Alpha and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Adaptation in an Upper Respiratory Tract Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Viruses
2.2. Infection of MucilAir
2.3. Infection of Vero E6
2.4. Plaque Assay
2.5. Immunofluorescence
2.6. RT-qPCR and Next-Generation Sequencing
2.7. Statistics and Analysis
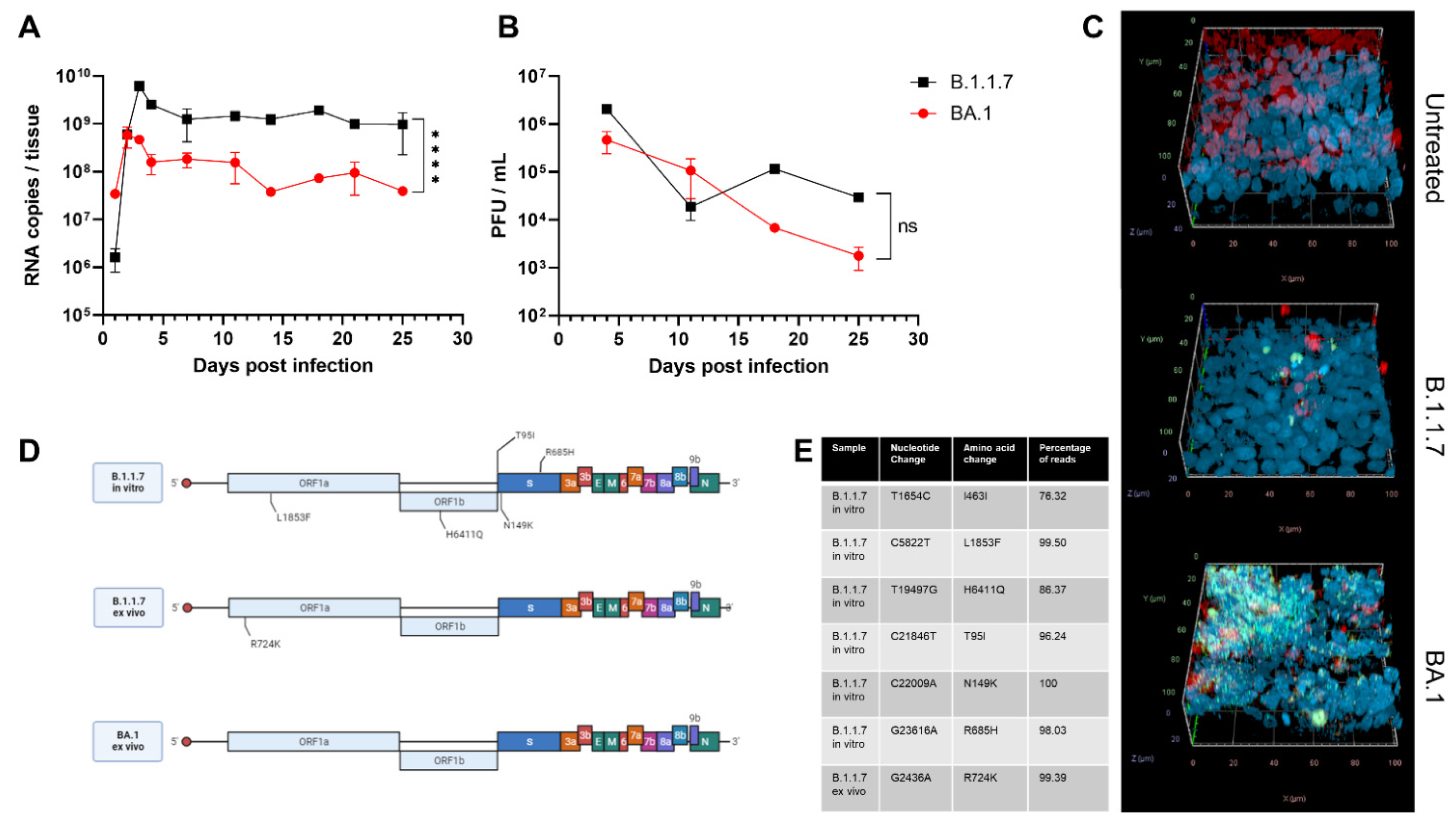
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Wang, X.G.; Hu, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, B.; Huang, C.L.; et al. A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin. Nature 2020, 579, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Who Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed on 25 August 2022).
