New Associations with the HIV Predisposing and Protective Alleles of the Human Leukocyte Antigen System in a Peruvian Population
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Design
2.2. Biological Samples and DNA Extraction
2.3. Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES)
2.4. Bioinformatics Pipeline to HLA Typing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Hardware and Software Environment
2.7. Ethics Statement
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Unaids. UNAIDS 2023 Data. 2023. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/UNAIDS_FactSheet_en.pdf (accessed on 7 October 2023).
- Horton, R.; Wilming, L.; Rand, V.; Lovering, R.C.; Bruford, E.A.; Khodiyar, V.K.; Lush, M.J.; Povey, S.; Talbot, C.C., Jr.; Wright, M.W.; et al. Gene map of the extended human MH. C. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, G.G.; Song, H.I.; Jang, M.M.; Lee, C.S.; Hong, J.Y.; Shin, M.G.; Choi, H.J. Validation and application of new NGS-based HLA genotyping to clinical diagnostic practice. HLA 2023, 101, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.; Barker, D.J.; Georgiou, X.; Cooper, M.A.; Flicek, P.; Marsh, S.G.E. IPD-IMGT/HLA Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D948–D955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, S.G.; Albert, E.D.; Bodmer, W.F.; Bontrop, R.E.; Dupont, B.; Erlich, H.A.; Fernández-Viña, M.; Geraghty, D.E.; Holdsworth, R.; Hurley, C.K.; et al. Nomenclature for factors of the HLA system, 2010. Tissue Antigens 2010, 75, 291–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M. Natural Immunity against HIV-1: Progression of Understanding after Association Studies. Viruses 2022, 14, 1243, Erratum in Viruses 2023, 15, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dashti, M.; Malik, M.Z.; Nizam, R.; Jacob, S.; Al-Mulla, F.; Thanaraj, T.A. Evaluation of HLA typing content of next-generation sequencing datasets from family trios and individuals of arab ethnicity. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1407285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, G.; Higuchi, R.; Hoglund, B.; Goodridge, D.; Sayer, D.; Trachtenberg, E.A.; Erlich, H.A. High-resolution, high-throughput HLA genotyping by next-generation sequencing. Tissue Antigens 2009, 74, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlich, H. HLA DNA typing: Past, present, and future. Tissue Antigens 2012, 80, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Dykes, D.; Polesky, H. A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R. The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szolek, A.; Schubert, B.; Mohr, C.; Sturm, M.; Feldhahn, M.; Kohlbacher, O. OptiType: Precision HLA typing from next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3310–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orenbuch, R.; Filip, I.; Comito, D.; Shaman, J.; Pe’er, I.; Rabadan, R. arcasHLA: High-resolution HLA typing from RNAseq. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Song, Y.Q. PyHLA: Tests for the association between HLA alleles and diseases. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yao, M.; Gong, Y.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ye, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, F.; Dong, H.; Meng, R.; et al. Benchmarking the Human Leukocyte Antigen Typing Performance of Three Assays and Seven Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Algorithms. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 652258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Mazas, A. A review of HLA allele and SNP associations with highly prevalent infectious diseases in human populations. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2020, 150, w20214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanzo-Vargas, M.P.; Arellano-Veintemilla, T.; González-Lagos, E.; Echevarría, J.; Mejía, F.; Graña, A.; Gotuzzo, E. Socio-Demographic, Clinical, and Mortality Differences between HIV-Infected and HIV/HTLV-1 Co-Infected Patients in Peru. Pathogens 2023, 12, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Galarza, F.F.; McCabe, A.; Santos, E.J.; Jones, J.; Takeshita, L.Y.; Ortega-Rivera, N.D.; Del Cid-Pavon, G.M.; Ramsbottom, K.; Ghattaoraya, G.S.; Alfirevic, A.; et al. Allele frequency net database (AFND) 2020 update: Gold-standard data classification, open access genotype data and new query tools. Nucleic Acid. Res. 2020, 48, D783–D788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaiz-Villena, A.; Gonzalez-Alcos, V.; Serrano-Vela, J.I.; Reguera, R.; Barbolla, L.; Parga-Lozano, C.; Gómez-Prieto, P.; Abd-El-Fatah-Khalil, S.; Moscoso, J. HLA genes in Uros from Titikaka Lake, Peru: Origin and relationship with other Amerindians and worldwide populations. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2009, 36, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera, A.; Pérez-Álvarez, S.; Ibarrondo, J.; Ganoza, C.; Lama, J.R.; Lucchetti, A.; Cate, S.; Hildebrand, W.; Bernard, N.; Gomez, L.; et al. The HLA-C*04: 01/KIR2DS4 gene combination and human leukocyte antigen alleles with high population frequency drive rate of HIV disease progression. AIDS 2015, 29, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blais, M.E.; Dong, T.; Rowland-Jones, S. HLA-C