Interactions between Common Bean Viruses and Their Whitefly Vector
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Whitefly-Transmitted Viruses Infecting Common Beans
2.1. Begomoviruses
2.2. Carlavirus
2.3. Cytorhabdovirus
2.4. Crinivirus
3. Molecular Interactions between Viruses and Insect Vectors
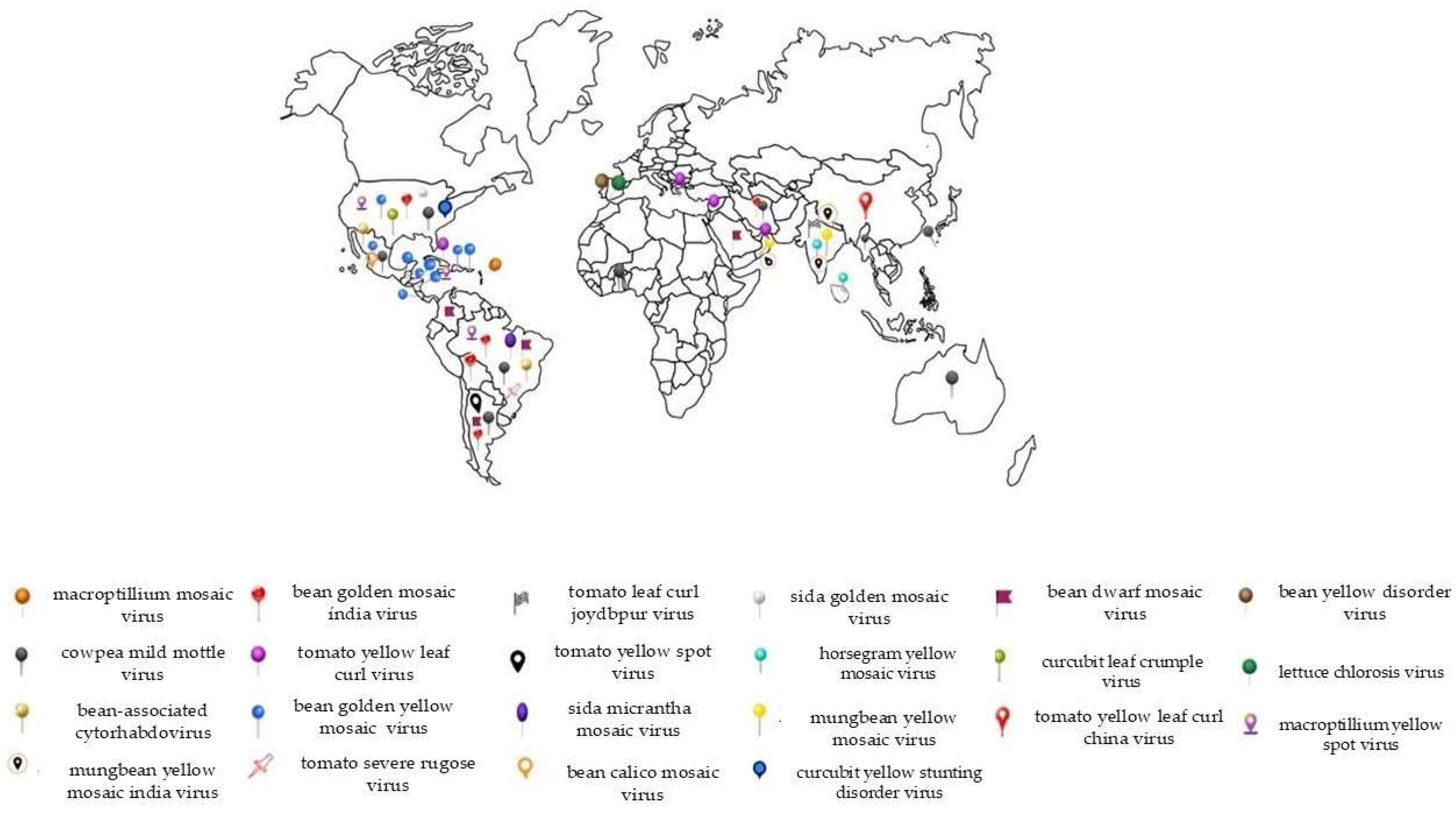
| Virus Family, Genus | Virus Name | Countries Where They Have Been Reported | Symptoms | Severity | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geminiviridae, Begomovirus is a genus that consists of twinned (geminate) particles with a single-stranded circular DNA genome (ssDNA) Virus species model: TYLCV in tomato Transmission mode: circulative, persistent, and nonpropagative (?) Highly efficient transmission (100% plants infected with 5–15 insects) Reviewed in [28] | tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) | Cuba, Greece, Oman, Syria, Israel, China, Brazil | Yellow mosaic and/or leaf crumple | The severity of TYLCV in bean crops can vary depending on the region. In most regions, the severity is low | [154,155,156,157,158] |
| bean golden mosaic virus (BGMV) | Brazil, Bolivia, Argentina, USA, Iran | Yellow mosaic on leaves, leaf deformation, reduced leaf size, plant dwarfism, significant reduction in productivity | High severity, causing up to 100% yield loss in cases of early infection | [66,159,160] | |
| bean Golden Yellow Mosaic Virus (BGYMV) | Dominican Republic, Guatemala, El Salvador, Haiti, Honduras, Costa Rica, Mexico, USA, Nicaragua, Iran | Intense yellowing, pod deformation, stunting, and flower abortion | High yield losses to common beans grown in tropical and sub-tropical countries of Latin America and the Caribbean | [10,71,159] | |
| macroptilium yellow spot virus (MaYSV) | Brazil, Jamaica, USA | Chlorotic spots on the soybean leaves | Not reported | [161,162,163] | |
| tomato leaf curl Joydebpur virus (ToLCJoV) | India | Curling, yellow mosaic, and stunting | High severity | [164] | |
| sida micrantha mosaic virus (SimMV) | Brazil | Golden mosaic, chlorotic spots, and leaf distortion | Low severity | [165] | |
| sida golden mosaic virus (SiGMV) | USA | Foliar mottling, puckering, and curl | High severity, particularly in the Southeastern United States | [70,166] | |
| horsegram yellow mosaic virus (HgYMV) | Sri Lanka, India | Included a bright yellow mosaic pattern on the leaves, rugosity, reduced leaf size, and stunting of the entire plant | High severity, depending on the timing of infection, plants produce fewer flowers and pods or none at all | [167,168] | |
| mungbean yellow mosaic virus (MBYMV) | India, Thailand | Yellow mosaic, puckering, and a reduction in size | High severity. Early-infected plants typically die without forming pods | [31,169] | |
| mungbean yellow mosaic India virus (MBYMIV) | India, Oman, Nepal | Yellowing of the veins and leaf crumpling | Low severity | [170,171] | |
| bean dwarf mosaic virus (BDMV) | Brazil, Argentina, Colombia, Saudi Arabia | Severe dwarfing, leaf distortion, mottling or mosaic, and chlorotic spots | High severity if infection occurs early | [10,32,66,172,173,174] | |
| cucurbit leaf crumple virus (CuLCrV) | USA | Leaf deformation, rugosity, and mild mosaic | Low severity | [175] | |
| tomato yellow leaf curl China virus (TYLCCNV) | China | Leaf curl | Low severity | [176] | |
| macroptilium mosaic virus (MaMV) | Puerto Rico | Green-yellow mosaic foliar symptoms and stunting | Low severity | [177] | |
| tomato yellow spot virus (ToYSV) | Argentina | Yellow spots, mosaic, chlorosis, stunting, leaf deformation | Low severity | [178] | |
| bean calico mosaic virus (BCMoV) | Mexico | Yellow or white spots, chlorosis, leaf deformation, and stunted growth | Low severity | [179] | |
| tomato severe rugose virus (ToSRV) | Brazil | Asymptomatic | Low severity | [180] | |
| Betaflexiviridae, Carlavirus | cowpea mild mottle virus (CPMMV) | Taiwan, Brazil, Australia, Argentina, USA, Mexico, Ghana, Thailand, Iran | Vein chlorosis, mild mottling, and leaf roughness | High severity | [66,93,94,102,181,182,183,184] |
| Rhabdoviridae, Cytorhabdovirus, | bean-associated cytorhabdovirus (BaCV) | Brazil, Mexico | mosaic, leaf distortion, crumpling, and dwarfing | Low severity | [96,125] |
| Crinivirus | bean yellow disorder virus (BnYDV) | Spain, Tanzania | Interveinal spots and leaf yellowing | Moderate severity | [131,132] |
| lettuce chlorosis virus (LCV-SP) | Spain | Internerval mottling and yellowing on middle and lower leaves | Low severity | [185] | |
| cucurbit yellow stunting disorder virus (CYSD) | USA | Severe stunting and desiccation of leaves | Low severity | [133] |
4. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO Crop Production and Trade Data. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Helgi Library Beans—Food Supply. 2019. Available online: https://www.helgilibrary.com/indicators/beans-food-supply-kcal-capita-day/ (accessed on 5 September 2024).
- Uebersax, M.A.; Cichy, K.A.; Gomez, F.E.; Porch, T.G.; Heitholt, J.; Osorno, J.M.; Kamfwa, K.; Snapp, S.S.; Bales, S. Dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as a vital component of sustainable agriculture and food security—A review. Legume Sci. 2023, 5, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaipopo, B.; Nchimbi-Msolla, S.; Njau, P.; Tairo, F.; William, M.; Binagwa, P.; Kweka, E.; Kilango, M.; Mbanzibwa, D. Viruses infecting common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Tanzania: A review on molecular characterization, detection and disease management options. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 12, 1486–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, W.J.; Hernández, G.; Blair, M.; Beebe, S.; Gepts, P.; Vanderleyden, J. Beans (Phaseolus Spp.)—Model food legumes. Plant Soil 2003, 252, 55–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mats, L.; Liu, R.; Deng, Z.; Mine, Y.; Tsao, R. Anti-inflammatory effect and cellular uptake mechanism of peptides from common bean (Phaseolus vulga L.) milk and yogurts in caco-2 mono- and caco-2/ea.hy926 co-culture models. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8370–8381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazzano, L.A.; He, J.; Ogden, L.G.; Loria, C.; Vupputuri, S.; Myers, L.; Whelton, P.K. Legume consumption and risk of coronary heart disease in us men and women: NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 2573–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Thompson, H.J. Edible Dry bean consumption (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) modulates cardiovascular risk factors and diet-induced obesity in rats and mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S66–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Barrios, L.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.A.; Serna-Saldívar, S.O. Bioactive peptides and hydrolysates from pulses and their potential use as functional ingredients. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, R273–R283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, F.J. Common beans. In Natural Resistance Mechanisms of Plants to Viruses; Loebenstein, G., Carr, J.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 367–382. ISBN 978-1-4020-3780-1. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, H.F.; Hall, R. Compendium of Bean Diseases; APS Press, American Phytopathological Society: Eagan, MN, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-89054-327-6. [Google Scholar]
