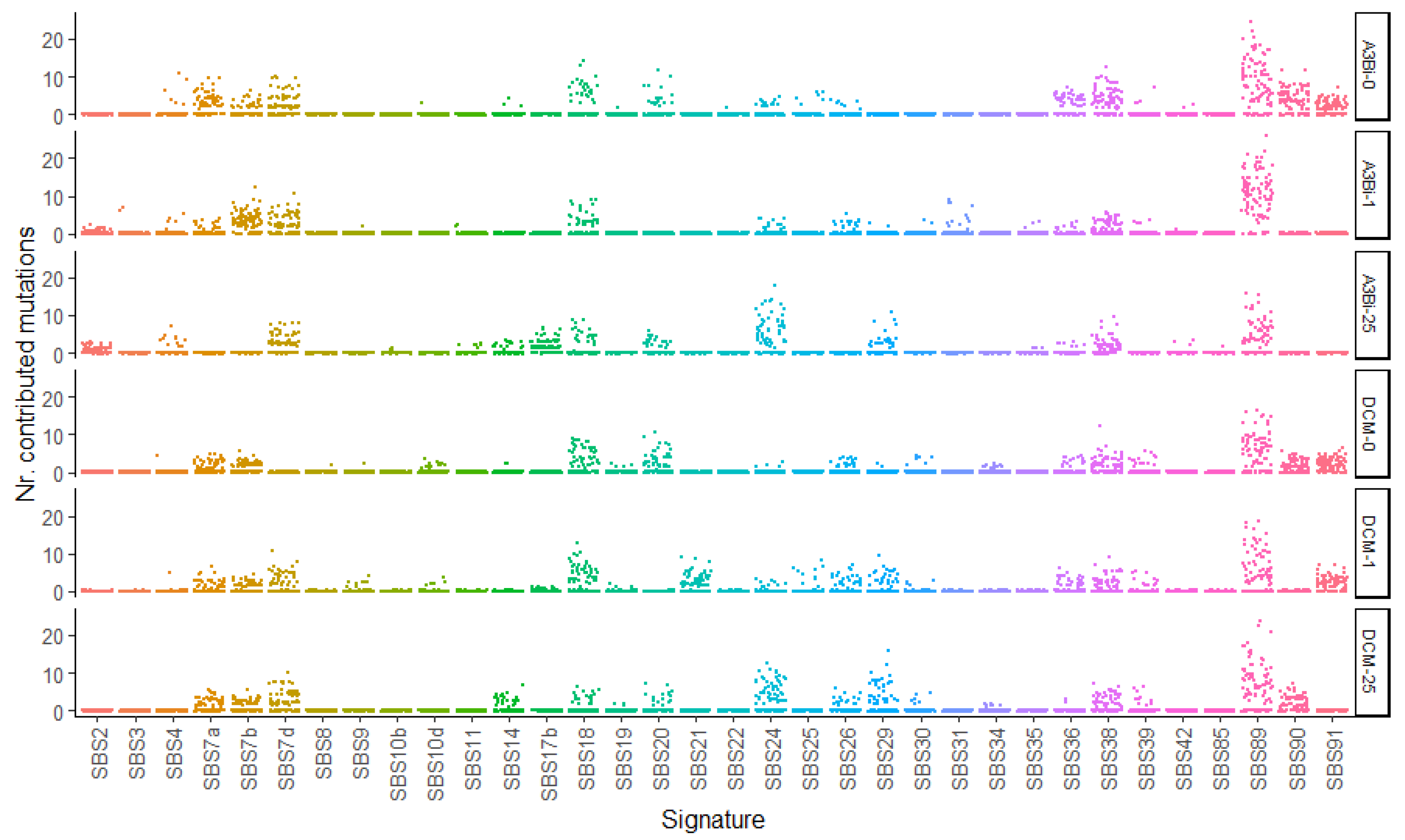
3.4. SBS89 Mutational Profile Is Found during BKPyV Replication in Cell Culture
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Knowles, W.A.; Gibson, P.E.; Gardner, S.D. Serological typing scheme for bk-like isolates of human polyomavirus. J. Med. Virol. 1989, 28, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastrana, D.V.; Ray, U.; Magaldi, T.G.; Schowalter, R.M.; Çuburu, N.; Buck, C.B. BK Polyomavirus Genotypes Represent Distinct Serotypes with Distinct Entry Tropism. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 10105–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Gibson, P.E.; Knowles, W.A.; Clewley, J.P. BK virus antigenic variants: Sequence analysis within the capsid VP1 epitope. J. Med. Virol. 1993, 39, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, P.S.; Khaleel-Ur-Rehman, K.; Swalsky, P.A.; Vats, A.; Scantlebury, V.; Shapiro, R.; Finkelstein, S. DNA sequencing of viral capsid protein VP-1 region in patients with BK virus interstitial nephritis. Transplantation 2002, 73, 1090–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlroy, D.; Hönemann, M.; Nguyen, N.-K.; Barbier, P.; Peltier, C.; Rodallec, A.; Halary, F.; Przyrowski, E.; Liebert, U.; Hourmant, M.; et al. Persistent BK Polyomavirus Viruria is Associated with Accumulation of VP1 Mutations and Neutralization Escape. Viruses 2020, 12, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peretti, A.; Geoghegan, E.M.; Pastrana, D.V.; Smola, S.; Feld, P.; Sauter, M.; Lohse, S.; Ramesh, M.; Lim, E.S.; Wang, D.; et al. Characterization of BK Polyomaviruses from Kidney Transplant Recipients Suggests a Role for APOBEC3 in Driving In-Host Virus Evolution. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 23, 628–635.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickeleit, V.; Singh, H.K.; Dadhania, D.; Cornea, V.; El-Husseini, A.; Castellanos, A.; Davis, V.G.; Waid, T.; Seshan, S.V. The 2018 Banff Working Group classification of definitive polyomavirus nephropathy: A multicenter validation study in the modern era. Am. J. Transplant. 2020, 21, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhalen, B.; Starrett, G.J.; Harris, R.S.; Jiang, M. Functional Upregulation of the DNA Cytosine Deaminase APOBEC3B by Polyomaviruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 6379–6386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.C.; Mason, A.S.; Slip, R.G.; Skinner, K.T.; Macdonald, A.; Masood, O.; Harris, R.S.; Fenton, T.R.; Periyasamy, M.; Ali, S.; et al. Induction of APOBEC3-mediated genomic damage in urothelium implicates BK polyomavirus (BKPyV) as a hit-and-run driver for bladder cancer. Oncogene 2022, 41, 2139–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, D.B.; Desman, G.T.; Amolat-Apiado, M.J.M.; Burstein, D.E.; Godbold, J.H.; Johnson, E.M. Polyoma virus infection is a prominent risk factor for bladder carcinoma in immunocompetent individuals. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2006, 34, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Klimczak, L.J.; A Grimm, S.A.; Fargo, D.; Stojanov, P.; Kiezun, A.; Kryukov, G.; Carter, S.L.; Saksena, G.; et al. An APOBEC cytidine deaminase mutagenesis pattern is widespread in human cancers. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, A.G.; Kim, J.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Bellmunt, J.; Guo, G.; Cherniack, A.D.; Hinoue, T.; Laird, P.W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Akbani, R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 540–556.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, M.; Temiz, N.A.; Harris, R.S. Evidence for APOBEC3B mutagenesis in multiple human cancers. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Wedge, D.C.; Aparicio, S.A.J.R.; Behjati, S.; Biankin, A.V.; Bignell, G.R.; Bolli, N.; Borg, A.; Børresen-Dale, A.-L.; et al. Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature 2013, 500, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Kim, J.; Haradhvala, N.J.; Huang, M.N.; Ng, A.W.T.; Wu, Y.; Boot, A.; Covington, K.R.; Gordenin, D.A.; Bergstrom, E.N.; et al. The repertoire of mutational signatures in human cancer. Nature 2020, 578, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blokzijl, F.; Janssen, R.; Van Boxtel, R.; Cuppen, E. MutationalPatterns: Comprehensive genome-wide analysis of mutational processes. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manders, F.; Brandsma, A.M.; de Kanter, J.; Verheul, M.; Oka, R.; van Roosmalen, M.J.; van der Roest, B.; van Hoeck, A.; Cuppen, E.; van Boxtel, R. MutationalPatterns: The one stop shop for the analysis of mutational processes. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deatherage, D.E.; Barrick, J.E. Identification of Mutations in Laboratory-Evolved Microbes from Next-Generation Sequencing Data Using breseq. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2014, 1151, 165–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takasaka, T.; Goya, N.; Tokumoto, T.; Tanabe, K.; Toma, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Hokama, S.; Momose, A.; Funyu, T.; Fujioka, T.; et al. Subtypes of BK virus prevalent in Japan and variation in their transcriptional control region. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodt, M.; Roehr, J.T.; Ahmed, R.; Dieterich, C. FLEXBAR—Flexible Barcode and Adapter Processing for Next-Generation Sequencing Platforms. Biology 2012, 1, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H. Minimap2: Pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3094–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. 1000 Genome Project Data Processing Subgroup. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilm, A.; Aw, P.P.K.; Bertrand, D.; Yeo, G.H.T.; Ong, S.H.; Wong, C.H.; Khor, C.C.; Petric, R.; Hibberd, M.L.; Nagarajan, N. LoFreq: A sequence-quality aware, ultra-sensitive variant caller for uncovering cell-population heterogeneity from high-throughput sequencing datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 11189–11201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagès, H. BSgenome: Software Infrastructure for Efficient Representation of Full Genomes and Their SNPs 2022. R package version 1.64.0. Seattle, WA, USA. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages/BSgenome (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Akre, M.K.; Starrett, G.J.; Quist, J.S.; Temiz, N.A.; Carpenter, M.A.; Tutt, A.N.J.; Grigoriadis, A.; Harris, R.S. Mutation Processes in 293-Based Clones Overexpressing the DNA Cytosine Deaminase APOBEC3B. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressollette-Bodin, C.; Coste-Burel, M.; Hourmant, M.; Sebille, V.; Andre-Garnier, E.; Imbert-Marcille, B.M. A Prospective Longitudinal Study of BK Virus Infection in 104 Renal Transplant Recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2005, 5, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartanian, J.-P.; Guétard, D.; Henry, M.; Wain-Hobson, S. Evidence for Editing of Human Papillomavirus DNA by APOBEC3 in Benign and Precancerous Lesions. Science 2008, 320, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suspène, R.; Aynaud, M.-M.; Koch, S.; Pasdeloup, D.; Labetoulle, M.; Gaertner, B.; Vartanian, J.-P.; Meyerhans, A.; Wain-Hobson, S. Genetic Editing of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and Epstein-Barr Herpesvirus Genomes by Human APOBEC3 Cytidine Deaminases in Culture and In Vivo. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7594–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakae, K.; Aoyama, S.; Wang, Z.; Kitamura, K.; Liu, G.; Monjurul, A.M.; Koura, M.; Imayasu, M.; Sakamoto, N.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Detection of hypermutated human papillomavirus type 16 genome by Next-Generation Sequencing. Virology 2015, 485, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirose, Y.; Onuki, M.; Tenjimbayashi, Y.; Mori, S.; Ishii, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Tasaka, N.; Satoh, T.; Morisada, T.; Iwata, T.; et al. Within-Host Variations of Human Papillomavirus Reveal APOBEC Signature Mutagenesis in the Viral Genome. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00017-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariaggi, A.-A.; Pere, H.; Perrier, M.; Visseaux, B.; Collin, G.; Veyer, D.; Le Hingrat, Q.; Ferré, V.M.; Joly, V.; Couvelard, A.; et al. Presence of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Apolipoprotein B Messenger RNA Editing, Catalytic Polypeptide-Like 3 (APOBEC)–Related Minority Variants in HPV-16 Genomes From Anal and Cervical Samples but Not in HPV-52 and HPV-58. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagström, S.; Løvestad, A.H.; Umu, S.U.; Ambur, O.H.; Nygård, M.; Rounge, T.B.; Christiansen, I.K. HPV16 and HPV18 type-specific APOBEC3 and integration profiles in different diagnostic categories of cervical samples. Tumour Virus Res. 2021, 12, 200221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koning, F.A.; Newman, E.N.C.; Kim, E.