Detection of Influenza D-Specific Antibodies in Bulk Tank Milk from Swedish Dairy Farms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Indirect ELISA
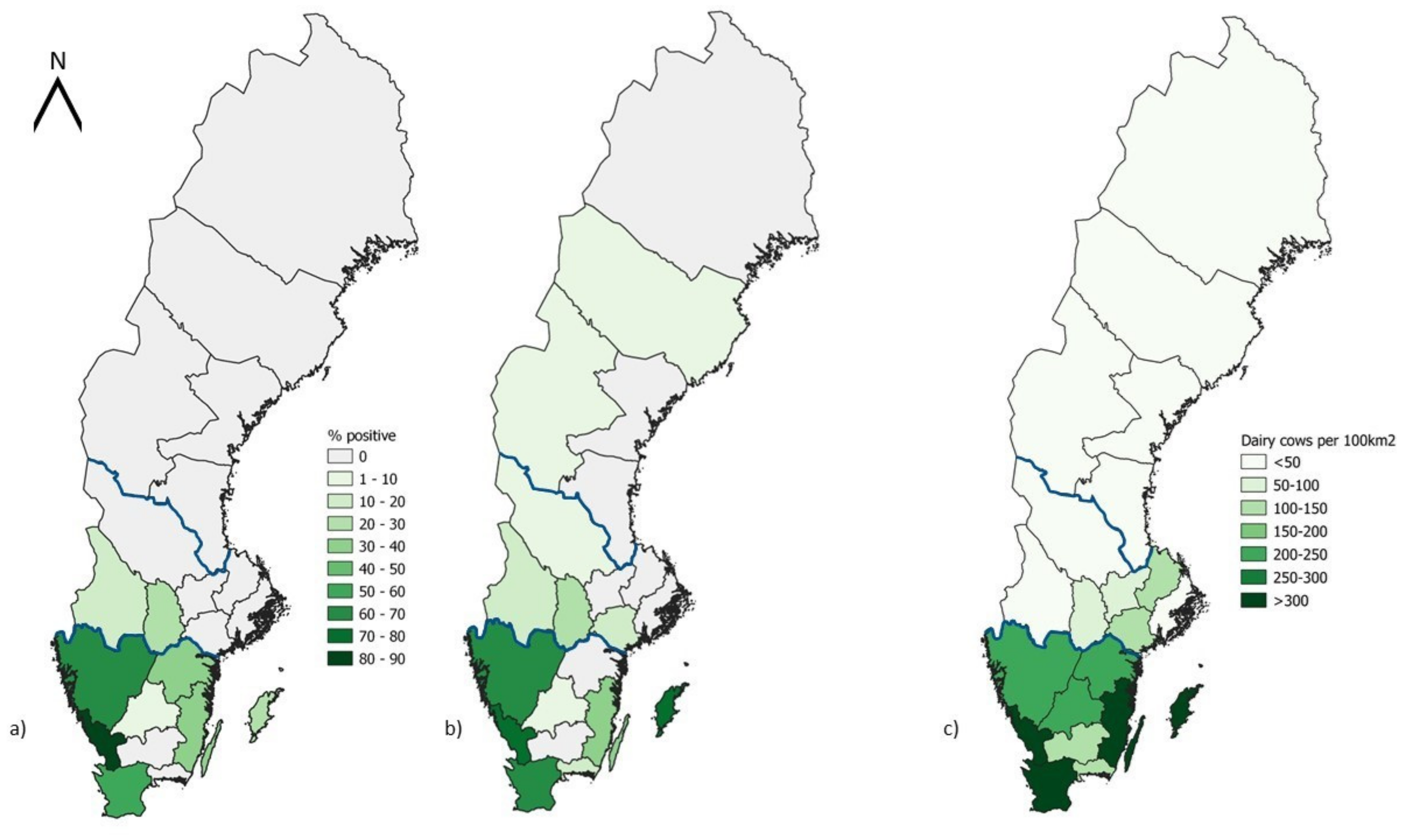
2.3. Map Design
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blakebrough-Hall, C.; McMeniman, J.P.; González, L.A. An evaluation of the economic effects of bovine respiratory disease on animal performance, carcass traits, and economic outcomes in feedlot cattle defined using four BRD diagnosis methods. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepak; Aly, S.S.; Love, W.J.; Blanchard, P.C.; Crossley, B.; Van Eenennaam, A.L.; Lehenbauer, T.W. Etiology and risk factors for bovine respiratory disease in pre-weaned calves on California dairies and calf ranches. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 197, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, R.W. Viruses in Bovine Respiratory Disease in North America Knowledge Advances Using Genomic Testing. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 36, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, N.; Cernicchiaro, N.; Torres, S.; Li, F.; Hause, B.M. Metagenomic characterization of the virome associated with bovine respiratory disease in feedlot cattle identified novel viruses and suggests an etiologic role for influenza D virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hause, B.M.; Collin, E.A.; Liu, R.X.; Huang, B.; Sheng, Z.Z.; Lu, W.X.; Wang, D.; Nelson, E.A.; Li, F. Characterization of a Novel Influenza Virus in Cattle and Swine: Proposal for a New Genus in the Orthomyxoviridae Family. mBio 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, I.J.; Fort, M.; Pasucci, J.; Moreno, F.; Gimenez, H.; Näslund, K.; Hägglund, S.; Zohari, S.; Valarcher, J.F. Seroprevalence of influenza D virus in bulls in Argentina. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, L.; Olivier, A.K.; Genova, S.; Epperson, W.B.; Smith, D.R.; Schneider, L.; Barton, K.; McCuan, K.; Webby, R.J.; Wan, X.-F. Pathogenesis of Influenza D Virus in Cattle. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5636–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horimoto, T.; Hiono, T.; Mekata, H.; Odagiri, T.; Lei, Z.; Kobayashi, T.; Norimine, J.; Inoshima, Y.; Hikono, H.; Murakami, K.; et al. Nationwide Distribution of Bovine Influenza D Virus Infection in Japan. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donovan, T.; Donohoe, L.; Ducatez, M.F.; Meyer, G.; Ryan, E. Seroprevalence of influenza D virus in selected sample groups of Irish cattle, sheep and pigs. Ir. Vet. J. 2019, 72, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, J.; Eichenbaum, A.; Belin, J.; Gaudino, M.; Guillotin, J.; Alzieu, J.-P.; Nicollet, P.; Brugidou, R.; Gueneau, E.; Michel, E.; et al. Serological Evidence of Influenza D Virus Circulation Among Cattle and Small Ruminants in France. Viruses 2019, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanogo, I.N.; Kouakou, C.; Batawui, K.; Djegui, F.; Byarugaba, D.K.; Adjin, R.; Adjabli, K.; Wabwire-Mangen, F.; Erima, B.; Atim, G.; et al. Serological Surveillance of Influenza D Virus in Ruminants and Swine in West and East Africa, 2017–2020. Viruses 2021, 13, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoeck, C.J.; Oliva, J.; Pauly, M.; Losch, S.; Wildschutz, F.; Muller, C.P.; Hübschen, J.M.; Ducatez, M.F. Influenza D Virus Circulation in Cattle and Swine, Luxembourg, 2012–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1388–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lion, A.; Secula, A.; Rançon, C.; Boulesteix, O.; Pinard, A.; Deslis, A.; Hägglund, S.; Salem, E.; Cassard, H.; Näslund, K.; et al. Enhanced Pathogenesis Caused by Influenza D Virus and Mycoplasma bovis Coinfection in Calves: A Disease Severity Linked with Overexpression of IFN-γ as a Key Player of the Enhanced Innate Immune Response in Lungs. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzetto, E.; Bortolami, A.; Fusaro, A.; Mazzacan, E.; Maniero, S.; Vascellari, M.; Beato, M.S.; Schiavon, E.; Chiapponi, C.; Terregino, C.; et al. Replication of Influenza D Viruses of Bovine and Swine Origin in Ovine Respiratory Explants and Their Attachment to the Respiratory Tract of Bovine, Sheep, Goat, Horse, and Swine. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, E.; Hägglund, S.; Cassard, H.; Corre, T.; Näslund, K.; Foret, C.; Gauthier, D.; Pinard, A.; Delverdier, M.; Zohari, S.; et al. Pathogenesis, Host Innate Immune Response, and Aerosol Transmission of Influenza D Virus in Cattle. J. Virol. 2019, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holwerda, M.; Kelly, J.; Laloli, L.; Stürmer, I.; Portmann, J.; Stalder, H.; Dijkman, R. Determining the Replication Kinetics and Cellular Tropism of Influenza D Virus on Primary Well-Differentiated Human Airway Epithelial Cells. Viruses 2019, 11, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Qi, J.; Khedri, Z.; Diaz, S.; Yu, H.; Chen, X.; Varki, A.; Shi, Y.; Gao, G.F. An Open Receptor-Binding Cavity of Hemagglutinin-Esterase-Fusion Glycoprotein from Newly-Identified Influenza D Virus: Basis for Its Broad Cell Tropism. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trombetta, C.M.; Marchi, S.; Manini, I.; Kistner, O.; Li, F.; Piu, P.; Manenti, A.; Biuso, F.; Sreenivasan, C.; Druce, J.; et al. Influenza D Virus: Serological Evidence in the Italian Population from 2005 to 2017. Viruses 2020, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.K.; Ma, W.; McDaniel, C.J.; Gray, G.C.; Lednicky, J.A. Serologic evidence of exposure to influenza D virus among persons with occupational contact with cattle. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 81, 31–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Gaunt, E.R.; Digard, P.; Templeton, K.; Simmonds, P. Detection of influenza C virus but not influenza D virus in Scottish respiratory samples. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 74, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlson, A.; Blanco-Penedo, I.; Fall, N. Comparison of Bovine coronavirus-specific and Bovine respiratory syncytial virus-specific antibodies in serum versus milk samples detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig 2014, 26, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautienius, A.; Dudas, G.; Simkute, E.; Grigas, J.; Zakiene, I.; Paulauskas, A.; Armonaite, A.; Zienius, D.; Slyzius, E.; Stankevicius, A. Bulk Milk Tank Samples Are Suitable to Assess Circulation of Tick-Borne Encephalitis Virus in High Endemic Areas. Viruses 2021, 13, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanlun, A.; Näslund, K.; Aiumlamai, S.; Björkman, C. Use of bulk milk for detection of Neospora caninum infection in dairy herds in Thailand. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 110, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, I.J.; Fort, M.; Pasucci, J.; Moreno, F.; Gimenez, H.; Naeslund, K.; Haegglund, S.; Zohari, S.; Valarcher, J.F. Seroprevalence of influenza D virus in bulls in Argentina—Authors’ response. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig 2020, 32, 633–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudeau, F.; Ohlson, A.; Emanuelson, U. Associations between bovine coronavirus and bovine respiratory syncytial virus infections and animal performance in Swedish dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Odagiri, T.; Melaku, S.K.; Bazartseren, B.; Ishida, H.; Takenaka-Uema, A.; Muraki, Y.; Sentsui, H.; Horimoto, T. Influenza D Virus Infection in Dromedary Camels, Ethiopia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1224–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedland, H.; Wollman, J.; Sreenivasan, C.; Quast, M.; Singrey, A.; Fawcett, L.; Christopher-Hennings, J.; Nelson, E.; Kaushik, R.S.; Wang, D.; et al. Serological evidence for the co-circulation of two lineages of influenza D viruses in equine populations of the Midwest United States. Zoonoses Public Health 2018, 65, E148–E154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, L.; Luo, K.; Olivier, A.K.; Cunningham, F.L.; Blackmon, S.; Hanson-Dorr, K.; Sun, H.; Baroch, J.; Lutman, M.W.; Quade, B.; et al. Influenza D Virus Infection in Feral Swine Populations, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, M.; Sreenivasan, C.; Sexton, G.; Nedland, H.; Singrey, A.; Fawcett, L.; Miller, G.; Lauer, D.; Voss, S.; Pollock, S.; et al. Serological evidence for the presence of influenza D virus in small ruminants. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 180, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägglund, S.; Näslund, K.; Svensson, A.; Lefverman, C.; Enül, H.; Pascal, L.; Siltenius, J.; Holzhauer, M.; Delabouglise, A.; Österberg, J.; et al. Longitudinal study of the immune response and memory following natural bovine respiratory syncytial virus infections in cattle of different age. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, J.; Litwińczuk, Z.; Brodziak, A.; Barłowska, J. Lactoferrin, lysozyme and immunoglobulin G content in milk of four breeds of cows managed under intensive production system. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2010, 13, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milovanović, M.; Milićević, V.; Radojičić, S.; Valčić, M.; Hoffmann, B.; Dietze, K. Suitability of individual and bulk milk samples to investigate the humoral immune response to lumpy skin disease vaccination by ELISA. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, D.E.; Nelson, S.V.; Reid, E.D.; Nagy, D.W.; Dahl, G.E.; Constable, P.D. Effect of colostral volume, interval between calving and first milking, and photoperiod on colostral IgG concentrations in dairy cows. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2010, 237, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 2019 | 2020 | Overall | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | County | Sample Size | NPS a (%) b | Sample Size | NPS a (%) b | Sample Size | NPS a (%) b | ||