as a mediator of natural killer and T-cell activation: Spectator or key player? Immunology 2011, 133, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereyra, F.; Jia, X.; McLaren, P.J.; Telenti, A.; de Bakker, P.I.; Walker, B.D.; Ripke, S.; Brumme, C.J.; Pulit, S.L.; Carrington, M.; et al. The major genetic determinants of HIV-1 control affect HLA class I peptide presentation. Science 2010, 330, 1551–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strettell, M.D.; Thomson, L.J.; Donaldson, P.T.; Bunce, M.; O’Neill, C.M.; Williams, R. HLA-C genes and susceptibility to type 1 autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 1997, 26, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Martin, M.P.; Gao, X.; Jacobson, L.; Goedert, J.J.; Buchbinder, S.; Kirk, G.D.; O’Brien, S.J.; Trowsdale, J.; Carrington, M. KIR/HLA pleiotropism: Protection against both HIV and opportunistic infections. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, L.B.; Dourado, R.M.; Amorim, L.M.; Ho, B.; Calonga-Solís, V.; Issler, H.C.; Marin, W.M.; Beltrame, M.H.; Petzl-Erler, M.L.; Hollenbach, J.A.; et al. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism in KIR2DL1 Is Associated With HLA-C Expression in Global Populations. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, J.E.; Hsu, K.C. Natural killer cell education in human health and disease. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2018, 50, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Deng, X.; Ding, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Z.; et al. Association Study Identified HLA-DQA1 as a Novel Genetic Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 75, 