Expanding the Hepatitis E Virus Toolbox: Selectable Replicons and Recombinant Reporter Genomes
Abstract
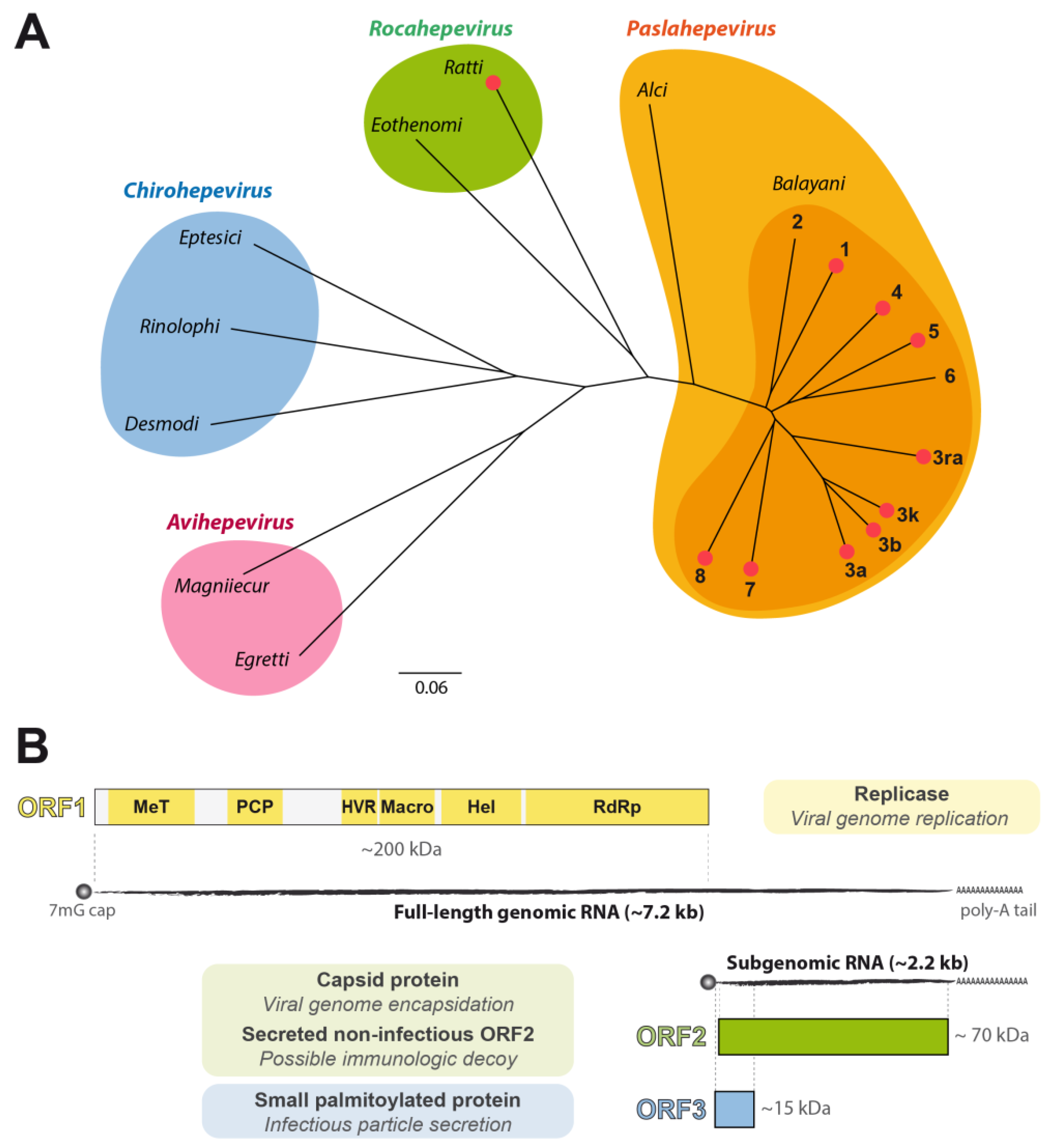
1. Introduction
2. Subgenomic Replicons as Tools to Study HEV RNA Replication
| Reporter/ Selection Gene | Size (bp) | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gluc | 555 | Replication kinetics | [21] |
| GFP | 720 | Evaluation replication level/cell sorting | [38] |
| Neo | 795 | Selection of a cell population | [48] |
| Rluc | 932 | Replication kinetics | [42] |
| GFP-Zeo | 1077 | Selection and eval. replication level | [53] |
| BSR-2A-ZsGreen | 1153 | Selection and eval. replication level | [54] |
| Gluc-2A-Neo | 1408 | Selection and replication kinetics | [55] |
| Fluc | 1659 | Replication kinetics | [44] |
3. Infectious HEV Clones Harboring Reporters

4. Challenges and Future Developments
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balayan, M.S.; Andjaparidze, A.G.; Savinskaya, S.S.; Ketiladze, E.S.; Braginsky, D.M.; Savinov, A.P.; Poleschuk, V.F. Evidence for a virus in non-A, non-B hepatitis transmitted via the fecal-oral route. Intervirology 1983, 20, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, G.R.; Purdy, M.A.; Kim, J.P.; Luk, K.C.; Young, L.M.; Fry, K.E.; Bradley, D.W. Isolation of a cDNA from the virus responsible for enterically transmitted non-A, non-B hepatitis. Science 1990, 247, 1335–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdy, M.A.; Drexler, J.F.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; de Souza, W.M.; Ulrich, R.G.; Smith, D.B. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepeviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.H.; Tan, B.H.; Teo, E.C.; Lim, S.G.; Dan, Y.Y.; Wee, A.; Aw, P.P.; Zhu, Y.; Hibberd, M.L.; Tan, C.K.; et al. Chronic infection with camelid hepatitis E virus in a liver transplant recipient who regularly consumes camel meat and milk. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 355–357.e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Juarez, A.; Frias, M.; Perez, A.B.; Pineda, J.A.; Reina, G.; Fuentes-Lopez, A.; Freyre-Carrillo, C.; Ramirez-Arellano, E.; Alados, J.C.; Rivero, A.; et al. Orthohepevirus C infection as an emerging cause of acute hepatitis in Spain: First report in Europe. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Yip, C.C.Y.; Lo, K.H.Y.; Wu, S.; Situ, J.; Chew, N.F.S.; Leung, K.H.; Chan, H.S.Y.; Wong, S.C.Y.; Leung, A.W.S.; et al. Hepatitis E virus species C Iinfection in humans, Hong Kong. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, K.E.; Labrique, A.B.; Kmush, B.L. Epidemiology of genotype 1 and 2 hepatitis E virus infections. Cold. Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a031732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heemelaar, S.; Hangula, A.L.; Chipeio, M.L.; Josef, M.; Stekelenburg, J.; van den Akker, T.H.; Pischke, S.; Mackenzie, S.B.P. Maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancies complicated by acute hepatitis E and the impact of HIV status: A cross-sectional study in Namibia. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debing, Y.; Moradpour, D.; Neyts, J.; Gouttenoire, J. Update on hepatitis E virology: Implications for clinical practice. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamar, N.; Izopet, J.; Pavio, N.; Aggarwal, R.; Labrique, A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Dalton, H.R. Hepatitis E virus infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on hepatitis E virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, V.P.; Anang, S.; Subramani, C.; Madhvi, A.; Bakshi, K.; Srivastava, A.; Shalimar; Nayak, B.; Ranjith Kumar, C.T.; Surjit, M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induced synthesis of a novel viral factor mediates efficient replication of genotype-1 hepatitis E virus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Debing, Y.; Jankevicius, G.; Neyts, J.; Ahel, I.; Coutard, B.; Canard, B. Viral macro domains reverse protein ADP-ribosylation. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 8478–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Purdy, M.A.; Rozanov, M.N.; Reyes, G.R.; Bradley, D.W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: Delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8259–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montpellier, C.; Wychowski, C.; Sayed, I.M.; Meunier, J.C.; Saliou, J.M.; Ankavay, M.; Bull, A.; Pillez, A.; Abravanel, F.; Helle, F.; et al. Hepatitis E virus lifecycle and identification of 3 forms of the ORF2 capsid protein. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 211–223.e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Ying, D.; Lhomme, S.; Tang, Z.; Walker, C.M.; Xia, N.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Z. Origin, antigenicity, and function of a secreted form of ORF2 in hepatitis E virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4773–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Tanggis; Nishizawa, T.; Nishiyama, T.; Primadharsini, P.P.; Okamoto, H. Characterization of the quasi-enveloped hepatitis E virus particles released by the cellular exosomal pathway. J. Virol. 2017, 91, e00822-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouttenoire, J.; Pollan, A.; Abrami, L.; Oechslin, N.; Mauron, J.; Matter, M.; Oppliger, J.; Szkolnicka, D.; Dao Thi, V.L.; van der Goot, F.G.; et al. Palmitoylation mediates membrane association of hepatitis E virus ORF3 protein and is required for infectious particle secretion. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, S.K.; Ansari, I.H.; Durgapal, H.; Agrawal, S.; Jameel, S. The in vitro-synthesized RNA from a cDNA clone of hepatitis E virus is infectious. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 2430–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, S.U.; Zhang, M.; Meng, X.J.; Nguyen, H.; St Claire, M.; Govindarajan, S.; Huang, Y.K.; Purcell, R.H. Recombinant hepatitis E virus genomes infectious for primates: Importance of capping and discovery of a cis-reactive element. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15270–15275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Faulk, K.; Mather, K.; Torian, U.; Engle, R.E.; Emerson, S.U. Adaptation of a genotype 3 hepatitis E virus to efficient growth in cell culture depends on an inserted human gene segment acquired by recombination. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5697–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiota, T.; Li, T.C.; Yoshizaki, S.; Kato, T.; Wakita, T.; Ishii, K. The hepatitis E virus capsid C-terminal region is essential for the viral life cycle: Implication for viral genome encapsidation and particle stabilization. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6031–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Ichiyama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Okamoto, H. Construction of an infectious cDNA clone of hepatitis E virus strain JE03-1760F that can propagate efficiently in cultured cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2009, 90, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, T.L.; Bruening, J.; Todt, D.; Steinmann, E. Cell culture systems for the study of hepatitis E virus. Antiviral Res. 2019, 163, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoba, L.; Feagins, A.R.; Opriessnig, T.; Cossaboom, C.M.; Dryman, B.A.; Huang, Y.W.; Meng, X.J. Rescue of a genotype 4 human hepatitis E virus from cloned cDNA and characterization of intergenotypic chimeric viruses in cultured human liver cells and in pigs. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2183–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.C.; Bai, H.; Yoshizaki, S.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Doan, Y.H.; Takahashi, K.; Mishiro, S.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T. Genotype 5 hepatitis E virus produced by a reverse genetics system has the potential for zoonotic infection. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.C.; Zhou, X.; Yoshizaki, S.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Takeda, N.; Wakita, T. Production of infectious dromedary camel hepatitis E virus by a reverse genetic system: Potential for zoonotic infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1104–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ami, Y.; Suzaki, Y.; Doan, Y.H.; Takeda, N.; Muramatsu, M.; Li, T.C. Generation of a bactrian camel hepatitis E virus by a reverse genetics system. J. Gen. Virol. 