Use of Remdesivir in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in a Real-Life Setting during the Second and Third COVID-19 Epidemic Waves
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
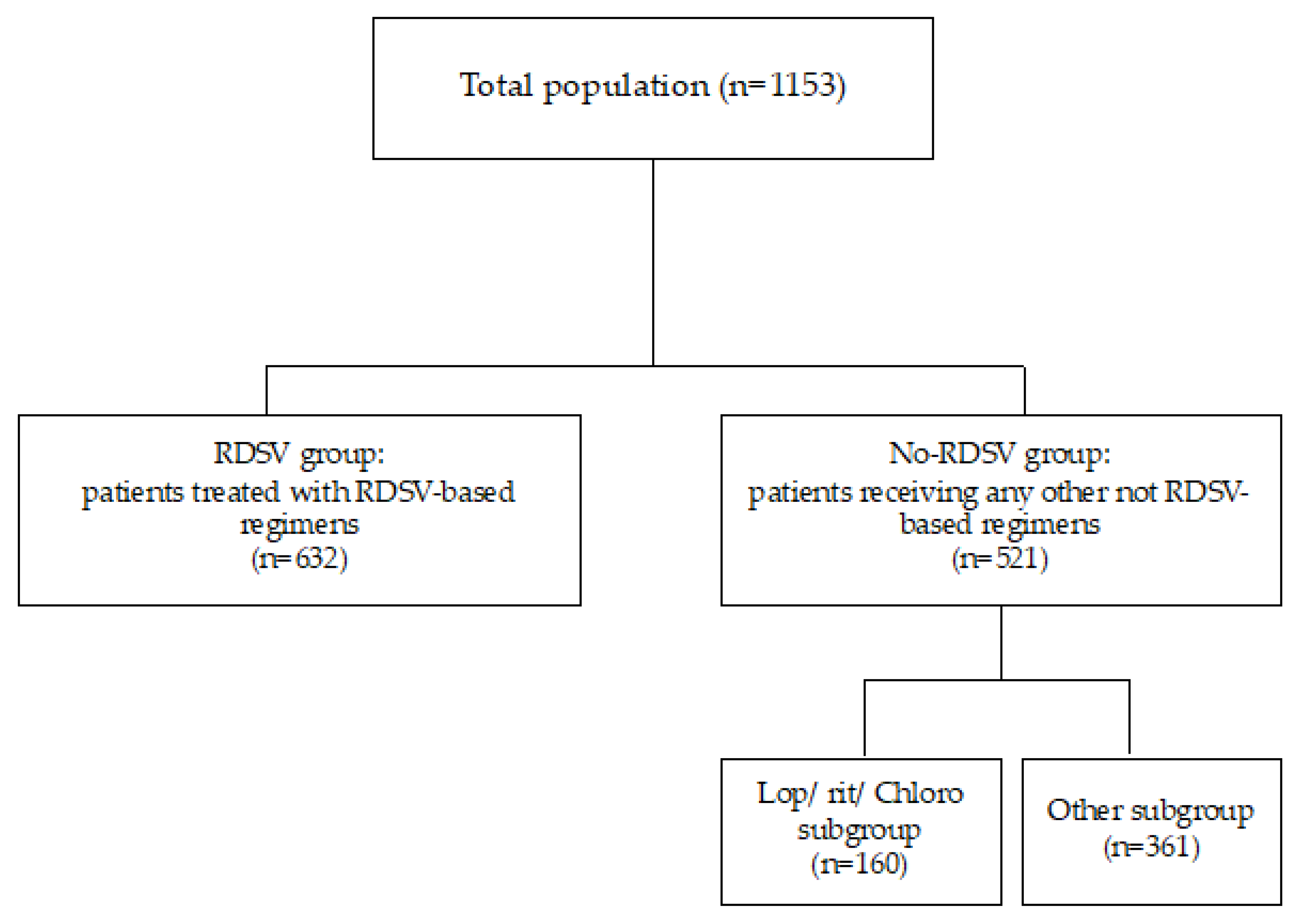
2.2. Study Design and Patients
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Clinical Progression of the Study Population
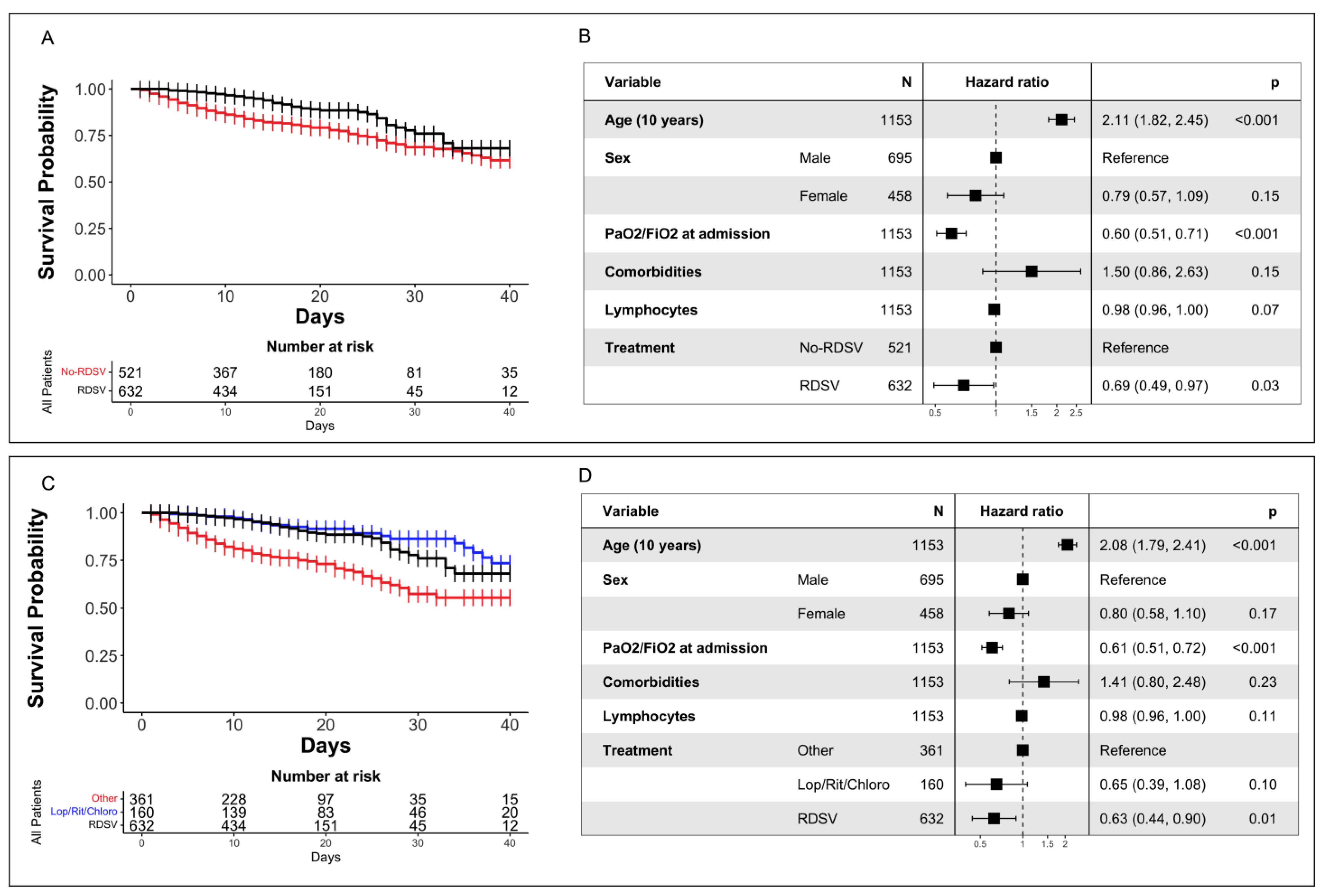
3.3. Survival Analysis