- Tosta, E. The Adaptation of SARS-CoV-2 to Humans. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2022, 116, e210127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.L.; Wang, J.L.; Ma, X.H.; Sun, X.M.; Li, J.S.; Yang, X.F.; Shi, W.F.; Duan, Z.J. A Novel SARS-CoV-2 Related Coronavirus with Complex Recombination Isolated from Bats in Yunnan Province, China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Giorgi, E.E.; Marichannegowda, M.H.; Foley, B.; Xiao, C.; Kong, X.P.; Chen, Y.; Gnanakaran, S.; Korber, B.; Gao, F. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 through Recombination and Strong Purifying Selection. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytras, S.; Hughes, J.; Martin, D.; Swanepoel, P.; de Klerk, A.; Lourens, R.; Pond, S.L.K.; Xia, W.; Jiang, X.; Robertson, D.L. Exploring the Natural Origins of SARS-CoV-2 in the Light of Recombination. Genome Biol. Evol. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekar, J.; Worobey, M.; Moshiri, N.; Scheffler, K.; Wertheim, J.O. Timing the SARS-CoV-2 Index Case in Hubei Province. Science 2021, 372, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fongaro, G.; PStoco, H.; Souza, D.S.M.; Grisard, E.C.; Magri, M.E.; Rogovski, P.; Schorner, M.A.; Barazzetti, F.H.; Christoff, A.P.; de Oliveira, L.F.V.; et al. The Presence of SARS-CoV-2 Rna in Human Sewage in Santa Catarina, Brazil, November 2019. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekar, J.E.; Magee, A.; Parker, E.; Moshiri, N.; Izhikevich, K.; Havens, J.L.; Gangavarapu, K.; Serrano, L.M.M.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Matteson, N.L.; et al. The Molecular Epidemiology of Multiple Zoonotic Origins of SARS-CoV-2. Science 2022, 377, eabp8337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harari, S.; Tahor, M.; Rutsinsky, N.; Meijer, S.; Miller, D.; Henig, O.; Halutz, O.; Levytskyi, K.; Ben-Ami, R.; Adler, A.; et al. Drivers of Adaptive Evolution during Chronic SARS-CoV-2 Infections. Nat. Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preliminary Genomic Characterisation of an Emergent SARS-CoV-2 Lineage in the UK Defined by a Novel Set of Spike Mutations. Available online: https://virological.org/t/preliminary-genomic-characterisation-of-an-emergent-SARS-CoV-2-lineage-in-the-uk-defined-by-a-novel-set-of-spike-mutations/563 (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Du, P.; Gao, G.F.; Wang, Q. The Mysterious Origins of the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2. Innovation 2022, 3, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Variant: 21k (Omicron). Available online: https://covariants.org/variants/21K.Omicron (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Classification of Omicron (B.1.1.529): SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/26-11-2021-classification-of-omicron-(b.1.1.529)-sars-cov-2-variant-of-concern (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Yurkovetskiy, L.; Wang, X.; Pascal, K.E.; Tomkins-Tinch, C.; Nyalile, T.P.; Wang, Y.; Baum, A.; Diehl, W.E.; Dauphin, A.; Carbone, C.; et al. Structural and Functional Analysis of the D614g SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Variant. Cell 2020, 183, 739–751.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, C.B.; Farzan, M.; Chen, B.; Choe, H. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Entry into Cells. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jian, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, W.; Yisimayi, A.; Huang, W.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; An, R.; et al. Omicron Escapes the Majority of Existing SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies. Nature 2022, 602, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planas, D.; Saunders, N.; Maes, P.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Planchais, C.; Buchrieser, J.; Bolland, W.H.; Porrot, F.; Staropoli, I.; Lemoine, F.; et al. Considerable Escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron to Antibody Neutralization. Nature 2022, 602, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Peng, P.; Cao, X.; Wu, K.; Chen, J.; Wang, K.; Tang, N.; Huang, A.L. Increased Immune Escape of the New SARS-CoV-2 Variant of Concern Omicron. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2022, 19, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulliam, J.R.C.; van Schalkwyk, C.; Govender, N.; von Gottberg, A.; Cohen, C.; Groome, M.J.; Dushoff, J.; Mlisana, K.; Moultrie, H. Increased Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Reinfection Associated with Emergence of Omicron in South Africa. Science 2022, 376, eabn4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subissi, L.; von Gottberg, A.; Thukral, L.; Worp, N.; Munnink, B.B.O.; Rathore, S.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Aguilera, X.; Alm, E.; Archer, B.N.; et al. An Early Warning System for Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.A.; Zhou, Y.; Lokugamage, K.G.; Vu, M.N.; Bopp, N.; Crocquet-Valdes, P.A.; Kalveram, B.; Schindewolf, C.; Liu, Y.; Scharton, D.; et al. Nucleocapsid Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Augment Replication and Pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.W.; Tang, C.; Wei, H.C.; Du, B.; Chen, C.