Epidemiology of Non-SARS-CoV2 Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in People Presenting with Influenza-like Illness (ILI) or Severe Acute Respiratory Infections (SARI) in Senegal from 2012 to 2020
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Sample and Data Collection
2.2. Nucleic Acid Extraction and Respiratory Viruses’ Detection
2.3. Human Coronaviruses’ (HCoVs) Molecular Characterization
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics of the Enrolled Patients
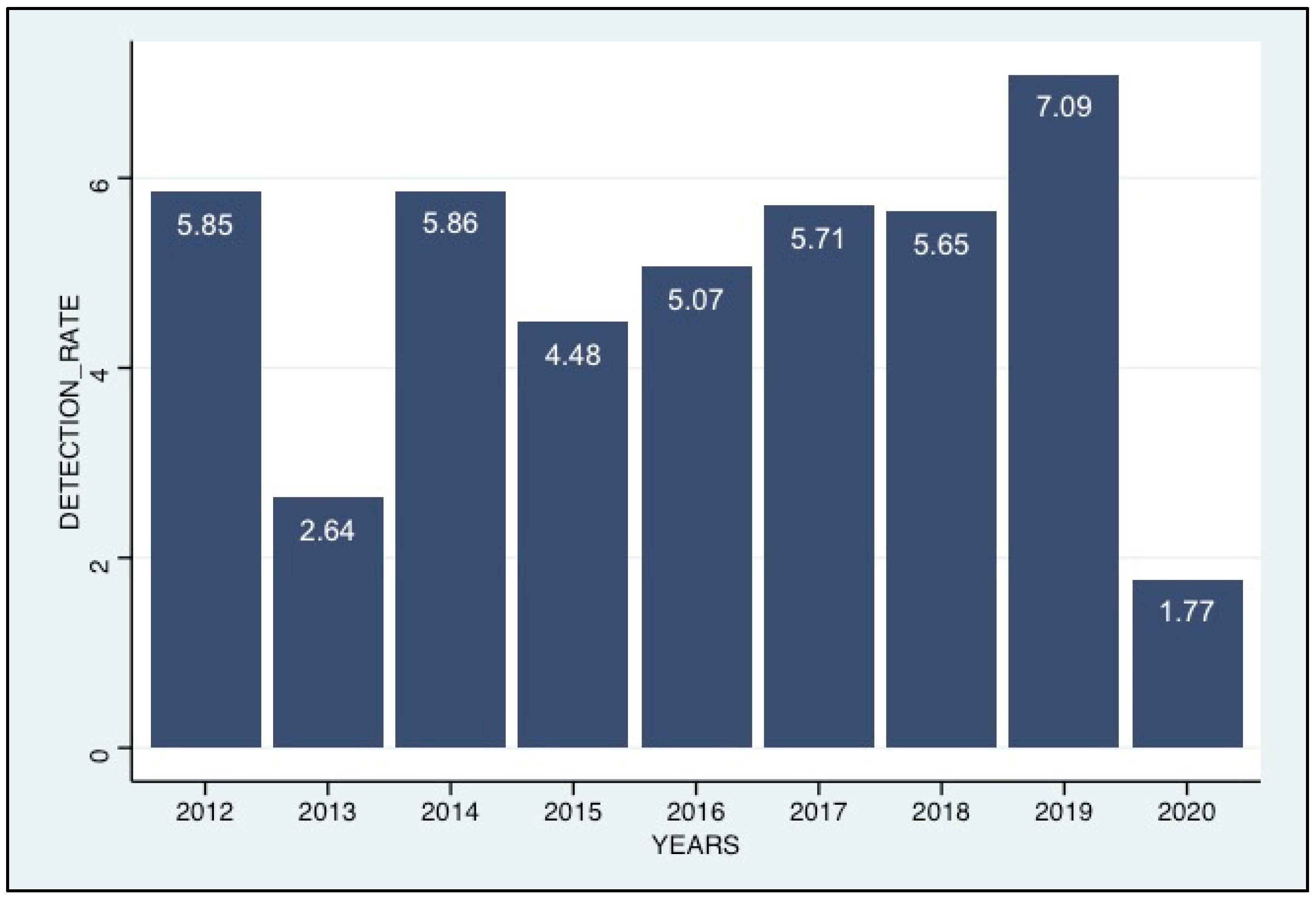
3.2. Detection of HCoVs among the ILI/SARI Patients
3.3. Co-Infection of HCoVs with Other Pathogens
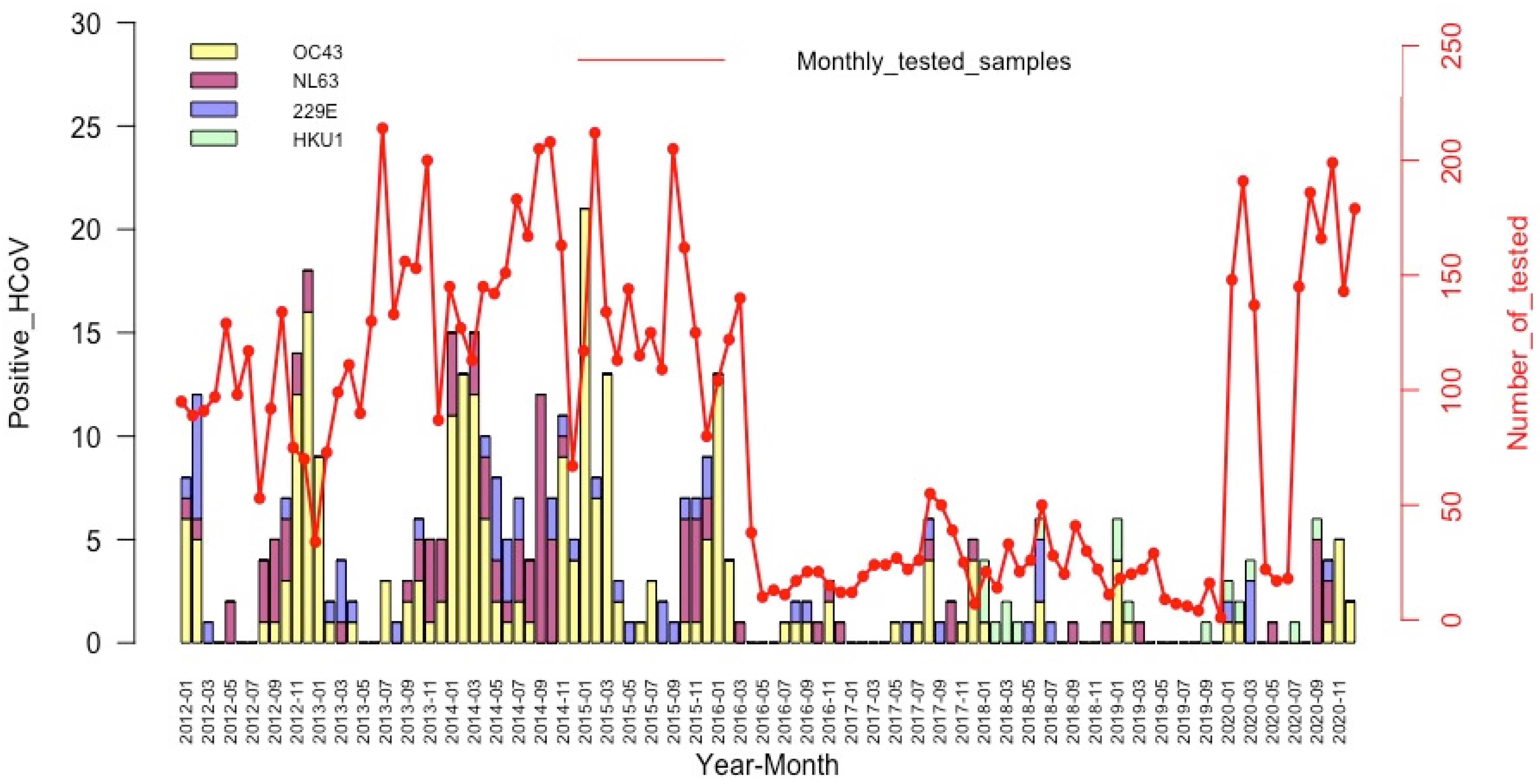
3.4. Seasonality of the HCoV Infections
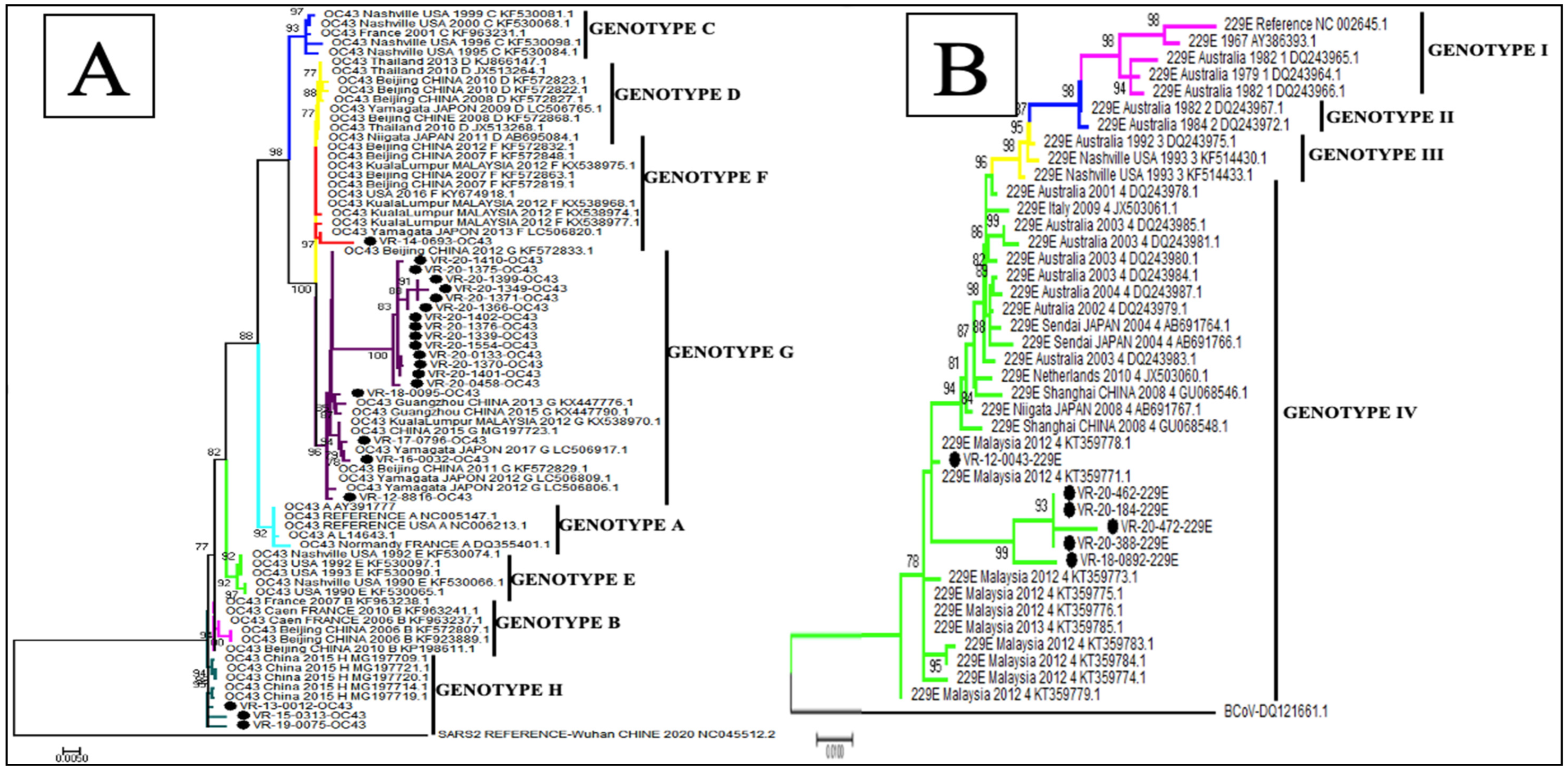
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arbour, N.; Day, R.; Newcombe, J.; Talbot, P.J. Neuroinvasion by Human Respiratory Coronaviruses. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8913–8921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacomy, H.; Fragoso, G.; Almazan, G.; Mushynski, W.E.; Talbot, P.J. Human coronavirus OC43 infection induces chronic encephalitis leading to disabilities in BALB/C mice. Virology 2006, 349, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kin, N.; Miszczak, F.; Diancourt, L.; Caro, V.; Moutou, F.; Vabret, A.; Gouilh, M.A. Comparative molecular epidemiology of two closely related coronaviruses, bovine coronavirus (BCoV) and human coronavirus OC43 (HCoV-OC43), reveals a different evolutionary pattern. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 40, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-R.; Cao, Q.-D.; Hong, Z.-S.; Tan, Y.-Y.; Chen, S.-D.; Jin, H.-J.; Tan, K.-S.; Wang, D.