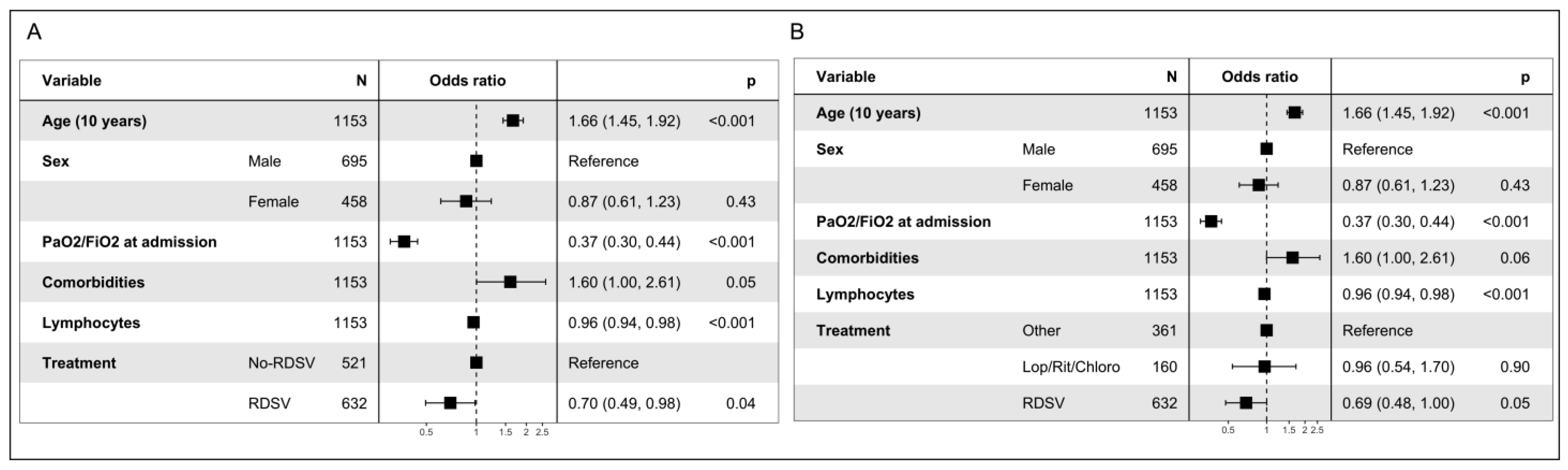
3.4. Analysis of Composite Endpoint
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- A Year without Precedent: WHO’s COVID-19 Response—World | ReliefWeb. Available online: https://reliefweb.int/report/world/year-without-precedent-who-s-COVID-19-response (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Dezza, F.C.; Oliva, A.; Mauro, V.; Romani, F.E.; Aronica, R.; Savelloni, G.; Casali, E.; Valeri, S.; Cancelli, F.; Mastroianni, C.M. Real-Life Use of Remdesivir-Containing Regimens in COVID-19: A Retrospective Case-Control Study. Infez. Med. 2022, 30, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 14.9 Million Excess Deaths Associated with the COVID-19 Pandemic in 2020 and 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/05-05-2022-14.9-million-excess-deaths-were-associated-with-the-COVID-19-pandemic-in-2020-and-2021 (accessed on 27 February 2023).
