Combating Lassa Fever in West African Sub-Region: Progress, Challenges, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology of Lassa Fever in West African Countries
2.1. Prevalence
2.2. Epidemiology
2.3. Transmission of LF
3. Clinical Perspectives
3.1. Pathology
3.2. Pathogenesis of LF
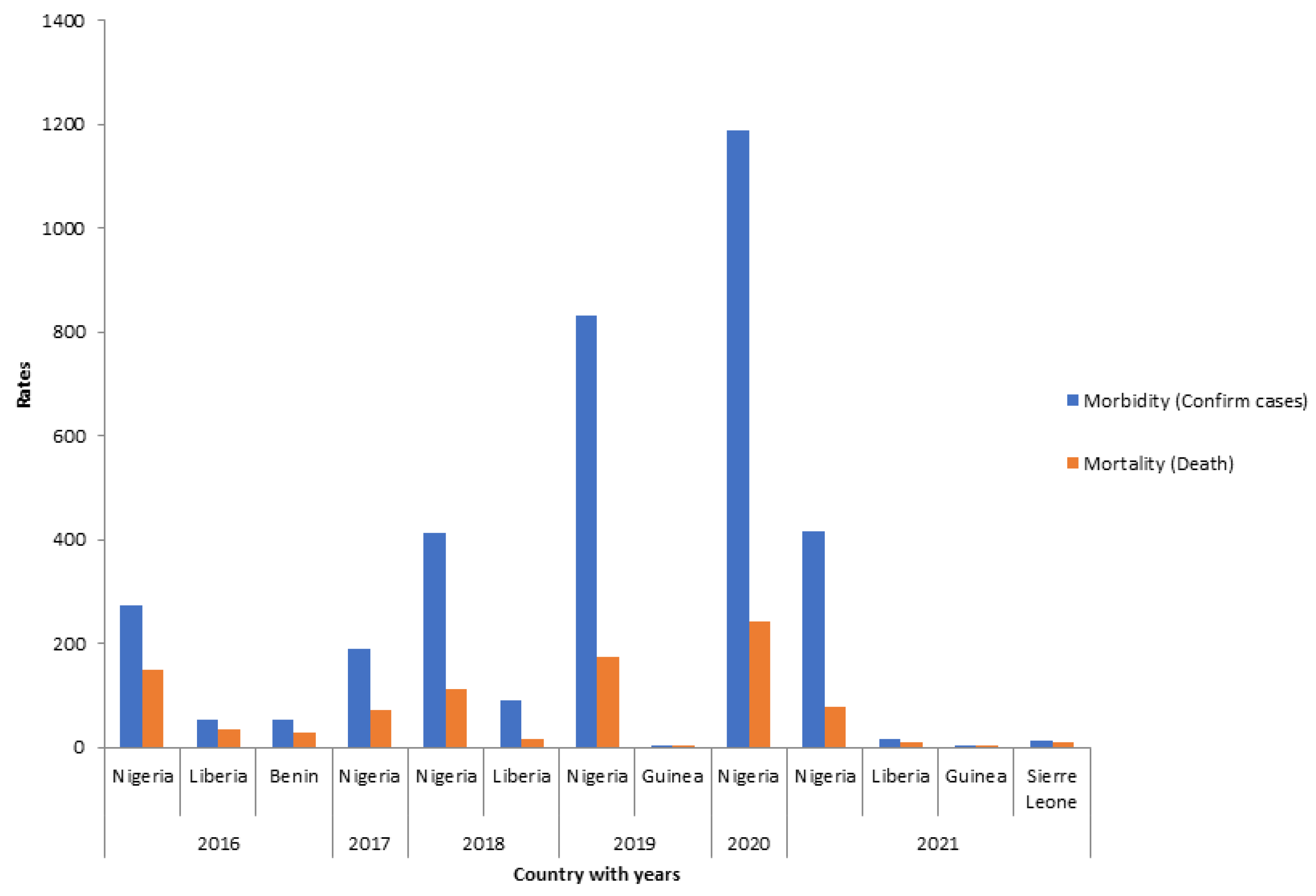
3.3. Morbidity and Mortality of LF
3.4. Clinical Manifestations
4. Management of LF
4.1. Prevention/Control
4.2. Vaccination as Feasible Control Measures for LF Curtailment
5. Needs and Future Directions
5.1. Validation of Druggable Targets
5.2. Drug Repurposing
6. Challenges in the Management/Control of LF
7. Discussion of Major Findings
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yessinou, R.E.; Waladjo, A.R.K.; Noudeke, N.; Dramou, I.; Adinsi, J.; Dougnon, V.T.; Sangnidjo, E.Y.; Osse, R.; Dansou, A.; Farougou, S. Dynamic and Epidemiology of Lassa Fever Infection in West Africa’s Population from 1969 to 2019. Hosts Viruses 2020, 7, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylne, A.Q.N.; Pigott, D.M.; Longbottom, J.; Shearer, F.; Duda, K.A.; Messina, J.P.; Weiss, D.J.; Moyes, C.I.; Golding, N.; Hay, S.I. Mapping the zoonotic niche of Lassa fever in Africa. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 109, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sogoba, N.; Feldmann, H.; Safronetz, D. Lassa Fever in West Africa: Evidence for an Expanded Region of Endemicity. Zoonoses Public Health 2012, 59, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Lassa fever in Nigeria, Benin, Togo-Recherche Google [WWW Document]. 2016. Available online: http://researcherslinks.com/current-issues/Dynamic-and-Epidemiology-Lassa-Fever/6/8/3811/html (accessed on 22 May 2019).
- Brosh-Nissimov, T. Lassa fever: Another threat from West Africa. Disaster Mil. Med. 2016, 2, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auperin, D.D.; Sasso, D.R.; McCormick, J.B. Nucleotide sequence of the glycoprotein gene and intergenic region of the Lassa virus S genome RNA. Virology 1986, 154, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danny, A.A.; George, O.A.; Chikwe, I.A.Z. Lassa Fever Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, Management and Prevention. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 33, 933–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, L.E.; Strong, J.E. Lassa fever: With 50 years of study, hundreds of thousands of patients and an extremely high disease burden, what have we learned? Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 37, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kofman, A.; Choi, M.J.; Rollin, P.E. Lassa fever in travelers from West Africa, 1969–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 236–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, A. The Politics of an Emerging Disease and the Scope for One Health, STEPS Working Paper 83. Brighton: STEPS Centre. 2015. Available online: https://lassafever.info/resources/lassa-fever-politics-emerging-disease-and-scope-one-health (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- McLay, L.; Lan, S.; Ansari, A.; Liang, Y.; Ly, H. Identification of Virulence Determinants within the L Genomic Segment of the Pichinde Arenavirus. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6635–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richmond, J.K.; Baglole, D.J. Lassa fever: Epidemiology, clinical features, and social consequences. BMJ 2003, 327, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.B.; Webb, P.A.; Krebs, J.W.; Johnson, K.M.; Smith, E.S. A Prospective Study of the Epidemiology and Ecology of Lassa Fever. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 155, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. List of Blueprint Priority Diseases. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/blueprint/priority-diseases/en/%0A%0A (accessed on 10 August 2017).
