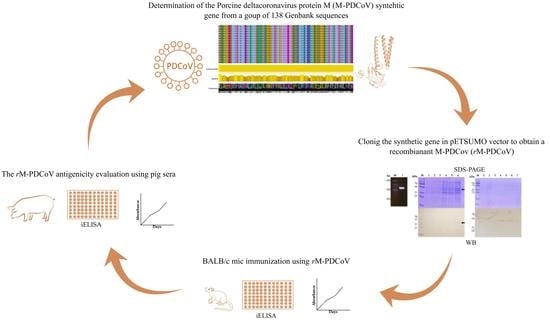
A Candidate Antigen of the Recombinant Membrane Protein Derived from the Porcine Deltacoronavirus Synthetic Gene to Detect Seropositive Pigs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
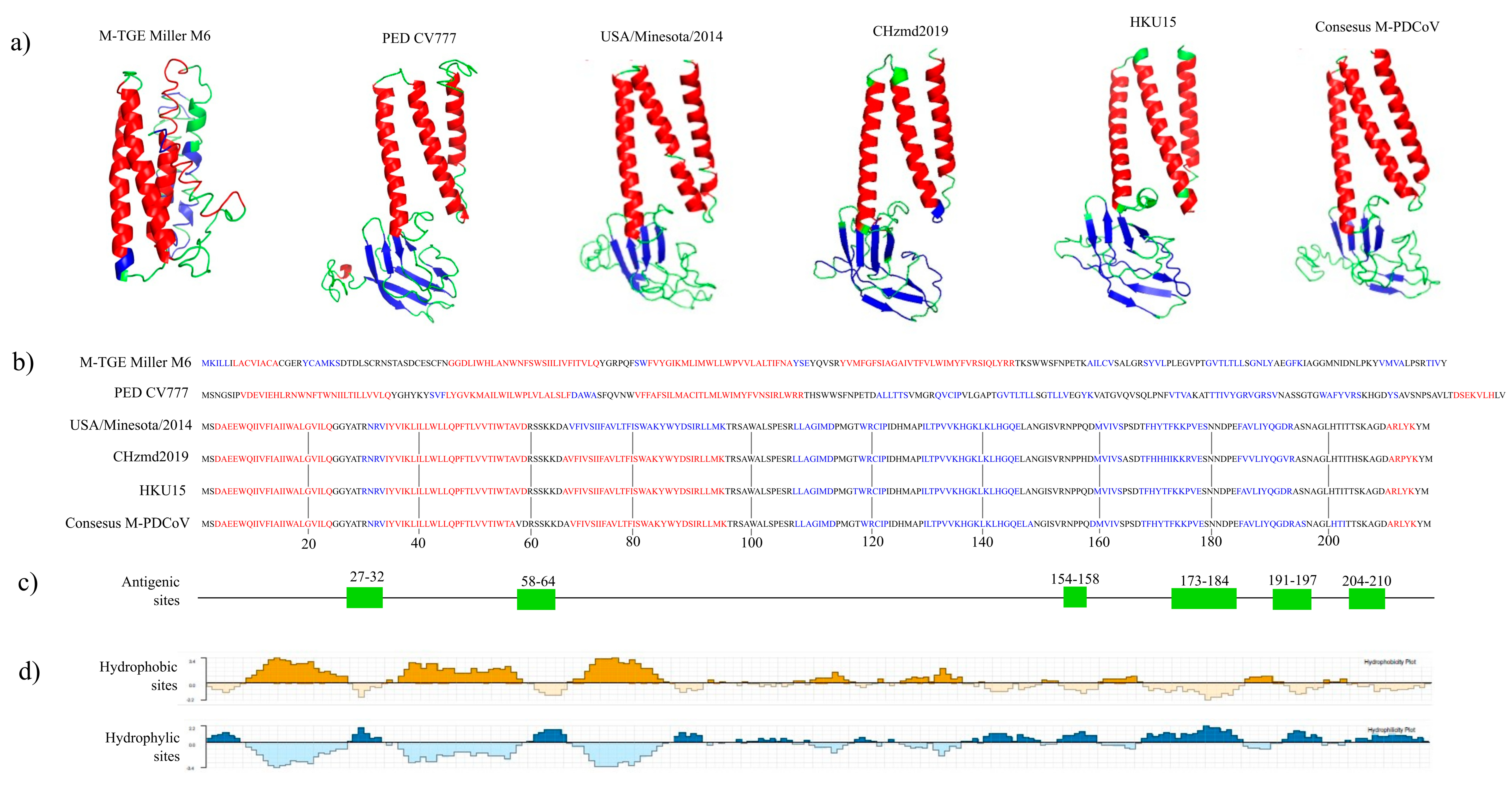
2.1. In Silico Analysis of M-PDCoV
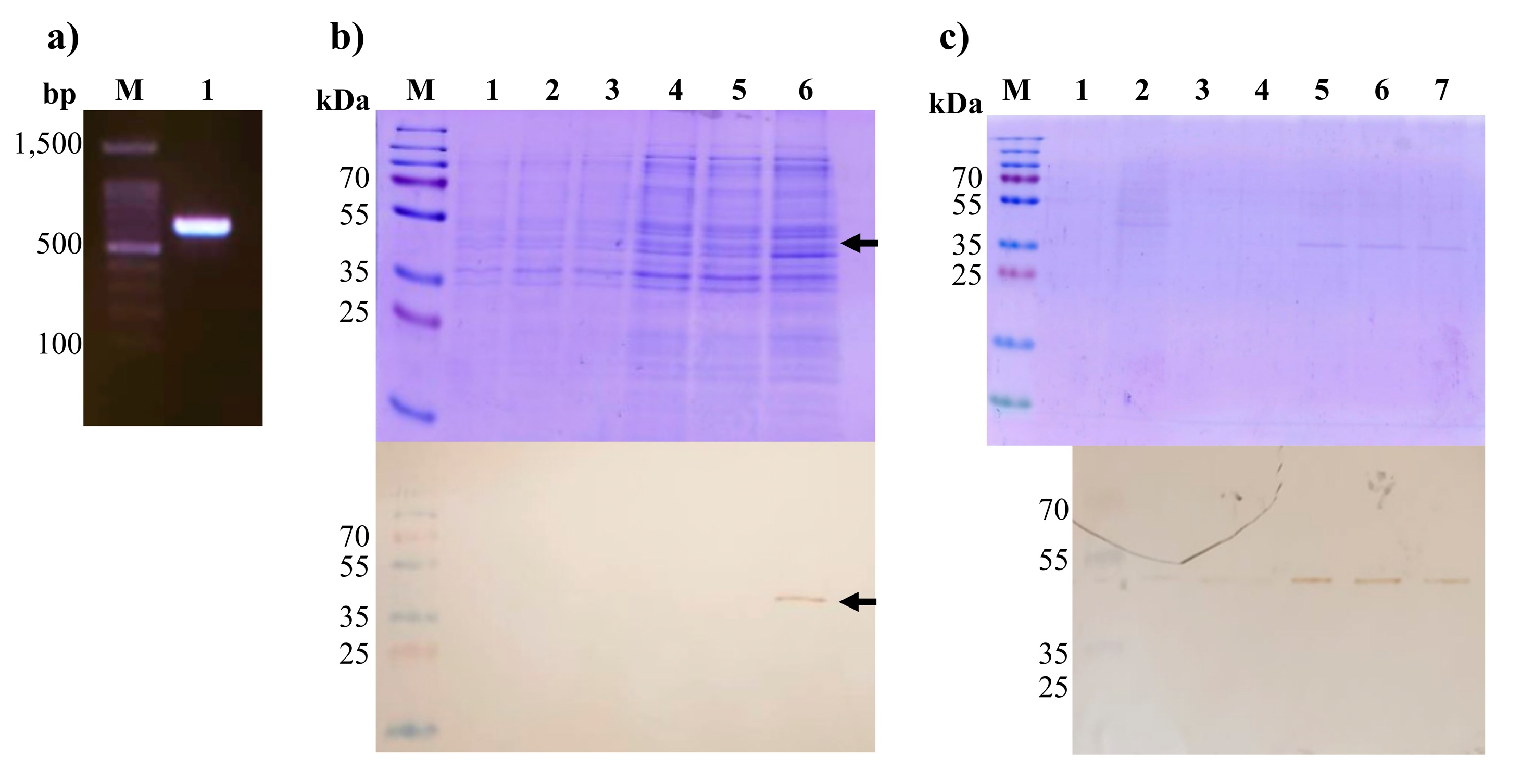
2.2. Molecular Cloning and Expression of M-PDCoV in a pETSUMO Plasmid
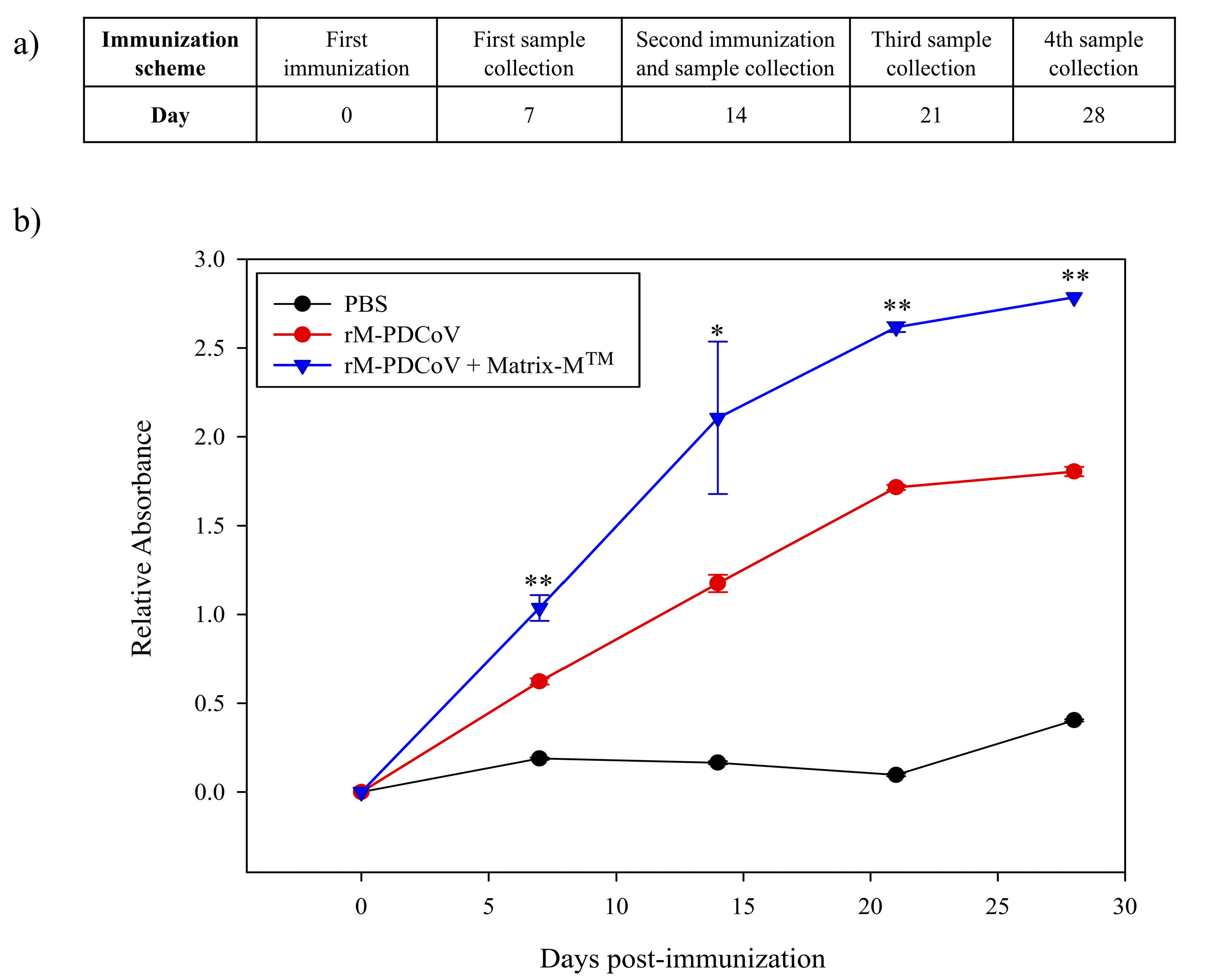
2.3. BALB/c Mice Immunization
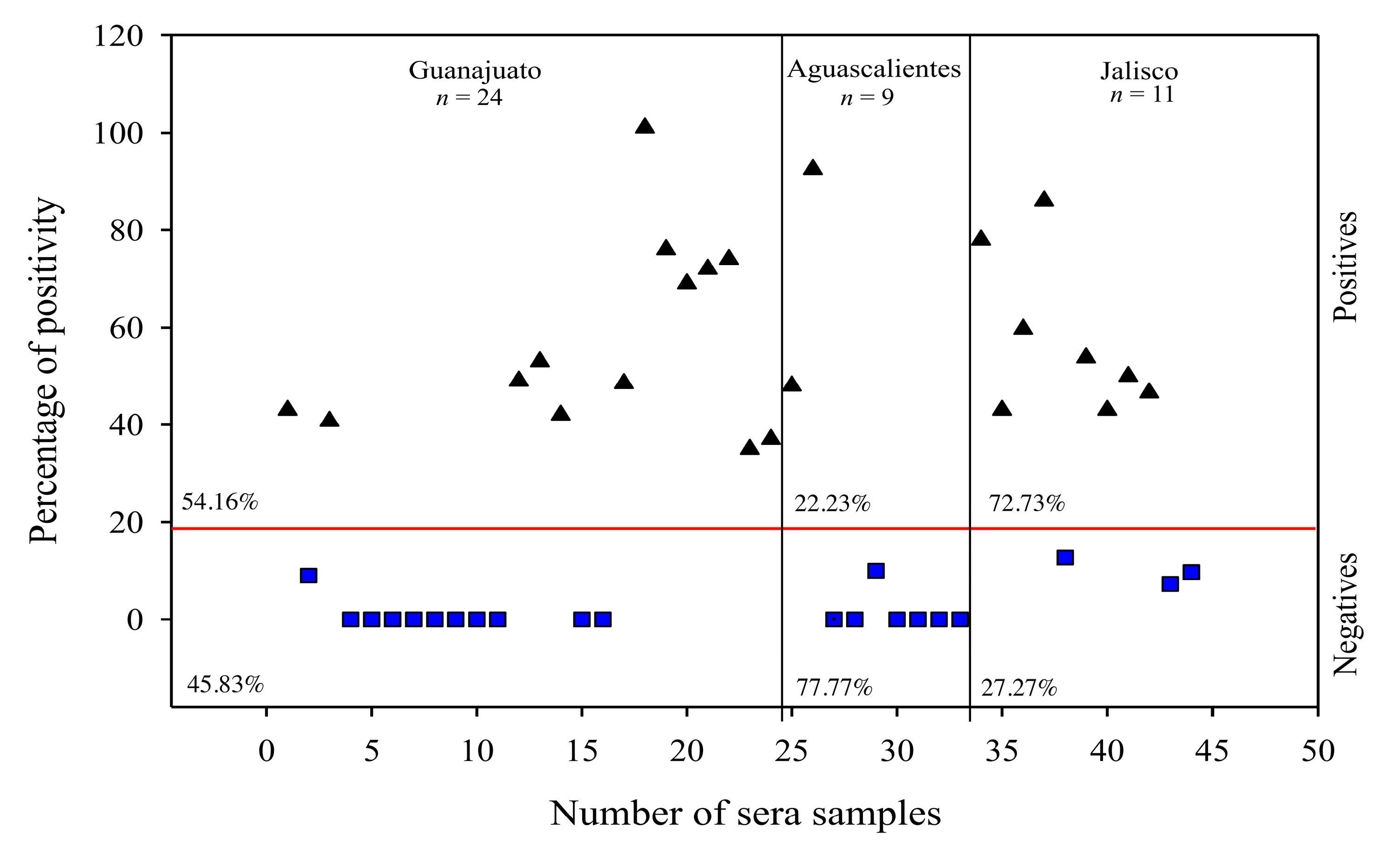
2.4. Antigenicity Evaluation Using Pig Farm Sera Samples by Indirect ELISA Assay
3. Results
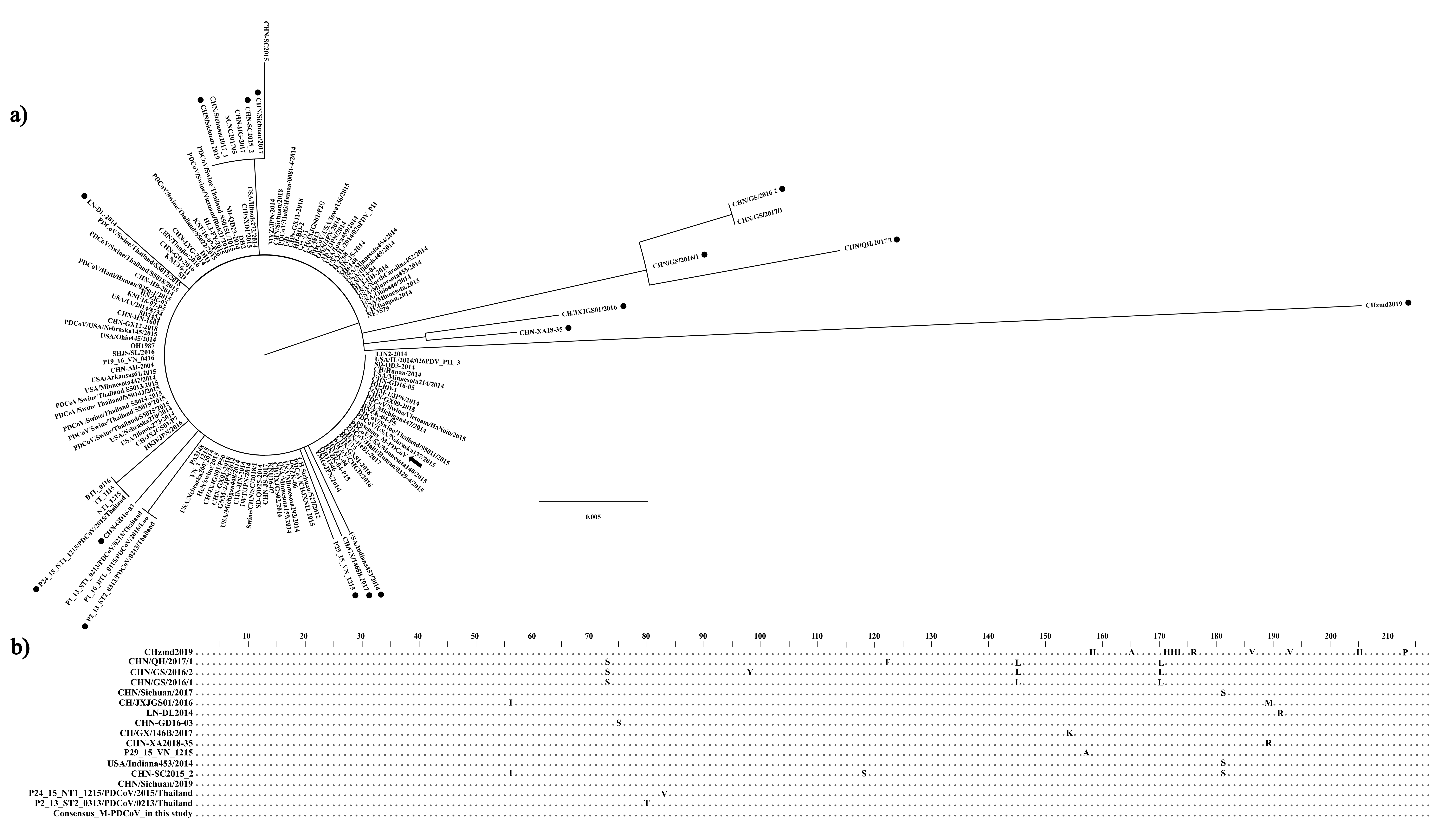
3.1. In Silico Analysis
3.2. Cloning and Expression of rM-PDCoV
3.3. The rM-PDCoV Immunogenicity Determination in BALB/c Mice
3.4. The Use of rM-PDCoV Antigenic Evaluations Using in Pig Farm Sera Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woo, P.C.; Lau, S.K.; Lam, C.S.; Lau, C.C.; Tsang, A.K.; Lau, J.H.; Bai, R.; Teng, J.L.; Tsang, C.C.; Wang, M.; et al. Discovery of seven novel Mammalian and avian coronaviruses in the genus deltacoronavirus supports bat coronaviruses as the gene source of alphacoronavirus and betacoronavirus and avian coronaviruses as the gene source of gammacoronavirus and deltacoronavirus. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 3995–4008. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Chen, Q.; Harmon, K.M.; Yoon, K.J.; Schwartz, K.J.; Hoogland, M.J.; Gauger, P.C.; Main, R.G.; Zhang, J. Full-Length Genome Sequence of Porcine Deltacoronavirus Strain USA/IA/2014/8734. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e00278-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Chung, H.C.; Nguyen, V.G.; Moon, H.J.; Kim, H.K.; Park, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, G.E.; Park, B.K. Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Porcine Deltacoronavirus in Korean Swine Farms, 2015. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorsirigool, A.; Saeng-Chuto, K.; Temeeyasen, G.; Madapong, A.; Tripipat, T.; Wegner, M.; Tuntituvanont, A.; Intrakamhaeng, M.; Nilubol, D. The first detection and full-length genome sequence of porcine deltacoronavirus isolated in Lao PDR. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 2909–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorsirigool, A.; Saeng-Chuto, K.; Madapong, A.; Temeeyasen, G.; Tripipat, T.; Kaewprommal, P.; Tantituvanont, A.; Piriyapongsa, J.; Nilubol, D. The genetic diversity and complete genome analysis of two novel porcine deltacoronavirus isolates in Thailand in 2015. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajayi, T.; Dara, R.; Misener, M.; Pasma, T.; Moser, L.; Poljak, Z. Herd-level prevalence and incidence of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus (PEDV) and porcine deltacoronavirus (PDCoV) in swine herds in Ontario, Canada. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.P.; Song, S.; An, B.H.; Park, G.N.; Pham, N.T.; Le, D.Q.; Nguyen, V.T.; Vu, T.T.H.; Kim, K.S.; Choe, S.; et al. A novel strain of porcine deltacoronavirus in Vietnam. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Rivera, C.; Ramírez-Mendoza, H.; Mendoza-Elvira, S.; Segura-Velázquez, R.; Sánchez-Betancourt, J.I. First report and phylogenetic analysis of porcine deltacoronavirus in Mexico. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Hu, H.; Saif, L.J. Porcine deltacoronavirus infection: Etiology, cell culture for virus isolation and propagation, molecular epidemiology and pathogenesis. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederwerder, M.C.; Hesse, R.A. Swine enteric coronavirus disease: A review of 4 years with porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus and porcine deltacoronavirus in the United States and Canada. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 660–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Vlasova, A.N.; Kenney, S.P.; Saif, L.J. Emerging and re-emerging coronaviruses in pigs. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2019, 34, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, L. Prevalence and phylogenetic analysis of porcine deltacoronavirus in Sichuan province, China. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2883–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Liu, X.; Hu, D.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liu, P. Swine Enteric Coronaviruses (PEDV, TGEV, and PDCoV) Induce Divergent Interferon-Stimulated Gene Responses and Antigen Presentation in Porcine Intestinal Enteroids. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 826882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Jung, K.; Vlasova, A.N.; Chepngeno, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Saif, L.J. Isolation and characterization of porcine deltacoronavirus from pigs with diarrhea in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Zhou, X.; Peng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Huang, T.; Zhang, T.; Li, A.; Huang, D.; Wu, Q.; et al. Newly Emerged Porcine Deltacoronavirus Associated with Diarrhoea in Swine in China: Identification, Prevalence and Full-Length Genome Sequence Analysis. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Han, F.; Shu, X.; Li, Q.; Ding, Q.; Hao, C.; Yan, X.; Xu, M.; Hu, H. Co-infection of porcine epidemic diarrhoea virus and porcine deltacoronavirus enhances the disease severity in piglets. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Porcine deltacoronavirus: Overview of infection dynamics, diagnostic methods, prevalence and genetic evolution. Virus Res. 2016, 226, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.T.; Ji, X.; He, W.; Dellicour, S.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Zhang, L.; Gilbert, M.; Zhu, H.; Xing, G.; et al. Genomic Epidemiology, Evolution, and Transmission Dynamics of Porcine Deltacoronavirus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 2641–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, A.L.; Larson, B.J.; Hogue, B.G. A Conserved Domain in the Coronavirus Membrane Protein Tail Is Important for Virus Assembly. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 11418–11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujike, M.; Taguchi, F. Incorporation of Spike and Membrane Glycoproteins into Coronavirus Virions. Viruses 2015, 7, 1700–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corse, E.; Machamer, C.E. Infectious bronchitis virus E protein is targeted to the Golgi complex and directs release of virus-like particles. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4319–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Bard, J.D.; Triche, T.J.; Judkins, A.R.; Biegel, J.A.; Gai, X. Emerging variants of concern in SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein: A highly conserved target with potential pathological and therapeutic implications. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Takeyama, N.; Katsumata, A.; Tuchiya, K.; Kodama, T.; Kusanagi, K. Mutations in the spike gene of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus associated with growth adaptation in vitro and attenuation of virulence in vivo. Virus Genes 2011, 43, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeman, D.; Fielding, B.C. Coronavirus envelope protein: Current knowledge. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, K.; Maeda, A.; Maeda, J.; Makino, S. Characterization of the coronavirus M protein and nucleocapsid interaction in infected cells. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8127–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escors, D.; Ortego, J.; Laude, H.; Enjuanes, L. The membrane M protein carboxy terminus binds to transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus core and contributes to core stability. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 1312–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, K.; Chen, C.J.; Maeda, J.; Makino, S. Nucleocapsid-independent specific viral RNA packaging via viral envelope protein and viral RNA signal. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2922–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, Y.A. Properties of Coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2. Malays. J. Pathol. 2020, 42, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- de Haan, C.A.; Vennema, H.; Rottier, P.J. Assembly of the coronavirus envelope: Homotypic interactions between the M proteins. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4967–4978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, B.W.; Adair, B.D.; Yeager, M.; Buchmeier, M.J. Purification and electron cryomicroscopy of coronavirus particles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 454, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, S.R.; Leibowitz, J.L. Coronavirus pathogenesis. Adv. Virus Res. 2011, 81, 85–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, H.; Chen, J.; Shi, D.; Zhu, Y.; Feng, L. Characterization of an Immunodominant Epitope in the Endodomain of the Coronavirus Membrane Protein. Viruses 2016, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Chen, X.; Shi, D.; Feng, L.; Yang, B. Identification of a conserved linear B-cell epitope in the M protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Siddiqui, P.; Niu, J.; Jiang, S. Identification of immunodominant epitopes on the membrane protein of the severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 3718–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, C.; Qin, D.; Tang, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Tang, G.; Lu, C. Identification of a B-cell antigenic epitope at the N-terminus of SARS-CoV M protein and characterization of monoclonal antibody against the protein. Virus Genes 2006, 33, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Qi, J.; Chu, F.; Wu, H.; Gao, F.; Li, T.; Yan, J.; Gao, G.F. The membrane protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus acts as a dominant immunogen revealed by a clustering region of novel functionally and structurally defined cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, T.; Morioka, H.; Gomi, K.; Tomizawa, K.; Doki, T.; Hohdatsu, T. Screening and identification of T helper 1 and linear immunodominant antibody-binding epitopes in spike 1 domain and membrane protein of feline infectious peritonitis virus. Vaccine 2014, 32, 1834–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Liu, S.; Han, Z.; Shao, Y.; Li, H.; Kong, X. Identification of a novel linear B-cell epitope in the M protein of avian infectious bronchitis coronaviruses. J. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gauger, P.; Stafne, M.; Thomas, J.; Arruda, P.; Burrough, E.; Madson, D.; Brodie, J.; Magstadt, D.; Derscheid, R.; et al. Pathogenicity and pathogenesis of a United States porcine deltacoronavirus cell culture isolate in 5-day-old neonatal piglets. Virology 2015, 482, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Lou, F.; Oglesbee, M.; Krakowka, S.; Li, J. Origin, evolution, and virulence of porcine deltacoronaviruses in the United States. mBio 2015, 6, e00064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Enriquez, A.; Herrera-Camacho, I.; Millán-Pérez-Peña, L.; Reyes-Leyva, J.; Santos-López, G.; Rivera-Benítez, J.F.; Rosas-Murrieta, N.H. Predicted 3D model of the M protein of Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus and analysis of its immunogenic potential. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Söding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickle, D.C.; Heath, L.; Jensen, M.A.; Gilbert, P.B.; Mullins, J.I.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. HIV-specific probabilistic models of protein evolution. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abascal, F.; Zardoya, R.; Posada, D. ProtTest: Selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2104–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clamp, M.; Cuff, J.; Searle, S.M.; Barton, G.J. The Jalview Java alignment editor. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 426–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasterer, T.N. PROTEAN. Protein sequence analysis and prediction. Mol. Biotechnol. 2000, 16, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emini, E.A.; Hughes, J.V.; Perlow, D.S.; Boger, J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J. Virol. 1985, 55, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: A unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Skolnick, J. Scoring function for automated assessment of protein structure template quality. Proteins 2004, 57, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P. The sequence manipulation suite: JavaScript programs for analyzing and formatting protein and DNA sequences. Biotechniques 2000, 28, 1102–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Romero, R.; Cerriteño-Sánchez, J.L.; Mendoza-Elvira, S.; García-Cambrón, J.B.; Castañeda-Montes, M.A.; Pérez-Aguilar, J.M.; Cuevas-Romero, J.S. Development of Novel Recombinant Antigens of Nucleoprotein and Matrix Proteins of Porcine Orthorubulavirus: Antigenicity and Structural Prediction. Viruses 2022, 14, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fossum, C.; Hjertner, B.; Ahlberg, V.; Charerntantanakul, W.; McIntosh, K.; Fuxler, L.; Balagunaseelan, N.; Wallgren, P.; Lövgren Bengtsson, K. Early inflammatory response to the saponin adjuvant Matrix-M in the pig. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 158, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerriteno-Sanchez, J.L.; Santos-López, G.; Rosas-Murrieta, N.H.; Reyes-Leyva, J.; Cuevas-Romero, S.; Herrera-Camacho, I. Production of an enzymatically active and immunogenic form of ectodomain of Porcine rubulavirus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase in the yeast Pichia pastoris. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 223, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaneda-Montes, M.A.; Cuevas-Romero, J.S.; Cerriteño-Sánchez, J.L.; de María Ávila-De la Vega, L.; García-Cambrón, J.B.; Ramírez-Álvarez, H. Small ruminant lentivirus capsid protein (SRLV-p25) antigenic structural prediction and immunogenicity to recombinant SRLV-rp25-coupled to immunostimulatory complexes based on glycyrrhizinic acid. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2023, 87, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haan, C.A.; Rottier, P.J. Molecular interactions in the assembly of coronaviruses. Adv. Virus Res. 2005, 64, 165–230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Grunewald, M.; Perlman, S. Coronaviruses: An Updated Overview of Their Replication and Pathogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2203, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Skolnick, J. TM-align: A protein structure alignment algorithm based on the TM-score. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2302–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balamurugan, V.; Venkatesan, G.; Sen, A.; Annamalai, L.; Bhanuprakash, V.; Singh, R.K. Recombinant protein-based viral disease diagnostics in veterinary medicine. Expert. Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 10, 731–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Zha, E.; Li, B.; Qiao, X.; Tang, L.; Ge, J.; Li, Y. High-level prokaryotic expression of envelope exterior of membrane protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 123, 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Suo, S.; Jang, Y.-S. Development of a porcine epidemic diarrhea virus M protein-based ELISA for virus detection. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Qin, Z.; Ge, X.; Yin, X.; Xia, C.; Bu, R.E.; Fang, Y.; Liu, J.; Gao, Y.; Ren, X. Generation of a monoclonal antibody to S1 protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2013, 32, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Kong, N.; Shan, T.; Zheng, H.; Tong, W.; Yang, S.; Li, G.; Zhou, E.; Tong, G. Monoclonal antibody to N protein of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus. Monoclon. Antib. Immunodiagn. Immunother. 