Evolutionary Qβ Phage Displayed Nanotag Library and Peptides for Biosensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Reagents, Facilities, and Providers
2.1.2. Microorganisms
2.1.3. Plasmids and Oligonucleotides
2.1.4. Protein A1 and Nanotag Peptide Fusion 3D Computer Simulation
2.1.5. Analysis of Protein A1 and Nanotag RNA Secondary Structures
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Construction of the RNA Phage Vector Library
2.2.2. Expression of the RNA Phage Vector Display Library
2.2.3. Construction of a Simple RNA Phage Display Vector for Tag Peptide Probe
2.2.4. Bacteria Transformation for Recombinant Phage Expression
2.2.5. Checking for Recombinant Plasmid Phage Production
2.2.6. Phage Scaling and Titration
Scaling of Phages from E. coli HB101
Phage Titration
Panning Procedure
2.2.7. Phage Characterization
Molecular Identification
Dot Blotting
ELISA
Microscopy
3. Results
3.1. RNA Qβ Phage Displaying 15-Mer Library
3.2. Biotin and Biotinylated RNA/Peptide Binding Sequences
3.3. Biosensor with Biotin-Binding Peptide
3.3.1. Design and Generation of Recombinant Plasmids
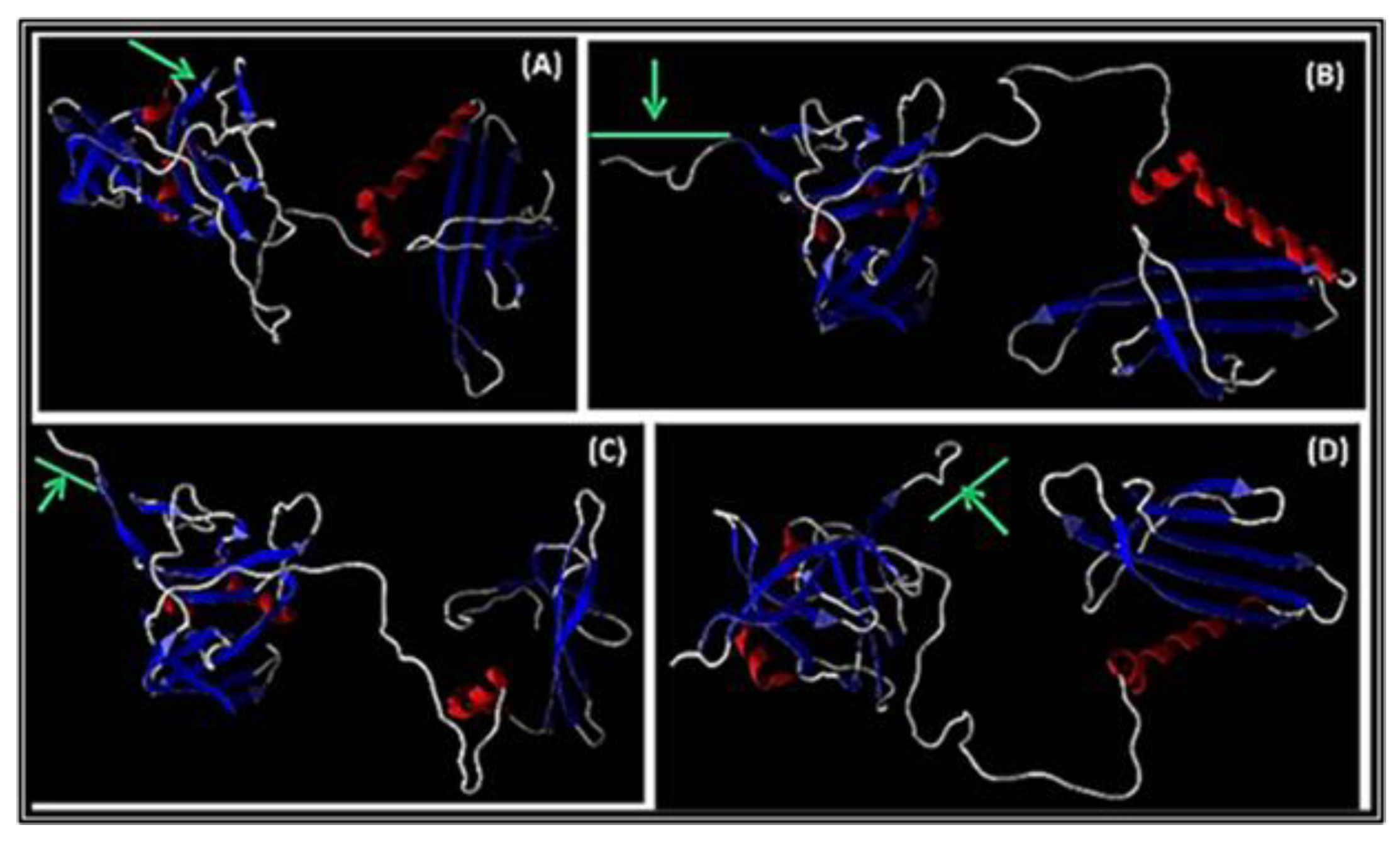
3.3.2. Modeling of A1 with Peptide Inserted at the C-Terminus
3.3.3. Secondary Structure of 5′ Untranslated RNA Region of the Replicase
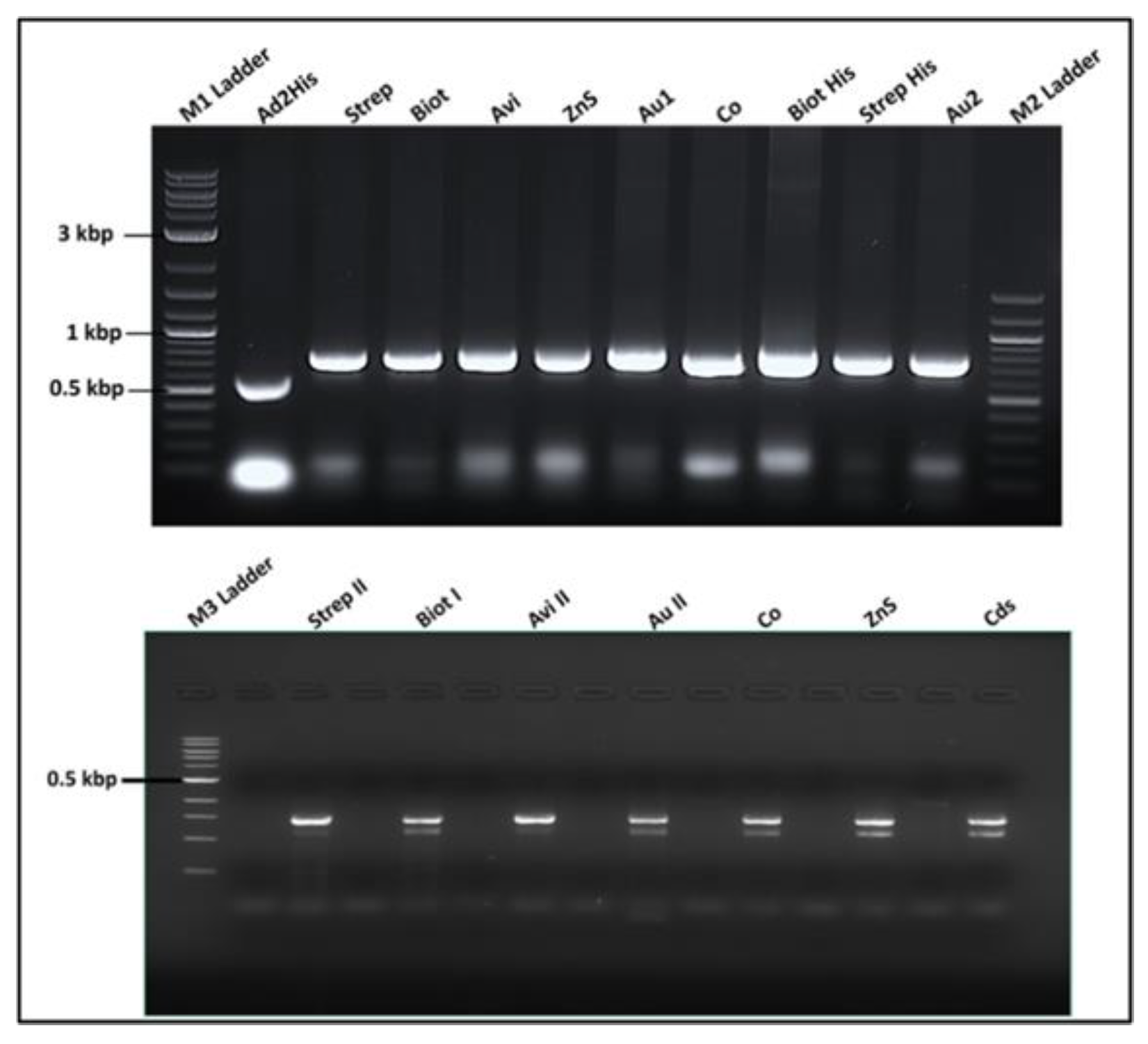
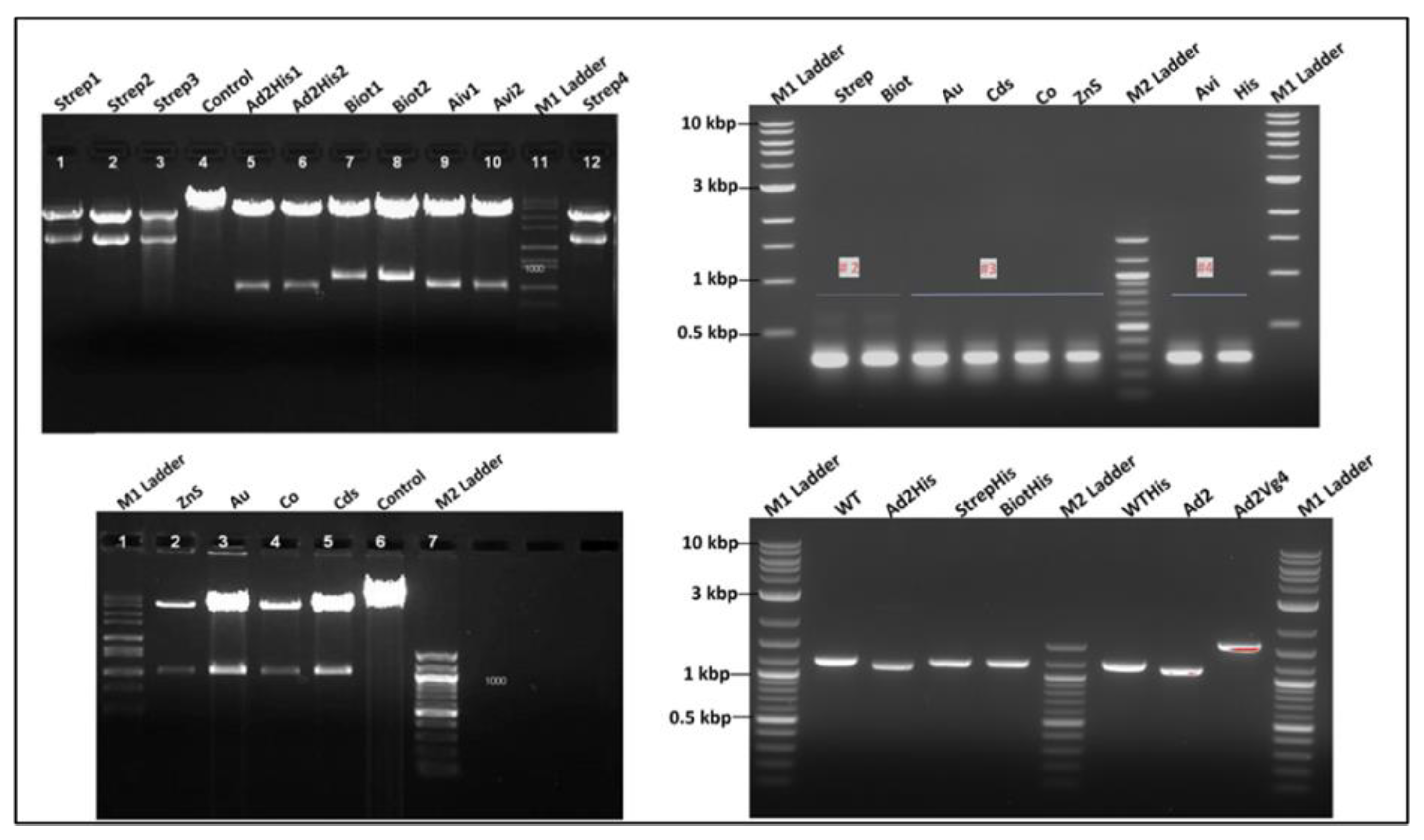
3.3.4. Recombinant Phage Vector Construction Strategy and Genetic Analysis
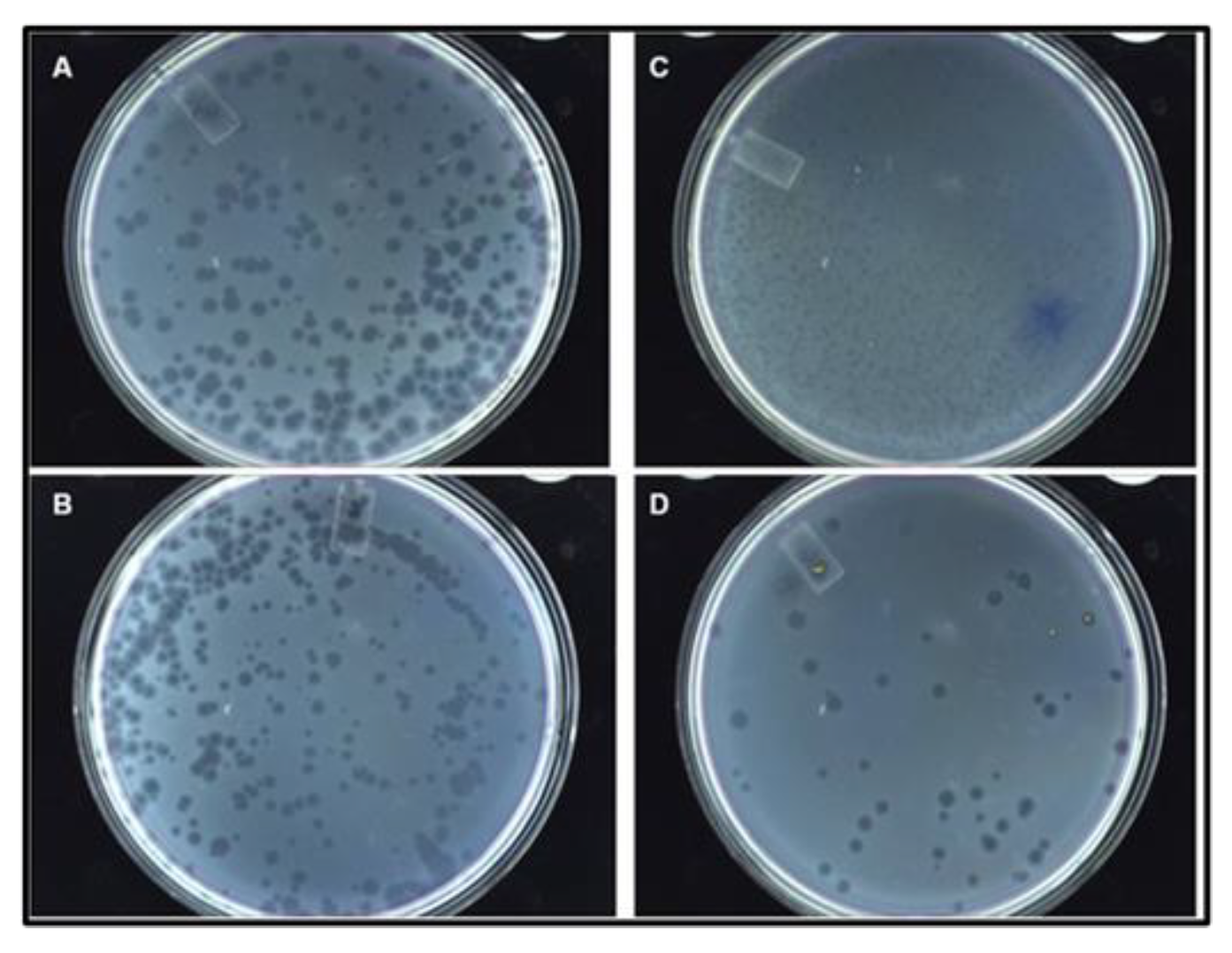
3.3.5. Recombinant Phage Morphology and Titer
3.3.6. Genotype Analysis of Recombinant Phages
3.3.7. Phenotype Analysis of Recombinant Phage
3.3.8. Competitive ELISA of Biotin-HRP and SD6 for Binding to QβBiotFMDV Recombinant Phage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, R.M.; Cox, S.J.; Aggarwal, N.; Mackay, D.J.; Davies, P.R.; Hamblin, P.A.; Dani, P.; Barnett, P.V.; Paton, D.J. Detection of antibody to the foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) non-structural polyprotein 3ABC in sheep by ELISA. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 125, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, P.; Kalaivanan, R.; Sied, N.; Mamo, B.; Kishore, S.; Suryanarayana, V.V.S.; Kondabattula, G. Montanide ISA™ 201 adjuvanted FMD vaccine induces improved immune responses and protection in cattle. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhang, D.; Deng, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Ma, P.; Song, D. A novel surface plasmon resonance biosensor based on the PDA-AgNPs-PDA-Au film sensing platform for horse IgG detection. Spectrochim Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 191, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdy, S.E.; Liu, S.; Su, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Pei, X.; Wang, C. Expression of the VP1 protein of FMDV integrated chromosomally with mutant Listeria monocytogenes strain induced both humoral and cellular immune responses. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshpour, M.; Chiodi, E.; Celebi, I.; Saylan, Y.; Ünlü, N.L.; Ünlü, M.S.; Denizli, A. Sensitive and real-time detection of IgG using interferometric reflecting imaging sensor system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 201, 113961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsson, B.; Löfås, S.; Lindquist, G.; Edström, Å.; Hillgren, R.M.M.; Hansson, A. Comparison of methods for immobilization to carboxymethyl dextran sensor surfaces by analysis of the specific activity of monoclonal antibodies. J. Mol. Recognit. 1995, 8, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivitsky, V.; Zverzhinetsky, M.; Patolsky, F. Antigen-dissociation from antibody-modified nanotransistor sensor arrays as a direct biomarker detection method in unprocessed biosamples. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6272–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamel, C.; Aller, S.G.; Bopda Waffo, A. In vitro evolution and affinity-maturation with coliphage Qβ display. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waffo, A.B.; Lissom, A.; Ouambo, H.F.; Ngu, L.N.; Ngoh, A.A.; Sanders, C.A.; Bawage, S.; Tchadji, C.J.; Assob, J.N.; Okoli, A.S.; et al. Surface Engineering of the RNA Coliphage Qβ to Display Plasmodium Falciparum Derived Asexual Blood Stage Antigens UB05 and Merozoite Surface Protein 3. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 7, 1000314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchouangueu, T.F.; Mabeku, L.B.K.; Lissom, A.; Ngu, L.N.; Tchuandom, S.B.; Tchadji, J.C.; Djukouo, L.; Ngane, C.S.S.; Ngoh, A.A.; Ouambo, H.F.; et al. Antibody Responses Specific to Hepatitis B Virus Vaccine in Children Exposed InUtero to Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Waffo, A.B.; Ngu, L.N.; Singleton, R.L.; Egbo, T.; Simo, J.L.; Sanders, C.A.; Chukwuanukwu, W.M.; Kaptue, L.; Nchinda, G.W. Surface Engineering of Recombinant RNA Coliphage Qβ to Display gp41 Membrane Proximal External-Region Epitopes from HIV-1. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sake, C.S.; Ngu, L.; Ambada, G.; Chedjou, J.P.; Nji, N.; Tchadji, J.C.; Lissom, A.; Tchouangueu, T.F.; Djukouo, L.; Waffo, A.B.; et al. The Effect of Antiretroviral Naïve HIV-1 Infection on the Ability of Natural Killer Cells to Produce IFN-γ upon Exposure to Plasmodium falciparum-Infected Erythrocytes. Biomed. Hub 2017, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priso, N.G.D.; Lissom, A.; Ngu, L.N.; Nji, N.N.; Tchadji, J.C.; Tchouangueu, T.F.; Ambada, G.E.; Ngane, C.S.S.; Dafeu, B.L.; Djukouo, L.; et al. Filaria specific antibody response profiling in plasma from anti-retroviral naïve Loa loa microfilaraemic HIV-1 infected people. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 160. [Google Scholar]
