Identification and Characterization of a Novel B Cell Epitope of ASFV Virulence Protein B125R Monoclonal Antibody
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Immune Serums
2.3. pB125R Prokaryotic Expression Vector Construction
2.4. pB125R Protein Expression and Purification
2.5. Production of mAbs against the ASFV pB125R Protein
2.6. Indirect ELISA
2.7. Western Blotting
2.8. Immunofluorescence Assay (IFA)
2.9. Antigenic Epitope Identification
2.10. Bioinformatic Analysis of the pB125R Protein
2.11. Immunogenicity of the Epitope of pB125R
2.12. Flow Cytometry
3. Results
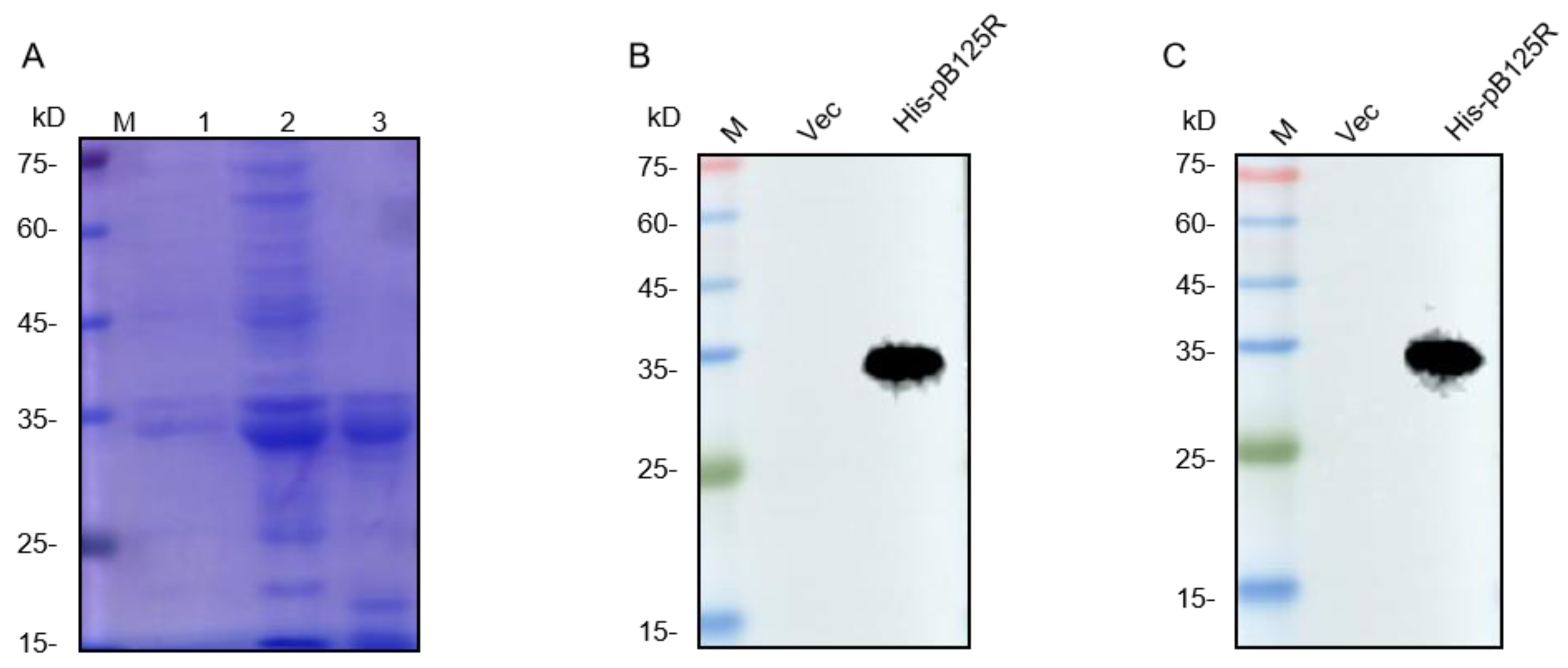
3.1. The Expression and Purification of ASFV pB125R Recombinant Protein
3.2. Antibody Titers of the Serum from Mice Immunized with pB125R Protein
3.3. Preparation and Identification of mAbs against the pB125R Recombinant Protein
3.4. Mapping mAb 9G11epitopes
3.5. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Epitope in Different ASFV Strains
3.6. Verification of the Epitope Immunoactivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ge, S.; Li, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, F.; Li, L.; Wang, Q.; Ren, W.; Bao, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; et al. Molecular Characterization of African Swine Fever Virus, China, 2018. Emerg Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2131–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, V.R.; Bevins, S.N. A Review of Classical Swine Fever Virus and Routes of Introduction into the United States and the Potential for Virus Establishment. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.-g.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ai, X.; Feng, X.-N.; Hu, W.; Zhang, X.-F.; Zhao, D.-M.; Bu, Z.-G.; He, X.-J. Viricidal activity of several disinfectants against African swine fever virus. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 3084–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L.K.; Stahl, K.; Jori, F.; Vial, L.; Pfeiffer, D.U. African Swine Fever Epidemiology and Control. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2020, 8, 221–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, D.Y.; Nah, J.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, J.Y.; Sohn, H.J.; Choi, J.G.; et al. Outbreak of African swine fever in South Korea, 2019. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2020, 67, 473–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.T.T.; Truong, A.D.; Ly, D.V.; Vu, T.H.; Hoang, V.T.; Nguyen, T.C.; Chu, T.N.; Nguyen, T.H.; Pham, N.T.; Nguyen, T.; et al. Genetic Characterisation of African Swine Fever Virus in Outbreaks in Ha Nam Province, Red River Delta Region of Vietnam, and Activity of Antimicrobial Products Against Virus Infection in Contaminated Feed. J. Vet. Res. 2020, 64, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Gao, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Bu, Z.; Rao, Z.; et al. Architecture of African swine fever virus and implications for viral assembly. Science 2019, 366, 640–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, D.A.G.; Tcherepanov, V.; Upton, C.; Dixon, L.K. Comparison of the genome sequences of non-pathogenic and pathogenic African swine fever virus isolates. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cackett, G.; Portugal, R.; Matelska, D.; Dixon, L.; Werner, F. African Swine Fever Virus and Host Response: Transcriptome Profiling of the Georgia 2007/1 Strain and Porcine Macrophages. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0193921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shi, X.-J.; Sun, H.-W.; Chen, H.-J. Insights into African swine fever virus immunoevasion strategies. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.-F.; Wang, M.; Shi, Z.-B.; Sun, Z.-Z.; Wei, L.-L.; Liu, Z.-S.; Wang, S.-D.; He, X.-J.; Wang, J.-F. Development of a recombinant pB602L-based indirect ELISA assay for detecting antibodies against African swine fever virus in pigs. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudreault, N.N.; Richt, J.A. Subunit Vaccine Approaches for African Swine Fever Virus. Vaccines 2019, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, H.C.; Glas, P.S.; Schumann, K.R. Diagnostic specificity of the African swine fever virus antibody detection enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in feral and domestic pigs in the United States. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1665–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovan, V.; Murgia, M.V.; Wu, P.; Lowe, A.D.; Jia, W.; Rowland, R.R.R. Epitope mapping of African swine fever virus (ASFV) structural protein, p54. Virus Res. 2020, 279, 197871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazakova, A.S.; Imatdinov, I.R.; Dubrovskaya, O.A.; Imatdinov, A.R.; Sidlik, M.V.; Balyshev, V.M.; Krasochko, P.A.; Sereda, A.D. Recombinant Protein p30 for Serological Diagnosis of African Swine Fever by Immunoblotting Assay. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1479–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epifano, C.; Krijnse-Locker, J.; Salas, M.L.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Salas, J. The African swine fever virus nonstructural protein pB602L is required for formation of the icosahedral capsid of the virus particle. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 12260–12270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Z.; Du, Y.; Li, R.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Fan, L.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Ding, P.; et al. Development and characterization of monoclonal antibody against the critical loop structure of african swine fever virus P72 protein. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 283, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, C.; Reis, A.L.; Kalema-Zikusoka, G.; Malta, J.; Soler, A.; Blanco, E.; Parkhouse, R.M.; Leitão, A. Recombinant antigen targets for serodiagnosis of African swine fever. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2009, 16, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borca, M.V.; Ramirez-Medina, E.; Silva, E.; Vuono, E.