Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Replication-Competent HIV-2 Isolated from Controllers and Progressors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants’ Characteristics and HIV-2 Isolates
2.2. DNA Isolation, Amplification, and Sequencing, and Sequence Analysis
2.3. Sequence Analyses
2.4. Plasmids
2.5. Transactivation Assays
2.6. Statistical Analysis
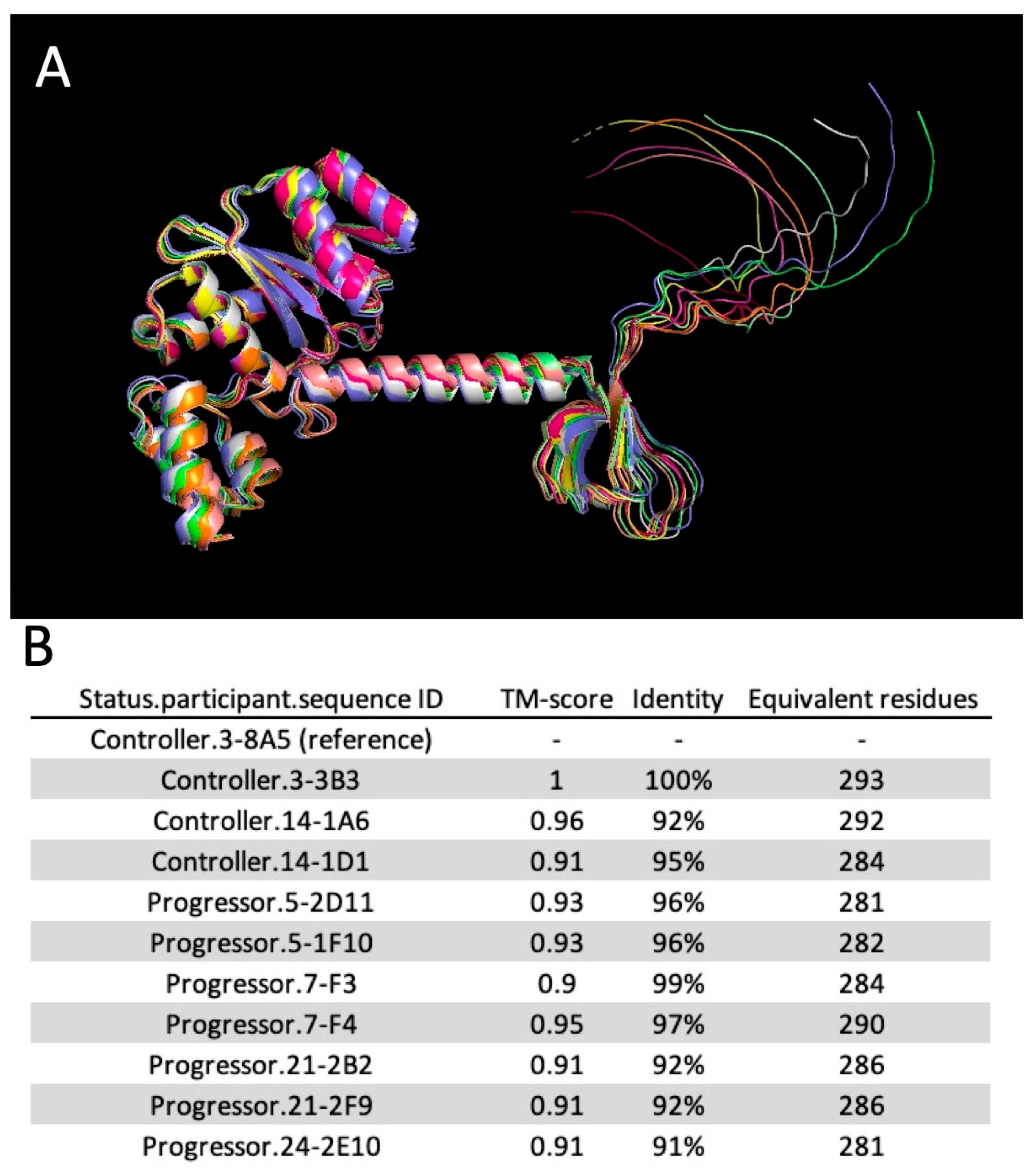
2.7. Molecular Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Participants’ Characteristics
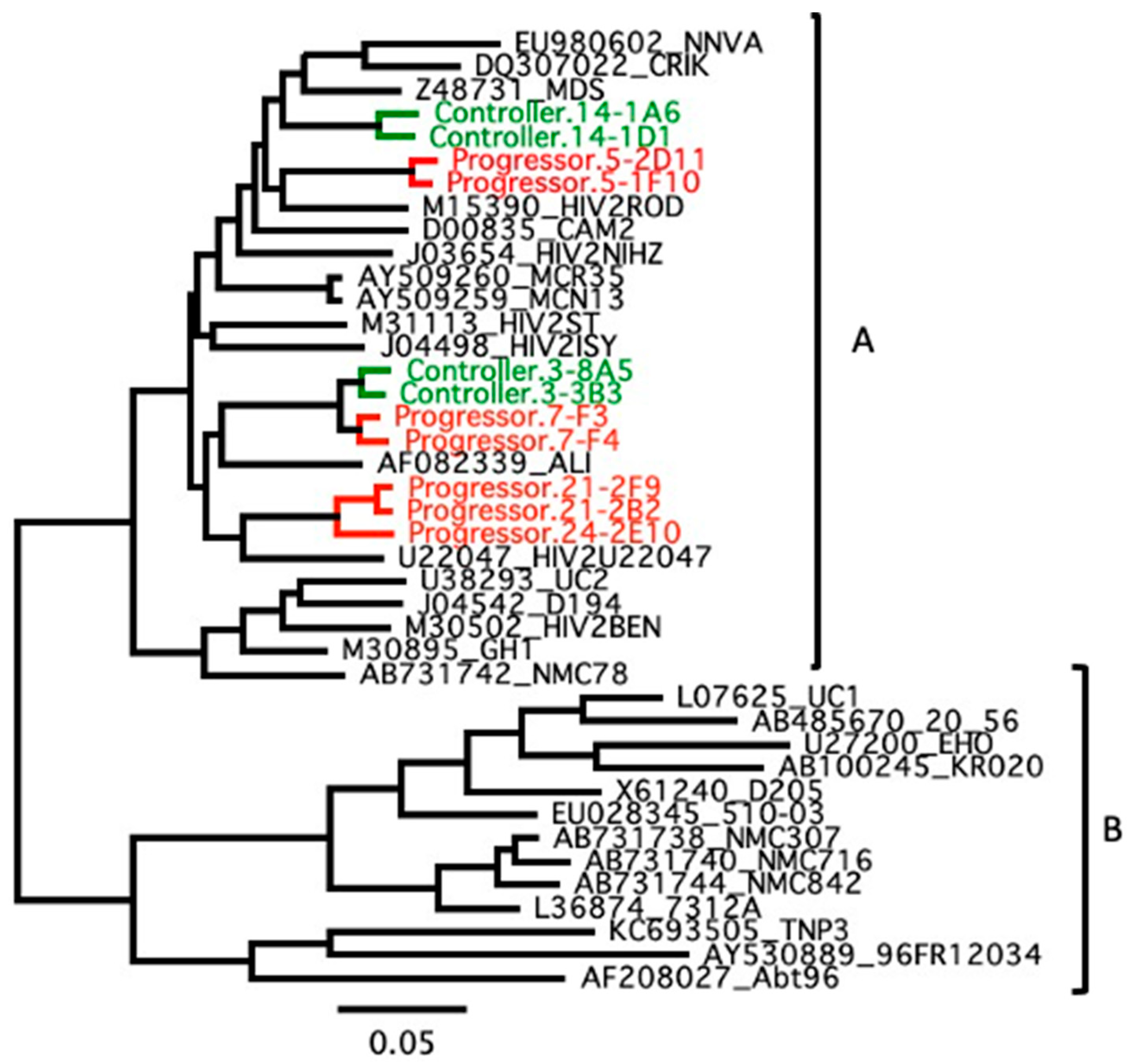
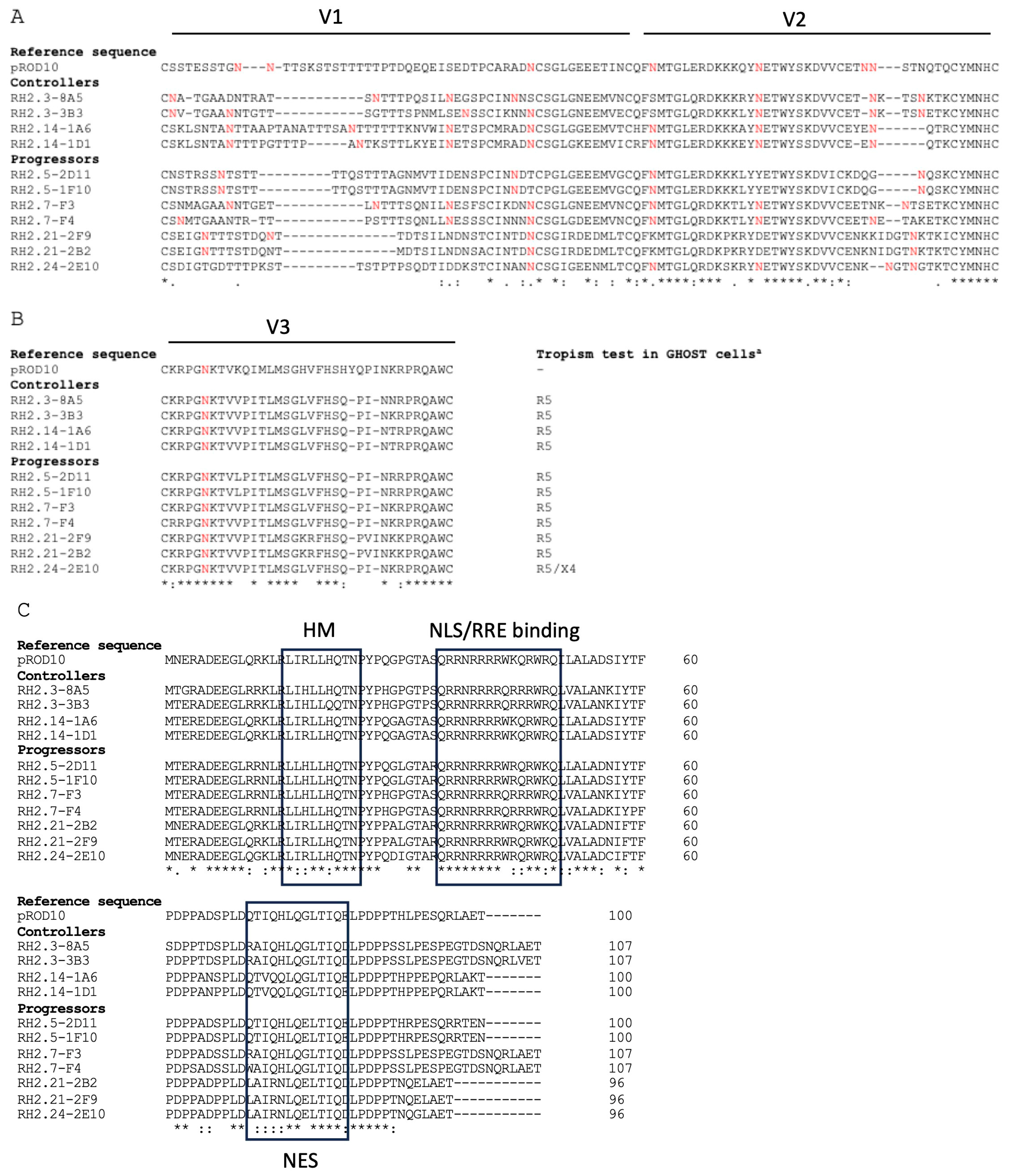
3.2. Genetic Association with HIV-2 Progression
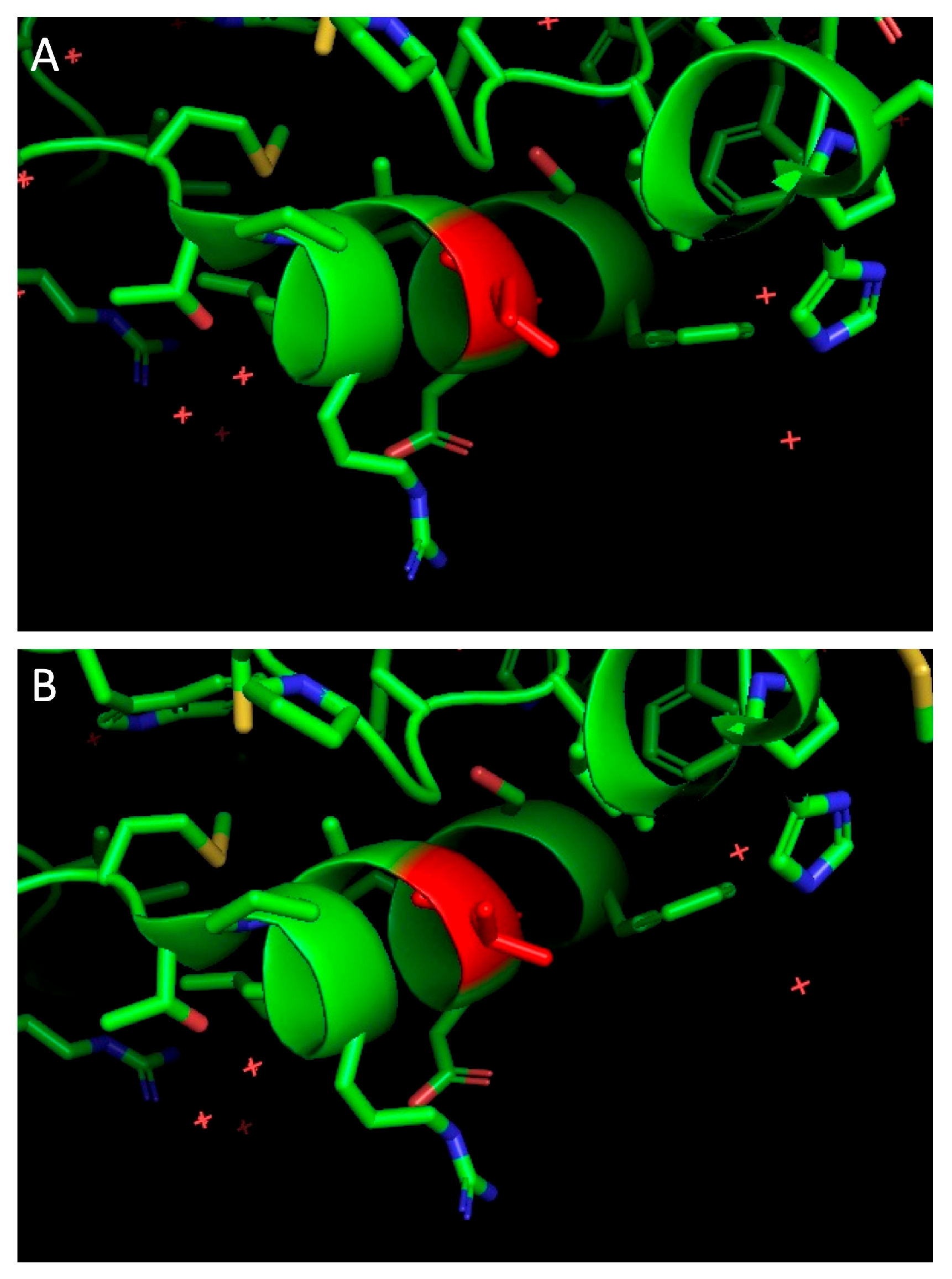
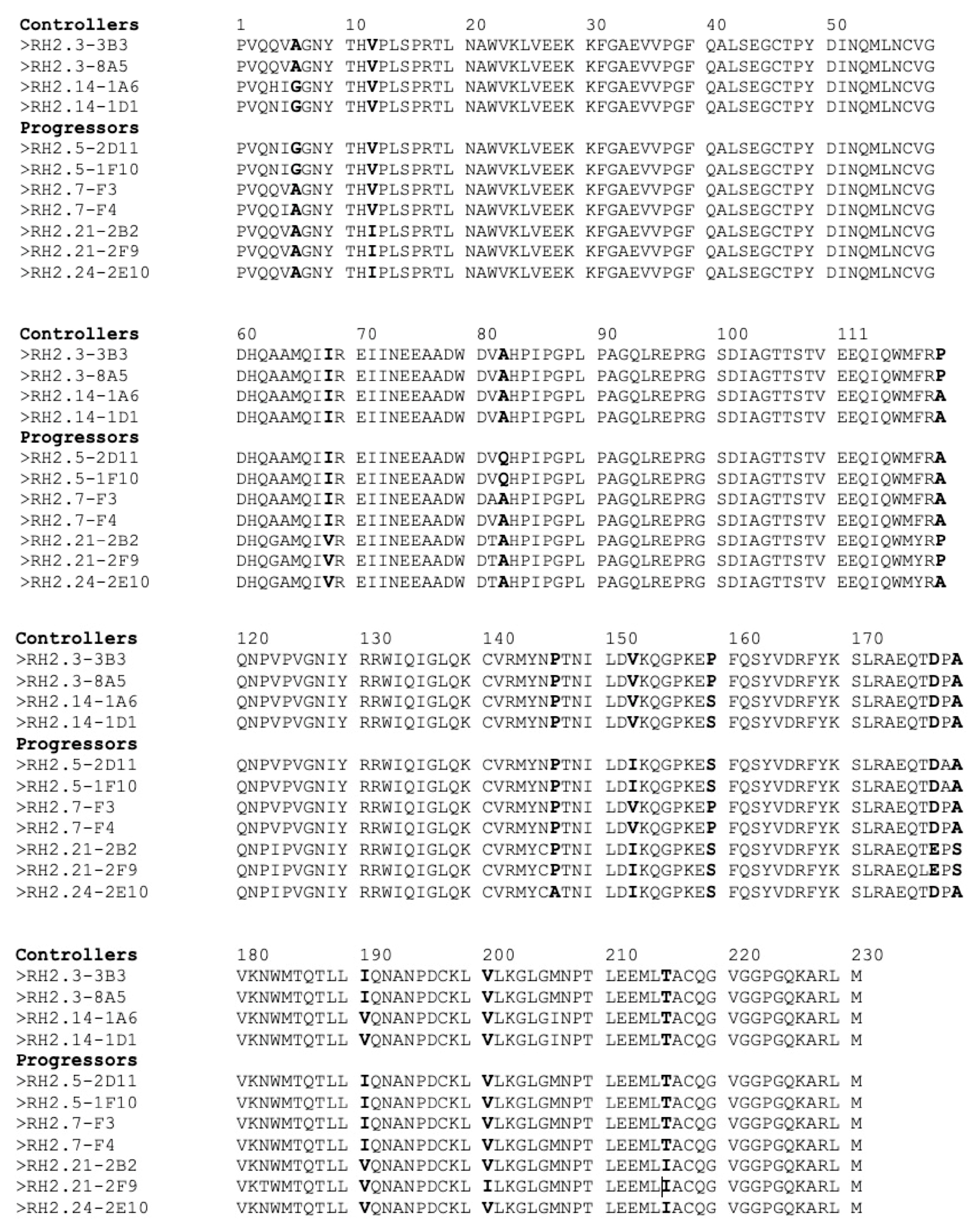
3.3. Individual Proteins’ Contribution to Virologic Progression
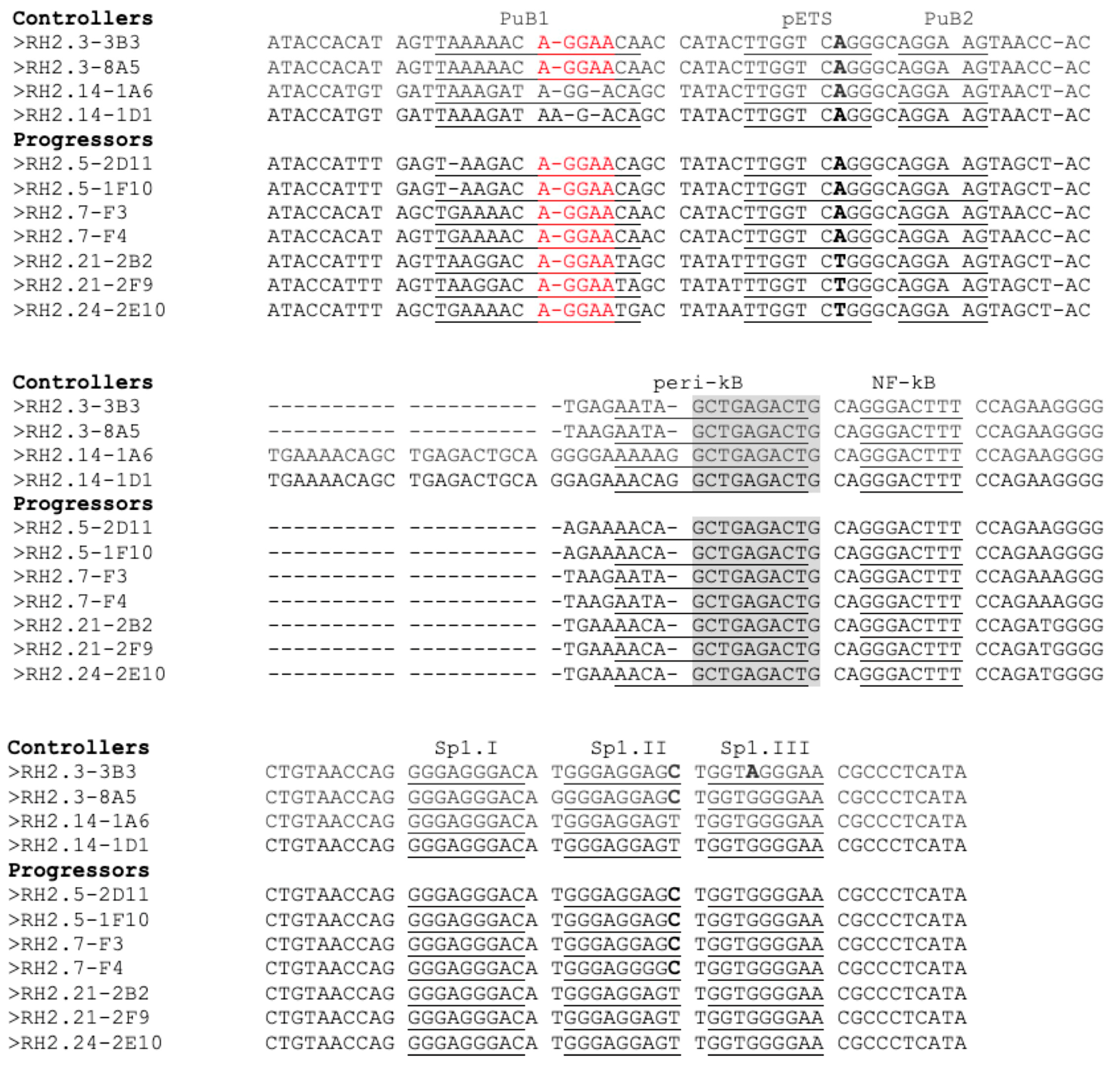
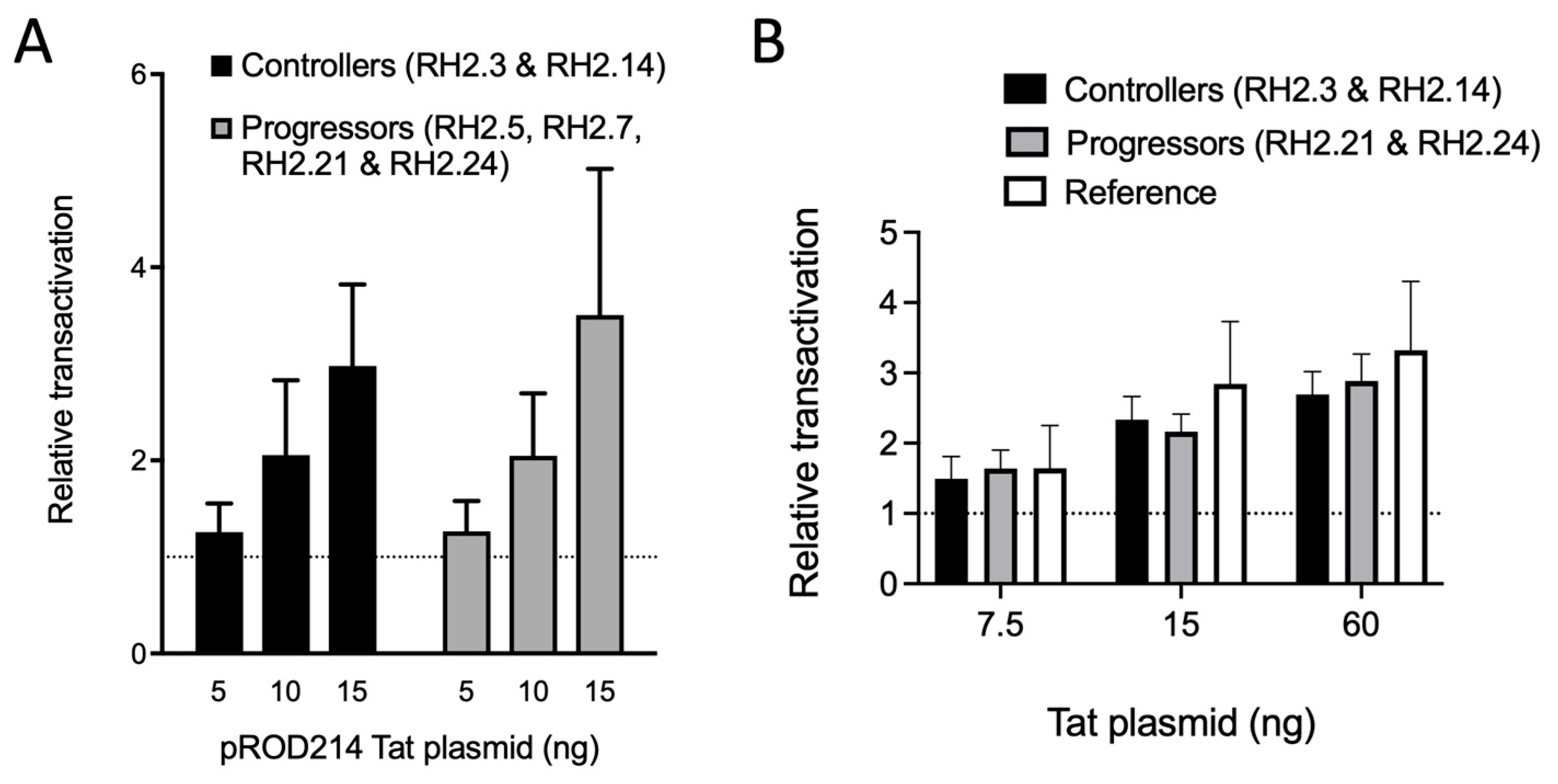
3.4. Transcription Regulation in HIV-2 Controllers and Progressors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bekker, L.G.; Beyrer, C.; Mgodi, N.; Lewin, S.R.; Delany-Moretlwe, S.; Taiwo, B.; Masters, M.C.; Lazarus, J.V. HIV infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finzi, D.; Hermankova, M.; Pierson, T.; Carruth, L.M.; Buck, C.; Chaisson, R.E.; Quinn, T.C.; Chadwick, K.; Margolick, J.; Brookmeyer, R.; et al. Identification of a reservoir for HIV-1 in patients on highly active antiretroviral therapy. Science 1997, 278, 1295–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.A.; Simonetti, F.R.; Beg, S.; McMyn, N.F.; Dai, W.; Bachmann, N.; Lai, J.; Ford, W.C.; Bunch, C.; Jones, J.L.; et al. Complex decay dynamics of HIV virions, intact and defective proviruses, and 2LTR circles following initiation of antiretroviral therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2120326119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Lian, X.; Gao, C.; Sun, X.; Einkauf, K.B.; Chevalier, J.M.; Chen, S.M.Y.; Hua, S.; Rhee, B.; Chang, K.; et al. Distinct viral reservoirs in individuals with spontaneous control of HIV-1. Nature 2020, 585, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etemad, B.; Esmaeilzadeh, E.; Li, J.Z. Learning from the Exceptions: HIV Remission in Post-treatment Controllers. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hokello, J.; Tyagi, P.; Dimri, S.; Sharma, A.L.; Tyagi, M. Comparison of the Biological Basis for Non-HIV Transmission to HIV-Exposed Seronegative Individuals, Disease Non-Progression in HIV Long-Term Non-Progressors and Elite Controllers. Viruses 2023, 15, 11362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Cirion, A.; Pancino, G.; Sinet, M.; Venet, A.; Lambotte, O. HIV controllers: How do they tame the virus? Trends Immunol. 