2207–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzurez, A.; Naka, I.; Miki, S.; Nakayama-Hosoya, K.; Isshiki, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakamura-Hoshi, M.; Seki, S.; Matsumura, T.; Takano, T.; et al. Association of HLA-DRB1*09:01 with severe COVID-19. HLA 2021, 98, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, S.Y. The HLA system: Genetics, immunology, clinical testing, and clinical implications. Yonsei Med. J. 2007, 48, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.L.; Kikuchi, M.; Huong, V.T.Q.; Ha, D.H.; Thuy, T.T.; Tham, V.D.; Tuan, H.M.; Tuong, V.V.; Nga, C.T.P.; Dat, T.V.; et al. Protective and enhancing HLA alleles, HLA-DRB1*0901 and HLA-A*24, for severe forms of dengue virus infection, dengue hemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 2, e304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarri, C.A.; Giannoulis, T.; Moutou, K.A.; Mamuris, Z. HLA class II peptide-binding-region analysis reveals funneling of polymorphism in action. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 238, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roe, D.L.; Lewis, R.E.; Cruse, J.M. Association of HLA-DQ and -DR alleles with protection from or infection with HIV-1. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2000, 68, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rallón, N.; Restrepo, C.; Vicario, J.; Romero, J.; Rodríguez, C.; García-Samaniego, J.; García, M.; Cabello, A.; Gorgolas, M.; Benito, L.M. Human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-DQB1*03:02 and HLA-A*02:01 have opposite patterns in their effects on susceptibility to HIV infection. HIV Med. 2017, 18, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, R.; Luo, M.; Bruneau, B.; Knight, E.; Nagelkerke, N.; Kimani, J.; Wachihi, C.; Ngugi, E.; Plummer, F. Human leukocyte antigen-DQ alleles and haplotypes and their associations with resistance and susceptibility to HIV-1 infection. AIDS 2008, 22, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Zhang, H.; Meng, Y.; Ji, Q.