Torquetenovirus Viremia Quantification Using Real-Time PCR Developed on a Fully Automated, Random-Access Platform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Manual TTV Real-Time PCRs
2.2. Clinical Samples and Positive Controls
2.3. Panther Fusion TTV Real-Time PCR
2.4. Analytical Performance Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of PCR Parameters
3.2. Analytical Sensitivity
3.3. Assessment of Intra- and Inter-Run Variabilities
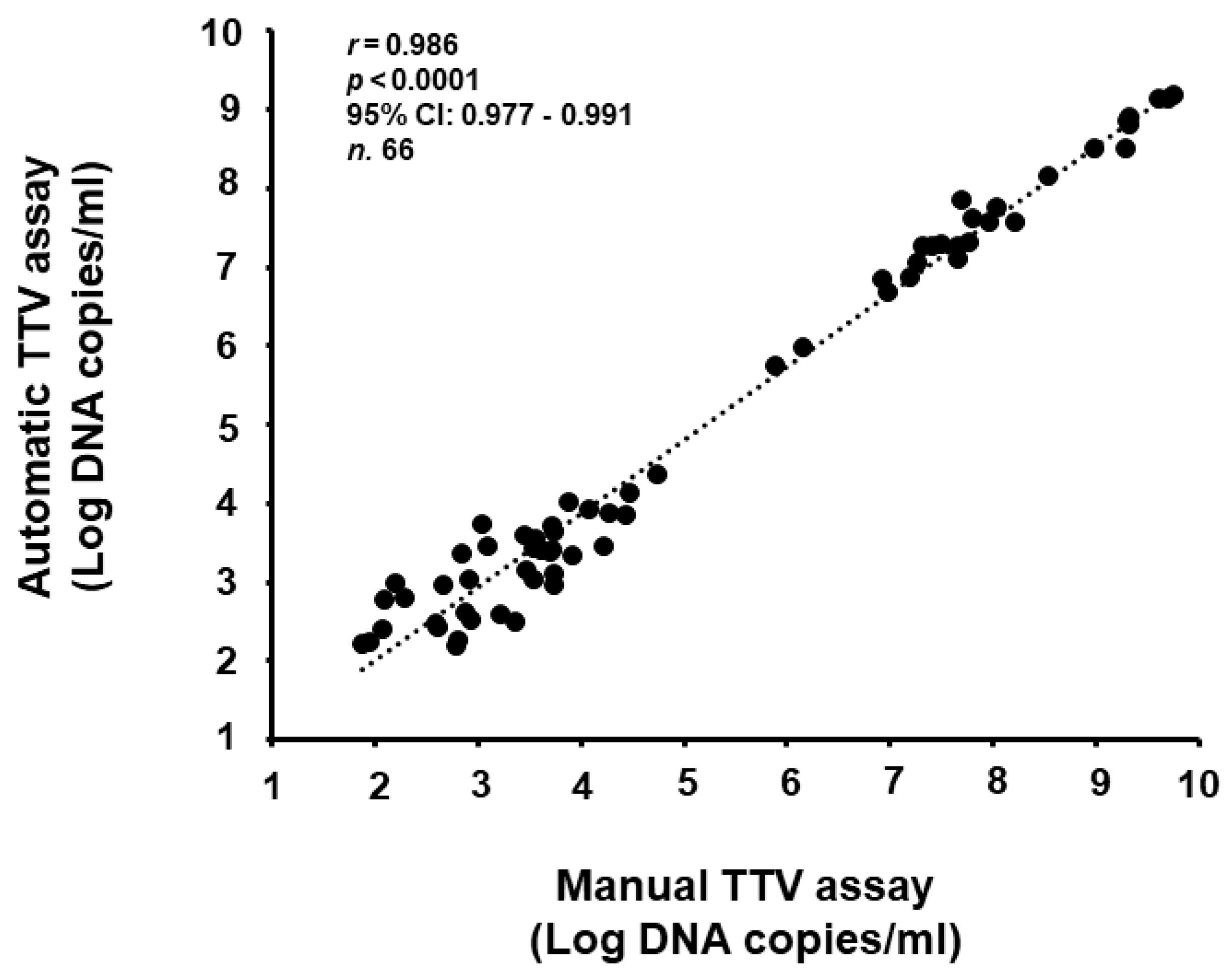
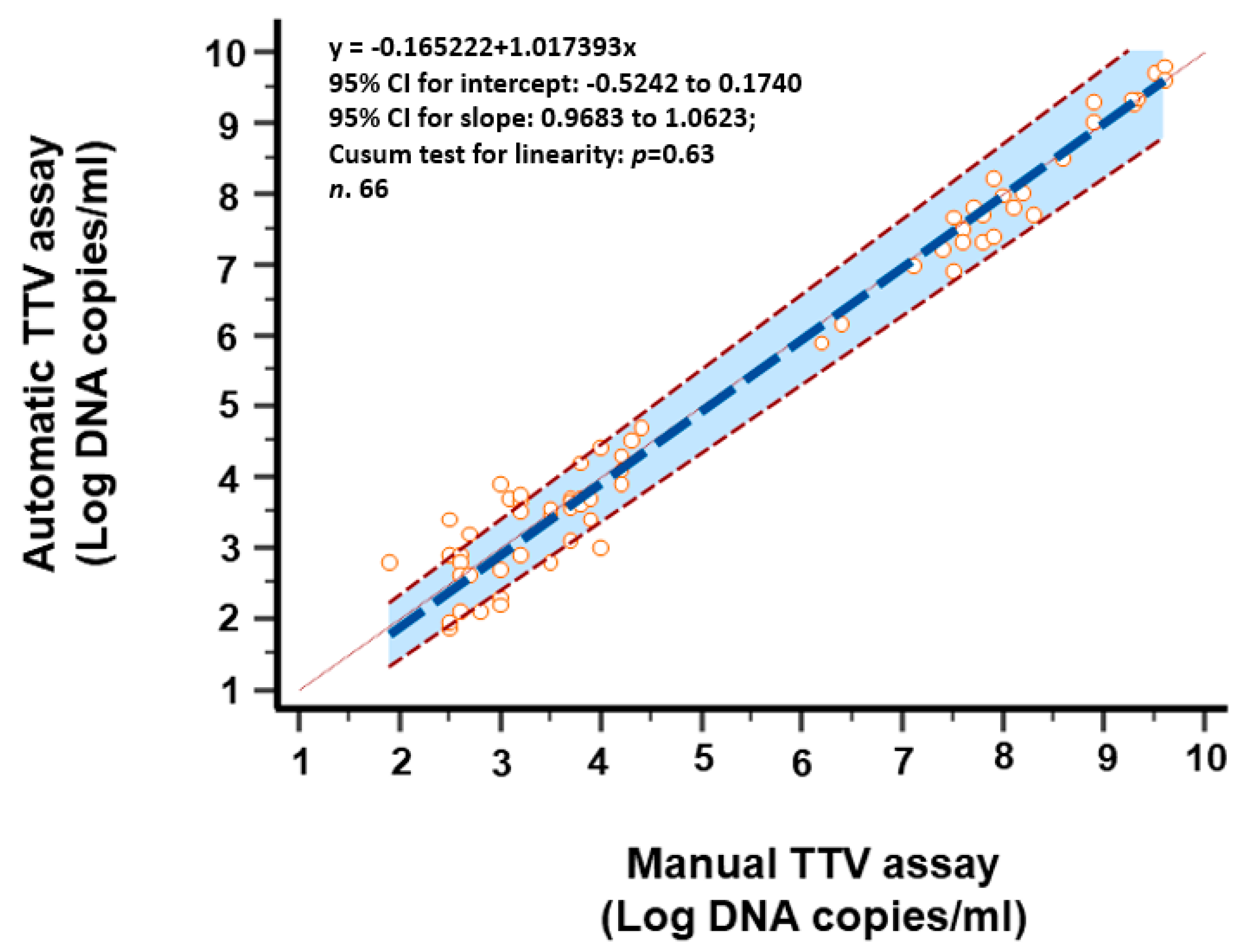
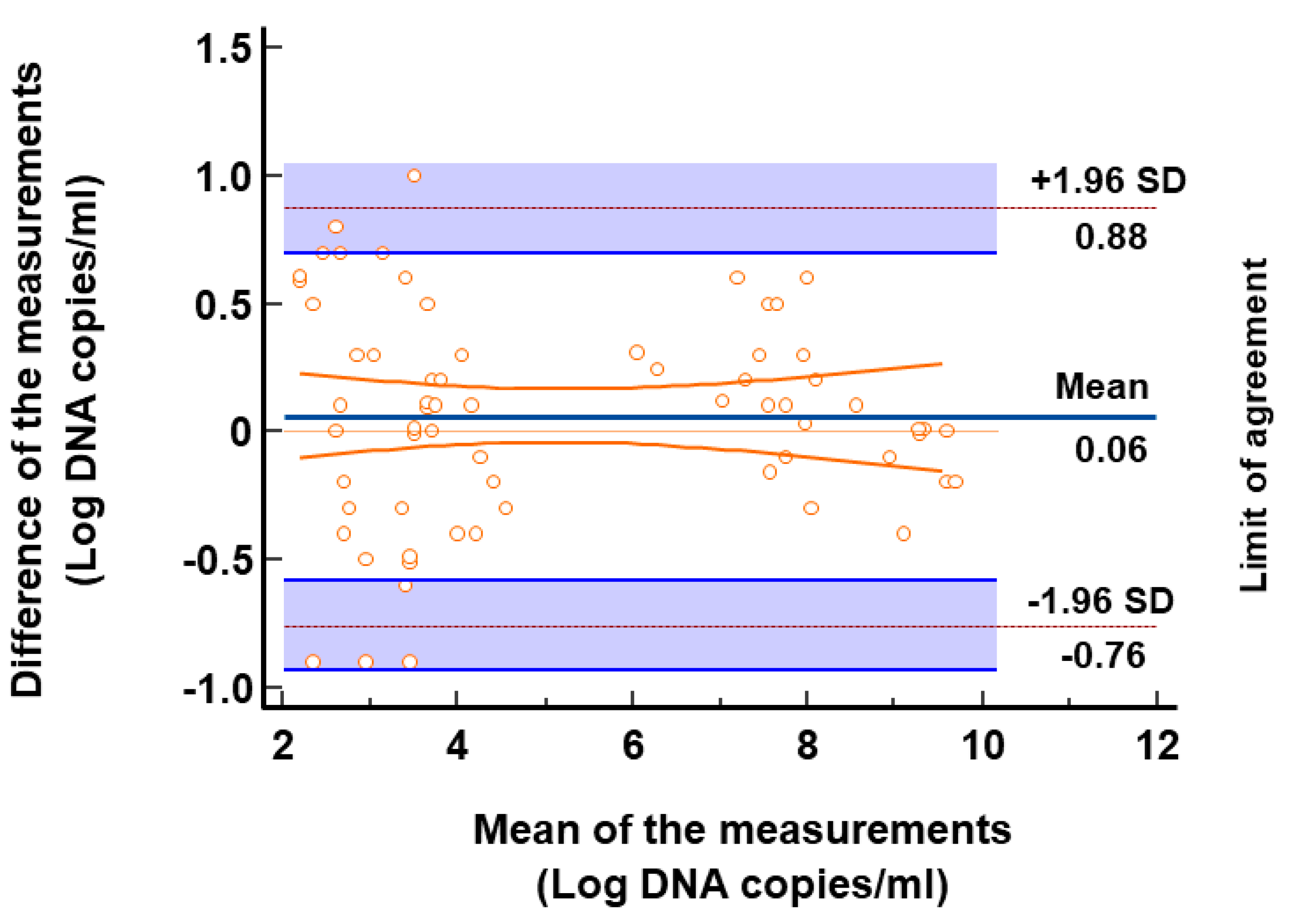
3.4. Comparison of TTV Detection and Quantification of Clinical Samples
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Focosi, D.; Antonelli, G.; Pistello, M.; Maggi, F. Torquetenovirus: The human virome from bench to bedside. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redondo, N.; Navarro, D.; Aguado, J.M.; Fernández-Ruiz, M. Viruses, friends, and foes: The case of Torque Teno Virus and the net state of immunosuppression. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2022, 24, e13778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EGore, J.; Gard, L.; Niesters, H.G.M.; Van Leer Buter, C.C. Understanding torquetenovirus (TTV) as an immune marker. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1168400. [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa, T.; Okamoto, H.; Konishi, K.; Yoshizawa, H.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mayumi, M. A novel DNA virus (TTV) associated with elevated transaminase levels in posttransfusion hepatitis of unknown etiology. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 241, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczorowska, J.; van der Hoek, L. Human anelloviruses: Diverse, omnipresent and commensal members of the virome. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbaghian, M.; Gheitasi, H.; Shekarchi, A.A.; Tavakoli, A.; Poortahmasebi, V. The mysterious anelloviruses: Investigating its role in human diseases. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.J.; Keeler, E.L.; Bushman, F.D.; Collman, R.G. The enigmatic roles of Anelloviridae and Redondoviridae in humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2022, 55, 101248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cebriá-Mendoza, M.; Beamud, B.; Andreu-Moreno, I.; Arbona, C.; Larrea, L.; Díaz, W.; Sanjuán, R.; Cuevas, J.M. Human anelloviruses: Influence of demographic factors, recombination, and worldwide diversity. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0492822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, E.; Giménez, E.; Hernani, R.; Piñana, J.L.; Solano, C.; Navarro, D. Torque Teno Virus DNA load in blood as an immune status biomarker in adult hematological patients: The state of the art and future prospects. Viruses 2024, 16, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczaj, A.; Przybyłowski, P.; Hrapkowicz, T. Torque Teno Virus (TTV)-a potential marker of immunocompetence in solid organ recipients. Viruses 2023, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esser, P.L.; Quintanares, G.H.R.; Langhans, B.; Heger, E.; Böhm, M.; Jensen, B.O.; Esser, S.; Lübke, N.; Fätkenheuer, G.; Lengauer, T.; et al. Torque Teno Virus load is associated with CDC stage and CD4+ cell count in people living with HIV but unrelated to AIDS-defining events and human Pegivirus load. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 17, jiae014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupenthal, F.; Bond, G. Torque Teno viral plasma load for immunologic monitoring in solid organ transplantation: One step further. Transplantation 2023, 107, e326–e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benning, L.; Reineke, M.; Bundschuh, C.; Klein, J.A.F.; Kühn, T.; Zeier, M.; Bartenschlager, R.; Schnitzler, P.; Morath, C.; Speer, C. Quantification