- Lamla, T.; Erdmann, V.A. The Nano-tag, a streptavidin-binding peptide for the purification and detection of recombinant proteins. Prot. Express. Purificat. 2004, 33, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidwell, A.; Yadav, S.P.S.; Maier, B.; Zollman, A.; Ni, K.; Halim, A.; Janosevic, D.; Myslinski, J.; Syed, F.; Zeng, L.; et al. Translation rescue by targeting Ppp1r15a upstream open reading frame in vivo. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kim, A.R.; Cheloha, R.W.; Fischer, F.A.; Li, J.S.S.; Feng, Y.; Stoneburner, E.; Binari, R.; Mohr, S.E.; Zirin, J.; et al. Protein visualization and manipulation in Drosophila through the use of epitope tags recognized by nanobodies. Elife 2022, 11, e74326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Fives-Taylor, P.; Wu, H. The utility of affinity-tags for detection of a streptococcal protein from a variety of streptococcal species. J. Microbiol. Methods 2008, 72, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, A.R.; Xu, J.; Cheloha, R.; Mohr, S.E.; Zirin, J.; Ploegh, H.L.; Perrimon, N. NanoTag Nanobody Tools for Drosophila In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Curr. Protocols 2022, 2, e628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollback, J.P.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. Phylogeny, genome evolution, and host specificity of single-stranded RNA bacteriophage (family Leviviridae). J. Mol. Evol. 2001, 52, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brion, G.M.; Meschke, J.S.; Sobsey, M.D. F-specific RNA coliphages: Occurrence, types, and survival in natural waters. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart-Pullaro, J.; Daugomah, J.W.; Chestnut, D.E.; Graves, D.A.; Sobsey, M.D.; Scott, G.I. F+ RNA coliphage typing for microbial source tracking in surface waters. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 101, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, D.R.; Priano, C.; Merz, P.A.; Binderow, B.D. Q beta RNA bacteriophage: Mapping cis-acting elements within an RNA genome. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 3872–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartard, C.; Rivet, R.; Banas, S.; Gantzer, C. Occurrence of and sequence variation among F-specific RNA bacteriophage subgroups in feces and wastewater of urban and animal origins. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 6505–6515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, S.; Blumenthal, T. Reconstitution of Qbeta RNA replicase from a covalently bonded elongation factor Tu-Ts complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, D.; Gold, L. RNA replication by Q beta replicase: A working model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 11558–11562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moody, M.D.; Burg, J.L.; DiFrancesco, R.; Lovern, D.; Stanick, W.; Lin-Goerke, J.; Mahdavi, K.; Wu, Y.; Farrell, M.P. Evolution of host cell RNA into efficient template RNA by Q beta replicase: The origin of RNA in untemplated reactions. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 13836–13847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.; Gold, L. Selection and characterization of RNAs replicated by Q. beta. replicase. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 14775–14782. [Google Scholar]
- Karnik, S.; Billeter, M. The lysis function of RNA bacteriophage Q beta is mediated by the maturation (A2) protein. EMBO J. 1983, 2, 1521–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callanan, J.; Stockdale, S.R.; Shkoporov, A.; Draper, L.A.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. RNA phage biology in a metagenomic era. Viruses 2018, 10, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rumnieks, J.; Tars, K. Crystal structure of the maturation protein from bacteriophage Qβ. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.Y.; Gorzelnik, K.V.; Thongchol, J.; Zhang, J. Structural assembly of Qβ virion and its diverse forms of virus-like particles. Viruses 2022, 14, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, A.M.; Weber, K. Natural read-through at the UGA termination signal of Qβ coat protein cistron. Nat. Cell Biol. 1971, 234, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Černý, J.; Černá Bolfíková, B.; Valdes, J.J.; Grubhoffer, L.; Růžek, D. Evolution of tertiary structure of viral RNA dependent polymerases. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drake, J.W. Rates of spontaneous mutation among RNA viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 4171–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaklee, P.N.; Miglietta, J.J.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Kaesberg, P. Infectious positive-and negative-strand transcript RNAs from bacteriophage Qβ cDNA clones. Virology 1988, 163, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissmann, C.; Weber, H.; Taniguchi, T.; Müller, W.; Meyer, F. Reversed genetics: A new approach to the elucidation of structure--function relationship. Ciba Found. Symp. 1979, 66, 47–61. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Jin, L.; Koh, S.B.S.; Atanasov, I.; Schein, S.; Wu, L.; Zhou, Z.H. Atomic structure of human adenovirus by cryo-EM reveals interactions among protein networks. Science 2010, 329, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldman, E.R.; Pazirandeh, M.P.; Mauro, J.M.; King, K.D.; Frey, J.C.; Anderson, G.P. Phage-displayed peptides as biosensor reagents. J. Mol. Recognit. 2000, 13, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Lee, Y.; Devaraj, V.; Nguyen, T.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, C.; Choi, E.J.; Han, D.W.; Oh, J.W. Investigation of colorimetric biosensor array based on programable surface chemistry of M13 bacteriophage towards artificial nose for volatile organic compound detection: From basic properties of the biosensor to practical application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 188, 113339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, K.; Finn, F.M.; Kiso, Y. Avidin-biotin affinity columns. General methods for attaching biotin to peptides and proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 3585–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, I.A.; Stanfield, R.L. Antibody-antigen interactions. Antibody-antigen interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1993, 3, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronian, K.H.R. The use of yeast and moulds as sensing elements in biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 19, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Chen, J. Development of biosensor technologies for analysis of environmental contaminants. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2014, 2, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.A.; Verrips, C.T. Nanobodies that neutralize HIV. Vaccines 2019, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hosseindokht, M.; Bakherad, H.; Zare, H. Nanobodies: A tool to open new horizons in diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.Q.; Hu, J.; Wen, C.Y.; Tian, Z.Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.L.; Shi, Y.B.; Pang, D.W. Fluorescent-magnetic-biotargeting multifunctional nanobioprobes for detecting and isolating multiple types of tumor cells. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, C.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, S.; Xian, Y. Multivalent aptamer functionalized Ag2S nanodots/hybrid cell membrane-coated magnetic nanobioprobe for the ultrasensitive isolation and detection of circulating tumor cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Names | Primer–DNA Sequences |
|---|---|
| ABW1 | ttaaGTCGATAAATGCC (NNN)15 TAGTAACTAAGGATGAAAtgca |
| ABW2 | CAGCTATTACGG |
| ABW3 | ATCATTGATTCCTACTTT |
| Au1 | AATGTCCAATTCAAGCTGTGATAGTCGTTCCTCGTGCTgaattCgtcagtggttcctctcccgacagttagTAActaaggatgaaatgcATGgg |
| Au2 | GTCCAATTCAAGCTGTGATAGTCGTTCCTCGTaaGCTtacaggtacttcagtcctcattgcaactccatacgtttagTAActaaggatgaaatgcATGgg |
| Silca | GTCCAATTCAAGCTGTGATAGTCGTTCCTCGTaaGCTtatgagccctcaccctcatccgcgacaccatcacaccTAGTAActaaggatgaaatgcATGgg |
