Functional Involvement of circRNAs in the Innate Immune Responses to Viral Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Physical and Chemical Characteristics of Circular RNAs
2.1. RNA Circularization
2.2. circRNAs versus mRNAs
2.3. Mechanisms Underlying Action of circRNAs
3. Involvement of circRNAs in Innate Immunity against Viral Infection
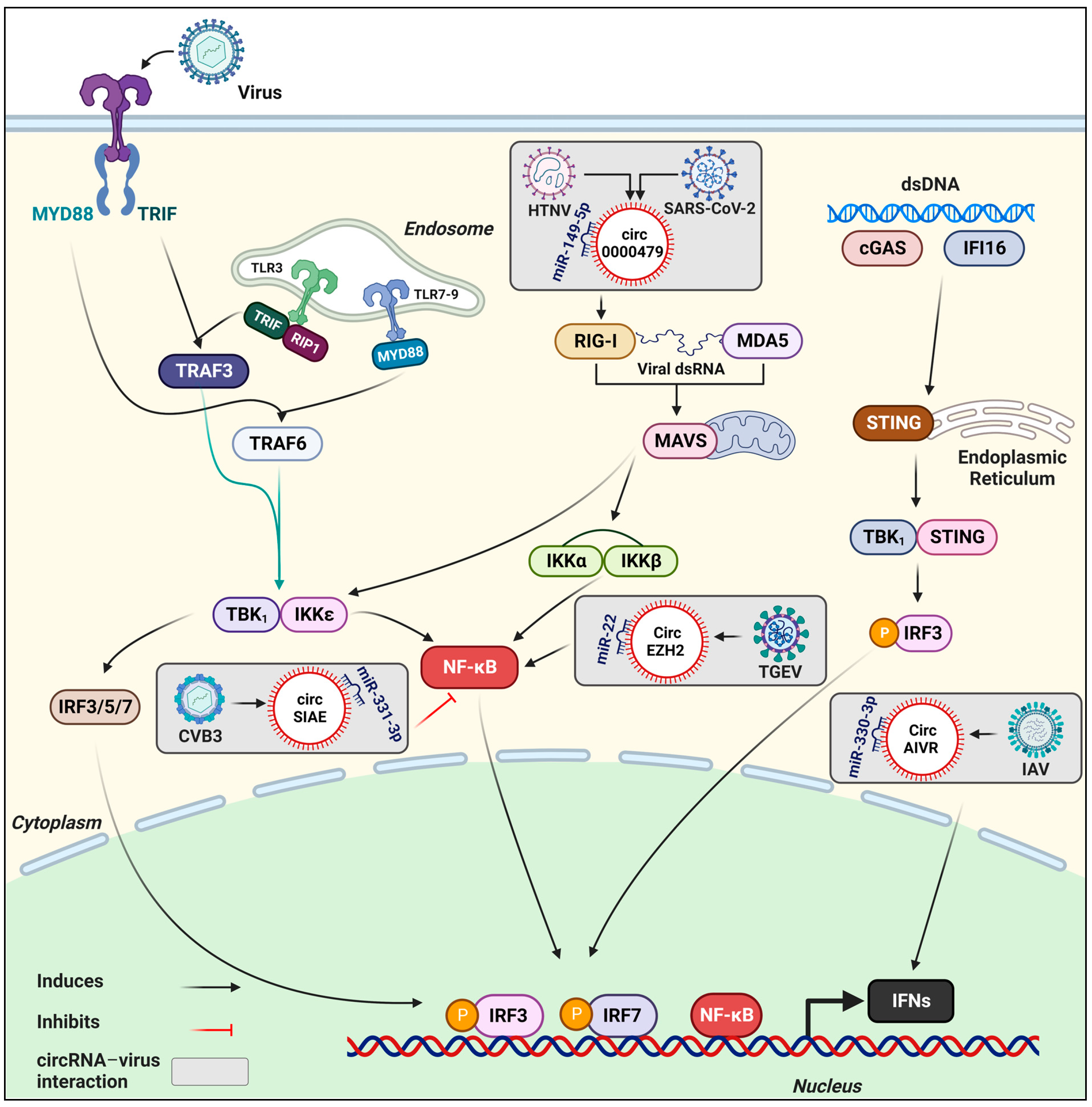
3.1. Host-Coded circRNAs Involved in Immune Responses
3.1.1. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
3.1.2. Influenza Virus
3.1.3. Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV)
3.1.4. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
3.1.5. Transmissible Gastroenteritis Coronavirus (TGEV)
3.1.6. Ebola Virus (EBOV)
3.1.7. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
3.1.8. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
3.1.9. Kaposi Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus (KSHV)
3.1.10. Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1)
3.1.11. Non-Mammalian Viruses
3.2. Virus-Coded circRNAs Affecting Innate Immunity
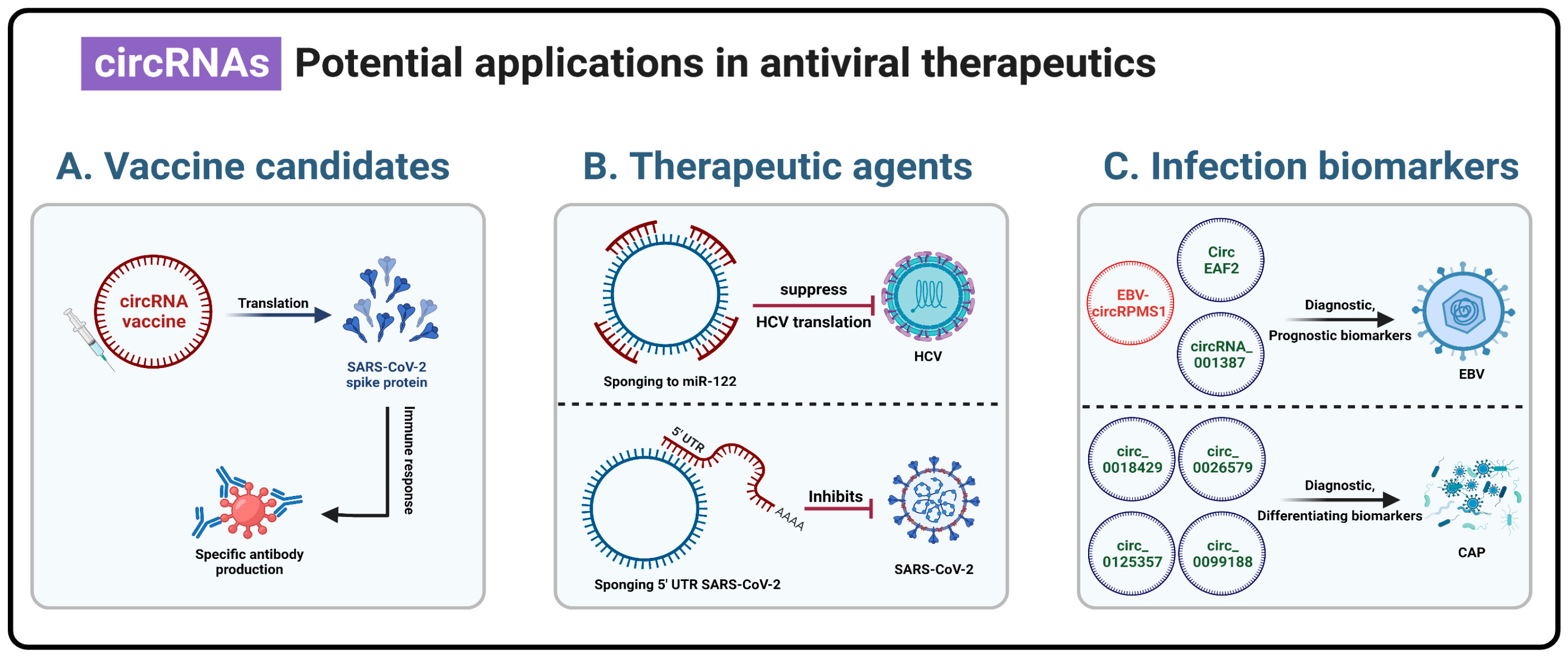
4. Practical Applications of Circular RNAs
4.1. Vaccine Candidates
4.2. Therapeutic Agents
4.3. Viral Infection Biomarker
5. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APC | Adenomatous polyposis coli |
| BmCPV | Bombyx mori cypovirus |
| BmNPV | Bombyx mori Nucleopolyhedrovirus |
| BSJ | Backsplice junction |
| Calu-3 | Human lung adenocarcinoma cells |
| CAP | Community-acquired pneumonia |
| CCNK | Cyclin-K |
| ceRNAs | Competing endogenous RNAs |
| CHB | Chronic Hepatitis B |
| circRNAs | Circular RNAs |
| ciRNAs | Circular intronic RNAs |
| CLDN18 | Claudin 18 |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| CREBBP | CREB-binding protein |
| CVB3 | Coxsackievirus B3 |
| CVB3 | Coxsackievirus B3 |
| CyHV-2 | Cyprinid herpesvirus 2 |
| DENV | Dengue virus |
| DLBCL | Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus. |
| ecircRNAs | Circular exonic RNAs |
| eiciRNAs | Exon–intron circRNAs |
| EVD | Ebola Virus Disease |
| G3BP1 | GTPase-activating protein SH3 domain-binding protein 1 |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HDV | Hepatitis D virus |
| HepG2 | Human hepatoma cell line |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| HK2 | Hexokinase 2 |
| hnRNP C | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C |
| HRSP12 | Heat-responsive protein 12 |
| HTNV | Hantaan virus |
| Huh7 | Human hepatocarcinoma cell line |
| IAV | Influenza A virus |
| ICAM1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IL-15 | Interleukin-15 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IPEC-J2 | Intestinal porcine enterocytes cell line |
| IRF3 | Interferon Regulatory Factor 3 |
| JAK-STAT | Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| KSHV | Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus |
| LNA | Locked nucleic acid |
| lncRNAs | Long non-coding RNAs |
| LNP | Lipid-based nanoparticle |
| MAP3K2 | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase 2 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MERS-CoV | Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| MIMV | maize Iranian mosaic virus |
| miRNAs | MicroRNAs |
| mPTP | Mitochondrial permeability transition pore |
| MREs | MiRNA response elements |
| mRNAs | Messenger RNAs |
| ncRNAs | Non-coding RNAs |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa light chain enhancer of activated B cells |
| NOD | Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain |
| NPC | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| p53 | Tumor protein P53 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death ligand 1 |
| PKR | Protein kinase R |
| RBD | Receptor binding domain |
| sncRNAs | Small non-coding RNAs |
| SRSF1 | Serine And Arginine-Rich Splicing Factor 1 |
| TAOK2 | Thousand-And-One Kinase 2 |
| TAP2 | Transporter 2 |
| TGEV | Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus |
| TNFAIP3 | TNF alpha-induced protein 3 |
| TRAF6 | TNF receptor associated factor 6 |
| TRIM59 | Tripartite Motif Containing 59 |
| VPS34 | Vacuolar protein sorting 34 |
| vSP27 | Viral small peptide 27 |
| VSP39 | Viral small peptide 39 |
| YTHDF2 | YTH N6-Methyladenosine RNA-Binding Protein F2 |
References
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carninci, P.; Kasukawa, T.; Katayama, S.; Gough, J.; Frith, M.C.; Maeda, N.; Oyama, R.; Ravasi, T.; Lenhard, B.; Wells, C.; et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 2005, 309, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Consortium, E.P. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Awan, H.M.; Shah, A.; Rashid, F.; Shan, G. Primate-specific Long Non-coding RNAs and MicroRNAs. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, S.K.; Kota, S.B. Noncoding RNA and epigenetic gene regulation in renal diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponting, C.P.; Oliver, P.L.; Reik, W. Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, K.R.; Liao, Y.; Cai, M.; Qiu, H.; Wen, F.; Peng, M.