Poly(I:C) Induces Distinct Liver Cell Type-Specific Responses in Hepatitis B Virus-Transgenic Mice In Vitro, but Fails to Induce These Signals In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. All-in-One Liver Cell Preparation
2.3. Mouse Experiments
2.4. Cell Culture and Cell Stimulation
2.5. LEGENDplex™
2.6. RNA Isolation and One-Step Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.7. Statistical Analysis
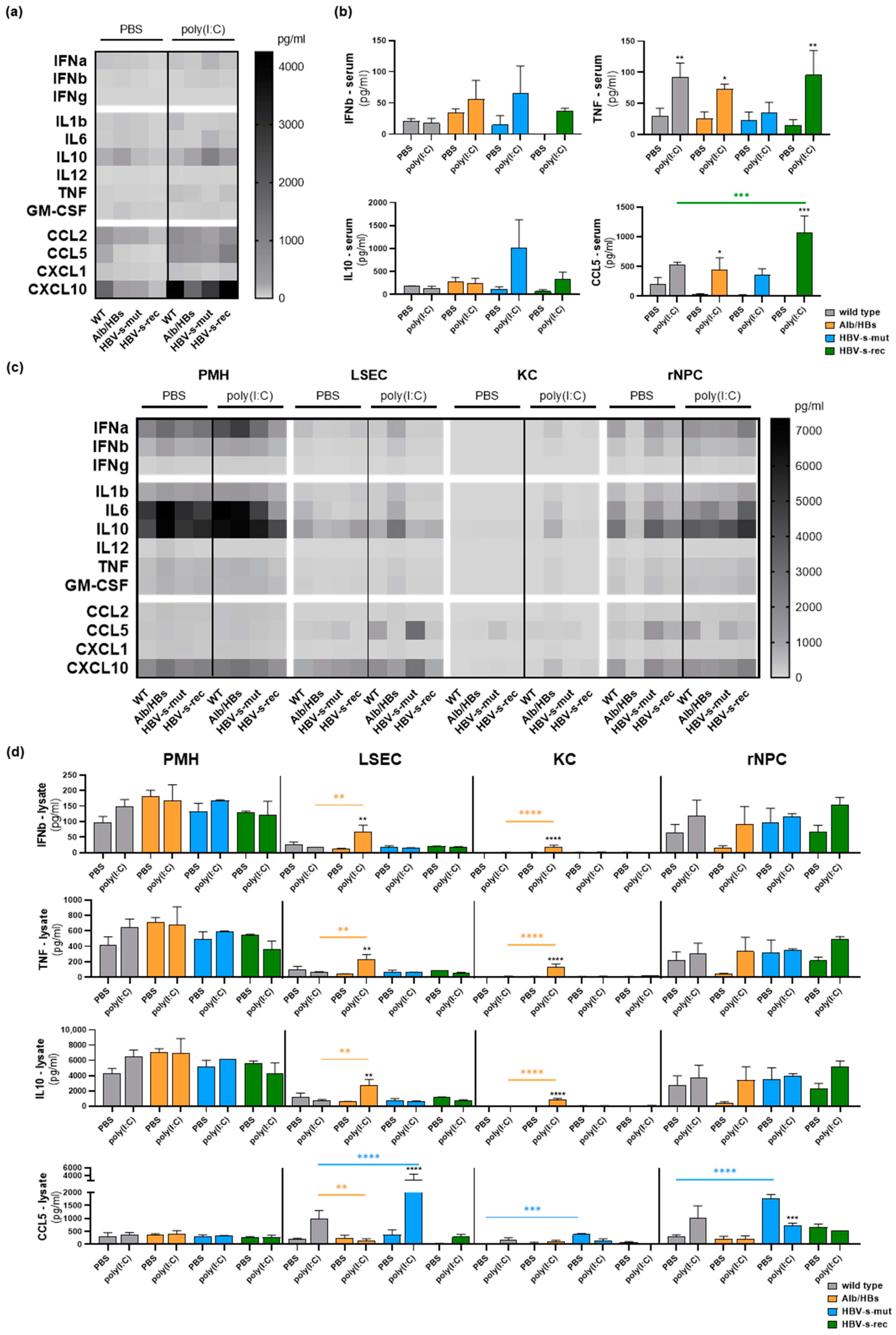
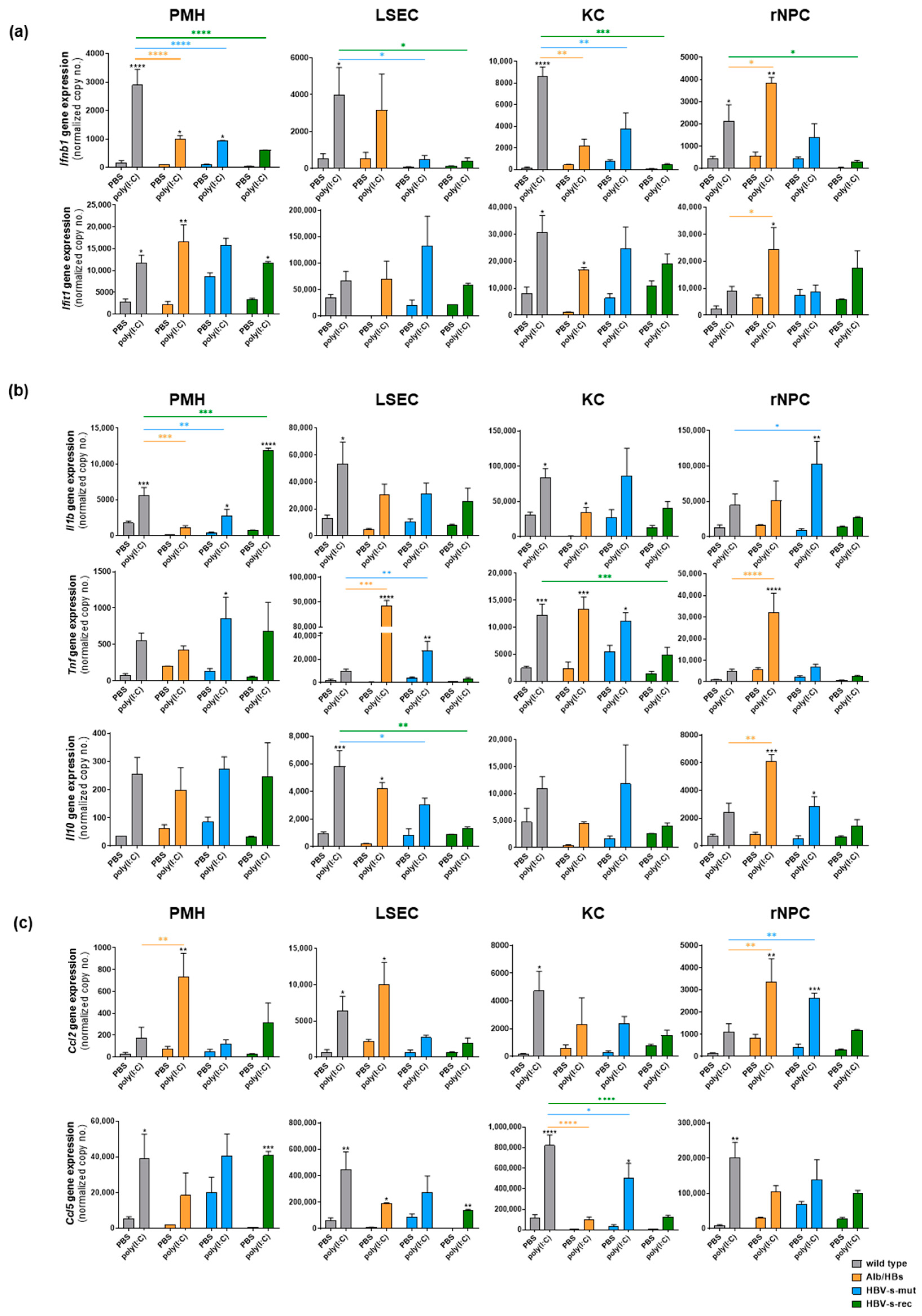
3. Results
3.1. Poly(I:C) Responsiveness In Vitro Is Cell Type- and Mouse Strain-Dependent
3.2. HBV-Transgenic Mouse Strains Exhibit Distinct Poly(I:C) Responsiveness In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Alberts, C.J.; Clifford, G.M.; Georges, D.; Negro, F.; Lesi, O.A.; Hutin, Y.J.; de Martel, C. Worldwide prevalence of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus among patients with cirrhosis at country, region, and global levels: A systematic review. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2019 Hepatitis B Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of hepatitis B, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 796–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suslov, A.; Boldanova, T.; Wang, X.; Wieland, S.; Heim, M.H. Hepatitis B Virus Does Not Interfere With Innate Immune Responses in the Human Liver. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1778–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Innate and adaptive immune responses in chronic hepatitis B virus infections: Towards restoration of immune control of viral infection. Gut 2012, 61, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland, S.F.; Chisari, F.V. Stealth and cunning: Hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 9369–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kagan, J.C. Toll-like Receptors and the Control of Immunity. Cell 2020, 180, 1044–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, K.T.; Gale, M., Jr.; Loo, Y.M. RIG-I and Other RNA Sensors in Antiviral Immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 667–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isogawa, M.; Robek, M.D.; Furuichi, Y.; Chisari, F.V. Toll-like receptor signaling inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in vivo. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7269–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Goyal, A.; Perelson, A.S.; Ishida, Y.; Saito, T.; Gale, M., Jr. Suppression of hepatitis B virus through therapeutic activation of RIG-I and IRF3 signaling in hepatocytes. iScience 2021, 24, 101969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lu, M.; Meng, Z.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Szczeponek, A.; Krux, F.; Dittmer, U.; Roggendorf, M.; Gerken, G.; et al. Toll-like receptor-mediated control of HBV replication by nonparenchymal liver cells in mice. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Real, C.I.; Lu, M.; Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Trippler, M.; Hossbach, M.; Deckert, J.; Jahn-Hofmann, K.; Ickenstein, L.M.; John, M.J.; et al. Hepatitis B virus genome replication triggers toll-like receptor 3-dependent interferon responses in the absence of hepatitis B surface antigen. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broering, R.; Lutterbeck, M.; Trippler, M.; Kleinehr, K.; Poggenpohl, L.; Paul, A.; Gerken, G.; Schlaak, J.F. Long-term stimulation of Toll-like receptor 3 in primary human hepatocytes leads to sensitization for antiviral responses induced by poly I:C treatment. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, M.; Schefczyk, S.; Trippler, M.; Treckmann, J.W.; Baba, H.A.; Gerken, G.; Schlaak, J.F.; Broering, R. Antiviral Toll-like Receptor Signaling in Non-Parenchymal Liver Cells Is Restricted to TLR3. Viruses 2022, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Hu, F.; Su, L. Cell Culture Models and Animal Models for HBV Study. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1179, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Prieto, A.M.; Cherry, C.; Gunn, H.; Dorner, M. In Vivo Model Systems for Hepatitis B Virus Research. ACS Infect Dis 2019, 5, 688–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Matzke, B.; Schaller, H.; Chisari, F.V. High-level hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mice. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 6158–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halverscheid, L.; Mannes, N.K.; Weth, R.; Kleinschmidt, M.; Schultz, U.; Reifenberg, K.; Schirmbeck, R.; Nassal, M.; Blum, H.E.; Reimann, J.; et al. Transgenic mice replicating hepatitis B virus but lacking expression of the major HBsAg. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, L.; Allweiss, L.; Guerrieri, F.; Pediconi, N.; Volz, T.; Pollicino, T.; Petersen, J.; Raimondo, G.; Dandri, M.; Levrero, M. IFN-α inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprichard, S.L.; Boyd, B.; Althage, A.; Chisari, F.V. Clearance of hepatitis B virus from the liver of transgenic mice by short hairpin RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, F.V.; Klopchin, K.; Moriyama, T.; Pasquinelli, C.; Dunsford, H.A.; Sell, S.; Pinkert, C.A.; Brinster, R.L.; Palmiter, R.D. Molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Cell 1989, 59, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisari, F.V.; Filippi, P.; Buras, J.; McLachlan, A.; Popper, H.; Pinkert, C.A.; Palmiter, R.D.; Brinster, R.L. Structural and pathological effects of synthesis of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide in transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 6909–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Werner, M.; Broering, R.; Yang, D.; Lu, M. Advanced Method for Isolation of Mouse Hepatocytes, Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells, and