Unfavorable Outcome and Long-Term Sequelae in Cases with Severe COVID-19
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Unfavorable Outcome
2.1. Mortality
2.2. Co-Infections (Bacterial, Fungal and Parasitic Infections)
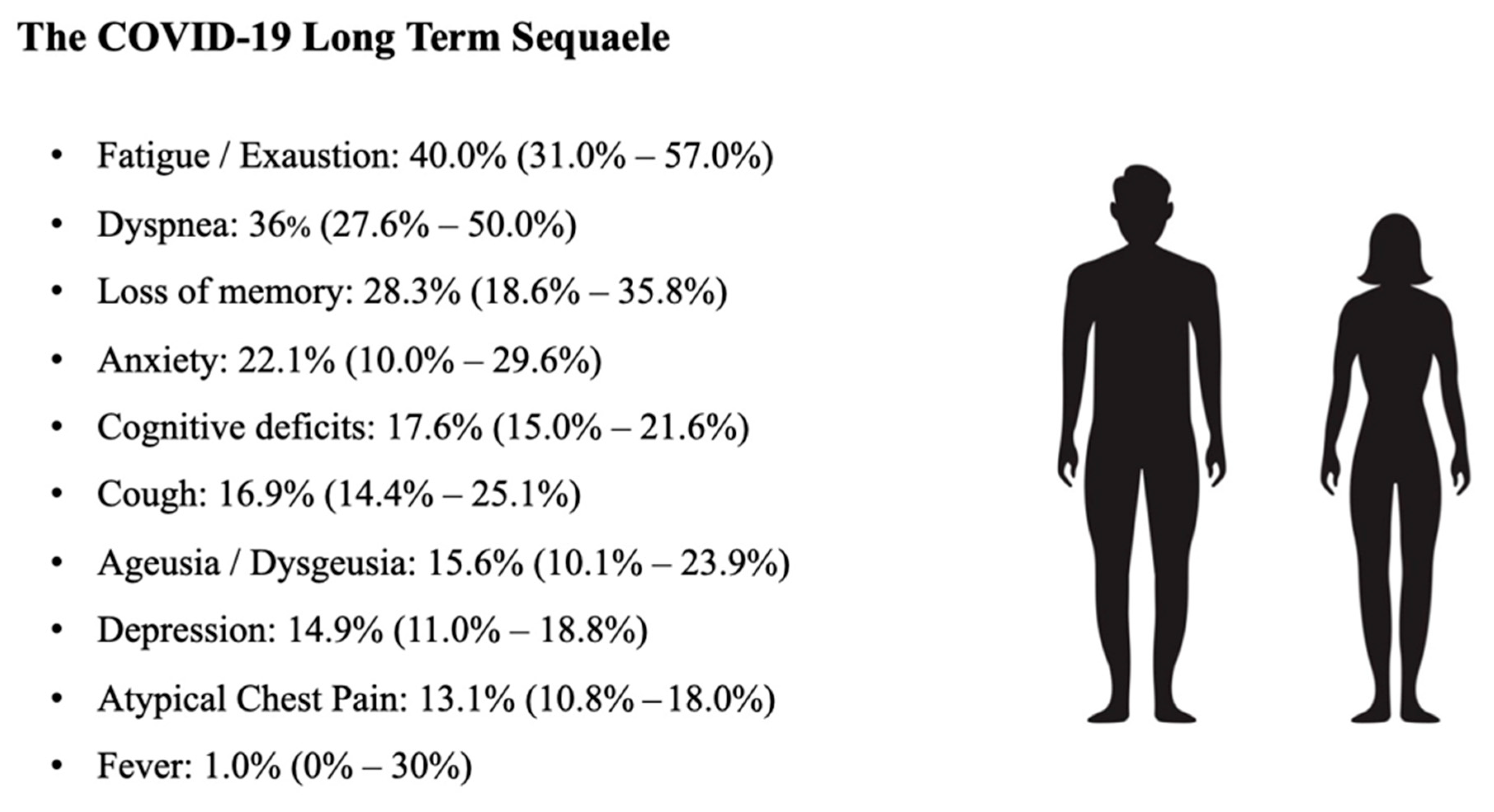
3. Long Term Sequelae
3.1. Pathophysiology
3.2. Vaccines and Long COVID-19
4. Post-COVID-19 Syndrome
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kabanova, A.; Gavriilaki, E.; Pelzer, B.W.; Brunetti, L.; Maiques-Diaz, A. Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on laboratory and clinical research: A testimony and a call to action from researchers. Hemasphere 2020, 4, e499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Q.; Yang, K.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L.; Song, J. Clinical predictors of mortality due to COVID-19 based on an analysis of data of 150 patients from Wuhan, China. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 846–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.S.; Capstick, T.; Ahmed, R.; Kow, C.S.; Mazhar, F.; Merchant, H.A.; Zaidi, S.T.R. Mortality in COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome and corticosteroids use: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2020, 14, 1149–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytriw, A.A.; Chibbar, R.; Chen, P.P.Y.; Traynor, M.D.; Kim, D.W.; Bruno, F.P.; Cheung, C.C.; Pareek, A.; Chou, A.C.C.; Graham, J.; et al. Outcomes of acute respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19 patients compared to the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2021, 15, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Calle, C.; Lalueza, A.; Mancheño-Losa, M.; de la Calle, G.M.; Lora-Tamayo, J.; Arrieta, E.; García-Reyne, A.; Losada, I.; de Miguel, B.; Díaz-Simón, R.; et al. Impact of viral load at admission on the development of respiratory failure in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 40, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Axfors, C.; Contopoulos-Ioannidis, D.G. Population-level COVID-19 mortality risk for non-elderly individuals overall and for non-elderly individuals without underlying diseases in pandemic epicenters. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, D.C.P.; Silva, D.F.O.; Costa, K.T.D.S.; de Morais, T.N.B.; de Andrade, F.B. Prevalence of comorbidities in deceased patients with COVID-19: A systematic review. Medicine 2022, 101, e30246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Liu, T.; Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Shao, L.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, H.; Peng, Z.; et al. Scoring systems for predicting mortality for severe patients with COVID-19. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 24, 100426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, S.R.; Ho, A.; Pius, R.; Buchan, I.; Carson, G.; Drake, T.M.; Dunning, J.; Fairfield, C.J.; Gamble, C.; Green, C.A.; et al. Risk stratification of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterization Protocol: Development and validation of the 4C Mortality Score. BMJ 2020, 370, m3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, N.K.; Shadrach, B.J.; Garg, M.K.; Bhatia, P.; Bhardwaj, P.; Gupta, M.K.; Dutt, N.; Jalandra, R.N.; Garg, P.; Nag, V.L.; et al. Predictors of Clinical Outcomes in Adult COVID-19 Patients Admitted to a Tertiary Care Hospital in India: An analytical cross-sectional study. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021024. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, W.; Liang, H.; Ou, L.; Chen, B.; Chen, A.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Guan, W.; Sang, L.; Lu, J.; et al. Development and Validation of a Clinical Risk Score to Predict the Occurrence of Critical Illness in Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, D.; Ranjan, A.H.A.; Pandey, S. Clinical and Laboratory Predictors of Mortality in COVID-19 Infection: A Retrospective Observational Study in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Eastern India. Cureus 2021, 13, e17660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, S.; Yu, M.; Wang, K.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhou, M.; Wu, B.; Yang, Z.; et al. Risk factors for severity and mortality in adult COVID-19 inpatients in Wuhan. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Zhao, P.; Chen, G.; Cheng, G.; Wang, Y.; Bi, J.; et al. Prediction for Progression Risk in Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia: The CALL Score. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, J.B.; Norton, S.; Barker, R.D.; Brookes, A.; Carey, I.; Clarke, B.D.; Jina, R.; Reid, C.; Russell, M.D.; Sneep, R.; et al. A clinical risk score to identify patients with COVID-19 at high risk of critical care admission or death: An observational cohort study. J. Infect. 2020, 81, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Lu, S.; Luo, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L. Mortality and Clinical Interventions in Critically ill Patient with Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 635560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docherty, A.B.; Mulholland, R.H.; Lone, N.I.; Cheyne, C.P.; De Angelis, D.; Diaz-Ordaz, K.; Donegan, C.; Drake, T.M.; Dunning, J.; Funk, S.; et al. Changes in in-hospital mortality in the first wave of COVID-19: A multicentre prospective observational cohort study using the WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol UK. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Chinn, J.; Nahmias, J.; Yuen, S.; Kirby, K.A.; Hohmann, S.; Amin, A. Outcomes and Mortality Among Adults Hospitalized With COVID-19 at US Medical Centers. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e210417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anesi, G.L.; Jablonski, J.; Harhay, M.O.; Atkins, J.H.; Bajaj, J.; Baston, C.; Brennan, P.J.; Candeloro, C.L.; Catalano, L.M.; Cereda, M.F.; et al. Characteristics, Outcomes, and Trends of Patients With COVID-19-Related Critical Illness at a Learning Health System in the United States. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, S.R.; Gupta, R.K.; Ho, A.; Pius, R.; Buchan, I.; Carson, G.; Drake, T.M.; Dunning, J.; Fairfield, C.J.; Gamble, C.; et al. Prospective validation of the 4C prognostic models for adults hospitalised with COVID-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol. Thorax 2022, 77, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langford, B.J.; So, M.; Raybardhan, S.; Leung, V.; Westwood, D.; MacFadden, D.R.; Soucy, J.R.; Daneman, N. Bacterial co-infection and secondary infection in patients with COVID-19: A living rapid review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderon, M.; Gysin, G.; Gujjar, A.; McMaster, A.; King, L.; Comandé, D.; Hunter, E.; Payne, B. Bacterial co-infection and antibiotic stewardship in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.P.; Gonçalves, L.C.; Oliveira, A.C.C.; Queiroz, P.H.P.; Ito, C.R.M.; Santos, M.O.; Carneiro, L.C. Bacterial Co-Infection in Patients with COVID-19 Hospitalized (ICU and Not ICU): Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, S.S.; Taherpour, N.; Bayat, S.; Ghajari, H.; Mohseni, P.; Hashemi Nazari, S.S. Epidemiologic characteristics of cases with reinfection, recurrence, and hospital readmission due to COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuley, A.J.; Kuiper, M.J.; Durr, P.A.; Bruce, M.P.; Barr, J.; Todd, S.; Au, G.G.; Blasdell, K.; Tachedjian, M.; Lowther, S.; et al. Experimental and in silico evidence suggests vaccines are unlikely to be affected by D614G mutation in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. NPJ Vaccines 2020, 5, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, V.J.; Foulkes, S.; Charlett, A.; Atti, A.; Monk, E.J.M.; Simmons, R.; Wellington, E.; Cole, M.J.; Saei, A.; Oguti, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection rates of antibody-positive compared with antibody-negative health-care workers in England: A large, multicentre, prospective cohort study (SIREN). Lancet 2021, 397, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowe, B.; Xie, Y.; Al-Aly, Z. Acute and postacute sequelae associated with SARS-CoV-2 reinfection. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2398–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Fan, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, S.; Guo, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Mou, H.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 in Adolescents and Young Adults. Innovation 2020, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ye, L.; Xia, R.