Comparison of Immune Responses between Inactivated and mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Used for a Booster Dose in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Vaccines
2.2. Mouse Studies
2.3. IgG/IgG1/IgG2a Titer Measurement
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunospot (ELISPOT) Assay
2.5. Pseudovirus-Based Neutralization Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. LNP-mRNA Vaccines Were Formulated with Efficient Encapsulation of mRNA with a Uniform Particle Size
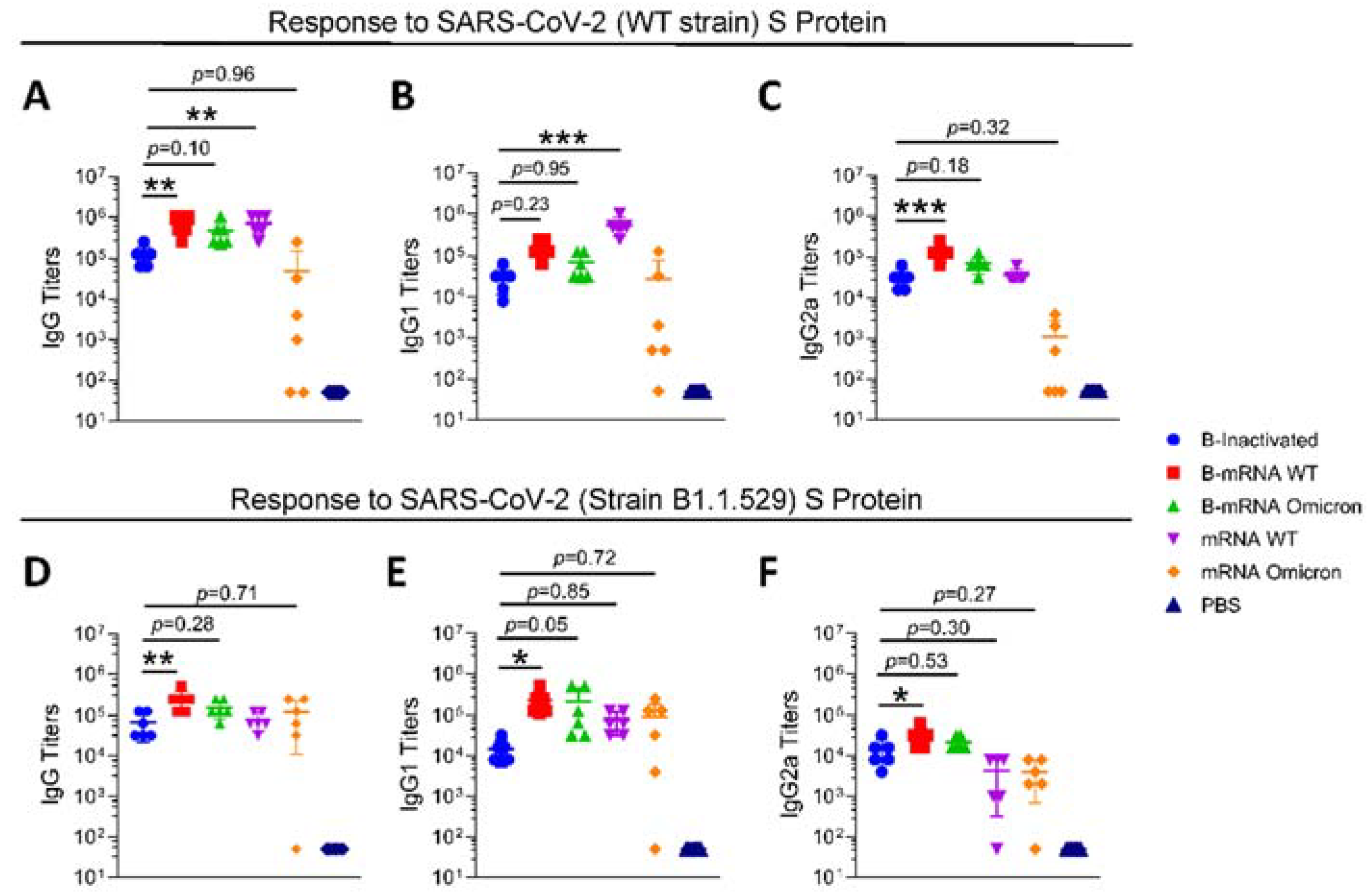
3.2. After Two Doses of an Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine, Boosting with the mRNA Vaccine Induces the Elevation of IgG Titers
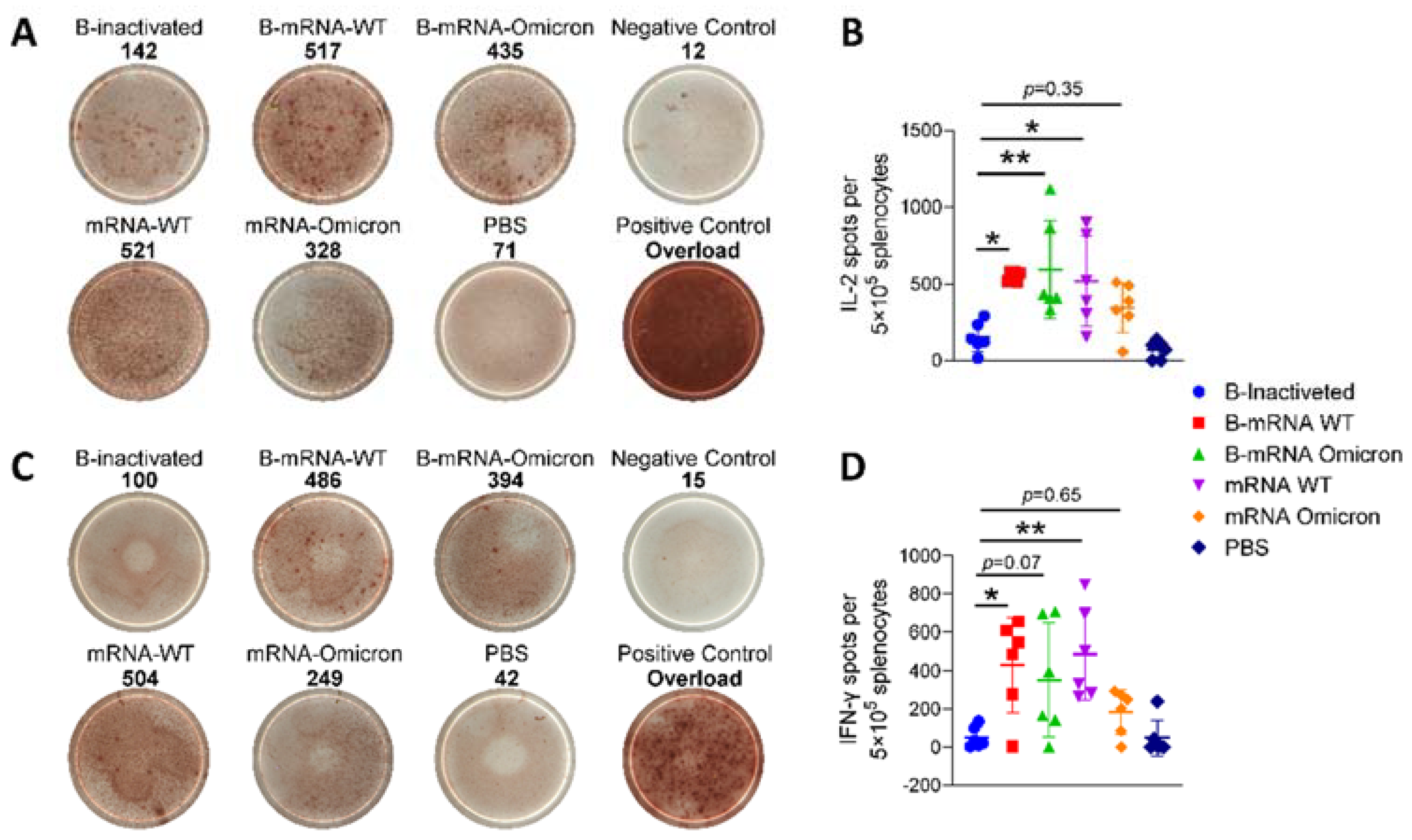
3.3. Regarding Two-Dose Inactivated Vaccine Immunization, Boosting with Two Doses of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines Induced Potent Cell-Mediated Immunity
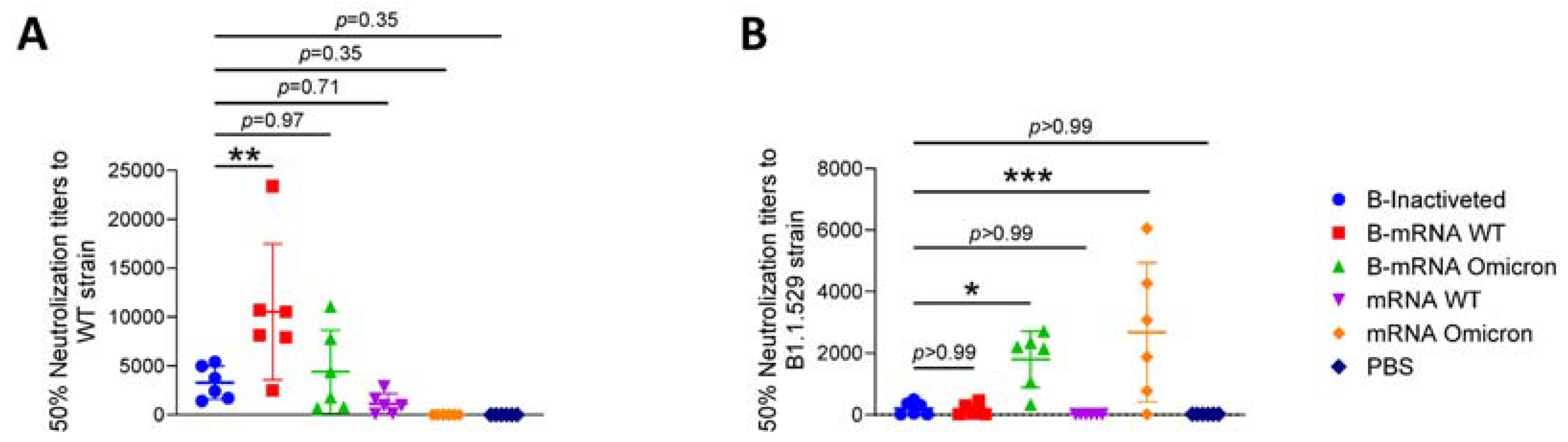
3.4. The Cross-Protection Afforded by Neutralizing Antibodies (nAbs) Produced in Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Was Reduced
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Huang, B.; Li, G.; Chang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chu, K.; Hu, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wu, J.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of a 3-Dose Regimen of a SARS-CoV-2 Inactivated Vaccine in Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Eygeris, Y.; Gupta, M.; Sahay, G. Self-assembled mRNA vaccines. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2021, 170, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Aguado, I.; Rodriguez-Castejon, J.; Vicente-Pascual, M.; Rodriguez-Gascon, A.; Solinis, M.A.; Del Pozo-Rodriguez, A. Nanomedicines to Deliver mRNA: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masuda, T.; Murakami, K.; Sugiura, K.; Sakui, S.; Philip Schuring, R.; Mori, M. A phase 1/2 randomised placebo-controlled study of the COVID-19 vaccine mRNA-1273 in healthy Japanese adults: An interim report. Vaccine 2022, 40, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. RNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccine BNT162b2 Selected for a Pivotal Efficacy Study. medRxiv, 2020; preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, E. The next generation of coronavirus vaccines: A graphical guide. Nature 2023, 614, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Rocha, C.; Kempf, A.; Nehlmeier, I.; Graichen, L.; Winkler, M.S.; Lier, M.; Schulz, S.; Jack, H.M.; Cossmann, A.; et al. The spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 variant A.30 is heavily mutated and evades vaccine-induced antibodies with high efficiency. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2673–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Lu, S.; He, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Tang, C.; Yang, T.; Yu, W.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; et al. Three doses of prototypic SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine induce cross-protection against its variants of concern. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, N.; Wang, Y.; Cao, H.; Lin, K.; Liu, C. Comparison of immune responses induced by two or three doses of an alum-adjuvanted inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in mice. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 2250–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Liu, X.; Pu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, Z.; Jiang, R.; Yin, Z.; Xu, M.; Yin, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial of an Inactivated Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Vaccine in Healthy Adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3949–e3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Luan, N.; Lin, K.; Liu, C. Effects of Varicella-Zoster Virus Glycoprotein E Carboxyl-Terminal Mutation on mRNA Vaccine Efficacy. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, N.; Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Lin, K.; Liu, C. LNP-CpG ODN-adjuvanted varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein E induced comparable levels of immunity with Shingrix(TM) in VZV-primed mice. Virol. Sin. 2022, 37, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creech, C.B.; Walker, S.C.; Samuels, R.J. SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines. JAMA 