Viral Components Trafficking with(in) Extracellular Vesicles
Abstract
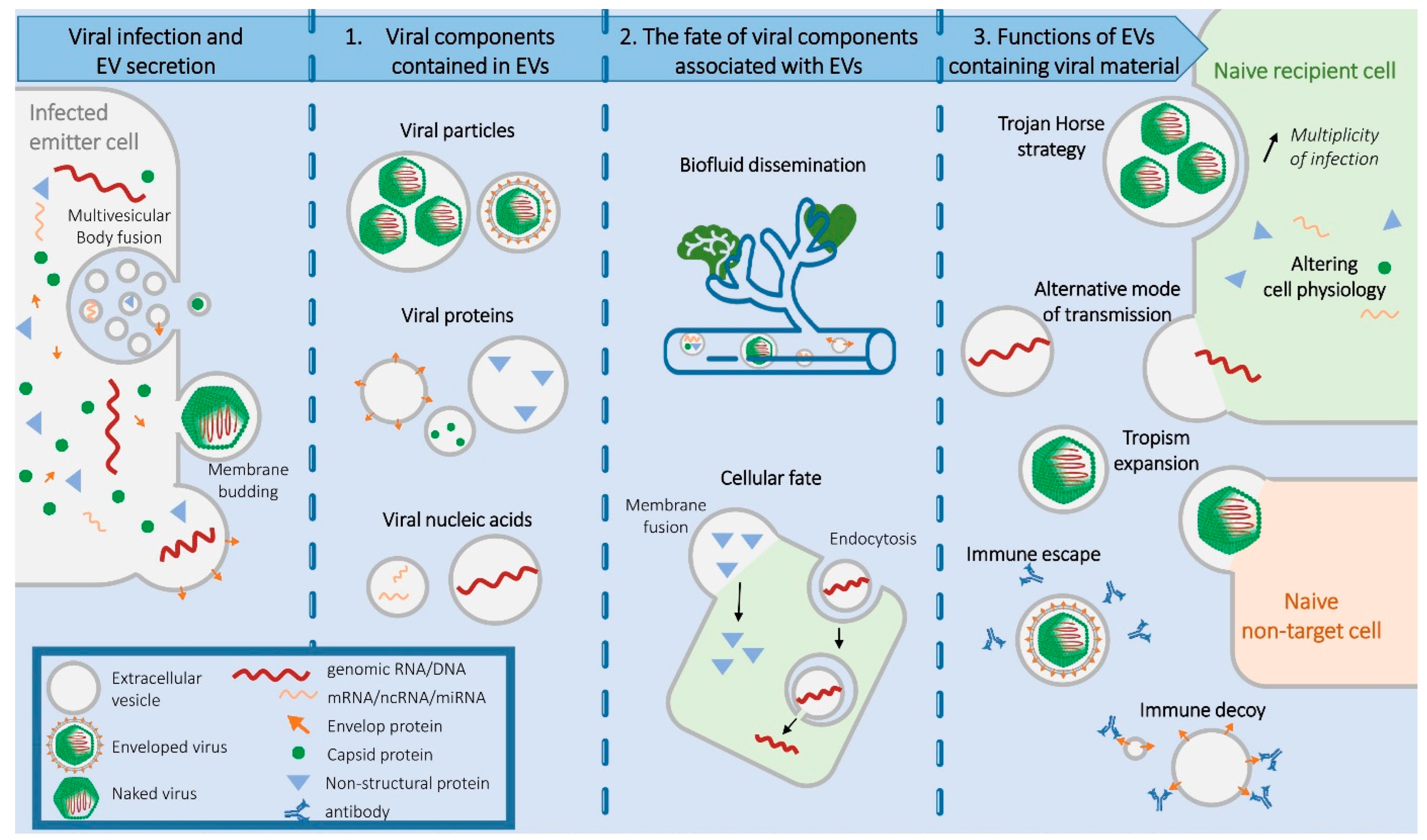
:1. Introduction to EVs and Viruses
2. Viral Components Contained in EVs
2.1. Entire Viral Particles
2.2. Viral Proteins
2.3. Viral Nucleic Acids
3. Fate of Viral Components Associated with EVs
3.1. Biofluid Dissemination
3.2. Cellular Fate
4. Functions of EVs Containing Viral Material
4.1. The Trojan Horse Strategy
4.2. An Alternative Mode of Viral Transmission
4.3. Expanding Viral Cellular Tropism
4.4. Pre-Emptive Alteration of the Cell Physiology
4.5. A Decoy for Humoral Immunity
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gelderblom, H.R. Structure and Classification of Viruses. In Medical Microbiology; Baron, S., Ed.; University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston: Galveston, TX, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0-9631172-1-2. [Google Scholar]
- Morens, D.M.; Fauci, A.S. Emerging Infectious Diseases: Threats to Human Health and Global Stability. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 13 January 2023).
