Virological Markers in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
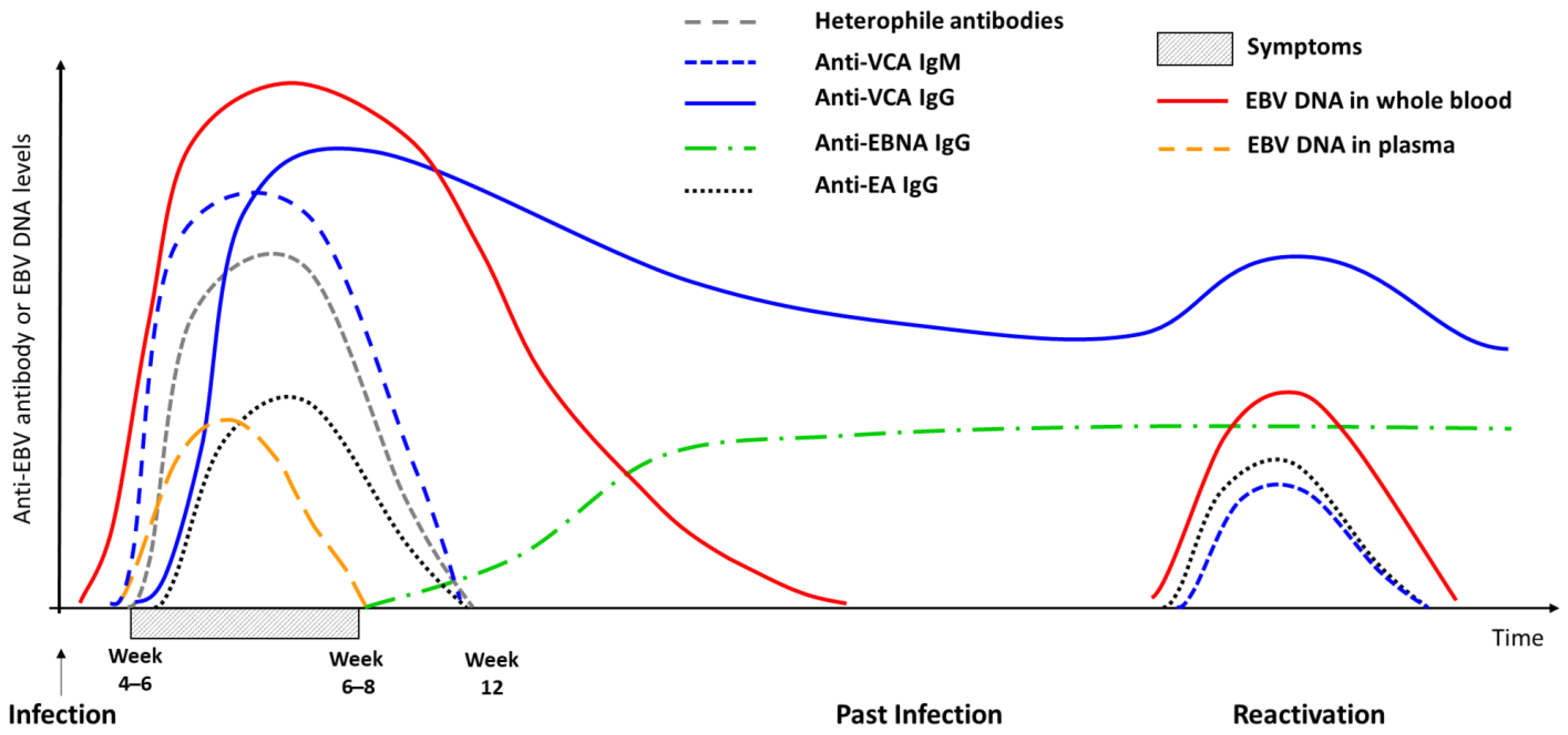
2. Infectious Mononucleosis
| Anti-VCA IgG | Anti-VCA IgM | Anti-EBNA IgG | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| − | − | − | Seronegative individual |
| −/+ | + | − | Primary infection |
| + | − | + | Past infection |
| + | − | − | Past infection (adults) or primary-infection (children) * |
| + | + | + | Past infection or end of primary infection ** |
| − | − | + | Indeterminate |
3. EBV-Associated Malignancies
3.1. Carcinomas
3.1.1. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
3.1.2. Gastric Carcinoma
3.2. Lymphomas
3.2.1. EBV-Positive Lymphoma in Immunocompetent Hosts
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Burkitt Lymphoma
Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Diseases
3.2.2. AIDS-Related Lymphoma
3.2.3. Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders
4. Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases (IMIDs)
4.1. EBV Infection and Multiple Sclerosis
4.2. Other Autoimmune Diseases
5. Sequencing, Next-Generation Sequencing, and New EBV Markers
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baer, R.; Bankier, A.T.; Biggin, M.D.; Deininger, P.L.; Farrell, P.J.; Gibson, T.J.; Hatfull, G.; Hudson, G.S.; Satchwell, S.C.; Séguin, C.; et al. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein—Barr virus genome. Nature 1984, 310, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, M.; Achong, B.; Barr, Y. Virus particles in cultured lymphoblasts from burkitt’s lymphoma. Lancet 1964, 1, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münz, C. Latency and lytic replication in Epstein–Barr virus-associated oncogenesis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 17, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Yap, L.F.; Murray, P.G. Epstein–Barr virus: More than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, P.J. Epstein-Barr Virus and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2019, 14, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.S.; Long, H.M.; Brooks, J.M.; Rickinson, A.B.; Hislop, A.D. The Immunology of Epstein-Barr Virus–Induced Disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 787–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesri, E.A.; Feitelson, M.A.; Munger, K. Human Viral Oncogenesis: A Cancer Hallmarks Analysis. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.P.; Kurzrock, R. Epstein-Barr Virus and Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 803–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jr, H.H.B.; Dunmire, S.K.; A Hogquist, K. Infectious mononucleosis. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2015, 4, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, J.M.; O Schmeling, D.; Dunmire, S.K.; A Knight, J.; Mullan, B.D.; A Ed, J.; Brundage, R.C.; A Hogquist, K.; Balfour, H.H. Prospective studies of infectious mononucleosis in university students. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2016, 5, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunmire, S.K.; Verghese, P.S.; Balfour, H.H., Jr. Primary Epstein-Barr virus infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2018, 102, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fafi-Kremer, S.; Morand, P.; Brion, J.; Pavese, P.; Baccard, M.; Germi, R.; Genoulaz, O.; Nicod, S.; Jolivet, M.; Ruigrok, R.W.H.; et al. Long-Term Shedding of Infectious Epstein-Barr Virus after Infectious Mononucleosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangye, S.G.; Palendira, U.; Edwards, E.S. Human immunity against EBV—Lessons from the clinic. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macsween, K.F.; Higgins, C.D.; McAulay, K.A.; Williams, H.; Harrison, N.; Swerdlow, A.; Crawford, D.H. Infectious Mononucleosis in University Students in the United Kingdom: Evaluation of the Clinical Features and Consequences of the Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.A. Epstein–Barr Virus and Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 8, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latour, S.; Winter, S. Inherited Immunodeficiencies With High Predisposition to Epstein–Barr Virus-Driven Lymphoproliferative Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, A.; Inoue, M.; Kawa, K. How we treat chronic active Epstein–Barr virus infection. Int. J. Hematol. 2017, 105, 406–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, A. Advances in the Study of Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus Infection: Clinical Features under the 2016 WHO Classification and Mechanisms of Development. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.; Edmunds, W. The Changing Epidemiology of Infectious Mononucleosis? J. Infect. 2002, 45, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tattevin, P.; Le Tulzo, Y.; Minjolle, S.; Person, A.; Chapplain, J.M.; Arvieux, C.; Thomas, R.; Michelet, C. Increasing Incidence of Severe Epstein-Barr Virus-Related Infectious Mononucleosis: Surveillance Study. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1873–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hocqueloux, L.; Causse, X.; Valery, A.; Jandali, J.-C.; Maitre, O.; Soin, C.; Buret, J.; Ouane, F.; Niang, M.; Mille, C.; et al. The high burden of hospitalizations for primary EBV infection: A 6-year prospective survey in a French hospital. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 1041.e1–1041.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourcade, G.; Germi, R.; Guerber, F.; Lupo, J.; Baccard, M.; Seigneurin, A.; Semenova, T.; Morand, P.; Epaulard, O. Evolution of EBV seroprevalence and primary infection age in a French hospital and a city laboratory network, 2000–2016. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramagopalan, S.V.; Valdar, W.; Dyment, D.A.; DeLuca, G.C.; Yee, I.M.; Giovannoni, G.; Ebers, G.C.; Sadovnick, A.D. Association of Infectious Mononucleosis with Multiple Sclerosis. Neuroepidemiology 2009, 32, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjalgrim, H.; Askling, J.; Rostgaard, K.; Hamilton-Dutoit, S.; Frisch, M.; Zhang, J.-S.; Madsen, M.; Rosdahl, N.; Konradsen, H.B.; Storm, H.H.; et al. Characteristics of Hodgkin’s Lymphoma after Infectious Mononucleosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, R.D. Routine Epstein-Barr Virus Diagnostics from the Laboratory Perspective: Still Challenging after 35 Years. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 3381–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, E.X.; Kussman, A.; Hwang, C.E. Use of Monospot Testing in the Diagnosis of Infectious Mononucleosis in the Collegiate Student–Athlete Population. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2021, 32, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall-Andon, T.; Heinz, P. How to use … the Monospot and other heterophile antibody tests. Arch. Dis. Child. Educ. Pract. Ed. 2017, 102, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klutts, J.; Ford, B.; Perez, N.R.; Gronowski, A.M. Evidence-Based Approach for Interpretation of Epstein-Barr Virus Serological Patterns. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 3204–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paschale, M.; Agrappi, C.; Manco, M.T.; Mirri, P.; Viganò, E.F.; Clerici, P. Seroepidemiology of EBV and interpretation of the “isolated VCA IgG” pattern. J. Med Virol. 2008, 81, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, J.; Germi, R.; Semenova, T.; Buisson, M.; Seigneurin, J.M.; Morand, P. Performance of Two Commercially Available Automated Immunoassays for the Determination of Epstein-Barr Virus Serological Status. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, J.; Tsougaev, M.; Blachier, S.; Chovelon, G.; Truffot, A.; Leroy, C.; Giai, J.; Epaulard, O.; Germi, R.; Morand, P. Comparison of Elecsys and Liaison immunoassays to determine Epstein–Barr virus serological status using further diagnostic approaches to clarify discrepant results. J. Med Virol. 2022, 95, e28166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nystad, T.W.; Myrmel, H. Prevalence of primary versus reactivated Epstein-Barr virus infection in patients with VCA IgG-, VCA IgM- and EBNA-1-antibodies and suspected infectious mononucleosis. J. Clin. Virol. 2007, 38, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geris, J.M.; Stancari, A.L.; Meirhaeghe, M.R.; Gautam, S.; Cayatte, C.; Schmeling, D.O.; Okour, M.F.; Brundage, R.C.; Hayes, G.M.; Balfour, H.H. Rapid antibody responses to Epstein-Barr virus correlate with reduced severity of primary infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2022, 155, 105267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, W.; Hayes, G.M.; Liu, H.; Gemmell, L.; Schmeling, D.O.; Radecki, P.; Aguilar, F.; Burbelo, P.D.; Woo, J.; Balfour, H.H.; et al. Kinetics of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Neutralizing and Virus-Specific Antibodies after Primary Infection with EBV. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, E.R.; Alter, G.; Ogembo, J.G.; Henderson, J.L.; Tabak, B.; Bakiş, Y.; Somasundaran, M.; Garber, M.; Selin, L.; Luzuriaga, K. High Epstein-Barr Virus Load and Genomic Diversity Are Associated with Generation of gp350-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies following Acute Infectious Mononucleosis. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e01562-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, S.W.; Tsang, C.M.; Lo, K.W. Epstein–Barr virus infection and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.L.K.; Wee, J.T.S.; Hui, E.P.; Chan, A.T.C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2016, 387, 1012–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.A.; Chan, A.T.C.; Leung, S.-F.; Pang, J.C.; Wang, A.Y.; Tong, J.H.; To, K.-F.; Chan, L.Y.; Tam, L.-S.; Chung, N.Y.; et al. Investigation into the Origin and Tumoral Mass Correlation of Plasma Epstein–Barr Virus DNA in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 2192–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Phua, S.K.A.; Soong, Y.L.; Oon, L.L.E.; Chan, K.S.; Lucky, S.S.; Mong, J.; Tan, M.H.; Lim, C.M. Clinical utility of Epstein-Barr virus DNA and other liquid biopsy markers in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Commun. 2020, 40, 564–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.A.; Woo, J.K.S.; King, A.; Zee, B.C.-Y.; Lam, W.K.J.; Chan, S.L.; Chu, S.W.I.; Mak, C.; Tse, I.O.L.; Leung, S.Y.M.; et al. Analysis of Plasma Epstein–Barr Virus DNA to Screen for Nasopharyngeal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakry, J.A.; Hegde, A.M.; Durand, C.M.; Massie, A.B.; Greer, A.E.; Ambinder, R.F.; Valsamakis, A. The clinical significance of EBV DNA in the plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with or without EBV diseases. Blood 2016, 127, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.A.; Hung, E.C.W.; Woo, J.K.S.; Chan, P.K.S.; Leung, S.-F.; Bn, F.P.T.L.; Cheng, A.S.M.; Yeung, S.W.; Chan, Y.W.; Tsui, T.K.C.; et al. Early detection of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA analysis in a surveillance program. Cancer 2013, 119, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.K.J.; Jiang, P.; Chan, K.C.A.; Cheng, S.H.; Zhang, H.; Peng, W.; Tse, O.Y.O.; Tong, Y.K.; Gai, W.; Zee, B.C.-Y.; et al. Sequencing-based counting and size profiling of plasma Epstein–Barr virus DNA enhance population screening of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E5115–E5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.M.; Chan, A.T.C.; Chan, L.Y.; Leung, S.F.; Lam, C.W.; Huang, D.P.; Johnson, P.J. Molecular prognostication of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by quantitative analysis of circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Cancer Res 2000, 60, 6878–6881. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, Y.M.; Chan, L.Y.; Chan, A.T.C.; Leung, S.F.; Lo, K.W.; Zhang, J.; Lee, J.C.; Hjelm, N.M.; Johnson, P.J.; Huang, D.P. Quantitative and temporal correlation between circulating cell-free Epstein-Barr virus DNA and tumor recurrence in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5452–5455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.M.D.; Leung, S.F.; Chan, L.Y.S.; Lo, K.W.; Zhang, J.; Chan, A.T.C.; Lee, J.C.K.; Hjelm, N.M.; Johnson, P.J.; Huang, D.P. Plasma Cell-free Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Quantitation in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Correlation with Clinical Staging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 906, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Nicholls, J.M.; Chua, D.; Chan, K.; Sham, J.; Lee, S.; Gulley, M.L. Laboratory markers of tumor burden in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A comparison of viral load and serologic tests for Epstein-Barr virus. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; King, A.; Lo, Y.D.; Yau, Y.; Zee, B.C.-Y.; Hui, E.P.; Leung, S.F.; Mo, F.; Kam, M.K.; Ahuja, A.T.; et al. Relationship between pretreatment level of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA, tumor burden, and metabolic activity in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2006, 66, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-C.; Wang, W.-Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Wei, Y.-H.; Liang, W.-M.; Jan, J.-S.; Jiang, R.-S. Quantification of Plasma Epstein–Barr Virus DNA in Patients with Advanced Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, S.-F.; Zee, B.; Ma, B.B.; Hui, E.P.; Mo, F.; Lai, M.; Chan, K.A.; Chan, L.Y.; Kwan, W.