Diagnostic Value of Anti-HTLV-1-Antibody Quantification in Cerebrospinal Fluid for HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Framework and Implementation Plan
2.2. Anti-HTLV-1 Antibody Test Kits
2.3. Ethical Considerations
2.4. Subjects, Specimen Sampling, and Laboratory Analysis
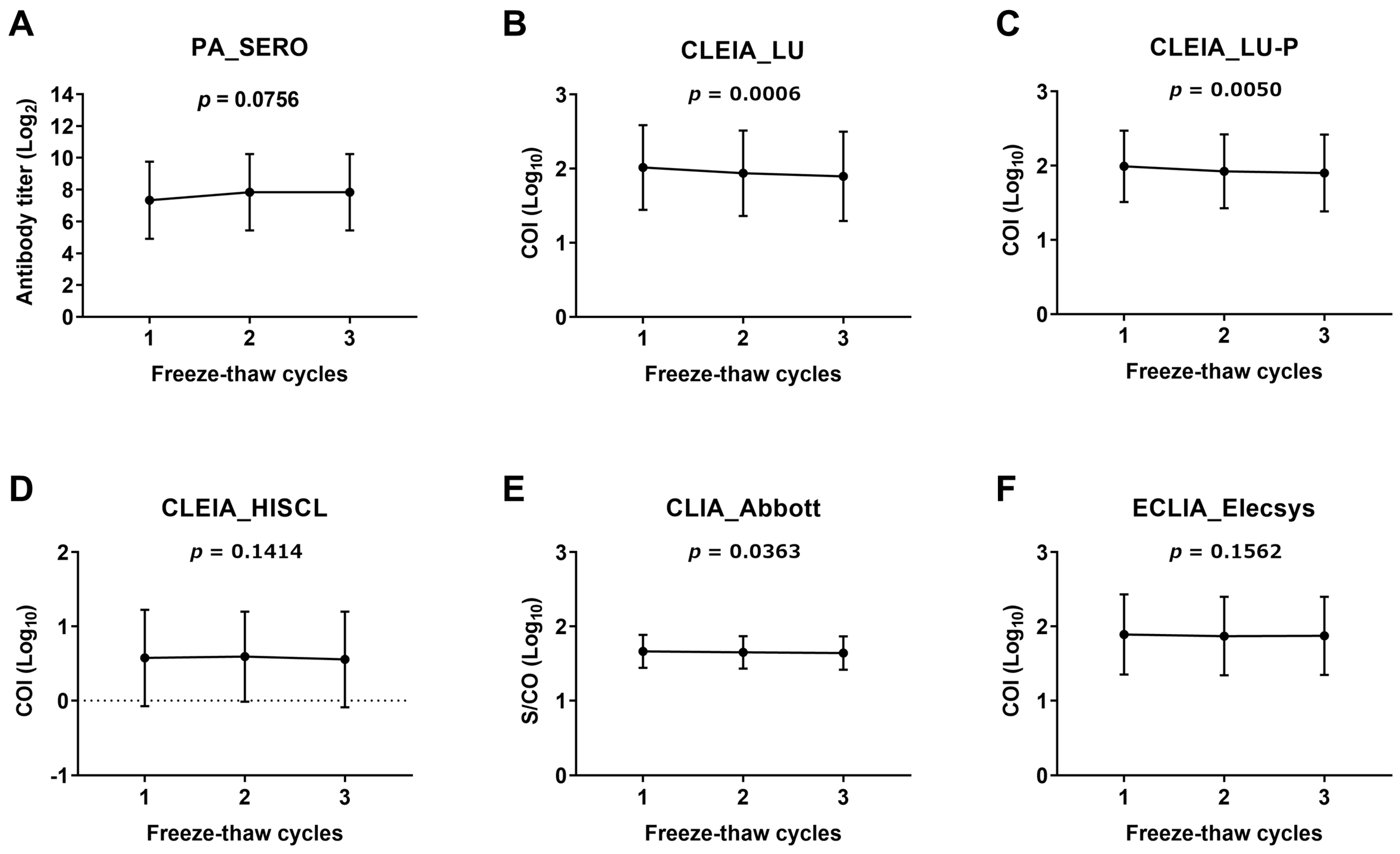
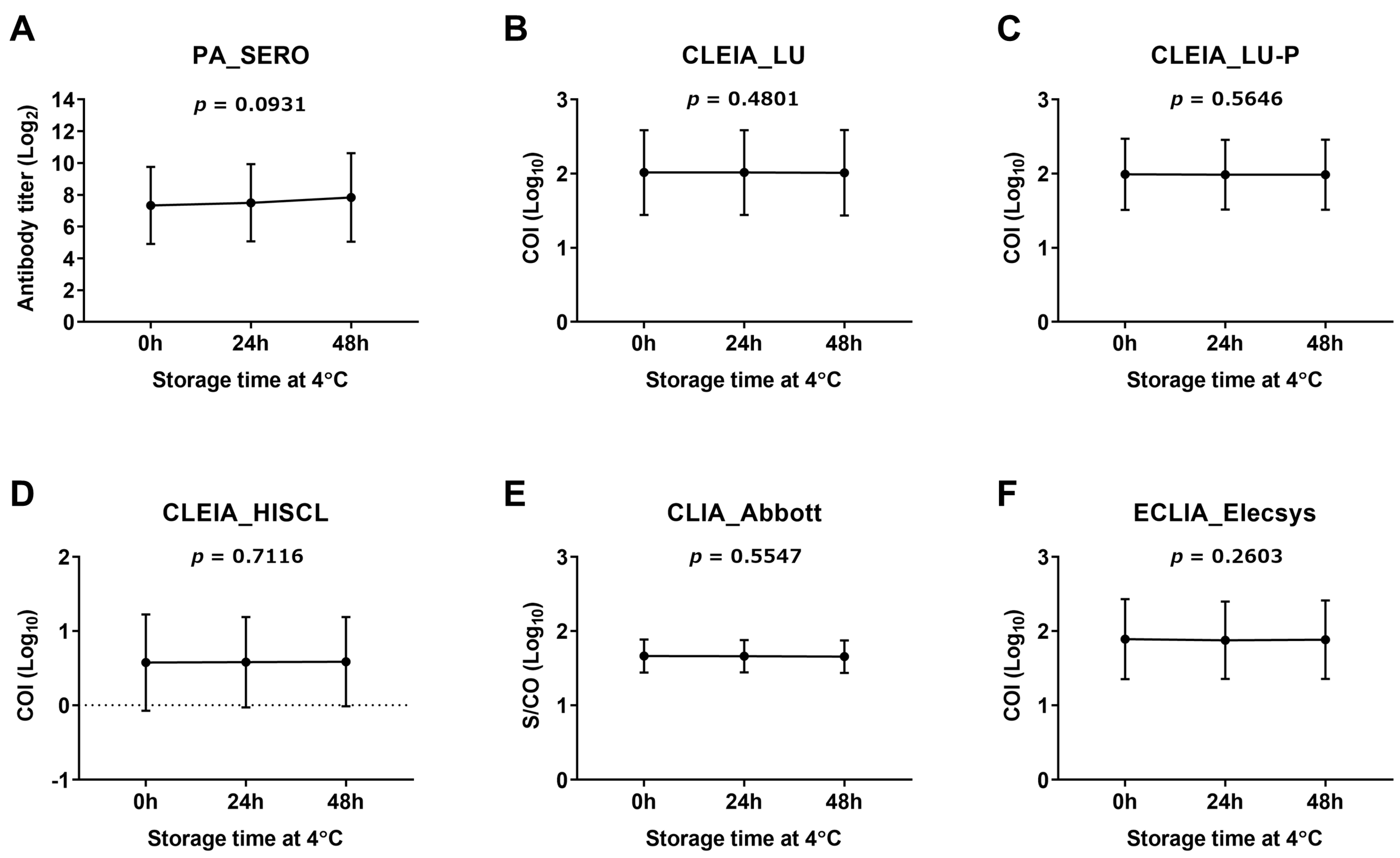