- Mehand, M.S.; Al-Shorbaji, F.; Millett, P.; Murgue, B. The WHO R&D Blueprint: 2018 review of emerging infectious diseases requiring urgent research and development efforts. Antiviral Res. 2018, 159, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Røttingen, J.A.; Gouglas, D.; Feinberg, M.; Plotkin, S.; Raghavan, K.V.; Witty, A.; Draghia-Akli, R.; Stoffels, P.; Piot, P. New vaccines against Epidemic Infectious Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, J.; King, I.; Webb, P.; Scribner, C.; Craven, R.; Johnson, K.; Luanne, H.; Elliott, M.S.; Belmont-Williams, M.D. Lassa fever. Effective therapy with ribavirin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 314, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddle, K.J.; Eromon, P.; Barnes, K.G.; Mehta, S.; Oguzie, J.U.; Odia, I.; Schaffner, S.F.; Winnicki, S.M.; Shah, R.R.; Qu, J. Genomic Analysis of Lassa Virus during an Increase in Cases in Nigeria in 2018. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Günther, S.; Emmerich, P.; Laue, T.; Kühle, O.; Asper, M.; Jung, A.; Grewing, T.; Meulen, J.T.; Schmitz, H. Imported Lassa fever in Germany: Molecular characterization of a new Lassa virus strain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2000, 6, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overbosch, F.; de Boer, M.; Veldkamp, K.E.; Ellerbroek, P.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; Goorhuis, B.; van Vugt, M.; van der Eijk, A.; Leenstra, T.; Khargi, M.; et al. Public health response to two imported, epidemiologically related cases of Lassa fever in the Netherlands (ex Sierra Leone), November 2019. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Disease Outbreak News; Lassa fever—United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/lassa-fever-united-kingdom-of-great-britain-and-northern-irel (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- McElroy, A.K.; Akondy, R.S.; Harmon, J.R.; Ellebedy, A.H.; Cannon, D.; Klena, J.D.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Mehta, A.K.; Kraft, C.S.; et al. A Case of Human Lassa Virus Infection with Robust Acute T-Cell Activation and Long-Term Virus-Specific T-Cell Responses. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1862–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quigley, R.L. How, where and why do we evacuate those infected with viral hemorrhagic fevers? Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 1–69. [Google Scholar]
- Ajayi, N.A.; Nwigwe, C.G.; Azuogu, B.N.; Onyire, B.N.; Nwonwu, E.U.; Ogbonnaya, L.U.; Onwe, F.I.; Ekaete, T.; Günther, S.; Ukwaja, K.N.; et al. Containing a Lassa fever epidemic in a resource-limited setting: Outbreak description and lessons learned from Abakaliki, Nigeria (January-March 2012). Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 17, e1011–e1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibekwe, T. Lassa fever: Challenges of curtailing a deadly disease. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2012, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dan-Nwafor, C.C.; Ipadeola, O.; Smout, E.; Ilori, E.; Adeyemo, A.; Umeokonkwo, C.; Nwidid, D.; Nwachukwua, W.; Ukponue, W.; Omabed, E.; et al. A cluster of nosocomial Lassa fever cases in a tertiary health facility in Nigeria: Description and lessons learned, 2018. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 83, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Lassa Fever. Newsletter, Geneva. 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/lassa-fever (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Africa Centre for Disease and Control. Annual Report on Lassa Fever Outbreak in Africa 2021. Available online: https://africacdc.org/disease/lassa-fever/ (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Mba, S.; Ukponu, W.; Adekanye, U.; Saleh, M.; Agogo, E.; Dan-Nwafor, C.; Amao, L.; Oparah, O.; Olajide, L.; Oyegoke, A.; et al. A description of Lassa Fever mortality during the 2019 outbreak in Nigeria. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyessa, A.B.; Maximore, L.; Keller, D.; Dogba, J.; Pajibo, M.; Johnson, K.; Saydee, E.; Monday, J.; Tuopileyi, R.; Mahmoud, N. Lesson learned from the investigation and response of Lassa fever outbreak, Margibi County, Liberia, 2018: Case report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Africa Centre for Disease and Control. Annual report on Lassa fever outbreak in Africa. 2018. Available online: https://africacdc.org/disease/lassa-fever/ (accessed on 17 June 2021).