-Y.; Yan, Y. The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak—An update on the status. Mil. Med. Res. 2020, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dia, N.; Lakh, N.A.; Diagne, M.M.; Mbaye, K.D.; Taieb, F.; Fall, N.M.; Barry, M.A.; Ka, D.; Fall, A.; Diallo, V.M.P.C.; et al. COVID-19 Outbreak, Senegal, 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 2771–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dia, N.; Diagne, M.M.; Fall, G.; Jallow, M.M.; Fall, A.; Barry, M.A.; Diallo, A.; Faye, O.; Dione, M.H.D.; Bop, N.S.; et al. COVID-19 and Children in Senegal: Epidemiological and Virological Insights. Arch. Clin. Biomed. Res. 2022, 06, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.X.; Liang, J.Q.; Fung, T.S. Human Coronavirus-229E, -OC43, -NL63, and -HKU1 (Coronaviridae). Encycl. Virol. 2021, 2, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Tse, H.; Tsoi, H.-W.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Lee, P.; Tang, B.S.F.; Cheung, C.H.Y.; Lee, R.A.; et al. Coronavirus HKU1 and Other Coronavirus Infections in Hong Kong. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Huang, Y.; Yuen, K.-Y. Coronavirus Diversity, Phylogeny and Interspecies Jumping. Exp. Biol. Med. 2009, 234, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, P.C.Y.; Lau, S.K.P.; Lam, C.S.F.; Lau, C.C.Y.; Tsang, A.K.L.; Lau, J.H.N.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.L.; Tsang, C.C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of Seven Novel Mammalian and Avian Coronaviruses in the Genus Deltacoronavirus Supports Bat Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Alphacoronavirus and Betacoronavirus and Avian Coronaviruses as the Gene Source of Gammacoronavirus and Deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Li, F.; Shi, Z.-L. Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Forni, D.; Cagliani, R.; Arrigoni, F.; Benvenuti, M.; Mozzi, A.; Pozzoli, U.; Clerici, M.; De Gioia, L.; Sironi, M. Adaptation of the endemic coronaviruses HCoV-OC43 and HCoV-229E to the human host. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesheh, M.M.; Hosseini, P.; Soltani, S.; Zandi, M. An overview on the seven pathogenic human coronaviruses. Rev. Med Virol. 2021, 32, e2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajapakse, N.; Dixit, D. Human and novel coronavirus infections in children: A review. Ann. Trop. Paediatr. 2020, 41, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendley, J.; Fishburne, H.B.; Gwaltney, J.M. Coronavirus infections in working adults. Eight-year study with 229 E and OC 43. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1972, 105, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baillie, V.; Moore, D.; Mathunjwa, A.; Park, D.; Thea, D.; Kwenda, G.; Mwananyanda, L.; Madhi, S. Epidemiology and Seasonality of Endemic Human Coronaviruses in South African and Zambian Children: A Case-Control Pneumonia Study. Viruses 2021, 13, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikawa, S.; Hiroi, S.; Kase, T. Detection of respiratory viruses in gargle specimens of healthy children. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 64, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus Associated with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Gan, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, A.; Li, F.; Sun, J.; et al. Discovery of a subgenotype of human coronavirus NL63 associated with severe lower respiratory tract infection in China, 2018. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peiris, J.S.; Yuen, K.Y.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Stöhr, K. The Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. New Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2431–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.M.; Van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Isolation of a Novel Coronavirus from a Man with Pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dia, N.; Sarr, F.D.; Thiam, D.; Sarr, T.F.; Espié, E.; OmarBa, I.; Coly, M.; Niang, M.; Richard, V. Influenza-Like Illnesses in Senegal: Not Only Focus on Influenza Viruses. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niang, M.N.; Diop, O.M.; Sarr, F.D.; Goudiaby, D.; Malou-Sompy, H.; Ndiaye, K.; Vabret, A.; Baril, L. Viral etiology of respiratory infections in children under 5 years old living in tropical rural areas of Senegal: The EVIRA project. J. Med Virol. 2010, 82, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fall, A.; Dieng, A.; Wade, S.F.; Diop, A.; Diouf, J.B.N.; Boiro, D.; Keita, Y.; Sylla, A.; Ndiaye, O.; Boye, C.S.B.; et al. Children under five years of age in senegal: A group highly exposed to respiratory viruses infections. Virol. Res. Rev. 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific. A Practical Guide to Harmonizing Virological and Epidemiological Influenza Surveillance; WHO Regional Office for the Western Pacific: Manila, Philippines, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jallow, M.M.; Fall, A.; Kiori, D.; Sy, S.; Goudiaby, D.; Barry, M.A.; Fall, M.; Niang, M.N.; Dia, N. Epidemiological, clinical and genotypic features of human Metapneumovirus in patients with influenza-like illness in Senegal, 2012 to 2016. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, T. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. In Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, Y.Y.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, J.M.; Chung, Y.S.; Han, M.G.; Choi, E.H. Epidemiological Characteristics of Common Human Coronaviruses in Korea, 2015–2019. Research Square. 2021. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348516057_Epidemiological_Characteristics_of_Common_Human_Coronaviruses_in_Korea_2015–2019 (accessed on 28 March 2022).