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Holinka, L.G.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Zhu, J.; Gladue, D.P. Development of a Highly Effective African Swine Fever Virus Vaccine by Deletion of the I177L Gene Results in Sterile Immunity against the Current Epidemic Eurasia Strain. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e02017-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmink, J.D.; Khazalwa, E.M.; Abkallo, H.M.; Oduor, B.; Khayumbi, J.; Svitek, N.; Henson, S.P.; Blome, S.; Keil, G.; Bishop, R.P.; et al. Deletion of the CD2v Gene from the Genome of ASFV-Kenya-IX-1033 Partially Reduces Virulence and Induces Protection in Pigs. Viruses 2022, 14, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuono, E.; Ramirez-Medina, E.; Silva, E.; Rai, A.; Pruitt, S.; Espinoza, N.; Valladares, A.; Velazquez-Salinas, L.; Gladue, D.P.; Borca, M.V. Deletion of the H108R Gene Reduces Virulence of the Pandemic Eurasia Strain of African Swine Fever Virus with Surviving Animals Being Protected against Virulent Challenge. J. Virol. 2022, 96, e0054522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, X.; Yue, H.; et al. Deletion of the B125R gene in the African swine fever virus SY18 strain leads to an A104R frameshift mutation slightly attenuating virulence in domestic pigs. Virus Res. 2024, 343, 199343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Jiang, D.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Shi, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, B.; Ji, P.; Zhang, G. Identification of Two Novel Linear B Cell Epitopes on the CD2v Protein of African Swine Fever Virus Using Monoclonal Antibodies. Viruses 2022, 15, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Yang, S.; Shao, J.; Zhou, G.; Ma, Y.; Wen, S.; Hou, Z.; Peng, D.; Guo, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Identification of p72 epitopes of African swine fever virus and preliminary application. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1126794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Wang, M.; Zhou, L.; Tian, P.; Sun, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, G.; Jiang, D.; Wu, Y.; et al. A candidate nanoparticle vaccine comprised of multiple epitopes of the African swine fever virus elicits a robust immune response. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Title | Primers | Sequences (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| pB125R | F | ATCGGATCCGAATTCATGGCGGTTTATGCG |
| R | GTGGTGGTGCTCGAGTCTAGACTCTAAAAATT |
| Segment | Sequences (5′-3′) | Positions (Amino Acid) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| pB125R-1 | F | ATCGGATCCGAATTCATGGCGGTTTATGCG | 1-40AA |
| R | GTGGTGGTGCTCGAGATACACCAAAAAGTT | ||
| pB125R-2 | F | GTGGTGGTGCTCGAGATACACCAAAAAGTT | 31-70AA |
| R | GTGGTGGTGCTCGAGCTCCTCGAGGCTTTT | ||
| pB125R-3 | F | ATCGGATCCGAATTCTACTATGCCATCATA | 61-100AA |
| R | GTGGTGGTGCTCGAGTTTGTTTATCTCAAT | ||
