Revealing Novel-Strain-Specific and Shared Epitopes of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Spike Glycoprotein Using Chemical Linkage of Peptides onto Scaffolds Precision Epitope Mapping
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Homologous and Heterologous Vaccination/Challenge Trials: Sera for Epitope Mapping
2.3. Synthesis of CLIPS Peptide Arrays
2.4. Serum Screening of CLIPS Peptide Arrays
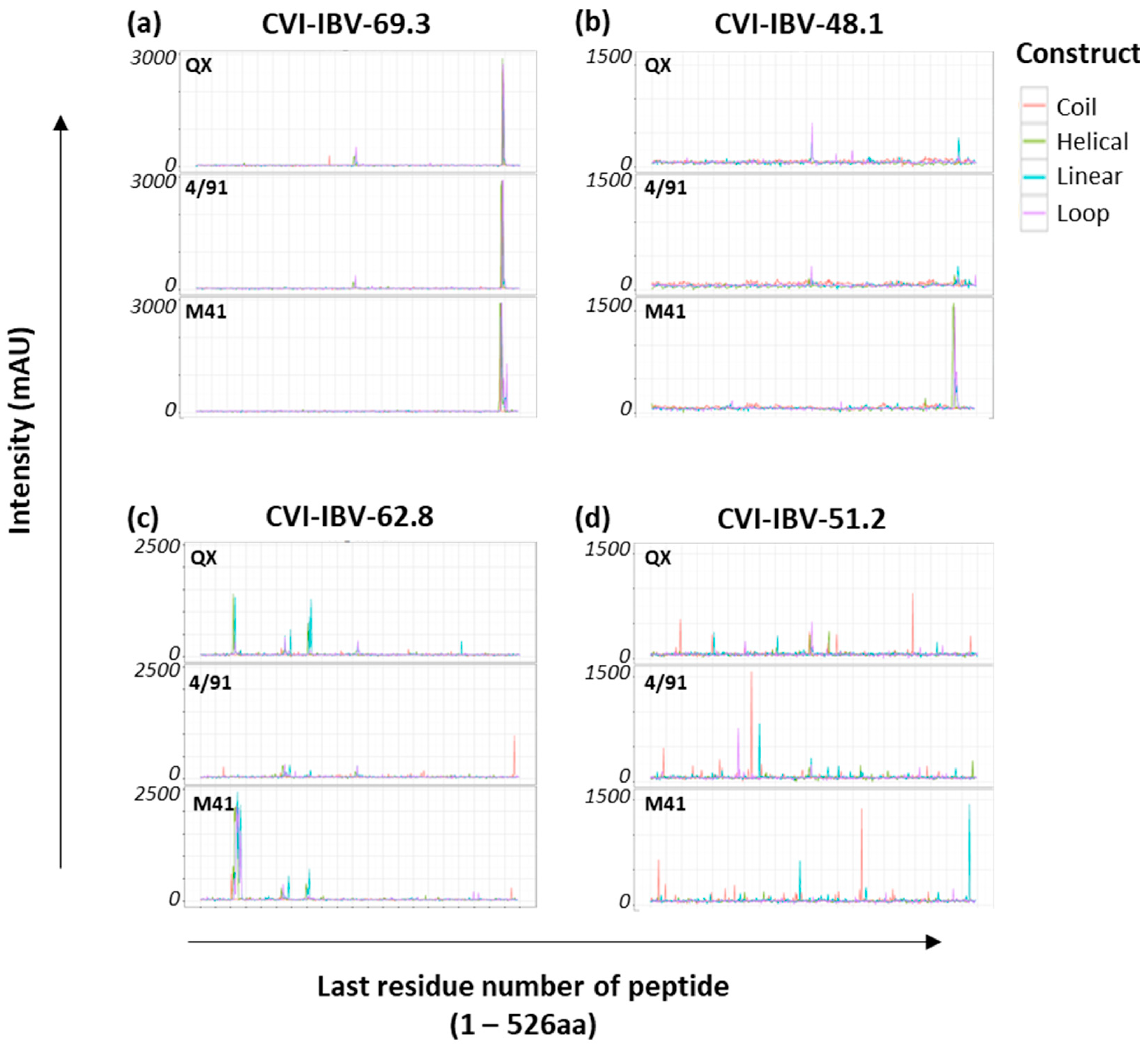
2.5. Quality Control Assessment of CLIPS Peptide Arrays
2.6. Analysis of Predicted Epitope Sequences
2.7. Linear Peptide ELISA
2.8. Conservation of Epitope Sequences and Structural Modelling
| Group | Antibody Type | Antibody Raised Against | Antigenic Region e | Challenge Virus | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Homologous | Polyclonal | M41(S) | N/A | M41 | [20] |
| M41(S1) | |||||
| QX(S1) | QX | ||||
| Heterologous | Polyclonal | M41(S) a | N/A | QX | [59] |
| M41(S) and 4/91(S) b | |||||
| 4/91(S) c | |||||
| Mock | Polyclonal | N/A | N/A | N/A | [20] |
| Mock/challenge | Polyclonal | N/A | N/A | M41 QX | [20,59] |
| Monoclonal antibodies | CVI-IBV-48.1 | IBV strain D207 S1 d | A/B (#N) | N/A | [21,22,65] |
| CVI-IBV-48.2 | C (#N) | ||||
| CVI-IBV-51.2 | ND | ||||
| CVI-IBV-52.1 | E (#N) | ||||
| CVI-IBV-62.1 | A (#N) | ||||
| CVI-IBV-62.8 | D (#N) | ||||
| CVI-IBV-69.1 | A (#N) | ||||
| CVI-IBV-69.3 | E/F |
3. Results
3.1. Construction of the IBV S1 Peptide Arrays
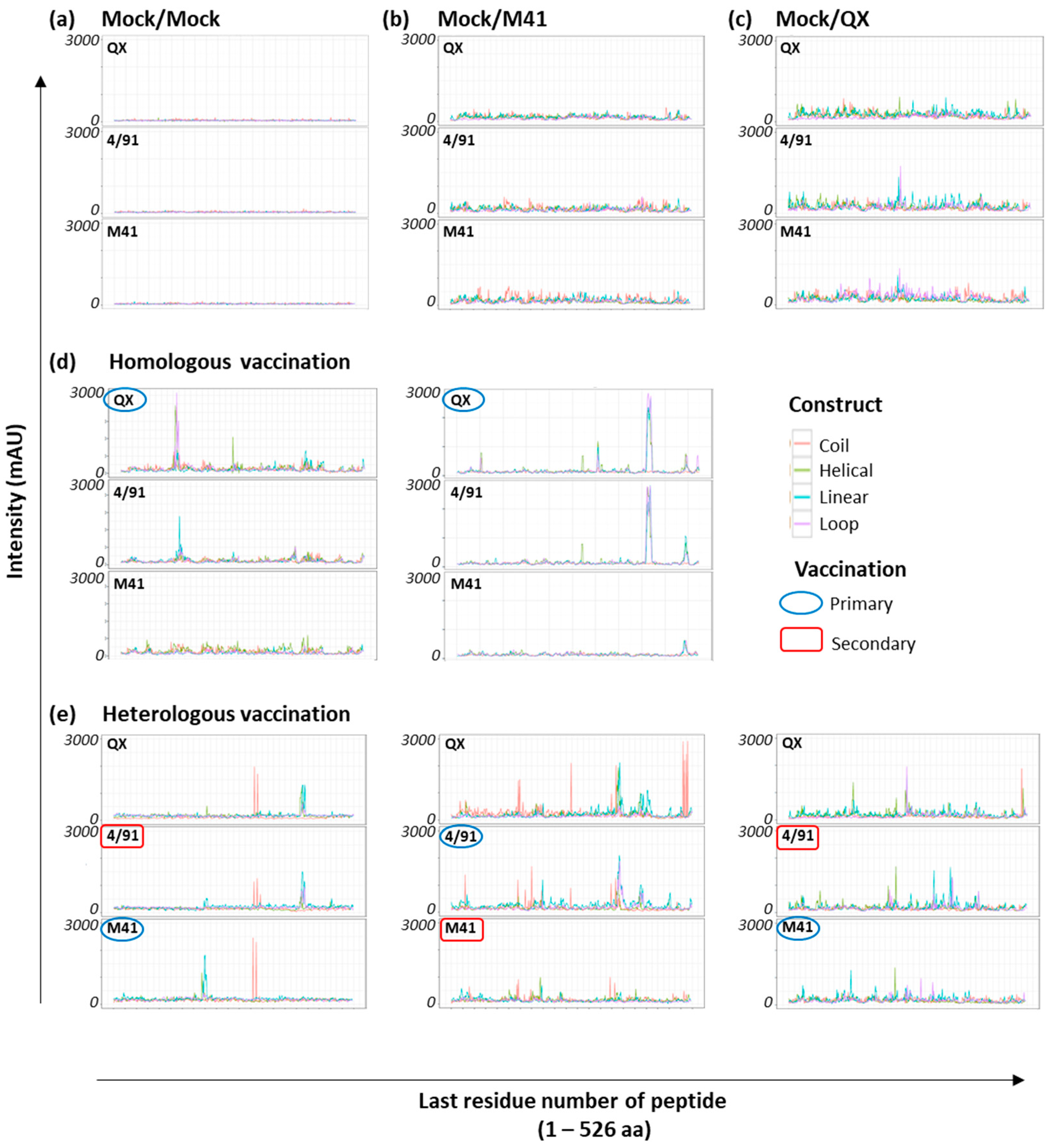
3.2. Array Screening with Sera from Homologous rIBV-Vaccinated Chickens
3.3. Identification of Shared Epitopes by Screening with Heterologous rIBV Sera
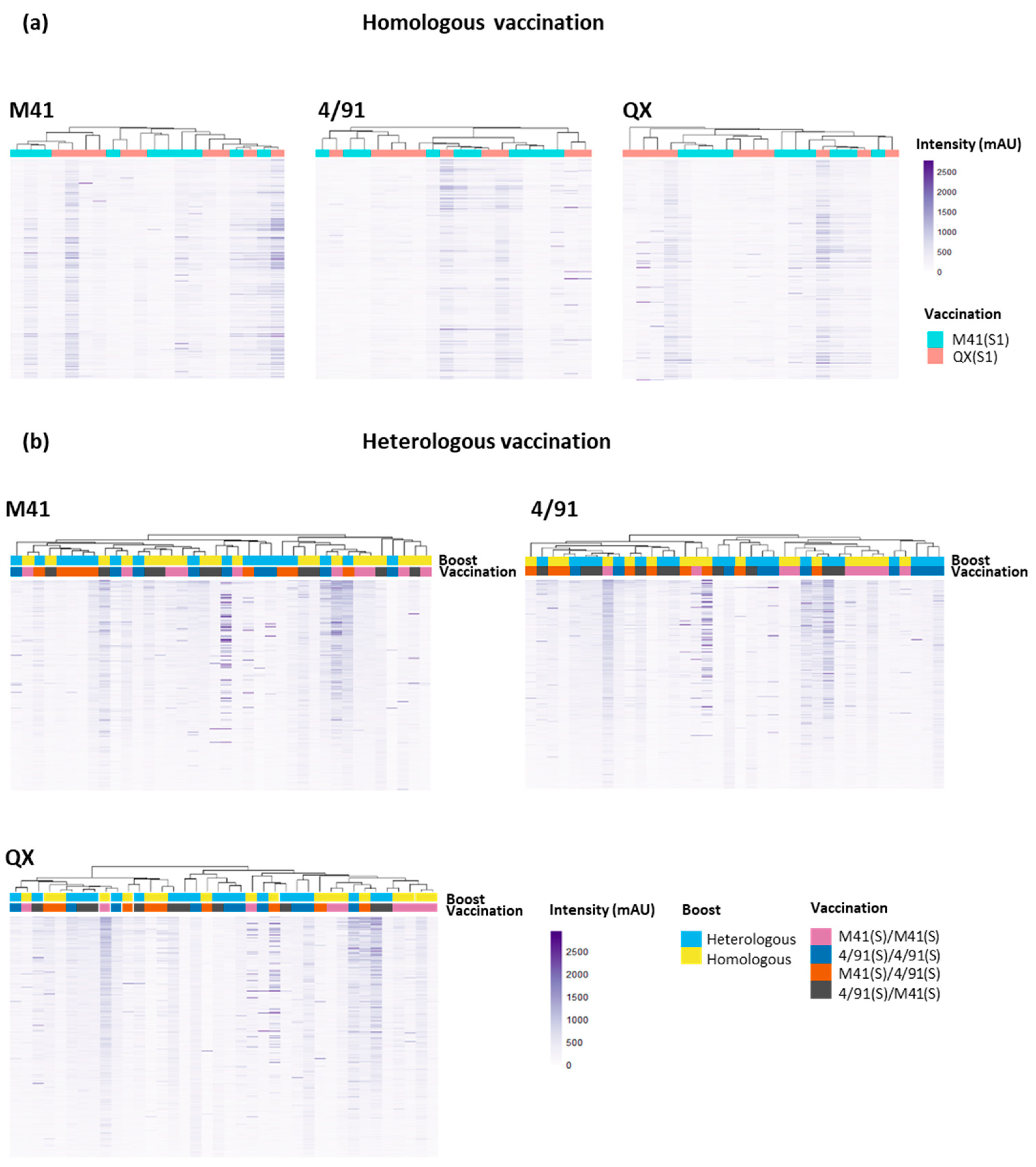
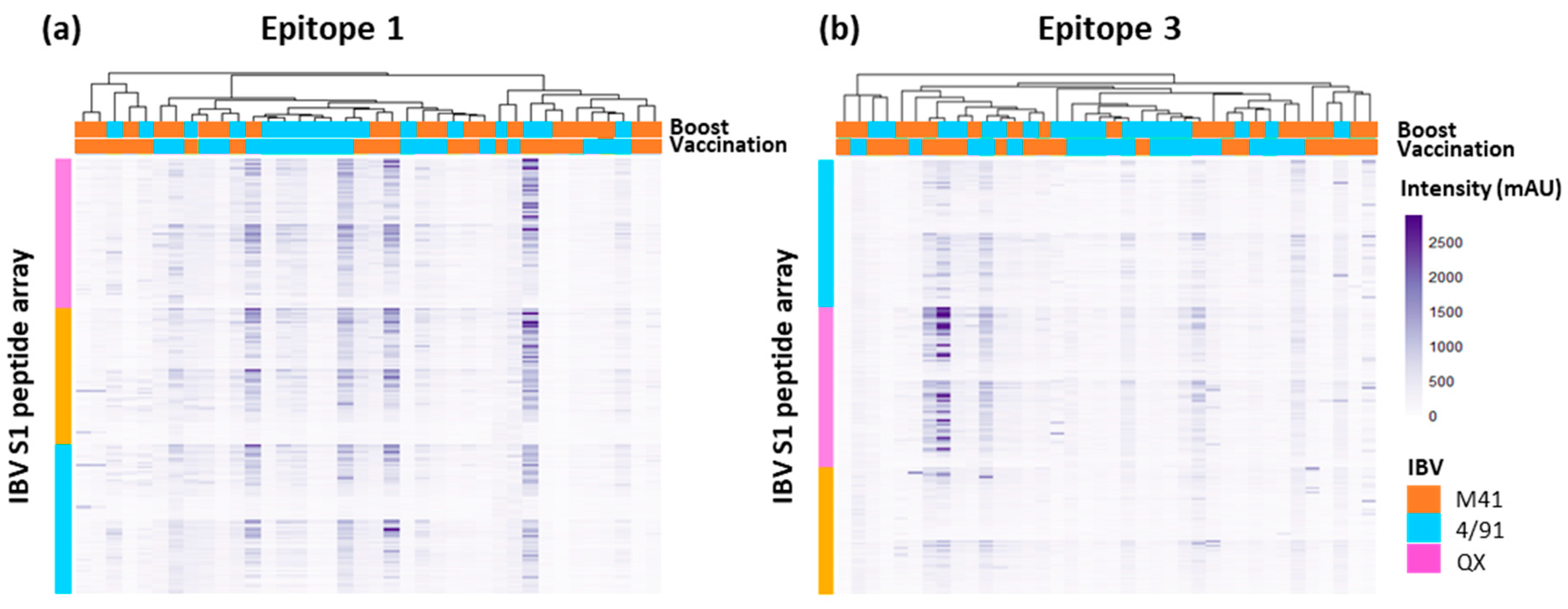
3.4. Clustering to Investigate Epitope Binding Profiles
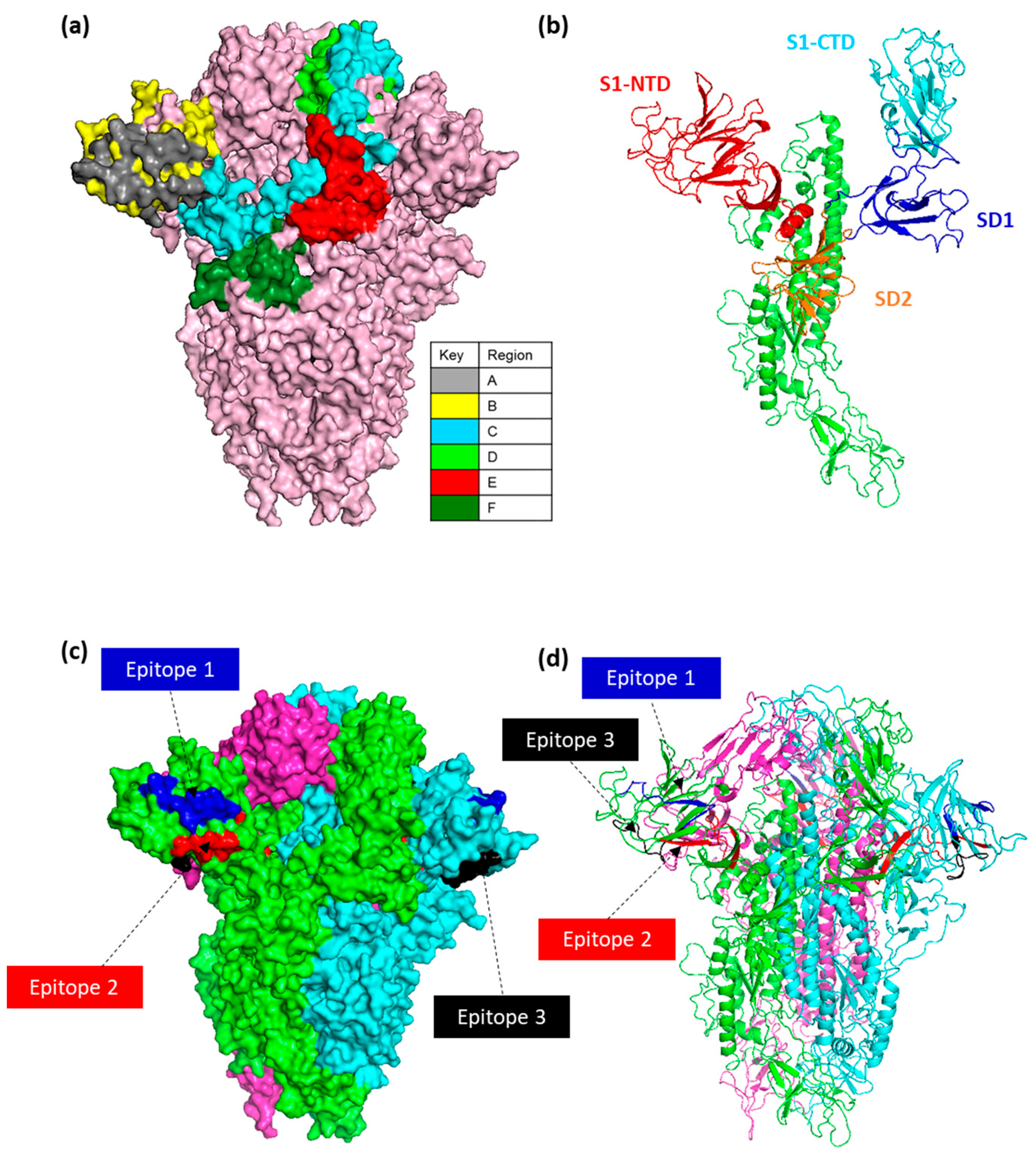
3.5. Accessibility and Location of IBV Spike Epitope Regions
3.6. Conservancy of Selected Epitope Candidates amongst IBV Serotypes
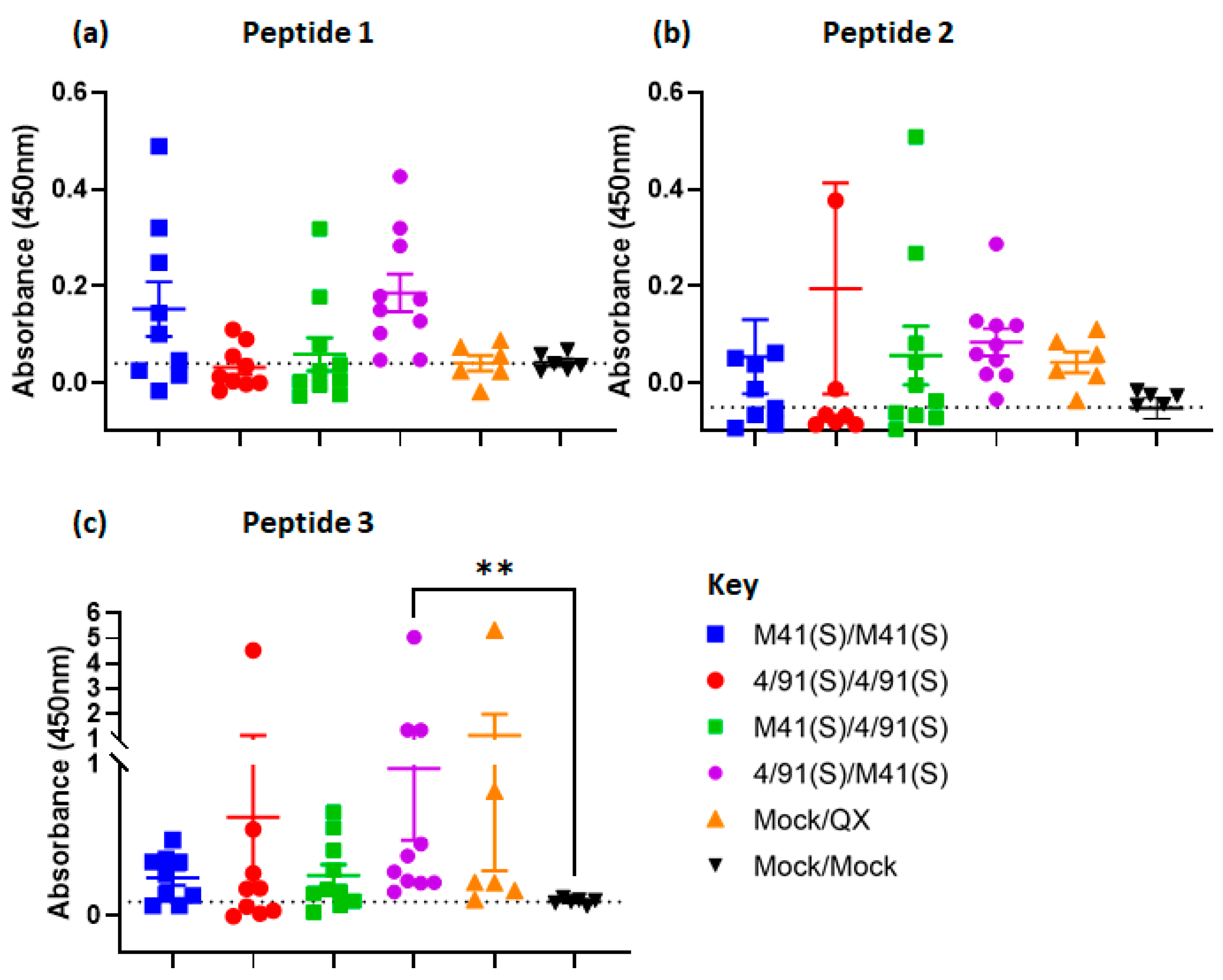
3.7. Assessment of Selected Epitopes 1–3 for Vaccine Candidate Potential
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cook, J.K.; Jackwood, M.; Jones, R.C. The Long View: 40 Years of Infectious Bronchitis Research. Avian Pathol. 2012, 41, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijs, M.G.; Ariaans, M.P.; Dwars, R.M.; Van Eck, J.H.; Bouma, A.; Stegeman, A.; Vervelde, L. Course of Infection and Immune Responses in the Respiratory Tract of IBV Infected Broilers after Superinfection with E. coli. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 127, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naqi, S.; Bauman, B.; Mohammed, H. The Exacerbating Effect of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Infection on the Infectious Bursal Disease Virus-Induced Suppression of Opsonization by Escherichia coli Antibody in Chickens. Avian Dis. 2001, 45, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandekerchove, D.; Herdt, P.D.; Laevens, H.; Butaye, P.; Meulemans, G.; Pasmans, F. Significance of Interactions between Escherichia coli and Respiratory Pathogens in Layer Hen Flocks Suffering from Colibacillosis-Associated Mortality. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bande, F.; Arshad, S.S.; Omar, A.R.; Hair-Bejo, M.; Mahmuda, A.; Nair, V. Global Distributions and Strain Diversity of Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus: A Review. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2017, 18, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelb, J.; Wolff, J.B.; Moran, C.A. Variant Serotypes of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Isolated from Commercial Layer and Broiler Chickens. Avian Dis. 1991, 35, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.K.; Orbell, S.J.; Woods, M.A.; Huggins, M.B. Breadth of Protection of the Respiratory Tract Provided by Different Live-Attenuated Infectious Bronchitis Vaccines against Challenge with Infectious Bronchitis Viruses of Heterologous Serotypes. Avian Pathol. 1999, 28, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Brandao, P.; Torres, C.A.; Koopman, R.; Villarreal, L.Y. Increased Level of Protection of Respiratory Tract and Kidney by Combining Different Infectious Bronchitis Virus Vaccines against Challenge with Nephropathogenic Brazilian Genotype Subcluster 4 Strains. Avian Pathol. 2015, 44, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.P.; Wakenell, P.S.; Woolcock, P.; O’Connor, B. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Two Infectious Bronchitis Virus Vaccine Programs for Preventing Disease Caused by a California IBV Field Isolate. Avian Dis. 2007, 51, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Malo, A.; Cook, J.K. Induction of IBV Strain-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies and Broad Spectrum Protection in Layer Pullets Primed with IBV Massachusetts (Mass) and 793B Vaccines Prior to Injection of Inactivated Vaccine Containing Mass Antigen. Avian Pathol. 2019, 48, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terregino, C.; Toffan, A.; Beato, M.S.; De Nardi, R.; Vascellari, M.; Meini, A.; Ortali, G.; Mancin, M.; Capua, I. Pathogenicity of a QX Strain of Infectious Bronchitis Virus in Specific Pathogen Free and Commercial Broiler Chickens, and Evaluation of Protection Induced by a Vaccination Programme Based on the Ma5 and 4/91 Serotypes. Avian Pathol. 2008, 37, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bru, T.; Vila, R.; Cabana, M.; Geerligs, H.J. Protection of Chickens Vaccinated with Combinations of Commercial Live Infectious Bronchitis Vaccines Containing Massachusetts, Dutch and QX-Like Serotypes against Challenge with Virulent Infectious Bronchitis Viruses 793B and Is/1494/06 Israel Variant 2. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmas, B.; Laude, H. Assembly of Coronavirus Spike Protein into Trimers and its Role in Epitope Expression. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 5367–5375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyson, C.L.M.; Jordan, B.J.; Jackwood, M.W. Insights from Molecular Structure Predictions of the Infectious Bronchitis Virus S1 Spike Glycoprotein. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 46, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Geng, Q.; Luo, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, F. Cryo-EM Structure of Infectious Bronchitis Coronavirus Spike Protein Reveals Structural and Functional Evolution of Coronavirus Spike Proteins. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promkuntod, N.; Van Eijndhoven, R.E.; De Vrieze, G.; Grone, A.; Verheije, M.H. Mapping of the Receptor-Binding Domain and Amino Acids Critical for Attachment in the Spike Protein of Avian Coronavirus Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Virology 2014, 448, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, G.; Hartog, L.; Kant, A.; van Roozelaar, D.J. Antigenic Domains on the Peplomer Protein of Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus: Correlation with Biological Functions. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D.; Davis, P.J.; Mockett, A.P. Amino Acids within Hypervariable Region 1 of Avian Coronavirus Ibv (Massachusetts Serotype) Spike Glycoprotein Are Associated with Neutralization Epitopes. Virus Res. 1988, 11, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D.; Davis, P.J.; Cook, J.K.; Li, D.; Kant, A.; Koch, G. Location of the Amino Acid Differences in the S1 Spike Glycoprotein Subunit of Closely Related Serotypes of Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Avian Pathol. 1992, 21, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, S.; Keep, S.; Britton, P.; de Wit, S.; Bickerton, E.; Vervelde, L. Recombinant Infectious Bronchitis Viruses Expressing Chimeric Spike Glycoproteins Induce Partial Protective Immunity against Homologous Challenge Despite Limited Replication In Vivo. J. Virol. 2018, 9292, e01473-18. [Google Scholar]
- Kant, A.; Koch, G.; van Roozelaar, D.J.; Kusters, J.G.; Poelwijk, F.A.; Van der Zeijst, B.A. Location of Antigenic Sites Defined by Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies on the S1 Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus Glycopolypeptide. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, G.; Kant, A. Binding of Antibodies That Strongly Neutralise Infectious Bronchitis Virus Is Dependent on the Glycosylation of the Viral Peplomer Protein. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1990, 276, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Callison, S.A.; Jackwood, M.W.; Hilt, D.A. Infectious Bronchitis Virus S2 Gene Sequence Variability May Affect S1 Subunit Specific Antibody Binding. Virus Genes 1999, 19, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldemery, F.; Joiner, K.S.; Toro, H.; van Santen, V.L. Protection against Infectious Bronchitis Virus by Spike Ectodomain Subunit Vaccine. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5864–5871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D.; Elus, M.M.; Cook, J.K. Relationship between Sequence Variation in the S1 Spike Protein of Infectious Bronchitis Virus and the Extent of Cross-Protection In Vivo. Avian Pathol. 1997, 26, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, D.; Picault, J.P.; Gough, R.; Hess, M.; Mawditt, K.; Britton, P. Variation in the Spike Protein of the 793/B Type of Infectious Bronchitis Virus, in the Field and During Alternate Passage in Chickens and Embryonated Eggs. Avian Pathol. 2005, 34, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armesto, M.; Evans, S.; Cavanagh, D.; Abu-Median, A.B.; Keep, S.; Britton, P. A Recombinant Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus Expressing a Heterologous Spike Gene Belonging to the 4/91 Serotype. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, T.; Casais, R.; Dove, B.; Britton, P.; Cavanagh, D. Recombinant Infectious Bronchitis Coronavirus Beaudette with the Spike Protein Gene of the Pathogenic M41 Strain Remains Attenuated but Induces Protective Immunity. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 13804–13811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, C.W.; Sung, H.W.; Kim, J.H.; Mo, I.P.; Izumiya, Y.; Jang, H.K.; Mikami, T. Induction of Protective Immunity in Chickens Vaccinated with Infectious Bronchitis Virus S1 Glycoprotein Expressed by a Recombinant Baculovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, H.; Zhang, J.F.; Gallardo, R.A.; van Santen, V.L.; van Ginkel, F.W.; Joiner, K.S.; Breedlove, C. S1 of Distinct IBV Population Expressed from Recombinant Adenovirus Confers Protection against Challenge. Avian Dis. 2014, 58, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Yu, L.; Duan, X.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z. Quaternized Chitosan Nanoparticles Loaded with the Combined Attenuated Live Vaccine against Newcastle Disease and Infectious Bronchitis Elicit Immune Response in Chicken after Intranasal Administration. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirvani, E.; Paldurai, A.; Manoharan, V.K.; Varghese, B.P.; Samal, S.K. A Recombinant Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) Expressing S Protein of Infectious Bronchitis Virus (IBV) Protects Chickens against IBV and NDV. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldemery, F.; Li, Y.; Yu, Q.; Van Santen, V.L.; Toro, H. Infectious Bronchitis Virus S2 of 4/91 Expressed from Recombinant Virus Does Not Protect Against Ark-Type Challenge. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.J.; Cook, J.K.; Van der Heijden, H.M.J.F. Infectious Bronchitis Virus Variants: A Review of the History, Current Situation and Control Measures. Avian Pathol. 2011, 40, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Lu, H.; Siddiqui, P.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, S. Receptor-Binding Domain of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Protein Contains Multiple Conformation-Dependent Epitopes That Induce Highly Potent Neutralizing Antibodies. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 4908–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnovitski, N.; Matthews, L.J.; Sui, J.; Gershoni, J.M.; Marasco, W.A. Mapping a Neutralizing Epitope on the SARS Coronavirus Spike Protein: Computational Prediction Based on Affinity-Selected Peptides. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 359, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Torres, J.; Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Cabello, C.; Montero, L.; Hernandez-Aceves, J.; Granados, G.; Calderón-Gallegos, A.; Zúñiga-Flores, F.; Ruiz-Rivera, M.; Abarca-Magaña, J.C.; et al. Towards the Development of an Epitope-Focused Vaccine for SARS-CoV-2. Vaccine 2022, 40, 6489–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsood, F.; Amiri, M.M.; Zarnani, A.H.; Salimi, V.; Kardar, G.A.; Khoshnoodi, J.; Mobini, M.; Ahmadi Zare, H.; Ghaderi, A.; Jeddi-Tehrani, M.; et al. Epitope Mapping of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Neutralizing Receptor Binding Domain-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 973036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, J.; Khan, H.; Rosa, A.; Calvaresi, V.; Graham, C.; Pickering, S.; Pye, V.E.; Cronin, N.B.; Huettner, I.; Malim, M.H.; et al. A Neutralizing Epitope on the SD1 Domain of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Targeted Following Infection and Vaccination. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, P.