- Worrall, E.A.; Wamonje, F.O.; Mukeshimana, G.; Harvey, J.J.W.; Carr, J.P.; Mitter, N. Bean common mosaic virus and bean common mosaic necrosis virus: Relationships, biology, and prospects for control. Adv. Virus Res. 2015, 93, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.L.P.O.; Faria, J.C.; Aragao, F.J.L.; Del Peloso, M.J.; Faria, L.C.; Aguiar, M.S.; Wendland, A.; Quintela, E.D.; Diaz, J.L.C.; Magaldi, M.; et al. BRS FC401 RMD: Cultivar de Feijão Carioca Geneticamente Modificada com Resistência ao Mosaico-Dourado; Embrapa: Brasilia, Brasil, 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro, P.V.; Kliot, A.; Ghanim, M.; Cilia, M. Is there a role for symbiotic bacteria in plant virus transmission by insects? Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 8, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, S.L.; Jia, L.; Goggin, F.L. Quantitative differences in aphid virulence and foliar symptom development on tomato plants carrying the mi resistance gene. Environ. Entomol. 2007, 36, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goggin, F.L. Plant–aphid interactions: Molecular and ecological perspectives. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2007, 10, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goggin, F.L.; Williamson, V.M.; Ullman, D.E. Variability in the response of Macrosiphum euphorbiae and Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) to the tomato resistance gene mi. Environ. Entomol. 2001, 30, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, S.; Powell, G. Conditional facilitation of an aphid vector, Acyrthosiphon pisum, by the plant pathogen, pea enation mosaic virus. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodge, S.; Powell, G. Do plant viruses facilitate their aphid vectors by inducing symptoms that alter behavior and performance? Environ. Entomol. 2008, 37, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barro, P.J.D.; Liu, S.-S.; Boykin, L.M.; Dinsdale, A.B. Bemisia tabaci: A statement of species status. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.R.; Ghanim, M.; Roditakis, E.; Nauen, R.; Ishaaya, I. Insecticide resistance and its management in Bemisia tabaci species. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 93, 893–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Hasegawa, D.K.; Kaur, N.; Kliot, A.; Pinheiro, P.V.; Luan, J.; Stensmyr, M.C.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, H.; et al. The draft genome of whitefly Bemisia tabaci MEAM1, a global crop pest, provides novel insights into virus transmission, host adaptation, and insecticide resistance. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skendžić, S.; Zovko, M.; Živković, I.P.; Lešić, V.; Lemić, D. The impact of climate change on agricultural insect pests. Insects 2021, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, P.; Ammunét, T.; Barton, M.; Battisti, A.; Eigenbrode, S.D.; Jepsen, J.U.; Kalinkat, G.; Neuvonen, S.; Niemelä, P.; Terblanche, J.S.; et al. Complex responses of global insect pests to climate warming. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2020, 18, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.R. Plant viruses transmitted by whiteflies. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2003, 109, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ghanim, M. Factors determining transmission of persistent viruses by Bemisia tabaci and emergence of new virus-vector relationships. Viruses 2021, 13, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navas-Castillo, J.; Fiallo-Olivé, E.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Emerging virus diseases transmitted by whiteflies. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 219–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, W.; Akutse, K.S.; Qasim, M.; Khan, K.A.; Ghramh, H.A.; Idrees, A.; Latif, S. Bemisia tabaci-mediated facilitation in diversity of begomoviruses: Evidence from recent molecular studies. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 123, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, R.; Kanakala, S.; Kliot, A.; Cathrin Pakkianathan, B.; Farich, B.A.; Santana-Magal, N.; Elimelech, M.; Kontsedalov, S.; Lebedev, G.; Cilia, M.; et al. Persistent, circulative transmission of begomoviruses by whitefly vectors. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, R.L.; Faria, J.C.; Hanson, S.F.; Morales, F.J.; Ahlquist, P.; Maxwell, D.P.; Russell, D.R. Cloning of the complete dna genomes of four bean-infecting geminivuses and determining their infectivity by electric discharge particle acceleration. Phytopathology. 1991, 81, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, Y.; Charchar, M.D.A.; Iizuka, N. Attempts of Mechanical Transmission and Serological Tests of Bean Golden Mosaic Virus in Brazil; Embrapa: Brasilia, Brasil, 1994; pp. 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanem, G.; Al-Ajlan, A.; Abdulsalam, K. A whitefly-transmitted geminivirus infecting bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) plants in Saudi Arabia. Egypt. J. Phytopathol. 2003, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Idriss, M.; Abdallah, N.; Aref, N.; Haridy, G.; Madkour, M. Biotypes of the castor bean whitefly Trialeurodes ricini (Misra) (Hom., Aleyrodidae) in Egypt: Biochemical characterization and efficiency of geminivirus transmission. J. Appl. Entomol. 1997, 121, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, S.; Cilia, M.; Ghanim, M. Chapter four—Circulative, “nonpropagative” virus transmission: An orchestra of virus-, insect-, and plant-derived instruments. In Advances in Virus Research; Maramorosch, K., Murphy, F.A., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 89, pp. 141–199. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, W.B.; Hiebert, E.; Webb, S.E.; Tsai, J.H.; Polston, J.E. Location of geminiviruses in the whitefly Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). Plant Dis. 1998, 82, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czosnek, H.; Ghanim, M. Chapter 15—Replication and transovarial transmission of tomato yellow leaf curl virus in its whitefly vector: Myth or reality? In Geminivirus: Detection, Diagnosis and Management; Gaur, R.K., Sharma, P., Czosnek, H., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 239–251. ISBN 978-0-323-90587-9. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanim, M.; Brumin, M.; Popovski, S. A simple, rapid and inexpensive method for localization of tomato yellow leaf curl virus and potato leafroll virus in plant and insect vectors. J. Virol. Methods 2009, 159, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, M.; Czosnek, H.; Morin, S. Rate of tomato yellow leaf curl virus translocation in the circulative transmission pathway of its vector, the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Phytopathology 2001, 91, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, M.; Medina, V. Localization of tomato yellow leaf curl virus in its whitefly vector Bemisia tabaci. In Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus Disease: Management, Molecular Biology, Breeding for Resistance; Czosnek, H., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 171–183. ISBN 978-1-4020-4769-5. [Google Scholar]