of Torque Teno Virus load to monitor short-term changes in immunosuppressive therapy in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation 2023, 107, e363–e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minosse, C.; Matusali, G.; Meschi, S.; Grassi, G.; Francalancia, M.; D’Offizi, G.; Spezia, P.G.; Garbuglia, A.R.; Montalbano, M.; Focosi, D.; et al. Torquetenovirus loads in peripheral blood predict both the humoral and cell-mediated responses to SARS-CoV-2 elicited by the mRNA vaccine in liver transplant recipients. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaksch, P.; Görzer, I.; Puchhammer-Stöckl, E.; Bond, G. Integrated immunologic monitoring in solid organ transplantation: The road toward Torque Teno Virus-guided immunosuppression. Transplantation 2022, 106, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezahosseini, O.; Drabe, C.H.; Sørensen, S.S.; Rasmussen, A.; Perch, M.; Ostrowski, S.R.; Nielsen, S.D. Torque-Teno virus viral load as a potential endogenous marker of immune function in solid organ transplantation. Transplant. Rev. 2019, 33, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, F.; Pifferi, M.; Fornai, C.; Andreoli, E.; Tempestini, E.; Vatteroni, M.L.; Presciuttini, S.; Marchi, S.; Pietrobelli, A.; Boner, A.; et al. TT virus in the nasal secretions of children with acute respiratory diseases: Relations to viremia and disease severity. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 2418–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macera, L.; Spezia, P.G.; Medici, C.; Rofi, E.; Del Re, M.; Focosi, D.; Mazzetti, P.; Navarro, D.; Antonelli, G.; Danesi, R.; et al. Comparative evaluation of molecular methods for the quantitative measure of torquetenovirus viremia, the new surrogate marker of immune competence. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IGörzer, I.; Haupenthal, F.; Maggi, F.; Gelas, F.; Kulifaj, D.; Brossault, L.; Puchhammer-Stöckl, E.; Bond, G. Validation of plasma Torque Teno viral load applying a CE-certified PCR for risk stratification of rejection and infection post kidney transplantation. J. Clin. Virol. 2023, 158, 105348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, F.; Bendinelli, M. Immunobiology of the Torque teno viruses and other anelloviruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 331, 65–90. [Google Scholar]
- Timmerman, A.L.; Schönert, A.L.M.; van der Hoek, L. Anelloviruses versus human immunity: How do we control these viruses? FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 48, fuae005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regele, F.; Haupenthal, F.; Doberer, K.; Görzer, I.; Kapps, S.; Strassl, R.; Bond, G. The kinetics of Torque Teno virus plasma load following calcineurin inhibitor dose change in kidney transplant recipients. J. Med. Virol. 2024, 96, e29554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzaquén, A.; Giménez, E.; Iacoboni, G.; Guerreiro, M.; Hernani, R.; Albert, E.; Carpio, C.; Balaguer, A.; Pérez, A.; de la Asunción, C.S.; et al. Torque Teno Virus plasma DNA load: A novel prognostic biomarker in CAR-T therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024, 59, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eibensteiner, F.; Messner, I.; Uhl, P.; Bond, G.; Puchhammer-Stoeckl, E.; Mueller-Sacherer, T.; Aufricht, C.; Rusai, K. The association of Torque Teno viral load with CMV and BKV infection in pediatric and adolescent kidney transplant patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2024, 172, 105673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, F.; Focosi, D.; Statzu, M.; Bianco, G.; Costa, C.; Macera, L.; Spezia, P.G.; Medici, C.; Albert, E.; Navarro, D.; et al. Early post-transplant Torquetenovirus viremia predicts Cytomegalovirus reactivations in solid organ transplant