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jia, W.; Wang, H.; Fan, A.; Wang, D.; Shi, X.; et al. Structural Definition of a Unique Neutralization Epitope on the Receptor-Binding Domain of MERS-CoV Spike Glycoprotein. Cell Rep. 2018, 24, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, H.; Yamada, Y.K.; Taguchi, F. Localization of Neutralizing Epitopes and the Receptor-Binding Site within the Amino-Terminal 330 Amino Acids of the Murine Coronavirus Spike Protein. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 5403–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shi, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Ji, Z.; Jing, Z.; Feng, L. A New Neutralization Epitope in the Spike Protein of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebauer, F.; Posthumus, W.P.; Correa, I.; Sune, C.; Smerdou, C.; Sanchez, C.M.; Lenstra, J.A.; Meloen, R.H.; Enjuanes, L. Residues Involved in the Antigenic Sites of Transmissible Gastroenteritis Coronavirus S Glycoprotein. Virology 1991, 183, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, S.; Kelm, S.; Baker, T.S.; Shi, J.; Martin, A.C.R. B-Cell Epitopes: Discontinuity and Conformational Analysis. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 114, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivalingam, G.N.; Shepherd, A.J. An Analysis of B-Cell Epitope Discontinuity. Mol. Immunol. 2012, 51, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laver, W.G.; Air, G.M.; Webster, R.G.; Smith-Gill, S.J. Epitopes on Protein Antigens: Misconceptions and Realities. Cell 1990, 61, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Regenmortel, M.H.V. Mapping Epitope Structure and Activity: From One-Dimensional Prediction to Four-Dimensional Description of Antigenic Specificity. Methods 1996, 9, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, N.D.; Mayrose, I.; Halperin, D.; Yekutieli, D.; Gershoni, J.M.; Pupko, T. Computational Characterization of B-Cell Epitopes. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 3477–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geysen, H.M.; Rodda, S.J.; Mason, T.J.; Tribbick, G.; Schoofs, P.G. Strategies for Epitope Analysis Using Peptide Synthesis. J. Immunol. Meth. 1987, 102, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, P.; Beld, J.; Puijk, W.C.; Meloen, R.H. Rapid and Quantitative Cyclization of Multiple Peptide Loops onto Synthetic Scaffolds for Structural Mimicry of Protein Surfaces. ChemBioChem 2005, 6, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmerman, P.; Puijk, W.C.; Meloen, R.H. Functional Reconstruction and Synthetic Mimicry of a Conformational Epitope Using Clips Technology. J. Mol. Recognit. 2007, 20, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeenk, L.E.; Timmers-Parohi, D.; Benschop, J.J.; Puijk, W.C.; Hiemstra, H.; van Maarseveen, J.H.; Timmerman, P. Reconstructing the Discontinuous and Conformational Beta1/Beta3-Loop Binding Site on HFSH/HCG by Using Highly Constrained Multicyclic Peptides. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, D.A.J.; Dupuy, L.C.; Sanchez-Lockhart, M.; Palacios, G.; Back, J.W.; Shimanovskaya, K.; Chaudhury, S.; Ripoll, D.R.; Wallqvist, A.; Schmaljohn, C.S. Epitope Mapping of Ebola Virus Dominant and Subdominant Glycoprotein Epitopes Facilitates Construction of an Epitope-Based DNA Vaccine Able to Focus the Antibody Response in Mice. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 2883–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripoll, D.R.; Mitchell, D.A.J.; Dupuy, L.C.; Wallqvist, A.; Schmaljohn, C.; Chaudhury, S. Combinatorial Peptide-Based Epitope Mapping from Ebola Virus DNA Vaccines and Infections Reveals Residue-Level Determinants of Antibody Binding. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 2953–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, B.; Thomas, M.; Sreenivasan, C.C.; Sheng, Z.; Yu, J.; Hause, B.M.; Wang, D.; Francis, D.H.; Kaushik, R.S.; et al. Detailed Mapping of the Linear B Cell Epitopes of the Hemagglutinin (HA) Protein of Swine Influenza Virus. Virology 2018, 522, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.I. Identification of an Epitope within the Bovine Herpesvirus 1 Glycoprotein E Cytoplasmic Tail and Use of a Monoclonal Antibody Directed against the Epitope for the Differentiation between Vaccinated and Infected Animals. J. Virol. Meth. 2016, 233, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Qi, T.; Guo, W.; Lu, G.; Xiang, W. Identification of a Conserved B-Cell Epitope in the Equine Arteritis Virus (EAV) N Protein Using the Pepscan Technique. Virus Genes 2013, 47, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhee, M.; Van Breedam, W.; Costers, S.; Geldhof, M.; Noppe, Y.; Nauwynck, H. Characterization of Antigenic Regions in the Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus by the Use of Peptide-Specific Serum Antibodies. Vaccine 2011, 29, 4794–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keep, S.; Sives, S.; Stevenson-Leggett, P.; Britton, P.; Vervelde, L.; Bickerton, E. Limited Cross-Protection against Infectious Bronchitis Provided by Recombinant Infectious Bronchitis Viruses Expressing Heterologous Spike Glycoproteins. Vaccines 2020, 8, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickerton, E.; Dowgier, G.; Britton, P. Recombinant Infectious Bronchitis Viruses Expressing Heterologous S1 Subunits: Potential for a New Generation of Vaccines That Replicate in Vero Cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1681–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickerton, E.; Maier, H.J.; Stevenson-Leggett, P.; Armesto, M.; Britton, P. The S2 Subunit of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Beaudette Is a Determinant of Cellular Tropism. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01044-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casais, R.; Dove, B.; Cavanagh, D.; Britton, P. Recombinant Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus Expressing a Heterologous Spike Gene Demonstrates that the Spike Protein Is a Determinant of Cell Tropism. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 9084–9089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posthumus, W.P.; Lenstra, J.A.; Schaaper, W.M.; Van Nieuwstadt, A.P.; Enjuanes, L.; Meloen, R.H. Analysis and Simulation of a Neutralizing Epitope of Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3304–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, A. Aliview: A Fast and Lightweight Alignment Viewer and Editor for Large Datasets. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, G.; Kant, A.; Cook, J.K.; Cavanagh, D. Epitopes of Neutralising Antibodies Are Localized within Three Regions of S1 Spike Protein of Infectious Bronchitis Virus In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Infectious Bronchitis, Rauischholzhausen, Germany, 3–6 June 1991.