2021, 102, 001618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Kim, A.S.; Kafai, N.M.; Earnest, J.T.; Shah, A.P.; Case, J.B.; Basore, K.; Gilliland, T.C.; Sun, C.; Nelson, C.A.; et al. LDLRAD3 is a receptor for Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus. Nature 2020, 588, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbajo-Lozoya, J.; Muller, M.A.; Kallies, S.; Thiel, V.; Drosten, C.; von Brunn, A. Replication of human coronaviruses SARS-CoV, HCoV-NL63 and HCoV-229E is inhibited by the drug FK506. Virus Res. 2012, 165, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.C.; Graham, R.L.; Lu, X.; Peek, C.T.; Denison, M.R. Coronavirus replicase-reporter fusions provide quantitative analysis of replication and replication complex formation. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5319–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- V’Kovski, P.; Gerber, M.; Kelly, J.; Pfaender, S.; Ebert, N.; Braga Lagache, S.; Simillion, C.; Portmann, J.; Stalder, H.; Gaschen, V.; et al. Determination of host proteins composing the microenvironment of coronavirus replicase complexes by proximity-labeling. eLife 2019, 8, e42037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, C.; Shi, P.Y. Construction of stable reporter flaviviruses and their applications. Viruses 2020, 12, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieger, N.; Lohmann, V.; Bartenschlager, R. Enhancement of hepatitis C virus RNA replication by cell culture-adaptive mutations. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 4614–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, E.; Pietschmann, T. Cell culture systems for hepatitis C virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 369, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannemann, H. Viral replicons as valuable tools for drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, V. Hepatitis C virus cell culture models: An encomium on basic research paving the road to therapy development. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2019, 208, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, S.U.; Nguyen, H.; Graff, J.; Stephany, D.A.; Brockington, A.; Purcell, R.H. In vitro replication of hepatitis E virus (HEV) genomes and of an HEV replicon expressing green fluorescent protein. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 4838–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerson, S.U.; Nguyen, H.T.; Torian, U.; Mather, K.; Firth, A.E. An essential RNA element resides in a central region of hepatitis E virus ORF2. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graff, J.; Nguyen, H.; Kasorndorkbua, C.; Halbur, P.G.; St Claire, M.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. In vitro and in vivo mutational analysis of the 3’-terminal regions of hepatitis E virus genomes and replicons. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudupakam, R.S.; Huang, Y.W.; Opriessnig, T.; Halbur, P.G.; Pierson, F.W.; Meng, X.J. Deletions of the hypervariable region (HVR) in open reading frame 1 of hepatitis E virus do not abolish virus infectivity: Evidence for attenuation of HVR deletion mutants in vivo. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Huang, Y.W.; Meng, X.J. The nucleotides on the stem-loop RNA structure in the junction region of the hepatitis E virus genome are critical for virus replication. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 13040–13044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Ni, Y.Y.; Meng, X.J. Substitution of amino acid residue V1213 in the helicase domain of the genotype 3 hepatitis E virus reduces virus replication. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netzler, N.E.; Enosi Tuipulotu, D.; Vasudevan, S.G.; Mackenzie, J.M.; White, P.A. Antiviral candidates for treating hepatitis E virus infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00003-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todt, D.; Francois, C.; Anggakusuma; Behrendt, P.; Engelmann, M.; Knegendorf, L.; Vieyres, G.; Wedemeyer, H.; Hartmann, R.; Pietschmann, T.; et al. Antiviral activities of different interferon types and subtypes against hepatitis E virus replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2132–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tian, D.; Sooryanarain, H.; Mahsoub, H.M.; Heffron, C.L.; Hassebroek, A.M.; Meng, X.J. Two