2.5. Assessment of CSF Anti-HTLV-1 Antibody Stability
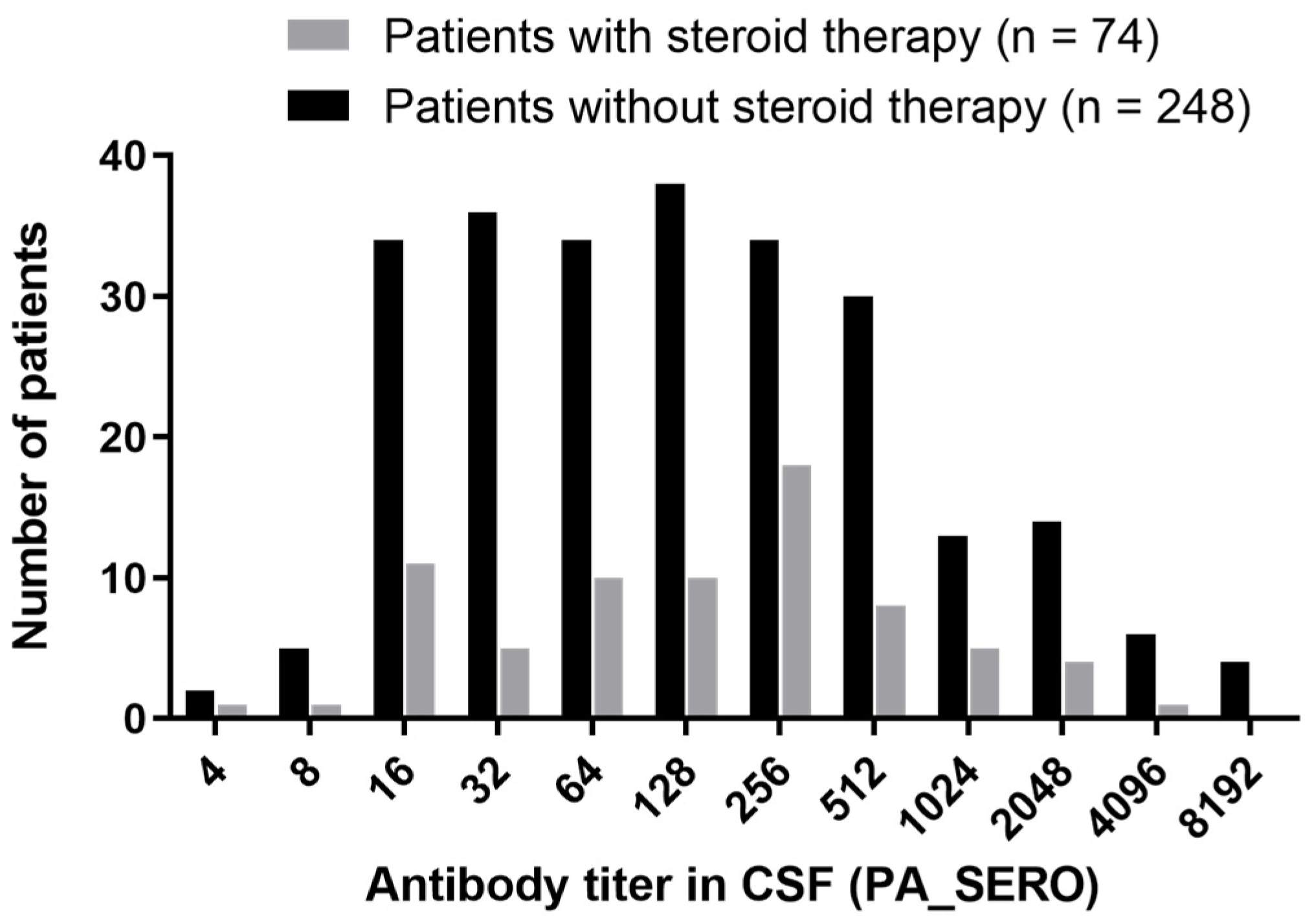
2.6. Distribution Study of CSF Anti-HTLV-1 Antibody Titers in Patients with HAM
2.7. Assessment of Diagnostic Performance of Anti-HTLV-1 Antibody Test Kits
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Stability of CSF Anti-HTLV-1 Antibody Measurement