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Guo, G.; Chi, X.; et al. MIR155HG Plays a Bivalent Role in Regulating Innate Antiviral Immunity by Encoding Long Noncoding RNA-155 and microRNA-155-5p. Mbio 2022, 13, e0251022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolakofsky, D. Isolation and characterization of Sendai virus DI-RNAs. Cell 1976, 8, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kos, A.; Dijkema, R.; Arnberg, A.C.; van der Meide, P.H.; Schellekens, H. The hepatitis delta (delta) virus possesses a circular RNA. Nature 1986, 323, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, D.; Huang, S. The emerging role and clinical implication of human exonic circular RNA. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsiao, K.Y.; Sun, H.S.; Tsai, S.J. Circular RNA-New member of noncoding RNA with novel functions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salzman, J.; Chen, R.E.; Olsen, M.N.; Wang, P.L.; Brown, P.O. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, S.P.; Salzman, J. Circular RNAs: Analysis, expression and potential functions. Development 2016, 143, 1838–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sharpless, N.E. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wilusz, J.E. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes. Dev. 2014, 28, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.X.; Chen, L.L. Circular RNAs: Characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell 2022, 185, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.J.; Shen, J. Circular RNA participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of cancer. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, I.; Chen, Y.G. Emerging roles of circular RNAs in innate immunity. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2021, 68, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, J.; Baird, A.M.; Brady, L.; Lim, M.; Gray, S.G.; McDermott, R.; Finn, S.P. Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, Function and Role in Human Diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2017, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. The Biogenesis, Functions, and Challenges of Circular RNAs. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrett, S.P.; Wang, P.L.; Salzman, J. Circular RNA biogenesis can proceed through an exon-containing lariat precursor. Elife 2015, 4, e07540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matera, A.G.; Wang, Z. A day in the life of the spliceosome. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.O.; Wang, H.B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell 2014, 159, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.L.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. The Biogenesis of Nascent Circular RNAs. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Wen, F.; Peng, M.; Wang, G.; Guo, G.; Chen, B.; Maarouf, M.; et al. Influenza A Virus-Induced circRNA circMerTK Negatively Regulates Innate Antiviral Responses. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0363722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enuka, Y.; Lauriola, M.; Feldman, M.E.; Sas-Chen, A.; Ulitsky, I.; Yarden, Y. Circular RNAs are long-lived and display only minimal early alterations in response to a growth factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 1370–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szabo, L.; Morey, R.; Palpant, N.J.; Wang, P.L.; Afari, N.; Jiang, C.; Parast, M.M.; Murry, C.E.; Laurent, L.C.; Salzman, J. Statistically based splicing detection reveals neural enrichment and tissue-specific induction of circular RNA during human fetal development. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.X.; Li, X.; Nan, F.; Jiang, S.; Gao, X.; Guo, S.K.; Xue, W.; Cui, Y.; Dong, K.; Ding, H.; et al. Structure and Degradation of Circular RNAs Regulate PKR Activation in Innate Immunity. Cell 2019, 177, 865–880.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Molinie, B.; Daneshvar, K.; Pondick, J.V.; Wang, J.; Van Wittenberghe, N.; Xing, Y.; Giallourakis, C.C.; Mullen, A.C. Genome-Wide Maps of m6A circRNAs Identify Widespread and Cell-Type-Specific Methylation Patterns that Are Distinct from mRNAs. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2262–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, O.H.; Ha, H.; Lee, Y.; Boo, S.H.; Kwon, D.H.; Song, H.K.; Kim, Y.K. Endoribonucleolytic Cleavage of m(6)A-Containing RNAs by RNase P/MRP Complex. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 494–507.e498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Wiklund, E.D.; Bramsen, J.B.; Villadsen, S.B.; Statham, A.L.; Clark, S.J.; Kjems, J. miRNA-dependent gene silencing involving Ago2-mediated cleavage of a circular antisense RNA. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4414–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischer, J.W.; Busa, V.F.; Shao, Y.; Leung, A.K.L. Structure-Mediated RNA Decay by UPF1 and G3BP1. Mol. Cell 2020, 78, 70–84.e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariko, K.; Buckstein, M.; Ni, H.; Weissman, D. Suppression of RNA recognition by Toll-like receptors: The impact of nucleoside modification and the evolutionary origin of RNA. Immunity 2005, 23, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Verbeke, R.; Hogan, M.J.; Lore, K.; Pardi, N. Innate immune mechanisms of mRNA vaccines. Immunity 2022, 55, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.G.; Kim, M.V.; Chen, X.; Batista, P.J.; Aoyama, S.; Wilusz, J.E.; Iwasaki, A.; Chang, H.Y. Sensing Self and Foreign Circular RNAs by Intron Identity. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wesselhoeft, R.A.; Kowalski, P.S.; Parker-Hale, F.C.; Huang, Y.X.; Bisaria, N.; Anderson, D.G. RNA Circularization Diminishes Immunogenicity and Can Extend Translation Duration In Vivo. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 508–520.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.X.; Guo, S.K.; Nan, F.; Xu, Y.F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. RNA circles with minimized immunogenicity as potent PKR inhibitors. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 420–434.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, J.; Chen, Y.G. Differences in the immunogenicity of engineered circular RNAs. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 15, mjad002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Andersen, M.S.; Stagsted, L.V.W.; Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M.R.; Sonenberg, N.; Filipowicz, W. Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010, 79, 351–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Zhao, Y. Circular RNAs: Characteristics, function, and role in human cancer. Histol. Histopathol. 2018, 33, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, I.; Shalamova, L.A.; Gerresheim, G.K.; Niepmann, M.; Bindereif, A.; Rossbach, O. Functional sequestration of microRNA-122 from Hepatitis C Virus by circular RNA sponges. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.-X.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yin, Q.-F.; Wei, J.; Yao, R.-W.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L. Coordinated circRNA Biogenesis and Function with NF90/NF110 in Viral Infection. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 214–227.e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, W.W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; Yong, T.; Awan, F.M.; Yang, B.B. Identifying and Characterizing circRNA-Protein Interaction. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4183–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Efficient backsplicing produces translatable circular mRNAs. RNA 2015, 21, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, L.; Yi, Z.Y.; Shen, Y.; Lin, L.R.; Chen, F.; Xu, Y.Y.; Wu, Z.G.; Tang, H.X.; Zhang, X.X.; Tian, F.; et al. Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants. Cell 2022, 185, 1728–1744.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, S.K.; Belk, J.A.; Amaya, L.; Li, Z.; Cardenas, A.; Abe, B.T.; Chen, C.K.; Wender, P.A.; Chang, H.Y. Engineering circular RNA for enhanced protein production. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, R.; Zhang, X.; Cui, L.; Ding, Y.; Shi, W.; Guo, C.; Shi, Y. Crosstalk between N6-methyladenosine modification and circular RNAs: Current understanding and future directions. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wei, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Wei, T.; Tang, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. A flexible, efficient, and scalable platform to produce circular RNAs as new therapeutics. bioRxiv 2022, 05, 494115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Goraya, M.U.; Maarouf, M.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.L. Host Immune Response to Influenza A Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, K.R.; Shrestha, P.; Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Liu, S.; Maarouf, M.; Chen, J.L. Acute Infection of Viral Pathogens and Their Innate Immune Escape. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 672026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarouf, M.; Rai, K.R.; Goraya, M.U.; Chen, J.L. Immune Ecosystem of Virus-Infected Host Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, Z.Y.; Meng, F.; Shi, J.Z.; Deng, G.H.; Zeng, X.Y.; Ge, J.Y.; Li, Y.B.; Liu, L.L.; Chen, P.C.; Jiang, Y.P.; et al. A Novel Intronic Circular RNA Antagonizes Influenza Virus by Absorbing a microRNA That Degrades CREBBP and Accelerating IFN-beta Production. Mbio 2021, 12, e0101721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadena, C.; Hur, S. Antiviral Immunity and Circular RNA: No End in Sight. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awan, F.M.; Yang, B.B.; Naz, A.; Hanif, A.; Ikram, A.; Obaid, A.; Malik, A.; Janjua, H.A.; Ali, A.; Sharif, S. The emerging role and significance of circular RNAs in viral infections and antiviral immune responses: Possible implication as theranostic agents. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, A.; Madbhagat, P.; Sreepadmanabh, M.; Bhardwaj, V.; Chande, A. Circular RNA as an Additional Player in the Conflicts Between the Host and the Virus. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 602006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhu, N.; Guo, W.; Wang, X.; Li, K.; Yan, J.; Jiang, C.; Han, S.; Xiang, H.; Wu, X.; et al. RNA-Seq Revealed a Circular RNA-microRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Hantaan Virus Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Firoozi, Z.; Mohammadisoleimani, E.; Shahi, A.; Naghizadeh, M.M.; Mirzaei, E.; Asad, A.G.; Salmanpour, Z.; Javad Nouri, S.M.; Mansoori, Y. Hsa_circ_0000479/Hsa-miR-149-5p/RIG-I, IL-6 Axis: A Potential Novel Pathway to Regulate Immune Response against COVID-19. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2022, 2022, 2762582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, H.; Shen, H. The circRNA circSIAE Inhibits Replication of Coxsackie Virus B3 by Targeting miR-331-3p and Thousand and One Amino-Acid Kinase 2. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 779919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Guo, J.; Mi, M.; Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Tang, X.; Chang, L.; Huang, Y.; Tong, D. Circular RNA CircEZH2 Suppresses Transmissible Gastroenteritis Coronavirus-induced Opening of Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore via Targeting MiR-22 in IPEC-J2. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, J.; Guan, L.; Li, J.; Mi, M.; Huang, Y.; Tong, D. Differentially expressed non-coding RNAs induced by transmissible gastroenteritis virus potentially regulate inflammation and NF-kappaB pathway in porcine intestinal epithelial cell line. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenner, R.G.; Young, R.A. Insights into host responses against pathogens from transcriptional profiling. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chu, H.; Wen, L.; Shuai, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yuan, S.; Yin, F.; et al. Competing endogenous RNA network profiling reveals novel host dependency factors required for MERS-CoV propagation. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 733–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Yang, H.; Shi, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W. Expression Profiles of Differentially Expressed Circular RNAs and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Networks in SH-SY5Y Cells Infected with Coxsackievirus B5. Int. J. Genom. 2022, 2022, 9298149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Su, J.; Wang, N.; Zhao, N.; Su, S. Expression Profiling and Bioinformatics Analysis of CircRNA in Mice Brain Infected with Rabies Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanuj, G.N.; Khan, O.; Malla, W.A.; Rajak, K.K.; Chandrashekar, S.; Kumar, A.; Dhara, S.K.; Gupta, P.K.; Mishra, B.P.; Dutt, T.; et al. Integrated analysis of long-noncoding RNA and circular RNA expression in Peste-des-Petits-Ruminants Virus (PPRV) infected marmoset B lymphocyte (B95a) cells. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 170, 105702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Jin, L.; Wang, L.; Huang, X.; Chen, W.; Yan, M.; Liu, G. Profile analysis of circRNAs induced by porcine endemic diarrhea virus infection in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Virology 2019, 527, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tang, W.; Jin, Y.; Dong, W.; Yan, Y.; Zhou, J. Differential CircRNA Expression Profiles in PK-15 Cells Infected with Pseudorabies Virus Type II. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Qi, M.; Xu, L.; Huang, P.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Shi, J.; Hu, Y. Differential host circRNA expression profiles in human lung epithelial cells infected with SARS-CoV-2. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 93, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yang, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Hao, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhao, D.; Yuan, X.; Chen, X.; Shen, C.; et al. Profiling and functional analysis of differentially expressed circular RNAs identified in foot-and-mouth disease virus infected PK-15 cells. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Fan, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, Y.; Cui, W.; Qiao, X.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of differentially expressed mRNAs, lncRNAs, and circRNAs in chicken bursae of Fabricius during infection with very virulent infectious bursal disease virus. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Q.; Tian, M.; Huang, N.; Fan, M.; Yu, M.; Xia, H.; Ping, J. Analysis of the circRNAs expression profile in mouse lung with H7N9 influenza A virus infection. Genomics 2021, 113, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W.; Li, B.; Gu, G.; Luo, Y.; Shuai, X.; Fan, C.; Wu, L.; et al. Identifying Circular RNAs in HepG2 Expressing Genotype IV Swine Hepatitis E Virus ORF3 Via Whole Genome Sequencing. Cell Transpl. 2021, 30, 9636897211055042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Deng, X.; Wang, R.; Li, R.; You, L.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. Comprehensive analysis of the circRNA expression profile and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in the pathogenesis of EV-A71 infection. Virus Res. 2021, 303, 198502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, F.; Chen, L.; Wei, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Huang, J.; Guo, Q.; Yang, X. CircRNA expression profiling and bioinformatics analysis indicate the potential biological role and clinical significance of circRNA in influenza A virus-induced lung injury. J. Biosci. 