Host Response of Syrian Hamster to SARS-CoV-2 Infection including Differences with Humans and between Sexes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiment
2.2. Histology and Immunofluorescence
2.3. Molecular Analyses for SARS-CoV-2 Detection and Quantification
2.4. Gene Expression Analyses by RNA-Seq
2.5. Serological Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analyses
2.7. Data Availability
3. Results
3.1. Infection and Seroconversion

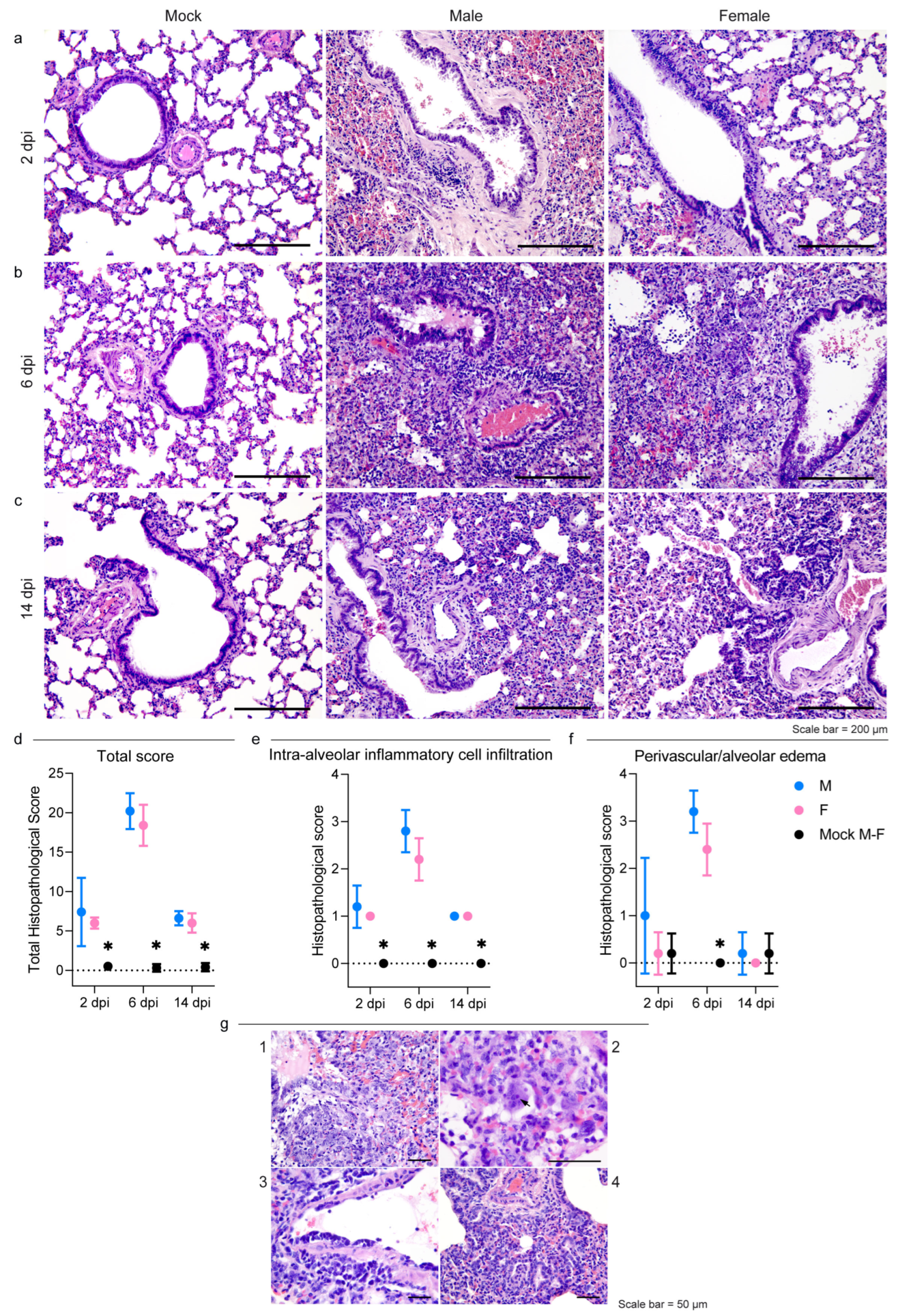
3.2. Pathology
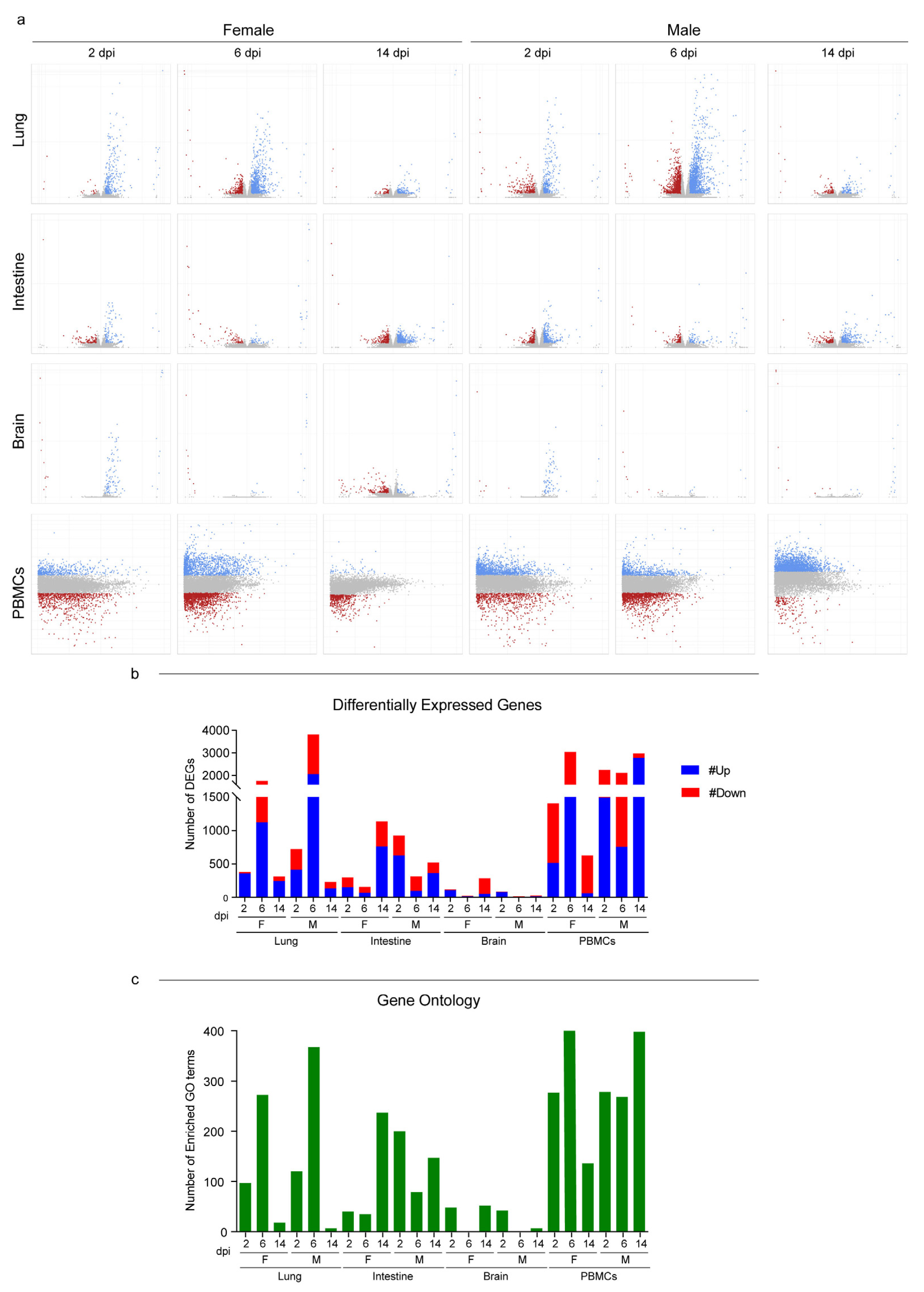
3.3. Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Infection

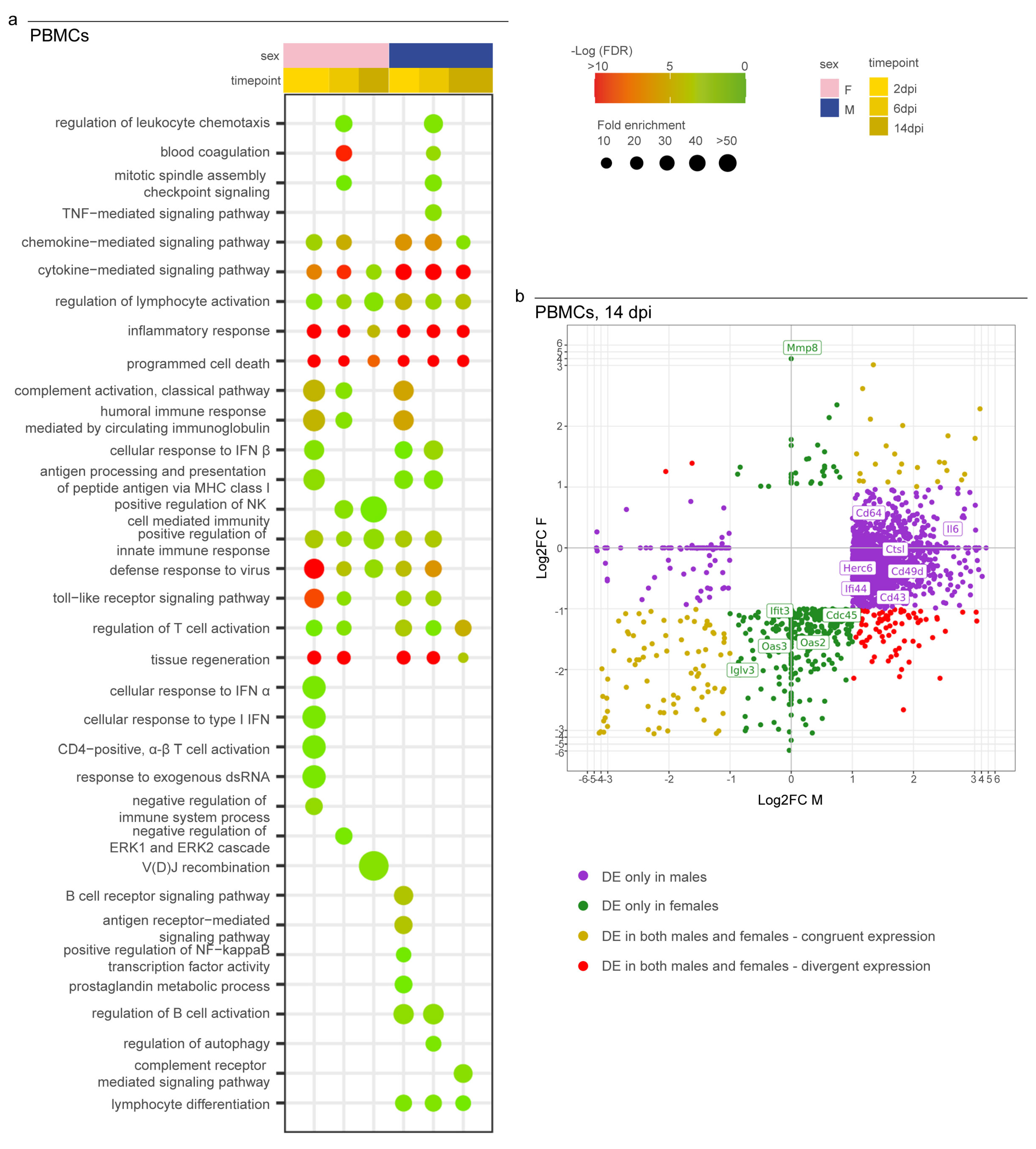
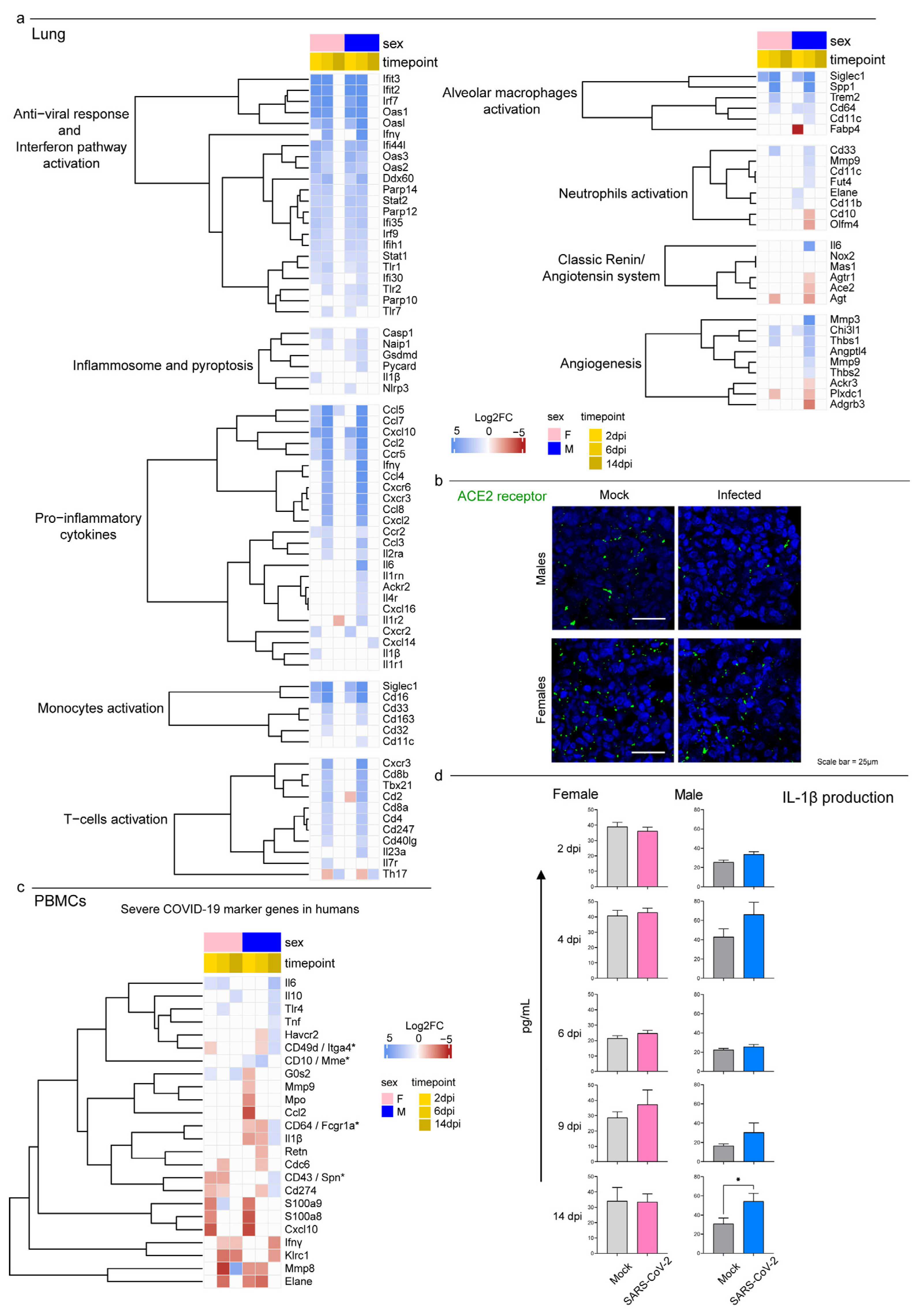
3.4. Syrian Hamster as Immunological Model for COVID-19
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlin, D.A.; Gulick, R.M.; Martinez, F.J. Severe COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2451–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, R.T.; Lynch, J.B.; del Rio, C. Mild or Moderate COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z. Probable Pangolin Origin of SARS-CoV-2 Associated with the COVID-19 Outbreak. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 1346–1351.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.C.; Goldstein, S.A.; Rasmussen, A.L.; Robertson, D.L.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Wertheim, J.O.; Anthony, S.J.; Barclay, W.S.; Boni, M.F.; Doherty, P.C.; et al. The Origins of SARS-CoV-2: A Critical Review. Cell 2021, 184, 4848–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worobey, M.; Levy, J.I.; Serrano, L.M.; Crits-Christoph, A.; Pekar, J.E.; Goldstein, S.A.; Rasmussen, A.L.; Kraemer, M.U.G.; Newman, C.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; et al. The Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market in Wuhan Was the Early Epicenter of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Science 2022, 377, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fullard, J.F.; Lee, H.C.; Voloudakis, G.; Suo, S.; Javidfar, B.; Shao, Z.; Peter, C.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, S.; Corvelo, A.; et al. Single-Nucleus Transcriptome Analysis of Human Brain Immune Response in Patients with Severe COVID-19. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spudich, S.; Nath, A. Nervous System Consequences of COVID-19. Science 2022, 375, 267–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.R.; Liu, J.; Liao, Z.G.; Zhou, J.; Peng, H.W.; Gong, F.; Hu, J.F.; Zhou, Y. COVID-19 and Gastroenteric Manifestations. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 4990–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, S.; Poloni, E.T.; Pandini, C.; Garofalo, M.; Dragoni, F.; Medici, V.; Davin, A.; Visonà, S.D.; Moretti, M.; Sproviero, D.; et al. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Genome and Whole Transcriptome Sequencing in Frontal Cortex of COVID-19 Patients. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2021, 97, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani Zangbar, H.; Gorji, A.; Ghadiri, T. A Review on the Neurological Manifestations of COVID-19 Infection: A Mechanistic View. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 536–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunachalam, P.S.; Wimmers, F.; Mok, C.K.P.; Perera, R.A.P.M.; Scott, M.; Hagan, T.; Sigal, N.; Feng, Y.; Bristow, L.; Tak-Yin Tsang, O.; et al. Systems Biological Assessment of Immunity to Mild versus Severe COVID-19 Infection in Humans. Science 2020, 369, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, M.Z.; Poh, C.M.; Rénia, L.; MacAry, P.A.; Ng, L.F.P. The Trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, Inflammation and Intervention. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, M.M.; Haagmans, B.L. SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrame, A.; Salguero, P.; Rossi, E.; Conesa, A.; Moro, L.; Bettini, L.R.; Rizzi, E.; D’Angió, M.; Deiana, M.; Piubelli, C.; et al. Association Between Sex Hormone Levels and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With COVID-19 Admitted to Hospital: An Observational, Retrospective, Cohort Study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanelle-Bertram, S.; Schaumburg, B.; Kouassi, N.M.; Beck, S.; Zickler, M.; Beythien, G.; Becker, K.; Bai, T.; Jania, H.; Müller, Z.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Induced CYP19A1 Expression in the Lung Correlates with Increased Aromatization of Testosterone-to-Estradiol in Male Golden Hamsters. 2020. Available online: https://assets.researchsquare.com/files/rs-107474/v2_covered.pdf?c=1639004338 (accessed on 29 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Ellingson, M.K.; Wong, P.; Israelow, B.; Lucas, C.; Klein, J.; Silva, J.; Mao, T.; Oh, J.E.; Tokuyama, M.; et al. Sex Differences in Immune Responses That Underlie COVID-19 Disease Outcomes. Nature 2020, 588, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnai, F.; De Bellis, G.; Dragani, T.A.; Colombo, F. COVID-19 Mortality in Italy Varies by Patient Age, Sex and Pandemic Wave. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davitt, E.; Davitt, C.; Mazer, M.B.; Areti, S.S.; Hotchkiss, R.S.; Remy, K.E. COVID-19 Disease and Immune Dysregulation. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2022, 35, 101401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, C.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wei, J.; Huang, F.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Xing, L.; et al. Plasma IP-10 and MCP-3 Levels Are Highly Associated with Disease Severity and Predict the Progression of COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 119–127.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, M.S.; Kanneganti, T.D. Innate Immunity: The First Line of Defense against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Spike Mutations and Immune Escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.S.; Sudre, C.H.; May, A.; Antonelli, M.; Murray, B.; Varsavsky, T.; Kläser, K.; Canas, L.S.; Molteni, E.; Modat, M.; et al. Changes in Symptomatology, Reinfection, and Transmissibility Associated with the SARS-CoV-2 Variant B.1.1.7: An Ecological Study. Lancet Public Health 2021, 6, e335–e345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, J.; Dol, J.; Boulos, L.; Somerville, M.; McCulloch, H.; Macdonald, M.; Leblanc, J.; Curran, J. Transmission Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Rev. Medrxiv 2021, 2021, 2021-04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellas, C.; Del Bello, A.; Debard, A.; Steinmeyer, Z.; Tribaudeau, L.; Ranger, N.; Jeanne, N.; Martin-Blondel, G.; Delobel, P.; Kamar, N.; et al. Influence of Treatment with Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibodies on the SARS-CoV-2 Nasopharyngeal Load and Quasispecies. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2022, 28, 139.e5–139.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.C.; Lu, R.M.; Su, S.C.; Chiang, P.Y.; Ko, S.H.; Ke, F.Y.; Liang, K.H.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Wu, H.C. Monoclonal Antibodies for COVID-19 Therapy and SARS-CoV-2 Detection. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanBlargan, L.A.; Errico, J.M.; Halfmann, P.J.; Zost, S.J.; Crowe, J.E.; Purcell, L.A.; Kawaoka, Y.; Corti, D.; Fremont, D.H.; Diamond, M.S. An Infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron Virus Escapes Neutralization by Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Sasi, S.; Pillai, S.G.; Nag, A.; Shukla, D.; Singhal, R.; Phalke, S.; Velu, G.S.K. SARS-CoV-2 Mutations and Their Impact on Diagnostics, Therapeutics and Vaccines. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 815389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Li, C.; Ye, C.; Ruan, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Luo, Z. Advances in the Development of Therapeutic Strategies against COVID-19 and Perspectives in the Drug Design for Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 824–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, C.; Bhattacharya, M.; Sharma, A.R. Emerging Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 Variants and Their Role in Antibody Escape to Small Molecule-Based Therapeutic Resistance. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2020, 62, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wu, Y.; Rui, X.; Yang, Y.; Ling, C.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; Wang, Y. Animal Models for COVID-19: Advances, Gaps and Perspectives. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, A.; Bergna, A.; Menzo, S.; Zehender, G.; Caucci, S.; Ghisetti, V.; Rizzo, F.; Maggi, F.; Cerutti, F.; Giurato, G.; et al. Circulating SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Italy, October 2020–March 2021. Virol. J. 2021, 18, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanelli, P.; Trentini, F.; Guzzetta, G.; Marziano, V.; Mammone, A.; Schepisi, M.S.; Poletti, P.; Grané, C.M.; Manica, M.; del Manso, M.; et al. Co-Circulation of SARS-CoV-2 Alpha and Gamma Variants in Italy, February and March 2021. Eurosurveillance 2022, 27, 2100429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Wen, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, R.; He, X.; Shuai, L.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Susceptibility of Ferrets, Cats, Dogs, and Different Domestic Animals to SARS-Coronavirus-2. Science 2020, 368, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honrubia, J.M.; Gutierrez-álvarez, J.; Sanz-bravo, A.; González-miranda, E.; Muñoz-santos, D.; Castaño-rodriguez, C.; Wang, L.; Villarejo-torres, M.; Ripoll-gómez, J.; Esteban, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Lung Edema and Replication Are Regulator Modulators. MBio 2023, e03136-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sia, S.F.; Yan, L.M.; Chin, A.W.H.; Fung, K.; Choy, K.T.; Wong, A.Y.L.; Kaewpreedee, P.; Perera, R.A.P.M.; Poon, L.L.M.; Nicholls, J.M.; et al. Pathogenesis and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in Golden Hamsters. Nature 2020, 583, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shou, S.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y.; Kang, N.; Song, Y.; Tan, D.; Liu, N.; Wang, F.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y. Animal Models for COVID-19: Hamsters, Mouse, Ferret, Mink, Tree Shrew, and Non-Human Primates. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 626553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.W.; Zhang, A.J.; Yuan, S.; Poon, V.K.M.; Chan, C.C.S.; Lee, A.C.Y.; Chan, W.M.; Fan, Z.; Tsoi, H.W.; Wen, L.; et al. Simulation of the Clinical and Pathological Manifestations of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a Golden Syrian Hamster Model: Implications for Disease Pathogenesis and Transmissibility. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2428–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Kanevsky, I.; Yildiz, S.; Sellers, R.S.; Swanson, K.A.; Franks, T.; Rathnasinghe, R.; Munoz-Moreno, R.; Jangra, S.; Gonzalez, O.; et al. Modeling SARS-CoV-2: Comparative Pathology in Rhesus Macaque and Golden Syrian Hamster Models. Toxicol. Pathol. 2022, 50, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, M.; Iwatsuki-Horimoto, K.; Hatta, M.; Loeber, S.; Halfmann, P.J.; Nakajima, N.; Watanabe, T.; Ujie, M.; Takahashi, K.; Ito, M.; et al. Syrian Hamsters as a Small Animal Model for SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Countermeasure Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 16587–16595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Fontela, C.; Dowling, W.E.; Funnell, S.G.P.; Gsell, P.-S.; Balta, X.R.; Albrecht, R.A.; Andersen, H.; Baric, R.S.; Carroll, M.W.; Cavaleri, M.; et al. Animal Models for COVID-19. Nature 2020, 586, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frere, J.J.; Serafini, R.A.; Pryce, K.D.; Zazhytska, M.; Oishi, K.; Golynker, I.; Panis, M.; Zimering, J.; Horiuchi, S.; Hoagland, D.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Hamsters and Humans Results in Lasting and Unique Systemic Perturbations after Recovery. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabq3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armando, F.; Beythien, G.; Kaiser, F.K.; Allnoch, L.; Heydemann, L.; Rosiak, M.; Becker, S.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.; Lamers, M.M.; Haagmans, B.L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Causes Mild Pathology in the Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract of Hamsters. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoagland, D.A.; Møller, R.; Uhl, S.A.; Oishi, K.; Frere, J.; Golynker, I.; Horiuchi, S.; Panis, M.; Blanco-Melo, D.; Sachs, D.; et al. Leveraging the Antiviral Type I Interferon System as a First Line of Defense against SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenicity. Immunity 2021, 54, 557–570.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giobbe, G.G.; Bonfante, F.; Jones, B.C.; Gagliano, O.; Luni, C.; Zambaiti, E.; Perin, S.; Laterza, C.; Busslinger, G.; Stuart, H.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Replication in Human Gastric Organoids. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, F.; Meade-White, K.; Clancy, C.; Rosenke, R.; Okumura, A.; Hawman, D.W.; Feldmann, F.; Kaza, B.; Jarvis, M.A.; Rosenke, K.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Reinfection Prevents Acute Respiratory Disease in Syrian Hamsters but Not Replication in the Upper Respiratory Tract. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, K.L.; Pinski, A.N.; Clancy, C.S.; Gourdine, T.; Shifflett, K.; Fletcher, P.; Messaoudi, I.; Marzi, A. Pathogenic and Transcriptomic Differences of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants in the Syrian Golden Hamster Model. eBioMedicine 2021, 73, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, M.V.; De Castro, S.O.; De Albuquerque, C.Z.; De Moura Mattaraia, V.G.; Santoro, M.L. The gingival vein as a minimally traumatic site for multiple blood sampling in guinea pigs and hamsters. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Zhao, K.; Yao, Y.; Guo, J.; Gao, X.; Yang, Q.; Guo, M.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; et al. RNA Binding Protein 24 Regulates the Translation and Replication of Hepatitis C Virus. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 930–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonova, K.; Safina, A.; Nesher, E.; Sandlesh, P.; Pratt, R.; Burkhart, C.; Lipchick, B.; Gitlin, I.; Frangou, C.; Koman, I.; et al. TRAIN (Transcription of Repeats Activates Interferon) in Response to Chromatin Destabilization Induced by Small Molecules in Mammalian Cells. Elife 2018, 7, e30842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlman, S.; Netland, J. Coronaviruses Post-SARS: Update on Replication and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Luisa Schmidt, M.; et al. Detection of 2019-NCoV by RT-PCR. Euro Surveill 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, C.M.; Dettinger, L.; Powell, J.W.; Seiders, M.; Condori, R.E.C.; Griesser, R.; Okogi, K.; Carlos, M.; Pesko, K.; Breckenridge, M.; et al. Multi-Site Evaluation of the LN34 Pan-Lyssavirus Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for Postmortem Rabies Diagnostics. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.A.; Raveendran, M.; Lyfoung, D.T.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Mahmoud, M.; Prall, T.M.; Karls, J.A.; Doddapaneni, H.; Meng, Q.; Han, Y.; et al. Construction of a New Chromosome-Scale, Long-Read Reference Genome Assembly of the Syrian Hamster, Mesocricetus auratus. GigaScience 2022, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq-A Python Framework to Work with High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S. Blast2GO: A Comprehensive Suite for Functional Analysis in Plant Genomics. Int. J. Plant Genom. 2008, 2008, 619832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emms, D.M.; Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: Phylogenetic Orthology Inference for Comparative Genomics. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliari, M.; Bonfante, F.; Padoan, A. Omicron Neutralization and the Inference of Correlates of Protection Based on Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG Levels in Boosted Individuals. Pre-Print The Lancet. 2022. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4016530 (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- Padoan, A.; Bonfante, F.; Cosma, C.; DI Chiara, C.; Sciacovelli, L.; Pagliari, M.; Bortolami, A.; Costenaro, P.; Musso, G.; Basso, D.; et al. Analytical and Clinical Performances of a SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG Assay: Comparison with Neutralization Titers. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2021, 59, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibin, V.; Mancin, M.; Pedersen, K.; Barrucci, F.; Belluco, S.; Roccato, A.; Cocola, F.; Ferrarini, S.; Sandri, A.; Lau Baggesen, D.; et al. Usefulness of Escherichia Coli and Enterobacteriaceae as Process Hygiene Criteria in Poultry: Experimental Study. EFSA Support. Publ. 2017, 11, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roccato, A.; Mancin, M.; Barco, L.; Cibin, V.; Antonello, K.; Cocola, F.; Ricci, A. Usefulness of Indicator Bacteria as Potential Marker of Campylobacter Contamination in Broiler Carcasses. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 276, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrin, S.; Mancin, M.; Losasso, C.; Deotto, S.; Olsen, J.E.; Barco, L. Effect of PH and Salinity on the Ability of Salmonella Serotypes to Form Biofilm. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 821679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterrieder, N.; Bertzbach, L.D.; Dietert, K.; Abdelgawad, A.; Vladimirova, D.; Kunec, D.; Hoffmann, D.; Beer, M.; Gruber, A.D.; Trimpert, J. Age-Dependent Progression of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Syrian Hamsters. Viruses 2020, 12, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daamen, A.R.; Bachali, P.; Owen, K.A.; Kingsmore, K.M.; Hubbard, E.L.; Labonte, A.C.; Robl, R.; Shrotri, S.; Grammer, A.C.; Lipsky, P.E. Comprehensive Transcriptomic Analysis of COVID-19 Blood, Lung, and Airway. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, M.; Niknam, Z.; Mohammadi Amirabad, L.; Amiri-Dashatan, N.; Koushki, M.; Nemati, M.; Danesh Pouya, F.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Rasmi, Y.; Tayebi, L. Molecular Pathways Involved in COVID-19 and Potential Pathway-Based Therapeutic Targets. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 145, 112420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze, J.L.; Aschenbrenner, A.C. COVID-19 and the Human Innate Immune System. Cell 2021, 184, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbrenner, A.C.; Mouktaroudi, M.; Krämer, B.; Oestreich, M.; Antonakos, N.; Nuesch-Germano, M.; Gkizeli, K.; Bonaguro, L.; Reusch, N.; Baßler, K.; et al. Disease Severity-Specific Neutrophil Signatures in Blood Transcriptomes Stratify COVID-19 Patients. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlas, C.-M.B.; Consortium, C. A Blood Atlas of COVID-19 Defines Hallmarks of Disease Severity and Specificity. Cell 2022, 185, 916–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z. Multiomics: Unraveling the Panoramic Landscapes of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2313–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warner, B.M.; Safronetz, D.; Kobinger, G.P. Syrian Hamsters as a Small Animal Model for Emerging Infectious Diseases: Advances in Immunologic Methods. Advs Exp. Med. Biol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Public Health 2016, 972, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tostanoski, L.H.; Wegmann, F.; Martinot, A.J.; Loos, C.; McMahan, K.; Mercado, N.B.; Yu, J.; Chan, C.N.; Bondoc, S.; Starke, C.E.; et al. Ad26 Vaccine Protects against SARS-CoV-2 Severe Clinical Disease in Hamsters. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopka, K.E.; Nguyen, T.; Jentzen, J.M.; Rayes, O.; Schmidt, C.J.; Wilson, A.M.; Farver, C.F.; Myers, J.L. Diffuse Alveolar Damage (DAD) Resulting from Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection Is Morphologically Indistinguishable from Other Causes of DAD. Histopathology 2020, 77, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veenhuis, R.T.; Zeiss, C.J. Animal Models of COVID-19 II. Comparative Immunology. ILAR J. 2021, 62, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, A.D.; Firsching, T.C.; Trimpert, J.; Dietert, K. Hamster Models of COVID-19 Pneumonia Reviewed: How Human Can They Be? Vet. Pathol. 2022, 59, 528–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, H.-L.; Sit BVSc, T.H.; Brackman BVSc, C.J.; Chuk BVSc, S.S.; Cheng MPhil, S.M.; Gu, H.; Chang MPH, L.D.; Krishnan, P.; Ng, D.Y.; Liu, G.Y.; et al. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (Variant Delta) from Pet Hamsters to Humans and Onward Human Propagation of the Adapted Strain: A Case Study. Pre-Print The Lancet. 2022. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4017393 (accessed on 29 January 2023).
