Novel Mode of nanoLuciferase Packaging in SARS-CoV-2 Virions and VLPs Provides Versatile Reporters for Virus Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmid Production
2.2. Expression and Purification of SARS-CoV-2 VLPs
2.2.1. Cells
2.2.2. Transfection
2.2.3. VLP Collection
2.2.4. VLP Concentration and Purification with Sucrose Cushion Ultracentrifugation
2.2.5. Gradient Purification of VLPs
2.3. Western Blotting
2.4. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
2.5. Microscopy
2.6. nanoLuciferase VLP Measurement
2.7. Virus Growth, Purification, and nanoLuciferase Measurement
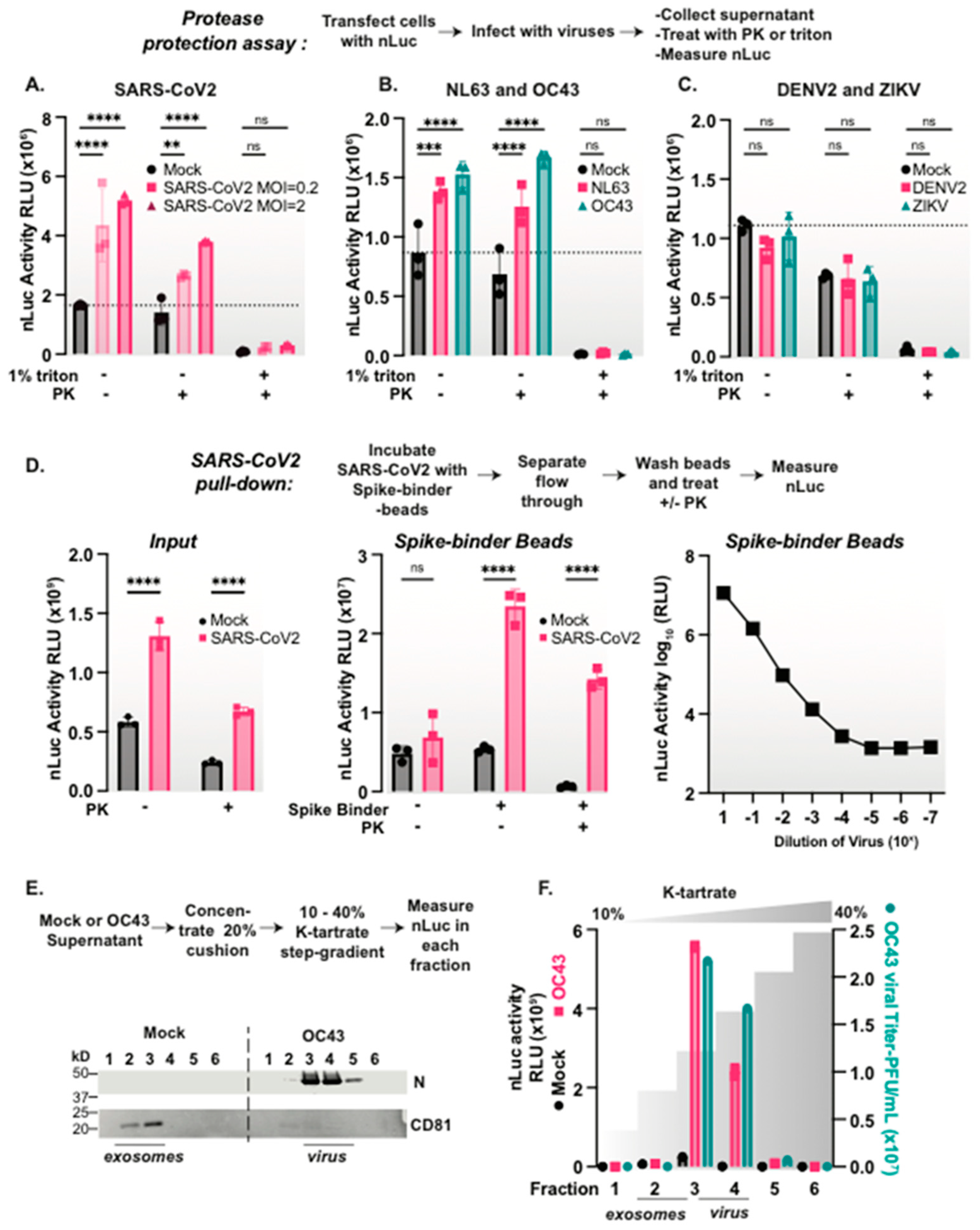
2.8. Protease Protection Assay
2.9. Spike Mini-Binder Pull-Down
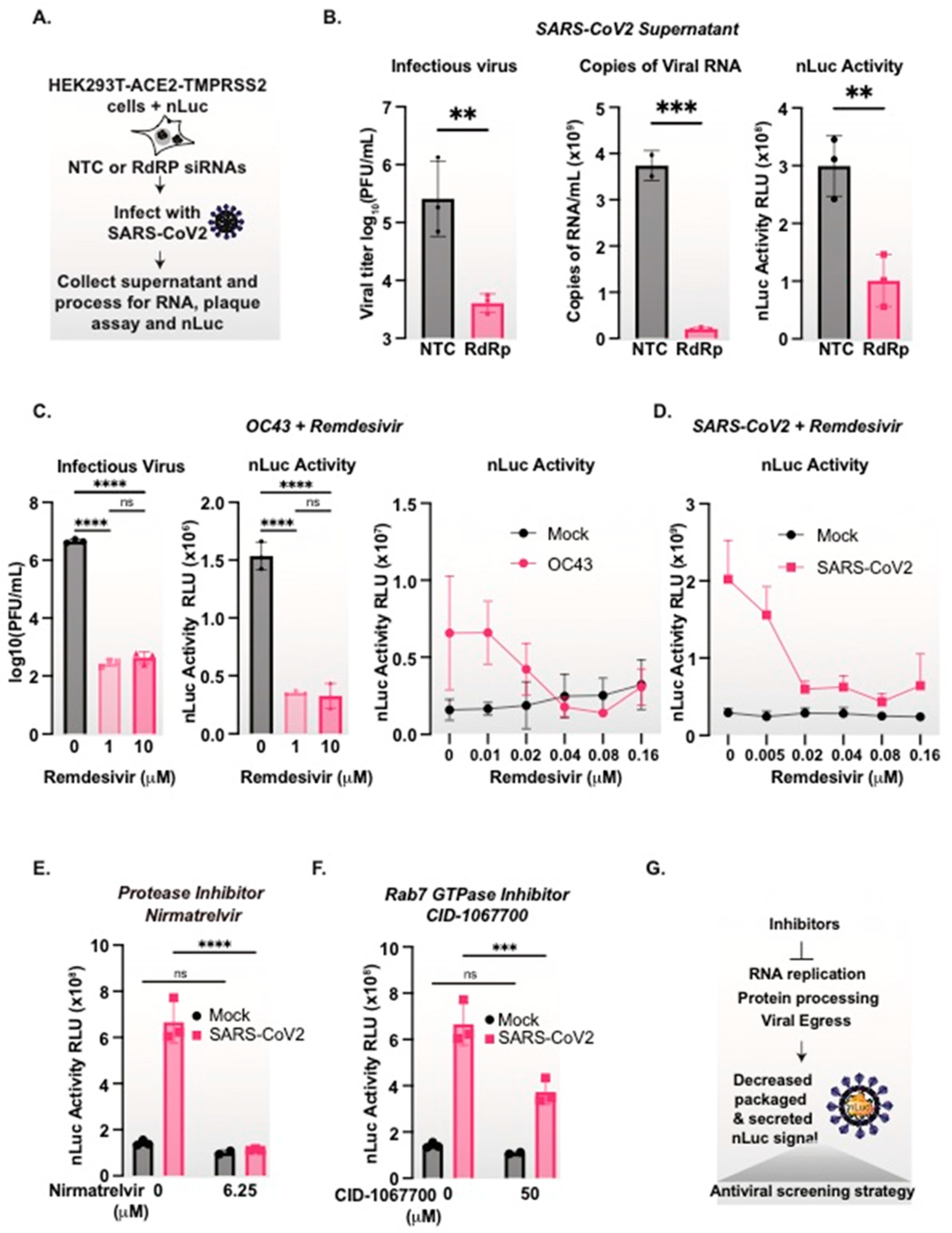
2.10. siRNA Treatments
2.11. Inhibitor Treatments
3. Results
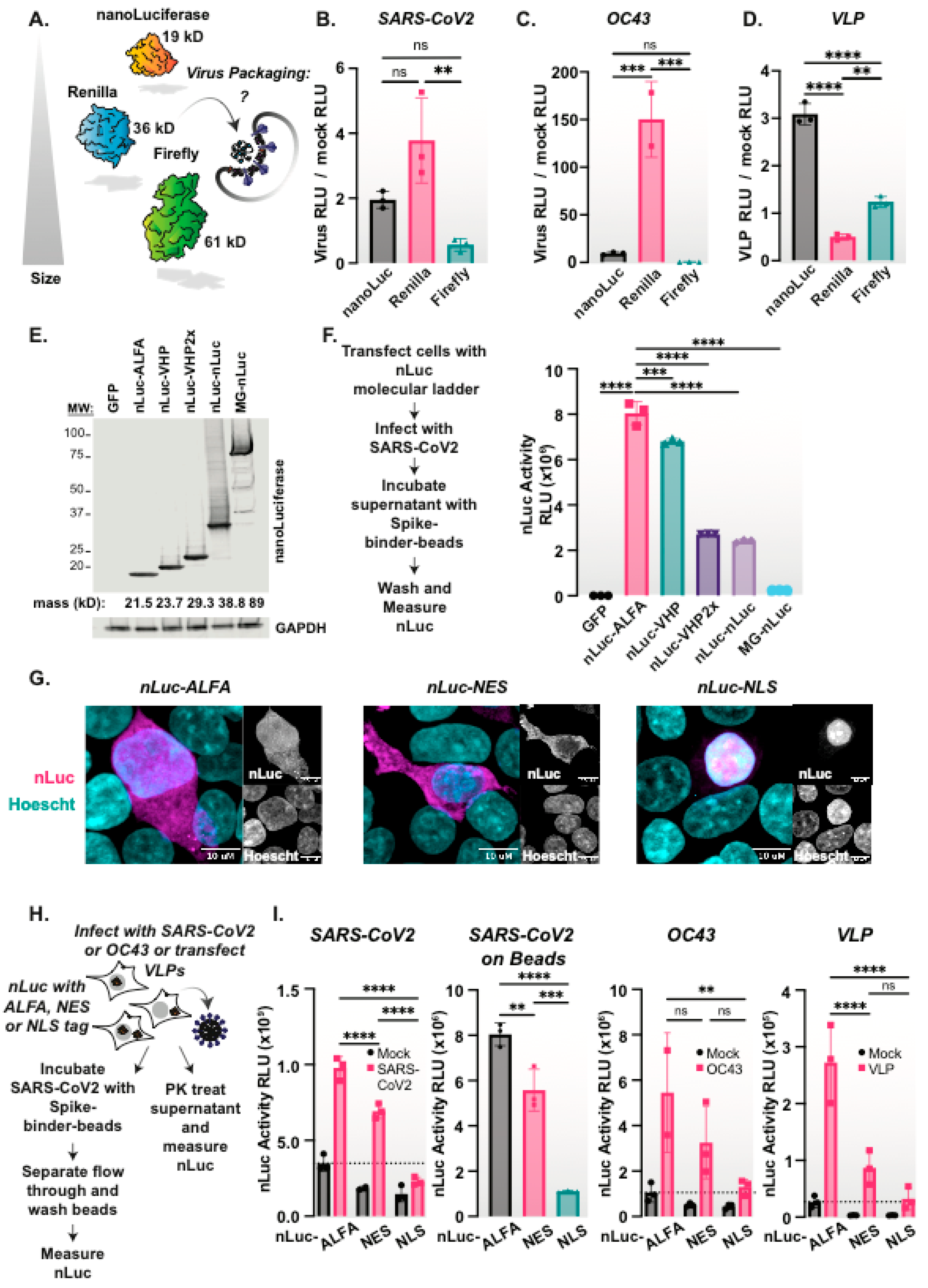
3.1. Development of SARS-CoV-2 Virus-Like Particles Bearing a Reporter mRNA
3.2. The nanoLuciferase Protein Is Packaged and Secreted in SARS-CoV-2 VLPs
3.3. Coronaviruses but Not Flaviviruses Package nanoLuciferase Reporters in Their Viral Particles
3.4. nLuc Is Packaged in SARS-CoV-2 Virus Particles
3.5. Size Constrains Non-Specific Protein Packaging into Coronavirus Particles
3.6. Subcellular Location Constrains nLuc Packaging into Coronaviruses
3.7. nanoLuciferase Activity Reports on SARS-CoV-2 Replication Levels
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufer, A.M.; Theis, T.; Lau, K.A.; Gray, J.L.; Rawlinson, W.D. Laboratory biosafety measures involving SARS-CoV-2 and the classification as a Risk Group 3 biological agent. Pathology 2020, 52, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Guo, H.; Zhou, P.; Shi, Z.L. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 19, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus Associated with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosten, C.; Günther, S.; Preiser, W.; Van Der Werf, S.; Brodt, H.-R.; Becker, S.; Rabenau, H.; Panning, M.; Kolesnikova, L.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; et al. Identification of a Novel Coronavirus in Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moh Zaki, A.; Van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E.; Fouchier, R.A.M. Isolation of a Novel Coronavirus from a Man with Pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, N.; Xu, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J.; Weng, T.