| Cds | aatgtccaattcaagctgtgatagtcgttcctcgtgctAGCCTGACCCCGCTGACCACCAGCCATCTGCGCAGCtagTAActaaggatgaaatgcATGgg |
| ZnS | tgtccaattcaagctgtgatagtcgttcctcgtgctGTGATTAGCAACCATGCGGGCAGCAGCCGCCGCCTGtagTAActaagCTTgatgaaatgcATGT |
| 6xhis-tag | gtccaattcaagctgtgatagtcgttcctcgtgctGGTCATCACCATCATCATCACGGGTCCtagtaaGCTAGCctaaggatgaaatgcatgtgg |
| Biotin-tag | GtccaattcaagctgtgatagtcgttcctcgtgcagcggccatcatcatcatcatcatggcagcTAGTAAGCTAGCctaaggatgaaatgcatgtgg |
| Strep II-tag | GtccaattcaagctgtgatagtcgttcctcgtgcGatgtggaatggctggatgaacgcgtgccgctggtggaaaccTAGTAActaagCTTgatgaaatgcATGT |
| Co | aaatgtccaattcaagctgtgatagtcgttcctcgtgctGCTagcGAAGAAGAAGAAtagTAActaaggatgaaatgcATGTCTAA |
| Host/Phages | Qβ | QβHis | QβStrep | QβBiot |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli HB101(1st) | 109 pfu/mL | 108 pfu/mL | 107 pfu/mL | 107 pfu/mL |
| E. coli Q13 (2nd) | 1012 pfu/mL | 1010 pfu/mL | 109 pfu/mL | 109 pfu/mL |
| E. coli K12 (3rd) | 1014 pfu/mL | 1012 pfu/mL | 1011 pfu/mL | 1011 pfu/mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ntemafack, A.; Dzelamonyuy, A.; Nchinda, G.; Bopda Waffo, A. Evolutionary Qβ Phage Displayed Nanotag Library and Peptides for Biosensing. Viruses 2023, 15, 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071414
Ntemafack A, Dzelamonyuy A, Nchinda G, Bopda Waffo A. Evolutionary Qβ Phage Displayed Nanotag Library and Peptides for Biosensing. Viruses. 2023; 15(7):1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071414
Chicago/Turabian StyleNtemafack, Augustin, Aristide Dzelamonyuy, Godwin Nchinda, and Alain Bopda Waffo. 2023. "Evolutionary Qβ Phage Displayed Nanotag Library and Peptides for Biosensing" Viruses 15, no. 7: 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071414
APA StyleNtemafack, A., Dzelamonyuy, A., Nchinda, G., & Bopda Waffo, A. (2023). Evolutionary Qβ Phage Displayed Nanotag Library and Peptides for Biosensing. Viruses, 15(7), 1414. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071414