- Mofolorunsho, K.C. Outbreak of lassa fever in nigeria: Measures for prevention and control. Pan. Afr. Med. J. 2016, 23, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbu, O.; Ajuluchukwu, E.; Uneke, C.J. Lassa fever in West African sub-region: An overview. J. Vector Borne Dis. 2007, 44, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dimie, O. Lassa fever: A clinical and epidemiological review. Niger Delta J. Med. Med. Res. 2013, 1, 1271–1275. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, H.; Köhler, B.; Laue, T.; Drosten, C.; Veldkamp, P.J.; Günther, S.; Emmerich, P.; Geisen, H.P.; Beersma, M.F.; Hoerauf, A. Monitoring of clinical and laboratory data in two cases of imported Lassa fever. Microbes. Infect. 2002, 4, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.E.; Fisher-Hoch, S.P.; Craven, R.B.; McCormick, J.B. A prospective study of maternal and fetal outcome in acute Lassa fever infection during pregnancy. Br. Med. J. 1988, 297, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omeh, D.; Achinge, G.; Echekwube, P. Lassa Fever in West Africa: A Clinical and Epidemiological Review. J. Adv. Med. Med. Res. 2017, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olayemi, A.; Cadar, D.; Magassouba, N.; Obadare, A.; Kourouma, F.; Oyeyiola, A.; Fasogbon, S.; Igbokwe, J.; Rieger, T.; Bockholt, S.; et al. New Hosts of The Lassa Virus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.H.; Goba, A.; Chu, M.; Roth, C.; Healing, T.; Marx, A.; Fair, J.; Guttieri, M.C.; Ferro, P.; Imes, T.; et al. New opportunities for field research on the pathogenesis and treatment of Lassa fever. Antiviral Res. 2008, 78, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, D.H.; McCormick, J.B.; Johnson, K.M.; Webb, P.A.; Komba-Kono, G.; Elliott, L.H.; Gardner, J.J. Pathologic and Virologic Study of Fatal Lassa Fever in Man. AJP 1982, 107, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Günther, S.O.L. Lassa fever. Br. Med. J. 1972, 4, 253–254. [Google Scholar]
- Winn, W.C.; Walker, D.H. The pathology of human Lassa fever. Bull. World Health Organ. 1975, 52, 535–545. [Google Scholar]
- Hastie, K.M.; Bale, S.; Kimberlin, C.R.; Saphire, E.O. Hiding the evidence: Two strategies for innate immune evasion by hemorrhagic fever viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojek, J.M.; Kunz, S. Cell entry by human pathogenic arenaviruses. Cell Microbiol. 2008, 10, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azeez-Akande, O. A review of lassa fever, an emerging old world haemorrhagic viral disease in Sub-Saharan Africa Azeez-Akande. Afr. J. CLN. Exper. Microbiol. 2016, 17, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Günther, S.; Weisner, B.; Roth, A.; Grewing, T.; Asper, M.; Drosten, C.; Emmerich, P.; Petersen, J.; Wilczek, M.; Schmitz, H. Lassa fever encephalopathy: Lassa virus in cerebrospinal fluid but not in serum. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 184, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, S.; Bausch, D.G.; Thomas, R.L.; Goba, A.; Bah, A.; Peters, C.J.; Rollin, P.E. Low levels of interleukin-8 and interferon-inducible protein-10 in serum are associated with fatal infections in acute Lassa fever. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lukashevich, I.S.; Maryankova, R.; Vladyko, A.S.; Nashkevich, N.; Koleda, S.; Djavani, M.; Horejsh, D.; Voitenok, N.N.; Salvato, M.S. Lassa and Mopeia Virus Replication in Human Monocytes/Macrophages and in Endothelial Cells: Different Effects on IL-8 and TNF-α Gene Expression. J. Med. Virol. 1999, 59, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, S.; Hutchinson, K.; Agarwal, S.; Mcrae, M.; Rollin, P.E.; Pulendran, B. Cutting Edge: Impairment of Dendritic Cells and Adaptive Immunity by Ebola and Lassa Viruses. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 2797–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baize, S.; Kaplon, J.; Faure, C.; Pannetier, D.; Georges-Courbot, M.-C.; Deubel, V. Lassa Virus Infection of Human Dendritic Cells and Macrophages Is Productive but Fails to Activate Cells. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowen, M.D.; Peters, C.J.; Nichol, S. Phylogenetic analysis of the Arenaviridae: Patterns of virus evolution and evidence for cospeciation between arenaviruses and their rodent hosts. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1997, 8, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannetier, D.; Reynard, S.; Russier, M.; Journeaux, A.; Tordo, N.; Deubel, V.; Baize, S. Human Dendritic Cells Infected with the Nonpathogenic Mopeia Virus Induce Stronger T-Cell Responses than Those Infected with Lassa Virus. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8293–8306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekpunobi Chime, P.; Nkechi Chime, E.; Chukwunonso Okechukwu, U. Mortality among Lassa Fever Patients: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 9, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Imported Lassa fever-New Jersey, 2004. MMWR Morb. Mortal Wkly. Rep. 2004, 53, 894–897. [Google Scholar]
- Ehichioya, D.U.; Asogun, D.A.; Ehimuan, J.; Okokhere, P.O.; Pahlmann, M.; Ölschläger, S.; Becker-Ziaja, B.; Günther, S.; Omilabu, S.A. Hospital-based surveillance for Lassa fever in Edo State, Nigeria, 2005-2008. Trop. Med. Int. Heal. 2012, 17, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, T. Lassa Fever. TKH Virology Notes 2004. Available online: http://www.tarakharper.com/v_lassa.htm.%0A%0A (accessed on 9 July 2022).
- Abdulkarim, M.A.; Babale, S.M.; Umeokonkwo, C.D.; Bamgboye, E.A.; Bashorun, A.T.; Usman, A.A.; Balogun, M.S. Epidemiology of Lassa fever and factors associated with deaths, Bauchi State, Nigeria, 2015–2018. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 799–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahmane, A.; van Griensven, J.; Van Herp, M.; Van den Bergh, R.; Nzomukunda, Y.; Prior, J.; Alders, P.; Jambai, A.; Zachariah, R. Constraints in the diagnosis and treatment of Lassa Fever and the effect on mortality in hospitalized children and women with obstetric conditions in a rural district hospital in Sierra Leone. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 108, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asogun, D.A.; Adomeh, D.I.; Ehimuan, J.; Odia, I.; Hass, M.; Gabriel, M.; Ölschläger, M.; Becker-Ziaja, B.; Folarin, O.; Phelan, E.; et al. Molecular Diagnostics for Lassa Fever at Irrua Specialist Teaching Hospital, Nigeria: Lessons Learnt from Two Years of Laboratory Operation. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J.G.; Grant, D.S.; Schieffelin, J.S.; Boisen, M.L.; Goba, A.; Hartnett, J.N.; Levy, D.C.; Yenni, R.E.; Moses, L.M.; Fullah, M.; et al. Lassa Fever in Post-Conflict Sierra Leone. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okokhere, P.; Colubri, A.; Azubike, C.; Osazuwa, O.; Tabrizi, S.; Chin, E.; Asad, S.; Rafiu, M.; Adomeh, D.; Odia, I.; et al. Clinical and laboratory predictors of Lassa fever outcome in a dedicated treatment facility in Nigeria: An observational cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buba, M.I.; Dalhat, M.M.; Nguku, P.M.; Waziri, N.; Mohammad, J.O.; Bomoi, I.M.; Onyiah, A.P.; Onwujei, J.; Balogun, M.S.; Bashorun, A.T.; et al. Mortality Among Confirmed Lassa Fever Cases During the 2015–2016 Outbreak in Nigeria. Am. J. Public. Health 2018, 108, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaro, C.A.; Kogi, E.; Opara, K.N.; Batiha, G.E.; Baty, R.S.; Albrakati, A.; Altalbawy, F.M.A.; Etuh, I.U.; Oni, J.P. Infection pattern, case fatality rate and spread of Lassa virus in Nigeria. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.M.; Jokinen, J.D.; Lukashevich, I.S. Attenuated replication of lassa virus vaccine candidate ML29 in STAT-1 -/- mice. Pathogens 2019, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Lassa Fever. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/lassa-fever (accessed on 5 February 2021).