2015, 34, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Kokuho, T.; Kubota, T.; Watanabe, S.; Inumaru, S.; Yokomizo, Y.; Onodera, T. A serodiagnostic ELISA using recombinant antigen of swine transmissible gastroenteritis virus nucleoprotein. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2001, 63, 1253–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Li, C.; Guo, D.; Wei, S.; Wang, X.; Geng, Y.; Yao, S.; Gao, J.; Wang, E.; Zhao, X.; et al. A recombinant nucleocapsid protein-based indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect antibodies against porcine deltacoronavirus. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 78, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.X.; Fan, J.H.; Opriessnig, T.; Di, J.M.; Liu, B.J.; Zuo, Y.Z. Development and application of a recombinant M protein-based indirect ELISA for the detection of porcine deltacoronavirus IgG antibodies. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 249, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thachil, A.; Gerber, P.F.; Xiao, C.T.; Huang, Y.W.; Opriessnig, T. Development and application of an ELISA for the detection of porcine deltacoronavirus IgG antibodies. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas-Romero, S.; Rivera-Benítez, J.F.; Blomström, A.L.; Ramliden, M.; Hernández-Baumgarten, E.; Hernández-Jáuregui, P.; Ramírez-Mendoza, H.; Berg, M. Molecular characterisation of Porcine rubulavirus (PorPV) isolates from different outbreaks in Mexico. Virus Genes 2016, 52, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas-Romero, J.S.; Cerriteño-Sánchez, J.L.; Lara-Romero, R.; Vega-López, M.A.; Ramírez-Estudillo, C.; Ramírez-Mendoza, H.; Berg, M.; Lövgren-Bengtsson, K. Immunogenicity of a recombinant hemagglutinin neuraminidase-Porcine rubulavirus produced by Escherichia coli of Porcine rubulavirus gives protective immunity of litter after challenge. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 1595–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.K.; Wu, H.; Yan, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M.; Tang, X.; Temperton, N.J.; Weiss, R.A.; Brenchley, J.M.; et al. T cell responses to whole SARS coronavirus in humans. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5490–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laude, H.; Gelfi, J.; Lavenant, L.; Charley, B. Single amino acid changes in the viral glycoprotein M affect induction of alpha interferon by the coronavirus transmissible gastroenteritis virus. J. Virol. 