Molecular Evolutionary Analyses of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp) Region and VP1 Gene in Human Norovirus Genotypes GII.P6-GII.6 and GII.P7-GII.6
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains Used in This Study
2.2. Time-Scaled Phylogenetic Analyses
2.3. Phylogenetic Distance Analyses
2.4. Phylodynamic Analyses
2.5. Selective Pressure Analyses
2.6. Construction of the 3D Structure of RdRp and VP1 Proteins
2.7. Conformational B-Cell Epitope Prediction
3. Results
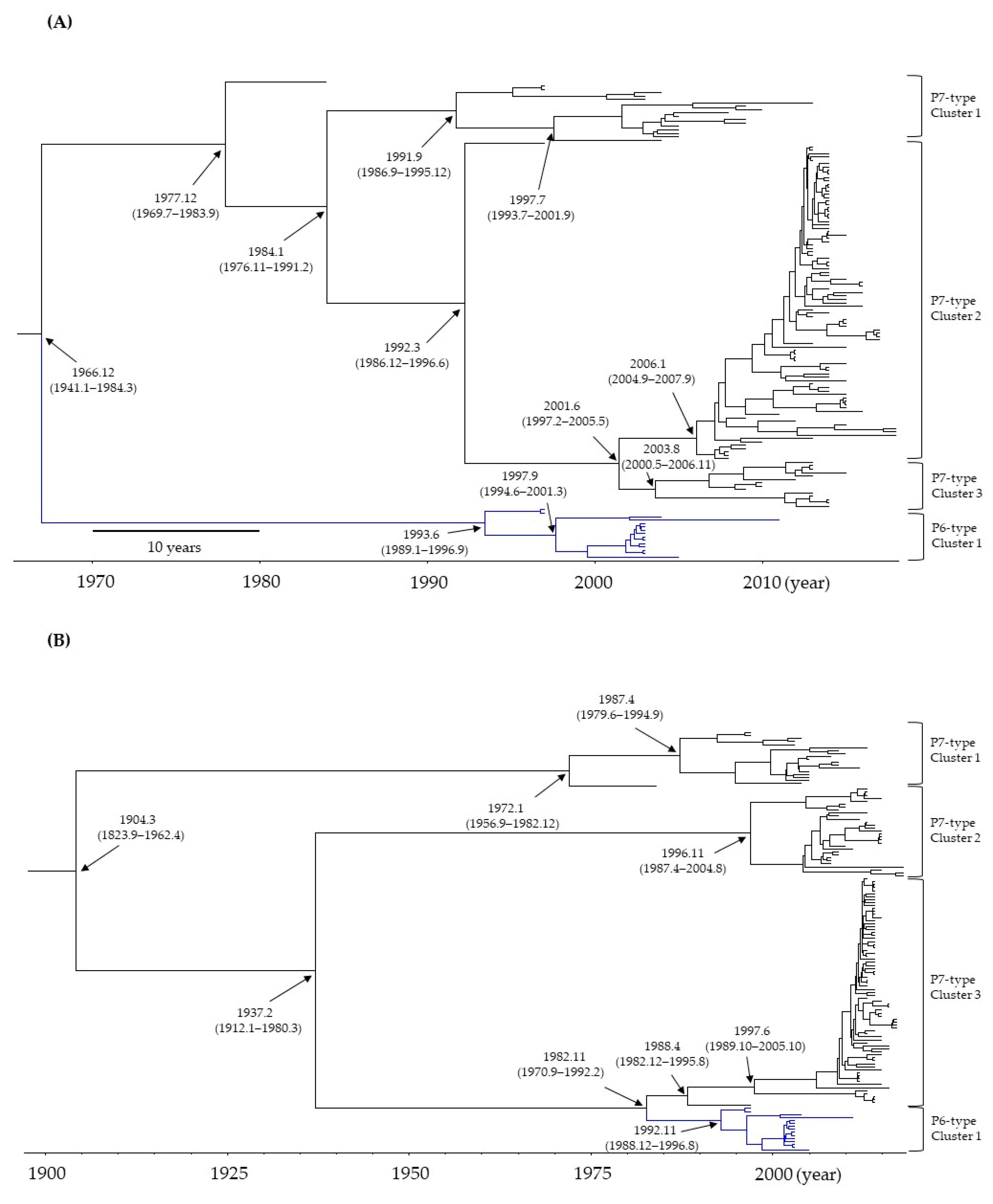
3.1. Time-Scaled Phylogeny of the RdRp Region and VP1 Gene in HuNoV GII.P6-GII.6 and GII.P7-GII.6
3.2. Evolutionary Rates of the RdRp Region and VP1 Gene in HuNoV GII.P6-GII.6 and GII.P7-GII.6
| Region/Gene | Evolutionary Rates (95% HPDs) (Substitutions/Site/Year) | Compared Groups and Statistical Values |
|---|---|---|
| All RdRp region (141 strains) P6-type 15 strains; P7-type 126 strains | 3.287 × 10−3 (2.489 × 10−3–4.098 × 10−3) | All RdRp region vs. All GII.6 VP1 gene p < 0.001 |
| All GII.6 VP1 gene (141 strains) P6-type 15 strains; P7-type 126 strains | 3.345 × 10−3 (2.295 × 10−3–4.419 × 10−3) | |
| P6-type RdRp region (15 strains) | 5.063 × 10−3 (3.525 × 10−3–6.595 × 10−3) | P6-type RdRp region vs. P7-type RdRp region p < 0.001 |
| P7-type RdRp region (126 strains) | 3.022 × 10−3 (2.268 × 10−3–3.775 × 10−3) | |
| GII.P6-GII.6 VP1 gene (15 strains) | 3.725 × 10−3 (1.843 × 10−3–5.549 × 10−3) | GII.P6-GII.6 VP1 gene vs. GII. P7-GII.6 VP1 gene p < 0.001 |
| GII.P7-GII.6 VP1 gene (126 strains) | 3.482 × 10−3 (2.419 × 10−3–4.568 × 10−3) |
3.3. Phylogenetic Distances among the Present Strains
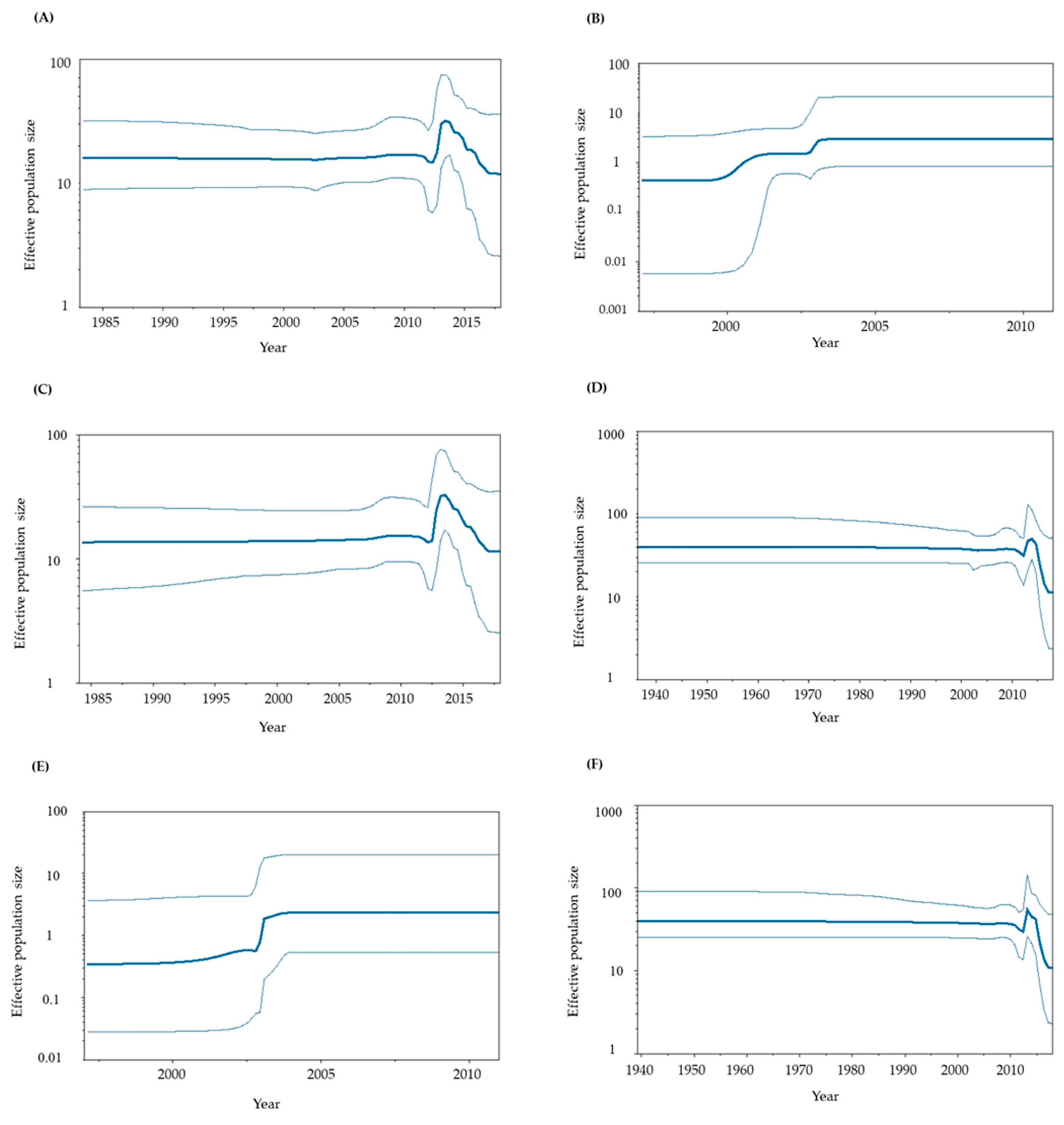
3.4. Phylodynamics of GII.P6-GII.6 and GII.P7-GII.6
3.5. Positive Selection Sites in the RdRp and VP1 Proteins
3.6. Negative Selection Sites in RdRp and VP1 Proteins
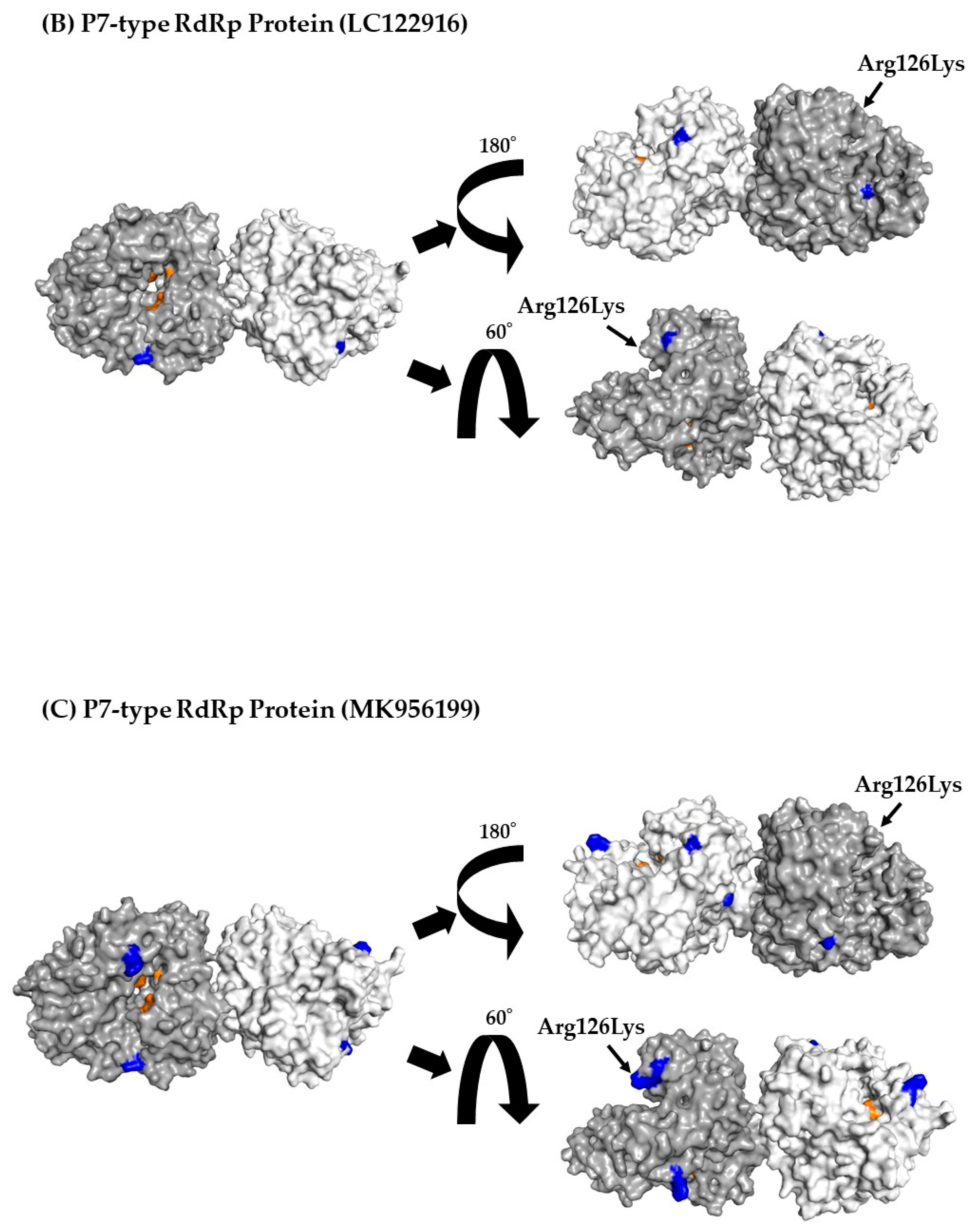
3.7. 3D Mapping Relationships between Amino Acid Substitutions and Active Sites of the RdRp Dimer Proteins
3.8. 3D Mapping of the Positive Selection Sites and Conformational Epitopes in the VP1 Trimer Proteins
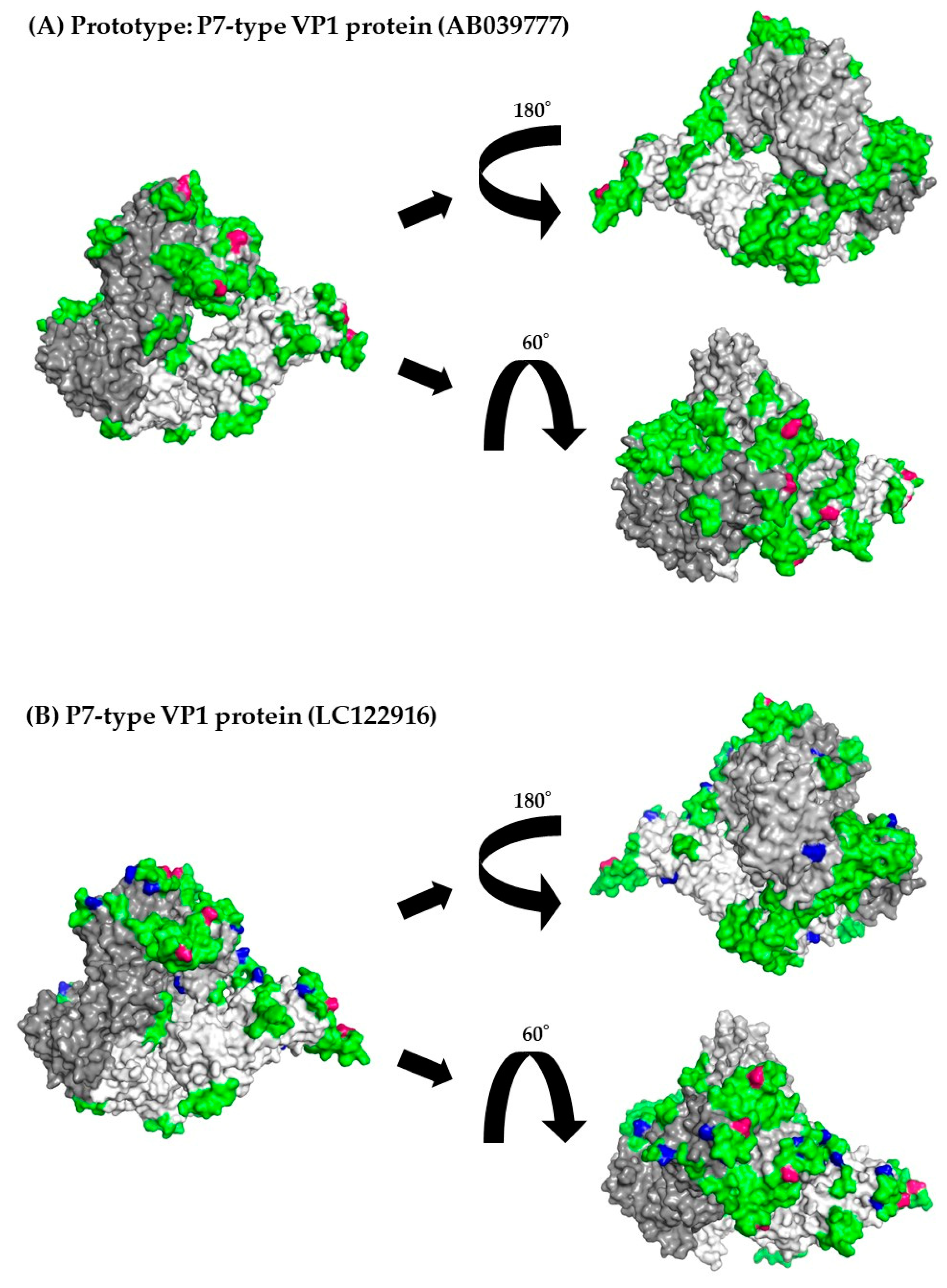
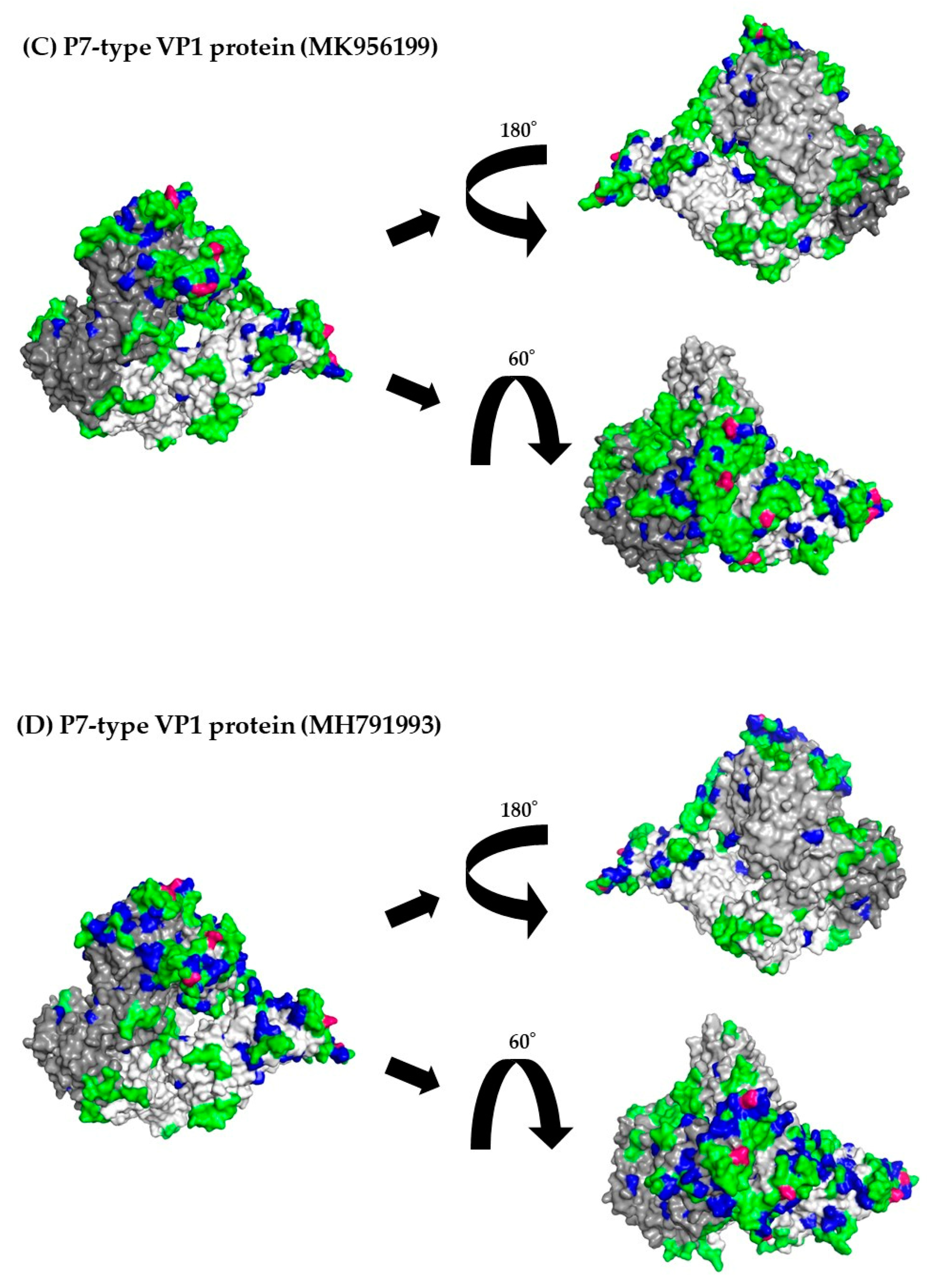
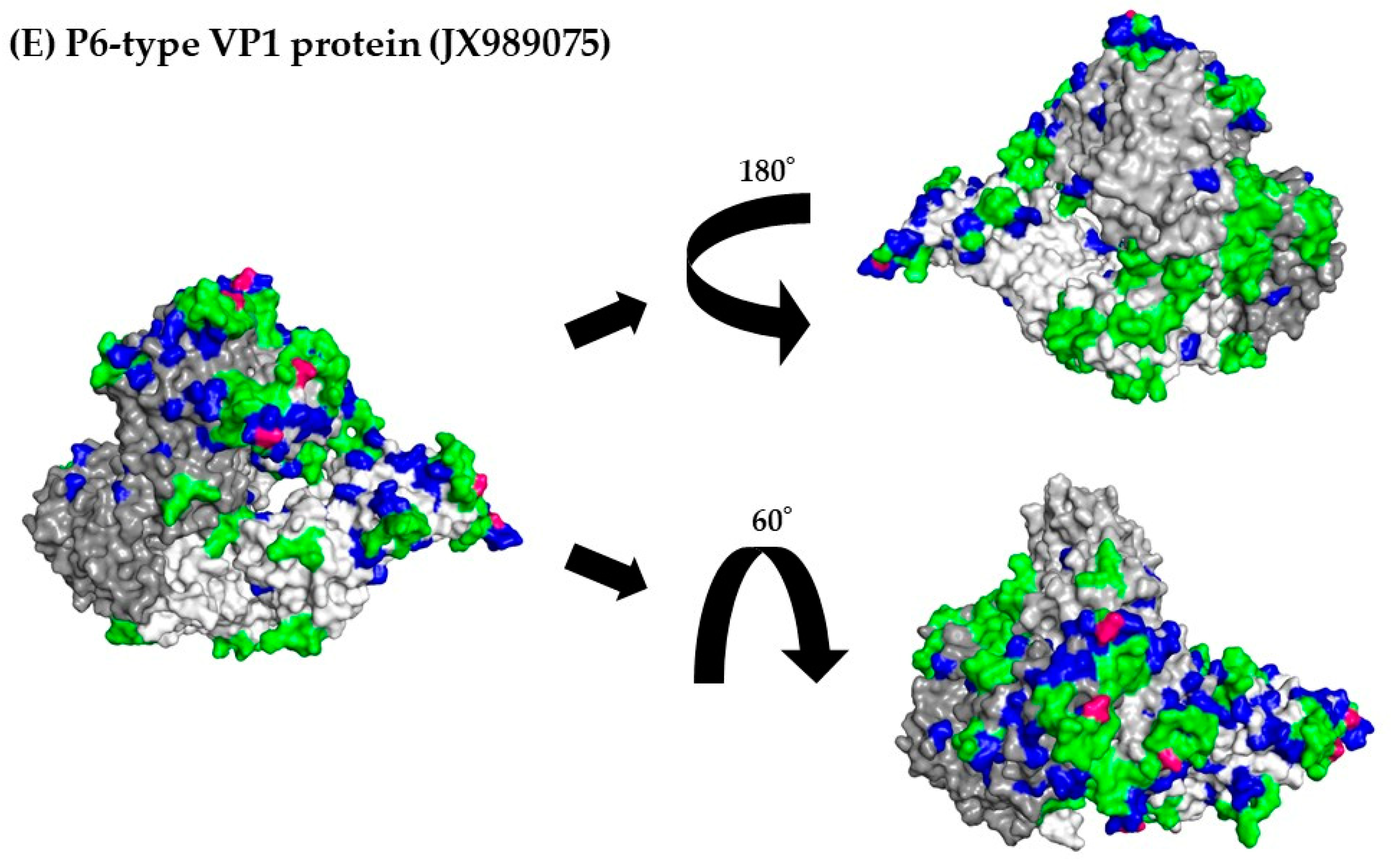