- Dhakal, S.; Ruiz-Bedoya, C.A.; Zhou, R.; Creisher, P.S.; Villano, J.S.; Littlefield, K.; Ruelas Castillo, J.; Marinho, P.; Jedlicka, A.E.; Ordonez, A.A.; et al. Sex Differences in Lung Imaging and SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses in a COVID-19 Golden Syrian Hamster Model. MBio 2021, 12, e0097421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizard, I. Sickness Behavior, Its Mechanisms and Significance. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2008, 9, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, L.; Rokni, M.; Mokhtari, T.; Noorbakhsh, F. Immunology, Immunopathogenesis and Immunotherapeutics of COVID-19; an Overview. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 93, 107364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, D.M.; Kim-Schulze, S.; Huang, H.H.; Beckmann, N.D.; Nirenberg, S.; Wang, B.; Lavin, Y.; Swartz, T.H.; Madduri, D.; Stock, A.; et al. An Inflammatory Cytokine Signature Predicts COVID-19 Severity and Survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yao, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; Ren, L.; Min, J.; Deng, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Tropism and Multiorgan Infection. Cell Discov. 2021, 7, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, V.; Motwani, R.; Kumar, A.; Kumari, C.; Raza, K. Histopathological Observations in COVID-19: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 74, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murira, A.; Lamarre, A. Type-I Interferon Responses: From Friend to Foe in the Battle against Chronic Viral Infection. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Sastre, A. Ten Strategies of Interferon Evasion by Viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.-C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Møller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Watanabe, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Nishi, K.; Yoshikawa, R.; Yasuda, J. Co-Infection of SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza Virus Causes More Severe and Prolonged Pneumonia in Hamsters. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.J.; Wei, T.C.; Hsu, C.H.; Ho, S.N.; Lai, C.Y.; Huang, S.F.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Yu, G.Y.; Dou, H.Y. Characterization of Virus Replication, Pathogenesis, and Cytokine Responses in Syrian Hamsters Inoculated with Sars-Cov-2. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 3781–3795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coomes, E.A.; Haghbayan, H. Interleukin-6 in COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamers, M.M.; Beumer, J.; van der Vaart, J.; Knoops, K.; Puschhof, J.; Breugem, T.I.; Ravelli, R.B.G.; Schayck, J.P. van; Mykytyn, Anna Z 3, E.; Duimel, H.Q.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Productively Infects Human Gut Enterocytes. Science 2020, 369, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, S.; Ngwa, C.; Morales Scheihing, D.A.; Al Mamun, A.; Ahnstedt, H.W.; Finger, C.E.; Colpo, G.D.; Sharmeen, R.; Kim, Y.; Choi, H.M.A.; et al. Sex Differences in the Immune Response to Acute COVID-19 Respiratory Tract Infection. Biol. Sex Differ. 2021, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.M.; Bai, P.; He, W.; Wu, F.; Liu, X.F.; Han, D.M.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.K. Gender Differences in Patients With COVID-19: Focus on Severity and Mortality. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peckham, H.; de Gruijter, N.M.; Raine, C.; Radziszewska, A.; Ciurtin, C.; Wedderburn, L.R.; Rosser, E.C.; Webb, K.; Deakin, C.T. Male Sex Identified by Global COVID-19 Meta-Analysis as a Risk Factor for Death and ITU Admission. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.J.; Kuo, K.C.; Wang, T.W.; Chang, C.W. Gender-Based Differences in COVID-19. New Microbes New Infect. 