3.2. Assessment of Diagnostic Performance of Anti-HTLV-1 Antibody Test Kits
3.2.1. Distribution of CSF Anti-HTLV-1 Antibody Titers Using the PA Method in Patients with HAM
3.2.2. Characteristics of HTLV-1 Carriers and Patients with HAM Used to Determine Diagnostic Performance
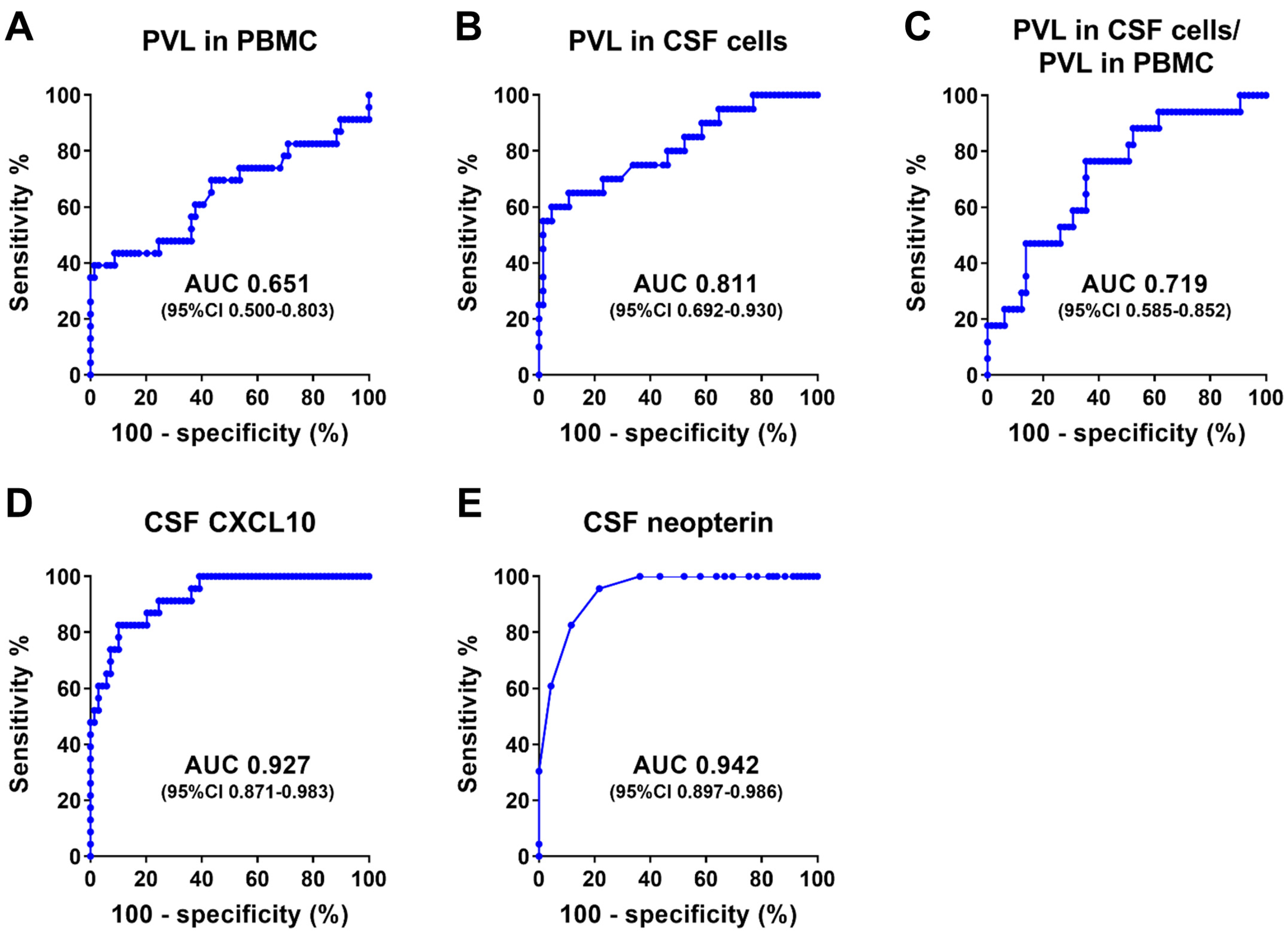
3.2.3. Diagnostic Performance of Anti-HTLV-1 Antibody Test Kits
3.2.4. Evaluation of the 4× Cutoff Value for the PA Method
3.2.5. Cutoff Values for Diagnosing HAM
3.2.6. Diagnostic Performance of IC_ESPLINE and LIA_INNO-LIA
4. Discussion
- The CSF specimens used to determine the cutoff values in this study were frozen and thawed twice and underwent a long storage time (5.2 ± 2.2 years) at −80 °C.