| PB125R-4 | F | ATCGGATCCGAATTCAAAAAAATACAATCC | 91-125AA |
| R | GTGGTGGTGCTCGAGTCTAGACTCTAAAAA | ||
| pB125R-2-1 | F | AATTCAACTTTTTGGTGTATGAACTACCTGCCCCTTTTGACTTTTCCTCCC | 36-50AA |
| R | TCGAGGGAGGAAAAGTCAAAAGGGGCAGGTAGTTCATACACCAAAAAGTTG | ||
| pB125R-2-2 | F | AATTCGAACTACCTGCCCCTTTTGACTTTTCCTCCGGCGACCCTTTGGCCC | 41-55AA |
| R | TCGAGGGCCAAAGGGTCGCCGGAGGAAAAGTCAAAAGGGGCAGGTAGTTCG | ||
| pB125R-2-3 | F | AATTCTTTGACTTTTCCTCCGGCGACCCTTTGGCCAGTCAGCGCGACATAC | 46-60AA |
| R | TCGAGTATGTCGCGCTGACTGGCCAAAGGGTCGCCGGAGGAAAAGTCAAAG | ||
| pB125R-2-4 | F | AATTCGGCGACCCTTTGGCCAGTCAGCGCGACATATACTATGCCATCATAC | 51-65AA |
| R | TCGAGTATGATGGCATAGTATATGTCGCGCTGACTGGCCAAAGGGTCGCCG | ||
| pB125R-2-5 | F | AATTCGACCCTTTGGCCAGTCAGCGCGACATATACTATGCCATCC | 52-64AA |
| R | TCGAGGATGGCATAGTATATGTCGCGCTGACTGGCCAAAGGGTCG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-1 | F | AATTCCCTTTGGCCAGTCAGCGCGACATATACTATGCCATCC | 53-64AA |
| R | TCGAGGATGGCATAGTATATGTCGCGCTGACTGGCCAAAGGG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-2 | F | AATTCTTGGCCAGTCAGCGCGACATATACTATGCCATCC | 54-64AA |
| R | TCGAGGATGGCATAGTATATGTCGCGCTGACTGGCCAAG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-3 | F | AATTCGCCAGTCAGCGCGACATATACTATGCCATCC | 55-64AA |
| R | TCGAGGATGGCATAGTATATGTCGCGCTGACTGGCG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-4 | F | AATTCAGTCAGCGCGACATATACTATGCCATCC | 56-64AA |
| R | TCGAGGATGGCATAGTATATGTCGCGCTGACTG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-5 | F | AATTCCAGCGCGACATATACTATGCCATCC | 57-64AA |
| R | TCGAGGATGGCATAGTATATGTCGCGCTGG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-6 | F | AATTCCGCGACATATACTATGCCATCC | 58-64AA |
| R | TCGAGGATGGCATAGTATATGTCGCGG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-7 | F | AATTCGACATATACTATGCCATCC | 59-64AA |
| R | TCGAGGATGGCATAGTATATGTCG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-8 | F | AATTCATATACTATGCCATCC | 60-64AA |
| R | TCGAGGATGGCATAGTATATG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-9 | F | AATTCGACCCTTTGGCCAGTCAGCGCGACATATACTATGCCC | 52-63AA |
| R | TCGAGGGCATAGTATATGTCGCGCTGACTGGCCAAAGGGTCG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-10 | F | AATTCGACCCTTTGGCCAGTCAGCGCGACATATACTATC | 52-62AA |
| R | TCGAGATAGTATATGTCGCGCTGACTGGCCAAAGGGTCG | ||
| pB125R-2-5-11 | F | AATTCGACCCTTTGGCCAGTCAGCGCGACATATACC | 52-61AA |
| R | TCGAGGTATATGTCGCGCTGACTGGCCAAAGGGTCG | ||
| Title | Amino Acid Sequence | |
|---|---|---|
| pB125R-1 | MAVYAKDLDNNKELNQKLINDQLKIIDTLLLAEKKNFLVY | 1-40AA |
| pB125R-2 | LAEKKNFLVYELPAPFDFSSGDPLASQRDIYYAIIKSLEE | 31-70AA |
| pB125R-3 | YYAIIKSLEERGFTVKICMKGDRALLFITWKKIQSIEINK | 61-100AA |
| PB125R-4 | KKIQSIEINKKEEYLRMHFIQDEEKAFYCKFLESR | 91-125AA |
| pB125R-2-1 | NFLVYELPAPFDFSS | 36-50AA |
| pB125R-2-2 | ELPAPFDFSSGDPLA | 41-55AA |
| pB125R-2-3 | FDFSSGDPLASQRDI | 46-60AA |
| pB125R-2-4 | GDPLASQRDIYYAII | 51-65AA |
| pB125R-2-5 | DPLASQRDIYYAI | 52-64AA |
| pB125R-2-5-1 | PLASQRDIYYAI | 53-64AA |
| pB125R-2-5-2 | LASQRDIYYAI | 54-64AA |
| pB125R-2-5-3 | ASQRDIYYAI | 55-64AA |