| Region/Gene | Number of Negative Selection Sites | Number of Positive Selection Sites | Estimated as Positive Selective Sites |
|---|---|---|---|
| P6 type and P7 type RdRp region | 258 | 0 | — |
| P6 type RdRp region | 3 | 0 | — |
| P7 type RdRp region | 205 | 1 | 126Lys, Lys126Arg |
| GII.P6-GII.6 and GII.P7-GII.6 VP1 gene | 298 | 2 | 354Pro, 390Asn |
| GII.P6-GII.6 VP1 gene | 8 | 1 | Lys386His |
| GII.P7-GII.6 VP1 gene | 274 | 2 | Pro354Thr, Ser and Gln, Asn390Thr and Asp |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robilotti, E.; Deresinski, S.; Pinsky, B.A. Norovirus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 134–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mans, J. Norovirus Infections and disease in lower-middle and low-income countries, 1997–2018. Viruses 2019, 11, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan-It, W.; Thongprachum, A.; Khamrin, P.; Kobayashi, M.; Okitsu, S.; Mizuguchi, M.; Ushijima, H. Emergence of a new norovirus GII.6 variant in Japan, 2008-2009. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.M.; Hall, A.J.; Vinjé, J.; Parashar, U.D. Noroviruses: A comprehensive review. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.M.; Widdowson, M.A.; Glass, R.I.; Akazawa, K.; Vinjé, J.; Parashar, U.D. Systematic literature review of role of noroviruses in sporadic gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrón, I.; Álvarez, J.; Jané, M.; Cornejo Sánchez, T.; Razquin, E.; Guix, S.; Camps, G.; Pérez, C.; Domínguez, À.; The Working Group for the Study of Outbreaks of Acute Gastroenteritis in Catalonia. A foodborne norovirus outbreak in a nursing home and spread to staff and their household contacts. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147, e225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winder, N.; Gohar, S.; Muthana, M. Norovirus: An overview of virology and preventative measures. Viruses 2022, 14, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, M.; van Beek, J.; Koopmans, M.P. Human norovirus transmission and evolution in a changing world. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Estes, M.K. Sequence and genomic organization of Norwalk virus. Virology 1993, 195, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, P.; de Graaf, M.; Parra, G.I.; Chan, M.C.