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, C.; Wang, Z.; Lin, R.; Shi, D.; Gao, Y.; Yao, J.; et al. Chest Computed Tomography and Clinical Follow-Up of Discharged Patients with COVID-19 in Wenzhou City, Zhejiang, China. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.M.; Shang, Y.M.; Song, W.B.; Li, Q.Q.; Xie, H.; Xu, Q.F.; Jia, J.L.; Li, L.M.; Mao, H.L.; Zhou, X.M.; et al. Follow-up study of the pulmonary function and related physiological characteristics of COVID-19 survivors three months after recovery. eClinicalMedicine 2020, 25, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelin, D.; Wirtheim, E.; Vetter, P.; Kalil, A.C.; Bruchfeld, J.; Runold, M.; Guaraldi, G.; Mussini, C.; Gudiol, C.; Pujol, M.; et al. Long-term consequences of COVID-19: Research needs. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carfì, A.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F.; Gemelli Against COVID-19 Post-Acute Care Study Group. Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 603–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Xu, M.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Y.; Dong, W. Clinical sequelae of COVID-19 survivors in Wuhan, China: A single-centre longitudinal study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tan, C.; Wu, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Huang, X.; Yuan, S.; et al. Impact of coronavirus disease 2019 on pulmonary function in early convalescence phase. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Leon, S.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Perelman, C.; Sepulveda, R.; Rebolledo, P.A.; Cuapio, A.; Villapol, S. More than 50 long-term effects of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamaschi, L.; Mescia, F.; Turner, L.; Hanson, A.L.; Kotagiri, P.; Dunmore, B.J.; Ruffieux, H.; De Sa, A.; Huhn, O.; Morgan, M.D.; et al. Longitudinal analysis reveals that delayed bystander CD8+ T cell activation and early immune pathology distinguish severe COVID-19 from mild disease. Immunity 2021, 54, 1257–1275.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Péré, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vabret, N.; Britton, G.J.; Gruber, C.; Hegde, S.; Kim, J.; Kuksin, M.; Levantovsky, R.; Malle, L.; Moreira, A.; Park, M.D.; et al. Immunology of COVID-19: Current State of the Science. Immunity 2020, 52, 910–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehandru, S.; Merad, M. Pathological sequelae of long-haul COVID. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetsouphanh, C.; Darley, D.R.; Wilson, D.B.; Howe, A.; Munier, C.M.L.; Patel, S.K.; Juno, J.A.; Burrell, L.M.; Kent, S.J.; Dore, G.J.; et al. Immunological dysfunction persists for 8 months following initial mild-to-moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, H.J.; Coutavas, E.; Pine, A.B.; Lee, A.I.; Yu, V.L.; Shallow, M.K.; Giovacchini, C.X.; Mathews, A.M.; Stephenson, B.; Que, L.G.; et al. Immunofibrotic drivers of impaired lung function in postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e148476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bost, P.; Giladi, A.; Liu, Y.; Bendjelal, Y.; Xu, G.; David, E.; Blecher-Gonen, R.; Cohen, M.; Medaglia, C.; Li, H.; et al. Host-Viral Infection Maps Reveal Signatures of Severe COVID-19 Patients. Cell 2020, 181, 1475–1488.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzerini, P.E.; Laghi-Pasini, F.; Boutjdir, M.; Capecchi, P.L. Cardioimmunology of arrhythmias: The role of autoimmune and inflammatory cardiac channelopathies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccioli, L.; Pensato, U.; Cani, I.; Guarino, M.; Cortelli, P.; Bisulli, F. COVID-19-Associated Encephalopathy and Cytokine-Mediated Neuroinflammation. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 860–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichard, R.R.; Kashani, K.B.; Boire, N.A.; Constantopoulos, E.; Guo, Y.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Neuropathology of COVID-19: A spectrum of vascular and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM)-like pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, Y.; Kudose, S.; D’Agati, V.; Siddall, E.; Ahmad, S.; Nickolas, T.; Kisselev, S.; Gharavi, A.; Canetta, P. Acute Kidney Injury Due to Collapsing Glomerulopathy Following COVID-19 Infection. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, S.; Strollo, F.; Mambro, A.; Ceriello, A. COVID-19, ketoacidosis and new-onset diabetes: Are there possible cause and effect relationships among them? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 2507–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarte, K.I.; Catahay, J.A.; Velasco, J.V.; Pastrana, A.; Ver, A.T.; Pangilinan, F.C.; Peligro, P.J.; Casimiro, M.; Guerrero, J.J.; Gellaco, M.M.L.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 vaccination on the risk of developing long-COVID and on existing long-COVID symptoms: A systematic review. eClinicalMedicine 2022, 5, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P. Do vaccines protect from long COVID? Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.; Ledford, H. Coronapod: Vaccines and long COVID, how protected are you? Nature 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledford, H. Do vaccines protect against long COVID? What the data say. Nature 2021, 599, 546–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Aly, Z.; Bowe, B.; Xie, Y. Long COVID after breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taquet, M.; Dercon, Q.; Harrison, P.J. Six-month sequelae of post-vaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection: A retrospective cohort study of 10,024 breakthrough infections. Brain Behav. Immun. 2022, 103, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglietta, G.; Diodati, F.; Puntoni, M.; Lazzarelli, S.; Marcomini, B.; Patrizi, L.; Caminiti, C. Prognostic Factors for Post-COVID-19 Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, M. The four most urgent questions about long-COVID. Nature 2021, 594, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soriano, J.B.; Murthy, S.; Marshall, J.C.; Relan, P.; Diaz, J.V.; WHO Clinical Case Definition Working Group on Post-COVID-19 Condition. A clinical case definition of post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, e102–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pinto, M.D.; Borelli, J.L.; Mehrabadi, M.A.; Abrahim, H.L.; Dutt, N.; Lambert, N.; Nurmi, E.L.; Chakraborty, R.; Rahmani, A.M.; et al. COVID Symptoms, Symptom Clusters, and Predictors for Becoming a Long-Hauler Looking for Clarity in the Haze of the Pandemic. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2022, 31, 1390–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, L.C.; Hallas, J.; Nielsen, H.; Koch, A.; Mogensen, S.H.; Brun, N.C.; Christiansen, C.F.; Thomsen, R.W.; Pottegård, A. Post-acute effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection in individuals not requiring hospital admission: A Danish population-based cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1373–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, M.; Schommers, P.; Stecher, M.; Dewald, F.; Gieselmann, L.; Gruell, H.; Horn, C.; Vanshylla, K.; Cristanziano, V.D.; Osebold, L.; et al. Post-COVID syndrome in non-hospitalised patients with COVID-19: A longitudinal prospective cohort study. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2021, 6, 100122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, J. The COVID Heart-One Year After SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Patients Have an Array of Increased Cardiovascular Risks. JAMA 2022, 327, 1113–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, P. NICE guideline on long COVID. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergül, E.; Yılmaz, A.S.; Öğütveren, M.M.; Emlek, N.; Kostakoğlu, U.; Çetin, M. COVID 19 disease independently predicted endothelial dysfunction measured by flow-mediated dilatation. Int. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2022, 38, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet. Facing up to long COVID. Lancet 2020, 396, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, M.; Abo Omirah, M.; Hussein, A.; Saeed, H. Assessment and characterisation of post-COVID-19 manifestations. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e13746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douaud, G.; Lee, S.