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. Molecular Architecture of the SARS-CoV-2 Virus. Cell 2020, 183, 730–738.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Cortese, M.; Winter, S.L.; Wachsmuth-Melm, M.; Neufeldt, C.J.; Cerikan, B.; Stanifer, M.L.; Boulant, S.; Bartenschlager, R. SARS-CoV-2 structure and replication characterized by in situ cryo-electron tomography. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicari, D.; Chatziioannou, A.; Koutsandreas, T.; Sitia, R.; Chevet, E. Role of the early secretory pathway in SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Cell Biol. 2020, 219, e202006005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, H.; Batool, S.; Asif, S.; Ali, M.; Abbasi, B.H. Virus-Like Particles: Revolutionary Platforms for Developing Vaccines Against Emerging Infectious Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Wang, H.; Deng, F. Minireview Open Access Advances and challenges in enveloped virus-like particle (VLP)-based vaccines. J. Immunol. Sci. 2018, 2, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Syed, A.M.; Taha, T.Y.; Tabata, T.; Chen, I.P.; Ciling, A.; Khalid, M.M.; Sreekumar, B.; Chen, P.Y.; Hayashi, J.M.; Soczek, K.M.; et al. Rapid assessment of SARS-CoV-2 evolved variants using virus-like particles. Science 2021, 374, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Hawkins, G.M.; Kicmal, T.; Qing, E.; Timm, E.; Gallagher, T. Assembly and Entry of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2): Evaluation Using Virus-Like Particles. Cells 2021, 10, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Shi, M.; Li, J.; Song, P.; Li, N. Construction of SARS-CoV-2 Virus-Like Particles by Mammalian Expression System. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plescia, C.B.; David, E.A.; Patra, D.; Sengupta, R.; Amiar, S.; Su, Y.; Stahelin, R.V. SARS-CoV-2 viral budding and entry can be modeled using BSL-2 level virus-like particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, K.B.; Jeon, J.H.; Choi, H.; Park, J.S.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Park, J.M.; Cho, H.S.; Moon, J.S.; Oh, H.; et al. Construction of SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles in plant. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Xie, T.; Zhu, B.; Tan, J.; Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, F.; Niu, H.; Han, J.; Lv, W.; et al. Production of SARS-CoV-2 virus-like particles in insect cells. Vaccines 2021, 9, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boson, B.; Legros, V.; Zhou, B.; Siret, E.; Mathieu, C.; Cosset, F.L.; Lavillette, D.; Denolly, S. The SARS-CoV-2 envelope and membrane proteins modulate maturation and retention of the spike protein, allowing assembly of virus-like particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, H.; Sharma, A.; Preece, B.; Peterson, A.; Eldridge, C.; Belnap, D.M.; Vershinin, M. Minimal system for assembly of SARS-CoV-2 virus like particles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malicoat, J.; Manivasagam, S.; Zuñiga, S.; Sola, I.; McCabe, D.; Rong, L.; Perlman, S.; Enjuanes, L.; Manicassamy, B. Development of a Single-Cycle Infectious SARS-CoV-2 Virus Replicon Particle System for Use in Biosafety Level 2 Laboratories. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e01837–e01921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Lokugamage, K.G.; Zhang, X.; Vu, M.N.; Muruato, A.E.; Menachery, V.D.; Shi, P.Y. Engineering SARS-CoV-2 using a reverse genetic system. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 163, 1761–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, M.P.; Unch, J.; Binkowski, B.F.; Valley, M.P.; Butler, B.L.; Wood, M.G.; Otto, P.; Zimmerman, K.; Vidugiris, G.; Machleidt, T.; et al. Engineered luciferase reporter from a deep sea shrimp utilizing a novel imidazopyrazinone substrate. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; O’Meara, M.J.; Rezelj, V.V.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Pierson, T.C.; Dowd, K.A. Pseudo-Infectious Reporter Virus Particles for Measuring Antibody-Mediated Neutralization and Enhancement of Dengue Virus Infection; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Tutucci, E.; Vera, M.; Biswas, J.; Garcia, J.; Parker, R.; Singer, R.H. An improved MS2 system for accurate reporting of the mRNA life cycle. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scavone, F.; Gumbin, S.C.; Da Rosa, P.A.; Kopito, R.R. RPL26/uL24 UFMylation is essential for ribosome-associated quality control at the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2220340120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, R.C.; Steel, J.J.; Pujari, V.; Rovnak, J.; Crick, D.C.; Perera, R. Stearoly-CoA desaturase 1 differentiates early and advanced dengue virus infections and determines virus particle infectivity. Randall, G., editor. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Goreshnik, I.; Coventry, B.; Case, J.B.; Miller, L.; Kozodoy, L.; Chen, R.E.; Carter, L.; Park, Y.-J.; Strauch, E.M. De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors. Science 2020, 370, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-F.; Chen, Y.-F.; Yang, C.-C.; Chou, Y.-L.; Chou, H.-W.; Chang, T.-Y.; Chao, T.-L.; Hsu, S.-C.; Ieong, S.-M.; et al. A siRNA targets and inhibits a broad range of SARS-CoV-2 infections including Delta variant. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e15298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, Y.L.; Teoh, K.T.; Lo, J.; Chan, C.M.; Kien, F.; Escriou, N.; Tsao, S.W.; Nicholls, J.M.; Altmeyer, R.; Peiris, J.S.M. The M, E, and N Structural Proteins of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Are Required for Efficient Assembly, Trafficking, and Release of Virus-Like Particles. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 11318–11330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.T.; Wang, S.M.; Huang, K.J.; I-Ru Lee, A.; Chiang, C.C.; Wang, C.T. Self-assembly of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus membrane protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 12862–12872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsin, W.C.; Chang, C.H.; Chang, C.Y.; Peng, W.H.; Chien, C.L.; Chang, M.F.; Chang, S.C. Nucleocapsid protein-dependent assembly of the RNA packaging signal of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortola, E.; Roy, P. Efficient assembly and release of SARS coronavirus-like particles by a heterologous expression system. FEBS Lett. 2004, 576, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoeman, D.; Fielding, B.C. Coronavirus Envelope Protein: Current Knowledge. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatagopalan, P.; Daskalova, S.M.; Lopez, L.A.; Dolezal, K.A.; Hogue, B.G. Coronavirus envelope (E) protein remains at the site of assembly. Virology 2015, 478, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, C.G.; Ehlerding, E.B.; Cai, W. NanoLuc: A Small Luciferase is Brightening up the Field of Bioluminescence. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, A.; Spahr, P.F. Nucleotide Sequence at the Binding Site for Coat Protein on RNA of Bacteriophage R17. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, R.M.; Butrapet, S.; Chang, G.