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, L. The association between HLA-DRB1 and systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9465. [Google Scholar]
- Anzurez, A.; Bello-López, J.M.; Rodríguez-Serrano, E.; Gómez-Martin, D.; De la Chesnaye, E. HLA associations and clinical outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Human. Immunol. 2021, 82, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval, J.; Salazar-Granara, A.; Acosta, O.; Castillo-Herrera, W.; Fujita, R.; Pena, S.D.; Santos, F.R. Tracing the genomic ancestry of Peruvians reveals a major legacy of pre-Columbian ancestors. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
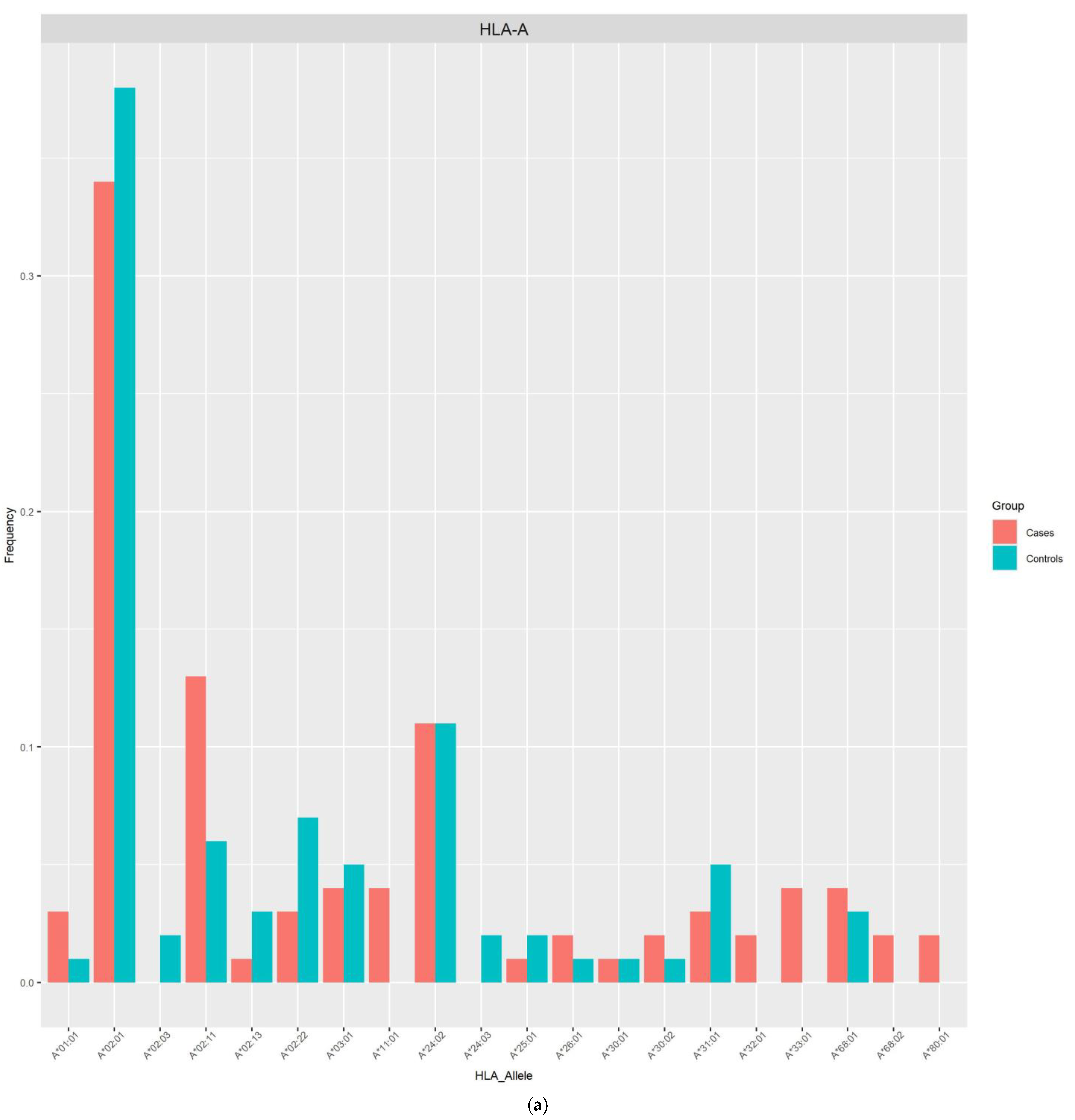
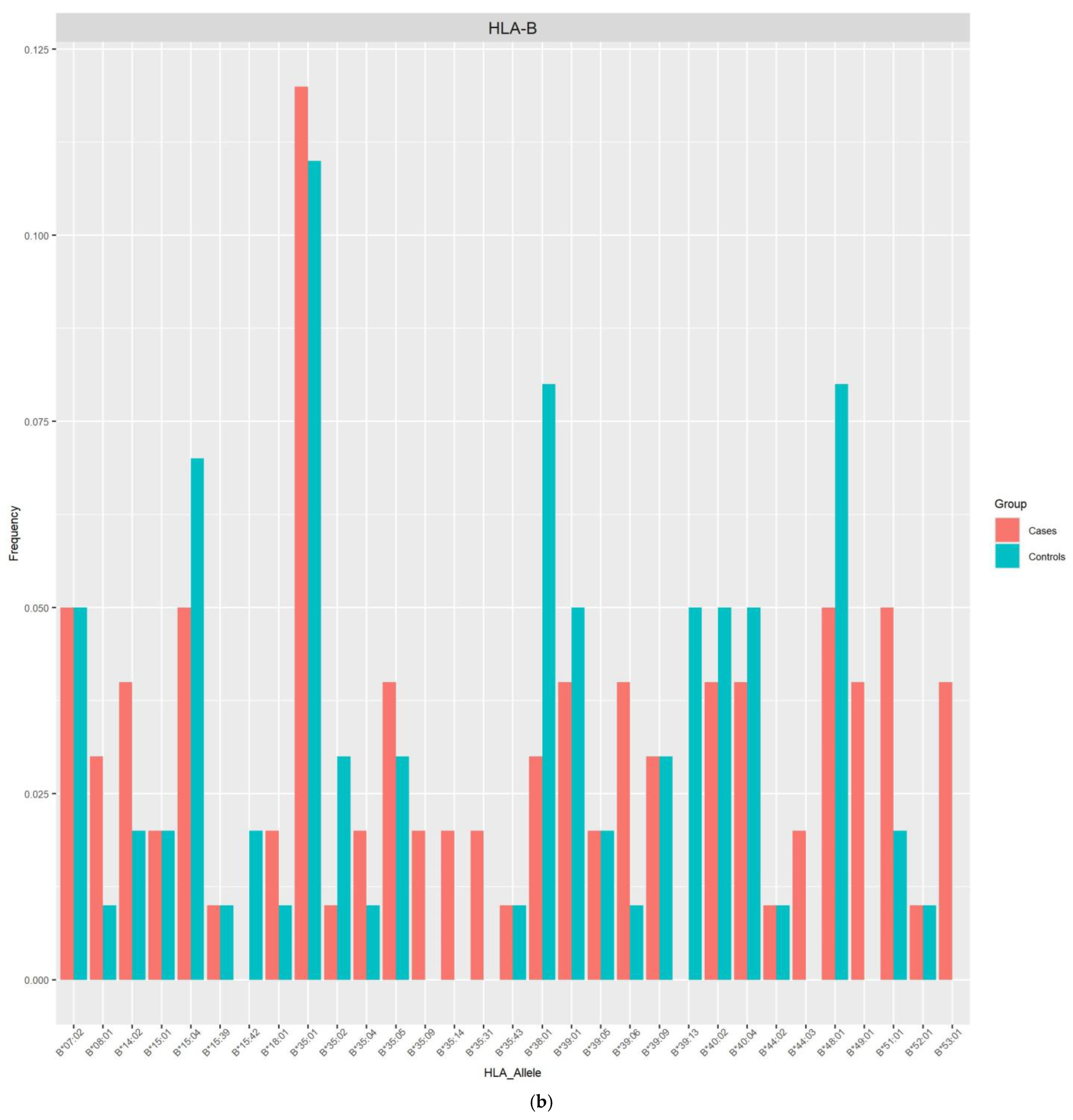
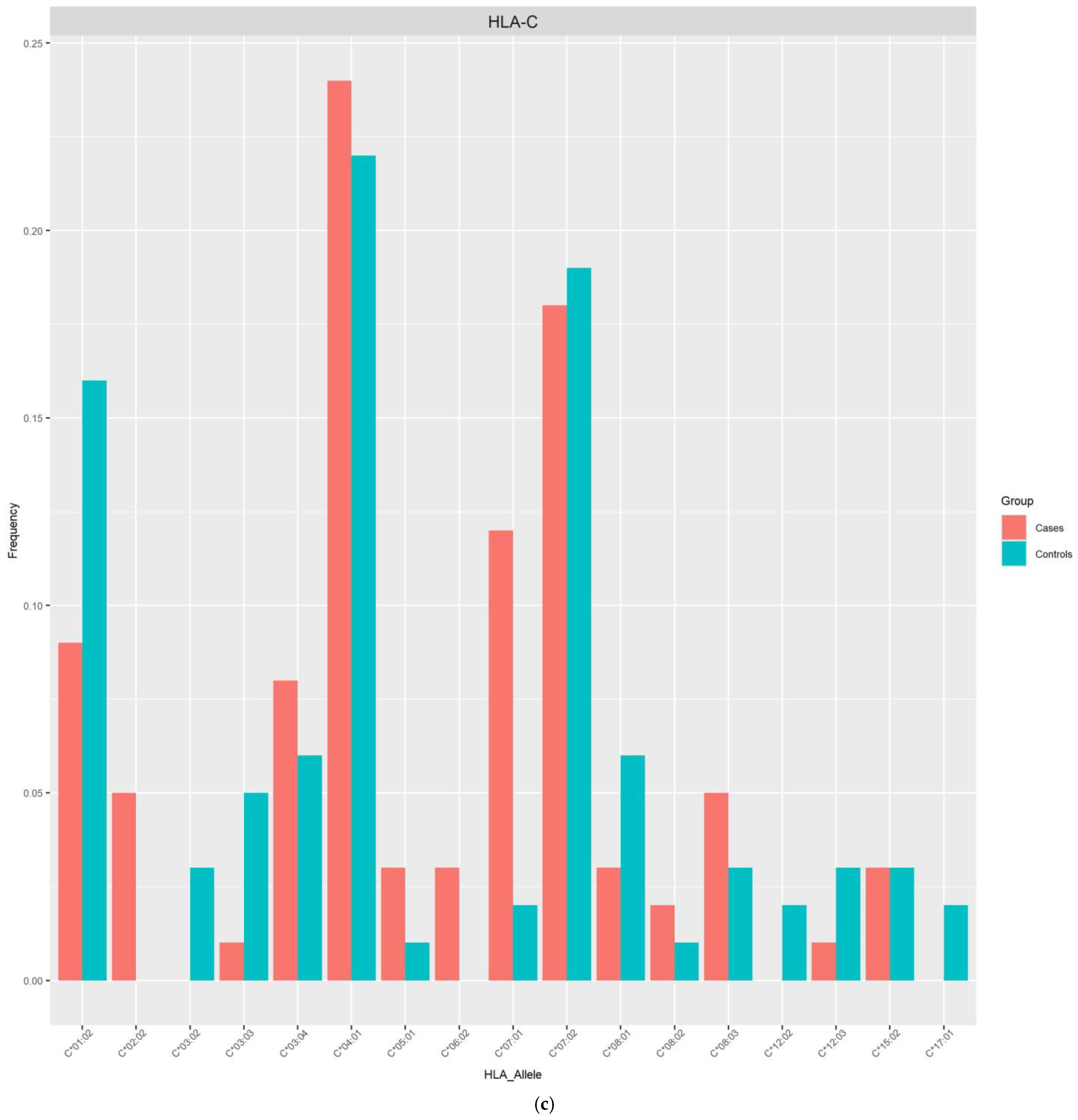
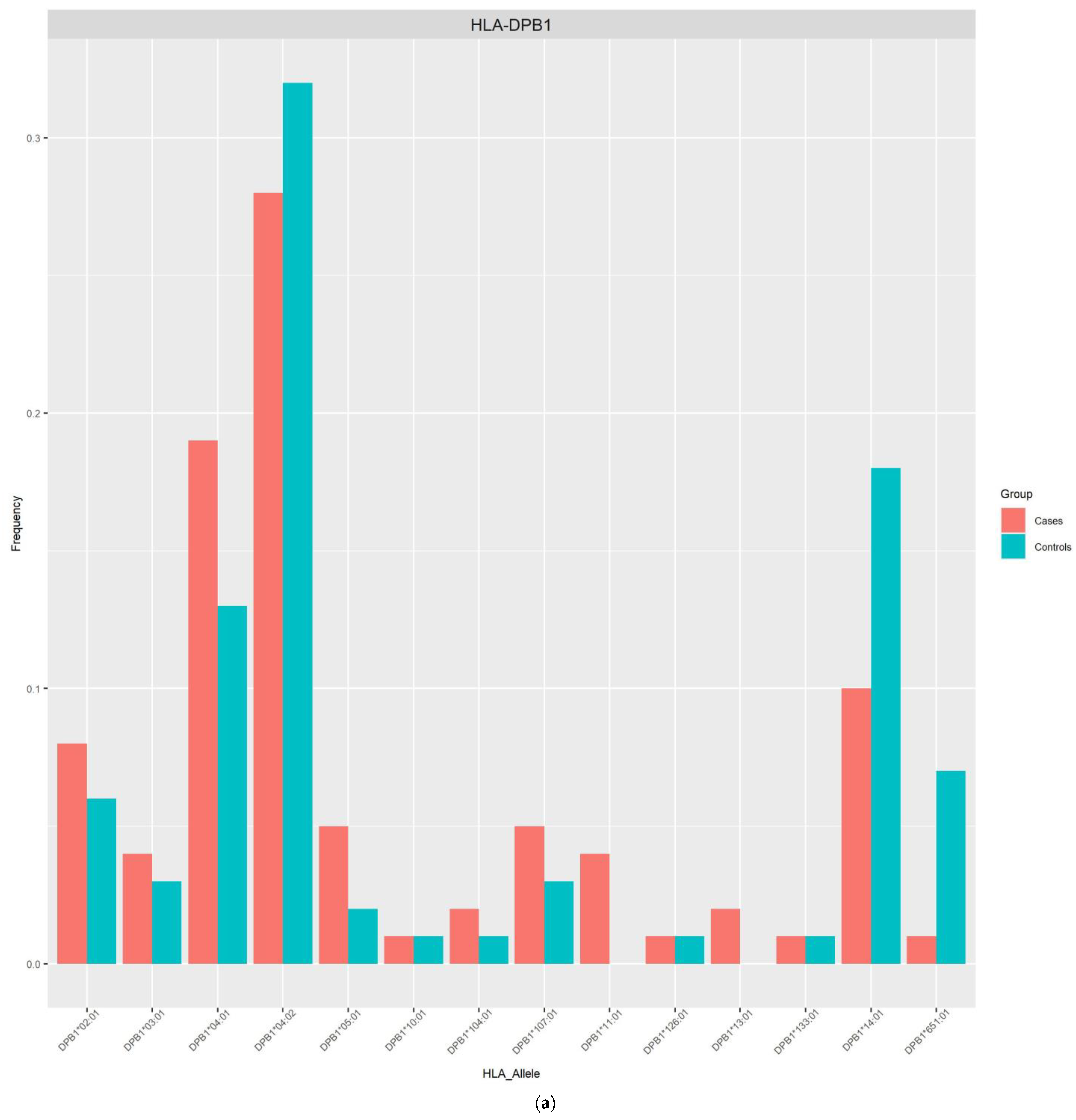
| Characteristics | PLHIV (n = 59) | HIV-Uninfected (n = 46) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Female | 36 (61.02) | 1 (2.17) | 0.0000 *a |
| Male | 23 (38.98) | 45 (97.83) | |
| Age at entry (Mean ± SD) | 41.05 ± 11.08 | 35.78 ± 10.23 | 0.0132 *a |
| Initial CD4 cell count (cells/mm3), n (%) | 634.00 ± 291.50 | 952.67 ± 316.36 | 0.0000 *b |
| <200 | 4 (6.78) | 0 | |
| 200–499 | 13 (22.03) | 2 (4.35) | |
| ≥500 | 42 (71.19) | 44 (95.65) | |
| Birthplace, n (%) | |||
| Central Coast region: Lima | 37 (62.71) | 38 (82.61) | |
| North Coast region | 15 (25.42) | 5 (10.87) | |
| Andean region | 7 (11.86) | 1 (2.17) | |
| Amazon region | 0 | 2 (4.35) | |
| Use of ART, n (%) | |||