-H.; Lo, Y.D.; et al. Plasma Epstein-Barr Viral Deoxyribonucleic Acid Quantitation Complements Tumor-Node-Metastasis Staging Prognostication in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5414–5418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Tang, L.-L.; Mao, Y.-P.; Du, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.-C.; Liu, L.-Z.; Tian, L.; Luo, X.-T.; Xie, Y.; et al. Proposed modifications and incorporation of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA improve the TNM staging system for Epstein-Barr virus-related nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer 2018, 125, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.M.; Leung, S.F.; Chan, L.Y.; Chan, A.T.C.; Lo, K.W.; Johnson, P.J.; Huang, D.P. Kinetics of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA during radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res 2000, 60, 2351–2355. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leung, S.; Chan, K.; Ma, B.; Hui, E.; Mo, F.; Chow, K.; Leung, L.; Chu, K.; Zee, B.C.-Y.; Lo, Y.; et al. Plasma Epstein–Barr viral DNA load at midpoint of radiotherapy course predicts outcome in advanced-stage nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1204–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.T.C.; Lo, Y.M.D.; Zee, B.C.-Y.; Chan, L.Y.S.; Ma, B.; Leung, S.-F.; Mo, F.; Lai, M.; Ho, S.; Huang, D.P.; et al. Plasma Epstein-Barr Virus DNA and Residual Disease After Radiotherapy for Undifferentiated Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2002, 94, 1614–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zhao, C.; Guo, Y.; Han, F.; Lu, L.-X.; Wu, S.-X.; Li, S.; Huang, P.-Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L. Different Clinical Significance of Pre- and Post-treatment Plasma Epstein–Barr Virus DNA Load in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Treated with Radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 23, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, R.-L.; Lin, C.-Y.; Ting, L.-L.; Ko, J.-Y.; Hsu, M.-M. Comparison of clinical and molecular surveillance in patients with advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma after primary therapy: The Potential Role of Quantitative Analysis of Circulating Epstein-Barr Virus DNA. Cancer 2004, 100, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-Y.; Liu, M.-Y.; Yang, H.-I.; Hsu, M.-M.; Chen, C.-J.; Yang, C.-S. Serologic Markers of Epstein–Barr Virus Infection and Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Taiwanese Men. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1877–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.J.; Hsu, W.-L.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Chiang, C.-J.; Wang, C.-P.; Lou, P.-J.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Gravitt, P.; Diehl, S.R.; Goldstein, A.M.; et al. Prognostic Utility of Anti-EBV Antibody Testing for Defining NPC Risk among Individuals from High-Risk NPC Families. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Warner, B.E.; Wang, R.; Adams-Haduch, J.; Reznik, A.S.; Dou, J.; Huang, Y.; Gao, Y.-T.; Koh, W.-P.; Bäckerholm, A.; et al. Serologic Profiling Using an Epstein-Barr Virus Mammalian Expression Library Identifies EBNA1 IgA as a Prediagnostic Marker for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 5221–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghill, A.E.; Bu, W.; Nguyen, H.; Hsu, W.-L.; Yu, K.J.; Lou, P.-J.; Wang, C.-P.; Chen, C.-J.; Hildesheim, A.; Cohen, J.I. High Levels of Antibody that Neutralize B-cell Infection of Epstein–Barr Virus and that Bind EBV gp350 Are Associated with a Lower Risk of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3451–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Coghill, A.; Bu, W.; Hsu, W.-L.; Nguyen, H.; Yu, K.J.; Chien, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-J.; I Cohen, J.; Hildesheim, A. Evaluation of Total and IgA-Specific Antibody Targeting Epstein-Barr Virus Glycoprotein 350 and Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Risk. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghill, A.E.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Proietti, C.; Hsu, W.-L.; Chien, Y.-C.; Lekieffre, L.; Krause, L.; Teng, A.; Pablo, J.; Yu, K.J.; et al. Identification of a Novel, EBV-Based Antibody Risk Stratification Signature for Early Detection of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Taiwan. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.; Liu, Z.; Brenner, N.; Yu, K.J.; Hsu, W.-L.; Wang, C.-P.; Chien, Y.-C.; Coghill, A.E.; Chen, C.-J.; Butt, J.; et al. Validation of an Epstein-Barr Virus Antibody Risk Stratification Signature for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Use of Multiplex Serology. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e00077-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Cao, S.-M.; Cai, Y.-L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Feng, G.-F.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Q.-S.; Chen, Y.; Chang, E.T.; et al. A comprehensive risk score for effective risk stratification and screening of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 51–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stępień, E.; Strycharz-Dudziak, M.; Malm, M.; Drop, B.; Polz-Dacewicz, M. Serum and Tissue Level of TLR9 in EBV-Associated Oropharyngeal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A. The Global Landscape of EBV-Associated Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.T.; Cristescu, R.; Bass, A.J.; Kim, K.-M.; Odegaard, J.I.; Kim, K.; Liu, X.Q.; Sher, X.; Jung, H.; Lee, M.; et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of clinical responses to PD-1 inhibition in metastatic gastric cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Miaozhen, Q.; Lu, S.; Guan, W.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Jin, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; Shao, J.; et al. Prospective observation: Clinical utility of plasma Epstein–Barr virus DNA load in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma patients. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 146, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoda, K.; Ichikawa, D.; Fujita, Y.; Masuda, K.; Hiramoto, H.; Hamada, J.; Arita, T.; Konishi, H.; Kosuga, T.; Komatsu, S.; et al. Clinical utility of circulating cell-free Epstein-Barr virus DNA in patients with gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28796–28804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghill, A.E.; Hildesheim, A. Epstein-Barr Virus Antibodies and the Risk of Associated Malignancies: Review of the Literature. Am. J. Epidemiology 2014, 180, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donzel, M.; Bonjour, M.; Combes, J.-D.; Broussais, F.; Sesques, P.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; de Martel, C. Lymphomas associated with Epstein-Barr virus infection in 2020: Results from a large, unselected case series in France. Eclinicalmedicine 2022, 54, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rickinson, A.B.; Bell, A.I. Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphomas. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahr, S.; Hentze, H.; Englisch, S.; Hardt, D.; Fackelmayer, F.O.; Hesch, R.D.; Knippers, R. DNA fragments in the blood plasma of cancer patients: Quantitations and evidence for their origin from apoptotic and necrotic cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, A.; Armstrong, A.A.; MacKenzie, J.; Shield, L.; Khan, G.; Lake, A.; Proctor, S.; Taylor, P.; Clements, G.B.; Jarrett, R.F. Detection of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Genomes in the Serum of Patients with EBV-Associated Hodgkin’s Disease. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 84, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakry, J.A.; Li, H.; Gellert, L.L.; Lemas, M.V.; Hsieh, W.-S.; Hong, F.; Tan, K.L.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Gordon, L.I.; Fisher, R.I.; et al. Plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA predicts outcome in advanced Hodgkin lymphoma: Correlative analysis from a large North American cooperative group trial. Blood 2013, 121, 3547–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, J.J.G.; Schwartz, C.L.; Higman, M.; Chen, L.; Buxton, A.; Kanakry, J.A.; Kahwash, S.B.; Hutchison, R.E.; Friedman, D.L.; Ambinder, R.F. Epstein-Barr virus DNA in serum as an early prognostic marker in children and adolescents with Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Yoon, D.H.; Kim, S.; Park, J.S.; Park, C.-S.; Sung, H.; Lee, S.-W.; Huh, J.; Suh, C. Pretreatment whole blood Epstein-Barr virus-DNA is a significant prognostic marker in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2016, 95, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.-Q.; Yin, H.; Wu, J.-Z.; Chen, R.-Z.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, H.-Y.; Fan, L.; Li, J.-Y.; Liang, J.-H.; et al. Pretreatment whole blood Epstein-Barr virus DNA predicts prognosis in Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk. Res. 2021, 107, 106607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohaus, S.; Santangelo, R.; Giachelia, M.; Vannata, B.; Massini, G.; Cuccaro, A.; Martini, M.; Cesarini, V.; Cenci, T.; D’Alo, F.; et al. The Viral Load of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) DNA in Peripheral Blood Predicts for Biological and Clinical Characteristics in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2885–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, N.; Evans, A.; Harris, N.L.; Comstock, G.W.; Jellum, E.; Magnus, K.; Orentreich, N.; Polk, B.F.; Vogelman, J. Hodgkin’s Disease and Epstein-Barr Virus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 320, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.I.; Chang, E.T.; Ambinder, R.F.; Lennette, E.T.; Rubertone, M.V.; Mann, R.B.; Borowitz, M.; Weir, E.G.; Abbondanzo, S.L.; Mueller, N.E. Atypical prediagnosis Epstein-Barr virus serology restricted to EBV-positive Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2012, 120, 3750–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Jarrett, R.F.; Hjalgrim, H.; Proietti, C.; Chang, E.T.; Smedby, K.E.; Yu, K.J.; Lake, A.; Troy, S.; McAulay, K.A.; et al. Evaluation of the antibody response to the EBV proteome in EBV-associated classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 147, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chene, A.; Donati, D.; Orem, J.; Björkman, A.; Mbidde, E.; Kironde, F.; Wahlgren, M.; Bejarano, M.T. Endemic Burkitt’s lymphoma as a polymicrobial disease: New insights on the interaction between Plasmodium falciparum and Epstein–Barr virus. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2009, 19, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulama, D.H.; Bailey, J.A.; Foley, J.; Chelimo, K.; Ouma, C.; Jura, W.G.; Otieno, J.; Vulule, J.; Moormann, A.M. Sickle cell trait is not associated with endemic Burkitt lymphoma: An ethnicity and malaria endemicity-matched case–control study suggests factors controlling EBV may serve as a predictive biomarker for this pediatric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 134, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westmoreland, K.D.; Montgomery, N.D.; Stanley, C.C.; El-Mallawany, N.K.; Wasswa, P.; van der Gronde, T.; Mtete, I.; Butia, M.; Itimu, S.; Chasela, M.; et al. Plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA for pediatric Burkitt lymphoma diagnosis, prognosis and response assessment in Malawi. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2509–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xian, R.R.; Kinyera, T.; Otim, I.; Sampson, J.N.; Nabalende, H.; Legason, I.D.; Stone, J.; Ogwang, M.D.; Reynolds, S.J.; Kerchan, P.; et al. Plasma EBV DNA: A Promising Diagnostic Marker for Endemic Burkitt Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 804083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geser, A.; De Thé, G.; Lenoir, G.; Day, N.E.; Williams, E.H. Final case reporting from the ugandan prospective study of the relationship between ebv and burktit’s lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 1982, 29, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, L.M.; Newton, R.; Casabonne, D.; Ziegler, J.; Mbulaiteye, S.; Mbidde, E.; Wabinga, H.; Jaffe, H.; Beral, V. Antibodies against malaria and Epstein-Barr virus in childhood Burkitt lymphoma: A case-control study in Uganda. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 122, 1319–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghill, A.E.; Proietti, C.; Liu, Z.; Krause, L.; Bethony, J.; Prokunina-Olsson, L.; Obajemu, A.; Nkrumah, F.; Biggar, R.J.; Bhatia, K.; et al. The Association between the Comprehensive Epstein–Barr Virus Serologic Profile and Endemic Burkitt Lymphoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2020, 29, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpica, L.; Marques-Piubelli, M.L.; Beltran, B.E.; Chavez, J.C.; Miranda, R.N.; Castillo, J.J. EBV -positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: 2022 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 951–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.-H.; Lu, T.-X.; Tian, T.; Wang, L.; Fan, L.; Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Gong, Q.-X.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Li, J.-Y.; et al. Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) DNA in whole blood as a superior prognostic and monitoring factor than EBV-encoded small RNA in situ hybridization in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisi, M.C.; Cupelli, E.; Santangelo, R.; Maiolo, E.; Alma, E.; Giachelia, M.; Martini, M.; Bellesi, S.; D’Alò, F.; Voso, M.T.; et al. Whole blood EBV-DNA predicts outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2015, 57, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, A.; Yanada, M.; Inaguma, Y.; Tokuda, M.; Morishima, S.; Kanie, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Mizuta, S.; Akatsuka, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; et al. The prognostic significance of EBV DNA load and EBER status in diagnostic specimens from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 35, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.; Park, Y. Utility of Epstein-Barr Viral Load in Blood for Diagnosing and Predicting Prognosis of Lymphoma: A Comparison with Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded RNA in Situ Hybridization. J. Mol. Diagn. 2022, 24, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Hu, L.; Yao, M.; He, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, F.; Gu, W.; Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; Zhu, T.; et al. Disparity analysis and prognostic value of pretreatment whole blood Epstein-Barr virus DNA load and Epstein-Barr encoding region status in lymphomas: A retrospective multicenter study in Huaihai Lymphoma Working Group. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 150, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teras, L.R.; Rollison, D.E.; Pawlita, M.; Michel, A.; Brozy, J.; de Sanjose, S.; Blase, J.L.; Gapstur, S.M. Epstein-Barr virus and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the cancer prevention study-II and a meta-analysis of serologic studies. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 136, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, K.A.; Birmann, B.M.; Chang, E.T.; Spiegelman, N.; Aster, J.C.; Zhang, S.M.; Laden, F. A prospective study of Epstein-Barr virus antibodies and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2010, 116, 3547–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassig, B.A.; Willhauck-Fleckenstein, M.; Shu, X.-O.; Koh, W.-P.; Gao, Y.-T.; Purdue, M.P.; Xiang, Y.-B.; Adams-Haduch, J.; Wang, R.; Brenner, N.; et al. Serologic markers of viral infection and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A pooled study of three prospective cohorts in China and Singapore. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Bao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Chen, L.; Zheng, K.; Zhou, J. The superiority of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in plasma over in peripheral blood mononuclear cells for monitoring EBV-positive NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Yamaguchi, M.; Izutsu, K.; Yamamoto, G.; Takada, K.; Harabuchi, Y.; Isobe, Y.; Gomyo, H.; Koike, T.; Okamoto, M.; et al. Prospective measurement of Epstein-Barr virus–DNA in plasma and peripheral blood mononuclear cells of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood 2011, 118, 6018–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-L.; Bi, X.-W.; Liu, P.-P.; Lei, D.-X.; Jiang, W.-Q.; Xia, Y. The Clinical Utility of Circulating Epstein-Barr Virus DNA Concentrations in NK/T-Cell Lymphoma: A Meta-Analysis. Dis. Markers 2018, 2018, 1961058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, W.-Y.; Pang, A.; Choy, C.; Chim, C.-S.; Kwong, Y.-L. Quantification of circulating Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA in the diagnosis and monitoring of natural killer cell and EBV-positive lymphomas in immunocompetent patients. Blood 2004, 104, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, K.I.K.; Chan, L.Y.S.; Chan, W.-Y.; Johnson, P.J.; Lo, Y.M.D. Diagnostic and prognostic implications of circulating cell-free Epstein-Barr virus DNA in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwong, Y.-L.; Pang, A.W.K.; Leung, A.Y.H.; Chim, C.; Tse, E. Quantification of circulating Epstein–Barr virus DNA in NK/T-cell lymphoma treated with the SMILE protocol: Diagnostic and prognostic significance. Leukemia 2013, 28, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Kimura, H.; Maeda, Y.; Hashimoto, C.; Ishida, F.; Izutsu, K.; Fukushima, N.; Isobe, Y.; Takizawa, J.; Hasegawa, Y.; et al. Pretreatment EBV-DNA Copy Number Is Predictive of Response and Toxicities to SMILE Chemotherapy for Extranodal NK/T-cell Lymphoma, Nasal Type. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4183–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.; Kim, S.J.; Park, S.; Yoo, K.H.; Ki, C.-S.; Ko, Y.; Kim, W.S. Significance of circulating Epstein-Barr virus DNA monitoring after remission in patients with extranodal natural killer T cell lymphoma. Ann. Hematol. 2018, 97, 1427–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-Y.; Liu, Q.-F.; Wang, H.; Jin, J.; Wang, W.-H.; Wang, S.-L.; Song, Y.-W.; Liu, Y.-P.; Fang, H.; Ren, H.; et al. Clinical implications of plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA in early-stage extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma patients receiving primary radiotherapy. Blood 2012, 120, 2003–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Rao, H.; Yan, S.; Wang, F.; Wu, Q.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y. Serum EBV EA-IgA and VCA-IgA antibodies can be used for risk group stratification and prognostic prediction in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma: 24-year experience at a single institution. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Sarathkumara, Y.D.; Chan, J.K.C.; Kwong, Y.-L.; Lam, T.H.; Ip, D.K.M.; Chiu, B.C.-H.; Xu, J.; Su, Y.-C.; Proietti, C.; et al. Characterization of the humoral immune response to the EBV proteome in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, A.; Volpi, C.C.; Gualeni, A.V.; Gloghini, A. Epstein–Barr virus associated lymphomas in people with HIV. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2017, 12, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arvey, A.; Ojesina, A.I.; Pedamallu, C.S.; Ballon, G.; Jung, J.; Duke, F.; Leoncini, L.; De Falco, G.; Bressman, E.; Tam, W.; et al. The tumor virus landscape of AIDS-related lymphomas. Blood 2015, 125, e14–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolcetti, R.; Gloghini, A.; Caruso, A.; Carbone, A. A lymphomagenic role for HIV beyond immune suppression? Blood 2016, 127, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, J.; Germi, R.; Lancar, R.; Algarte-Genin, M.; Hendel-Chavez, H.; Taoufik, Y.; Mounier, N.; Partisani, M.; Bonnet, F.; Meyohas, M.-C.; et al. Epstein–Barr virus biomarkers have no prognostic value in HIV-related Hodgkin lymphoma in the modern combined antiretroviral therapy era. Aids 2019, 33, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muncunill, J.; Baptista, M.-J.; Hernandez-Rodríguez, Á.; Dalmau, J.; Garcia, O.; Tapia, G.; Moreno, M.; Sancho, J.-M.; Martínez-Picado, J.; Feliu, E.; et al. Plasma Epstein-Barr Virus Load as an Early Biomarker and Prognostic Factor of Human Immunodeficiency Virus–related Lymphomas. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 68, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul-Haq, I.; Dalla Pria, A.; Suardi, E.; Pinato, D.J.; Froeling, F.; Forni, J.; Randell, P.; Bower, M. Blood Epstein–Barr virus DNA does not predict outcome in advanced HIV-associated Hodgkin lymphoma. Med. Oncol. 2018, 35, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, J.; Germi, R.; Costagliola, D.; Morand, P.; Besson, C. Utility of Epstein-Barr Virus Biomarkers in Human Immunodeficiency Virus–related Lymphomas in the Modern Combined Antiretroviral Therapy Era. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 68, 891–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, N.D.; Randall, C.; Painschab, M.; Seguin, R.; Kaimila, B.; Kasonkanji, E.; Zuze, T.; Krysiak, R.; Sanders, M.K.; Elliott, A.; et al. High pretreatment plasma Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA level is a poor prognostic marker in HIV-associated, EBV-negative diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Malawi. Cancer Med. 2019, 9, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, J.; Germi, R.; Lancar, R.; Algarte-Genin, M.; Hendel-Chavez, H.; Taoufik, Y.; Mounier, N.; Partisani, M.; Bonnet, F.; Meyohas, M.-C.; et al. Prospective evaluation of blood Epstein–Barr virus DNA load and antibody profile in HIV-related non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Aids 2021, 35, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halec, G.; Waterboer, T.; Brenner, N.; Butt, J.; Hardy, W.D.; D’Souza, G.; Wolinsky, S.; Macatangay, B.J.; Pawlita, M.; Detels, R.; et al. Serological Assessment of 18 Pathogens and Risk of AIDS-Associated Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Am. J. Ther. 2019, 80, e53–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, S.J.; Blank, B.S.N.; Smits, P.H.M.; Meenhorst, P.L.; Middeldorp, J. High Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) DNA loads in HIV-infected patients: Correlation with antiretroviral therapy and quantitative EBV serology. Aids 2002, 16, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, S.J.; Smits, P.H.; Verkuijlen, S.A.; AP Rockx, D.; van Gorp, E.C.; Mulder, J.W.; Middeldorp, J.M. Aberrant Epstein–Barr virus persistence in HIV carriers is characterized by anti-Epstein–Barr virus IgA and high cellular viral loads with restricted transcription. Aids 2007, 21, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piriou, E.R.; van Dort, K.; Nanlohy, N.M.; Miedema, F.; van Oers, M.H.; van Baarle, D. Altered EBV Viral Load Setpoint after HIV Seroconversion Is in Accordance with Lack of Predictive Value of EBV Load for the Occurrence of AIDS-Related Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 6931–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamay, M.; Kanakry, J.A.; Low, J.S.W.; Horowitz, N.A.; Journo, G.; Ahuja, A.; Eran, Y.; Barzilai, E.; Dann, E.J.; Stone, J.; et al. CpG methylation in cell-free Epstein-Barr virus DNA in patients with EBV-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1624–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierickx, D.; Habermann, T.M. Post-Transplantation Lymphoproliferative Disorders in Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styczynski, J.; Van Der Velden, W.; Fox, C.P.; Engelhard, D.; de la Camara, R.; Cordonnier, C.; Ljungman, P. Management of Epstein-Barr Virus infections and post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders in patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Sixth European Conference on Infections in Leukemia (ECIL-6) guidelines. Haematologica 2016, 101, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, U.D.; Preiksaitis, J.K. Practice, the A.I.D.C. of Post-Transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorders, Epstein-Barr Virus Infection, and Disease in Solid Organ Transplantation: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin. Transplant. 2019, 33, e13652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borde, C.; Quignon, F.; Amiel, C.; Gozlan, J.; Marechal, V.; Brissot, E. Methyl-qPCR: A new method to investigate Epstein–Barr virus infection in post-transplant lymphoproliferative diseases. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germi, R.; Guigue, N.; Lupo, J.; Semenova, T.; Grossi, L.; Vermeulen, O.; Epaulard, O.; de Fraipont, F.; Morand, P. Methylation of Epstein-Barr virus Rta promoter in EBV primary infection, reactivation and lymphoproliferation. J. Med Virol. 2016, 88, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, T.; Lupo, J.; Alain, S.; Perrin-Confort, G.; Grossi, L.; Dimier, J.; Epaulard, O.; Morand, P.; Germi, R. Multicenter Evaluation of Whole-Blood Epstein-Barr Viral Load Standardization Using the WHO International Standard. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 1746–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarotto, T.; Chiereghin, A.; Piralla, A.; Gibertoni, D.; Piccirilli, G.; Turello, G.; Campanini, G.; Gabrielli, L.; Costa, C.; Comai, G.; et al. Kinetics of cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus DNA in whole blood and plasma of kidney transplant recipients: Implications on management strategies. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, J.; Yong, M.; Greenwood, M.; Kong, D.C.M.; Chen, S.C.A.; Rawlinson, W.; Slavin, M. Epstein-Barr virus related post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder prevention strategies in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, e2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Yang, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhu, M.; Ai, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, B.; Shao, L.; Zhang, W. Clinical application of Epstein-Barr virus DNA loads in Epstein-Barr virus-associated diseases: A cohort study. J. Infect. 2020, 82, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Juan, R.; Fernández-Ruiz, M.; Ruiz-Ruigómez, M.; López-Medrano, F.; Ruiz-Merlo, T.; Andrés, A.; Loinaz, C.; Len, O.; Azancot, M.A.; Montejo, M.; et al. A New Clinical and Immunovirological Score for Predicting the Risk of Late Severe Infection in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients: The CLIV Score. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.; Buisson, M.; Lupo, J.; Agbalika, F.; Socié, G.; Germi, R.; Baccard, M.; Imbert-Marcille, B.-M.; Dantal, J.; Morand, P.; et al. Lytic EBV infection investigated by detection of Soluble Epstein-Barr virus ZEBRA in the serum of patients with PTLD. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, J.; Wielandts, A.-S.; Buisson, M.; CRYOSTEM Consortium; Habib, M.; Hamoudi, M.; Morand, P.; Verduyn-Lunel, F.; Caillard, S.; Drouet, E. High Predictive Value of the Soluble ZEBRA Antigen (Epstein-Barr Virus Trans-Activator Zta) in Transplant Patients with PTLD. Pathogens 2022, 11, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, J.; Dean, J.; De Gascun, C.F.; Riordan, M.; Sweeney, C.; Connell, J.; Awan, A. Plasma EBV microRNAs in paediatric renal transplant recipients. J. Nephrol. 