Poly I:C Pre-Treatment Induced the Anti-Viral Interferon Response in Airway Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
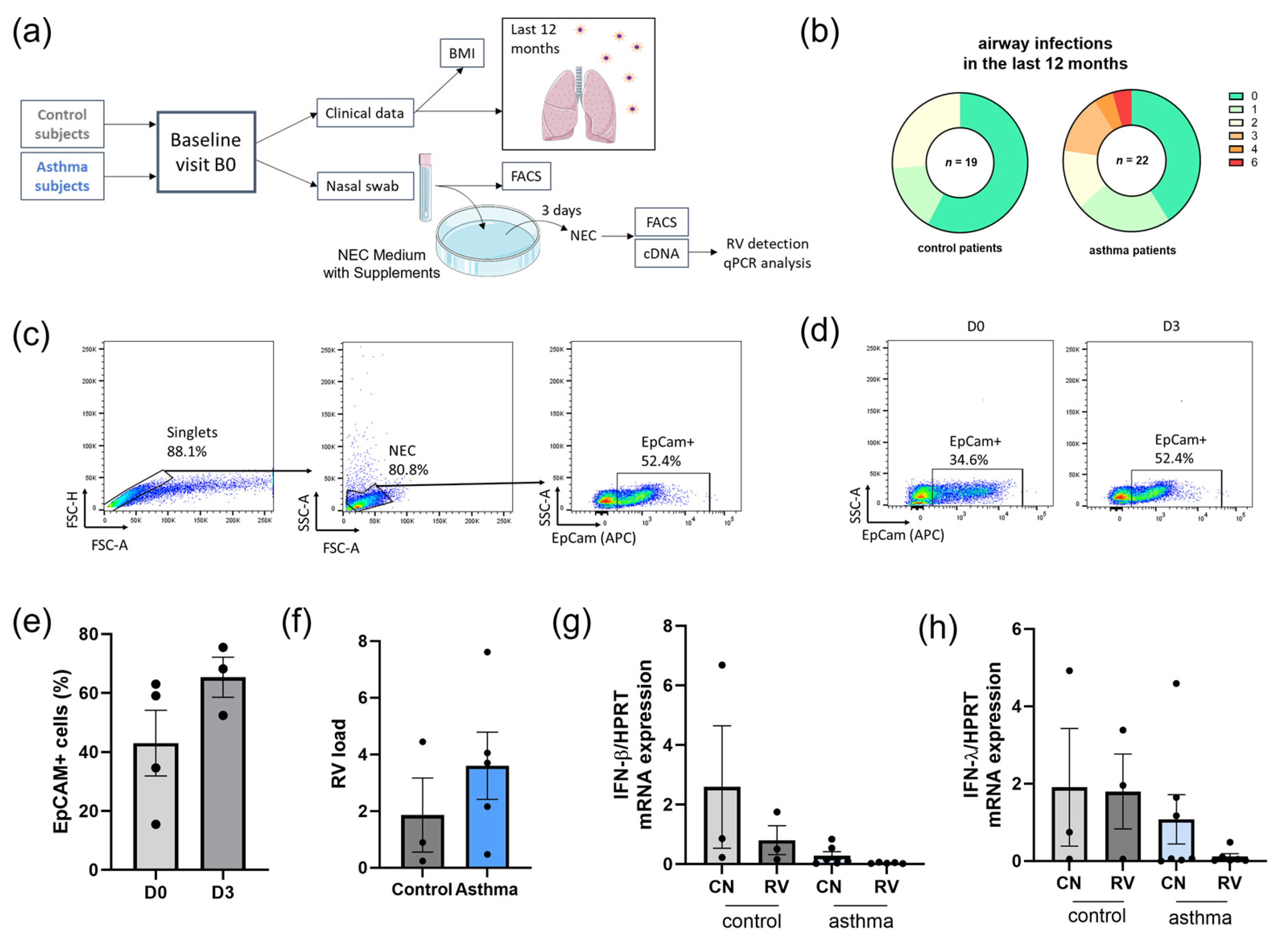
2.1. Human Cohort Study “AZCRA”
2.2. Nasal Epithelial Cell Culture
2.3. A549 Cell Culture
2.4. RV Infection
2.5. qPCR
2.6. ELISA for IFN-λ
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Asthmatic Patients Had Increased Airway Infections in the Last 12 Months and Decreased Levels of IFN Type I and III in Nasal Epithelial Cells (NECs) Compared to Control Subjects
3.2. TLR3 Correlated Positively with RV-A1b Clearance in Epithelial Cells
3.3. Pre-Treatment with Poly I:C before RV-A1b Infection Induced IFN-λ and OAS-1 Antiviral Immune Responses in Lung Epithelial Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grünewaldt, A.; Hügel, C.; Rohde, G.G.U. Rhinoviruses. Internist 2019, 60, 1151–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khetsuriani, N.; Lu, X.; Teague, W.G.; Kazerouni, N.; Anderson, L.J.; Erdman, D.D. Novel Human Rhinoviruses and Exacerbation of Asthma in Children. Emerg. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 14, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, A.; Edwards, M.R.; Macintyre, J.; del Rosario, A.; Bakhsoliani, E.; Trujillo-Torralbo, M.B.; Kon, O.M.; Mallia, P.; McHale, M.; Johnston, S.L. Rhinovirus 16-induced IFN-α and IFN-β are deficient in bronchoalveolar lavage cells in asthmatic patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1506–1514.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulou, L.; Holt, A.C.; Medzhitov, R.; Flavell, R.A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 2001, 413, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.S.; Ong, H.H.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Ong, Y.K.; Thong, K.T.; Choi, H.W.; Wang, D.Y.; Chow, V.T. In Vitro Model of Fully Differentiated Human Nasal Epithelial Cells Infected With Rhinovirus Reveals Epithelium-Initiated Immune Responses. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 217, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakebread, J.A.; Haitchi, H.M.; Xu, Y.; Holgate, S.T.; Roberts, G.; Davies, D.E. Rhinovirus-16 induced release of IP-10 and IL-8 is augmented by Th2 cytokines in a pediatric bronchial epithelial cell model. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custovic, A.; Belgrave, D.; Lin, L.; Bakhsoliani, E.; Telcian, A.G.; Solari, R.; Murray, C.S.; Walton, R.P.; Curtin, J.; Edwards, M.R.; et al. Cytokine Responses to Rhinovirus and Development of Asthma, Allergic Sensitization, and Respiratory Infections during Childhood. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 197, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heim, M.H.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Contribution of STAT SH2 groups to specific interferon signaling by the Jak-STAT pathway. Science 1995, 267, 1347–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.Y.; Kessler, D.S.; Veals, S.A.; Levy, D.E.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. ISGF3, the transcriptional activator induced by interferon alpha, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8555–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.E.; Kessler, D.S.; Pine, R.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. Cytoplasmic activation of ISGF3, the positive regulator of interferon-alpha-stimulated transcription, reconstituted in vitro. Genes Dev. 1989, 3, 1362–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerati, P.C.; Troy, N.M.; Reid, A.T.; Li, N.F.; Nichol, K.S.; Kaur, P.; Maltby, S.; Wark, P.A.; Knight, D.A.; Bosco, A.; et al. Airway Epithelial Cell Immunity Is Delayed During Rhinovirus Infection in Asthma and COPD. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Message, S.D.; Mallia, P.; Kebadze, T.; Contoli, M.; Ward, C.K.; Barnathan, E.S.; Mascelli, M.A.; Kon, O.M.; Papi, A.; et al. Bronchial mucosal IFN-α/β and pattern recognition receptor expression in patients with experimental rhinovirus-induced asthma exacerbations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 114–125.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergauer, A.; Sopel, N.; Kroß, B.; Vuorinen, T.; Xepapadaki, P.; Weiss, S.T.; Blau, A.; Sharma, H.; Kraus, C.; Springel, R.; et al. IFN-α/IFN-λ responses to respiratory viruses in paediatric asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1600969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuthill, T.J.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Jourdan, P.; Challinor, L.J.; Sharp, N.A.; Plumpton, C.; Shah, K.; Barnard, S.; Dash, L.; Burnet, J.; et al. Mouse respiratory epithelial cells support efficient replication of human rhinovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84 Pt 10, 2829–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrosovich, M.N.; Matrosovich, T.Y.; Gray, T.; Roberts, N.A.; Klenk, H.D. Human and avian influenza viruses target different cell types in cultures of human airway epithelium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4620–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkman, R.; Jebbink, M.F.; Koekkoek, S.M.; Deijs, M.; Jónsdóttir, H.R.; Molenkamp, R.; Ieven, M.; Goossens, H.; Thiel, V.; van der Hoek, L. Isolation and characterization of current human coronavirus strains in primary human epithelial cell cultures reveal differences in target cell tropism. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6081–6090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumm, R.E.; Wellford, S.A.; Moseman, E.A.; Heaton, N.S. Heterogeneity of Antiviral Responses in the Upper Respiratory Tract Mediates Differential Non-lytic Clearance of Influenza Viruses. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graser, A.; Ekici, A.B.; Sopel, N.; Melichar, V.O.; Zimmermann, T.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Taka, S.; Ferrazzi, F.; Vuorinen, T.; Finotto, S. Rhinovirus inhibits IL-17A and the downstream immune responses in allergic asthma. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Mitlander, H.; Vuorinen, T.; Finotto, S. Mechanism of Rhinovirus Immunity and Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 731846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, J.; Kiefer, A.; Koelle, J.; Vuorinen, T.; Xepapadaki, P.; Stanic, B.; Chiriac, M.T.; Akdis, M.; Zimmermann, T.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; et al. TLR7/8 regulates type I and type III interferon signalling in rhinovirus 1b-induced allergic asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2001562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koltsida, O.; Hausding, M.; Stavropoulos, A.; Koch, S.; Tzelepis, G.; Übel, C.; Kotenko, S.V.; Sideras, P.; Lehr, H.A.; Tepe, M.; et al. IL-28A (IFN-lambda2) modulates lung DC function to promote Th1 immune skewing and suppress allergic airway disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2011, 3, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krammer, S.; Sicorschi Gutu, C.; Grund, J.C.; Chiriac, M.T.; Zirlik, S.; Finotto, S. Regulation and Function of Interferon-Lambda (IFNlambda) and Its Receptor in Asthma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 731807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krammer, S.; Yang, Z.; Mitländer, H.; Grund, J.C.; Trump, S.; Mittler, S.; Zirlik, S.; Finotto, S. Rhinovirus Suppresses TGF-β-GARP Presentation by Peripheral NK Cells. Cells 2022, 12, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michi, A.N.; Yipp, B.G.; Dufour, A.; Lopes, F.; Proud, D. PGC-1α mediates a metabolic host defense response in human airway epithelium during rhinovirus infections. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjan, U.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Gruenert, D.C.; Hershenson, M.B. Rhinovirus disrupts the barrier function of polarized airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 178, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passariello, C.; Schippa, S.; Conti, C.; Russo, P.; Poggiali, F.; Garaci, E.; Palamara, A.T. Rhinoviruses promote internalisation of Staphylococcus aureus into non-fully permissive cultured pneumocytes. Microbes Infect. 2006, 8, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizuka, S.; Yamaya, M.; Suzuki, T.; Takahashi, H.; Ida, S.; Sasaki, T.; Inoue, D.; Sekizawa, K.; Nishimura, H.; Sasaki, H. Effects of rhinovirus infection on the adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae to cultured human airway epithelial cells. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 1928–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kicic, A.; Stevens, P.T.; Sutanto, E.N.; Kicic-Starcevich, E.; Ling, K.M.; Looi, K.; Martinovich, K.M.; Garratt, L.W.; Iosifidis, T.; Shaw, N.C.; et al. Impaired airway epithelial cell responses from children with asthma to rhinoviral infection. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 1441–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Puddicombe, S.M.; Field, S.; Haywood, J.; Broughton-Head, V.; Puxeddu, I.; Haitchi, H.M.; Vernon-Wilson, E.; Sammut, D.; Bedke, N.; et al. Defective epithelial barrier function in asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, e1–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, W.I.; Sharma, H.S.; Baelemans, S.M.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Braunstahl, G.J. Altered expression of epithelial junctional proteins in atopic asthma: Possible role in inflammation. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2008, 86, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.P.; Schögler, A.; Ebener, S.; Vielle, N.J.; Casaulta, C.; Jung, A.; Moeller, A.; Geiser, T.; Regamey, N. Comparison of innate immune responses towards rhinovirus infection of primary nasal and bronchial epithelial cells. Respirology 2016, 21, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Han, M.S.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, D.B.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, T.H. Rhinovirus-induced anti-viral interferon secretion is not deficient and not delayed in sinonasal epithelial cells of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1025796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weerd, N.A.; Nguyen, T. The interferons and their receptors’distribution and regulation. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.S.; Levy, H.B. Phase I–II trials of poly IC stabilized with poly-L-lysine. Cancer Treat Rep. 1978, 62, 1907–1912. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, M.; Sabado, R.L.; La Mar, M.; Mohri, H.; Salazar, A.M.; Dong, H.; Correa Da Rosa, J.; Markowitz, M.; Bhardwaj, N.; Miller, E. Poly-ICLC, a TLR3 Agonist, Induces Transient Innate Immune Responses in Patients With Treated HIV-Infection: A Randomized Double-Blinded Placebo Controlled Trial. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waele, J.; Verhezen, T.; van der Heijden, S.; Berneman, Z.N.; Peeters, M.; Lardon, F.; Wouters, A.; Smits, E.L. A systematic review on poly(I:C) and poly-ICLC in glioblastoma: Adjuvants coordinating the unlocking of immunotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subrata, L.S.; Bizzintino, J.; Mamessier, E.; Bosco, A.; McKenna, K.L.; Wikstrm, M.E.; Goldblatt, J.; Sly, P.D.; Hales, B.J.; Thomas, W.R.; et al. Interactions between innate antiviral and atopic immunoinflammatory pathways precipitate and sustain asthma exacerbations in children. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 2793–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, P.G.; Sly, P.D. Viral infections and atopy in asthma pathogenesis: New rationales for asthma prevention and treatment. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunding, L.P.; Webering, S.; Vock, C.; Behrends, J.; Wagner, C.; Hölscher, C.; Fehrenbach, H.; Wegmann, M. Poly(inosinic-cytidylic) acid-triggered exacerbation of experimental asthma depends on IL-17A produced by NK cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5615–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trumpfheller, C.; Caskey, M.; Nchinda, G.; Longhi, M.P.; Mizenina, O.; Huang, Y.; Schlesinger, S.J.; Colonna, M.; Steinman, R.M. The microbial mimic poly IC induces durable and protective CD4+ T cell immunity together with a dendritic cell targeted vaccine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2574–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Clinical Characteristics | Control | Asthma | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 19 | 22 | |
| Male gender | 10 (52.63%) | 10 (45.5%) | |
| Female gender | 9 (47.36%) | 12 (54.5%) | |
| Age (in years) | 39 ± 15.83 (21–64) | 42.18 ± 13.09 (23–63) | |
| BMI (in kg/m2) | 23.52 ± 4.220 (17.15–32.50) | 26.75 ± 4.973 (21.80–44.79) | 0.0214 |
| Number of airway infections in the last 12 months | 0.6842 ± 0.8852 (0.0–2.0) | 1.364 ± 1.620 (0.0–6.0) | 0.1886 |
| Allergic asthma phenotype | / | 22 (100%) | |
| Allergic rhinitis | 0 (0%) | 17 (77.26%) | |
| Asthma medication | 0 (0%) | 17 (77.26%) | |
| Family history of atopy/asthma | 4 (21.05%) | 12 (54.55%) | 0.0529 |
| Lung function FEV1 (%) | 100.6 ± 10.92 (84.0–126.0) | 93.91 ± 13.41 (74.0–126.0) | 0.0919 |
| Lung function FVC (%) | 99.68 ± 10.47 (80.0–117.0) | 96.32 ± 10.73 (81.0–120.0) | 0.3173 |
| Lung function: FEV1/FVC (%) | 82.50 ± 7.59 (69.38–97.24) | 78.55 ± 7.984 (64.24–94.54) | 0.1142 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mitländer, H.; Yang, Z.; Krammer, S.; Grund, J.C.; Zirlik, S.; Finotto, S. Poly I:C Pre-Treatment Induced the Anti-Viral Interferon Response in Airway Epithelial Cells. Viruses 2023, 15, 2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122328
Mitländer H, Yang Z, Krammer S, Grund JC, Zirlik S, Finotto S. Poly I:C Pre-Treatment Induced the Anti-Viral Interferon Response in Airway Epithelial Cells. Viruses. 2023; 15(12):2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122328
Chicago/Turabian StyleMitländer, Hannah, Zuqin Yang, Susanne Krammer, Janina C. Grund, Sabine Zirlik, and Susetta Finotto. 2023. "Poly I:C Pre-Treatment Induced the Anti-Viral Interferon Response in Airway Epithelial Cells" Viruses 15, no. 12: 2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122328
APA StyleMitländer, H., Yang, Z., Krammer, S., Grund, J. C., Zirlik, S., & Finotto, S. (2023). Poly I:C Pre-Treatment Induced the Anti-Viral Interferon Response in Airway Epithelial Cells. Viruses, 15(12), 2328. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122328