- Bouwman, K.M.; Parsons, L.M.; Berends, A.J.; de Vries, R.P.; Cipollo, J.F.; Verheije, M.H. Three Amino Acid Changes in Avian Coronavirus Spike Protein Allow Binding to Kidney Tissue. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01363-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesters, H.G.; Bleumink-Pluym, N.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Horzinek, M.C.; van der Zeijst, B.A. Epitopes on the Peplomer Protein of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Strain M41 as Defined by Monoclonal Antibodies. Virology 1987, 161, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusters, J.; Jager, E.; Lenstra, J.; Koch, G.; Posthumus, W.P.A.; Meloen, R.; Van der Zeijst, B. Analysis of an Immunodominant Region of Infectious Bronchitis Virus. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 2692–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Lin, Z.; Qian, K.; Shao, H.; Ye, J.; Qin, A. Peptides with 16R in S2 Protein Showed Broad Reactions with Sera against Different Types of Infectious Bronchitis Viruses. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 236, 108391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Tu, K.; Teng, Q.; Feng, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, G. Identification of Novel T-Cell Epitopes on Infectious Bronchitis Virus N Protein and Development of a Multi-Epitope Vaccine. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e0066721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andoh, K.; Ashikaga, K.; Suenaga, K.; Endo, S.; Yamazaki, K. Identification of Novel Linear Epitopes Located in the Infectious Bronchitis Virus Spike S2 Region. Avian Dis. 2018, 62, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignjatovic, J.; Sapats, S. Identification of Previously Unknown Antigenic Epitopes on the S and N Proteins of Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Arch. Virol. 2005, 150, 1813–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bande, F.; Arshad, S.S.; Hair Bejo, M.; Kadkhodaei, S.; Omar, A.R. Prediction and In Silico Identification of Novel B-Cells and T-Cells Epitopes in the S1-Spike Glycoprotein of M41 and CR88 (793/B) Infectious Bronchitis Virus Serotypes for Application in Peptide Vaccines. Adv. Bioinform. 2016, 2016, 5484972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Liao, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, X.; Sun, Y.; Song, C.; Qiu, X.; Meng, C.; Ding, C. Prediction and Identification of Novel IBV S1 Protein Derived CTL Epitopes in Chicken. Vaccine 2016, 34, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, X.; Meng, C.; Song, C.; Ding, C. Infectious Bronchitis Virus Poly-Epitope-Based Vaccine Protects Chickens from Acute Infection. Vaccine 2016, 34, 5209–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, N.; Xia, J.; Wang, F.; Duan, Z.; Miao, D.; Yan, Q.; Cao, S.; Wen, X.; Liu, P.; Huang, Y. Two Novel Neutralizing Antigenic Epitopes of the S1 Subunit Protein of a QX-Like Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus Strain SCZY3 as Revealed Using a Phage Display Peptide Library. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 168, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barlow, D.J.; Edwards, M.S.; Thornton, J.M. Continuous and Discontinuous Protein Antigenic Determinants. Nature 1986, 322, 747–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, J.D.; Hay, K.; Rini, J.M.; Yu, M.; Wang, L.; Plummer, F.A.; Corbett, C.R.; Andonov, A. Neutralizing Epitopes of the SARS-CoV S-Protein Cluster Independent of Repertoire, Antigen Structure or Mab Technology. mAbs 2010, 2, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, D.; Voss, J.; Gamblin, S.J.; Codoni, G.; Macagno, A.; Jarrossay, D.; Vachieri, S.G.; Pinna, D.; Minola, A.; Vanzetta, F.; et al. A Neutralizing Antibody Selected from Plasma Cells That Binds to Group 1 and Group 2 Influenza a Hemagglutinins. Science 2011, 333, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Parr, R.L.; King, D.J.; Collisson, E.W. A Highly Conserved Epitope on the Spike Protein of Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Arch. Virol. 1995, 140, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, R.L.; Collissor, E.W. Epitopes on the Spike Protein of a Nephropathogenic Strain of Infectious Bronchitis Virus. Arch. Virol. 1993, 133, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salarpour, A.; Toroghi, R.; Nikbakht Brujeni, G.; Momayez, R. In Silico Prediction of Linear B-Cell Epitopes for S1 Protein of Two Iranian 793/B Isolates and Their Changes after 90 Serial Passages. Vet. Res. Forum 2020, 11, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Wen, G.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, M.; Sun, Y.; Liao, Y.; Song, C.; Liu, W.; Shi, Y.; Shao, H.; et al. Development of a Recombinant Thermostable Newcastle Disease Virus Vaccine Express Infectious Bronchitis Virus Multiple Epitopes for Protecting against IBV and NDV Challenges. Vaccines 2020, 8, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.H.; Collisson, E.W. Specific Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Are Involved in in Vivo Clearance of Infectious Bronchitis Virus. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 5173–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walls, A.C.; Tortorici, M.A.; Frenz, B.; Snijder, J.; Li, W.; Rey, F.A.; DiMaio, F.; Bosch, B.-J.; Veesler, D. Glycan Shield and Epitope Masking of a Coronavirus Spike Protein Observed by Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Shi, W.; Chappell, J.D.; Joyce, M.G.; Zhang, Y.; Kanekiyo, M.; Becker, M.M.; van Doremalen, N.; Fischer, R.; Wang, N.; et al. Importance of Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies Targeting Multiple Antigenic Sites on the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Glycoprotein to Avoid Neutralization Escape. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e02002-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okda, F.A.; Lawson, S.; Singrey, A.; Nelson, J.; Hain, K.S.; Joshi, L.R.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Nelson, E.A.; Diel, D.G. The S2 Glycoprotein Subunit of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Contains Immunodominant Neutralizing Epitopes. Virology 2017, 509, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.J.; Chang, Y.C.; Ko, T.P.; Draczkowski, P.; Chien, Y.C.; Chang, Y.C.; Wu, K.P.; Khoo, K.H.; Chang, H.W.; Hsu, S.D. Cryo-EM Analysis of a Feline Coronavirus Spike Protein Reveals a Unique Structure and Camouflaging Glycans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallesen, J.; Wang, N.; Corbett, K.S.; Wrapp, D.; Kirchdoerfer, R.N.; Turner, H.L.; Cottrell, C.A.; Becker, M.M.; Wang, L.; Shi, W.; et al. Immunogenicity and Structures of a Rationally Designed Prefusion MERS-CoV Spike Antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7348–E7357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, B.J.; Jiang, S. The Spike Protein of SARS-CoV—A Target for Vaccine and Therapeutic Development. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhao, G.; Chan, C.C.; Sun, S.; Chen, M.; Liu, Z.; Guo, H.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, B.J.; et al. Recombinant Receptor-Binding Domain of SARS-CoV Spike Protein Expressed in Mammalian, Insect and E. coli Cells Elicits Potent Neutralizing Antibody and Protective Immunity. Virology 2009, 393, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Kwon, Y.D.; Zhou, T.; Wu, X.; O’Dell, S.; Cavacini, L.; Hessell, A.J.; Pancera, M.; Tang, M.; Xu, L.; et al. Structural Basis of Immune Evasion at the Site of CD4 Attachment on HIV-1 Gp120. Science 2009, 326, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, P.D.; Mascola, J.R.; Nabel, G.J. Rational Design of Vaccines to Elicit Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies to HIV-1. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a007278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulp, D.W.; Schief, W.R. Advances in Structure-Based Vaccine Design. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, L.; Haynes, L.; Struble, E.B.; Tamin, A.; Virata-Theimer, M.L.; Zhang, P. Antibody-Mediated Synergy and Interference in the Neutralization of SARS-CoV at an Epitope Cluster on the Spike Protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Yamada, Y.; Fung, T.S.; Huang, M.; Chia, R.; Liu, D.X. Identification of N-Linked Glycosylation Sites in the Spike Protein and Their Functional Impact on the Replication and Infectivity of Coronavirus Infectious Bronchitis Virus in Cell Culture. Virology 2018, 513, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickramasinghe, I.N.; De Vries, R.P.; Grone, A.; De Haan, C.A.; Verheije, M.H. Binding of Avian Coronavirus Spike Proteins to Host Factors Reflects Virus Tropism and Pathogenicity. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 8903–8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, L.M.; Bouwman, K.M.; Azurmendi, H.; De Vries, R.P.; Cipollo, J.F.; Verheije, M.H. Glycosylation of the Viral Attachment Protein of Avian Coronavirus Is Essential for Host Cell and Receptor Binding. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 7797–7809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.R.; Puigbo, P.; Hensley, S.E.; Hurt, D.E.; Bennink, J.R.; Yewdell, J.W. Glycosylation Focuses Sequence Variation in the Influenza a Virus H1 Hemagglutinin Globular Domain. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Berndsen, Z.T.; Raghwani, J.; Seabright, G.E.; Allen, J.D.; Pybus, O.G.; McLellan, J.S.; Wilson, I.A.; Bowden, T.A.; Ward, A.B.; et al. Vulnerabilities in Coronavirus Glycan Shields Despite Extensive Glycosylation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, J.; Vasiljevic, S.; Gangadharan, B.; Hensen, M.; Chandran, A.V.; Hill, M.L.; Kiappes, J.L.; Dwek, R.A.; Alonzi, D.S.; Struwe, W.B.; et al. Assessing Antigen Structural Integrity through Glycosylation Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Viral Spike. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Allen, J.D.; Wrapp, D.; McLellan, J.S.; Crispin, M. Site-Specific Glycan Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike. Science 2020, 369, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson-Leggett, P.; Armstrong, S.; Keep, S.; Britton, P.; Bickerton, E. Analysis of the Avian Coronavirus Spike Protein Reveals Heterogeneity in the Glycans Present. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, K.S.; Chowdhury, E.U.; Poudel, A.; Ruettger, A.; Sachse, K.; Kaltenboeck, B. Defining Species-Specific Immunodominant B Cell Epitopes for Molecular Serology of Chlamydia Species. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2015, 22, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, J.E.; Lund, A.R.; McCarron, A.M.; Pinegar, K.N.; Korver, D.R.; Classen, H.L.; Aggrey, S.; Utterbach, C.; Anthony, N.B.; Berres, M.E. MHC Variability in Heritage Breeds of Chickens. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banat, G.R.; Tkalcic, S.; Dzielawa, J.A.; Jackwood, M.W.; Saggese, M.D.; Yates, L.; Kopulos, R.; Briles, W.E.; Collisson, E.W. Association of the Chicken MHC B Haplotypes with Resistance to Avian Coronavirus. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2013, 39, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bumstead, N.; Huggins, M.B.; Cook, J.K. Genetic Differences in Susceptibility to a Mixture of Avian Infectious Bronchitis Virus and Escherichia coli. Br. Poult. Sci. 1989, 30, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, F.T.; Bed’Hom, B.; Naghizadeh, M.; Kjaerup, R.B.; Zohari, S.; Dalgaard, T.S. Immunoprofiling of Peripheral Blood from Infectious Bronchitis Virus Vaccinated MHC-B Chicken Lines—Monocyte MHC-II Expression as a Potential Correlate of Protection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 96, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.P.; Hauck, R.; Zhou, H.; Gallardo, R.A. Understanding Immune Resistance to Infectious Bronchitis Using Major Histocompatibility Complex Chicken Lines. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type | CLIPS Description 1 | Number of Peptides 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Linear | All overlapping linear 15-mers (offset of one residue) | 1574 |
| Looped | Constrained linear 15-mers (flanked by Cys residues) on mP2 CLIPS | 1574 |
| Helical | Constrained 15-mers with additional Cys residues on mP2 CLIPS | 1564 |
| Coils | Structured 15-mers with additional Ile residues | 1553 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sives, S.; Keep, S.; Bickerton, E.; Vervelde, L. Revealing Novel-Strain-Specific and Shared Epitopes of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Spike Glycoprotein Using Chemical Linkage of Peptides onto Scaffolds Precision Epitope Mapping. Viruses 2023, 15, 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112279
Sives S, Keep S, Bickerton E, Vervelde L. Revealing Novel-Strain-Specific and Shared Epitopes of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Spike Glycoprotein Using Chemical Linkage of Peptides onto Scaffolds Precision Epitope Mapping. Viruses. 2023; 15(11):2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112279
Chicago/Turabian StyleSives, Samantha, Sarah Keep, Erica Bickerton, and Lonneke Vervelde. 2023. "Revealing Novel-Strain-Specific and Shared Epitopes of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Spike Glycoprotein Using Chemical Linkage of Peptides onto Scaffolds Precision Epitope Mapping" Viruses 15, no. 11: 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112279
APA StyleSives, S., Keep, S., Bickerton, E., & Vervelde, L. (2023). Revealing Novel-Strain-Specific and Shared Epitopes of Infectious Bronchitis Virus Spike Glycoprotein Using Chemical Linkage of Peptides onto Scaffolds Precision Epitope Mapping. Viruses, 15(11), 2279. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15112279