recipients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haupenthal, F.; Rahn, J.; Maggi, F.; Gelas, F.; Bourgeois, P.; Hugo, C.; Jilma, B.; Böhmig, G.A.; Herkner, H.; Wolzt, M.; et al. TTVguideTX consortium partners. A multicentre, patient- and assessor-blinded, non-inferiority, randomised and controlled phase II trial to compare standard and torque teno virus-guided immunosuppression in kidney transplant recipients in the first year after transplantation: TTVguideIT. Trials 2023, 24, 213. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Gea-Banacloche, J.; Heilman, R.L.; Yaman, R.N.; Me, H.M.; Zhang, N.; Vikram, H.R.; Kodali, L. Impact of early rejection treatment on infection development in kidney transplant recipients: A propensity analysis. J. Transplant. 2024; 2024, 6663086. [Google Scholar]
- de Castro Rodrigues Ferreira, F.; Cristelli, M.P.; Paula, M.I.; Proença, H.; Felipe, C.R.; Tedesco-Silva, H.; Medina-Pestana, J.O. Infectious complications as the leading cause of death after kidney transplantation: Analysis of more than 10,000 transplants from a single center. J. Nephrol. 2017, 30, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PCR Reagents Concentration | TTV |
|---|---|
| Water | – |
| 1 M KCl (Hologic®) | 50 mM |
| 1 M MgCl2 (Hologic®) | 4 mM |
| 1 M Tris, pH 8.0 (Hologic®) | 10 mM |
| Forward Primer | 1 µM |
| Reverse Primer | 1 µM |
| Probe | 0.3 µM |
| Internal Control Primer (Hologic®) | 0.6 µM |
| Internal Control Probe (Hologic®) | 0.6 µM |
| PCR cycling conditions | Temperature—Time |
| 1 | 95 °C—2 min |
| 2 | 95 °C—8 s |
| 3 | 55 °C—28 s |
| 4 | Repeat steps 2–3 for a total of 45 cycles |
| TTV DNA Plasmid Concentrations (Log Copies/mL) | No. Detected/Replicates | % Detected |
|---|---|---|
| 10.2 | 20/20 | 100% |
| 9.2 | 20/20 | 100% |
| 8.2 | 20/20 | 100% |
| 7.2 | 20/20 | 100% |
| 6.2 | 20/20 | 100% |
| 5.2 | 20/20 | 100% |
| 4.2 | 20/20 | 100% |
| 3.2 | 20/20 | 100% |
| 2.2 | 20/20 | 100% |
| 1.9 | 20/20 | 100% |
| 1.6 | 19/20 | 95% |