- Akhuemokhan, O.C.; Ewah-Odiase, R.O.; Akpede, N.; Ehimuan, J.; Adomeh, D.I.; Odia, I.; Olomu, S.C.; Pahlmann, M.; Becker-Ziaja, B.; Happi, C.T.; et al. Prevalence of Lassa Virus Disease (LVD) in Nigerian children with fever or fever and convulsions in an endemic area. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Lassa Fever. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/lassa/index.html (accessed on 15 June 2019).
- Dunmade, A.D.; Segun-Busari, S.; Olajide, T.G.; Ologe, F.E. Profound bilateral sensorineural hearing loss in Nigerian children: Any shift in etiology? J. Deaf. Stud. Deaf. Educ. 2007, 12, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateer, E.J.; Huang, C.; Shehu, N.Y.; Paessler, S. Lassa fever–induced sensorineural hearing loss: A neglected public health and social burden. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2018, 12, e0006187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibekwe, T.S.; Okokhere, P.O.; Asogun, D.; Blackie, F.F.; Nwegbu, M.M.; Wahab, K.W.; Omilabu, S.A.; Akpede, G.O. Early-onset sensorineural hearing loss in Lassa fever. Eur. Arch. Oto. Rhino. Laryngol. 2011, 268, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccormick, J.B. Clinical, epidemiology, and therapeutic aspects of Lassa fever. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1986, 175, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, J.B.; King, I.J.; Webb, P.A.; Johnson, K.M.; O’Sullivan, R.; Smith, E.S.; Trippel, S.; Tong, T.C. A Case-Control Study of the Clinical Diagnosis and Course of Lassa Fever. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 155, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okokhere, P.O.; Ibekwe, T.S.; Akpede, G.O. Sensorineural hearing loss in Lassa fever: Two case reports. J. Med. Case Rep. 2009, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. WHO Lassa Fever Fact Sheet No 179; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, N.E.; Ronca, S.; Tamura, A.; Koma, T.; Seregin, A.V.; Dineley, K.T.; Miller, M.; Cook, R.; Shimizu, N.; Walker, A.G.; et al. Animal Model of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Associated with Lassa Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 2920–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maruyama, J.; Reyna, R.A.; Kishimoto-Urata, M.; Urata, S.; Manning, J.T.; Harsell, N.; Cook, R.; Huang, C.; Nikolich-Zugich, J.; Makishima, T.; et al. CD4 T-cell depletion prevents Lassa fever associated hearing loss in the mouse model. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Disease Control. CDC Fact Sheet on Lassa Fever. 2015. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/vhf/lassa/pdf/factsheet.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Mire, C.E.; Cross, R.W.; Geisbert, J.B.; Borisevich, V.; Agans, K.N.; Deer, D.J.; Heinrich, M.L.; Rowland, M.M.; Goba, A.; Momoh, M.; et al. Human-monoclonal-antibody therapy protects nonhuman primates against advanced Lassa fever. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlkes, L.; George, M.; Samosny, G.; Burckhardt, F.; Vogt, M.; Bent, S.; Jahn, K.; Zanger, P. Management of a lassa fever outbreak, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, 2016. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 16-00728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, W.H.; Breuer, T.; Pfaff, G.; Schmitz, H.; Köhler, P.; Asper, M.; Emmerich, P.; Drosten, C.; Gölnitz, U.G.; Fleischer, K.; et al. Imported Lassa fever in Germany: Surveillance and management of contact persons. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 36, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroezindu, M.O.; Unigwe, U.S.; Okwara, C.C.; Ozoh, G.A.; Ndu, A.C.; Ohanu, M.E.; Nwoko, U.O.; Okoroafor, U.W.; Ejimudo, E.; Tobin, E.A.; et al. Lessons learnt from the management of a case of Lassa fever and follow-up of nosocomial primary contacts in Nigeria during Ebola virus disease outbreak in West Africa. Trop. Med. Int. Heal 2015, 20, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J.G.; Schieffelin, J.S.; Grant, D.S.; Goba, A.; Momoh, M.; Kanneh, L.; Levy, D.C.; Hartnett, J.N.; Boisen, M.L.; Branco, L.M.; et al. Data set on Lassa fever in post-conflict Sierra Leone. Data Br. 2019, 23, 103673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristian, G.; Andersen, B.; Shapiro, J.; Matranga, B.M.; Sealfon, R.; Lin, A.E.; Moses, L.M.; Onikepe, A.F.; Goba, A.; Odia, I.; et al. Clinical sequencing uncovers origins and evolution of Lassa virus. Cell 2015, 162, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowen, M.D.; Rollin, P.E.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Hustad, H.L.; Bausch, D.G.; Demby, A.H.; Bajani, M.D.; Peters, C.J.; Nichol, S.T. Genetic Diversity among Lassa Virus Strains. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6992–7004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emmerich, P.; Günther, S.; Schmitz, H. Strain-specific antibody response to Lassa virus in the local population of west Africa. J. Clin. Virol. 2008, 42, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, R.W.; Mire, C.E.; Branco, L.M.; Geisbert, J.B.; Rowland, M.M.; Heinrich, M.L.; Goba, A.; Momoh, M.; Grant, D.S.; Fullah, M.; et al. Treatment of Lassa virus infection in outbred guinea pigs with first-in-class human monoclonal antibodies. Antiviral. Res. 2016, 133, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crotty, S.; Maag, D.; Arnold, J.J.; Zhong, W.; Lau, J.Y.N.; Hong, Z.; Andino, R.; Cameron, C.E. The broad-spectrum antiviral ribonucleoside ribavirin is an RNA virus mutagen. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1375–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idemyor, V. Lassa virus infection in Nigeria: Clinical perspective overview. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2010, 102, 1243–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, S.; Cameron, C.E.; Andino, R. RNA virus error catastrophe: Direct molecular test by using ribavirin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 6895–6900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takaki, S.; Tsubota, A.; Hosaka, T.; Akuta, N.; Someya, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, F.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Arase, Y.; et al. Factors contributing to ribavirin dose reduction due to anemia during interferon alfa2b and ribavirin combination therapy for chronic hepatitis C. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soota, K.; Maliakkal, B. Ribavirin induced hemolysis: A novel mechanism of action against chronic hepatitis C virus infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16184–16190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, C.E.; Castro, C. The mechanism of action of ribavirin: Lethal mutagenesis of RNA virus genomes mediated by the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 14, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun-Sand, S.B.; Peetz, M. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase as a target for antiviral, anticancer, antimicrobial and immunosuppressive therapeutics. Future Med. Chem. 2010, 2, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, J.; Almquist, S.J.; Ford, P.J.; Shlyakhter, D.; Wang, Y.; Nimmesgern, E.; Germann, U.A. Regulation of inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase type I and type II isoforms in human lymphocytes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 67, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streeter, D.G.; Witkowski, J.T.; Khare, G.P.; Sidwell, R.W.; Bauer, R.J.; Robins, R.K.; Simon, L.N. Mechanism of Action of 1-i3-D-Ribofuranosyl-1, 2, 4-Triazole-3-Carboxamide. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 1174–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno, H.; Gallego, I.; Sevilla, N.; de la Torre, J.C.; Domingo, E.; Martin, V. Ribavirin Can Be Mutagenic for Arenaviruses. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 7246–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrillo-Bustamante, P.; Nguyen, T.H.T.; Oestereich, L.; Günther, S.; Guedj, J.; Graw, F. Determining Ribavirin’s mechanism of action against Lassa virus infection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oestereich, L.; Rieger, T.; Lüdtke, A.; Ruibal, P.; Wurr, S.; Pallasch, E.; Bockholt, S.; Krasemann, S.; Muñoz-Fontela, C.; Günther, S. Efficacy of Favipiravir Alone and in Combination With Ribavirin in a Lethal, Immunocompetent Mouse Model of Lassa Fever. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raabe, V.N.; Kann, G.; Ribner, B.S.; Andres, A.M.; Varkey, J.B.; Mehta, A.K.; Lyon, G.M.; Vanairsdale, S.; Faber, K.; Becker, S.; et al. Favipiravir and ribavirin treatment of epidemiologically linked cases of lassa fever. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safronetz, D.; Rosenke, K.; Westover, J.B.; Martellaro, C.; Okumura, A.; Furuta, Y.; Geisbert, J.; Saturday, G.; Komeno, T.; Geisbert, T.W.; et al. The broad-spectrum antiviral favipiravir protects Guinea pigs from lethal Lassa virus infection post-disease onset. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sepúlveda, C.S.; García, C.C.; Damonte, E.B. Determining the virus life-cycle stage blocked by an antiviral. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1604, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenke, K.; Feldmann, H.; Westover, J.B.; Hanley, P.W.; Martellaro, C.; Feldmann, F.; Saturday, G.; Lovaglio, J.; Scott, D.P.; Furuta, Y.; et al. Use of favipiravir to treat lassa virus infection in Macaques. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1696–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hensley, L.E.; Smith, M.A.; Geisbert, J.B.; Fritz, E.A.; Daddario-Dicaprio, K.M.; Larsen, T.; Geisbert, T.W. Pathogenesis of lassa fever in cynomolgus macaques. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furuta, Y.; Komeno, T.; Nakamura, T. Review Favipiravir (T-705), a broad spectrum inhibitor of viral RNA polymerase. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2017, 93, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agrawal, U.; Raju, R.; Udwadia, Z.F. Favipiravir: A new and emerging antiviral option in COVID-19. Med. J. Armed Forces India 2020, 76, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Kuno-Maekawa, M.; Sangawa, H.; Uehara, S.; Kozaki, K.; Nomura, N.; Egawa, H.; Shiraki, K. Mechanism of action of T-705 against influenza virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, Z.; Smith, L.K.; Rajwanshi, V.K.; Kim, B.; Deval, J. The Ambiguous Base-Pairing and High Substrate Efficiency of T-705 (Favipiravir) Ribofuranosyl 5′-Triphosphate towards Influenza A Virus Polymerase. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranovich, T.; Wong, S.-S.; Armstrong, J.; Marjuki, H.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G.; Govorkova, E.A. T-705 (Favipiravir) Induces Lethal Mutagenesis in Influenza A H1N1 Viruses In Vitro. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3741–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahrling, P.B. Protection of lassa virus-infected guinea pigs with lassa-immune plasma of guinea pig, primate, and human origin. J. Med. Virol. 1983, 12, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahrling, P.B.; Peters, C.J. Passive antibody therapy of Lassa fever in cynomolgus monkeys: Importance of neutralizing antibody and Lassa virus strain. Infect. Immun. 1984, 44, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Briggiler, A.N.A.M.; Enria, D.A.; Levis, S.C.; Fernandez, N.J. Importance Of Dose Of Neutralising Antibodies In Treatment Of Argentine Haemorrhagic Fever With Immune Plasma. Lancet 1984, 2, 255–256. [Google Scholar]
- Maiztegui, J.I.; Fernandez, N.J.; de Damilano, A.J. Efficacy of immune plasma in treatment of argentine haemorrhagic fever and association between treatment and a late neurological syndrome. Lancet 1979, 2, 1216–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahrling, P.B.; Frame, J.D.; Rhoderick, J.B.; Monson, M.H. Endemic lassa fever in liberia. iv. selection of optimally effective plasma for treatment by passive immunization. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1985, 79, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frame, J.D.; Verbrugge, G.P.; Gill, R.G.; Pinneo, L. The use of Lassa fever convalescent plasma in Nigeria. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1984, 78, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar Leifer David JGocke, H.B. Lassa Fever, a New Virus Disease of Man from West Africa II. Report of a Laboratory-Acquired Infection Treated with Plasma from a person recently recovered from the disease. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1970, 19, 677–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaucourt, S.; Vignuzzi, M. Ribavirin: A drug active against many viruses with multiple effects on virus replication and propagation. Molecular basis of ribavirin resistance. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 8, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bausch, D.G.; Hadi, C.M.; Khan, S.H.; Lertora, J.J.L. Review of the literature and proposed guidelines for the use of oral ribavirin as postexposure prophylaxis for lassa fever. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, 1435–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Model List of Essential Medicines. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/groups/expert-committee-on-selection-and-use-of-essential-medicines/essential-medicines-lists (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Brian, B.; Gowen, M.B. Progress in the experimental therapy of severe arenaviral infections. Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goeijenbier, M.; van Kampen, J.J.A.; Reusken, C.B.E.M.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; van Gorp, E.C.M. Ebola virus disease: A review on epidemiology, symptoms, treatment and pathogenesis. Neth. J. Med. 2014, 72, 442–448. [Google Scholar]
- Nagata, T.; Lefor, A.K.; Hasegawa, M.; Ishii, M. Favipiravir: A New Medication for the Ebola Virus Disease Pandemic. Disaster Med. Public Health Prep. 2015, 9, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marano, G.; Vaglio, S.; Pupella, S.; Facco, G.; Catalano, L.; Liumbruno, G.M.; Grazzini, G. Convalescent plasma: New evidence for an old therapeutic tool? Blood Transfus. 2016, 14, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gowen, B.B.; Barnard, D.L.; Smee, D.F.; Wong, M.-H.; Pace, A.M.; Jung, K.-H.; Winslow, S.G.; Bailey, K.W.; Blatt, L.M.; Sidwell, R.W. Interferon Alfacon-1 Protects Hamsters from Lethal Pichinde Virus Infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baize, S.; Marianneau, P.; Loth, P.; Reynard, S.; Journeaux, A.; Chevallier, M.; Tordo, N.; Deubel, V.; Contamin, H. Early and Strong Immune Responses Are Associated with Control of Viral Replication and Recovery in Lassa Virus-Infected Cynomolgus Monkeys. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5890–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Melian, E.B.; Plosker, G.L. Interferon alfacon-1: A review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Drugs 2001, 61, 1661–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowen, B.B.; Smee, D.F.; Wong, M.H.; Pace, A.M.; Jung, K.H.; Bailey, K.W.; Blatt, L.M.; Sidwell, R.W. Combinatorial ribavirin and interferon alfacon-1 therapy of acute arenaviral disease in hamsters. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2006, 17, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- (CREDO). C Research during Outbreak. Lassa fever—Information Sheet n.d. Available online: https://isaric.tghn.org/site_media/media/medialibrary/2017/03/Lassa_Fever_Information_Sheet_participants.docx (accessed on 28 December 2021).