-J.J.; Tsuchiya, K.R.; Roehrig, J.T.; Bhamarapravati, N.; Gubler, D.J. Construction of Infectious cDNA Clones for Dengue 2 Virus: Strain 16681 and Its Attenuated Vaccine Derivative, Strain PDK-53. Virology 1997, 230, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Lambert, A.J.; Holodniy, M.; Saavedra, S.; del Carmen Castillo, S.L. Phylogeny of Zika Virus in Western Hemisphere, 2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 933–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götzke, H.; Kilisch, M.; Martínez-Carranza, M.; Sograte-Idrissi, S.; Rajavel, A.; Schlichthaerle, T.; Engels, N.; Jungmann, R.; Stenmark, P.; Opazo, F.; et al. The ALFA-tag is a highly versatile tool for nanobody-based bioscience applications. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, L.; Howe, A.; Gilchrist, J.B.; Sheng, Y.; Sun, D.; Knight, M.L.; Zanetti-Domingues, L.C.; Bateman, B.; Krebs, A.-S.; Chen, L.; et al. Correlative multi-scale cryo-imaging unveils SARS-CoV-2 assembly and egress. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheahan, T.P.; Sims, A.C.; Graham, R.L.; Menachery, V.D.; Gralinski, L.E.; Case, J.B.; Leist, S.R.; Pyrc, K.; Feng, J.Y.; Trantcheva, I.; et al. Broad-spectrum antiviral GS-5734 inhibits both epidemic and zoonotic coronaviruses. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19—Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinosoglou, K.; Schinas, G.; Gogos, C. Oral Antiviral Treatment for COVID-19: A Comprehensive Review on Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir. Viruses 2022, 14, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, D.R.; Allerton, C.M.N.; Anderson, A.S.; Aschenbrenner, L.; Avery, M.; Berritt, S.; Boras, B.; Cardin, R.D.; Carlo, A.; Coffman, K.J.; et al. An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science 2021, 374, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Dellibovi-Ragheb, T.A.; Kerviel, A.; Pak, E.; Qiu, Q.; Fisher, M.; Takvorian, P.M.; Bleck, C.; Hsu, V.W.; Fehr, A.R.; et al. β-Coronaviruses Use Lysosomes for Egress Instead of the Biosynthetic Secretory Pathway. Cell 2020, 183, 1520–1535.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, R.J.; Zhang, W.; Rossmann, M.G.; Pletnev, S.V.; Corver, J.; Lenches, E.; Jones, C.T.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Chipman, P.R.; Strauss, E.G.; et al. Structure of Dengue Virus Implications for Flavivirus Organization, Maturation, and Fusion. Cell 2002, 108, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, S.D.; Xia, D.; Wastling, J.M.; Neuman, B.W.; Britton, P.; Maier, H.J. The proteome of the infectious bronchitis virus Beau-R virion. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96 Pt 12, 3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, B.W.; Joseph, J.S.; Saikatendu, K.S.; Serrano, P.; Chatterjee, A.; Johnson, M.A.; Liao, L.; Klaus, J.P.; Yates, J.R., III; Wu, K.; et al. Proteomics Analysis Unravels the Functional Repertoire of Coronavirus Nonstructural Protein 3. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5279–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Xue, C.; Ren, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Shu, D.; Bi, Y.; Cao, Y. Proteomic analysis of purified coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus particles. Proteome Sci. 2010, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zandi, R. Biophysical Modeling of SARS-CoV-2 Assembly: Genome Condensation and Budding. Viruses 2022, 14, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer Name | Sequence |
|---|---|
| EGFP-qRTPCR-FWD | TCGCCGACCACTACCAGCAGAA |
| EGFP-qRTPCR-REV | CGCGCTTCTCGTTGGGGTCTTT |
| NSP15-qRTPCR_FWD | TTTGGGTGTGGACATTGCTGCT |
| NSP15-qRTPCR_REV | ACAGTGAGTGGTGCACAAATCGT |
| GAPDH-qRTPCR_FWD | TTCGACAGTCAGCCGCATCTTCTT |
| GAPDH-qRTPCR_REV | GCCCAATACGACCAAATCCGTTGA |
| nLuc-12xMBL-FL_FWD | ATGGTCTTCACACTCGAAGATTTCG |
| nLuc-12xMBL-FL_REV | CAGGTTCAGGGGGAGGTGTG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gullberg, R.C.; Frydman, J. Novel Mode of nanoLuciferase Packaging in SARS-CoV-2 Virions and VLPs Provides Versatile Reporters for Virus Production. Viruses 2023, 15, 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061335
Gullberg RC, Frydman J. Novel Mode of nanoLuciferase Packaging in SARS-CoV-2 Virions and VLPs Provides Versatile Reporters for Virus Production. Viruses. 2023; 15(6):1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061335
Chicago/Turabian StyleGullberg, Rebekah C., and Judith Frydman. 2023. "Novel Mode of nanoLuciferase Packaging in SARS-CoV-2 Virions and VLPs Provides Versatile Reporters for Virus Production" Viruses 15, no. 6: 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061335
APA StyleGullberg, R. C., & Frydman, J. (2023). Novel Mode of nanoLuciferase Packaging in SARS-CoV-2 Virions and VLPs Provides Versatile Reporters for Virus Production. Viruses, 15(6), 1335. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061335