2007, 28, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connell, K.A.; Bailey, J.R.; Blankson, J.N. Elucidating the elite: Mechanisms of control in HIV-1 infection. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankson, J.N. Effector mechanisms in HIV-1 infected elite controllers: Highly active immune responses? Antiviral Res. 2010, 85, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, W.B.; Zaunders, J.J.; Yuan, F.F.; Wang, B.; Learmont, J.C.; Geczy, A.F.; Saksena, N.K.; McPhee, D.A.; Gorry, P.R.; Sullivan, J.S. Mechanisms of HIV non-progression; robust and sustained CD4+ T-cell proliferative responses to p24 antigen correlate with control of viraemia and lack of disease progression after long-term transfusion-acquired HIV-1 infection. Retrovirology 2008, 5, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaunders, J.; Dyer, W.B.; Churchill, M. The Sydney Blood Bank Cohort: Implications for viral fitness as a cause of elite control. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2011, 6, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Yanes, S.; Pernas, M.; Marfil, S.; Cabrera-Rodriguez, R.; Ortiz, R.; Urrea, V.; Rovirosa, C.; Estevez-Herrera, J.; Olivares, I.; Casado, C.; et al. The Characteristics of the HIV-1 Env Glycoprotein Are Linked with Viral Pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 763039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, H.; Borrego, P.; Bartolo, I.; Marcelino, J.M.; Familia, C.; Quintas, A.; Taveira, N. Evolutionary and structural features of the C2, V3 and C3 envelope regions underlying the differences in HIV-1 and HIV-2 biology and infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, T.H.; Dai, L.; Zheng, X.; Gorin, A.M.; Oishi, J.; Wu, T.T.; Yoshizawa, J.M.; Li, X.; Yang, O.O.; et al. Effects of Mutations on Replicative Fitness and Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Binding Affinity Are Among the Determinants Underlying Cytotoxic-T-Lymphocyte Escape of HIV-1 Gag Epitopes. mBio 2017, 8, e01050-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, X.; Gao, C.; Sun, X.; Jiang, C.; Einkauf, K.B.; Seiger, K.W.; Chevalier, J.M.; Yuki, Y.; Martin, M.; Hoh, R.; et al. Signatures of immune selection in intact and defective proviruses distinguish HIV-1 elite controllers. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabl4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Loeff, M.F.; Larke, N.; Kaye, S.; Berry, N.; Ariyoshi, K.; Alabi, A.; van Tienen, C.; Leligdowicz, A.; Sarge-Njie, R.; da Silva, Z.; et al. Undetectable plasma viral load predicts normal survival in HIV-2-infected people in a West African village. Retrovirology 2010, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marlink, R.; Kanki, P.; Thior, I.; Travers, K.; Eisen, G.; Siby, T.; Traore, I.; Hsieh, C.C.; Dia, M.C.; Gueye, E.H.; et al. Reduced rate of disease development after HIV-2 infection as compared to HIV-1. Science 1994, 265, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, S.J.; Sarr, A.D.; Travers, K.U.; Gueye-Ndiaye, A.; Mboup, S.; Essex, M.E.; Kanki, P.J. Lower human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 2 viral load reflects the difference in pathogenicity of HIV-1 and HIV-2. J. Infect. Dis. 1999, 180, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, T.I.; Peng, Y.; Leligdowicz, A.; Zaidi, I.; Li, L.; Griffin, H.; Blais, M.E.; Vincent, T.; Saraiva, M.; Yindom, L.M.; et al. Correlates of T-cell-mediated viral control and phenotype of CD8(+) T cells in HIV-2, A naturally contained human retroviral infection. Blood 2013, 121, 4330–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamweya, S.; Hegedus, A.; Jaye, A.; Rowland-Jones, S.; Flanagan, K.L.; Macallan, D.C. Comparing HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection: Lessons for viral immunopathogenesis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2013, 23, 221–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.; Vranckx, L.; Gijsbers, R.; Christ, F.; Debyser, Z. Insight into HIV-2 latency may disclose strategies for a cure for HIV-1 infection. J. Virus Erad. 2017, 3, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, A.D.; Meyer, L.; Prins, M.; Thiebaut, R.; Gurdasani, D.; Guiguet, M.; Chaix, M.L.; Amornkul, P.; Babiker, A.; Sandhu, M.S.; et al. An evaluation of HIV elite controller definitions within a large seroconverter cohort collaboration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland-Jones, S. Protective immunity against HIV infection: Lessons from HIV-2 infection. Future Microbiol. 2006, 1, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leligdowicz, A.; Rowland-Jones, S. Tenets of protection from progression to AIDS: Lessons from the immune responses to HIV-2 infection. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2008, 7, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wejse, C.; Honge, B.L. Is it time to revise the notion that HIV-2 is benign? Lancet HIV 2018, 6, e3–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esbjornsson, J.; Mansson, F.; Kvist, A.; da Silva, Z.J.; Andersson, S.; Fenyo, E.M.; Isberg, P.E.; Biague, A.J.; Lindman, J.; Palm, A.A.; et al. Long-term follow-up of HIV-2-related AIDS and mortality in Guinea-Bissau: A prospective open cohort study. Lancet HIV 2018, 6, e25–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNeil, A.; Sarr, A.D.; Sankale, J.L.; Meloni, S.T.; Mboup, S.; Kanki, P. Direct evidence of lower viral replication rates in vivo in human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) infection than in HIV-1 infection. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 5325–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchant, D.; Neil, S.J.D.; McKnight, A. Human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2 have different replication kinetics in human primary macrophage culture. J. Gen. Virol. 2006, 87 Pt 2, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, S.J.; Sarr, A.D.; Gueye-Ndiaye, A.; Mboup, S.; Essex, M.E.; Kanki, P.J. Low plasma human immunodeficiency virus type 2 viral load is independent of proviral load: Low virus production in vivo. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 1554–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruggemans, A.; Vansant, G.; Van de Velde, P.; Debyser, Z. The HIV-2 OGH double reporter virus shows that HIV-2 is less cytotoxic and less sensitive to reactivation from latency than HIV-1 in cell culture. J. Virus Erad. 2023, 9, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, H. Isolation of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 biological clones from peripheral blood lymphocytes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 304, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blaak, H.; Brouwer, M.; Ran, L.J.; de Wolf, F.; Schuitemaker, H. In vitro replication kinetics of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) variants in relation to virus load in long-term survivors of HIV-1 infection. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 177, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaak, H.; van der Ende, M.E.; Boers, P.H.; Schuitemaker, H.; Osterhaus, A.D. In vitro replication capacity of HIV-2 variants from long-term aviremic individuals. Virology 2006, 353, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinones-Mateu, M.E.; Ball, S.C.; Marozsan, A.J.; Torre, V.S.; Albright, J.L.; Vanham, G.; van Der Groen, G.; Colebunders, R.L.; Arts, E.J. A dual infection/competition assay shows a correlation between ex vivo human immunodeficiency virus type 1 fitness and disease progression. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 9222–9233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claiborne, D.T.; Prince, J.L.; Scully, E.; Macharia, G.; Micci, L.; Lawson, B.; Kopycinski, J.; Deymier, M.J.; Vanderford, T.H.; Nganou-Makamdop, K.; et al. Replicative fitness of transmitted HIV-1 drives acute immune activation, proviral load in memory CD4+ T cells, and disease progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1480–E1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaak, H.; Boers, P.H.; Gruters, R.A.; Schuitemaker, H.; van der Ende, M.E.; Osterhaus, A.D. CCR5, GPR15, and CXCR6 are major coreceptors of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 variants isolated from individuals with and without plasma viremia. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1686–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, M.; Yu, H.; Sauter, D.; Usmani, S.M.; Schmokel, J.; Feldman, J.; Gruters, R.A.; van der Ende, M.E.; Geyer, M.; Rowland-Jones, S.; et al. Efficient Nef-mediated downmodulation of TCR-CD3 and CD28 is associated with high CD4+ T cell counts in viremic HIV-2 infection. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 4906–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Usmani, S.M.; Borch, A.; Kramer, J.; Sturzel, C.M.; Khalid, M.; Li, X.; Krnavek, D.; van der Ende, M.E.; Osterhaus, A.D.; et al. The efficiency of Vpx-mediated SAMHD1 antagonism does not correlate with the potency of viral control in HIV-2-infected individuals. Retrovirology 2013, 10, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ende, M.E.; Schutten, M.; Ly, T.D.; Gruters, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D. HIV-2 infection in 12 European residents: Virus characteristics and disease progression. AIDS 1996, 10, 1649–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, B.; Jeang, K.T. Transactivation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is sequence specific for both the single-stranded bulge and loop of the trans-acting-responsive hairpin: A quantitative analysis. J. Virol. 1989, 63, 5501–5504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdita, M.; Schutze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirao, K.; Andrews, S.; Kuroki, K.; Kusaka, H.; Tadokoro, T.; Kita, S.; Ose, T.; Rowland-Jones, S.L.; Maenaka, K. Structure of HIV-2 Nef Reveals Features Distinct from HIV-1 Involved in Immune Regulation. iScience 2020, 23, 100758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.T.; Alves, B.M.; Yoo, S.; Xiao, M.A.; Leng, J.; Quashie, P.K.; Soares, E.A.; Routy, J.P.; Soares, M.A.; Mesplede, T. Progressive emergence of an S153F plus R263K combination of integrase mutations in the proviral DNA of one individual successfully treated with dolutegravir. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jallow, S.; Leligdowicz, A.; Kramer, H.B.; Onyango, C.; Cotten, M.; Wright, C.; Whittle, H.C.; McMichael, A.; Dong, T.; Kessler, B.M.; et al. The presence of prolines in the flanking region of an immunodominant HIV-2 gag epitope influences the quality and quantity of the epitope generated. Eur. J. Immunol. 