mutations in the ORF1 of genotype 1 hepatitis E virus enhance virus replication and may associate with fulminant hepatic failure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2207503119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cierniak, F.; Ulrich, R.G.; Groschup, M.H.; Eiden, M. A modular hepatitis E virus replicon system for studies on the role of ORF1-encoded polyprotein domains. Pathogens 2022, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, J.; Torian, U.; Nguyen, H.; Emerson, S.U. A bicistronic subgenomic mRNA encodes both the ORF2 and ORF3 proteins of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 5919–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao Thi, V.L.; Debing, Y.; Wu, X.; Rice, C.M.; Neyts, J.; Moradpour, D.; Gouttenoire, J. Sofosbuvir inhibits hepatitis E virus replication in vitro and results in an additive effect when combined with ribavirin. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 82–85.e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szkolnicka, D.; Pollan, A.; Da Silva, N.; Oechslin, N.; Gouttenoire, J.; Moradpour, D. Recombinant hepatitis E viruses harboring tags in the ORF1 protein. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e00459-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oechslin, N.; Da Silva, N.; Szkolnicka, D.; Cantrelle, F.X.; Hanoulle, X.; Moradpour, D.; Gouttenoire, J. Hepatitis E virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is involved in RNA replication and infectious particle production. Hepatology 2022, 75, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trozzi, C.; Bartholomew, L.; Ceccacci, A.; Biasiol, G.; Pacini, L.; Altamura, S.; Narjes, F.; Muraglia, E.; Paonessa, G.; Koch, U.; et al. In vitro selection and characterization of hepatitis C virus serine protease variants resistant to an active-site peptide inhibitor. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 3669–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.D.; Zhang, F.; Peng, L.; Luo, W.T.; Chen, C.; Xu, P.; Huang, Y.W. Stable Expression of a hepatitis E virus (HEV) RNA replicon in two mammalian cell lines to assess mechanism of innate immunity and antiviral response. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 603699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimgaonkar, I.; Archer, N.F.; Becher, I.; Shahrad, M.; LeDesma, R.A.; Mateus, A.; Caballero-Gomez, J.; Berneshawi, A.R.; Ding, Q.; Douam, F.; et al. Isocotoin suppresses hepatitis E virus replication through inhibition of heat shock protein 90. Antiviral Res. 2021, 185, 104997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Freistaedter, A.; Schmelas, C.; Gunkel, M.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Grimm, D. An RNA interference/adeno-associated virus vector-based combinatorial gene therapy approach against hepatitis E virus. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debing, Y.; Mishra, N.; Verbeken, E.; Ramaekers, K.; Dallmeier, K.; Neyts, J. A rat model for hepatitis E virus. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, T.L.; Bruggemann, Y.; Nocke, M.K.; Ulrich, R.G.; Schuhenn, J.; Sutter, K.; Gomer, A.; Bader, V.; Winklhofer, K.F.; Broering, R.; et al. A ribavirin-induced ORF2 single-nucleotide variant produces defective hepatitis E virus particles with immune decoy function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2202653119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Heller, B.; Capuccino, J.M.; Song, B.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Hrebikova, G.; Contreras, J.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis E virus ORF3 is a functional ion channel required for release of infectious particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Nimgaonkar, I.; Archer, N.F.; Bram, Y.; Heller, B.