- Murphy, H.; Ly, H. Understanding Immune Responses to Lassa Virus Infection and to Its Candidate Vaccines. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Target Product Profiles for Lassa Virus Vaccine 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/observatories/global-observatoryon-health-research-and-development/analyses-and-syntheses/target-product-profile/who-target-product-profiles (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Lukashevich, S.; Paessler, S.; de la Torre, J. Lassa virus diversity and feasibility for universal prophylactic vaccine. F1000Research 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hallam, H.J.; Hallam, S.; Rodriguez, S.E.; Barrett, A.D.T.; Beasley, D.W.C.; Chua, A.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Milligan, G.N.; Sathiyamoorthy, V.; Reece, L. Baseline Mapping of Lassa Fever Virology, Epidemiology and Vaccine Research and Development. NPJ Vaccines 2018, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibukun, F. Inter-lineage variation of lassa virus glycoprotein epitopes: A challenge to lassa virus vaccine development. Viruses 2020, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flatz, L.; Rieger, T.; Merkler, D.; Bergthaler, A.; Regen, T.; Schedensack, M.; Bestmann, L.; Verschoor, A.; Kreutzfeldt, M.; Brück, W.; et al. T Cell-Dependence of Lassa Fever Pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushotham, J.; Lambe, T.; Gilbert, S.C. Vaccine platforms for the prevention of Lassa fever. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 215, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIH, U.S.; National Library of Medicine. Dose-Ranging Study: Safety, Tolerability and Immunogenicity of INO-4500 in Healthy Volunteers in Ghana. Case Medical Research. 2022. Available online: https://doi.org/https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04093076 (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Stein, D.R.; Warner, B.M.; Soule, G.; Tierney, K.; Frost, K.L.; Booth, S.; Safronetz, D. A recombinant vesicular stomatitis-based Lassa fever vaccine elicits rapid and long-term protection from lethal Lassa virus infection in guinea pigs. NPJ Vaccines 2019, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateo, M.; Reynard, S.; Carnec, X.; Journeaux, A.; Baillet, N.; Schaeffer, J.; Picard, C.; Legras-Lachuer, C.; Allan, R.; Perthame, E.; et al. Vaccines inducing immunity to Lassa virus glycoprotein and nucleoprotein protect macaques after a single shot. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrba, S.M.; Kirk, N.M.; Brisse, M.E.; Liang, Y.; Ly, H. Development and applications of viral vectored vaccines to combat zoonotic and emerging public health threats. Vaccines 2020, 8, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, M.; Reynard, S.; Journeaux, A.; Germain, C.; Hortion, J.; Carnec, X.; Picard, C.; Baillet, N.; Borges-Cardoso, V.; Merabet, O.; et al. A single-shot Lassa vaccine induces long-term immunity and protects cynomolgus monkeys against heterologous strains. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabf6348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Ly, H. Advances in Development and Application of Influenza Vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2021, 13, 711997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.J.; Purushotham, J.N.; van Doremalen, N.; Sebastian, S.; Meade-White, K.; Cordova, K.; Letko, M.; Jeremiah Matson, M.; Feldmann, F.; Haddock, E.; et al. ChAdOx1-vectored Lassa fever vaccine elicits a robust cellular and humoral immune response and protects guinea pigs against lethal Lassa virus challenge. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashevich, I.S.; Patterson, J.; Carrion, R.; Moshkoff, D.; Ticer, A.; Zapata, J.; Brasky, K.; Geiger, R.; Hubbard, G.B.; Bryant, J.; et al. A Live Attenuated Vaccine for Lassa Fever Made by Reassortment of Lassa and Mopeia Viruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 13934–13942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrion, R.; Patterson, J.L.; Johnson, C.; Gonzales, M.; Moreira, C.R.; Ticer, A.; Brasky, K.; Hubbard, G.B.; Moshkoff, D.; Zapata, J.; et al. A ML29 reassortant virus protects guinea pigs against a distantly related Nigerian strain of Lassa virus and can provide sterilizing immunity. Vaccine 2007, 25, 4093–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrion, R.; Patterson, J.L. An animal model that reflects human disease: The common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus). Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukashevich, I.S.; Carrion, R.; Salvato, M.S.; Mansfield, K.; Brasky, K.; Zapata, J.; Cairo, C.; Goicochea, M.; Hoosien, G.E.; Ticer, A.; et al. Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the ML29 reassortant vaccine for Lassa fever in small non-human primates. Vaccine 2008, 26, 5246–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, S.; Papamichail, D.; Coleman, J.R.; Skiena, S.; Wimmer, E. Reduction of the Rate of Poliovirus Protein Synthesis through Large-Scale Codon Deoptimization Causes Attenuation of Viral Virulence by Lowering Specific Infectivity. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 9687–9696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Ye, C.; Cheng, B.; Nogales, A.; Iwasaki, M.; Yu, S.; Cooper, K.; Liu, D.X.; Hart, R.; Adams, R.; et al. A Lassa Fever Live-Attenuated Vaccine Based on Codon Deoptimization of the Viral Glycoprotein Gene. MBio 2020, 11, e00039-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, J.; Lee, S.; Hotard, A.L.; Moore, M.L. Refining the balance of attenuation and immunogenicity of respiratory syncytial virus by Targeted codon deoptimization of virulence genes. MBio 2014, 5, e01704-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Iwasaki, M.; Motooka, D.; Liu, D.X.; Yu, S.; Cooper, K.; Hart, R.; Adams, R.; Burdette, T.; Postnikova, E.N.; et al. A Lassa Virus Live-Attenuated Vaccine Candidate Based on Rearrangement of the Intergenic Region. MBio 2020, 11, e00186-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henao-Restrepo, A.M.; Camacho, A.; Longini, I.M.; Watson, C.H.; Edmunds, W.J.; Egger, M.; Carroll, M.W.; Dean, N.E.; Diatta, I.; Doumbia, M.; et al. Efficacy and effectiveness of an rVSV-vectored vaccine in preventing Ebola virus disease: Final results from the Guinea ring vaccination, open-label, cluster-randomised trial (Ebola Ça Suffit!). Lancet 2017, 389, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huttner, A. EPFG. The