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Wang, Q.; White, P.A.; Katayama, K.; Vennema, H.; et al. Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes. J. Gen. Virol. 2019, 100, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Espul, C.; Zhong, W.M.; Cuello, H.; Matson, D.O. Characterization of a novel human calicivirus that may be a naturally occurring recombinant. Arch. Virol. 1999, 144, 2377–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig-Begall, L.F.; Mauroy, A.; Thiry, E. Norovirus recombinants: Recurrent in the field, recalcitrant in the lab—A scoping review of recombination and recombinant types of noroviruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 970–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroneman, A.; Vega, E.; Vennema, H.; Vinjé, J.; White, P.A.; Hansman, G.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Katayama, K.; Koopmans, M. Proposal for a unified norovirus nomenclature and genotyping. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 2059–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhavanam; Freedman, S.; Lee, S.B.; Zhuo, B.E.; Qiu, R.; Chui, Y.; Xie, L.; Ali, J.; Vanderkooi, S.; Pang, O.G.; et al. Differences in Illness Severity among Circulating Norovirus Genotypes in a Large Pediatric Cohort with Acute Gastroenteritis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beek, J.; de Graaf, M.; Al-Hello, H.; Allen, D.J.; Ambert-Balay, K.; Botteldoorn, N.; Brytting, M.; Buesa, J.; Cabrerizo, M.; Chan, M.; et al. Molecular surveillance of norovirus, 2005–16: An epidemiological analysis of data collected from the NoroNet network. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamrin, P.; Kumthip, K.; Yodmeeklin, A.; Jampanil, N.; Phengma, P.; Yamsakul, P.; Okitsu, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Ushijima, H.; Maneekarn, N. Changing Predominance of Norovirus Recombinant Strains GII.2[P16] to GII.4[P16] and GII.4[P31] in Thailand, 2017 to 2018. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0044822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, E.; Barclay, L.; Gregoricus, N.; Shirley, S.H.; Lee, D.; Vinj, J. Genotypic and epidemiologic trends of norovirus outbreaks in the United States, 2009 to 2013. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannon, J.L.; Bonifacio, J.; Bucardo, F.; Buesa, J.; Bruggink, L.; Chan, M.C.