- Lin, H.X.J.; Cho, S.; Meyyur Aravamudan, V.; Sanda, H.Y.; Palraj, R.; Molton, J.S.; Venkatachalam, I. Remdesivir in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment: A Review of Evidence. Infection 2021, 49, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID Live—Coronavirus Statistics—Worldometer. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Gottlieb, R.L.; Vaca, C.E.; Paredes, R.; Mera, J.; Webb, B.J.; Perez, G.; Oguchi, G.; Ryan, P.; Nielsen, B.U.; Brown, M.; et al. Early Remdesivir to Prevent Progression to Severe COVID-19 in Outpatients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleissa, M.M.; Silverman, E.A.; Paredes Acosta, L.M.; Nutt, C.T.; Richterman, A.; Marty, F.M. New Perspectives on Antimicrobial Agents: Remdesivir Treatment for COVID-19. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2020, 65, e01814-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ader, F.; Bouscambert-Duchamp, M.; Hites, M.; Peiffer-Smadja, N.; Poissy, J.; Belhadi, D.; Diallo, A.; Lê, M.-P.; Peytavin, G.; Staub, T.; et al. Remdesivir plus Standard of Care versus Standard of Care Alone for the Treatment of Patients Admitted to Hospital with COVID-19 (DisCoVeRy): A Phase 3, Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label Trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium. Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for COVID-19—Interim WHO Solidarity Trial Results. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostini, M.L.; Andres, E.L.; Sims, A.C.; Graham, R.L.; Sheahan, T.P.; Lu, X.; Smith, E.C.; Case, J.B.; Feng, J.Y.; Jordan, R.; et al. Coronavirus Susceptibility to the Antiviral Remdesivir (GS-5734) Is Mediated by the Viral Polymerase and the Proofreading Exoribonuclease. mBio 2018, 9, e00221-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, B.; Thakur, S.S. Remdesivir and Its Combination with Repurposed Drugs as COVID-19 Therapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 830990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulangu, S.; Dodd, L.E.; Davey, R.T.; Tshiani Mbaya, O.; Proschan, M.; Mukadi, D.; Lusakibanza Manzo, M.; Nzolo, D.; Tshomba Oloma, A.; Ibanda, A.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Ebola Virus Disease Therapeutics. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2293–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cao, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, G. Remdesivir and Chloroquine Effectively Inhibit the Recently Emerged Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) In Vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Mao, C.; Luan, X.; Shen, D.-D.; Shen, Q.; Su, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, W.; Gao, M.; et al. Structural Basis for Inhibition of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase from SARS-CoV-2 by Remdesivir. Science 2020, 368, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheahan, T.P.; Sims, A.C.; Graham, R.L.; Menachery, V.D.; Gralinski, L.E.; Case, J.B.; Leist, S.R.; Pyrc, K.; Feng, J.Y.; Trantcheva, I.; et al. Broad-Spectrum Antiviral GS-5734 Inhibits Both Epidemic and Zoonotic Coronaviruses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malin, J.J.; Suárez, I.; Priesner, V.; Fätkenheuer, G.; Rybniker, J. Remdesivir against COVID-19 and Other Viral Diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 34, e00162-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, B.N.; Feldmann, F.; Schwarz, B.; Meade-White, K.; Porter, D.P.; Schulz, J.; van Doremalen, N.; Leighton, I.; Yinda, C.K.; Pérez-Pérez, L.; et al. Clinical Benefit of Remdesivir in Rhesus Macaques Infected with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 585, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, K.; Azher, T.; Baqi, M.; Binnie, A.; Borgia, S.; Carrier, F.M.; Cavayas, Y.A.; Chagnon, N.; Cheng, M.P.; Conly, J.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Patients in Hospital with COVID-19 in Canada: A Randomized Controlled Trial. CMAJ 2022, 194, E242–E251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA First COVID-19 Treatment Recommended for EU Authorisation. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/first-COVID-19-treatment-recommended-eu-authorisation (accessed on 23 November 2022).
- Prevalenza e Distribuzione Delle Varianti di SARS-CoV-2 di Interesse per la Sanità Pubblica in Italia. Available online: https://www.iss.it/cov19-cosa-fa-iss-varianti/-/asset_publisher/yJS4xO2fauqM/content/id/5802322 (accessed on 2 February 2023).