1992, 66, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudoux, P.; Carrat, C.; Besnardeau, L.; Charley, B.; Laude, H. Coronavirus pseudoparticles formed with recombinant M and E proteins induce alpha interferon synthesis by leukocytes. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 8636–8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lednicky, J.A.; Tagliamonte, M.S.; White, S.K.; Elbadry, M.A.; Alam, M.M.; Stephenson, C.J.; Bonny, T.S.; Loeb, J.C.; Telisma, T.; Chavannes, S.; et al. Independent infections of porcine deltacoronavirus among Haitian children. Nature 2021, 600, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Consensus M-PDCoV | CHzmd2019 | HKU15 | M-PED CV777 | M-TGE Miller M6 | USA/Minnesota292/2014 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Consensus M-PDCoV | 0.867 * | 0.835 * | 0.220 | 0.189 | 0.797 * | |
| CHzmd2019 | 0.867 * | 0.803 * | 0.214 | 0.190 | 0.787 * | |
| HKU15 | 0.835 * | 0.803 * | 0.217 | 0.175 | 0.846 * | |
| M-PED CV777 | 0.220 | 0.214 | 0.217 | 0.235 | 0.216 | |
| M-TGE Miller M6 | 0.189 | 0.190 | 0.175 | 0.235 | 0.181 | |
| USA/Minnsota292/2014 | 0.797 * | 0.797 * | 0.846 * | 0.216 | 0.216 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Castañeda-Montes, F.J.; Cerriteño-Sánchez, J.L.; Castañeda-Montes, M.A.; Cuevas-Romero, J.S.; Mendoza-Elvira, S. A Candidate Antigen of the Recombinant Membrane Protein Derived from the Porcine Deltacoronavirus Synthetic Gene to Detect Seropositive Pigs. Viruses 2023, 15, 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051049
Castañeda-Montes FJ, Cerriteño-Sánchez JL, Castañeda-Montes MA, Cuevas-Romero JS, Mendoza-Elvira S. A Candidate Antigen of the Recombinant Membrane Protein Derived from the Porcine Deltacoronavirus Synthetic Gene to Detect Seropositive Pigs. Viruses. 2023; 15(5):1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051049
Chicago/Turabian StyleCastañeda-Montes, Francisco Jesus, José Luis Cerriteño-Sánchez, María Azucena Castañeda-Montes, Julieta Sandra Cuevas-Romero, and Susana Mendoza-Elvira. 2023. "A Candidate Antigen of the Recombinant Membrane Protein Derived from the Porcine Deltacoronavirus Synthetic Gene to Detect Seropositive Pigs" Viruses 15, no. 5: 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051049
APA StyleCastañeda-Montes, F. J., Cerriteño-Sánchez, J. L., Castañeda-Montes, M. A., Cuevas-Romero, J. S., & Mendoza-Elvira, S. (2023). A Candidate Antigen of the Recombinant Membrane Protein Derived from the Porcine Deltacoronavirus Synthetic Gene to Detect Seropositive Pigs. Viruses, 15(5), 1049. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051049