2021, 46, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.R.; Zhang, H.R.; Zhang, Z.F.; Lai, S.Y.; Huang, L.J.; Liu, J.; Bai, X.; Ding, K.; Zhou, J.Y. Human papillomavirus 16 E7 oncoprotein alters the expression profiles of circular RNAs in Caski cells. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3755–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Ashraf, U.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, D.; Imran, M.; Ye, J.; Chen, H.; Cao, S. Genome-wide profiling of host-encoded circular RNAs highlights their potential role during the Japanese encephalitis virus-induced neuroinflammatory response. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Zeng, T.; Xu, W.; Gu, T.; Lu, L. RNA Sequencing Reveals circRNA Expression Profiles in Chicken DF1 Cells Infected with H5N1 Influenza Virus. Animals 2022, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Qiu, L.; Bai, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Chen, G.; Chang, G. Identification, biogenesis and function prediction of novel circRNA during the chicken ALV-J infection. Anim. Biotechnol. 2022, 33, 981–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, R.; Zhao, W.; Liu, C.; Tan, Y.; Pu, D.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y. circRNA expression patterns and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks during CV-A16 infection of SH-SY5Y cells. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 3023–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; An, M.H.; Zhao, B.; Ding, H.B.; Zhang, Z.N.; He, Y.W.; Shang, H.; Han, X.X. Crosstalk in competing endogenous RNA networks reveals new circular RNAs involved in the pathogenesis of early HIV infection. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 3023–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Izadpanah, K.; Peters, J.R.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Mitter, N. Detection and profiling of circular RNAs in uninfected and maize Iranian mosaic virus-infected maize. Plant Sci. 2018, 274, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tagawa, T.; Gao, S.; Koparde, V.N.; Gonzalez, M.; Spouge, J.L.; Serquiña, A.P.; Lurain, K.; Ramaswami, R.; Uldrick, T.S.; Yarchoan, R.; et al. Discovery of Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus-encoded circular RNAs and a human antiviral circular RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12805–12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0004812 impairs IFN-induced immune response by sponging miR-1287-5p to regulate FSTL1 in chronic hepatitis B. Virol. J. 2020, 17, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, N.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Zhou, X.; Duan, S. CircRNA circBACH1 facilitates hepatitis B virus replication and hepatoma development by regulating the miR-200a-3p/MAP3K2 axis. Histol. Histopathol. 2022, 37, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Circ-ATP5H Induces Hepatitis B Virus Replication and Expression by Regulating miR-138-5p/TNFAIP3 Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 11031–11040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chu, H.; Chik, K.K.; Wen, L.; Shuai, H.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Yuen, T.T.; Cai, J.P.; et al. hnRNP C modulates MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 replication by governing the expression of a subset of circRNAs and cognitive mRNAs. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, N.; Zhang, S.; Guo, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, M.; Guan, Z.; Duan, M. CircRNA_0050463 promotes influenza A virus replication by sponging miR-33b-5p to regulate EEF1A1. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 254, 108995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Lei, J.; Zhou, J.; Song, S.; Hu, B. Circular RNA GATAD2A promotes H1N1 replication through inhibiting autophagy. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 231, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Cao, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Liu, W.; Li, J. RNA Sequencing Demonstrates That Circular RNA Regulates Avian Influenza Virus Replication in Human Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C.; Tallo-Parra, M.; Cao, Q.M.; Kadener, S.; Bottcher, R.; Perez-Vilaro, G.; Boonchuen, P.; Somboonwiwat, K.; Diez, J.; Sarnow, P. Host-derived circular RNAs display proviral activities in Hepatitis C virus-infected cells. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Singh, A.; Dalavi, R.; Ralte, L.; Chawngthu, R.L.; Kumar, N.S.; Vijay, N.; Chande, A. HIV-1 Vpr induces ciTRAN to prevent transcriptional silencing of the provirus. bioRxiv 2022, 11, 515166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.X.; Yan, Z.X.; Wen, J.J.; Fu, D.; Xu, P.P.; Wang, L.; Cheng, S.; Hu, J.D.; Zhao, W.L. CircEAF2 counteracts Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma progression via miR-BART19-3p/APC/beta-catenin axis. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memish, Z.A.; Perlman, S.; Van Kerkhove, M.D.; Zumla, A. Middle East respiratory syndrome. Lancet 2020, 395, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C.W.; Dusheiko, G.M.; Hellard, M.; Sonderup, M. Hepatitis C. Lancet 2019, 394, 1451–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.T.; Crozier, I.; Fischer, W.A.; Hewlett, A.; Kraft, C.S.; Vega, M.