| Yes | 59 (100.00) ** | - | |
| No | - | - | |
| ART regimen, n (%) | |||
| 2 PIs + 1 IIs | 1 (1.69) | - | |
| 2 PIs + 2 NRTIs | 5 (8.47) | - | |
| 2 NRTIs + 1 IIs | 24 (40.68) | - | |
| 2 NRTIs + 1 NNRTIs | 26 (44.07) | - | |
| Drugs, n (%) | |||
| NRTIs | |||
| Lamivudine (3TC) | 50 (84.75) | - | |
| Tenofovir (TDF) | 51 (86.44) | - | |
| Emtricitabine (FTC) | 5 (8.47) | - | |
| Abacavir (ABC) | 3 (5.08) | - | |
| Zidovudine (AZT) | 1 (1.69) | - | |
| NNRTIs | |||
| Efavirenz (EFV) | 26 (44.07) | - | |
| PIs | |||
| Ritonavir (RTV) | 6 (10.17) | - | |
| Lopinavir (LPV) | 4 (6.78) | - | |
| Atazanavir (ATV) | 1 (1.69) | - | |
| Darunavir (DRV) | 1 (1.69) | - | |
| IIs | |||
| Dolutegravir (DTG) | 21 (35.59) | - | |
| Raltegravir (RAL) | 4 (6.78) | - | |
| Sexual Orientation, n (%) | |||
| Homosexual | - | 14 (30.43) | |
| Heterosexual | - | 26 (56.52) | |
| Bisexual | - | 6 (13.04) | |
| Sex encounters with sex workers, n (%) | |||
| Yes | - | 46 (100.00) | |
| No | - | - | |
| No. of sexual partners in the last 12 months | |||
| Less than 5 sexual partners | - | 3 (6.52) | |
| 5–15 sexual partners | - | 35 (76.09) | |
| More than 15 sexual partners | - | 8 (17.39) | |
| HLA Locus | Number of Alleles | Alleles by Locus, Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLHIV (n = 56) | Without HIV (n = 44) | ||
| HLA-A | 112 | 88 | 200 |
| HLA-B | 112 | 88 | 200 |
| HLA-C | 110 | 88 | 198 |
| HLA-DPB1 | 112 | 88 | 200 |
| HLA-DQA1 | 108 | 88 | 196 |
| HLA-DQB1 | 112 | 88 | 200 |
| HLA-DRB1 | 112 | 88 | 200 |
| HLA Alleles | Allele Frequency | Allele Effect | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLHIV | Without HIV | OR (95% CI) | p | p Perm | |
| Susceptible | |||||
| C*07:01 | 0.1182 | 0.0227 | 10.222 (1.40–74.55) | 0.0219 | 0.0101 |