- Zeng, Z.-Q.; Chen, D.-H.; Tan, W.-P.; Qiu, S.-Y.; Xu, D.; Liang, H.-X.; Chen, M.-X.; Li, X.; Lin, Z.-S.; Liu, W.-K.; et al. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of human coronaviruses OC43, 229E, NL63, and HKU1: A study of hospitalized children with acute respiratory tract infection in Guangzhou, China. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 37, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theamboonlers, A.; Samransamruajkit, R.; Thongme, C.; Amonsin, A.; Chongsrisawat, V.; Poovorawan, Y. Human Coronavirus Infection among Children with Acute Lower Respiratory Tract Infection in Thailand. Intervirology 2006, 50, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njouom, R.; Yekwa, E.L.; Cappy, P.; Vabret, A.; Boisier, P.; Rousset, D. Viral Etiology of Influenza-Like Illnesses in Cameroon, January–December 2009. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, S29–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, I.M.; Arden, K.E.; Speicher, D.J.; O’Neil, N.T.; McErlean, P.K.; Greer, R.M.; Nissen, M.D.; Sloots, T.P. Co-circulation of Four Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in Queensland Children with Acute Respiratory Tract Illnesses in 2004. Viruses 2012, 4, 637–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Elden, L.; Van Loon, A.M.; Van Alphen, F.; Hendriksen, K.A.W.; Hoepelman, A.I.M.; Van Kraaij, M.G.J.; Oosterheert, J.; Schipper, P.; Schuurman, R.; Nijhuis, M. Frequent Detection of Human Coronaviruses in Clinical Specimens from Patients with Respiratory Tract Infection by Use of a Novel Real-Time Reverse-Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction. J. Infect. Dis. 2004, 189, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, C.C.Y.; Lam, C.S.F.; Luk, H.K.H.; Wong, E.Y.M.; Lee, R.A.; So, L.-Y.; Chan, K.-H.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Yuen, K.-Y.; Woo, P.C.Y.; et al. A six-year descriptive epidemiological study of human coronavirus infections in hospitalized patients in Hong Kong. Virol. Sin. 2016, 31, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vijgen, L.; Keyaerts, E.; Moës, E.; Maes, P.; Duson, G.; Van Ranst, M. Development of One-Step, Real-Time, Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase PCR Assays for Absolute Quantitation of Human Coronaviruses OC43 and 229E. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5452–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Xu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Prevalence of human coronaviruses in adults with acute respiratory tract infections in Beijing, China. J. Med Virol. 2010, 83, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannakarn, K.; Chieochansin, T.; Vichiwattana, P.; Korkong, S.; Theamboonlers, A.; Poovorawan, Y. Prevalence and genetic characterization of human coronaviruses in southern Thailand from July 2009 to January 2011. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2014, 45, 326–336. [Google Scholar]