- The CSF specimens were collected exclusively from Japanese patients, and the sample size was relatively small.
- Some HTLV-1 carriers in this study exhibited neurological symptoms, although HAM was ruled out.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poiesz, B.J.; Ruscetti, F.W.; Gazdar, A.F.; Bunn, P.A.; Minna, J.D.; Gallo, R.C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7415–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinuma, Y.; Nagata, K.; Hanaoka, M.; Nakai, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Kinoshita, K.I.; Shirakawa, S.; Miyoshi, I. Adult T-cell leukemia: Antigen in an ATL cell line and detection of antibodies to the antigen in human sera. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 6476–6480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessain, A.; Barin, F.; Vernant, J.C.; Gout, O.; Maurs, L.; Calender, A.; de The, G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet 1985, 2, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osame, M.; Usuku, K.; Izumo, S.; Ijichi, N.; Amitani, H.; Igata, A.; Matsumoto, M.; Tara, M. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet 1986, 1, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamano, Y.; Sato, T. Clinical pathophysiology of human T-lymphotropic virus-type 1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, C.R.; Araujo, A.; Yamano, Y.; Taylor, G.P. HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, C.M.; Ribeiro, L.C.; Puccioni-Sohler, M. Difficulties in HAM/TSP diagnosis. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2012, 70, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Fujino, R.; Matsui, T.; Yoshida, T.; Komoda, H.; Imai, J. A new agglutination test for serum antibodies to adult T-cell leukemia virus. Gan 1984, 75, 845–848. [Google Scholar]
- HTLV-1 Kanren Sekizuisyou (HAM) Sinryou Gaidorain 2019 [Clinical Practical Guideline for HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy 2019]; Nankodo Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2019; p. xviii. Available online: https://www.neurology-jp.org/guidelinem/ham/ham_2019.pdf (accessed on 6 October 2024).