2021, 325, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleem, A.; Akbar Samad, A.B.; Vaqar, S. Emerging Variants of SARS-CoV-2 and Novel Therapeutics Against Coronavirus (COVID-19) [Updated 2023 May 8]. In StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK570580/ (accessed on 15 May 2023).
- Tseng, H.F.; Ackerson, B.K.; Luo, Y.; Sy, L.S.; Talarico, C.A.; Tian, Y.; Bruxvoort, K.J.; Tubert, J.E.; Florea, A.; Ku, J.H.; et al. Effectiveness of mRNA-1273 against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta variants. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espenhain, L.; Funk, T.; Overvad, M.; Edslev, S.M.; Fonager, J.; Ingham, A.C.; Rasmussen, M.; Madsen, S.L.; Espersen, C.H.; Sieber, R.N.; et al. Epidemiological characterisation of the first 785 SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant cases in Denmark, December 2021. Euro Surveill. 2021, 26, 2101146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewnard, J.A.; Hong, V.X.; Patel, M.M.; Kahn, R.; Lipsitch, M.; Tartof, S.Y. Clinical outcomes associated with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron (B.1.1.529) variant and BA.1/BA.1.1 or BA.2 subvariant infection in Southern California. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ju, B.; Zhou, X.; Cheng, L.; Wang, H.; Liao, X.; Wang, M.; Wei, L.; Song, S.; Zhou, B.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine enhances the broad neutralization against variants in individuals recovered from COVID-19 up to one year. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saure, D.; O’Ryan, M.; Torres, J.P.; Zuniga, M.; Santelices, E.; Basso, L.J. Dynamic IgG seropositivity after rollout of CoronaVac and BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccines in Chile: A sentinel surveillance study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Gonzalez, F.; Soto, J.A.; Gonzalez, L.A.; Fernandez, J.; Duarte, L.F.; Schultz, B.M.; Galvez, N.M.S.; Pacheco, G.A.; Rios, M.; Vazquez, Y.; et al. Recognition of Variants of Concern by Antibodies and T Cells Induced by a SARS-CoV-2 Inactivated Vaccine. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 747830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarebska-Michaluk, D.; Hu, C.; Brzdek, M.; Flisiak, R.; Rzymski, P. COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Strategies for Omicron SARS-CoV-2 Variant: Effectiveness and Future Prospects. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Luan, N.; Liu, C. Immunogenicity of Varicella-Zoster Virus Glycoprotein E Formulated with Lipid Nanoparticles and Nucleic Immunostimulators in Mice. Vaccines 2021, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lee, A.; Grigoryan, L.; Arunachalam, P.S.; Scott, M.K.D.; Trisal, M.; Wimmers, F.; Sanyal, M.; Weidenbacher, P.A.; Feng, Y.; et al. Mechanisms of innate and adaptive immunity to the Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, G.; Ols, S.; Liang, F.; Thompson, E.A.; Lin, A.; Hellgren, F.; Bahl, K.; John, S.; Yuzhakov, O.; Hassett, K.J.; et al. Induction of Robust B Cell Responses after Influenza mRNA Vaccination Is Accompanied by Circulating Hemagglutinin-Specific ICOS+ PD-1+ CXCR3+ T Follicular Helper Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Naradikian, M.S.; Parkhouse, K.; Cain, D.W.; Jones, L.; Moody, M.A.; Verkerke, H.P.; Myles, A.; Willis, E.; et al. Nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccines induce potent T follicular helper and germinal center B cell responses. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1571–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczko, D.; Hogan, M.J.; Toulmin, S.A.; Hicks, P.; Lederer, K.; Gaudette, B.T.; Castano, D.; Amanat, F.; Muramatsu, H.; Oguin, T.H., 3rd; et al. A Single Immunization with Nucleoside-Modified mRNA Vaccines Elicits Strong Cellular and Humoral Immune Responses against SARS-CoV-2 in Mice. Immunity 2020, 53, 724–732.e727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Intapiboon, P.; Seepathomnarong, P.; Ongarj, J.; Surasombatpattana, S.; Uppanisakorn, S.; Mahasirimongkol, S.; Sawaengdee, W.; Phumiamorn, S.; Sapsutthipas, S.; Sangsupawanich, P.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of an Intradermal BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine Booster after Two Doses of Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine in Healthy Population. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignier, N.; Berot, V.; Bonnave, N.; Peugny, S.; Ballet, M.; Jacoud, E.; Michaud, C.; Gaillet, M.; Djossou, F.; Blanchet, D.; et al. Breakthrough Infections of SARS-CoV-2 Gamma Variant in Fully Vaccinated Gold Miners, French Guiana, 2021. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 2673–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Song, J.; Fu, Z.; et al. Omicron variant showed lower neutralizing sensitivity than other SARS-CoV-2 variants to immune sera elicited by vaccines after boost. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Luan, N.; Yin, X.; Lin, K.; Liu, C. An Established Th2-Oriented Response to an Alum-Adjuvanted SARS-CoV-2 Subunit Vaccine Is Not Reversible by Sequential Immunization with Nucleic Acid-Adjuvanted Th1-Oriented Subunit Vaccines. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luan, N.; Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Lin, K.; Hu, J.; Liu, C. Comparison of Immune Responses between Inactivated and mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Used for a Booster Dose in Mice. Viruses 2023, 15, 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061351
Luan N, Cao H, Wang Y, Lin K, Hu J, Liu C. Comparison of Immune Responses between Inactivated and mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Used for a Booster Dose in Mice. Viruses. 2023; 15(6):1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061351
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuan, Ning, Han Cao, Yunfei Wang, Kangyang Lin, Jingping Hu, and Cunbao Liu. 2023. "Comparison of Immune Responses between Inactivated and mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Used for a Booster Dose in Mice" Viruses 15, no. 6: 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061351
APA StyleLuan, N., Cao, H., Wang, Y., Lin, K., Hu, J., & Liu, C. (2023). Comparison of Immune Responses between Inactivated and mRNA SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines Used for a Booster Dose in Mice. Viruses, 15(6), 1351. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15061351