effect of dose on the safety and immunogenicity of the VSV Ebola candidate vaccine: A randomised double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 trial. Lancet 2019, 15, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, J.P.; Rees, S.S.; Kalindjian, S.B.; Philpott, K.L. Principles of early drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C. Drug target validation: Hitting the target. Nature 2003, 422, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashburn, T.T.; Thor, K.B. Drug repositioning: Identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, G. An Overview of Drug Repurposing: Review Article. J. Med. Sci. Clin. Res. 2019, 7, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deotarse, P.P.; Jain, A.S.; Baile, M.B.; Kolhe, N.S.; Kulkarni, A.A. Drug Repositioning: A Review. Int. J. Pharma. Res. Rev. 2015, 4, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Pantziarka, P.; Pirmohamed, M.; Mirza, N. New uses for old drugs. Nature 2007, 448, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, H.; Li, J.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y. Review of drug repositioning approaches and resources. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalita, J.; Chetia, D.R.M. Design, synthesis, antimalarial activity and docking study of 7-chloro-4-(2- (substituted benzylidene)hydrazineyl) quinolines. Med. Chem. 2020, 16, 928–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, P. Artificial Intelligence in Drug Discovery and Development. J. Pharmacovigil. 2018, 6, e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, T.I.; Overington, J.P. Computational and practical aspects of drug repositioning. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2015, 13, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lionta, E.; Spyrou, G.; Vassilatis, D.; Cournia, Z. Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Drug Discovery: Principles, Applications and Recent Advances. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talevi, A. Drug repositioning: Current approaches and their implications in the precision medicine era. Expert Rev. Precis. Med. Drug Dev. 2018, 3, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W. Drug Repositioning Approaches for the Discovery of New Therapeutics for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Pietzsch, C.; Witwit, H.; Tsaprailis, G.; Crynen, G.; Cho, K.F.; Ting, A.Y.; Bukreyev, A.; Saphire, E.O.; De la Torre, J.C. Proximity interactome analysis of Lassa polymerase reveals eRF3a/GSPT1 as a druggable target for host-directed antivirals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2201208119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademusire, B.I.; Wieczorek, K.; Alonge, A.T.; Rajen, A.; Egbe, J.; Adebambo, D.; Offorbuike, C.B.; Trojan, F.; Przypaśniak, Z.; Oduguwa, I.O.; et al. Prospects of Lassa Fever Candidate Vaccines. Afr. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 16, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holy, R.; Navara, M.; Dosel, P.; Fundova, P.; Prazenica, P.; Hahn, A. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) in association with combined treatment. Undersea Hyperb. Med. 2011, 38, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sano, H.; Kamijo, T.; Ino, T.; Okamoto, M. Edaravone, a free radical scavenger, in the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with profound hearing loss. Auris Nasus Larynx 2010, 37, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, H.; Fehling, S.K.; Dorna, J.; Urbanowicz, R.A.; Oestereich, L.; Krebs, Y.; Kolesnikova, L.; Schauflinger, M.; Krähling, V.; Magassouba, N.F.; et al. Adjuvant formulated virus-like particles expressing native-like forms of the Lassa virus envelope surface glycoprotein are immunogenic and induce antibodies with broadly neutralizing activity. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher-Hoch, S.P.; Hutwagner, L.; Brown, B.; McCormick, J.B. Effective Vaccine for Lassa Fever. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 6777–6783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fisher-Hoch, S.P.; McCormick, J.B.; Auperin, D.; Brown, B.G.; Castor, M.; Perez, G.; Ruo, S.; Conaty, A.; Brammer, L.; Bauer, S. Protection of rhesus monkeys from fatal Lassa fever by vaccination with a recombinant vaccinia virus containing the Lassa virus glycoprotein gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fisher-Hoch, S.P.; McCormick, J.B. Lassa fever vaccine. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2004, 3, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, J.T.; Forrester, N.; Paessler, S. Lassa virus isolates from Mali and the Ivory Coast represent an emerging fifth lineage. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitmer, S.L.M.; Strecker, T.; Cadar, D.; Dienes, H.P.; Faber, K.; Patel, K.; Brown, S.M.; Davis, W.G.; Klena, J.D.; Rollin, P.E. New lineage of lassa virus, Togo, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.E.; Hastie, K.M.; Cross, R.W.; Yenni, R.E.; Elliott, D.H.; Rouelle, J.A.; Kannadka, C.B.; Smira, A.A.; Garry, C.E.; Bradley, B.T.; et al. Most neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies target novel epitopes requiring both Lassa virus glycoprotein subunits. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafetzopoulou, L.E.; Pullan, S.T.; Lemey, P.; Suchard, M.A.; Ehichioya, D.U.; Pahlmann, M.; Thielebein, A.; Hinzmann, J.; Oestereich, L.; Wozniak, D.M.; et al. Metagenomic sequencing at the epicenter of the Nigeria 2018 Lassa fever outbreak. Science 2019, 363, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdullahi, I.N.; Anka, A.U.; Ghamba, P.E.; Onukegbe, N.B.; Amadu, D.O.; Salami, M.O. Need for preventive and control measures for Lassa fever through the One Health strategic approach. Proc. Singapore Healthc. 2020, 29, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, R.; Moses, L.M.; Redding, D.W.; Jones, K.E. Understanding the cryptic nature of Lassa fever in West Africa. Pathog. Glob. Health 2017, 111, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aigbiremolen, A.O.; Lawal-Luka, R.K.; Abejegah, C.; Aigberemwon, J.A.; Abah, E.O.; Abah, S.O. Environmental risk factors in the transmission of Lassa fever in college students’ hostels in Ekpoma, a semi urban town in South-South Nigeria. Annals 2017, 3, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Lassa fever—Nigeria. 2020. Available online: www9.who.int/csr/don/20-february-2020-lassa-fever-nigeria/en/ (accessed on 27 April 2020).