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Arthofer, C.; Wang, C.; McCarthy, P.; Lange, F.; Andersson, J.L.R.; Griffanti, L.; Duff, E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 is associated with changes in brain structure in UK Biobank. Nature 2022, 604, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Emergency Use ICD Codes for COVID-19 Disease Outbreak; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021; Available online: https://www.who.int/standards/classifications/classification-of-diseases/emergency-use-icd-codes-for-covid-19-disease-outbreak (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Deuel, J.W.; Lauria, E.; Lovey, T.; Zweifel, S.; Meier, M.I.; Züst, R.; Gültekin, N.; Stettbacher, A.; Schlagenhauf, P. Persistence, prevalence, and polymorphism of sequelae after COVID-19 in unvaccinated, young adults of the Swiss Armed Forces: A longitudinal, cohort study (LoCoMo). Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1694–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Lázaro, D.; Sánchez-Serrano, N.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; García-Hernández, J.L.; González-Bernal, J.J.; Seco-Calvo, J. Long COVID a New Derivative in the Chaos of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The Emergent Pandemic? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimeno-Almazán, A.; Pallarés, J.G.; Buendía-Romero, Á.; Martínez-Cava, A.; Franco-López, F.; Martínez, B.J.S.-A.; Bernal-Morel, E.; Courel-Ibáñez, J. Post-COVID-19 Syndrome and the Potential Benefits of Exercise. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, T.; Knight, M.; A’Court, C.; Buxton, M.; Husain, L. Management of post-acute COVID-19 in primary care. BMJ 2020, 370, m3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, S.; Webster, A.; Paul, L. Systematic Review of Changes and Recovery in Physical Function and Fitness After Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus Infection: Implications for COVID-19 Rehabilitation. Phys. Ther. 2020, 100, 1717–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belli, S.; Balbi, B.; Prince, I.; Cattaneo, D.; Masocco, F.; Zaccaria, S.; Bertalli, L.; Cattini, F.; Lomazzo, A.; Dal Negro, F.; et al. Low physical functioning and impaired performance of activities of daily life in COVID-19 patients who survived hospitalisation. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2002096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytür, Y.K.; Köseoğlu, B.F.; Taşkıran, Ö.Ö.; Ordu-Gökkaya, N.K.; Delialioğlu, S.Ü.; Tur, B.S.; Sarıkaya, S.; Şirzai, H.; Tekdemir Tiftik, T.; Alemdaroğlu, E.; et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation principles in SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19): A guideline for the acute and subacute rehabilitation. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 66, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasserie, T.; Hittle, M.; Goodman, S.N. Assessment of the Frequency and Variety of Persistent Symptoms Among Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fabbri, A.; Voza, A.; Riccardi, A.; Vanni, S.; De Iaco, F., on behalf of the Study & Research Center of the Italian Society of Emergency Medicine (SIMEU). Unfavorable Outcome and Long-Term Sequelae in Cases with Severe COVID-19. Viruses 2023, 15, 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020485
Fabbri A, Voza A, Riccardi A, Vanni S, De Iaco F on behalf of the Study & Research Center of the Italian Society of Emergency Medicine (SIMEU). Unfavorable Outcome and Long-Term Sequelae in Cases with Severe COVID-19. Viruses. 2023; 15(2):485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020485
Chicago/Turabian StyleFabbri, Andrea, Antonio Voza, Alessandro Riccardi, Simone Vanni, and Fabio De Iaco on behalf of the Study & Research Center of the Italian Society of Emergency Medicine (SIMEU). 2023. "Unfavorable Outcome and Long-Term Sequelae in Cases with Severe COVID-19" Viruses 15, no. 2: 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020485
APA StyleFabbri, A., Voza, A., Riccardi, A., Vanni, S., & De Iaco, F., on behalf of the Study & Research Center of the Italian Society of Emergency Medicine (SIMEU). (2023). Unfavorable Outcome and Long-Term Sequelae in Cases with Severe COVID-19. Viruses, 15(2), 485. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15020485