- Chokkalingam, A.P.; Hayden, J.; Goldman, J.D.; Li, H.; Asubonteng, J.; Mozaffari, E.; Bush, C.; Wang, J.R.; Kong, A.; Osinusi, A.O.; et al. Association of Remdesivir Treatment with Mortality among Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19 in the United States. JAMA Netw. Open. 2022, 5, e2244505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibaldi, B.T.; Wang, K.; Robinson, M.L.; Zeger, S.L.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Wang, M.-C.; Alexander, G.C.; Gupta, A.; Bollinger, R.; Xu, Y. Comparison of Time to Clinical Improvement With vs Without Remdesivir Treatment in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e213071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozaffari, E.; Chandak, A.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, S.; Thrun, M.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Kuritzkes, D.R.; Sax, P.E.; Wohl, D.A.; Casciano, R.; et al. Remdesivir Treatment in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Comparative Analysis of In-Hospital All-Cause Mortality in a Large Multicenter Observational Cohort. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, e450–e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olender, S.A.; Walunas, T.L.; Martinez, E.; Perez, K.K.; Castagna, A.; Wang, S.; Kurbegov, D.; Goyal, P.; Ripamonti, D.; Balani, B.; et al. Remdesivir Versus Standard-of-Care for Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection: An Analysis of 28-Day Mortality. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfield, T.; Bodilsen, J.; Brieghel, C.; Harboe, Z.B.; Helleberg, M.; Holm, C.; Israelsen, S.B.; Jensen, J.; Jensen, T.Ø.; Johansen, I.S.; et al. Improved Survival among Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treated with Remdesivir and Dexamethasone. A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, G.A.; Christensen, A.B.; Pusch, T.; Goulet, D.; Chang, S.-C.; Grunkemeier, G.L.; McKelvey, P.A.; Robicsek, A.; French, T.; Parsons, G.T.; et al. Remdesivir and Mortality in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 74, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Vidal, C.; Alonso, R.; Camon, A.M.; Cardozo, C.; Albiach, L.; Agüero, D.; Marcos, M.A.; Ambrosioni, J.; Bodro, M.; Chumbita, M.; et al. Impact of Remdesivir According to the Pre-Admission Symptom Duration in Patients with COVID-19. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 3296–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vito, A.; Poliseno, M.; Colpani, A.; Zauli, B.; Puci, M.V.; Santantonio, T.; Meloni, M.C.; Fois, M.; Fanelli, C.; Saderi, L.; et al. Reduced Risk of Death in People with SARS-CoV-2 Infection Treated with Remdesivir: A Nested Case–Control Study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2022, 38, 2029–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metchurtchlishvili, R.; Chkhartishvili, N.; Abutidze, A.; Endeladze, M.; Ezugbaia, M.; Bakradze, A.; Tsertsvadze, T. Effect of Remdesivir on Mortality and the Need for Mechanical Ventilation among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: Real-World Data from Resource-Limited Country. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanafusa, M.; Nawa, N.; Goto, Y.; Kawahara, T.; Miyamae, S.; Ueki, Y.; Nosaka, N.; Wakabayashi, K.; Tohda, S.; Tateishi, U.; et al. Effectiveness of Remdesivir with Corticosteroids for COVID-19 Patients in Intensive Care Unit: A Hospital-based Observational Study. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Tenorio, C.; García-Vallecillos, C.; Sequera-Arquelladas, S. COVID-19 Virgen de las Nieves TEAM Real-World Outcomes of COVID-19 Treatment with Remdesivir in a Spanish Hospital. Medicine 2021, 100, e27228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadi, A.; Hachimi, A.; Admou, B.; Hazime, R.; Brahim, I.; Douirek, F.; Zarrouki, Y.; El Adib, A.R.; Younous, S.; Samkaoui, A.M. Lymphopenia in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: A Predictor Factor of Severity and Mortality. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021, 43, e38–e40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Cao, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, D.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; He, W.; Chen, L.; Dong, F.; Chen, W.; et al. Hematological Features of Persons with COVID-19. Leukemia 2020, 34, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, Y.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, X.; Du, C.; et al. Risk Factors Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 934–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.C.; Boulware, D.R. Ongoing Need for Clinical Trials and Contemporary End Points for Outpatient COVID-19. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Pan, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Ma, K.; Fan, C.; Lv, Y.; Guan, X.; Yang, Y.; Ye, X.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Paxlovid in Severe Adult Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Multicenter Randomized Controlled Study. Lancet Reg. Health—West. Pac. 2023, 100694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamontagne, F.; Agarwal, A.; Rochwerg, B.; Siemieniuk, R.A.; Agoritsas, T.; Askie, L.; Lytvyn, L.; Leo, Y.-S.; Macdonald, H.; Zeng, L.; et al. A Living WHO Guideline on Drugs for COVID-19. BMJ 2020, 370, m3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Gao, W.; Bao, H.; Feng, H.; Mei, S.; Chen, P.; Gao, Y.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, X.; et al. VV116 versus Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir for Oral Treatment of COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, G.; Moreira Silva, E.A.S.; Medeiros Silva, D.C.; Thabane, L.; Campos, V.H.S.; Ferreira, T.S.; Santos, C.V.Q.; Nogueira, A.M.R.; Almeida, A.P.F.G.; Savassi, L.C.M.; et al. Early Treatment with Pegylated Interferon Lambda for COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | All | No-RDSV Group | RDSV Group | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 1153 | 521 | 632 | |
| Sex (f/m) (n, %) | 458/695 | 221 (42.4)/300 (57.6) | 237 (37.5)/395 (62.5) | 0.101 |
| Age | 65.00 [53.00–76.00] | 68.00 [55.00–81.00] | 62.00 [53.00–73.00] | <0.001 |
| PaO2/FiO2 at admission | 309.00 [243.00–366.00] | 311.00 [233.00–372.00] | 308.00 [251.75–361.00] | 0.919 |
| PaO2/FiO2 nadir | 194.00 [118.00–316.00] | 196.00 [116.00–322.00] | 191.50 [120.00–312.00] | 0.879 |
| Neutrophils | 76.50 [66.70–84.50] | 76.80 [65.60–85.20] | 76.10 [67.18–83.90] | 0.454 |
| Lymphocytes | 15.40 [9.10–23.00] | 14.70 [8.60–23.40] | 15.75 [9.70–22.60] | 0.568 |
| t_hospitalization symptoms | 6.00 [3.00–10.00] | 7.00 [3.00–11.00] | 6.00 [4.00–9.00] | 0.088 |
| Glycemia_mg_dl_.1 | 112.00 [97.00–141.00] | 112.00 [97.00–143.00] | 112.00 [98.00–137.00] | 0.627 |
| Creatinine_mg_dl_.1 | 0.88 [0.76–1.09] | 0.93 [0.77–1.27] | 0.84 [0.75–1.01] | <0.001 |
| CRP_mg_dl_.1 | 4.39 [1.47–9.60] | 4.68 [1.42–10.78] | 4.05 [1.48–8.38] | 0.176 |
| Comorbidities (n, %) | 808/1153 (70.1) | 384/521 (73.7) | 424/632 (67.1) | 0.017 |