- Skaljac, M.; Ghanim, M. Tomato yellow leaf curl disease and plant-virus vector interactions. Isr. J. Plant Sci. 2010, 58, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Nitzany, F.E. Transmission and host range of the tomato yellow leaf curl virus. Phytopathology 1966, 56, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Rienzie, R.; Costa, D.D.; Wickramaarachchi, T. Transmission and host range of horsegram yellow mosaic virus (HGYMV) causing common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) yellowing disease in Sri Lanka. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2020, 48, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caciagli, P.; Bosco, D.; Al-Bitar, L. Relationships of the Sardinian isolate of tomato yellow leaf curl geminivirus with its whitefly vector Bemisia tabaci Gen. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1995, 101, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, M.; Morin, S.; Zeidan, M.; Czosnek, H. Evidence for transovarial transmission of tomato yellow leaf curl virus by its vector, the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Virology 1998, 240, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, D.; Mason, G.; Accotto, G.P. TYLCSV DNA, but not infectivity, can be transovarially inherited by the progeny of the whitefly vector Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius). Virology 2004, 323, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Liu, J.; Jiu, M.; Qian, Y.J.; Liu, S.S. Low frequency of horizontal and vertical transmission of two begomoviruses through whiteflies exhibits little relevance to the vector infectivity. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2010, 157, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanim, M.; Czosnek, H. Tomato yellow leaf curl geminivirus (TYLCV-IS) is transmitted among whiteflies (Bemisia tabaci) in a sex-related manner. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 4738–4745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadhave, K.R.; Gautam, S.; Dutta, B.; Coolong, T.; Adkins, S.; Srinivasan, R. Low frequency of horizontal and vertical transmission of cucurbit leaf crumple virus in whitefly Bemisia tabaci Gennadius. Phytopathology 2020, 110, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-L.; Wang, X.-R.; Wei, X.-M.; Huang, H.; Wu, J.-X.; Chen, X.-X.; Liu, S.-S.; Wang, X.-W. The autophagy pathway participates in resistance to tomato yellow leaf curl virus infection in whiteflies. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1560–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakkianathan, B.C.; Kontsedalov, S.; Lebedev, G.; Mahadav, A.; Zeidan, M.; Czosnek, H.; Ghanim, M. Replication of tomato yellow leaf curl virus in its whitefly vector, Bemisia tabaci. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 9791–9803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, G.; Czosnek, H. Long-term association of tomato yellow leaf curl virus with its whitefly vector Bemisia tabaci: Effect on the insect transmission capacity, longevity and fecundity. J. Gen. Virol. 1997, 78, 2683–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Oliver, K.M.; Pan, H.; Jiao, X.; Liu, B.; Xie, W.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; Xu, B.; White, J.A.; et al. Facultative symbiont Hamiltonella confers benefits to Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae), an invasive agricultural pest worldwide. Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paula, N.T.; de Faria, J.C.; Aragão, F.J.L. Reduction of viral load in whitefly (Bemisia Tabaci Gen.) feeding on RNAi-mediated bean golden mosaic virus resistant transgenic bean plants. Virus Res. 2015, 210, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkashian, J.; Ramos-Reynoso, E.D.; Maxwell, D.P.; Ramírez, P. Begomoviruses associated with bean golden mosaic disease in Nicaragua. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 901–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiquito-Almanza, E.; Caballero-Pérez, J.; Acosta-Gallegos, J.A.; Montero-Tavera, V.; Mariscal-Amaro, L.A.; Anaya-López, J.L. Diversity and distribution of viruses infecting wild and domesticated Phaseolus spp. in the Mesoamerican center of domestication. Viruses 2021, 13, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, R.; Faria, J.; Ahlquist, P.; Maxwell, D. Genetic diversity in geminiviruses causing bean golden mosaic disease—The nucleotide-sequence of the infectious cloned dna components of a brazilian isolate of bean golden mosaic geminivirus. Phytopathology 1993, 83, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Chen, Q.; Guo, T.; Wang, X.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Liu, S. Differential efficiency of a begomovirus to cross the midgut of different species of whiteflies results in variation of virus transmission by the vectors. Sci. China Life Sci. 2018, 61, 1254–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Pan, L.-L.; Bouvaine, S.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Liu, S.-S.; Seal, S.; Wang, X.-W. Differential transmission of Sri Lankan cassava mosaic virus by three cryptic species of the whitefly Bemisia Tabaci complex. Virology 2020, 540, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Guo, Q.; Cui, X.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Hu, J.; Liu, S.-S. Comparison of transmission of papaya leaf curl china virus among four cryptic species of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci complex. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, A.M.; de Oliveira, C.S.; Bello, V.H.; Favara, G.M.; Vicentin, E.; Marubayashi, J.M.; da Cruz Martines, C.; Watanabe, L.F.M.; Barbosa, T.M.C.; de Lima Alvarez, D.; et al. Populations of Bemisia tabaci Mediterranean in São Paulo state are inefficient vectors of Brazilian begomoviruses. Plant Pathol. 