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ploss, A. Identification of the intragenomic promoter controlling hepatitis E virus subgenomic RNA transcription. mBio 2018, 9, e00769-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todt, D.; Friesland, M.; Moeller, N.; Praditya, D.; Kinast, V.; Bruggemann, Y.; Knegendorf, L.; Burkard, T.; Steinmann, J.; Burm, R.; et al. Robust hepatitis E virus infection and transcriptional response in human hepatocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 1731–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradpour, D.; Evans, M.J.; Gosert, R.; Yuan, Z.; Blum, H.E.; Goff, S.P.; Lindenbach, B.D.; Rice, C.M. Insertion of green fluorescent protein into nonstructural protein 5A allows direct visualization of functional hepatitis C virus replication complexes. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 7400–7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Fu, H.; Wang, L.; Bu, Q.; Liu, P.; Wang, M.; Sui, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhuang, H. Phylogenetic analysis of the full genome of rabbit hepatitis E virus (rbHEV) and molecular biologic study on the possibility of cross species transmission of rbHEV. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 2020–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izopet, J.; Dubois, M.; Bertagnoli, S.; Lhomme, S.; Marchandeau, S.; Boucher, S.; Kamar, N.; Abravanel, F.; Guerin, J.L. Hepatitis E virus strains in rabbits and evidence of a closely related strain in humans, France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahli, R.; Fraga, M.; Semela, D.; Moradpour, D.; Gouttenoire, J. Rabbit HEV in immunosuppressed patients with hepatitis E acquired in Switzerland. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhomme, S.; Garrouste, C.; Kamar, N.; Saune, K.; Abravanel, F.; Mansuy, J.M.; Dubois, M.; Rostaing, L.; Izopet, J. Influence of polyproline region and macro domain genetic heterogeneity on HEV persistence in immunocompromised patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 209, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Chimeno, M.; Cenalmor, A.; Garcia-Lugo, M.A.; Hernandez, M.; Rodriguez-Lazaro, D.; Avellon, A. Proline-rich hypervariable region of hepatitis E virus: Arranging the disorder. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todt, D.; Meister, T.L.; Steinmann, E. Hepatitis E virus treatment and ribavirin therapy: Viral mechanisms of nonresponse. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 32, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhomme, S.; Nicot, F.; Jeanne, N.; Dimeglio, C.; Roulet, A.; Lefebvre, C.; Carcenac, R.; Manno, M.; Dubois, M.; Peron, J.M.; et al. Insertions and duplications in the polyproline region of the hepatitis E virus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Torian, U.; Engle, R.E.; Faulk, K.; Dalton, H.R.; Bendall, R.P.; Keane, F.E.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Cross-species infections of cultured cells by hepatitis E virus and discovery of an infectious virus-host recombinant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2438–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debing, Y.; Ramiere, C.; Dallmeier, K.; Piorkowski, G.; Trabaud, M.A.; Lebosse, F.; Scholtes, C.; Roche, M.; Legras-Lachuer, C.; de Lamballerie, X.; et al. Hepatitis E virus mutations associated with ribavirin treatment failure result in altered viral fitness and ribavirin sensitivity. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, C.P.; Biedermann, P.; Harms, D.; Wang, B.; Kebelmann, M.; Choi, M.; Helmuth, J.; Corman, V.M.; Thurmer, A.; Altmann, B.; et al. Advanced sequencing approaches detected insertions of viral and human origin in the viral genome of chronic hepatitis E virus patients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, H.R.; Bendall, R.P.; Keane, F.E.; Tedder, R.S.; Ijaz, S. Persistent carriage of hepatitis E virus in patients with HIV infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1025–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, K.; Bentaleb, C.; Hervouet, K.; Alexandre, V.; Montpellier, C.; Saliou, J.M.; Ferrie, M.; Camuzet, C.; Rouille, Y.; Lecoeur, C.; et al. Processing and subcellular localization of the hepatitis E virus replicase: Identification of candidate viral factories. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 828636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Torian, U.; Faulk, K.; Mather, K.; Engle, R.E.; Thompson, E.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Emerson, S.U. A naturally occurring human/hepatitis E recombinant virus predominates in serum but not in faeces of a chronic hepatitis E patient and has a growth advantage in cell culture. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Nishiyama, T.; Takahashi, M.; Murata, K.; Okamoto, H. Development of recombinant infectious hepatitis E virus harboring the nanoKAZ gene and its application in drug screening. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0190621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crooks, G.E.; Hon, G.; Chandonia, J.M.; Brenner, S.E. WebLogo: A sequence logo generator. Genome. Res. 2004, 14, 1188–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johne, R.; Reetz, J.; Ulrich, R.G.; Machnowska, P.; Sachsenroder, J.; Nickel, P.; Hofmann, J. An ORF1-rearranged hepatitis E virus derived from a chronically infected patient efficiently replicates in cell culture. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Sato, K.; Takizawa, D.; Yamada, M.; Okamoto, H. Full genome analysis of a European-type genotype 3 hepatitis E virus variant obtained from a Japanese patient with autochthonous acute hepatitis E. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, T.; Umezawa, K.; Yamada, K.; Takahashi, M.; Kunita, S.; Mulyanto; Kii, I.; Okamoto, H. The capsid (ORF2) protein of hepatitis E virus in feces is C-terminally truncated. Pathogens 2021, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao Thi, V.L.; Wu, X.; Belote, R.L.; Andreo, U.; Takacs, C.N.; Fernandez, J.P.; Vale-Silva, L.A.; Prallet, S.; Decker, C.C.; Fu, R.M.; et al. Stem cell-derived polarized hepatocytes. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Lavrijsen, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Verstegen, M.M.A.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.C.; et al. Recapitulating hepatitis E virus-host interactions and facilitating antiviral drug discovery in human liver-derived organoids. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabj5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marceau, C.D.; Puschnik, A.S.; Majzoub, K.; Ooi, Y.S.; Brewer, S.M.; Fuchs, G.; Swaminathan, K.; Mata, M.A.; Elias, J.E.; Sarnow, P.; et al. Genetic dissection of Flaviviridae host factors through genome-scale CRISPR screens. Nature 2016, 535, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, W.M.; Luna, J.M.; Hoffmann, H.H.; Sanchez-Rivera, F.J.; Leal, A.A.; Ashbrook, A.W.; Le Pen, J.; Ricardo-Lax, I.; Michailidis, E.; Peace, A.; et al. Genome-scale identification of SARS-CoV-2 and pan-coronavirus host factor networks. Cell 2021, 184, 120–132.e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.S.; Beesabathuni, N.S.; Fishburn, A.T.; Kenaston, M.W.; Minami, S.A.; Pham, O.H.; Tucker, I. Systems biology of virus-host protein interactions: From hypothesis generation to mechanisms of replication and pathogenesis. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2022, 9, 397–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, P.; Ahmed, N.; Yeo, G.W. Illuminating RNA biology through imaging. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, B.; Nikolaitchik, O.A.; Mohan, P.R.; Chen, J.; Pathak, V.K.; Hu, W.S. Visualizing the translation and packaging of HIV-1 full-length RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6145–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oechslin, N.; Ankavay, M.; Moradpour, D.; Gouttenoire, J. Expanding the Hepatitis E Virus Toolbox: Selectable Replicons and Recombinant Reporter Genomes. Viruses 2023, 15, 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040869
Oechslin N, Ankavay M, Moradpour D, Gouttenoire J. Expanding the Hepatitis E Virus Toolbox: Selectable Replicons and Recombinant Reporter Genomes. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):869. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040869
Chicago/Turabian StyleOechslin, Noémie, Maliki Ankavay, Darius Moradpour, and Jérôme Gouttenoire. 2023. "Expanding the Hepatitis E Virus Toolbox: Selectable Replicons and Recombinant Reporter Genomes" Viruses 15, no. 4: 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040869
APA StyleOechslin, N., Ankavay, M., Moradpour, D., & Gouttenoire, J. (2023). Expanding the Hepatitis E Virus Toolbox: Selectable Replicons and Recombinant Reporter Genomes. Viruses, 15(4), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040869