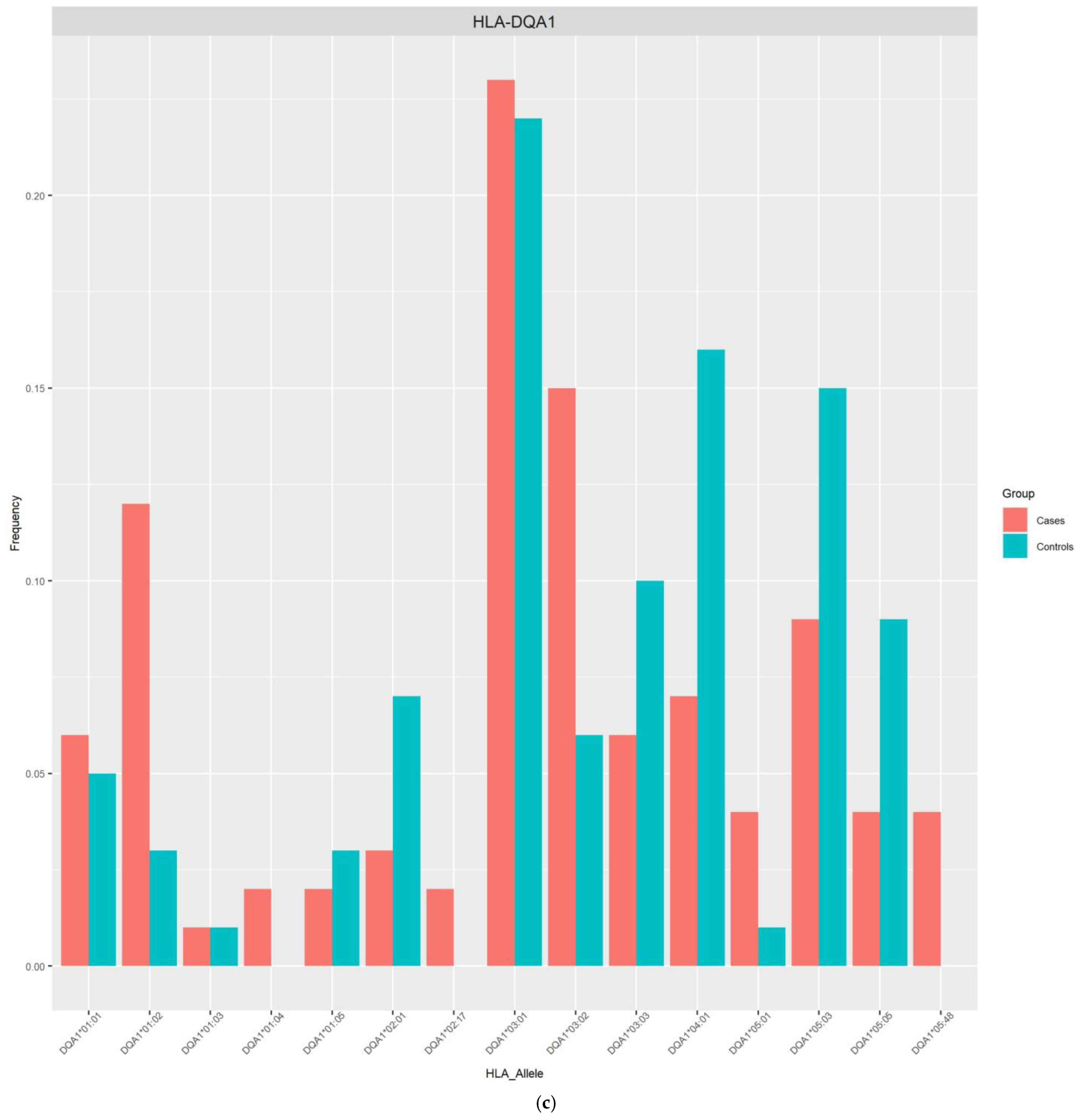
| DQA1*03:02 | 0.1481 | 0.0568 | 5.2972 (1.48–19.02) | 0.0106 | 0.0051 |
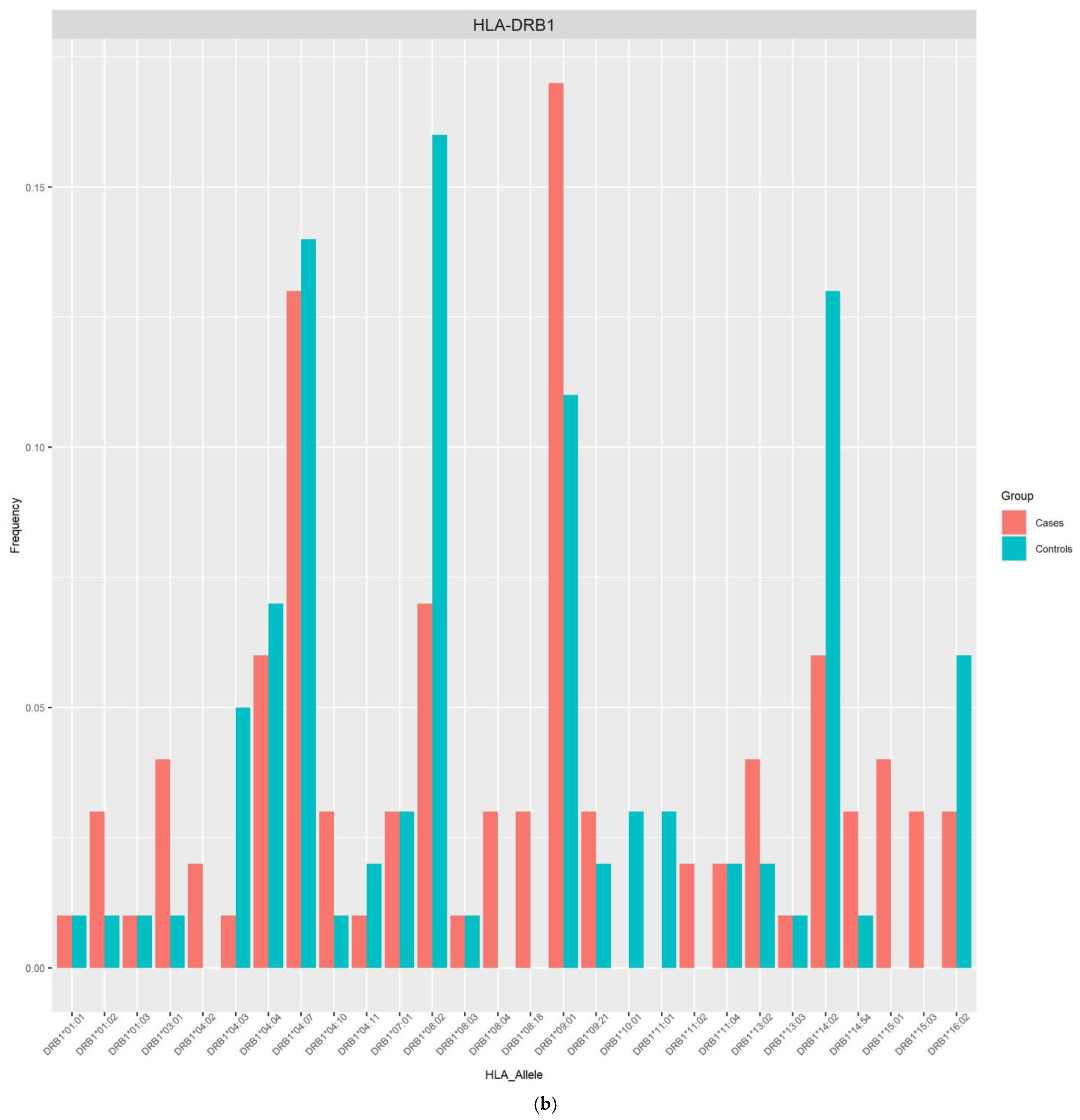
| DRB1*09:01 | 0.1696 | 0.1136 | 4.7880 (1.39–16.44) | 0.0129 | 0.0119 |
| Protective | |||||
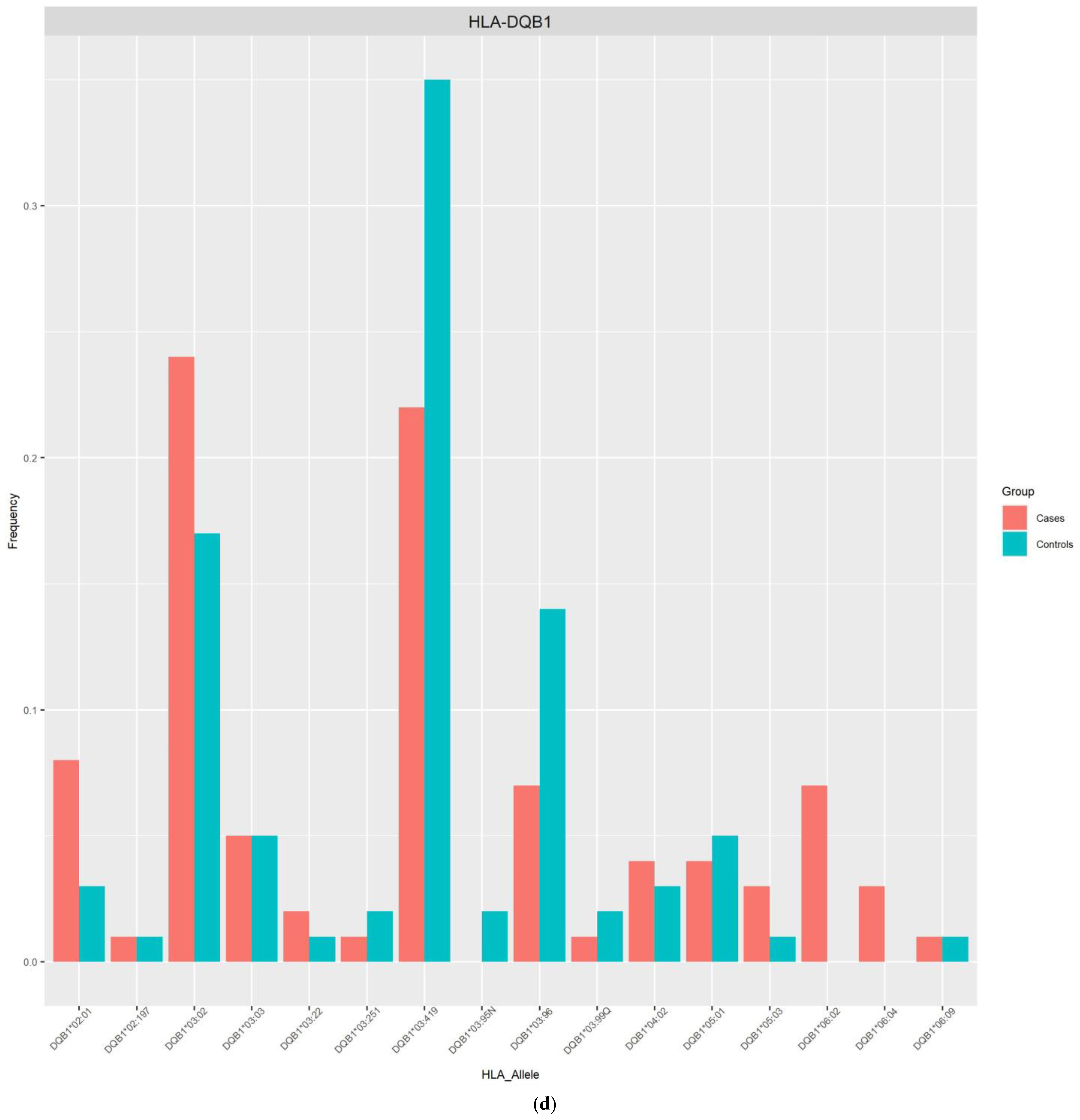
| DQB1*03:419 | 0.2232 | 0.3523 | 0.3273 (0.11–0.96) | 0.0412 | 0.0478 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Obispo, D.; Acosta, O.; Guevara, M.L.; Echavarría, S.; Espetia, S.; Dedios, M.; Yabar, C.A.; Fujita, R. New Associations with the HIV Predisposing and Protective Alleles of the Human Leukocyte Antigen System in a Peruvian Population. Viruses 2024, 16, 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16111708
Obispo D, Acosta O, Guevara ML, Echavarría S, Espetia S, Dedios M, Yabar CA, Fujita R. New Associations with the HIV Predisposing and Protective Alleles of the Human Leukocyte Antigen System in a Peruvian Population. Viruses. 2024; 16(11):1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16111708
Chicago/Turabian StyleObispo, Daisy, Oscar Acosta, Maria L. Guevara, Susan Echavarría, Susan Espetia, María Dedios, Carlos Augusto Yabar, and Ricardo Fujita. 2024. "New Associations with the HIV Predisposing and Protective Alleles of the Human Leukocyte Antigen System in a Peruvian Population" Viruses 16, no. 11: 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16111708
APA StyleObispo, D., Acosta, O., Guevara, M. L., Echavarría, S., Espetia, S., Dedios, M., Yabar, C. A., & Fujita, R. (2024). New Associations with the HIV Predisposing and Protective Alleles of the Human Leukocyte Antigen System in a Peruvian Population. Viruses, 16(11), 1708. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16111708