- Heimdal, I.; Moe, N.; Krokstad, S.; Christensen, A.; Skanke, L.H.; Nordbø, S.A.; Døllner, H. Human Coronavirus in Hospitalized Children With Respiratory Tract Infections: A 9-Year Population-Based Study From Norway. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 219, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masse, S.; Capai, L.; Villechenaud, N.; Blanchon, T.; Charrel, R.; Falchi, A. Epidemiology and Clinical Symptoms Related to Seasonal Coronavirus Identified in Patients with Acute Respiratory Infections Consulting in Primary Care over Six Influenza Seasons (2014–2020) in France. Viruses 2020, 12, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkman, R.; Jebbink, M.F.; Gaunt, E.; Rossen, J.W.; Templeton, K.E.; Kuijpers, T.W.; van der Hoek, L. The dominance of human coronavirus OC43 and NL63 infections in infants. J. Clin. Virol. 2012, 53, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moës, E.; Vijgen, L.; Keyaerts, E.; Zlateva, K.; Li, S.; Maes, P.; Pyrc, K.; Berkhout, B.; Van Der Hoek, L.; Van Ranst, M. A novel pancoronavirus RT-PCR assay: Frequent detection of human coronavirus NL63 in children hospitalized with respiratory tract infections in Belgium. BMC Infect. Dis. 2005, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trombetta, H.; Faggion, H.Z.; Leotte, J.; Nogueira, M.B.; Vidal, L.R.R.; Raboni, S.M. Human coronavirus and severe acute respiratory infection in Southern Brazil. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2016, 110, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fall, A.; Dia, N.; Cisse, E.H.A.K.; Kiori, D.E.; Sarr, F.D.; Sy, S.; Goudiaby, D.; Richard, V.; Niang, M.N. Epidemiology and Molecular Characterization of Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus in Senegal after Four Consecutive Years of Surveillance, 2012–2015. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niang, M.N.; Diop, N.S.; Fall, A.; Kiori, D.E.; Sarr, F.D.; Sy, S.; Goudiaby, D.; Barry, M.A.; Fall, M.; Dia, N. Respiratory viruses in patients with influenza-like illness in Senegal: Focus on human respiratory adenoviruses. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dare, R.; Fry, A.M.; Chittaganpitch, M.; Sawanpanyalert, P.; Olsen, S.J.; Erdman, D.D. Human Coronavirus Infections in Rural Thailand: A Comprehensive Study Using Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction Assays. J. Infect. Dis. 2007, 196, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaunt, E.R.; Hardie, A.; Claas, E.C.J.; Simmonds, P.; Templeton, K.E. Epidemiology and Clinical Presentations of the Four Human Coronaviruses 229E, HKU1, NL63, and OC43 Detected over 3 Years Using a Novel Multiplex Real-Time PCR Method. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 2940–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soonnarong, R.; Thongpan, I.; Payungporn, S.; Vuthitanachot, C.; Vuthitanachot, V.; Vichiwattana, P.; Vongpunsawad, S.; Poovorawan, Y. Molecular epidemiology and characterization of human coronavirus in Thailand, 2012–2013. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Friedman, N.; Alter, H.; Hindiyeh, M.; Mendelson, E.; Avni, Y.S.; Mandelboim, M. Human Coronavirus Infections in Israel: Epidemiology, Clinical Symptoms and Summer Seasonality of HCoV-HKU1. Viruses 2018, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.-F.; Tuo, J.-L.; Huang, X.-B.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, D.-M.; Zhou, K.; Yuan, L.; Luo, H.-J.; Zheng, B.-J.; Yuen, K.-Y.; et al. Epidemiology characteristics of human coronaviruses in patients with respiratory infection symptoms and phylogenetic analysis of HCoV-OC43 during 2010–2015 in Guangzhou. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, R.K.; Rinaldo, C.R.; Nowalk, M.P.; Gk, B.; Thompson, M.G.; Moehling, K.K.; Bullotta, A.; Wisniewski, S. Influenza and other respiratory virus infections in outpatients with medically attended acute respiratory infection during the 2011-12 influenza season. Influ. Other Respir. Viruses 2014, 8, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esper, F.; Weibel, C.; Ferguson, D.; Landry, M.L.; Kahn, J.S. Coronavirus HKU1 Infection in the United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 775–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, R.W.; Lewer, D.; Beale, S.; Johnson, A.M.; Zambon, M.; Hayward, A.C.; Fragaszy, E.B. Flu Watch Group Seasonality and immunity to laboratory-confirmed seasonal coronaviruses (HCoV-NL63, HCoV-OC43, and HCoV-229E): Results from the Flu Watch cohort study. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owusu, M.; Annan, A.; Corman, V.M.; Larbi, R.; Anti, P.; Drexler, J.F.; Agbenyega, O.; Adu-Sarkodie, Y.; Drosten, C. Human Coronaviruses Associated with Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Three Rural Areas of Ghana. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khannaq, M.N.; Takebe, Y.; Pang, Y.K.; Oong, X.Y.; Tee, K.K.; Ng, K.T.; Kamarulzaman, A.; Hanafi, N.S.; Chook, J.B. Diversity and Evolutionary Histories of Human Coronaviruses NL63 and 229E Associated with Acute Upper Respiratory Tract Symptoms in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Year | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | TOTAL (100) |
| Sample, n (%) | 1213 (7.9) | 1518 (9.9) | 1929 (12.5) | 1718 (11.2) | 1810 (11.8) | 2341 (15.3) | 1779 (11.6) | 1433 (9.3) | 1580 (10.3) | |
| Tested for HCoV n (%) | 1213 (13) | 1518 (16.3) | 1929 (20.7) | 1718 (18.4) | 552 (5.9) | 350 (3.7) | 336 (3.6) | 141 (1.5) | 1580 (16.9) | 9337 (100) |
| Positive for HCoV n (%) | 71 (5.8) | 40 (2.6) | 113 (5.9) | 77 (4.4) | 28 (5.1) | 20 (5.7) | 19 (5.6) | 10 (7.1) | 28 (1.8) | 406 (4.3) |
| Gender, n (%) | ||||||||||
| Female | 587 (48.4) | 767 (50.5) | 986 (51.1) | 844 (49.1) | 912 (50.4) | 1182 (50.5) | 886 (49.8) | 708 (49.4) | 788 (49.9) | 7660 (50) |
| Male | 610 (50.3) | 743 (48.9) | 936 (48.5) | 873 (50.8) | 895 (49.4) | 1158 (49.5) | 890 (50) | 725 (50.6) | 790 (50) | 7620 (49.7) |
| Age Group, n (%) | ||||||||||
| [0–5] | 749 (61.7) | 757 (49.9) | 941 (48.8) | 849 (49.4) | 979 (54.1) | 1263 (53.9) | 895 (50.3) | 672 (46.9) | 560 (35.4) | 7665 (50.0) |
| [05–10] | 117 (9.6) | 163 (10.7) | 208 (10.8) | 243 (14.1) | 227 (12.5) | 345 (14.7) | 267 (15) | 204 (14.2) | 144 (9.1) | 1918 (12.5) |
| [10–15] | 68 (5.6) | 84 (5.5) | 121 (6.3) | 109 (6.3) | 127 (7) | 153 (6.5) | 107 (6) | 113 (7.9) | 100 (6.3) | 982 (6.4) |
| [15–25] | 71 (5.8) | 122 (8) | 229 (11.9) | 155 (9) | 175 (9.7) | 237 (10.1) | 185 (10.4) | 160 (11.2) | 162 (10.2) | 1496 (9.8) |
| [25–50] | 59 (4.9) | 120 (7.9) | 265 (13.7) | 228 (13.2) | 202 (11.2) | 208 (8.9) | 208 (11.7) | 187 (13) | 286 (18.1) | 1763 (11.5) |
| >50 | 19 (1.6) | 18 (1.2) | 83 (4.3) | 75 (4.4) | 52 (2.9) | 56 (2.4) | 78 (4.4) | 65 (4.5) | 262 (16.6) | 708 (4.6) |
| Hospitalization, n (%) | ||||||||||
| Yes | 1 (0.1) | 0 (0) | 2 (0.1) | 29 (1.7) | 29 (1.6) | 94 (4) | 118 (6.6) | 43 (3) | 124 (7.8) | 440 (2.9) |
| No | 1209 (99.7) | 830 (54.7) | 1794 (93) | 277 (16.1) | 975 (53.9) | 2160 (92.3) | 1582 (88.9) | 1355 (94.6) | 1232 (78) | (74.5) |
| Clinical Signs, n (%) | ||||||||||
| Cough | 824 (67.9) | 1098 (72.3) | 1553 (80.5) | 1393 (81.1) | 1469 (81.2) | 1945 (83.1) | 1527 (85.8) | 1248 (87.1) | 1434 (90.8) | (81.5) |