- Brady, O.J.; Gething, P.W.; Bhatt, S.; Messina, J.P.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Moyes, C.L.; Farlow, A.W.; Scott, T.W.; Hay, S.I. Refining the Global Spatial Limits of Dengue Virus Transmission by Evidence-Based Consensus. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, S.; Gething, P.W.; Brady, O.J.; Messina, J.P.; Farlow, A.W.; Moyes, C.L.; Drake, J.M.; Brownstein, J.S.; Hoen, A.G.; Sankoh, O.; et al. The Global Distribution and Burden of Dengue. Nature 2013, 496, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, S.T.; Arikawa, J.; Kawaoka, Y. Emerging Viral Diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12411–12412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, C.J.; Albery, G.F.; Merow, C.; Trisos, C.H.; Zipfel, C.M.; Eskew, E.A.; Olival, K.J.; Ross, N.; Bansal, S. Climate Change Increases Cross-Species Viral Transmission Risk. Nature 2022, 607, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng’uni, T.; Chasara, C.; Ndhlovu, Z.M. Major Scientific Hurdles in HIV Vaccine Development: Historical Perspective and Future Directions. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 590780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, D.R.; Metz, S.W.; Baric, R.S. Dengue Vaccines: The Promise and Pitfalls of Antibody-Mediated Protection. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halstead, S.B. Is Dengue Vaccine Protection Possible? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beachboard, D.C.; Horner, S.M. Innate Immune Evasion Strategies of DNA and RNA Viruses. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2016, 32, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, S. Virus Interactions with the Cell. Viruses 2017, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, E.J.D.; Williamson, J.C.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Naamati, A.; Matheson, N.J.; Lehner, P.J. Promiscuous Targeting of Cellular Proteins by Vpr Drives Systems-Level Proteomic Remodeling in HIV-1 Infection. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 1579–1596.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab-Traub, N.; Dittmer, D.P. Viral Effects on the Content and Function of Extracellular Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding Light on the Cell Biology of Extracellular Vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A Position Statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and Update of the MISEV2014 Guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixson, A.C.; Dawson, T.R.; Di Vizio, D.; Weaver, A.M. Context-Specific Regulation of Extracellular Vesicle Biogenesis and Cargo Selection. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 454–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular Vesicles: Exosomes, Microvesicles, and Friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witwer, K.W.; Théry, C. Extracellular Vesicles or Exosomes? On Primacy, Precision, and Popularity Influencing a Choice of Nomenclature. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1648167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badierah, R.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Redwan, E.M. Dancing with Trojan Horses: An Interplay between the Extracellular Vesicles and Viruses. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 3034–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte-‘t Hoen, E.; Cremer, T.; Gallo, R.C.; Margolis, L.B. Extracellular Vesicles and Viruses: Are They Close Relatives? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9155–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vora, A.; Zhou, W.; Londono-Renteria, B.; Woodson, M.; Sherman, M.B.; Colpitts, T.M.; Neelakanta, G.; Sultana, H. Arthropod EVs Mediate Dengue Virus Transmission through Interaction with a Tetraspanin Domain Containing Glycoprotein Tsp29Fb. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6604–E6613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J.; Brandt, W.E.; Swanson, J.L.; McCown, J.M.; Buescher, E.L. Physical and Biological Properties of Dengue-2 Virus and Associated Antigens. J. Virol. 1970, 5, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Xu, Y.; Liu, N.; Lv, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jin, X.; Xiao, M.; Lavillette, D.; Zhong, J.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Zika Virus-Infected Cells Display Viral E Protein That Binds ZIKV-Neutralizing Antibodies to Prevent Infection Enhancement. EMBO J. 2023, 42, e112096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saphire, A.C.S.; Gallay, P.A.; Bark, S.J. Proteomic Analysis of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Using Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry Effectively Distinguishes Specific Incorporated Host Proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2006, 5, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakelyan, A.; Fitzgerald, W.; Zicari, S.; Vanpouille, C.; Margolis, L. Extracellular Vesicles Carry HIV Env and Facilitate Hiv Infection of Human Lymphoid Tissue. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Jaular, L.; Nevo, N.; Schessner, J.P.; Tkach, M.; Jouve, M.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Witwer, K.W.; Ostrowski, M.; Borner, G.H.H.; et al. Unbiased Proteomic Profiling of Host Cell Extracellular Vesicle Composition and Dynamics upon HIV-1 Infection. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e105492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, R.P.; Dittmer, D.P. Modern Techniques for the Isolation of Extracellular Vesicles and Viruses. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2020, 15, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caobi, A.; Nair, M.; Raymond, A.D. Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis of Viral Infections in Humans. Viruses 2020, 12, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutchy, N.A.; Peeples, E.S.; Sil, S.; Liao, K.; Chivero, E.T.; Hu, G.; Buch, S. Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections of the Nervous System. Viruses 2020, 12, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hensley, L.; McKnight, K.L.; Hu, F.; Madden, V.; Ping, L.; Jeong, S.-H.; Walker, C.; Lanford, R.E.; Lemon, S.M. A Pathogenic Picornavirus Acquires an Envelope by Hijacking Cellular Membranes. Nature 2013, 496, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.M.; Tsueng, G.; Sin, J.; Mangale, V.; Rahawi, S.; McIntyre, L.L.; Williams, W.; Kha, N.; Cruz, C.; Hancock, B.M.; et al. Coxsackievirus B Exits the Host Cell in Shed Microvesicles Displaying Autophagosomal Markers. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Du, W.; Hagemeijer, M.C.; Takvorian, P.M.; Pau, C.; Cali, A.; Brantner, C.A.; Stempinski, E.S.; Connelly, P.S.; Ma, H.-C.; et al. Phosphatidylserine Vesicles Enable Efficient En Bloc Transmission of Enteroviruses. Cell 2015, 160, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris-Love, J.; Gee, G.V.; O’Hara, B.A.; Assetta, B.; Atkinson, A.L.; Dugan, A.S.; Haley, S.A.; Atwood, W.J. JC Polyomavirus Uses Extracellular Vesicles To Infect Target Cells. mBio 2019, 10, e00379-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Hara, B.A.; Morris-Love, J.; Gee, G.V.; Haley, S.A.; Atwood, W.J. JC Virus Infected Choroid Plexus Epithelial Cells Produce Extracellular Vesicles That Infect Glial Cells Independently of the Virus Attachment Receptor. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handala, L.; Blanchard, E.; Raynal, P.-I.; Roingeard, P.; Morel, V.; Descamps, V.; Castelain, S.; Francois, C.; Duverlie, G.; Brochot, E.; et al. BK Polyomavirus Hijacks Extracellular Vesicles for En Bloc Transmission. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e01834-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, B.; Pan, X.; Luo, R.-H.; Shen, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zuo, X.; Wu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xiao, G.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Antibody-Resistant Transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Cell Discov. 2023, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadiu, I.; Narayanasamy, P.; Dash, P.K.; Zhang, W.; Gendelman, H.E. Biochemical and Biologic Characterization of Exosomes and Microvesicles as Facilitators of HIV-1 Infection in Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnaiah, V.; Thumann, C.; Fofana, I.; Habersetzer, F.; Pan, Q.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Willemsen, R.; Demmers, J.A.A.; Stalin Raj, V.; Jenster, G.; et al. Exosome-Mediated Transmission of Hepatitis C Virus between Human Hepatoma Huh7.5 Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13109–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Q.; He, J.J. Exosome-Associated Hepatitis C Virus in Cell Cultures and Patient Plasma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 455, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troyer, Z.; Alhusaini, N.; Tabler, C.O.; Sweet, T.; de Carvalho, K.I.L.; Schlatzer, D.M.; Carias, L.; King, C.L.; Matreyek, K.; Tilton, J.C. Extracellular Vesicles Carry SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Serve as Decoys for Neutralizing Antibodies. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.M.; Fang, Y.; Fallon, J.K.; Yang, J.-M.; Hildreth, J.E.K.; Gould, S.J. Exosomes and HIV Gag Bud from Endosome-like Domains of the T Cell Plasma Membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehls, J.; Businger, R.; Hoffmann, M.; Brinkmann, C.; Fehrenbacher, B.; Schaller, M.; Maurer, B.; Schönfeld, C.; Kramer, D.; Hailfinger, S.; et al. Release of Immunomodulatory Ebola Virus Glycoprotein-Containing Microvesicles Is Suppressed by Tetherin in a Species-Specific Manner. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 1841–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pleet, M.L.; Mathiesen, A.; DeMarino, C.; Akpamagbo, Y.A.; Barclay, R.A.; Schwab, A.; Iordanskiy, S.; Sampey, G.C.; Lepene, B.; Nekhai, S.; et al. Ebola VP40 in Exosomes Can Cause Immune Cell Dysfunction. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, A.D.; Campbell-Sims, T.C.; Khan, M.; Lang, M.; Huang, M.B.; Bond, V.C.; Powell, M.D. HIV Type 1 Nef Is Released from Infected Cells in CD45(+) Microvesicles and Is Present in the Plasma of HIV-Infected Individuals. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2011, 27, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenassi, M.; Cagney, G.; Liao, M.; Vaupotic, T.; Bartholomeeusen, K.; Cheng, Y.; Krogan, N.J.; Plemenitas, A.; Peterlin, B.M. HIV Nef Is Secreted in Exosomes and Triggers Apoptosis in Bystander CD4+ T Cells. Traffic 2010, 11, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenaccio, C.; Chiozzini, C.; Columba-Cabezas, S.; Manfredi, F.; Affabris, E.; Baur, A.; Federico, M. Exosomes from Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1)-Infected Cells License Quiescent CD4+ T Lymphocytes to Replicate HIV-1 through a Nef- and ADAM17-Dependent Mechanism. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 11529–11539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, J.; Middeldorp, J.; Sculley, T. Localization of the Epstein-Barr Virus Protein LMP 1 to Exosomes. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 1871–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutzeit, C.; Nagy, N.; Gentile, M.; Lyberg, K.; Gumz, J.; Vallhov, H.; Puga, I.; Klein, E.; Gabrielsson, S.; Cerutti, A.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Burkitt’s Lymphoma Cell Lines Induce Proliferation, Differentiation, and Class-Switch Recombination in B Cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5852–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, N.R.; Chadha, R.; Kumar, S.; Choedon, T.; Reddy, V.S.; Kumar, V. The HBx Gene of Hepatitis B Virus Can Influence Hepatic Microenvironment via Exosomes by Transferring Its mRNA and Protein. Virus Res. 2017, 240, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safadi, D.E.; Lebeau, G.; Lagrave, A.; Mélade, J.; Grondin, L.; Rosanaly, S.; Begue, F.; Hoareau, M.; Veeren, B.; Roche, M.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Are Conveyors of the NS1 Toxin during Dengue Virus and Zika Virus Infection. Viruses 2023, 15, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, S.; Sharma, P.; Theodoraki, M.-N.; Pietrowska, M.; Yerneni, S.S.; Lang, S.; Ferrone, S.; Whiteside, T.L. Molecular and Functional Profiles of Exosomes From HPV(+) and HPV(−) Head and Neck Cancer Cell Lines. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Nukala, S.B.; Srivastava, S.; Miyamoto, H.; Ismail, N.I.; Ong, S.-B.; Lee, W.H.; Ong, S.-G. Exosomes Facilitate Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Genome into Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. bioRxiv 2020. bioRxiv:2020.05.14.093583. [Google Scholar]
- Columba Cabezas, S.; Federico, M. Sequences within RNA Coding for HIV-1 Gag P17 Are Efficiently Targeted to Exosomes. Cell Microbiol. 2013, 15, 412–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukong, T.N.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Kodys, K.; Bala, S.; Szabo, G. Exosomes from Hepatitis C Infected Patients Transmit HCV Infection and Contain Replication Competent Viral RNA in Complex with Ago2-miR122-HSP90. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chivero, E.T.; Bhattarai, N.; Rydze, R.T.; Winters, M.A.; Holodniy, M.; Stapleton, J.T. Human Pegivirus RNA Is Found in Multiple Blood Mononuclear Cells in Vivo and Serum-Derived Viral RNA-Containing Particles Are Infectious in Vitro. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1307–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, T.; Hirata, Y.; Naito, Y.; Yamamoto, N.; Kikkawa, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Yamasaki, C.; Tateno, C.; Ochiya, T.; Kohara, M. Transmission of HBV DNA Mediated by Ceramide-Triggered Extracellular Vesicles. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 3, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukriti, S.; Choudhary, M.C.; Maras, J.S.; Sharma, S.; Thangariyal, S.; Singh, A.; Das, S.; Islam, M.; Sharma, S.; Trehanpati, N.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Hepatitis B Patients Serve as Reservoir of Hepatitis B Virus DNA. J. Viral Hepat. 2019, 26, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saari, H.; Turunen, T.; Lohmus, A.; Turunen, M.; Jalasvuori, M.; Butcher, S.J.; Yla-Herttuala, S.; Viitala, T.; Cerullo, V.; Siljander, P.R.M.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Provide a Capsid-Free Vector for Oncolytic Adenoviral DNA Delivery. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1747206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Rocha, M.; Rodríguez-Hernández, R.M.; Chávez-Olmos, P.; Garrido, E.; Robles-Vázquez, C.; Aguilar-Ruiz, S.; Torres-Aguilar, H.; González-Torres, C.; Gaytan-Cervantes, J.; Mejía-Aranguré, J.M.; et al. Presence of HPV DNA in Extracellular Vesicles from HeLa Cells and Cervical Samples. Enfermedades Infecc. Y Microbiol. Clínica 2020, 38, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canitano, A.; Venturi, G.; Borghi, M.; Ammendolia, M.G.; Fais, S. Exosomes Released in Vitro from Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Infected Cells Contain EBV-Encoded Latent Phase mRNAs. Cancer Lett. 2013, 337, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamvoki, M.; Du, T.; Roizman, B. Cells Infected with Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Export to Uninfected Cells Exosomes Containing STING, Viral mRNAs, and microRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4991–E4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, M.A.; Zhao, H.; Yue, S.C.; Anandaiah, A.; Koziel, H.; Tachado, S.D. Novel HIV-1 miRNAs Stimulate TNFα Release in Human Macrophages via TLR8 Signaling Pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, A.; Iordanskiy, S.; Das, R.; Van Duyne, R.; Santos, S.; Jaworski, E.; Guendel, I.; Sampey, G.; Dalby, E.; Iglesias-Ussel, M.; et al. Exosomes Derived from HIV-1-Infected Cells Contain Trans-Activation Response Element RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20014–20033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W.; Philip, P.S.; Tariq, S.; Khan, G. Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded Small RNAs (EBERs) Are Present in Fractions Related to Exosomes Released by EBV-Transformed Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, S.-C.; Strilets, T.; Tan, W.-L.; Castillo, D.; Medkour, H.; Rey-Cadilhac, F.; Serrato-Pomar, I.M.; Rachenne, F.; Chowdhury, A.; Chuo, V.; et al. The Anti-Immune Dengue Subgenomic Flaviviral RNA Is Present in Vesicles in Mosquito Saliva and Is Associated with Increased Infectivity. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Ma, P.; Deng, L.