Kupffer Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1540, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Kohno, T.; Yasui, K.; Murota, H.; Kimura, T.; Duncan, G.S.; Nakashima, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Katayama, I.; Ma, Y.; et al. Characterization of dsRNA-induced pancreatitis model reveals the regulatory role of IFN regulatory factor 2 (Irf2) in trypsinogen5 gene transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18766–18771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busnadiego, I.; Fernbach, S.; Pohl, M.O.; Karakus, U.; Huber, M.; Trkola, A.; Stertz, S.; Hale, B.G. Antiviral Activity of Type I, II, and III Interferons Counterbalances ACE2 Inducibility and Restricts SARS-CoV-2. mBio 2020, 11, e01928-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallusto, F.; Mackay, C.R.; Lanzavecchia, A. The role of chemokine receptors in primary, effector, and memory immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2000, 18, 593–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megahed, F.A.K.; Zhou, X.; Sun, P. The Interactions between HBV and the Innate Immunity of Hepatocytes. Viruses 2020, 12, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Olagnier, D.; Lin, R. Host and Viral Modulation of RIG-I-Mediated Antiviral Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfner, K.P.; Hornung, V. Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutz, P.; Metz, P.; Lempp, F.A.; Bender, S.; Qu, B.; Schoneweis, K.; Seitz, S.; Tu, T.; Restuccia, A.; Frankish, J.; et al. HBV Bypasses the Innate Immune Response and Does Not Protect HCV From Antiviral Activity of Interferon. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 1791–1804.e1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Li, K.; Kameyama, T.; Hayashi, T.; Ishida, Y.; Murakami, S.; Watanabe, T.; Iijima, S.; Sakurai, Y.; Watashi, K.; et al. The RNA sensor RIG-I dually functions as an innate sensor and direct antiviral factor for hepatitis B virus. Immunity 2015, 42, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrier, E.R.; Yim, S.A.; Heydmann, L.; El Saghire, H.; Bach, C.; Turon-Lagot, V.; Mailly, L.; Durand, S.C.; Lucifora, J.; Durantel, D.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Evasion From Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate-Adenosine Monophosphate Synthase Sensing in Human Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1695–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Trippler, M.; Real, C.I.; Werner, M.; Luo, X.; Schefczyk, S.; Kemper, T.; Anastasiou, O.E.; Ladiges, Y.; Treckmann, J.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Particles Activate Toll-Like Receptor 2 Signaling Initially Upon Infection of Primary Human Hepatocytes. Hepatology 2020, 72, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, R.; Lu, M.; Liu, S.; Baba, H.A.; Gerken, G.; Wedemeyer, H.; Broering, R. Hippo Pathway Counter-Regulates Innate Immunity in Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 684424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Tang, H. Mechanism of inhibiting type I interferon induction by hepatitis B virus X protein. Protein Cell 2010, 1, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Mao, A.