2017, 31, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, O.M. Biomarkers for PTLD diagnosis and therapies. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 35, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Enriquez, J.; Rao, M.; Glass, M.; Balachandran, Y.; Syed, S.; Twist, C.J.; Weinberg, K.; Boyd, S.D.; Bernstein, D.; et al. Host microRNAs are decreased in pediatric solid-organ transplant recipients during EBV+ Post-transplant Lymphoproliferative Disorder. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 994552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dojcinov, S.D.; Venkataraman, G.; Pittaluga, S.; Wlodarska, I.; Schrager, J.A.; Raffeld, M.; Hills, R.K.; Jaffe, E.S. Age-related EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders in the Western population: A spectrum of reactive lymphoid hyperplasia and lymphoma. Blood 2011, 117, 4726–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hujoel, I.A.; Rubio-Tapia, A.; Dao, L.N.; Porrata, L.F.; Kane, S.V. Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Mucocutaneous Ulcer in an Immunosuppressed Patient. ACG Case Rep. J. 2018, 5, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormack, C.; Huang, Q. EBV+ mucocutaneous ulcer: A new entity of WHO 2017. Blood 2018, 131, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinit, R.B.; Horan, K.L.; Dorer, R.K.; Aboulafia, D.M. Epstein-Barr Virus–Positive Mucocutaneous Ulcer: Case Report and Review of the First 100 Published Cases. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018, 19, e81–e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L. A common mechanism links Epstein-Barr virus infections and autoimmune diseases. J. Med Virol. 2023, 95, e28363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, M.P.; Goldschmidt, C.H.; Rae-Grant, A.D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA 2021, 325, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldan, S.S.; Lieberman, P.M. Epstein–Barr virus and multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2022, 21, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisi, F.; Cross, A.H. MINI-review of Epstein-Barr virus involvement in multiple sclerosis etiology and pathogenesis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2022, 371, 577935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attfield, K.E.; Jensen, L.T.; Kaufmann, M.; Friese, M.A.; Fugger, L. The immunology of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 734–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjornevik, K.; Cortese, M.; Healy, B.C.; Kuhle, J.; Mina, M.J.; Leng, Y.; Elledge, S.J.; Niebuhr, D.W.; Scher, A.I.; Munger, K.L.; et al. Longitudinal analysis reveals high prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus associated with multiple sclerosis. Science 2022, 375, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanz, T.V.; Brewer, R.C.; Ho, P.P.; Moon, J.-S.; Jude, K.M.; Fernandez, D.; Fernandes, R.A.; Gomez, A.M.; Nadj, G.-S.; Bartley, C.M.; et al. Clonally expanded B cells in multiple sclerosis bind EBV EBNA1 and GlialCAM. Nature 2022, 603, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, M.; Kitamura, N.; Nagasawa, Y.; Tsuzuki, H.; Iwata, M.; Nagatsuka, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Imai, K.; Fujiwara, S. Are Viral Infections Key Inducers of Autoimmune Diseases? Focus on Epstein–Barr Virus. Viruses 2022, 14, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, J.B.; Chen, X.; Pujato, M.; Miller, D.; Maddox, A.; Forney, C.; Magnusen, A.F.; Lynch, A.; Chetal, K.; Yukawa, M.; et al. Transcription factors operate across disease loci, with EBNA2 implicated in autoimmunity. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwana, Y.; Takei, M.; Yajima, M.; Imadome, K.-I.; Inomata, H.; Shiozaki, M.; Ikumi, N.; Nozaki, T.; Shiraiwa, H.; Kitamura, N.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus Induces Erosive Arthritis in Humanized Mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample, J.; Young, L.; Martin, B.; Chatman, T.; Kieff, E.; Rickinson, A. Epstein-Barr virus types 1 and 2 differ in their EBNA-3A, EBNA-3B, and EBNA-3C genes. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 4084–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palser, A.L.; Grayson, N.E.; White, R.E.; Corton, C.; Correia, S.; Ba Abdullah, M.M.; Watson, S.J.; Cotten, M.; Arrand, J.R.; Murray, P.G.; et al. Genome Diversity of Epstein-Barr Virus from Multiple Tumor Types and Normal Infection. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 5222–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Smith, N.; Baresel, P.C.; Jackson, C.L.; Ogolla, S.; Toko, E.N.; Heit, S.; Piriou, E.; Sumba, O.P.; Middeldorp, J.; Colborn, K.L.; et al. Differences in the Epstein-Barr Virus gp350 IgA Antibody Response Are Associated With Increased Risk for Coinfection With a Second Strain of Epstein-Barr Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 219, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Wang, X.; Strong, M.; Concha, M.; Baddoo, M.; Xu, G.; Baribault, C.; Fewell, C.; Hulme, W.; Hedges, D.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of the Akata and Mutu Epstein-Barr Virus Strains. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Li, T.; Li, B.; Tsai, S.; Biggar, R.J.; Nkrumah, F.; Neequaye, J.; Gutierrez, M.; Epelman, S.; Mbulaiteye, S.M.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus from Burkitt Lymphoma biopsies from Africa and South America share novel LMP-1 promoter and gene variations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, L.; Riquelme, I.; Buchegger, K.; Abanto, M.; Ili, C.; Brebi, P. A reliable Epstein-Barr Virus classification based on phylogenomic and population analyses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, H.; Chiang, A.K.S. From Conventional to Next Generation Sequencing of Epstein-Barr Virus Genomes. Viruses 2016, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.; Zeng, Z.; Qi, P.; Li, X.; Guo, C.; Xiong, F.; Xiang, B.; Zhou, M.; Liao, Q.; Yu, J.; et al. Identification of genomic alterations in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived Epstein–Barr virus by whole-genome sequencing. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1517–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Fu, M.; Zheng, B.; Qiu, Q.; Huang, Z. Implication of viral microRNAs in the genesis and diagnosis of Epstein-Barr virus-associated tumors (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3433–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusalah, M.A.H.; Irekeola, A.A.; Shueb, R.H.; Jarrar, M.; Yean, C.Y. Prognostic Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) miRNA biomarkers for survival outcome in EBV-associated epithelial malignancies: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan-Jie, T.; Wei-Ting, W.; Yun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yi-Ning, L.; Yu-Lin, W.; Yi-Yi, L. EBV-microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in EBV-Related Fever: A Narrative Review. Curr. Mol. Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.-E.; Ng, W.L.; Marinov, G.K.; Yu, K.H.-O.; Tan, L.P.; Liau, E.S.; Goh, S.Y.; Yeo, K.S.; Yip, K.Y.; Lo, K.-W.; et al. Identification and characterization of a novel Epstein-Barr Virus-encoded circular RNA from LMP-2 Gene. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungerleider, N.; Concha, M.; Lin, Z.; Roberts, C.; Wang, X.; Cao, S.; Baddoo, M.; Moss, W.N.; Yu, Y.; Seddon, M.; et al. The Epstein Barr virus circRNAome. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernaudat, F.; Gustems, M.; Günther, J.; Oliva, M.F.; Buschle, A.; Göbel, C.; Pagniez, P.; Lupo, J.; Signor, L.; Müller, C.W.; et al. Structural basis of DNA methylation-dependent site selectivity of the Epstein–Barr virus lytic switch protein ZEBRA/Zta/BZLF1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 50, 490–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.K.J.; Jiang, P.; Chan, K.C.A.; Peng, W.; Shang, H.; Heung, M.M.S.; Cheng, S.H.; Zhang, H.; Tse, O.Y.O.; Raghupathy, R.; et al. Methylation analysis of plasma DNA informs etiologies of Epstein-Barr virus-associated diseases. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.F.; Rosales, C.; Lopez-Nieva, P.; Graña, O.; Ballestar, E.; Ropero, S.; Espada, J.; Melo, S.A.; Lujambio, A.; Fraga, M.F.; et al. The dynamic DNA methylomes of double-stranded DNA viruses associated with human cancer. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Su, X.; Choi, G.C.G.; Cao, Y.; Ambinder, R.F.; Tao, Q. Methylation profiling of Epstein-Barr virus immediate-early gene promoters, BZLF1 and BRLF1in tumors of epithelial, NK- and B-cell origins. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean-Pierre, V.; Lupo, J.; Buisson, M.; Morand, P.; Germi, R. Main Targets of Interest for the Development of a Prophylactic or Therapeutic Epstein-Barr Virus Vaccine. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 701611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, H.; Homad, L.J.; Wan, Y.-H.; Poudel, B.; Fiala, B.; Borst, A.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Walkey, C.; Price, J.; Wall, A.; et al. Immunization with a self-assembling nanoparticle vaccine displaying EBV gH/gL protects humanized mice against lethal viral challenge. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.-J.; Bu, W.; Nguyen, L.A.; Batchelor, J.D.; Kim, J.; Pittaluga, S.; Fuller, J.R.; Nguyen, H.; Chou, T.-H.; Cohen, J.I.; et al. A bivalent Epstein-Barr virus vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies that block infection and confer immunity in humanized mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabf3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Kim, J.; Bu, W.; Board, N.L.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hostal, A.; Andrews, S.F.; Gillespie, R.A.; Choe, M.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus gH/gL has multiple sites of vulnerability for virus neutralization and fusion inhibition. Immunity 2022, 55, 2135–2148.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| EBV-Associated Diseases | EBV Association | Latency Type |
|---|---|---|
| Infectious mononucleosis | 100% | Latency type III |
| Carcinomas | ||
| Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | 100% | Latency type II |
| Gastric carcinoma | 10% | Latency type I |
| Lymphomas | ||
| Hodgkin lymphoma In HIV-infected patients | 30% 90% | Latency type II |
| Endemic Burkitt lymphoma | >95% | Latency type I |
| Sporadic Burkitt lymphoma In HIV-infected patients | 20% 40% | Latency type I |
| Diffuse large B cell lymphoma | 5–15% | Latency type III |
| Extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma | 100% | Latency type II |
| Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders SOT HSCT | 60–80% 100% | Latency type III |
| Multiple sclerosis | NA | NA |
| Category | Clonality | |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Destructive PTLD | Nonclonal | |
| Plasmacytic hyperplasia | ||
| Infectious mononucleosis | ||
| Florid follicular hyperplasia | ||
| Polymorphic PTLD | clonal | |
| Monomorphic PTLD (classified according to the lymphoma to which they correspond) | clonal | |
| B-cell neoplasm | ||
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | ||
| Burkitt lymphoma | ||
| Plasma cell myeloma | ||
| Plasmacytoma | ||
| Others * | ||
| T-cell neoplasm | ||
| Peripheral T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified | ||
| Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma | ||
| Others | ||
| Classic Hodgkin lymphoma PTLD | clonal | |
| EBV-Associated Diseases | Anti-EBV Antibodies | Blood EBV DNA |
|---|---|---|
| Infectious mononucleosis | Diagnosis | Positive in serum for 15 days |
| Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Screening | ++ plasma/serum (screening, prognosis, treatment response) |
| EBV-positive Gastric carcinoma | No | require further evaluations |
| EBV-positive Hodgkin lymphoma | ? (atypical profile) | + (prognosis) |
| Endemic Burkitt lymphoma | Research | require further evaluations |
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma | No | + (prognosis) |
| Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma | Research | ++ (prognosis, treatment response) |
| AIDS-related lymphoma | ? | require further evaluations (prognosis?) |
| Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders | Serological status | ++ (prevention, diagnosis) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lupo, J.; Truffot, A.; Andreani, J.; Habib, M.; Epaulard, O.; Morand, P.; Germi, R. Virological Markers in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Diseases. Viruses 2023, 15, 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15030656
Lupo J, Truffot A, Andreani J, Habib M, Epaulard O, Morand P, Germi R. Virological Markers in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Diseases. Viruses. 2023; 15(3):656. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15030656
Chicago/Turabian StyleLupo, Julien, Aurélie Truffot, Julien Andreani, Mohammed Habib, Olivier Epaulard, Patrice Morand, and Raphaële Germi. 2023. "Virological Markers in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Diseases" Viruses 15, no. 3: 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15030656
APA StyleLupo, J., Truffot, A., Andreani, J., Habib, M., Epaulard, O., Morand, P., & Germi, R. (2023). Virological Markers in Epstein–Barr Virus-Associated Diseases. Viruses, 15(3), 656. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15030656