| Headache | 105 (8.7) | 182 (12) | 262 (13.6) | 304 (17.6) | 258 (14.2) | 538 (23) | 411 (23.1) | 414 (28.9) | 416 (26.3) | 2890 (18.9) |
| Fever | 1129 (93.1) | 1349 (88.9) | 1863 (96.6) | 1653 (96.2) | 1761 (97.3) | 2247 (96) | 1648 (92.6) | 1387 (96.8) | 1077 (68.2) | (92.1) |
| Myalgia | 124 (10.2) | 326 (21.5) | 0 (0) | 301 (17.5) | 280 (15.5) | 0 (0) | 188 (10.6) | 199 (13.9) | 0 (0) | 1418 (9.3) |
| OC43 | NL63 | 229E | HKU1 | TOTAL | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pathogens n (%) | 235 (57.9) | 102 (25.1) | 58 (14.3) | 17 (4.2) | 406 (100) | |
| Gender, n (%) | ||||||
| Male | 113 (48.1) | 47 (46.2) | 29 (50) | 13 (76.5) | 202 (49.7) | 0.8047 |
| Female | 121 (51.5) | 53 (52) | 29 (50) | 4 (23) | 207 (51) | |
| Age Group, n (%) | 2.2 × 10−16 | |||||
| [0–5] | 139 (59.1) | 47 (46.1) | 32 (55.2) | 10 (58.8) | 228 (56.2) | |
| [05–10] | 28 (11.9) | 8 (7.8) | 6 (10.3) | 0 (0) | 42 (10.3) | |
| [10–15] | 6 (2.5) | 5 (4.9) | 2 (3.4) | 1 (5.9) | 14 (3.4) | |
| [15–25] | 11 (4.7) | 12 (11.8) | 5 (8.6) | 3 (17.6) | 31 (7.6) | |
| [25–50] | 30 (12.8) | 14 (13.7) | 8 (13.8) | 2 (11.8) | 54 (13.3) | |
| >50 | 2 (0.8) | 4 (3.9) | 1 (1.7) | 1 (5.9) | 8 (2) | |
| Hospitalization, n (%) | ||||||
| Yes | 10 (4.3) | 8 (7.8) | 8 (13.8) | 8 (47.1) | 34 (8.4) | 0.03 |
| No | 133 (56.6) | 82 (80.4) | 35 (60.3) | 6 (35.3) | 256 (63) | |
| Clinical Signs, n (%) | 2.2 × 10−16 | |||||
| Cough | 190 (80.8) | 76 (74.5) | 44 (75.9) | 15 (88.2) | 325 (80) | |
| Headache | 25 (10.6) | 16 (15.7) | 5 (8.6) | 4 (23.5) | 50 (12.3) | |
| Fever | 199 (84.7) | 87 (85.3) | 51 (87.9) | 10 (58.8) | 347 (85.5) | |
| Myalgia | 24 (10.2) | 8 (7.8) | 10 (17.2) | 2 (11.8) | 44 (10.8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faye, M.N.; Barry, M.A.; Jallow, M.M.; Wade, S.F.; Mendy, M.P.; Sy, S.; Fall, A.; Kiori, D.E.; Ndiaye, N.K.; Goudiaby, D.; et al. Epidemiology of Non-SARS-CoV2 Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in People Presenting with Influenza-like Illness (ILI) or Severe Acute Respiratory Infections (SARI) in Senegal from 2012 to 2020. Viruses 2023, 15, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010020
Faye MN, Barry MA, Jallow MM, Wade SF, Mendy MP, Sy S, Fall A, Kiori DE, Ndiaye NK, Goudiaby D, et al. Epidemiology of Non-SARS-CoV2 Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in People Presenting with Influenza-like Illness (ILI) or Severe Acute Respiratory Infections (SARI) in Senegal from 2012 to 2020. Viruses. 2023; 15(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaye, Modeste Name, Mamadou Aliou Barry, Mamadou Malado Jallow, Serigne Fallou Wade, Marie Pedapa Mendy, Sara Sy, Amary Fall, Davy Evrard Kiori, Ndiende Koba Ndiaye, Deborah Goudiaby, and et al. 2023. "Epidemiology of Non-SARS-CoV2 Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in People Presenting with Influenza-like Illness (ILI) or Severe Acute Respiratory Infections (SARI) in Senegal from 2012 to 2020" Viruses 15, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010020
APA StyleFaye, M. N., Barry, M. A., Jallow, M. M., Wade, S. F., Mendy, M. P., Sy, S., Fall, A., Kiori, D. E., Ndiaye, N. K., Goudiaby, D., Diamanka, A., Niang, M. N., & Dia, N. (2023). Epidemiology of Non-SARS-CoV2 Human Coronaviruses (HCoVs) in People Presenting with Influenza-like Illness (ILI) or Severe Acute Respiratory Infections (SARI) in Senegal from 2012 to 2020. Viruses, 15(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010020