-W.; Fumian, T.M.; Giri, S.; Gonzalez, M.D.; Hewitt, J.; et al. Global Trends in Norovirus Genotype Distribution among Children with Acute Gastroenteritis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Zou, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhan, J.; Cheng, J. Epidemiology and genetic diversity of norovirus GII genogroups among children in Hubei, China, 2017–2019. Virol. Sin. 2023, 38, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pybus, O.G.; Rambaut, A. Evolutionary analysis of the dynamics of viral infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, Y.; Mizukoshi, F.; Sakon, N.; Doan, Y.H.; Ueki, Y.; Ogawa, Y.; Motoya, T.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Nakamura, N.; Shigemoto, N.; et al. Evolutionary Analysis of the VP1 and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase regions of human norovirus GII.P17-GII.17 in 2013–2017. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukoshi, F.; Nagasawa, K.; Doan, Y.H.; Haga, K.; Yoshizumi, S.; Ueki, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Ishikawa, M.; Sakon, N.; Shigemoto, N.; et al. Molecular Evolution of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase and Capsid Genes of Human Norovirus Genotype GII.2 in Japan during 2004–2015. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Motoya, T.; Mizukoshi, F.; Ueki, Y.; Sakon, N.; Murakami, K.; Shimizu, T.; Okabe, N.; Nagata, N.; et al. Phylogeny and Immunoreactivity of Norovirus GII.P16-GII.2, Japan, Winter 2016-17. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diakoudi, G.; Lanave, G.; Catella, C.; Medici, M.C.; De Conto, F.; Calderaro, A.; Loconsole, D.; Chironna, M.; Bonura, F.; Giammanco, G.M.; et al. Analysis of GII.P7 and GII.6 noroviruses circulating in Italy during 2011-2016 reveals a replacement of lineages and complex recombination history. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Vinj, J.; Elkins, C.A.; Kulka, M. Complete Genome Sequence of Human Norovirus Strain GII.P7-GII.6 Detected in a Patient in the United States in 2014. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e01211-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, N.; Li, M.; Zhou, L.U.; Huang, Y. Genetic characterizations and molecular evolution of human norovirus GII.6 genotype during the past five decades. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouckaert, R.; Heled, J.; Kühnert, D.; Vaughan, T.; Wu, C.-H.; Xie, D.; Suchard, M.A.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J. BEAST 2: A software platform for Bayesian evolutionary analysis. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saito, M.; Tsukagoshi, H.; Sada, M.; Sunagawa, S.; Shirai, T.; Okayama, K.; Sugai, T.; Tsugawa, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Ryo, A.; et al. Detailed Evolutionary Analyses of the F gene in the respiratory syncytial virus subgroup A. Viruses 2021, 13, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fourment, M.; Gibbs, M.J. PATRISTIC: A program for calculating patristic distances and graphically comparing the components of genetic change. BMC Evol. Biol. 2006, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior Summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weaver, S.; Shank, S.D.; Spielman, S.J.; Li, M.; Muse, S.V.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Datamonkey 2.0: A modern web application for characterizing selective and other evolutionary processes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Protein structure modeling with MODELLER. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1137, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and development of coot. Acta. Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kringelum, J.V.; Lundegaard, C.; Lund, O.; Nielsen, M. Reliable B cell epitope predictions: Impacts of method development and improved benchmarking. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, J.; Bui, H.H.; Li, W.; Fusseder, N.; Bourne, P.E.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. ElliPro: A new structure-based tool for the prediction of antibody epitopes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shashkova, T.I.; Umerenkov, D.; Salnikov, M.; Strashnov, P.V.; Konstantinova, A.V.; Lebed, I.; Shcherbinin, D.N.; Asatryan, M.N.; Kardymon, O.L.; Ivanisenko, N.V. SEMA: Antigen B-cell conformational epitope prediction using deep transfer learning. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 960985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Yan, D.; Mao, T.; Tang, K.; Qiu, T.; Cao, Z. SEPPA 3.0-enhanced spatial epitope prediction enabling glycoprotein antigens. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W388–W394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Nagasawa, K.; Motoya, T.; Ryo, A.; Kuroda, M.; Katayama, K.; Kimura, H. Molecular evolutionary analyses of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase region in norovirus genogroup II. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vinjé, J. Advances in laboratory methods for detection and typing of norovirus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bidalot, M.; Théry, L.; Kaplon, J.; De Rougemont, A.; Ambert-Balay, K. Emergence of new recombinant noroviruses GII.p16-GII.4 and GII.p16-GII.2, France, winter 2016 to 2017. Eurosurveillance 2017, 22, 30508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ao, Y.; Wang, J.; Ling, H.; He, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, X.; Peng, J.; Zhang, H.; Jin, M.; Duan, Z. Norovirus GII.P16/GII.2-Associated Gastroenteritis, China, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1172–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.T.; Kuo, T.Y.; Wu, C.Y.; Liao, W.T.; Hall, A.J.; Wu, F.T. Recombinant GII.P16-GII.2 Norovirus, Taiwan, 2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 1180–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siebenga, J.J.; Vennema, H.; Zheng, D.P.; Vinjé, J.; Lee, B.E.; Pang, X.L.; Ho, E.C.; Lim, W.; Choudekar, A.; Broor, S.; et al. Norovirus illness is a global problem: Emergence and spread of norovirus GII.4 variants, 2001–2007. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eden, J.S.; Tanaka, M.M.; Boni, M.F.; Rawlinson, W.D.; White, P.A. Recombination within the pandemic norovirus GII.4 lineage. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6270–6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smertina, E.; Urakova, N.; Strive, T.; Frese, M. Calicivirus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases: Evolution, Structure, Protein Dynamics, and Function. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, M.C.W.; Lee, N.; Hung, T.-N.; Kwok, K.; Cheung, K.; Tin, E.K.Y.; Lai, R.W.M.; Nelson, E.A.S.; Leung, T.F. Rapid emergence and predominance of a broadly recognizing and fast-evolving norovirus GII.17 variant in late 2014. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, M.; Matsushima, Y.; Motoya, T.; Sakon, N.; Shigemoto, N.; Okamoto-Nakagawa, R.; Nishimura, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Kuroda, M.; Saruki, N.; et al. Molecular evolution of the capsid gene in human norovirus genogroup II. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bull, R.A.; Eden, J.S.; Rawlinson, W.D.; White, P.A. Rapid evolution of pandemic noroviruses of the GII.4 lineage. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Zhong, H.; Xu, M.; Su, L.; Cao, L.; Jia, R.; Xu, J. Genetic diversity and epidemiology of Genogroup II noroviruses in children with acute sporadic gastroenteritis in Shanghai, China, 2012-2017. Bmc Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Utsumi; Lusida; Dinana, T.; Wahyuni, M.I.; Soegijanto, Z.; Soetjipto, R.M.; Athiyyah, S.; Sudarmo, A.F.; Ranuh, S.M.; Darma, R.G.; et al. Molecular epidemiology and genetic diversity of norovirus infection in children hospitalized with acute gastroenteritis in East Java, Indonesia in 2015–2019. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 88, 104703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, L.U.; Li, M.; Jin, H. Molecular Evolution of RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Region in Norovirus Genogroup I. Viruses 2023, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutson, A.M.; Atmar, R.L.; Marcus, D.M.; Estes, M.K. Norwalk virus-like particle hemagglutination by binding to h histo-blood group antigens. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schroten, H.; Hanisch, F.G.; Hansman, G.S. Human norovirus interactions with histo-blood group antigens and human milk oligosaccharides. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 5855–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, E.C. Virus evolution. In Fields Virology, 6th ed.; Knipe, D.M., Howley, P.M., Cohen, J.I., Griffin, D.E., Lamb, R.A., Martin, M.A., Racaniello, V.D., Roizman, B., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 286–313. [Google Scholar]
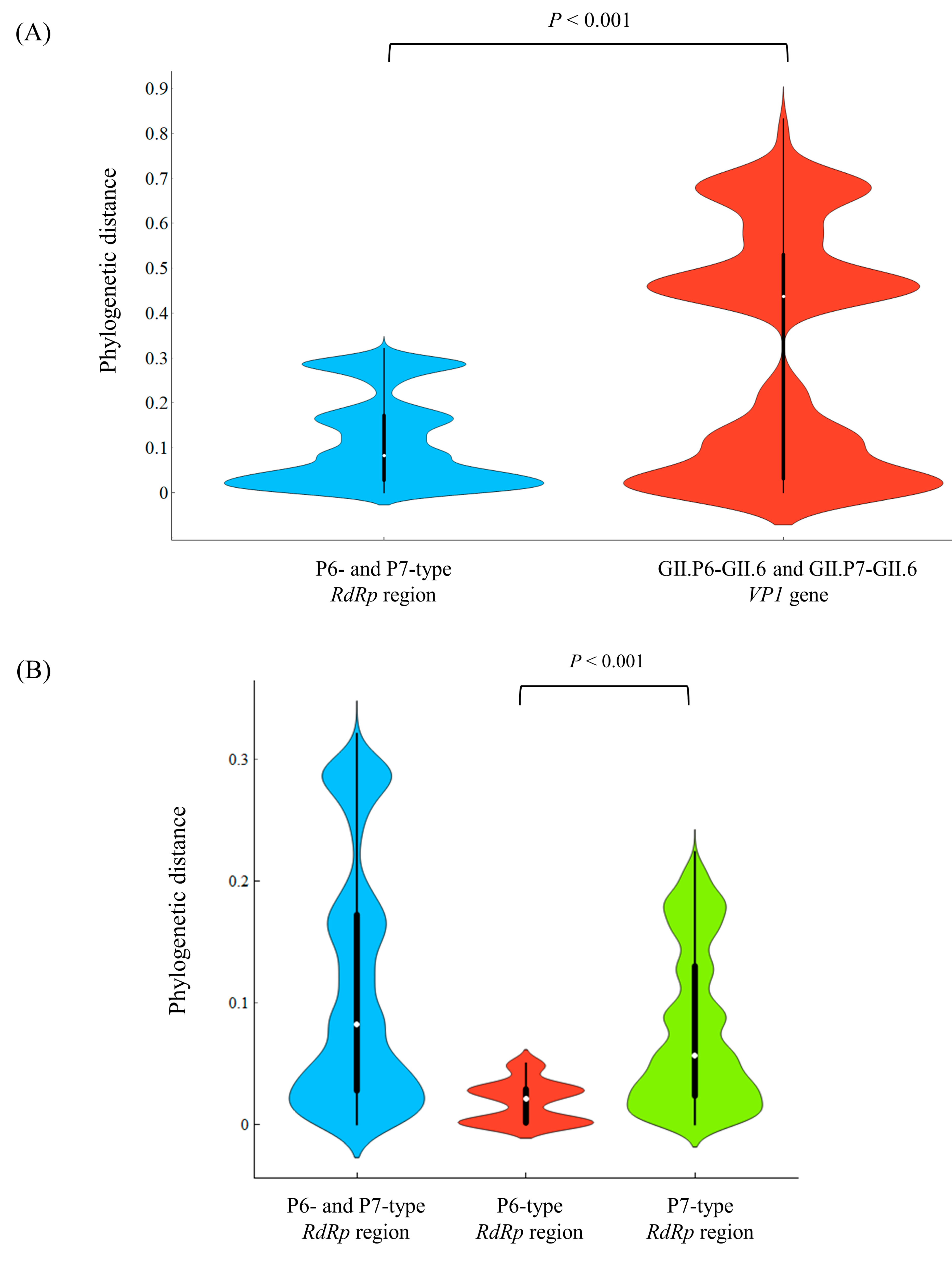
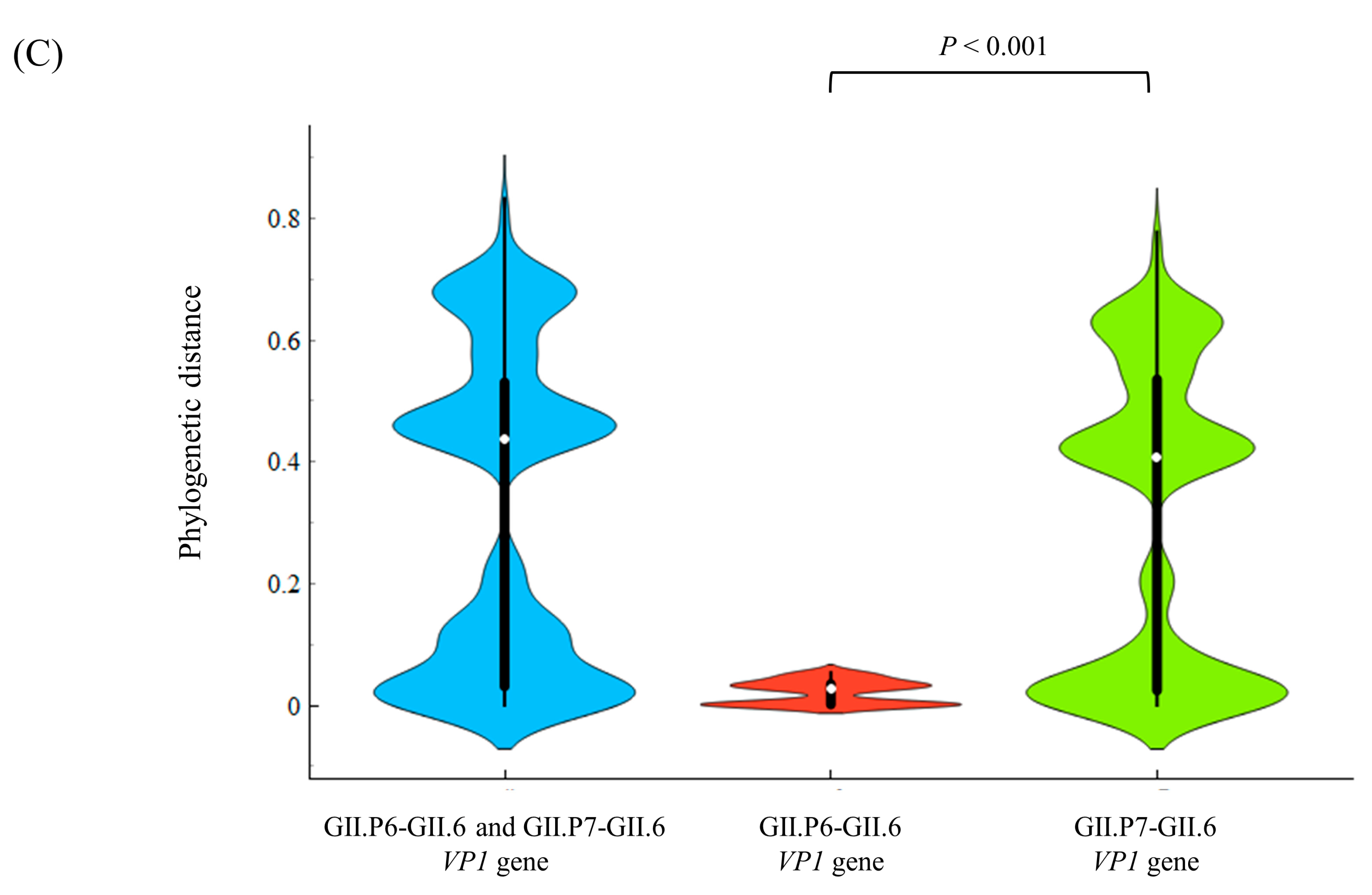


| Region/Gene | Phylogenetic Distance (Mean ± SD) | Phylogenetic Distance (Median [IQR]) |