- Tambo, E.; Adetunde, O.T.; Olalubi, O.A. Re-emerging Lassa fever outbreaks in Nigeria: Re-enforcing “One Health” community surveillance and emergency response practice. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2018, 7, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamam, H.; Raza, A.; Alqarni, M.M.; Awrejcewicz, J.; Rafiq, M.; Ahmed, N.; Mahmoud, E.E.; Pawłowski, W.; Mohsin, M. Stochastic Modelling of Lassa Fever Epidemic Disease. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolo, P.N.; Nwabufo, I.V.; Abu, O. Mathematical Model for the Transmission Dynamics of Lassa Fever with Control. Sci. World J. 2020, 15, 62–68. [Google Scholar]
- Mariën, J.; Borremansb, B.; Kouroumad, F.; Bafordaye, J.; Riegere, T.; Günther, S.; Magassouba, N.; Leirs, H.; Fichet-Calvet, E. Evaluation of Rodent Control to fight Lassa Fever Based on field Data and Mathematical Modelling. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Mavingui, P.; Boetsch, G.; Boissier, J.; Darriet, F.; Duboz, P.; Fritsch, C.; Giraudoux, P.; Roux, F.L.; Morand, S.; et al. The one health concept: 10 years old and a long road ahead. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akhmetzhanov, A.R.; Asai, Y.; Nishiura, H. Quantifying the seasonal drivers of transmission for Lassa fever in Nigeria. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Drug | Type of Drug | Mechanism of Action | In Vitro Activity for Lassa | Animal Efficacy for Lassa | NHP Efficacy for Lassa | Investigated in Humans | Investigated in Humans Infected with Lassa | Precautions | Side Effects | Approval Status | Remarks | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ribavirin | Analogue of guanosine | Broad- spectrum of antiviral effect. Mode of action varies depending on the virus [116]. | Yes | Yes. Administration of 160 mg/kg per day. Post-infection from days 4 to 11 markedly elongated survival in 20% of mice infected with LASV. | - | Yes. Investigated using different viruses like HCV, VHFs, etc. | Yes. Most potent Within 6 days Post-infection. | Pregnancy lactation (teratogenic and embryotoxic in rodents). | Dose-dependent hemolysis, seen in about 20% of infected individuals normally culminating in a modest diminution in hematocrit. | Yes, for VHFs. | Found to have a cell-protective activity in mice in comparison to Favipiravir. No evidence to corroborate its post-exposure prophylactic treatment for LF. Ribavirin has not shown a strong effect on advanced LF. | [17,60,98,116,117,118] |
| Favipiravir | Analogue of purine nucleoside, broad- spectrum effect against RNA viruses. | Inhibition of the viral (RdRp) | Yes | Yes. Post infection intake of 300 mg/kg daily from days 4 to 11 prevents death in 100% infected mice. Potent even when given 9 days post-infection in guinea pigs [101]. | - | Stage-2 concluded (influenza) and stage-3 in progress (influenza). | No | Pregnancy lactation. Contraception is required at the end of treatment in women of childbearing age. | - | Yes, in Japan for novel and re-emerging influenza viruses. | Favipiravir and Ribavirin interact synergistically in vitro, prolonged survival rate and survival time when combining suboptimal doses in vivo. | [98,100,119,120,121] |
| CP | Blood products | Provokes passive immunization | Yes. It shows protection in monkeys studies. | Yes. Early intake provides protection in a guinea pig model. | Human CP protected recipient monkey. | Yes | Yes. Discordant reports. No activity limited activity however geographically matched plasma seems to be more efficacious. | The threat of transfusion transmitted infections, convalescent patients needed for donation. | Effect of transfusion reactions. Bloodborne viruses. | NA | Insufficient high-quality studies (i.e., randomized clinical trials) short window of efficacy in combination with ribavirin, has been revealed to be protective in NHP infected with LASV. | [17,86,110,113,117,122] |
| IFN alfacon-1 | Non-naturally occurring bio-engineered alpha interferon. | Regulation of host innate immune responses. | No | No. Treatment remarkably protected PCV infected hamster model from death, extended the survival of those that died over time, lowered virus titers. | Yes. In monkeys infected with LASV. Timely and effective immune responses and modulation of viral replication were linked with recovery while fatal infection was marked by weak immune responses and unregulated viral replication. | Yes, for HCV. | No | ? Pregnancy | Administration in bolus results in systemic toxicity, leucopenia thrombocy topaenia reduced Hb, psychiatric adverse events. | Yes, for treatment of chronic hepatitis C. | A combination of suboptimal doses of ribavirin (5–10 mg/kg/day) with IFN alfacon-1 (5–10 µg/kg/day) was shown to have both additive and synergistic activity when given within 24 h post infection with PCV (an arenavirus) in hamsters. IFN alfacon-1 treatment was more efficacious when given intranasally in comparison to delivery by i.p. injection. | [119,123,124,125,126] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aloke, C.; Obasi, N.A.; Aja, P.M.; Emelike, C.U.; Egwu, C.O.; Jeje, O.; Edeogu, C.O.; Onisuru, O.O.; Orji, O.U.; Achilonu, I. Combating Lassa Fever in West African Sub-Region: Progress, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Viruses 2023, 15, 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010146
Aloke C, Obasi NA, Aja PM, Emelike CU, Egwu CO, Jeje O, Edeogu CO, Onisuru OO, Orji OU, Achilonu I. Combating Lassa Fever in West African Sub-Region: Progress, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Viruses. 2023; 15(1):146. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010146
Chicago/Turabian StyleAloke, Chinyere, Nwogo Ajuka Obasi, Patrick Maduabuchi Aja, Chinedum Uche Emelike, Chinedu Ogbonnia Egwu, Olamide Jeje, Chuks Oswald Edeogu, Olalekan Olugbenga Onisuru, Obasi Uche Orji, and Ikechukwu Achilonu. 2023. "Combating Lassa Fever in West African Sub-Region: Progress, Challenges, and Future Perspectives" Viruses 15, no. 1: 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010146
APA StyleAloke, C., Obasi, N. A., Aja, P. M., Emelike, C. U., Egwu, C. O., Jeje, O., Edeogu, C. O., Onisuru, O. O., Orji, O. U., & Achilonu, I. (2023). Combating Lassa Fever in West African Sub-Region: Progress, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Viruses, 15(1), 146. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010146