| 1.3 | 12/20 | 60% |
| 1.0 | 9/20 | 45% |
| 0.7 | 5/20 | 25% |
| 0.4 | 0/20 | 0% |
| Manual TTV Assay (Mean of 2 Manual rt-PCR Assays) | No. Examined | TTV DNA with Automatic TTV Assay | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Negative (No./Percentage) | Positive (No./Percentage) | ||
| Negative | 29 | 29 (100) | 0 (0) |
| Positive | 83 | 8 (10) | 75 (90) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spezia, P.G.; Carletti, F.; Novazzi, F.; Specchiarello, E.; Genoni, A.; Drago Ferrante, F.; Minosse, C.; Matusali, G.; Mancini, N.; Focosi, D.; et al. Torquetenovirus Viremia Quantification Using Real-Time PCR Developed on a Fully Automated, Random-Access Platform. Viruses 2024, 16, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060963
Spezia PG, Carletti F, Novazzi F, Specchiarello E, Genoni A, Drago Ferrante F, Minosse C, Matusali G, Mancini N, Focosi D, et al. Torquetenovirus Viremia Quantification Using Real-Time PCR Developed on a Fully Automated, Random-Access Platform. Viruses. 2024; 16(6):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060963
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpezia, Pietro Giorgio, Fabrizio Carletti, Federica Novazzi, Eliana Specchiarello, Angelo Genoni, Francesca Drago Ferrante, Claudia Minosse, Giulia Matusali, Nicasio Mancini, Daniele Focosi, and et al. 2024. "Torquetenovirus Viremia Quantification Using Real-Time PCR Developed on a Fully Automated, Random-Access Platform" Viruses 16, no. 6: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060963
APA StyleSpezia, P. G., Carletti, F., Novazzi, F., Specchiarello, E., Genoni, A., Drago Ferrante, F., Minosse, C., Matusali, G., Mancini, N., Focosi, D., Antonelli, G., Girardi, E., & Maggi, F. (2024). Torquetenovirus Viremia Quantification Using Real-Time PCR Developed on a Fully Automated, Random-Access Platform. Viruses, 16(6), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16060963