-Y.; Kunstman, K.J.; Wolinsky, S.M.; Malim, M.H. Defining APOBEC3 Expression Patterns in Human Tissues and Hematopoietic Cell Subsets. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9474–9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Lei, K.J.; Jin, W.; Greenwell-Wild, T.; Wahl, S.M. Induction of APOBEC3 family proteins, a defensive maneuver underlying interferon-induced anti–HIV-1 activity. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedegaard, J.; Lamy, P.; Nordentoft, I.; Algaba, F.; Høyer, S.; Ulhøi, B.P.; Vang, S.; Reinert, T.; Hermann, G.G.; Mogensen, K.; et al. Comprehensive Transcriptional Analysis of Early-Stage Urothelial Carcinoma. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natesan, D.; Zhang, L.; Martell, H.J.; Jindal, T.; Devine, P.; Stohr, B.; Espinosa-Mendez, C.; Grenert, J.; Van Ziffle, J.; Joseph, N.; et al. APOBEC Mutational Signature and Tumor Mutational Burden as Predictors of Clinical Outcomes and Treatment Response in Patients With Advanced Urothelial Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 816706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, J.; Newman, T.L.; Tuzun, E.; Kaul, R.; E Eichler, E. Population Stratification of a Common APOBEC Gene Deletion Polymorphism. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Lee, C.-C.; Liu, H.; Wu, C.-S.; Pickering, C.; Huang, P.-J.; Wang, J.; Chang, I.; Yeh, Y.-M.; Chen, C.-D.; et al. APOBEC3A is an oral cancer prognostic biomarker in Taiwanese carriers of an APOBEC deletion polymorphism. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xiao, Y.; Yeager, M.; Clifford, G.; Wentzensen, N.; Cullen, M.; Boland, J.F.; Bass, S.; Steinberg, M.K.; Raine-Bennett, T.; et al. Mutations in the HPV16 genome induced by APOBEC3 are associated with viral clearance. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starrett, G.J.; Serebrenik, A.A.; Roelofs, P.A.; McCann, J.L.; Verhalen, B.; Jarvis, M.C.; Stewart, T.A.; Law, E.K.; Krupp, A.; Jiang, M.; et al. Polyomavirus T Antigen Induces APOBEC3B Expression Using an LXCXE-Dependent and TP53-Independent Mechanism. mBio 2019, 10, e02690-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosert, R.; Rinaldo, C.H.; Funk, G.A.; Egli, A.; Ramos, E.; Drachenberg, C.B.; Hirsch, H.H. Polyomavirus BK with rearranged noncoding control region emerge in vivo in renal transplant patients and increase viral replication and cytopathology. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lejeune, N.; Poulain, F.; Willemart, K.; Blockx, Z.; Mathieu, S.; Gillet, N.A. Infection of Bronchial Epithelial Cells by the Human Adenoviruses A12, B3, and C2 Differently Regulates the Innate Antiviral Effector APOBEC3B. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02413-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, V.C.; Leonard, B.; White, E.A.; Starrett, G.J.; Temiz, N.A.; Lorenz, L.D.; Lee, D.; Soares, M.A.; Lambert, P.F.; Howley, P.; et al. Human Papillomavirus E6 Triggers Upregulation of the Antiviral and Cancer Genomic DNA Deaminase APOBEC3B. mBio 2014, 5, e02234-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Takeuchi, T.; Ishii, Y.; Yugawa, T.; Kiyono, T.; Nishina, H.; Kukimoto, I. Human Papillomavirus 16 E6 Upregulates APOBEC3B via the TEAD Transcription Factor. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02413-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee-Six, H.; Olafsson, S.; Ellis, P.; Osborne, R.J.; Sanders, M.A.; Moore, L.; Georgakopoulos, N.; Torrente, F.; Noorani, A.; Goddard, M.; et al. The landscape of somatic mutation in normal colorectal epithelial cells. Nature 2019, 574, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nik-Zainal, S.; Kucab, J.E.; Morganella, S.; Glodzik, D.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Arlt, V.M.; Weninger, A.; Hollstein, M.; Stratton, M.R.; Phillips, D.H. The genome as a record of environmental exposure. Mutagenesis 2015, 30, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Forward Primer | Sequence | Reverse Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| VPS1-1 | TGATCACGCAAGTGCCAAAACTACTAAT | VPS2-1 | CAATCACGTGCATGAAGGTTAAGCATGC |
| VPS1-2 | TGCGATGTCAAGTGCCAAAACTACTAAT | VPS2-2 | CACGATGTTGCATGAAGGTTAAGCATGC |
| VPS1-3 | TGTTAGGCCAAGTGCCAAAACTACTAAT | VPS2-3 | CATTAGGCTGCATGAAGGTTAAGCATGC |
| VPS1-4 | TGTGACCACAAGTGCCAAAACTACTAAT | VPS2-4 | CATGACCATGCATGAAGGTTAAGCATGC |
| VPS1-5 | TGACATGTCAAGTGCCAAAACTACTAAT | VPS2-5 | CAACATGTTGCATGAAGGTTAAGCATGC |
| VPS1-6 | TGGCCAATCAAGTGCCAAAACTACTAAT | VPS2-6 | CAGCCAATTGCATGAAGGTTAAGCATGC |
| VPS1-7 | TGCAGATCCAAGTGCCAAAACTACTAAT | VPS2-7 | CACAGATCTGCATGAAGGTTAAGCATGC |
| VPS1-8 | TGGATCAGCAAGTGCCAAAACTACTAAT | VPS2-8 | CAGATCAGTGCATGAAGGTTAAGCATGC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McIlroy, D.; Peltier, C.; Nguyen, M.-L.; Manceau, L.; Mobuchon, L.; Le Baut, N.; Nguyen, N.-K.; Tran, M.-C.; Nguyen, T.-C.; Bressollette-Bodin, C. Quantification of APOBEC3 Mutation Rates Affecting the VP1 Gene of BK Polyomavirus In Vivo. Viruses 2022, 14, 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092077
McIlroy D, Peltier C, Nguyen M-L, Manceau L, Mobuchon L, Le Baut N, Nguyen N-K, Tran M-C, Nguyen T-C, Bressollette-Bodin C. Quantification of APOBEC3 Mutation Rates Affecting the VP1 Gene of BK Polyomavirus In Vivo. Viruses. 2022; 14(9):2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092077
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcIlroy, Dorian, Cécile Peltier, My-Linh Nguyen, Louise Manceau, Lenha Mobuchon, Nicolas Le Baut, Ngoc-Khanh Nguyen, Minh-Chau Tran, The-Cuong Nguyen, and Céline Bressollette-Bodin. 2022. "Quantification of APOBEC3 Mutation Rates Affecting the VP1 Gene of BK Polyomavirus In Vivo" Viruses 14, no. 9: 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092077
APA StyleMcIlroy, D., Peltier, C., Nguyen, M.-L., Manceau, L., Mobuchon, L., Le Baut, N., Nguyen, N.-K., Tran, M.-C., Nguyen, T.-C., & Bressollette-Bodin, C. (2022). Quantification of APOBEC3 Mutation Rates Affecting the VP1 Gene of BK Polyomavirus In Vivo. Viruses, 14(9), 2077. https://doi.org/10.3390/v14092077