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Long, G. Hepatitis A Virus Structural Protein pX Interacts with ALIX and Promotes the Secretion of Virions and Foreign Proteins through Exosome-like Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2020, 9, 1716513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, S.N.; Nkosi, D.; Conlon, M.M.; York, S.B.; Liu, X.; Tremblay, D.C.; Meckes, D.G. CD63 Regulates Epstein-Barr Virus LMP1 Exosomal Packaging, Enhancement of Vesicle Production, and Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e02251-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Wu, N.; Gan, X.; Yan, W.; Morrell, J.C.; Gould, S.J. Higher-Order Oligomerization Targets Plasma Membrane Proteins and HIV Gag to Exosomes. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waury, K.; Gogishvili, D.; Nieuwland, R.; Chatterjee, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Abeln, S. Proteome Encoded Determinants of Protein Sorting into Extracellular Vesicles. bioRxiv 2023. bioRxiv:2023.02.01.526570. [Google Scholar]
- Ras-Carmona, A.; Gomez-Perosanz, M.; Reche, P.A. Prediction of Unconventional Protein Secretion by Exosomes. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Gonzalo, O.; Fernandez-Delgado, I.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Post-Translational Add-Ons Mark the Path in Exosomal Protein Sorting. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fordjour, F.K.; Guo, C.; Ai, Y.; Daaboul, G.G.; Gould, S.J. A Shared, Stochastic Pathway Mediates Exosome Protein Budding along Plasma and Endosome Membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosset, F.-L.; Dreux, M. HCV Transmission by Hepatic Exosomes Establishes a Productive Infection. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 674–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalsky, R.L.; Cullen, B.R. Viruses, microRNAs, and Host Interactions. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegtel, D.M.; van de Garde, M.D.B.; Middeldorp, J.M. Viral miRNAs Exploiting the Endosomal-Exosomal Pathway for Intercellular Cross-Talk and Immune Evasion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1809, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slonchak, A.; Khromykh, A.A. Subgenomic Flaviviral RNAs: What Do We Know after the First Decade of Research. Antivir. Res. 2018, 159, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irion, U.; St Johnston, D. Bicoid RNA Localization Requires Specific Binding of an Endosomal Sorting Complex. Nature 2007, 445, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barajas, D.; de Castro Martín, I.F.; Pogany, J.; Risco, C.; Nagy, P.D. Noncanonical Role for the Host Vps4 AAA+ ATPase ESCRT Protein in the Formation of Tomato Bushy Stunt Virus Replicase. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statello, L.; Maugeri, M.; Garre, E.; Nawaz, M.; Wahlgren, J.; Papadimitriou, A.; Lundqvist, C.; Lindfors, L.; Collén, A.; Sunnerhagen, P.; et al. Identification of RNA-Binding Proteins in Exosomes Capable of Interacting with Different Types of RNA: RBP-Facilitated Transport of RNAs into Exosomes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.-C.; Diosa-Toro, M.; Tan, W.-L.; Rachenne, F.; Hain, A.; Yeo, C.P.X.; Bribes, I.; Xiang, B.W.W.; Sathiamoorthy Kannan, G.; Manuel, M.C.; et al. Characterization of Dengue Virus 3’UTR RNA Binding Proteins in Mosquitoes Reveals That AeStaufen Reduces Subgenomic Flaviviral RNA in Saliva. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwers, E.; Wang, Y.-C.; Gallardo, R.; Van der Kant, R.; Michiels, E.; Swerts, J.; Baatsen, P.; Zaiter, S.S.; McAlpine, S.R.; Gounko, N.V.; et al. Hsp90 Mediates Membrane Deformation and Exosome Release. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 689–702.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostak, N.; Royo, F.; Rybarczyk, A.; Szachniuk, M.; Blazewicz, J.; del Sol, A.; Falcon-Perez, J.M. Sorting Signal Targeting mRNA into Hepatic Extracellular Vesicles. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caby, M.-P.; Lankar, D.; Vincendeau-Scherrer, C.; Raposo, G.; Bonnerot, C. Exosomal-like Vesicles Are Present in Human Blood Plasma. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, M.P.; Ismail, N.; Zhang, X.; Aguda, B.D.; Lee, E.J.; Yu, L.; Xiao, T.; Schafer, J.; Lee, M.-L.T.; Schmittgen, T.D.; et al. Detection of microRNA Expression in Human Peripheral Blood Microvesicles. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lässer, C.; Seyed Alikhani, V.; Ekström, K.; Eldh, M.; Torregrosa Paredes, P.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Gabrielsson, S.; Lötvall, J.; Valadi, H. Human Saliva, Plasma and Breast Milk Exosomes Contain RNA: Uptake by Macrophages. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Vancells, J.; Falcon-Perez, J.M. Isolation of Urinary Exosomes from Animal Models to Unravel Noninvasive Disease Biomarkers. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 909, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poliakov, A.; Spilman, M.; Dokland, T.; Amling, C.L.; Mobley, J.A. Structural Heterogeneity and Protein Composition of Exosome-like Vesicles (Prostasomes) in Human Semen. Prostate 2009, 69, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skriner, K.; Adolph, K.; Jungblut, P.R.; Burmester, G.R. Association of Citrullinated Proteins with Synovial Exosomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3809–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, Y.; Ohkubo, T.; Kawaji, H.; Machida, A.; Miyata, H.; Goda, S.; Roy, S.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Yokota, T. Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Small RNA Profiling of Cerebrospinal Fluid Exosomes. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 636, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, A.C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Xu, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, B.; Sun, H.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 Contributes to Immunosuppression and Is Associated with Anti-PD-1 Response. Nature 2018, 560, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Jordan, V.; Blenkiron, C.; Chamley, L.W. Biodistribution of Extracellular Vesicles Following Administration into Animals: A Systematic Review. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The Biology, Function, and Biomedical Applications of Exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaput, N.; Théry, C. Exosomes: Immune Properties and Potential Clinical Implementations. Semin. Immunopathol. 2011, 33, 419–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinestrosa, J.P.; Kurzrock, R.; Lewis, J.M.; Schork, N.J.; Schroeder, G.; Kamat, A.M.; Lowy, A.M.; Eskander, R.N.; Perrera, O.; Searson, D.; et al. Early-Stage Multi-Cancer Detection Using an Extracellular Vesicle Protein-Based Blood Test. Commun. Med. 2022, 2, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodlet, K.J.; Bansal, S.; Arjuna, A.; Nailor, M.D.; Buddhdev, B.; Abdelrazek, H.; Mohamed, H.; Omar, A.; Walia, R.; Mohanakumar, T.; et al. COVID-19 in a Lung Transplant Recipient: Exploring the Diagnostic Role of Circulating Exosomes and the Clinical Impact of Advanced Immunosuppression. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2021, 23, e13480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The Exosome Journey: From Biogenesis to Uptake and Intracellular Signalling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, M.I.; Busko, P.; Ozer-Partuk, E.; Khan, S.; Zarfati, G.; Elbaz-Alon, Y.; Abou Karam, P.; Napso Shogan, T.; Ginini, L.; Gil, Z.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle Fusion Visualized by Cryo-Electron Microscopy. PNAS Nexus 2022, 1, pgac156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-Mediated Transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs Is a Novel Mechanism of Genetic Exchange between Cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlgren, J.; De L Karlson, T.; Brisslert, M.; Vaziri Sani, F.; Telemo, E.; Sunnerhagen, P.; Valadi, H. Plasma Exosomes Can Deliver Exogenous Short Interfering RNA to Monocytes and Lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsergent, E.; Grisard, E.; Buchrieser, J.; Schwartz, O.; Théry, C.; Lavieu, G. Quantitative Characterization of Extracellular Vesicle Uptake and Content Delivery within Mammalian Cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somiya, M.; Kuroda, S. Reporter Gene Assay for Membrane Fusion of Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiana, M.; Ghosh, S.; Ho, B.A.; Rajasekaran, V.; Du, W.-L.; Mutsafi, Y.; Jésus-Diaz, D.A.D.; Sosnovtsev, S.V.; Levenson, E.A.; Parra, G.I.; et al. Vesicle-Cloaked Virus Clusters Are Optimal Units for Inter-Organismal Viral Transmission. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Zaldívar, H.M.; Polakovicova, I.; Salas-Huenuleo, E.; Corvalán, A.H.; Kogan, M.J.; Yefi, C.P.; Andia, M.E. Extracellular Vesicles through the Blood–Brain Barrier: A Review. Fluids Barriers CNS 2022, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.O.; Huang, M.-B.; Khan, M.; Garcia-Barrio, M.; Powell, M.D.; Bond, V.C. Extracellular Nef Protein Targets CD4+ T Cells for Apoptosis by Interacting with CXCR4 Surface Receptors. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 3099–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Santini, P.A.; Sullivan, J.S.; He, B.; Shan, M.; Ball, S.C.; Dyer, W.B.; Ketas, T.J.; Chadburn, A.; Cohen-Gould, L.; et al. HIV-1 Evades Virus-Specific IgG2 and IgA Responses by Targeting Systemic and Intestinal B Cells via Long-Range Intercellular Conduits. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumptner-Cuvelette, P.; Jouve, M.; Helft, J.; Dugast, M.; Glouzman, A.-S.; Jooss, K.; Raposo, G.; Benaroch, P. Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 Nef Expression Induces Intracellular Accumulation of Multivesicular Bodies and Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Complexes: Potential Role of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 4857–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Li, B.; Peng, J.; Wu, X.; Luo, X.; Yang, L. LMP1-positive Extracellular Vesicles Promote Radioresistance in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells through P38 MAPK Signaling. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6082–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerviel, A.; Zhang, M.; Altan-Bonnet, N. A New Infectious Unit: Extracellular Vesicles Carrying Virus Populations. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 37, 171–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.; Nukala, S.B.; Srivastava, S.; Miyamoto, H.; Ismail, N.I.; Jousma, J.; Rehman, J.; Ong, S.-B.; Lee, W.H.; Ong, S.-G. Detection of Viral RNA Fragments in Human iPSC Cardiomyocytes Following Treatment with Extracellular Vesicles from SARS-CoV-2 Coding Sequence Overexpressing Lung Epithelial Cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreux, M.; Garaigorta, U.; Boyd, B.; Décembre, E.; Chung, J.; Whitten-Bauer, C.; Wieland, S.; Chisari, F.V. Short-Range Exosomal Transfer of Viral RNA from Infected Cells to Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Triggers Innate Immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longatti, A.; Boyd, B.; Chisari, F.V. Virion-Independent Transfer of Replication-Competent Hepatitis C Virus RNA between Permissive Cells. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 2956–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Woodson, M.; Neupane, B.; Bai, F.; Sherman, M.B.; Choi, K.H.; Neelakanta, G.; Sultana, H. Exosomes Serve as Novel Modes of Tick-Borne Flavivirus Transmission from Arthropod to Human Cells and Facilitates Dissemination of Viral RNA and Proteins to the Vertebrate Neuronal Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, Y. Protease-Dependent Virus Tropism and Pathogenicity. Trends Microbiol. 1993, 1, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morizono, K.; Chen, I.S.Y. Receptors and Tropisms of Envelope Viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2011, 1, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, T.D.; Khan, M.; Huang, M.-B.; Bond, V.C.; Powell, M.D. HIV-1 Nef Protein Is Secreted into Vesicles That Can Fuse with Target Cells and Virions. Ethn. Dis. 2008, 18, S2-14-9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Han, Q.; Hou, Z.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, J. Exosomes Mediate Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Transmission and NK-Cell Dysfunction. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manokaran, G.; Finol, E.; Wang, C.; Gunaratne, J.; Bahl, J.; Ong, E.Z.; Tan, H.C.; Sessions, O.M.; Ward, A.M.; Gubler, D.J.; et al. Dengue Subgenomic RNA Binds TRIM25 to Inhibit Interferon Expression for Epidemiological Fitness. Science 2015, 350, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidet, K.; Dadlani, D.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. G3BP1, G3BP2 and CAPRIN1 Are Required for Translation of Interferon Stimulated mRNAs and Are Targeted by a Dengue Virus Non-Coding RNA. PLOS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, H.; Neelakanta, G. Arthropod Exosomes as Bubbles with Message(s) to Transmit Vector-Borne Diseases. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 40, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, H.S.; Bao, X.; Casola, A. Exosomes and Their Role in the Life Cycle and Pathogenesis of RNA Viruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 3204–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, H.; Song, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, P.; Wang, X. Meet Changes with Constancy: Defence, Antagonism, Recovery, and Immunity Roles of Extracellular Vesicles in Confronting SARS-CoV-2. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzan, A.L.; Nedeva, C.; Mathivanan, S. Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolism and Metabolic Diseases. Subcell. Biochem. 2021, 97, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanwlani, R.; Gangoda, L. Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Cell Death and Inflammation. Cells 2021, 10, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornillos, O.; Higginson, D.S.; Stray, K.M.; Fisher, R.D.; Garrus, J.E.; Payne, M.; He, G.-P.; Wang, H.E.; Morham, S.G.; Sundquist, W.I. HIV Gag Mimics the Tsg101-Recruiting Activity of the Human Hrs Protein. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 162, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozmyslowicz, T.; Majka, M.; Kijowski, J.; Murphy, S.L.; Conover, D.O.; Poncz, M.; Ratajczak, J.; Gaulton, G.N.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Platelet- and Megakaryocyte-Derived Microparticles Transfer CXCR4 Receptor to CXCR4-Null Cells and Make Them Susceptible to Infection by X4-HIV. AIDS 2003, 17, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M.; Kleinschmidt, A.; Brühl, H.; Klier, C.; Nelson, P.J.; Cihak, J.; Plachý, J.; Stangassinger, M.; Erfle, V.; Schlöndorff, D. Transfer of the Chemokine Receptor CCR5 between Cells by Membrane-Derived Microparticles: A Mechanism for Cellular Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 Infection. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Grein, S.G.; Defourny, K.A.Y.; Rabouw, H.H.; Goerdayal, S.S.; van Herwijnen, M.J.C.; Wubbolts, R.W.; Altelaar, M.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.M. The Encephalomyocarditis Virus Leader Promotes the Release of Virions inside Extracellular Vesicles via the Induction of Secretory Autophagy. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Viral Cargo | Type of Cargo | Examples | Information about the Type of EV (Methods of Purification and Analysis) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virions | Naked viral particles | HAV | Uncharacterized EV type but distinct from viral particle (separation by iodixanol density gradient) | [31] |
| CVB3 | Uncharacterized EV type but distinct from viral particle (separation by iodixanol density gradient and visualization by EM) | [32] | ||
| PV | Large phosphatidylserine-enriched vesicle (pelleted at 5000 g pellet and visualization by EM) | [33] | ||
| JCPyV | sEV (Pelleted at 100,000 g and visualization with EM) | [34,35] | ||
| Enveloped viral particles | BKPyV | Uncharacterized EV type but distinct from viral particle (separation by iodixanol density gradients and visualization by EM) | [36] | |
| SARS-CoV-2 | lEV (pelleted at 400× g and visualization by EM) | [37] | ||
| HIV-1 | Putative exosome and ectosome (isolation by immunoaffinity and sucrose cushion centrifugation) | [38] | ||
| HCV | sEV related to exosomes (pelleted at 64,000 g with sucrose cushion and characterization by marker detection) | [39,40] | ||
| Proteins | Structural proteins | SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein | Uncharacterized EV (Isolation by tangential flow filtration and EM/Nanoscale flow cytometry) | [41] |
| HIV-1 Envelope protein | Uncharacterized EV type but distinct from viral particle (Isolation by magnetic nanoparticles capture) | [26] | ||