2023, 73, 2224–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Mugerwa, H.; Buck, J.W.; Dutta, B.; Coolong, T.; Adkins, S.; Srinivasan, R. Differential transmission of old and new world begomoviruses by Middle East-Asia Minor 1 (MEAM1) and Mediterranean (MED) cryptic species of Bemisia tabaci. Viruses 2022, 14, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchi, B.R.; Marubayashi, J.M.; Favara, G.M.; Yuki, V.A.; Watanabe, L.F.M.; Barbosa, L.F.; Pavan, M.A.; Krause-Sakate, R. Comparative transmission of five viruses by Bemisia tabaci NW2 and MEAM1. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2017, 42, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, Y.; Zchori-Fein, E.; Mozes-Daube, N.; Kontsedalov, S.; Skaljac, M.; Brumin, M.; Sobol, I.; Czosnek, H.; Vavre, F.; Fleury, F.; et al. The transmission efficiency of tomato yellow leaf curl virus by the whitefly Bemisia tabaci is correlated with the presence of a specific symbiotic bacterium species. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 9310–9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Pan, H.; Liu, B.; Chu, D.; Xie, W.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Xu, B.; Zhang, Y. Insect symbiont facilitates vector acquisition, retention, and transmission of plant virus. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, V.H.; Watanabe, L.F.M.; Santos, B.R.; Marubayashi, J.M.; Yuki, V.A.; De Marchi, B.R.; Pavan, M.A.; Krause-Sakate, R. Evidence for increased efficiency of virus transmission by populations of mediterranean species of Bemisia tabaci with high Hamiltonella prevalence. Phytoparasitica 2019, 47, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.S. Three whitefly-transmitted virus diseases of beans in São Paulo, Brazil. FAO Plant Prot. Bull. 1965, 13, 121–130. [Google Scholar]
- Batista, J.G.; Nery, F.M.B.; Melo, F.F.S.; Malheiros, M.F.; Rezende, D.V.; Boiteux, L.S.; Fonseca, M.E.N.; de Miranda, B.E.C.; Pereira-Carvalho, R.C. Complete genome sequence of a novel bipartite begomovirus infecting the legume weed Macroptilium erythroloma. Arch. Virol. 2022, 167, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracero, V.; Rivera, L.I.; Beaver, J.S. DNA analysis confirms Macroptilium lathyroides as alternative host of bean golden yellow mosaic virus. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codod, C.B.; Severns, P.M.; Sparks, A.N.; Srinivasan, R.; Kemerait, R.C.; Dutta, B. Assessment of prickly sida as a potential inoculum source for sida golden mosaic virus in commercial snap bean farms in Georgia, United States. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 1776–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Buck, J.W.; Dutta, B.; Coolong, T.; Sanchez, T.; Smith, H.A.; Adkins, S.; Srinivasan, R. Sida golden mosaic virus, an emerging pathogen of snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in the Southeastern United States. Viruses 2023, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, M.W.; Rodriguez, L.M.; Pedraza, F.; Morales, F.; Beebe, S. Genetic mapping of the bean golden yellow mosaic geminivirus resistance gene bgm-1 and linkage with potyvirus resistance in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). TAG Theor. Appl. Genet. Theor. Angew. Genet. 2007, 114, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklas, P.N.; Seo, Y.-S.; Gilbertson, R.L. Quantitative resistance to bean dwarf mosaic virus in common bean is associated with the bct gene for resistance to beet curly top virus. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaya-López, J.L.; Garrido-Ramírez, E.R.; Chiquito-Almanza, E.; Tosquy-Valle, O.H.; Ibarra-Pérez, F.J.; López-Salinas, E.; Anaya-López, J.L.; Garrido-Ramírez, E.R.; Chiquito-Almanza, E.; Tosquy-Valle, O.H.; et al. Identification of opaque black bean recombinant lines resistant to BCMV, BCMNV and BGYMV using molecular markers. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agríc. 2018, 9, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler-Garzón, A.; Oladzad, A.; Beaver, J.; Beebe, S.; Lee, R.; Lobaton, J.D.; Macea, E.; McClean, P.; Raatz, B.; Rosas, J.C.; et al. NAC candidate gene marker for bgm-1 and interaction with QTL for resistance to bean golden yellow mosaic virus in common bean. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 628443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, U.C.; Nayyar, H.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Beena, R.; Lone, A.A.; Naik, Y.D.; Thudi, M.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Gupta, S.; Dixit, G.P.; et al. Major viral diseases in grain legumes: Designing disease resistant legumes from plant breeding and OMICS integration. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1183505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-C.; Garrido-Ramirez, E.R.; Sudarshana, M.R.; Yendluri, S.; Gilbertson, R.L. The n-terminus of the begomovirus nuclear shuttle protein (bv1) determines virulence or avirulence in Phaseolus vulgaris. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.-S.; Gepts, P.; Gilbertson, R.L. Genetics of resistance to the geminivirus, bean dwarf mosaic virus, and the role of the hypersensitive response in common bean. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 108, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas-Vanzo, A.T.; Da Silva, C.D.C.; De Novaes, T.G.; Mazzieri Walz, D.; Marcelino Guimaraes, F.C.; Kuwahara, M.K.; De Oliveira Molina, R.; Leite Junior, R.P. Evaluation of disease severity caused by bean golden mosaic virus in different bean cultivars. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 43, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meziadi, C.; Blanchet, S.; Geffroy, V.; Pflieger, S. Genetic resistance against viruses in Phaseolus vulgaris L.: State of the art and future prospects. Plant Sci. Int. J. Exp. Plant Biol. 2017, 265, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragão, F.J.L.; Barros, L.M.G.; Brasileiro, A.C.M.; Ribeiro, S.G.; Smith, F.D.; Sanford, J.C.; Faria, J.C.; Rech, E.L. Inheritance of foreign genes in transgenic bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) co-transformed via particle bombardment. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1996, 93, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragão, F.J.L.; Ribeiro, S.G.; Barros, L.M.G.; Brasileiro, A.C.M.; Maxwell, D.P.; Rech, E.L.; Faria, J.C. Transgenic beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) engineered to express viral antisense RNAs show delayed and attenuated symptoms to bean golden mosaic geminivirus. Mol. Breed. 1998, 4, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfim, K.; Faria, J.C.; Nogueira, E.O.P.L.; Mendes, É.A.; Aragão, F.J.L. RNAi-mediated resistance to bean golden mosaic virus in genetically engineered common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Mol. Plant. Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragão, F.J.L.; Faria, J.C. First transgenic geminivirus-resistant plant in the field. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 1086–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.C.; Albino, M.M.; Dias, B.B.; Cançado, L.J.; da Cunha, N.B.; Silva, L.D.M.; Vianna, G.R.; Aragão, F.J. Partial resistance to bean golden mosaic virus in a transgenic common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) line expressing a mutated rep gene. Plant Sci. 2006, 171, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragão, F.J.L.; Nogueira, E.O.P.L.; Tinoco, M.L.P.; Faria, J.C. Molecular characterization of the first commercial transgenic common bean immune to the bean golden mosaic virus. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 166, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, P.V.; de Faria, J.C.; Paranagua e Lago Nogueira, E.O.; Lima Aragao, F.J. Transgene inheritances and genetic similarities of near isogenic lines of genetically modified common beans. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2009, 44, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.C.; Valdisser, P.A.M.R.; Nogueira, E.O.P.L.; Aragão, F.J.L. RNAi-based bean golden mosaic virus-resistant common bean (Embrapa 5.1) shows simple inheritance for both transgene and disease resistance. Plant Breed. 2014, 133, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, T.L.P.O.; Faria, J.C.; Aragão, F.J.L.; Peloso, M.J.D.; Faria, L.C.; Wendland, A.; Aguiar, M.S.; Quintela, E.D.; Melo, C.L.P.; Hungria, M.; et al. Agronomic performance and yield stability of the RNA interference-based bean golden mosaic virus-resistant common bean. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.L.; FARIA, J.; Moura, M.C.; Zaidem, A.L.M.; Pizetta, C.S.R.; Freitas, E.; Coelho, G.R.; Silva, J.F.A.; Barrigossi, J.A.F.; Hoffmann, L.V.; et al. Whitefly-tolerant transgenic common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) line. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 984804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardo, L.G.; Carvalho, C.M. Cowpea mild mottle virus (Carlavirus, Betaflexiviridae): A review. Trop. Plant Pathol. 2017, 42, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Piuga, F.F.; Kitajima, E.W.; Gaspar, J.O.; Valentin, N.; Benato, L.; Marin, S.R.R.; Binneck, E.; Oliveira, T.; Belintani, P.; et al. Necrose da Haste da Soja; Embrapa: Londrina, Brasil, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.S.; Faria, J.C.; Vianello, R.P.; Valdisser, P.A.M.R.; Pereira, H.S.; Melo, L.C.; Pinheiro, P.V.; Souza, T.L.P.O. Inheritance and genetic mapping of the first CPMMV tolerance locus in common bean. Plant Pathol. 2024, 73, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaki, M.; Thongmeearkom, P.; Prommin, M.; Honda, Y.; Hibi, T. Whitefly transmission and some properties of cowpea mild mottle virus on soybean in Thailand. Plant Dis. 1982, 66, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyanandarajah, P.; Brunt, A.A. The natural occurrence, transmission, properties and possible affinities of cowpea mild mottle virus. J. Phytopathol. 1993, 137, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappa, V.; Reddy, D.V. Transmission of cowpea mild mottle virus by Bemisia tabaci in a nonpersistent manner. Plant Dis. 1983, 67, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves-Freitas, D.M.T.; Pinheiro-Lima, B.; Faria, J.C.; Lacorte, C.; Ribeiro, S.G.; Melo, F.L. Double-stranded RNA high-throughput sequencing reveals a new Cytorhabdovirus in a bean golden mosaic virus-resistant common bean transgenic line. Viruses 2019, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.M.Q.; Adams, M.J.; Carstens, E.B.; Lefkowitz, E.J. (Eds.) Family—Betaflexiviridae. In Virus Taxonomy; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 920–941. ISBN 978-0-12-384684-6. [Google Scholar]
- Marubayashi, J.M.; Yuki, V.A.; Wutke, E.B. Transmission of the cowpea mild mottle virus by whitefly Bemisia tabaci biotype b for plants of beans and soy. Summa Phytopathol. 2010, 36, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thekke-Veetil, T.; McCoppin, N.K.; Hobbs, H.A.; Hartman, G.L.; Lambert, K.N.; Lim, H.-S.; Domier, L.L. Discovery of a novel member of the carlavirus genus from soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Pathogens 2021, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, J.; Aragao, F.J.L.; Souza, T.L.P.O.; Quintela, E.D.; Kitajima, E.W.; Ribeiro, S.G. Golden mosaic of common beans in Brazil: Management with a transgenic approach. APS Featur. 2016, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polston, J.E.; De Barro, P.; Boykin, L.M. Transmission specificities of plant viruses with the newly identified species of the Bemisia tabaci species complex. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, K.; Capobianco, H.; Ng, T.F.F.; Breitbart, M.; Polston, J.E. RNA viral metagenome of whiteflies leads to the discovery and characterization of a whitefly-transmitted carlavirus in North America. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, R.A.; Gowda, S.; Satyanarayana, T.; Boyko, V.; Reddy, A.S.; Dawson, W.O.; Reddy, D.V. Evidence that whitefly-transmitted cowpea mild mottle virus belongs to the genus Carlavirus Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 769–780. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, M.; Fernández-Rodríguez, T.; Garrido, M.J.; Mejías, A.; Romano, M.; Marys, E. First report of cowpea mild mottle Carlavirus on yardlong bean (Vigna unguiculata Subsp. Sesquipedalis) in Venezuela. Viruses 2012, 4, 3804–3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunt, A.A.; Kenten, R.H. Cowpea mild mottle, a newly recognized virus infecting cowpeas (Vigna unguiculata) in Ghana. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1973, 74, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, V.H.; da Silva, F.B.; Watanabe, L.F.M.; Vicentin, E.; Muller, C.; de Freitas Bueno, R.C.O.; Santos, J.C.; De Marchi, B.R.; Nogueira, A.M.; Yuki, V.A.; et al. Detection of Bemisia tabaci mediterranean cryptic species on soybean in São Paulo and Paraná states (Brazil) and interaction of cowpea mild mottle virus with whiteflies. Plant Pathol. 2021, 70, 1508–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingwell, L.L.; Eigenbrode, S.D.; Bosque-Pérez, N.A. Plant viruses alter insect behavior to enhance their spread. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Ortega, K.J.; Bosque-Pérez, N.A.; Ngumbi, E.; Jiménez-Martínez, E.S.; Eigenbrode, S.D. Rhopalosiphum padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae) responses to volatile cues from barley yellow dwarf virus–infected wheat. Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 836–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.E.; Garzo, E.; Verbeek, M.; Vosman, B.; Dicke, M.; Tjallingii, W.F. Infection of potato plants with potato leafroll virus changes attraction and feeding behaviour of Myzus persicae. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2007, 125, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereres, A.; Kampmeier, G.E.; Irwin, M.E. Aphid attraction and preference for soybean and pepper plants infected with potyviridae. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1999, 92, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngumbi, E.; Eigenbrode, S.D.; Bosque-Perez, N.A.; Ding, H.; Rodriguez, A. Myzus persicae is arrested more by blends than by individual compounds elevated in headspace of PLRV-infected potato. J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 1733–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigenbrode, S.D.; Ding, H.; Shiel, P.; Berger, P.H. Volatiles from potato plants infected with potato leafroll virus attract and arrest the virus vector, Myzus persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Proc. Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gildow, F.E. Increased production of alatae by aphids reared on oats infected with barley yellow dwarf virus. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1980, 73, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, S.J.; Mowry, T.M.; Berger, P.H. Differential settling by Myzus persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae) on various virus infected host plants. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1998, 91, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castle, S.J.; Berger, P.H. Rates of growth and increase of Myzus persicae on virus-infected potatoes according to type of virus-vector relationship. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1993, 69, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blua, M.J.; Perring, T.M.; Madore, M.A. Plant virus-induced changes in aphid population development and temporal fluctuations in plant nutrients. J. Chem. Ecol. 1994, 20, 691–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliure, B.; Janssen, A.; Maris, P.C.; Peters, D.; Sabelis, M.W. Herbivore arthropods benefit from vectoring plant viruses. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, R.T.; Inbar, M.; McKenzie, C.L.; Shatters, R.; Borowicz, V.; Albrecht, U.; Powell, C.A.; Doostdar, H. Multitrophic interactions of the silverleaf whitefly, host plants, competing herbivores, and phytopathogens. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2002, 51, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, G.; Pan, H.; Xie, W.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Plants pre-infested with viruliferous MED/Q cryptic species promotes subsequent Bemisia tabaci infestation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Su, Q.; Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Peng, Z.; Zheng, H.; Xie, W.; Xu, B.; Wang, S.; Wu, Q.; et al. Odor, not performance, dictates Bemisia tabaci’s selection between healthy and virus infected plants. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Freitas-Astúa, J.; Bejerman, N.; Blasdell, K.R.; Breyta, R.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Fooks, A.R.; Kondo, H.; Kurath, G.; Kuzmin, I.V.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Rhabdoviridae 2022: This article is part of the ICTV virus taxonomy profiles collection. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 001689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, S.; Li, L.; Yang, Z.; Hong, N. A novel actinidia Cytorhabdovirus characterized using genomic and viral protein interaction features. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1271–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitfield, A.E.; Huot, O.B.; Martin, K.M.; Kondo, H.; Dietzgen, R.G. Plant rhabdoviruses-their origins and vector interactions. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2018, 33, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahy, B.W.J.; Van Regenmortel, M.H.V. Desk Encyclopedia of Plant and Fungal Virology; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-0-12-375148-5. [Google Scholar]
- Pinheiro-Lima, B.; Pereira-Carvalho, R.C.; Alves-Freitas, D.M.T.; Kitajima, E.W.; Vidal, A.H.; Lacorte, C.; Godinho, M.T.; Fontenele, R.S.; Faria, J.C.; Abreu, E.F.M.; et al. Transmission of the bean-associated cytorhabdovirus by the whitefly Bemisia tabaci MEAM1. Viruses 2020, 12, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, Z.A.; Medina, V.; Falk, B. Crinivirus replication and host interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanetakis, I.E.; Martin, R.R.; Wintermantel, W.M. Epidemiology of criniviruses: An emerging problem in world agriculture. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Rubio, L.; Yeh, H.-H.; Crawford, B.; Falk, B.W. Lettuce infectious yellows virus: In vitro acquisition analysis using partially purified virions and the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 1111–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffus, J.E.; Liu, H.-Y.; Wisler, G.C.; Li, R. Lettuce chlorosis virus—A new whitefly-transmitted Closterovirus. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 1996, 102, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.R.; Janssen, D. Epidemiology and control of emerging criniviruses in bean. Virus Res. 2020, 280, 197902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwaipopo, B.; Nchimbi-Msolla, S.; Njau, P.J.R.; Mark, D.; Mbanzibwa, D.R. Comprehensive surveys of bean common mosaic virus and bean common mosaic necrosis virus and molecular evidence for occurrence of other Phaseolus vulgaris viruses in Tanzania. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 2361–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, G.; Cuadrado, I.M.; Janssen, D. Bean yellow disorder virus: Parameters of transmission by Bemisia Tabaci and host plant range. Insect Sci. 2011, 1, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintermantel, W.M.; Gilbertson, R.L.; Natwick, E.T.; McCreight, J.D. Emergence and epidemiology of cucurbit yellow stunting disorder virus in the american desert southwest, and development of host plant resistance in melon. Virus Res. 2017, 241, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, M.E.; Caillaud, M.C.; Smith, D.M.; Benson, E.C.; Gildow, F.E.; Gray, S.M. Genetic regulation of polerovirus and luteovirus transmission in the aphid Schizaphis graminum. Phytopathology 2006, 96, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, M.E.; Caillaud, M.C.; Smith, D.M.; Gray, S.M. Biometrical genetic analysis of luteovirus transmission in the aphid Schizaphis graminum. Heredity 2007, 98, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilia, M.; Howe, K.; Fish, T.; Smith, D.; Mahoney, J.; Tamborindeguy, C.; Burd, J.; Thannhauser, T.W.; Gray, S. Biomarker discovery from the top down: Protein biomarkers for efficient virus transmission by insects (Homoptera: Aphididae) discovered by coupling genetics and 2-D DIGE. Proteomics 2011, 11, 2440–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, P.; Bereman, M.S.; Burd, J.; Pals, M.; Armstrong, S.; Howe, K.J.; Thannhauser, T.W.; MacCoss, M.J.; Gray, S.M.; Cilia, M. Evidence of the biochemical basis of host virulence in the greenbug aphid, Schizaphis graminum (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 2094–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborindeguy, C.; Bereman, M.S.; DeBlasio, S.; Igwe, D.; Smith, D.M.; White, F.; MacCoss, M.J.; Gray, S.M.; Cilia, M. Genomic and proteomic analysis of Schizaphis graminum reveals cyclophilin proteins are involved in the transmission of cereal yellow dwarf virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, P.V.; Ghanim, M.; Alexander, M.; Rebelo, A.R.; Santos, R.S.; Orsburn, B.C.; Gray, S.; Cilia, M. Host Plants indirectly influence plant virus transmission by altering gut cysteine protease activity of aphid vectors. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16, S230–S243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiel, E.; Gottlieb, Y.; Zchori-Fein, E.; Mozes-Daube, N.; Katzir, N.; Inbar, M.; Ghanim, M. Biotype-dependent secondary symbiont communities in sympatric populations of Bemisia tabaci. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2007, 97, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, P.G.; Bedford, I.D.; Liu, S.; Pinner, M.S. The transmission of geminiviruses by Bemisia tabaci. Pestic. Sci. 1994, 42, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, O.; Frazer, J.; De La Rosa, D.; Beaver, J.S.; Ahlquist, P.; Maxwell, D.P. Whitefly transmission and efficient ssDNA accumulation of bean golden mosaic geminivirus require functional coat protein. Virology 1994, 204, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noris, E.; Vaira, A.M.; Caciagli, P.; Masenga, V.; Gronenborn, B.; Accotto, G.P. Amino acids in the capsid protein of tomato yellow leaf curl virus that are crucial for systemic infection, particle formation, and insect transmission. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 10050–10057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caciagli, P.; Piles, V.M.; Marian, D.; Vecchiati, M.; Masenga, V.; Mason, G.; Falcioni, T.; Noris, E. Virion stability is important for the circulative transmission of tomato yellow leaf curl sardinia virus by Bemisia tabaci, but virion access to salivary glands does not guarantee transmissibility. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5784–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, S.; Ghanim, M.; Zeidan, M.; Czosnek, H.; Verbeek, M.; van den Heuvel, J.F.J.M. A GroEL homologue from endosymbiotic bacteria of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci is implicated in the circulative transmission of tomato yellow leaf curl virus. Virology 1999, 256, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.-B.; Li, J.; Chen, E.-H.; Niu, J.-Z.; Chu, D. Transcriptome profiling of the whitefly Bemisia tabaci MED in response to single infection of tomato yellow leaf curl virus, tomato chlorosis virus, and their co-infection. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, M.; Popovski, S.; Kollenberg, M.; Gorovits, R.; Brown, J.K.; Cicero, J.M.; Czosnek, H.; Winter, S.; Ghanim, M. Implication of Bemisia tabaci heat shock protein 70 in Begomovirus-whitefly interactions. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13241–13252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Chen, W.; Zheng, Y.; Hasegawa, D.K.; Ling, K.-S.; Fei, Z.; Wintermantel, W.M. Transcriptome analysis of the whitefly, Bemisia tabaci MEAM1 during feeding on tomato infected with the Crinivirus, tomato chlorosis virus, identifies a temporal shift in gene expression and differential regulation of novel orphan genes. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugerwa, H.; Gautam, S.; Catto, M.A.; Dutta, B.; Brown, J.K.; Adkins, S.; Srinivasan, R. Differential transcriptional responses in two old world Bemisia tabaci cryptic species post acquisition of old and new world begomoviruses. Cells 2022, 11, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, J.; Su, Y.-L. Transcriptome analysis of gene expression profiles of tomato yellow leaf curl virus-infected whiteflies over different viral acquisition access periods. Insects 2020, 11, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.-B.; Li, J.-M.; Varela, N.; Wang, Y.-L.; Li, F.-F.; Bao, Y.-Y.; Zhang, C.-X.; Liu, S.-S.; Wang, X.-W. Global analysis of the transcriptional response of whitefly to tomato yellow leaf curl china virus reveals the relationship of coevolved adaptations. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 3330–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, D.K.; Chen, W.; Zheng, Y.; Kaur, N.; Wintermantel, W.M.; Simmons, A.M.; Fei, Z.; Ling, K.-S. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals networks of genes activated in the whitefly, Bemisia tabaci when fed on tomato plants infected with tomato yellow leaf curl virus. Virology 2018, 513, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.; Qian, L.-X.; Shao, R.-X.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Liu, S.-S.; Wang, X.-W. Transcriptome profiling of whitefly guts in response to tomato yellow leaf curl virus infection. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez Zubiaur, Y.; Quiñones, M.; Fonseca, D.; Potter, J.L.; Maxwell, D.P. First report of tomato yellow leaf curl virus associated with beans, Phaseolus vulgaris, in Cuba. Plant Dis. 2002, 86, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segundo, E.; Martín, G.; Cuadrado, I.M.; Janssen, D. A New yellowing disease in Phaseolus vulgaris associated with a whitefly-transmitted virus. Plant Pathol. 2004, 53, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayiannis, L.C.; Paraskevopoulos, A.; Katis, N.I. First report of tomato yellow leaf curl virus infecting common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) in Greece. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akel, E.; Qusayi, A.R.; Nadine, A.; Ismail, I.D. First report of a mixed infection with tomato yellow leaf curl virus TYLCV and tomato spotted wilt virus tswv in some economic crops in the Syrian coastal region. Can. J. Pestic. Pest Manag. 2010, 1, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.S.; Al-Shihi, A.A.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Briddon, R.W. Identification of tomato yellow leaf curl virus-IR and associated tomato leaf curl betasatellite infecting common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) in Oman. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, S.G.M.; Shahraeena, N.; Elahinia, S.A. Distribution and impact of virus associated diseases of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in Northern Iran. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2010, 43, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, M.W.; Basset, M.J.; Abouzid, A.M.; Hiebert, E.; Polston, J.E.; McMillan, R.J.; Graves, W.; Lamberts, M. Occurrence of bean golden mosaic virus in Florida. Plant Dis. 1995, 79, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenele, R.S.; Poppiel, R.; Matos, V.O.R.L.; Costa, F.; Faria, J.C.; Ribeiro, S.G. First report of macroptilium yellow spot virus in Desmodium glabrum in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarakoon, I.I.; Roye, M.E.; Briddon, R.W.; Bedford, I.D.; Stanley, J. Molecular and biological characterization of macroptilium yellow mosaic virus from Jamaica. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coco, D.; Calil, I.P.; Brustolini, O.J.B.; Santos, A.A.; Inoue-Nagata, A.K.; Fontes, E.P.B. Soybean chlorotic spot virus, a novel begomovirus infecting soybean in Brazil. Arch. Virol. 2013, 158, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes-Acioli, N.a.N.; Pereira-Carvalho, R.C.; Fontenele, R.S.; Lacorte, C.; Ribeiro, S.G.; Fonseca, M.E.N.; Boiteux, L.S. First report of sida micrantha mosaic virus in Phaseolus vulgaris in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2011, 95, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansar, M.; Agnihotri, A.K.; Akram, M.; Bhagat, A.P. First report of tomato leaf curl joydebpur virus infecting french bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2019, 85, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, T.C.; Baker, C.; Jones, L.; Snyder, L.U. First Report of sida golden mosaic virus infecting snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) in Florida. Plant Dis. 2010, 94, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monger, W.A.; Harju, V.; Nixon, T.; Bennett, S.; Reeder, R.; Kelly, P.; Ariyarathne, H.M. First report of horsegram yellow mosaic virus infecting Phaseolus vulgaris in Sri Lanka. New Dis. Rep. 2010, 21, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindu, J.; Kumar, H.D.V.; Hiremath, S.; Muttappagol, M.; Nandan, M.; Devaraj Basha, C.R.J.; Shankarappa, K.S.; Venkataravanappa, V.; Reddy, C.N.L. Genetic diversity and evidence of recombination of horsegram yellow mosaic virus infecting pole bean (Phaseolus Vulgaris L.) from South India 2023. bioRxiv, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.N. Natural infection of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) by mung bean yellow mosaic virus. Indian J. Mycol. Plant Pathol. 1979, 9, 124–126. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.S.; Briddon, R.W.; Al-Sadi, A.M. Identification of mungbean yellow mosaic indian virus associated with tomato leaf curl betasatellite infecting Phaseolus vulgaris in Oman. J. Phytopathol. 2017, 165, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.S.; Pudashini, B.J.; Khatri-Chhetri, G.B.; Ikegami, M.; Natsuaki, K.T. First report of mungbean yellow mosaic india virus on kidney bean in Nepal. New Dis. Rep. 2012, 25, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.; Tzfira, T. Bean Dwarf Mosaic Virus: A model system for the study of viral movement. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2010, 11, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, F.; Niessen, A.; Ramirez, B.T.; Castano, M. Isolation and partial characterization of a geminivirus causing bean dwarf mosaic. Phytopathology 1990, 80, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, S.H. Complete nucleotide sequences of the infectious cloned DNAs of bean dwarf mosaic geminivirus. Phytopathology 1993, 83, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, S.; Polston, J.E.; Turechek, W.W. Cucurbit leaf crumple virus identified in common bean in Florida. Plant Dis. 2009, 93, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.H.; Luo, Y.Q.; Ding, M.; Zhang, Z.K.; Yang, C.K. First report of tomato yellow leaf curl china virus infecting kidney bean in China. Plant Pathol. 2007, 56, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, A.M.; Bird, J.; Brown, J.K. First report of a bean-infecting begomovirus from Macroptilium lathyroides in Puerto Rico that is distinct from bean golden mosaic virus. Plant Dis. 1999, 83, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, G.; Ávalos, V.; Reyna, P.; Laguna, I.G.; Pardina, P.R. Identification, molecular characterization and relative incidence of begomoviruses infecting bean crops in Northwestern Argentina: An update. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2018, 47, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.K.; Ostrow, K.M.; Idris, A.M.; Stenger, D.C. Biotic, molecular, and phylogenetic characterization of bean calico mosaic virus, a distinct begomovirus species with affiliation in the squash leaf curl virus cluster. Phytopathology 1999, 89, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, M.A.; Barreto, S.S.; Costa, T.M.; Rocha, G.A.; Dianese, E.C.; Gilbertson, R.L.; Inoue-Nagata, A.K. First report of tomato severe rugose virus, a tomato-infecting begomovirus, in soybean plants in Brazil. Plant Dis. 2017, 101, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.A.; Chien, L.Y.; Tsai, C.F.; Lin, Y.Y.; Cheng, Y.H. First report of cowpea mild mottle virus in cowpea and french bean in Taiwan. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, W.; Winter, S.; Vetten, H.J. Complete nucleotide sequence of the type isolate of cowpea mild mottle virus from Ghana. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 2069–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Pardina, P.E.; Arneodo, J.D.; Truol, G.A.; Herrera, P.S.; Laguna, I.G. First record of cowpea mild mottle virus in bean crops in Argentina. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2004, 33, 129–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persley, D.; Steele, V.; Sharman, M.; Campbell, P.; Geering, A.; Gambley, C. First report of a carlavirus infecting plants in the Fabaceae in Australia. New Dis. Rep. 2020, 41, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.L.; Simón, A.; García, M.C.; Janssen, D. First report of lettuce chlorosis virus infecting bean in Spain. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferreira, A.L.; Ghanim, M.; Xu, Y.; Pinheiro, P.V. Interactions between Common Bean Viruses and Their Whitefly Vector. Viruses 2024, 16, 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101567
Ferreira AL, Ghanim M, Xu Y, Pinheiro PV. Interactions between Common Bean Viruses and Their Whitefly Vector. Viruses. 2024; 16(10):1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101567
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerreira, Amanda L., Murad Ghanim, Yi Xu, and Patricia V. Pinheiro. 2024. "Interactions between Common Bean Viruses and Their Whitefly Vector" Viruses 16, no. 10: 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101567
APA StyleFerreira, A. L., Ghanim, M., Xu, Y., & Pinheiro, P. V. (2024). Interactions between Common Bean Viruses and Their Whitefly Vector. Viruses, 16(10), 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101567