- Kodama, D.; Tanaka, M.; Matsuzaki, T.; Nozuma, S.; Matsuura, E.; Takashima, H.; Izumo, S.; Kubota, R. Anti-human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) antibody assays in cerebrospinal fluid for the diagnosis of HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Murata, M.; Karasawa, H.; Kaneko, A.; Aoyagi, K. Peformance evaluation of LumipulseG HTLV-I/II. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, S158. [Google Scholar]
- Guiraud, V.; Cremoux, F.; Leroy, I.; Cohier, J.; Hernandez, P.; Mansaly, S.; Gautheret-Dejean, A. Comparison of two new HTLV-I/II screening methods, Abbott Alinity i rHTLV-I/II and Diasorin LIAISON(R) XL murex recHTLV-I/II, to Abbott architect rHTLVI/II assay. J. Clin. Virol. 2023, 164, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Hodges, S.; Lukaszewska, T.; Hino, S.; Arai, H.; Yamaguchi, J.; Swanson, P.; Schochetman, G.; Devare, S.G. Evaluation of a new, fully automated immunoassay for detection of HTLV-I and HTLV-II antibodies. J. Med. Virol. 2008, 80, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laperche, S.; Sauleda, S.; Piron, M.; Muhlbacher, A.; Schennach, H.; Schottstedt, V.; Queiros, L.; Uno, N.; Yanagihara, K.; Imdahl, R.; et al. Evaluation of Sensitivity and Specificity Performance of Elecsys HTLV-I/II Assay in a Multicenter Study in Europe and Japan. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2180–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramitsu, M.; Momose, H.; Uchida, Y.; Ishitsuka, K.; Kubota, R.; Tokunaga, M.; Utsunomiya, A.; Umekita, K.; Hashikura, Y.; Nosaka, K.; et al. Performance evaluation of Espline HTLV-I/II, a newly developed rapid immunochromatographic antibody test for different diagnostic situations. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0207823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabino, E.C.; Zrein, M.; Taborda, C.P.; Otani, M.M.; Ribeiro-Dos-Santos, G.; Saez-Alquezar, A. Evaluation of the INNO-LIA HTLV I/II assay for confirmation of human T-cell leukemia virus-reactive sera in blood bank donations. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuma, K.; Kuramitsu, M.; Niwa, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Masaki, Y.; Ueda, G.; Matsumoto, C.; Sobata, R.; Sagara, Y.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Establishment of a novel diagnostic test algorithm for human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 infection with line immunoassay replacement of western blotting: A collaborative study for performance evaluation of diagnostic assays in Japan. Retrovirology 2020, 17, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osame, M. Review of WHO Kagoshima Meeting and Diagnostic Guidelines for HAM/TSP. In Human Retrovirology; Blattner, W.A., Ed.; Raven Press, Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Yamano, Y.; Nagai, M.; Brennan, M.; Mora, C.A.; Soldan, S.S.; Tomaru, U.; Takenouchi, N.; Izumo, S.; Osame, M.; Jacobson, S. Correlation of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) mRNA with proviral DNA load, virus-specific CD8(+) T cells, and disease severity in HTLV-1-associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP). Blood 2002, 99, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kira, J.; Koyanagi, Y.; Yamada, T.; Itoyama, Y.; Goto, I.; Yamamoto, N.; Sasaki, H.; Sakaki, Y. Increased HTLV-I proviral DNA in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy: A quantitative polymerase chain reaction study. Ann Neurol 1991, 29, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezin, A.; Olindo, S.; Oliere, S.; Varrin-Doyer, M.; Marlin, R.; Cabre, P.; Smadja, D.; Cesaire, R. Human T lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) proviral load in cerebrospinal fluid: A new criterion for the diagnosis of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis? J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccioni-Sohler, M.; Yamano, Y.; Rios, M.; Carvalho, S.M.; Vasconcelos, C.C.; Papais-Alvarenga, R.; Jacobson, S. Differentiation