|---|---|---|
| All RdRp region (141 strains) | 0.112 ± 0.098 | 0.082 (0.028–0.172) |
| All GII.6 VP1 gene (141 strains) | 0.317 ± 0.259 | 0.437 (0.031–0.530) |
| P6-type RdRp region (15 strains) | 0.018 ± 0.017 | 0.021 (0.001–0.029) |
| P7-type RdRp region (126 strains) | 0.078 ± 0.064 | 0.057 (0.023–0.130) |
| GII.P6-GII.6 VP1 gene (15 strains) | 0.021 ± 0.019 | 0.027 (0.001–0.035) |
| GII.P7-GII.6 VP1 gene (126 strains) | 0.305 ± 0.249 | 0.408 (0.024–0.535) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, T.; Kimura, R.; Shirai, T.; Sada, M.; Sugai, T.; Murakami, K.; Harada, K.; Ito, K.; Matsushima, Y.; Mizukoshi, F.; et al. Molecular Evolutionary Analyses of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp) Region and VP1 Gene in Human Norovirus Genotypes GII.P6-GII.6 and GII.P7-GII.6. Viruses 2023, 15, 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071497
Takahashi T, Kimura R, Shirai T, Sada M, Sugai T, Murakami K, Harada K, Ito K, Matsushima Y, Mizukoshi F, et al. Molecular Evolutionary Analyses of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp) Region and VP1 Gene in Human Norovirus Genotypes GII.P6-GII.6 and GII.P7-GII.6. Viruses. 2023; 15(7):1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071497
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Tomoko, Ryusuke Kimura, Tatsuya Shirai, Mitsuru Sada, Toshiyuki Sugai, Kosuke Murakami, Kazuhiko Harada, Kazuto Ito, Yuki Matsushima, Fuminori Mizukoshi, and et al. 2023. "Molecular Evolutionary Analyses of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp) Region and VP1 Gene in Human Norovirus Genotypes GII.P6-GII.6 and GII.P7-GII.6" Viruses 15, no. 7: 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071497
APA StyleTakahashi, T., Kimura, R., Shirai, T., Sada, M., Sugai, T., Murakami, K., Harada, K., Ito, K., Matsushima, Y., Mizukoshi, F., Okayama, K., Hayashi, Y., Kondo, M., Kageyama, T., Suzuki, Y., Ishii, H., Ryo, A., Katayama, K., Fujita, K., & Kimura, H. (2023). Molecular Evolutionary Analyses of the RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RdRp) Region and VP1 Gene in Human Norovirus Genotypes GII.P6-GII.6 and GII.P7-GII.6. Viruses, 15(7), 1497. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15071497