2015, 45, 2232–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, T.L.; Doms, R.W. HIV-1 envelope determinants for cell tropism and chemokine receptor use. Mol. Membr. Biol. 1999, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Trent, J.O.; Tomaras, G.D.; Wang, Z.; Murray, J.L.; Conolly, S.M.; Navenot, J.M.; Barry, A.P.; Greenberg, M.L.; Peiper, S.C. Identification of ENV determinants in V3 that influence the molecular anatomy of CCR5 utilization. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 302, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, R.J.; Yi, Y.; Singh, A.; Collman, R.G. Determinants of entry cofactor utilization and tropism in a dualtropic human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolate. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 4478–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrosse, B.; Treboute, C.; Brelot, A.; Alizon, M. Cooperation of the V1/V2 and V3 domains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 for interaction with the CXCR4 receptor. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 5457–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, A.; Honnen, W.J.; He, Y.; Gorny, M.K.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Kayman, S.C. The V1/V2 domain of gp120 is a global regulator of the sensitivity of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates to neutralization by antibodies commonly induced upon infection. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 5205–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabatov, A.A.; Pollakis, G.; Linnemann, T.; Kliphius, A.; Chalaby, M.I.; Paxton, W.A. Intrapatient alterations in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 V1V2 and V3 regions differentially modulate coreceptor usage, virus inhibition by CC/CXC chemokines, soluble CD4, and the b12 and 2G12 monoclonal antibodies. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollakis, G.; Kang, S.; Kliphuis, A.; Chalaby, M.I.; Goudsmit, J.; Paxton, W.A. N-linked glycosylation of the HIV type-1 gp120 envelope glycoprotein as a major determinant of CCR5 and CXCR4 coreceptor utilization. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 13433–13441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouchier, R.A.; Groenink, M.; Kootstra, N.A.; Tersmette, M.; Huisman, H.G.; Miedema, F.; Schuitemaker, H. Phenotype-associated sequence variation in the third variable domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 molecule. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 3183–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, J.; Stalhandske, P.; Marquina, S.; Karis, J.; Fouchier, R.A.; Norrby, E.; Chiodi, F. Biological phenotype of HIV type 2 isolates correlates with V3 genotype. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 1996, 12, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onyango, C.O.; Leligdowicz, A.; Yokoyama, M.; Sato, H.; Song, H.; Nakayama, E.E.; Shioda, T.; de Silva, T.; Townend, J.; Jaye, A.; et al. HIV-2 capsids distinguish high and low virus load patients in a West African community cohort. Vaccine 2010, 28 (Suppl. 2), B60–B67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boswell, M.T.; Nazziwa, J.; Kuroki, K.; Palm, A.; Karlson, S.; Mansson, F.; Biague, A.; da Silva, Z.J.; Onyango, C.O.; de Silva, T.I.; et al. Intrahost evolution of the HIV-2 capsid correlates with progression to AIDS. Virus Evol. 2022, 8, veac075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Hingrat, Q.; Visseaux, B.; Bertine, M.; Chauveau, L.; Schwartz, O.; Collin, F.; Damond, F.; Matheron, S.; Descamps, D.; Charpentier, C. Genetic Variability of Long Terminal Repeat Region between HIV-2 Groups Impacts Transcriptional Activity. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01504-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, N.M.; Hannibal, M.C.; Markovitz, D.M. The peri-kappa B site mediates human immunodeficiency virus type 2 enhancer activation in monocytes but not in T cells. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 4854–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerman, M.; Guyader, M.; Montagnier, L.; Baltimore, D.; Muesing, M.A. The specificity of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 transactivator is different from that of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3755–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, B.; Gatignol, A.; Silver, J.; Jeang, K.T. Efficient trans-activation by the HIV-2 Tat protein requires a duplicated TAR RNA structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, H.; Rice, A.P. Exon2 of HIV-2 Tat contributes to transactivation of the HIV-2 LTR by increasing binding affinity to HIV-2 TAR RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4405–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.S.; Ramos, V.; Oliveira, T.Y.; Gaebler, C.; Jankovic, M.; Nussenzweig, M.C.; Cohn, L.B. Integration features of intact latent HIV-1 in CD4+ T cell clones contribute to viral persistence. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20211427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, C.; Louvat, C.; Miele, A.E.; Batisse, J.; Guillon, C.; Ballut, L.; Lener, D.; Negroni, M.; Ruff, M.; Gouet, P.; et al. The HIV-1 Integrase C-Terminal Domain Induces TAR RNA Structural Changes Promoting Tat Binding. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Status, Participant ID and Year | CD4+ T-Cell Count | Viral Load | Viral Isolates (Replication Rate) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controllers: | |||
| RH2.3 | |||
| 2000 | 770 | <50 | 3B3/3C3/8A5 (low) |
| 2016 | 580 | <50 | |
| RH2.14 | |||
| 2000 | 550 | <50 | 1D1/1A6 (low) |
| 2015 | 650 | <50 | |
| Progressors: | |||
| RH2.5 | |||
| 1997 | 120 | 110,000 | 1F10/2D11 (intermediate) |
| 2016 | 370 | <50 * | |
| RH2.7 | |||
| 1996 | 10 | >500 | F3/F4 (intermediate) |
| 2016 | deceased | - | |
| RH2.21 | |||
| 1998 | 60 | 59,000 | 2B2/2F9 (high) |
| 2016 | deceased | - | |
| RH2.24 | |||
| 1999 | 70 | 23,000 | 2D8/2E10 (high) |
| 2016 | lost-to-follow-up | - |
| Status, Participant ID | 119 | 159 | 178 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Controllers: | |||
| RH2.3 | Proline | Proline | Proline |
| RH2.14 | Alanine | Serine | Proline |
| Progressors: | |||
| RH2.5 | Alanine | Serine | Alanine |
| RH2.7 | Alanine | Proline | Proline |
| RH2.21 | Proline | Serine | Proline |
| RH2.24 | Alanine | Serine | Proline |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lungu, C.; Overmars, R.J.; Grundeken, E.; Boers, P.H.M.; van der Ende, M.E.; Mesplède, T.; Gruters, R.A. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Replication-Competent HIV-2 Isolated from Controllers and Progressors. Viruses 2023, 15, 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112236
Lungu C, Overmars RJ, Grundeken E, Boers PHM, van der Ende ME, Mesplède T, Gruters RA. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Replication-Competent HIV-2 Isolated from Controllers and Progressors. Viruses. 2023; 15(11):2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112236
Chicago/Turabian StyleLungu, Cynthia, Ronald J. Overmars, Esmée Grundeken, Patrick H. M. Boers, Marchina E. van der Ende, Thibault Mesplède, and Rob A. Gruters. 2023. "Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Replication-Competent HIV-2 Isolated from Controllers and Progressors" Viruses 15, no. 11: 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112236
APA StyleLungu, C., Overmars, R. J., Grundeken, E., Boers, P. H. M., van der Ende, M. E., Mesplède, T., & Gruters, R. A. (2023). Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Replication-Competent HIV-2 Isolated from Controllers and Progressors. Viruses, 15(11), 2236. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112236