of HAM/TSP from patients with multiple sclerosis infected with HTLV-I. Neurology 2007, 68, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Coler-Reilly, A.; Utsunomiya, A.; Araya, N.; Yagishita, N.; Ando, H.; Yamauchi, J.; Inoue, E.; Ueno, T.; Hasegawa, Y.; et al. CSF CXCL10, CXCL9, and neopterin as candidate prognostic biomarkers for HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suehara, M.; Izumo, S.; Kumamoto, I.; Osame, M. Significance of anti-HTLV-I antibody in cerebrospinal fluid in diagnosis of HTLV-I associated myelopathy (HAM). Rinsho Byori 1992, 40, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, L.C.; Goncalves, C.C.; Slater, C.M.; Carvalho, S.M.; Puccioni-Sohler, M. Standardisation of Western blotting to detect HTLV-1 antibodies synthesised in the central nervous system of HAM/TSP patients. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitze, B.; Usuku, K.; Izumo, S.; Nakamura, M.; Shiraki, H.; Ijichi, S.; Yashiki, S.; Fujiyoshi, T.; Sonoda, S.; Osame, M. Diversity of intrathecal antibody synthesis against HTLV-I and its relation to HTLV-I associated myelopathy. J. Neurol. 1996, 243, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinsky, N.A.; Huddleston, J.M.; Jacobson, R.M.; Wollan, P.C.; Poland, G.A. Effect of multiple freeze-thaw cycles on detection of measles, mumps, and rubella virus antibodies. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2003, 10, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Petzold, A.; Bennett, J.L.; Berven, F.S.; Brundin, L.; Comabella, M.; Franciotta, D.; Frederiksen, J.L.; Fleming, J.O.; Furlan, R.; et al. A consensus protocol for the standardization of cerebrospinal fluid collection and biobanking. Neurology 2009, 73, 1914–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klener, J.; Hofbauerova, K.; Bartos, A.; Ricny, J.; Ripova, D.; Kopecky, V. Instability of cerebrospinal fluid after delayed storage and repeated freezing: A holistic study by drop coating deposition Raman spectroscopy. Clin. Chem. Lab Med. 2014, 52, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, B.N.; Rudge, P.; Thompson, E.J. Viral specific IgG and IgM antibodies in the CSF of patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. J. Neurol. 1989, 236, 351–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puccioni-Sohler, M.; Rios, M.; Carvalho, S.M.; Goncalves, R.R.; Oliveira, C.; Correa, R.B.; Novis, S.; de Oliveira, M.S.; Bianco, C. Diagnosis of HAM/TSP based on CSF proviral HTLV-I DNA and HTLV-I antibody index. Neurology 2001, 57, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibzadeh, F.; Habibzadeh, P.; Yadollahie, M. On determining the most appropriate test cut-off value: The case of tests with continuous results. Biochem. Medica 2016, 26, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessain, A.; Gout, O. Chronic myelopathy associated with human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I). Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 117, 933–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Methods | Kit’s Name | Abbrev. | Manufacturer | Ind/Sand | Cutoff Values for Blood |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PA | Serodia HTLV-I | SERO | Fujirebio | n/a | Titer ≥ 16× |
| CLEIA | Lumipulse HTLV-I/II | LU | Fujirebio | Sand | COI ≥ 1.0 |
| Lumipulse Presto HTLV-I/II | LU-P | Fujirebio | Sand | COI ≥ 1.0 | |
| HISCL HTLV-I | HISCL | Sysmex | Ind | COI ≥ 1.0 | |
| HISCL_UD (under development) | UD | Sysmex | Sand | COI ≥ 1.0 | |
| CLIA | HTLV·Abbott (Alinity) | Abbott | Abbott Japan | Sand | S/CO ≥ 1.0 |
| ECLIA | Elecsys HTLV-I/II | Elecsys | Roche Diagnostics | Sand | COI ≥ 1.0 |
| IC | ESPLINE HTLV-I/II | ESPLINE | Fujirebio | Sand | * |
| LIA | INNO-LIA HTLV-I/II Score | INNO-LIA | Fujirebio | Ind | * |
| HTLV-1 Carriers | Patients with HAM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n = 23 | n = 69 | ||