-A.d.L.; Soka, M.J.; Wahl, V.; Griffiths, A.; Bollinger, L.; et al. Ebola virus disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Guo, Z.D.; Li, J.M.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Fu, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.N.; Qian, J.; Liu, L.N. Genome-Wide Search for Competing Endogenous RNAs Responsible for the Effects Induced by Ebola Virus Replication and Transcription Using a trVLP System. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeks, S.G.; Overbaugh, J.; Phillips, A.; Buchbinder, S. HIV infection. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, K.K.; Bertozzi, S.; Bloom, B.R.; Jha, P.; Piot, P. Major Infectious Diseases, 3rd ed.; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. xviii. 486p. [Google Scholar]
- Tagawa, T.; Oh, D.; Dremel, S.; Mahesh, G.; Koparde, V.N.; Duncan, G.; Andresson, T.; Ziegelbauer, J.M. A virus-induced circular RNA maintains latent infection of Kaposi’s sarcoma herpesvirus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2212864120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.D.; Hu, N.Z.; Mo, L.; Zeng, Z.P.; Sun, J.; Hu, Y.Z. Deep RNA Sequencing Reveals a Repertoire of Human Fibroblast Circular RNAs Associated with Cellular Responses to Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 2031–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Sun, L.; Yang, L.; Xu, T. The circular RNA circBCL2L1 regulates innate immune responses via microRNA-mediated downregulation of TRAF6 in teleost fish. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lee, E.E.; Kim, J.; Yang, R.; Chamseddin, B.; Ni, C.; Gusho, E.; Xie, Y.; Chiang, C.M.; Buszczak, M.; et al. Transforming activity of an oncoprotein-encoding circular RNA from human papillomavirus. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abere, B.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Toptan, T.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Kaposi’s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus-Encoded circRNAs Are Expressed in Infected Tumor Tissues and Are Incorporated into Virions. Mbio 2020, 11, e03027-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, H.; Liu, M.; Jaijyan, D.; Cruz-Cosme, R.; Ramasamy, S.; Subbian, S.; Liu, D.; Xu, J.; Niu, X.; et al. SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV encode circular RNAs of spliceosome-independent origin. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 3203–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Lu, C.; He, J.; Liu, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, X.; Wu, A.; Jiang, T.; et al. Identification and characterization of circRNAs encoded by MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, Z.; Wang, C.; Shen, Z.; Sun, S.; Gong, C.; Hu, X. Viral Circular RNAs and Their Possible Roles in Virus-Host Interaction. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 939768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.E.; Lim, Y.Y. Viruses join the circular RNA world. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 4488–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, F.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Y.; Mo, Y.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, Y.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded Circular RNA CircBART2.2 Promotes Immune Escape of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma by Regulating PD-L1. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5074–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abere, B.; Zhou, H.; Li, J.; Cao, S.; Toptan, T.; Grundhoff, A.; Fischer, N.; Moore, P.S.; Chang, Y. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Encodes Circular RNAs (circRNAs) Enabling a Dynamic circRNA/microRNA/mRNA Regulatory Network. Mbio 2020, 11, e03059-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, S.; Wu, W.; Tang, W.; Dong, Y.; Shen, M.; Wu, P.; Guo, X. Identification of long noncoding RNAs in silkworm larvae infected with Bombyx mori cypovirus. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 106, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.T.; Ling, X.D.; Xiao, L.F.; Hu, J.J.; Zhao, X.X.; Liu, J.X.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus on serpin and antibacterial peptide expression in B. mori. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Qiu, Q.; Tong, X.; Pan, J.; Zhu, M.; Hu, X.; Gong, C. BmNPV circular RNA-encoded peptide VSP39 promotes viral replication. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 228, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Zhou, L. Genetic basis and breeding application of clonal diversity and dual reproduction modes in polyploid Carassius auratus gibelio. Sci. China Life Sci. 2010, 53, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Dai, Y.; Tong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Cao, G.; et al. Circ-Udg Derived from Cyprinid Herpesvirus 2 Promotes Viral Replication. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0094322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, F.; Wu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, W.; Ponnusamy, M.; Wang, K.; Li, P. Circular RNAs: A novel type of non-coding RNA and their potential implications in antiviral immunity. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Breuer, J.; Barth, P.; Noe, Y.; Shalamova, L.; Goesmann, A.; Weber, F.; Rossbach, O. What goes around comes around: Artificial circular RNAs bypass cellular antiviral responses. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2022, 28, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselhoeft, R.A.; Kowalski, P.S.; Anderson, D.G. Engineering circular RNA for potent and stable translation in eukaryotic cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banerji, A.; Wickner, P.G.; Saff, R.; Stone, C.A.; Robinson, L.B.; Long, A.A.; Wolfson, A.R.; Williams, P.; Khan, D.A.; Phillips, E.; et al. mRNA Vaccines to Prevent COVID-19 Disease and Reported Allergic Reactions: Current Evidence and Suggested Approach. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meganck, R.M.; Borchardt, E.K.; Rivera, R.M.C.; Scalabrino, M.L.; Wilusz, J.E.; Marzluff, W.F.; Asokan, A. Tissue-Dependent Expression and Translation of Circular RNAs with Recombinant AAV Vectors In Vivo. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines-a new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, D.; He, Q.; Liu, J.; Mao, Q.; Liang, Z. Research progress on circular RNA vaccines. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1091797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seephetdee, C.; Bhukhai, K.; Buasri, N.; Leelukkanaveera, P.; Lerdwattanasombat, P.; Manopwisedjaroen, S.; Phueakphud, N.; Kuhaudomlarp, S.; Olmedillas, E.; Saphire, E.O.; et al. A circular mRNA vaccine prototype producing VFLIP-X spike confers a broad neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 variants by mouse sera. Antivir. Res. 2022, 204, 105370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.K.; Cheng, R.; Demeter, J.; Chen, J.; Weingarten-Gabbay, S.; Jiang, L.H.; Snyder, M.P.; Weissman, J.S.; Segal, E.; Jackson, P.K.; et al. Structured elements drive extensive circular RNA translation. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 4300–4318.E13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfafenrot, C.; Schneider, T.; Muller, C.; Hung, L.H.; Schreiner, S.; Ziebuhr, J.; Bindereif, A. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus proliferation by designer antisense-circRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 12502–12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, M.; Huang, L. High Expression of hsa_circRNA_001387 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma and the Effect on Efficacy of Radiotherapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 3965–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Shuai, M.; Xia, Y. Knockdown of EBV-encoded circRNA circRPMS1 suppresses nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation and metastasis through sponging multiple miRNAs. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 8023–8031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, T.; Zheng, Y.; Hao, D.; Jin, X.; Luo, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Xi, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Blood circRNAs as biomarkers for the diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 16483–16494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavenniah, A.; Luu, T.D.A.; Li, Y.Q.P.; Lim, T.S.B.; Jiang, J.M.; Ackers-Johnson, M.; Foo, R.S.Y. Engineered Circular RNA Sponges Act as miRNA Inhibitors to Attenuate Pressure Overload-Induced Cardiac Hypertrophy. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 1506–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.C.; Thum, T. RNA-based diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, H.L.; Reesink, H.W.; Lawitz, E.J.; Zeuzem, S.; Rodriguez-Torres, M.; Patel, K.; van der Meer, A.J.; Patick, A.K.; Chen, A.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, P.-W.; Chen, T.-T.; Zhao, W.-X.; Liu, G.-W.; Feng, X.-J.; Wang, S.-M.; Pan, Y.-C.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.-H. Scutellaria barbata D.Don and Oldenlandia diffusa (Willd.) Roxb crude extracts inhibit hepatitis-B-virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma growth through regulating circRNA expression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 275, 114110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Sun, T.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, G.; Wu, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; et al. Exosomal circRNAs: Biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, X.; Wang, B.; Feng, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, K.; Sun, M. circRNAs and Exosomes: A Mysterious Frontier for Human Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.M.; Zhang, K.; Tan, S.Y.; Xin, J.Y.; Yuan, Q.Y.; Xu, H.H.; Xu, X.; Liang, Q.; Christiani, D.C.; Wang, M.L.; et al. Circular RNAs in body fluids as cancer biomarkers: The new frontier of liquid biopsies. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Yin, G.; Lin, L.; Liang, C. Identification of urinary hsa_circ_0137439 as a potential biomarker and tumor regulator of bladder cancer. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ding, W.B.; Wang, M.C.; Guo, X.G.; Xu, J.; Xu, Q.G.; Yang, Y.; Sun, S.H.; Liu, J.F.; Qin, L.X.; et al. Plasma circular RNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: A large-scale, multicenter study. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahn, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Chan, T.M.; Lin, X.; Kim, Y.; Wong, D.T.; Xiao, X. The landscape of microRNA, Piwi-interacting RNA, and circular RNA in human saliva. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Song, F.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Shao, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, Q.; Hou, Y.; Xie, J. Characterization of tissue-specific biomarkers with the expression of circRNAs in forensically relevant body fluids. Int. J. Leg. Med. 2019, 133, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J. Circular RNA Expression: Its Potential Regulation and Function. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Ming, Y.; MinLi, Y.; Han, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, J.; Dai, B.; Lv, Y.; He, M.L.; Fang, M.; et al. hsa_circ_0006459 and hsa_circ_0015962 affect prognosis of Dengue fever. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| circRNA | Stimuli | Differential Expression | Functions/Mechanisms | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa_circ_0001400 | KSHV | Up | During KSHV de novo infections, circ_0001400 expression suppressed the expression of vital latent and lytic viral genes without significantly altering the viral genome copy number. | [89] |
| circ_0000479 | HTNV | Up | Circ_0000479 sponged miR-149-5p and regulated RIG-I expression, thus dampening viral replication. | [63] |
| hsa_circ_0004812 | HBV | Up | Circ_0004812 silencing enhanced the expression of IFN-α and β in HBV-infected Huh7 cells. | [90] |
| circBACH1 | HBV | Up | CircBACH1 regulated HBV propagation through the miR-200a-3p/MAP3K2 pathway. | [91] |
| circ-ATP5H | HBV | Up | Circ-ATP5H boosted HBV replication by modulating the miR-138-5p/TNFAIP3 axis. | [92] |
| circFNDC3B | MERS-CoV | UP | The silencing of circFNDC3B and circCNOT1 significantly suppressed the MERS-CoV viral load and its target mRNA expression, modulating various biological pathways, including the MAPK and ubiquitination pathways. | [69] |
| circCNOT1 | ||||
| hsa_circ_0004445 | MERS-CoV | UP | The knockdown of hsa_circ_0004445 inhibited MERS-CoV replication. | [93] |
| hsa_circ_0000479 | SARS-CoV-2 | UP | SARS-CoV-2 could regulate IL-6 and RIG-I activity via hsa_circ_0000479/hsa-miR-149-5p/RIG-I, IL-6axis. | [64] |
| ssc_circ_009380 (circEZH2) | TGEV | Down | CircEZH2 promoted the activation of NF-κB via sponging miR-22. | [67] |
| circMerTK | IAV | Up | CircMerTK inhibited IFN-beta production and suppressed IFN signaling, thus boosting IAV replication. | [31] |
| circRNA AIVR | IAV | Up | circRNA AIVR inhibited IAV replication by predominantly absorbing miR-330-3p. | [59] |
| circRNA_0050463 | IAV | Up | CircRNA_0050463 was found to sponge to miR-33b-5p and thereby enhanced IAV replication. | [94] |
| circ-GATAD2A | IAV | Up | Circ-GATAD2A promoted influenza virus multiplication by inhibiting VPS34-dependent autophagy in vitro | [95] |
| hsa_circ_0005870 | IAV | UP | The overexpression of these three circRNAs inhibited AIV replication and proliferation, whereas silencing these circRNAs enhanced AIV multiplication. | [96] |
| hsa_circ_0006104 | ||||
| hsa_circ_0009365 | ||||
| circEXOSC | HCV | UP | Depleting circEXOSC in HCV-infected cells markedly reduced viral infectivity. | [97] |
| circTIAL | A significant reduction in HCV infectivity was observed after circTIAL silencing. | |||
| circPSD3 | HCV | UP | CircPSD3 promoted HCV RNA abundances at a post-translational level. | |
| DENV | UP | CircPSD3 was found to reduce viral infectivity in Dengue virus-infected cells significantly. | ||
| ciTRAN | HIV | UP | HIV-1-Vpr-induced ciTRAN-sequestered SRSF1 from the HIV viral transcriptional complex to enhance viral transcription. | [98] |
| circSIAE | CVB3 | Down | CircSIAE suppressed CVB3 replication by targeting miR-331-3p and TAOK2. | [65] |
| CircEAF2 | EBV | Down | CircEAF2 inhibited the replication of EBV and the progression of DLBCL via the miR-BART19-3p/APC/β-catenin axis. | [99] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maarouf, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Rai, K.R.; Chen, Y.; Fang, M.; Chen, J.-L. Functional Involvement of circRNAs in the Innate Immune Responses to Viral Infection. Viruses 2023, 15, 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15081697
Maarouf M, Wang L, Wang Y, Rai KR, Chen Y, Fang M, Chen J-L. Functional Involvement of circRNAs in the Innate Immune Responses to Viral Infection. Viruses. 2023; 15(8):1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15081697
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaarouf, Mohamed, Lulu Wang, Yiming Wang, Kul Raj Rai, Yuhai Chen, Min Fang, and Ji-Long Chen. 2023. "Functional Involvement of circRNAs in the Innate Immune Responses to Viral Infection" Viruses 15, no. 8: 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15081697
APA StyleMaarouf, M., Wang, L., Wang, Y., Rai, K. R., Chen, Y., Fang, M., & Chen, J.-L. (2023). Functional Involvement of circRNAs in the Innate Immune Responses to Viral Infection. Viruses, 15(8), 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15081697