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, M.X.; Cheng, L.; Kuivanen, S.; et al. Genomic Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 Uncovers an Nsp1 Deletion Variant That Modulates Type I Interferon Response. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 489–502.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, M.Z.; Eschke, K.; Hoffmann, M.; Grashoff, M.; Abassi, L.; Kim, Y.; Brunotte, L.; Ludwig, S.; Kroger, A.; Klawonn, F.; et al. Rapid SARS-CoV-2 Adaptation to Available Cellular Proteases. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0218621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, L.A.; Beddingfield, B.J.; Goff, K.; Killeen, S.Z.; Chirichella, N.R.; Melton, A.; Roy, C.J.; Maness, N.J. Intra-Host SARS-CoV-2 Evolution in the Gut of Mucosally-Infected Chlorocebus Aethiops (African Green Monkeys). Viruses 2022, 14, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathnasinghe, R.; Jangra, S.; Ye, C.; Cupic, A.; Singh, G.; Martinez-Romero, C.; Mulder, L.C.F.; Kehrer, T.; Yildiz, S.; Choi, A.; et al. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Mutations Important for Infection of Mice and Escape from Human Immune Sera. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epithelix. Mucilair™: In Vitro 3d Human upper Airway Epithelium. Available online: https://www.epithelix.com/products/mucilair (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Mercier, C.; Jacqueroux, E.; He, Z.; Hodin, S.; Constant, S.; Perek, N.; Boudard, D.; Delavenne, X. Pharmacological Characterization of the 3d Mucilair Nasal Model. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 139, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, R.J.; Lloyd, C.M. Regulation of Immune Responses by the Airway Epithelial Cell Landscape. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medaglia, C.; Kolpakov, I.; Zwygart, A.C.A.; Zhu, Y.; Constant, S.; Huang, S.; Cagno, V.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Stellacci, F.; Xenarios, I.; et al. An anti-influenza combined therapy assessed by single cell RNA-sequencing. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essaidi-Laziosi, M.; Brito, F.; Benaoudia, S.; Royston, L.; Cagno, V.; Fernandes-Rocha, M.; Piuz, I.; Zdobnov, E.; Huang, S.; Constant, S.; et al. Propagation of Respiratory Viruses in Human Airway Epithelia Reveals Persistent Virus-Specific Signatures. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreto-Duran, E.; Artur, S.; Adrianna, G.-B.; Marcin, S.; Maciej, S.; Marek, S.; Zenon, R.; Aleksandra, M.; Marzena, L.; Krzysztof, P. The Interplay between the Airway Epithelium and Tissue Macrophages During the SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaidi-Laziosi, M.; Alvarez, C.; Puhach, O.; Sattonnet-Roche, P.; Torriani, G.; Tapparel, C.; Kaiser, L.; Eckerle, I. Sequential Infections with Rhinovirus and Influenza Modulate the Replicative Capacity of SARS-CoV-2 in the Upper Respiratory Tract. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varricchio, C.; Gregory, M.; Trestan, P.; Claire, B.; Laurent, K.; Caroline, T.; Andrea, B.; Valeria, C. Geneticin Shows Selective Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2 by Interfering with Programmed −1 Ribosomal Frameshifting. Antivir. Res. 2022, 208, 105452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathez, G.; Cagno, V. Clinical Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Isolation and Antiviral Testing. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2021, 29, 20402066211061063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brunink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-Ncov) by Real-Time Rt-Pcr. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacot, D.; Pillonel, T.; Greub, G.; Bertelli, C. Assessment of SARS-CoV-2 Genome Sequencing: Quality Criteria and Low-Frequency Variants. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0094421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, K.P.Y.; Ho, J.C.W.; Cheung, M.C.; Ng, K.C.; Ching, R.H.H.; Lai, K.L.; Kam, T.T.; Gu, H.; Sit, K.Y.; Hsin, M.K.Y.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Replication in Human Bronchus and Lung Ex Vivo. Nature 2022, 603, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mache, C.; Schulze, J.; Holland, G.; Bourquain, D.; Gensch, J.M.; Oh, D.Y.; Nitsche, A.; Durrwald, R.; Laue, M.; Wolff, T. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Is Attenuated for Replication in a Polarized Human Lung Epithelial Cell Model. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, B.J.; Grove, J.; MacLean, O.A.; Wilkie, C.; de Lorenzo, G.; Furnon, W.; Cantoni, D.; Scott, S.; Logan, N.; Ashraf, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Is an Immune Escape Variant with an Altered Cell Entry Pathway. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, T.P.; Jonathan, C.B.; Jie, Z.; Nazia, T.; Ksenia, S.; Joseph, N.; Ruthiran, K.; Yan, A.W.C.; Wilhelm, F.; Giuditta, D.L.; et al. The Altered Entry Pathway and Antigenic Distance of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Map to Separate Domains of Spike Protein. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Pia, L.; Rowland-Jones, S. Omicron Entry Route. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, D.; Pomeroy, M.A.; Lewis, N.M.; Wadhwa, A.; Yousaf, A.R.; Whitaker, B.; Dietrich, E.; Hall, A.J.; Chu, V.; Thornburg, N.; et al. Persistent SARS-CoV-2 Rna Shedding without Evidence of Infectiousness: A Cohort Study of Individuals with COVID-19. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 224, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Ishikane, M.; Ujiie, M.; Iwamoto, N.; Okumura, N.; Sato, T.; Nagashima, M.; Moriya, A.; Suzuki, M.; Hojo, M.; et al. Duration of Infectious Virus Shedding by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant-Infected Vaccinees. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 998–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucau, J.; Marino, C.; Regan, J.; Uddin, R.; Choudhary, M.C.; Flynn, J.P.; Chen, G.; Stuckwisch, A.M.; Mathews, J.; Liew, M.Y.; et al. Duration of Shedding of Culturable Virus in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (Ba.1) Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Kim, J.; Hong, S.P.; Choi, S.Y.; Yang, M.J.; Ju, Y.S.; Kim, Y.T.; Kim, H.M.; Rahman, M.D.T.; Chung, M.K.; et al. Nasal Ciliated Cells Are Primary Targets for SARS-CoV-2 Replication in the Early Stage of COVID-19. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinot, R.; Hubert, M.; de Melo, G.D.; Lazarini, F.; Bruel, T.; Smith, N.; Levallois, S.; Larrous, F.; Fernandes, J.; Gellenoncourt, S.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Induces the Dedifferentiation of Multiciliated Cells and Impairs Mucociliary Clearance. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slavov, S.N.; Patane, J.S.L.; Bezerra, R.D.S.; Giovanetti, M.; Fonseca, V.; Martins, A.J.; Viala, V.L.; Rodrigues, E.S.; Santos, E.V.; Barros, C.R.S.; et al. Genomic Monitoring Unveil the Early Detection of the SARS-CoV-2 B.1.351 (Beta) Variant (20h/501y.V2) in Brazil. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 6782–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Choi, J.H.; Dai, D.L.; Luo, J.; Ladak, R.J.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wiebe, S.; Liu, A.C.H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Impairs Interferon Production Via Nsp2-Induced Repression of Mrna Translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2204539119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Moch, C.; Graille, M.; Chapat, C. The SARS-CoV-2 Protein Nsp2 Impairs the Silencing Capacity of the Human 4ehp-Gigyf2 Complex. iScience 2022, 25, 104646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, J.K.; Sengupta, A.; Choudhury, P.P.; Roy, S. Characterizing Genomic Variants and Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Proteins from Indian Isolates. Gene Rep. 2021, 25, 101044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, R.; Moyo, S.; Amoako, D.G.; Tegally, H.; Scheepers, C.; Althaus, C.L.; Anyaneji, U.J.; Bester, P.A.; Boni, M.F.; Chand, M.; et al. Rapid Epidemic Expansion of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant in Southern Africa. Nature 2022, 603, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.P., Jr.; Wertheim, J.O.; Wang, J.C.; Vasylyeva, T.I.; Havens, J.L.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Gonzalez, E.; Fang, C.E.; di Lonardo, S.S.; Hughes, S.; et al. Detection and Characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 Lineage B.1.526 in New York. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Qin, S.; Dai, L.; Tian, Z. The Glycosylation in SARS-CoV-2 and Its Receptor Ace2. Signal. Transduct Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mykytyn, A.Z.; Breugem, T.I.; Riesebosch, S.; Schipper, D.; van den Doel, P.B.; Rottier, R.J.; Lamers, M.M.; Haagmans, B.L. SARS-CoV-2 Entry into Human Airway Organoids Is Serine Protease-Mediated and Facilitated by the Multibasic Cleavage Site. eLife 2021, 10, e64508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mathez, G.; Pillonel, T.; Bertelli, C.; Cagno, V. Alpha and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Adaptation in an Upper Respiratory Tract Model. Viruses 2023, 15, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010013
Mathez G, Pillonel T, Bertelli C, Cagno V. Alpha and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Adaptation in an Upper Respiratory Tract Model. Viruses. 2023; 15(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleMathez, Gregory, Trestan Pillonel, Claire Bertelli, and Valeria Cagno. 2023. "Alpha and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Adaptation in an Upper Respiratory Tract Model" Viruses 15, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010013
APA StyleMathez, G., Pillonel, T., Bertelli, C., & Cagno, V. (2023). Alpha and Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Adaptation in an Upper Respiratory Tract Model. Viruses, 15(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010013