| HIV-1 Gag protein | sEV related to exosomes (Pelleted at 70,000 g and isolated by sucrose gradient and identification by exosome markers) | [42] | ||
| ZIKV Envelope protein | Uncharacterized EV type but distinct from viral particle (Isolation by sequential ultracentrifugation and affinity capture) | [24] | ||
| EBOV GP protein | Uncharacterized EV (Isolation by 21,000× g centrifugation and sucrose gradient) | [43] | ||
| EBOV VP40 protein | Uncharacterized EVs (Isolation by nanotrap particle capture) | [44] | ||
| Non-structural proteins | HIV-1 Nef accessory protein | sEV related to exosomes (Pelleted at 70,000 g to 400,000 g in different studies and association with exosome markers) | [45,46,47] | |
| EBV LMP-1 protein | sEV (Pelleted at 70,000 g) | [48,49] | ||
| HBV HBx protein | sEV (Pelleted at 110,000× g with sucrose cushion centrifugation) | [50] | ||
| ZIKV NS1 protein | Uncharacterized EV related to exosome (Isolation with exosome isolation kit, Size exclusion chromatography, PEG purification and ELISA capture) | [51] | ||
| HPV-16 E6 and E7 protein | Uncharacterized EV related to exosome (Isolation with Size exclusion chromatography, EM visualization and marker detection) | [52] | ||
| Nucleic acids | Genomes | SARS-CoV-2 gRNA | Uncharacterized EV (Isolation by Total Exosome Isolation Reagent) | [53] |
| HIV-1 gRNA | sEV (Pelleted at 70,000 g with iodixanol density gradient) | [54] | ||
| HCV gRNA | Uncharacterized CD63+ EV (Isolation with exosome isolation kit and capture with CD63 immuno-magnetic beads) | [55] | ||
| HGgV gRNA | Uncharacterized EV (Isolation with Total Exosome Isolation Reagent) | [56] | ||
| HBV gDNA | sEV (Pelleted at 110,000 g and visualization by stimulated emission depletion microscopy) | [57,58] | ||
| oncolytic AdV gDNA | Uncharacterized EV type but distinct from viral particle (Isolation by iodixanol density gradients and visualization by EM) | [59] | ||
| HPV-18 parts of gDNA | sEV (Pelleted at 95,000 g and visualization by EM) | [60] | ||
| Messenger RNAs | HBV HBx mRNA | sEV (Pelleted at 110,000× g with sucrose cushion centrifugation) | [50] | |
| EBV latency-associated protein mRNA | sEV (Pelleted at 100,000 g and isolation with CD63 immunoprecipitation) | [61] | ||
| HIV-1 Gag P17 mRNA | sEV (Pelleted at 70,000 g with iodixanol density gradient) | [54] | ||
| HSV-1 ICP27, VP16 and LAT mRNA | sEV different from viral particle (Pelleted at 70,000 g with Dextran 10 density gradient) | [62] | ||
| Non-coding RNAs | HIV-1 vmiR88, vmiR99 and vmiR-TAR | Uncharacterized EV (Isolation with exosome isolation kit and CD63 detection) | [63] | |
| HIV-1 TAR RNA | sEV related to exosome (Pelleted at 100,000 g with iodixanol density gradient and characterization with marker detection) | [64] | ||
| HSV-1 miR-H3, miR-H5 and miR-H6 | sEV different from viral particle (Pelleted at 70,000 g with Dextran 10 density gradient) | [62] | ||
| EBV EBER-1 and EBER-2 RNA | CD63+ sEV (Pelleted at 100,000 g, characterization with marker detection and visualization with EM) | [65] | ||
| DENV2 sfRNA | Uncharacterized EV different from viral particle (RNase protection essay, Visualization with super-resolution microscopy combined with RNAish) | [66] |
| Strategy | Proviral Mechanism | Viral Components Contained in EVs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trojan horse | Immune evasion | Virion of HAV | [31] |
| virion of SARS-CoV-2 | [37] | ||
| virion of HCV | [39] | ||
| virion of JCPyV | [34] | ||
| Increased MOI | virions of Rotavirus and Norovirus | [103] | |
| virions of BKPyV | [36] | ||
| virions of PV | [33] | ||
| Non-lytic egress for non-enveloped viruses | Virions of CVB3 | [32] | |
| Alternative mode of infection | EV-mediated transfer of viral genome | gDNA of oncolytic AdV | [59] |
| gRNA of DENV2 | [22] | ||
| gRNA of HCV | [55] | ||
| gRNA of HPgV | [56] | ||
| Tropism expansion | EV-mediated cell entry | JCPyV virion | [35] |
| EV-mediated diffusion | EV-mediated translocation through blood-brain barrier | [104] | |
| Cell physiology alteration | Hamper immunity | Nef protein of HIV-1 | [46,105] |
| VP40 protein of EBOV | [44] | ||
| DENV subgenomic flaviviral RNA | [66] | ||
| Induce cell permissiveness | Nef protein of HIV-1 | [47] | |
| miRNA and RNA TAR element of HIV-1 | [63,64] | ||
| Evasion from humoral immunity | Nef protein of HIV-1 | [106] | |
| miRNA of HSV-1 | [62] | ||
| Activation of EV biogenesis | Nef protein of HIV-1 | [107] | |
| Aggravate pathology | Hbx protein and mRNA of HCV | [50] | |
| LMP-1 protein and mRNA of EBV | [49,61,108] | ||
| Humoral immunity decoy | Sequestration of neutralizing antibodies | Spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 | [41] |
| GP protein of EBOV | [43] | ||
| E protein of ZIKV | [24] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rey-Cadilhac, F.; Rachenne, F.; Missé, D.; Pompon, J. Viral Components Trafficking with(in) Extracellular Vesicles. Viruses 2023, 15, 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122333
Rey-Cadilhac F, Rachenne F, Missé D, Pompon J. Viral Components Trafficking with(in) Extracellular Vesicles. Viruses. 2023; 15(12):2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122333
Chicago/Turabian StyleRey-Cadilhac, Félix, Florian Rachenne, Dorothée Missé, and Julien Pompon. 2023. "Viral Components Trafficking with(in) Extracellular Vesicles" Viruses 15, no. 12: 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122333
APA StyleRey-Cadilhac, F., Rachenne, F., Missé, D., & Pompon, J. (2023). Viral Components Trafficking with(in) Extracellular Vesicles. Viruses, 15(12), 2333. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15122333