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Tien, P. Hepatitis B virus X protein suppresses virus-triggered IRF3 activation and IFN-beta induction by disrupting the VISA-associated complex. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Chen, H.; Kato, N.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B virus polymerase inhibits RIG-I- and Toll-like receptor 3-mediated beta interferon induction in human hepatocytes through interference with interferon regulatory factor 3 activation and dampening of the interaction between TBK1/IKKepsilon and DDX3. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, T.; Lo, C.; Skinner, N.; Locarnini, S.; Visvanathan, K.; Mansell, A. The hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) targets and suppresses activation of the toll-like receptor signaling pathway. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Jiang, M.; Pei, R.; Trippler, M.; Broering, R.; Bucchi, A.; Sowa, J.P.; Dittmer, U.; Yang, D.; et al. Hepatitis B virus suppresses toll-like receptor-mediated innate immune responses in murine parenchymal and nonparenchymal liver cells. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Prieto, A.M.; Dorner, M. Immune Evasion Strategies during Chronic Hepatitis B and C Virus Infection. Vaccines 2017, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebosse, F.; Testoni, B.; Fresquet, J.; Facchetti, F.; Galmozzi, E.; Fournier, M.; Hervieu, V.; Berthillon, P.; Berby, F.; Bordes, I.; et al. Intrahepatic innate immune response pathways are downregulated in untreated chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broering, R.; Wu, J.; Meng, Z.; Hilgard, P.; Lu, M.; Trippler, M.; Szczeponek, A.; Gerken, G.; Schlaak, J.F. Toll-like receptor-stimulated non-parenchymal liver cells can regulate hepatitis C virus replication. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolay, W.; Moeller, R.; Kahl, S.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Pietschmann, T.; Kunz, S.; Gerold, G. Characterization of RNA Sensing Pathways in Hepatoma Cell Lines and Primary Human Hepatocytes. Cells 2021, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.K.; Jeevan-Raj, B.; Netter, H.J. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Subviral Particles as Protective Vaccines and Vaccine Platforms. Viruses 2020, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Z.; Hu, C.; Qian, F.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, M.; Shi, B.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, Z. Hepatitis B virus surface antigen selectively inhibits TLR2 ligand-induced IL-12 production in monocytes/macrophages by interfering with JNK activation. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5142–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Chang, L.; Wu, L.; Yuan, Y.F. IL-6 Plays a Crucial Role in HBV Infection. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2015, 3, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Lu, M. Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated innate immune responses in the control of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 204, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, R.L.; Legras, X.; Barzi, M. Cre/LoxP-HBV plasmids generating recombinant covalently closed circular DNA genome upon transfection. Virus Res 2021, 292, 198224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, Y.; Shao, D.; Chang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, D.; Gao, Y.; Lan, K.; Deng, Q. Recombinant covalently closed circular DNA of hepatitis B virus induces long-term viral persistence with chronic hepatitis in a mouse model. Hepatology 2018, 67, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Target | Company | Order No. | Forward Primer | REVERSE PRIMER |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tnf | Qiagen | QT00104006 | ||
| Il1b | Qiagen | QT01048355 | ||
| Il10 | Qiagen | QT00106169 | ||
| Ccl2 | Qiagen | QT00167832 | ||
| Ccl5 | Qiagen | QT01747165 | ||
| Ifnb | Qiagen | QT00249662 | ||
| Ifit1 | 5’-CTGAAATGCCAAGTAGCAAGG-3′ | 5′-CCAAAGGCACAGACATAAGGA-3′ | ||
| Gapdh | 5′-AAATTCAACGGCACAGTCAA-3′ | 5′-TCTCCATGGTGGTGAAGACA-3′ | ||
| Tlr3 * | 5′-TTGTCTTCTGCACGAACCTG -3′ | 5′-CCCGTTCCCAACTTTGTAGA-3′ | ||
| Rig-I * | 5′-TTGCTGAGTGCAATCTCGTC-3′ | 5′-GTATGCGGTGAACCGTCTTT-3′ | ||
| HBx region | 5′-CCGTCTGTGCCTTCTCATCT-3′ | 5′-TAATCTCCTCCCCCAACTCC-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schefczyk, S.; Luo, X.; Liang, Y.; Trippler, M.; Lu, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Schmidt, H.H.; Broering, R. Poly(I:C) Induces Distinct Liver Cell Type-Specific Responses in Hepatitis B Virus-Transgenic Mice In Vitro, but Fails to Induce These Signals In Vivo. Viruses 2023, 15, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051203
Schefczyk S, Luo X, Liang Y, Trippler M, Lu M, Wedemeyer H, Schmidt HH, Broering R. Poly(I:C) Induces Distinct Liver Cell Type-Specific Responses in Hepatitis B Virus-Transgenic Mice In Vitro, but Fails to Induce These Signals In Vivo. Viruses. 2023; 15(5):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051203
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchefczyk, Stefan, Xufeng Luo, Yaojie Liang, Martin Trippler, Mengji Lu, Heiner Wedemeyer, Hartmut H. Schmidt, and Ruth Broering. 2023. "Poly(I:C) Induces Distinct Liver Cell Type-Specific Responses in Hepatitis B Virus-Transgenic Mice In Vitro, but Fails to Induce These Signals In Vivo" Viruses 15, no. 5: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051203
APA StyleSchefczyk, S., Luo, X., Liang, Y., Trippler, M., Lu, M., Wedemeyer, H., Schmidt, H. H., & Broering, R. (2023). Poly(I:C) Induces Distinct Liver Cell Type-Specific Responses in Hepatitis B Virus-Transgenic Mice In Vitro, but Fails to Induce These Signals In Vivo. Viruses, 15(5), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15051203