| pB125R-2-5-4 | SQRDIYYAI | 56-64AA |
| pB125R-2-5-5 | QRDIYYAI | 57-64AA |
| pB125R-2-5-6 | RDIYYAI | 58-64AA |
| pB125R-2-5-7 | DIYYAI | 59-64AA |
| pB125R-2-5-8 | IYYAI | 60-64AA |
| pB125R-2-5-9 | DPLASQRDIYYA | 52-63AA |
| pB125R-2-5-10 | DPLASQRDIYY | 52-62AA |
| pB125R-2-5-11 | DPLASQRDIY | 52-61AA |
| Accession Number | Title | Country | Collection Date | Lengths of pB125R(AA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MK128995.1 | ASFV China/2018/AnhuiXCGQ | China | 2021 | 125 |
| FR682468.2 | ASFV Georgia 2007 | UK | 2020 | 125 |
| LR536725.1 | ASFV Belgium 2018 | Germany | 2019 | 125 |
| ON456300.2 | ASFV China/Yangzhou | China | 2023 | 125 |
| LR899193.1 | ASFV Germany 2020 | Germany | 2020 | 125 |
| MW049116.1 | ASFV Korea/2019 | Korea | 2022 | 125 |
| OP856591.1 | China/LN/2018 | China | 2023 | 125 |
| MT748042.2 | ASFV/Korea/2019 | Korea | 2023 | 125 |
| MN715134.1 | ASFV_HU_2018 | Hungary | 2021 | 125 |
| ON380539.1 | HB03A | China | 2022 | 125 |
| MN393476.1 | ASFV Wuhan 2019 | China | 2020 | 125 |
| OP605386.1 | 20355/RM/2022_Italy | Italy | 2023 | 125 |
| MZ614662.1 | CADC_HN09 | China | 2021 | 125 |
| MW396979.1 | ASFV/Timor-Leste/2019 | Australia | 2022 | 125 |
| LS478113.1 | Estonia 2014 | Germany | 2018 | 125 |
| ON409979.1 | TAN/17/Kibaha | Tanzania | 2023 | 125 |
| LR813622.1 | Tanzania/Rukwa/2017 | Kenya | 2020 | 125 |
| MT180393.1 | ASFV_NgheAn_2019 | S. Korea | 2021 | 125 |
| MH681419.1 | ASFV/POL/2015/Podlaskie | Denmark | 2019 | 125 |
| MW788407.1 | 31479_2005 | Italy | 2021 | 125 |
| MZ202520.1 | K49 | Russia | 2021 | 125 |
| ON075797.1 | Korea/YC1/2019 | Korea | 2022 | 125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Ren, H.; Lin, Z.; Shi, S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S.; He, W.-R.; Wan, B.; Hu, M.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a Novel B Cell Epitope of ASFV Virulence Protein B125R Monoclonal Antibody. Viruses 2024, 16, 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081257
Zhao Y, Ren H, Lin Z, Shi S, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Han S, He W-R, Wan B, Hu M, et al. Identification and Characterization of a Novel B Cell Epitope of ASFV Virulence Protein B125R Monoclonal Antibody. Viruses. 2024; 16(8):1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081257
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yanyan, Haojie Ren, Zhizhao Lin, Saiyan Shi, Biao Zhang, Yuhang Zhang, Shichong Han, Wen-Rui He, Bo Wan, Man Hu, and et al. 2024. "Identification and Characterization of a Novel B Cell Epitope of ASFV Virulence Protein B125R Monoclonal Antibody" Viruses 16, no. 8: 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081257
APA StyleZhao, Y., Ren, H., Lin, Z., Shi, S., Zhang, B., Zhang, Y., Han, S., He, W.-R., Wan, B., Hu, M., & Zhang, G.-P. (2024). Identification and Characterization of a Novel B Cell Epitope of ASFV Virulence Protein B125R Monoclonal Antibody. Viruses, 16(8), 1257. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081257