| Sex: Female | 14 (60.9%) | 55 (79.7%) | 0.10 (a) |
| Age 1 | 53 [50, 69.5] | 67 [60, 72] | 0.02 (b) |
| PVL in PBMCs 1 | 2.57 [0.20, 4.13] | 3.52 [1.90, 5.07] | 0.03 (b) |
| PVL in CSF cells 1 | 1.46 [0.57, 4.59] 2 | 5.32 [3.89, 8.60] 3 | <0.0001 (b) |
| PVL in CSF cells/PVL in PBMCs 1 | 0.93 [0.63, 1.33] 2 | 1.69 [0.92, 3.20] 3 | 0.005 (b) |
| CXCL10 in CSF (pg/mL) 1 | 249.6 [142.0, 322.7] | 1090.5 [598.0, 2247.7] | <0.0001 (b) |
| Neopterin in CSF (pmol/mL) 1 | 3 [2, 4] | 8 [6, 18] | <0.0001 (b) |
| PA_SERO | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (≥4×) | Negative (<4×) | |||
| CLEIA_LU | Positive (COI ≥ 1.0) | 85 | 5 | 90 |
| Negative (COI < 1.0) | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Total | 85 | 7 | 92 | |
| Overall concordance rate | 94.6% | |||
| PA_SERO | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive (≥16×) | Negative (<16×) | |||
| CLEIA_LU | Positive (COI ≥ 1.0) | 73 | 17 | 90 |
| Negative (COI < 1.0) | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Total | 73 | 19 | 92 | |
| Overall concordance rate | 81.5% | |||
| LU | LU-P | HISCL | UD | Abbott | Elecsys | ESPLINE | INNO-LIA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SERO (≥4× positive) | 94.6% | 95.7% | 72.8% | 95.7% | 94.5% | 96.7% | 97.8% | 79.3% |
| SERO (≥16× positive) | 81.5% | 82.6% | 84.8% | 82.6% | 83.5% | 88.0% | 87.0% | 90.2% |
| SERO | LU | LU-P | HISCL | UD | Abbott | Elecsys | ESPLINE | INNO-LIA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutoff values for blood | Titer 16× | COI 1.0 | COI 1.0 | COI 1.0 | COI 1.0 | S/CO 1.0 | COI 1.0 | * | * |
| Sensitivity | 97.1% | 100% | 100% | 84.1% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% | 91.3% |
| Specificity | 73.9% | 8.7% | 13.0% | 91.3% | 13.0% | 18.2% | 34.8% | 30.4% | 65.2% |
| Cutoff values equivalent to the 4× titer of the PA method | Titer 4× | COI 4.7 | COI 5.4 | COI 0.15 | COI 3.3 | S/CO 2.8 | COI 2.3 | n/a | n/a |
| Sensitivity | 100% | 100% | 98.6% | 98.6% | 100% | 98.6% | 100% | n/a | n/a |
| Specificity | 30.4% | 52.2% | 47.8% | 34.8% | 43.5% | 54.5% | 43.5% | n/a | n/a |
| Cutoff values for maximum specificity with 100% sensitivity | Titer 4× | COI 4.7 | COI 4.7 | COI 0.25 | COI 3.3 | S/CO 2.5 | COI 2.5 | n/a | n/a |
| Sensitivity | 100% | 100% | 100% | 98.6% ** | 100% | 100% | 100% | n/a | n/a |
| Specificity | 30.4% | 52.2% | 47.8% | 39.1% | 43.5% | 54.5% | 56.5% | n/a | n/a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sato, T.; Yagishita, N.; Araya, N.; Nakashima, M.; Horibe, E.; Takahashi, K.; Kunitomo, Y.; Nawa, Y.; Hamaguchi, I.; Yamano, Y. Diagnostic Value of Anti-HTLV-1-Antibody Quantification in Cerebrospinal Fluid for HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy. Viruses 2024, 16, 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101581
Sato T, Yagishita N, Araya N, Nakashima M, Horibe E, Takahashi K, Kunitomo Y, Nawa Y, Hamaguchi I, Yamano Y. Diagnostic Value of Anti-HTLV-1-Antibody Quantification in Cerebrospinal Fluid for HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy. Viruses. 2024; 16(10):1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101581
Chicago/Turabian StyleSato, Tomoo, Naoko Yagishita, Natsumi Araya, Makoto Nakashima, Erika Horibe, Katsunori Takahashi, Yasuo Kunitomo, Yukino Nawa, Isao Hamaguchi, and Yoshihisa Yamano. 2024. "Diagnostic Value of Anti-HTLV-1-Antibody Quantification in Cerebrospinal Fluid for HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy" Viruses 16, no. 10: 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101581
APA StyleSato, T., Yagishita, N., Araya, N., Nakashima, M., Horibe, E., Takahashi, K., Kunitomo, Y., Nawa, Y., Hamaguchi, I., & Yamano, Y. (2024). Diagnostic Value of Anti-HTLV-1-Antibody Quantification in Cerebrospinal Fluid for HTLV-1-Associated Myelopathy. Viruses, 16(10), 1581. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16101581