| Hypertension | 538/1153 (47.0) | 253/521 (48.6) | 285/632 (45.1) | 0.265 |
| Diabetes | 196/1153 (17.0) | 100/521 (19.2) | 96/632 (15.2) | 0.085 |
| CRF | 76/1153 (6.5) | 62/521 (11.9) | 14/632 (2.2) | <0.001 |
| Obesity | 95/1153 (8.2) | 35/521 (6.7) | 60/632 (9.5) | 0.110 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 294/1153 (25.5) | 168/521 (32.2) | 126/632 (19.9) | <0.001 |
| Neoplasia | 81/1153 (7.0) | 52/521 (10.0) | 29/632 (4.6) | 0.001 |
| Neurological diseases | 17/1153 (1.5) | 7/521 (1.3) | 10/632 (1.6) | 0.929 |
| Respiratory diseases | 156/1153 (13.5) | 79/521 (15.2) | 77/632 (12.2) | 0.166 |
| Dementia | 56/1153 (4.9) | 42/521 (8.1) | 14/632 (2.2) | <0.001 |
| Hypothyroidism | 55/1153 (4.8) | 25/521 (4.8) | 30/632 (4.7) | 1.000 |
| Variant-period (n, %) | <0.001 | |||
| Wuhan-period (21 February 2020– 1 June 2021) | 981/1153 (85.1) | 464/521 (89.1) | 517/632 (81.8) | |
| Delta-period (2 June 2021–15 December 2021) | 104/1153 (9.0) | 27/521 (5.2) | 77/632 (12.2) | |
| Omicron-period (16 December 2021–present) | 68/1153 (5.9) | 30/521 (5.8) | 38/632 (6.0) | |
| Vaccination status (n, %) | 84/1153 (7.3) | 29/521 (5.6) | 55/632 (8.7) | 0.054 |
| Variable | All | No-RDSV Group | RDSV Group | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | 1153 | 521 | 632 | |
| Mortality (n, %) | 167/1153 (14.5) | 113/521 (21.7) | 54/632 (8.5) | <0.001 |
| ARDS (n, %) | ||||
| No ARDS | 319/1153 (29.9) | 147/521 (28.2) | 172/632 (27.2) | 0.524 |
| Mild | 230/1153 (19.9) | 107/521 (20.5) | 123/632 (19.5) | |
| Moderate | 404/1153 (35.0) | 171/521 (32.8) | 233/632 (36.9) | |
| Severe | 200/1153 (17.3) | 96/521 (18.4) | 104/632 (16.5) | |
| Hospital stay (days) | 14 [8–21] | 14 [8–24] | 13 [8–19] | 0.017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marocco, R.; Del Borgo, C.; Tortellini, E.; Garattini, S.; Carraro, A.; Di Trento, D.; Gasperin, A.; Grimaldi, A.; Tieghi, T.; Belvisi, V.; et al. Use of Remdesivir in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in a Real-Life Setting during the Second and Third COVID-19 Epidemic Waves. Viruses 2023, 15, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040947
Marocco R, Del Borgo C, Tortellini E, Garattini S, Carraro A, Di Trento D, Gasperin A, Grimaldi A, Tieghi T, Belvisi V, et al. Use of Remdesivir in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in a Real-Life Setting during the Second and Third COVID-19 Epidemic Waves. Viruses. 2023; 15(4):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040947
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarocco, Raffaella, Cosmo Del Borgo, Eeva Tortellini, Silvia Garattini, Anna Carraro, Daniela Di Trento, Andrea Gasperin, Alessandra Grimaldi, Tiziana Tieghi, Valeria Belvisi, and et al. 2023. "Use of Remdesivir in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in a Real-Life Setting during the Second and Third COVID-19 Epidemic Waves" Viruses 15, no. 4: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040947
APA StyleMarocco, R., Del Borgo, C., Tortellini, E., Garattini, S., Carraro, A., Di Trento, D., Gasperin, A., Grimaldi, A., Tieghi, T., Belvisi, V., Kertusha, B., Guardiani, M., Zuccalà, P., Alunni Fegatelli, D., Spagnoli, A., Lichtner, M., & LATINA COVID-group. (2023). Use of Remdesivir in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in a Real-Life Setting during the Second and Third COVID-19 Epidemic Waves. Viruses, 15(4), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15040947