2021, 42, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, B.D.; Warner, B.M.; Chan, M.; Valcourt, E.; Tailor, N.; Banadyga, L.; Leung, A.; He, S.; Boese, A.S.; Audet, J.; et al. Host Parameters and Mode of Infection Influence Outcome in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Hamsters. iScience 2021, 24, 103530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, M.; Ma, J.; Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, K.; Cai, M.; Hong, J.; et al. Gender Associates with Both Susceptibility to Infection and Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 in Syrian Hamster. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xie, X.; Tu, Z.; Fu, J.; Xu, D.; Zhou, Y. The Signal Pathways and Treatment of Cytokine Storm in COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sia, S.F.; Yan, L.-M.; Chin, A.W.; Fung, K.; Poon, L.L.; Nicholls, J.M.; School, M.P.; Yen, H.-L. Pathogenesis and Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 Virus in Golden Syrian Hamsters. Nat. Res. Rev. 2020, 583, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalbandian, A.; Sehgal, K.; Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; McGroder, C.; Stevens, J.S.; Cook, J.R.; Nordvig, A.S.; Shalev, D.; Sehrawat, T.S.; et al. Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudre, C.H.; Murray, B.; Varsavsky, T.; Graham, M.S.; Penfold, R.S.; Bowyer, R.C.; Pujol, J.C.; Klaser, K.; Antonelli, M.; Canas, L.S.; et al. Attributes and Predictors of Long COVID. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Vaart, J.; Lamers, M.M.; Haagmans, B.L.; Clevers, H. Advancing Lung Organoids for COVID-19 Research. DMM Dis. Model. Mech. 2021, 14, dmm049060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yang, L.; Lacko, L.A.; Chen, S. Human Organoid Models to Study SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K. Sex as an Important Biological Variable in Biomedical Research. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Meyer, C.A.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Liu, X.S.; Zhang, Y. GFOLD: A Generalized Fold Change for Ranking Differentially Expressed Genes from RNA-Seq Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2782–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castellan, M.; Zamperin, G.; Franzoni, G.; Foiani, G.; Zorzan, M.; Drzewnioková, P.; Mancin, M.; Brian, I.; Bortolami, A.; Pagliari, M.; et al. Host Response of Syrian Hamster to SARS-CoV-2 Infection including Differences with Humans and between Sexes. Viruses 2023, 15, 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020428
Castellan M, Zamperin G, Franzoni G, Foiani G, Zorzan M, Drzewnioková P, Mancin M, Brian I, Bortolami A, Pagliari M, et al. Host Response of Syrian Hamster to SARS-CoV-2 Infection including Differences with Humans and between Sexes. Viruses. 2023; 15(2):428. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020428
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastellan, Martina, Gianpiero Zamperin, Giulia Franzoni, Greta Foiani, Maira Zorzan, Petra Drzewnioková, Marzia Mancin, Irene Brian, Alessio Bortolami, Matteo Pagliari, and et al. 2023. "Host Response of Syrian Hamster to SARS-CoV-2 Infection including Differences with Humans and between Sexes" Viruses 15, no. 2: 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020428
APA StyleCastellan, M., Zamperin, G., Franzoni, G., Foiani, G., Zorzan, M., Drzewnioková, P., Mancin, M., Brian, I., Bortolami, A., Pagliari, M., Oggiano, A., Vascellari, M., Panzarin, V., Crovella, S., Monne, I., Terregino, C., De Benedictis, P., & Leopardi, S. (2023). Host Response of Syrian Hamster to SARS-CoV-2 Infection including Differences with Humans and between Sexes. Viruses, 15(2), 428. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020428