| Norrland (North) | Gävleborg | 13 | 0 (0) | 7 | 0 (0) | 20 | 0 | ||
| Norrbotten | 5 | 0 (0) | 6 | 0 (0) | 11 | 0 | |||
| Västerbotten | 14 | 0 (0) | 41 | 1 (2.4) | 55 | 1 (1.8) | |||
| Västernorrland | 14 | 0 (0) | 6 | 0 (0) | 20 | 0 | |||
| Jämtland | 5 | 0 (0) | 14 | 1 (7.1) | 19 | 1 (5.3) | |||
| Total Norrland | 51 | 0 (0) | 74 | 2 (2.7) | 125 | 2 (1.6) | |||
| Svealand (Center) | Örebro | 8 | 2 (25) | 13 | 3 (23.1) | 21 | 5 (23.8) | ||
| Västmanland | 10 | 0 (0) | 3 | 0 (0) | 13 | 0 | |||
| Dalarna | 14 | 0 (0) | 12 | 1 (8.3) | 26 | 1 (3.8) | |||
| Värmland | 16 | 2 (13) | 10 | 1 (10) | 26 | 3 (11.5) | |||
| Stockholm | 5 | 0 (0) | 7 | (0) | 12 | 0 | |||
| Uppsala | 13 | 0 (0) | 12 | (0) | 25 | 0 | |||
| Södermanland | 19 | 0 (0) | 15 | 2 (13.3) | 34 | 2 (5.9) | |||
| Total Svealand | 85 | 4 (4.7) | 72 | 7 (9.7) | 157 | 11(7) | |||
| Götaland (South) | Östergötland | 16 | 6 (38) | 6 | 0 (0) | 22 | 6 (27.3) | ||
| Västra Götaland | 76 | 51 (67) | 57 | 39 (68.4) | 133 | 90 (67.7) | |||
| Gotaland | 24 | 5 (21) | 7 | 5 (71.4) | 31 | 10 (32.2) | |||
| Halland | 37 | 31 (84) | 13 | 10 (76.9) | 50 | 41 (82) | |||
| Blekinge | 5 | 0 (0) | 7 | 1 (14.3) | 12 | 1 (8.3) | |||
| Skåne | 56 | 33 (59) | 40 | 25 (62.5) | 96 | 58 (60.4) | |||
| Kalmar | 47 | 15 (32) | 61 | 46 (75.4) | 108 | 61 (56.5) | |||
| Jönköping | 40 | 2 (5) | 1 | 0 (0) | 41 | 2 (4.9) | |||
| Kronoberg | 24 | 0 (0) | 0 | 0 | 24 | 0 | |||
| Total Götaland | 325 | 143 (44) | 192 | 126 (65.6) | 517 | 269 (52) | |||
| Total Sweden | 461 | 147 (31.8) | 338 | 135 (39.9) | 799 | 282 (35.2) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarez, I.; Hägglund, S.; Näslund, K.; Eriksson, A.; Ahlgren, E.; Ohlson, A.; Ducatez, M.F.; Meyer, G.; Valarcher, J.-F.; Zohari, S. Detection of Influenza D-Specific Antibodies in Bulk Tank Milk from Swedish Dairy Farms. Viruses 2023, 15, 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040829
Alvarez I, Hägglund S, Näslund K, Eriksson A, Ahlgren E, Ohlson A, Ducatez MF, Meyer G, Valarcher J-F, Zohari S. Detection of Influenza D-Specific Antibodies in Bulk Tank Milk from Swedish Dairy Farms. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):829. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040829
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarez, Ignacio, Sara Hägglund, Katarina Näslund, Axel Eriksson, Evelina Ahlgren, Anna Ohlson, Mariette F. Ducatez, Gilles Meyer, Jean-Francois Valarcher, and Siamak Zohari. 2023. "Detection of Influenza D-Specific Antibodies in Bulk Tank Milk from Swedish Dairy Farms" Viruses 15, no. 4: 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040829
APA StyleAlvarez, I., Hägglund, S., Näslund, K., Eriksson, A., Ahlgren, E., Ohlson, A., Ducatez, M. F., Meyer, G., Valarcher, J.-F., & Zohari, S. (2023). Detection of Influenza D-Specific Antibodies in Bulk Tank Milk from Swedish Dairy Farms. Viruses, 15(4), 829. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040829






