Chromatin Regulator SMARCA4 Is Essential for MHV-Induced Inflammatory Cell Death, PANoptosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Hepatitis Virus (MHV) Culture
2.2. CRISPR Screen Analysis
2.3. Cas9-iBMDM Culture and Infection
2.4. Cell Death Analysis
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. Quantitative PCR
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
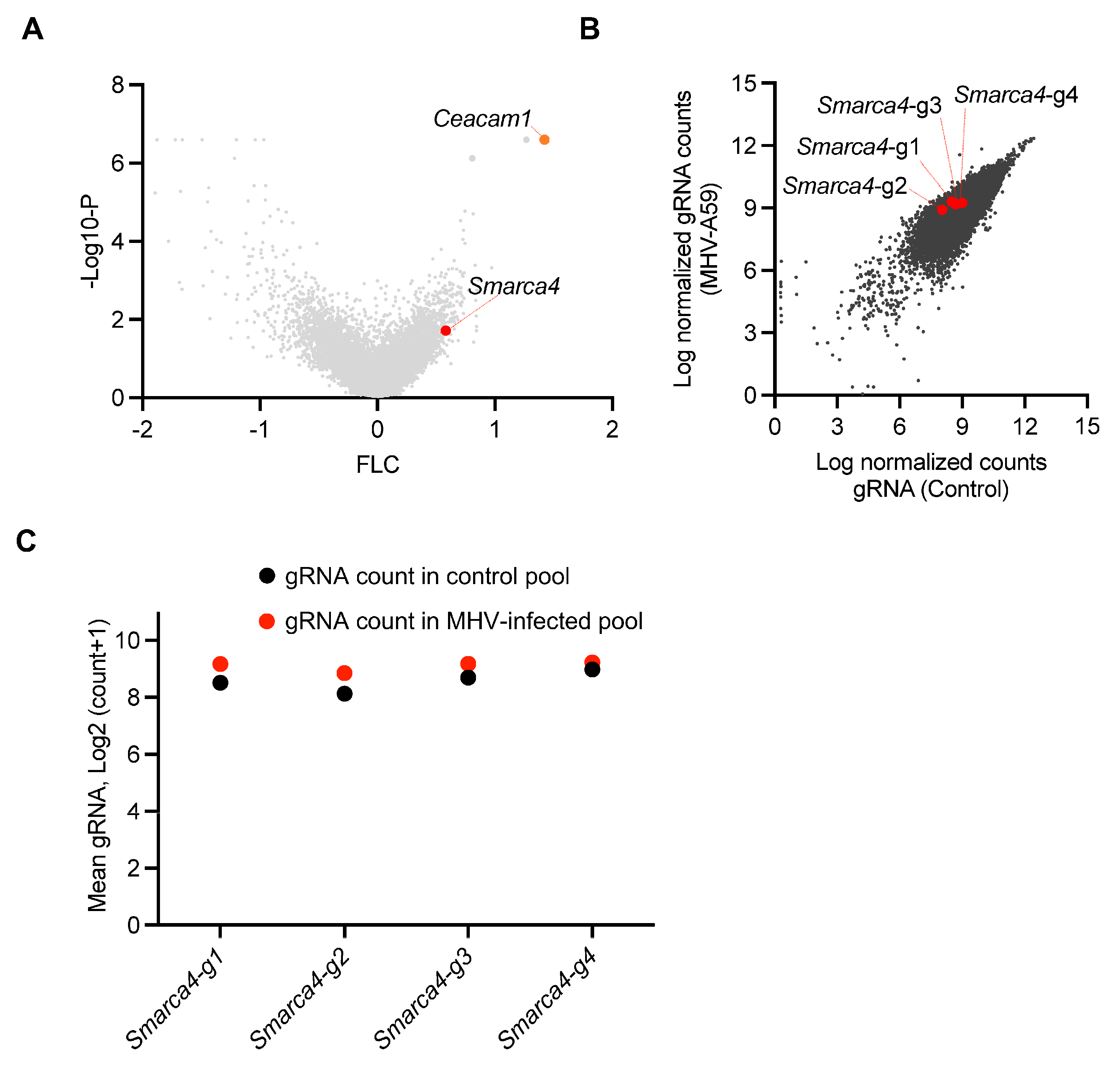
3.1. A Genome-Wide CRISPR Screen for Regulators of MHV-Induced Cell Death Identifies Critical Host Genes in β-CoV Infection
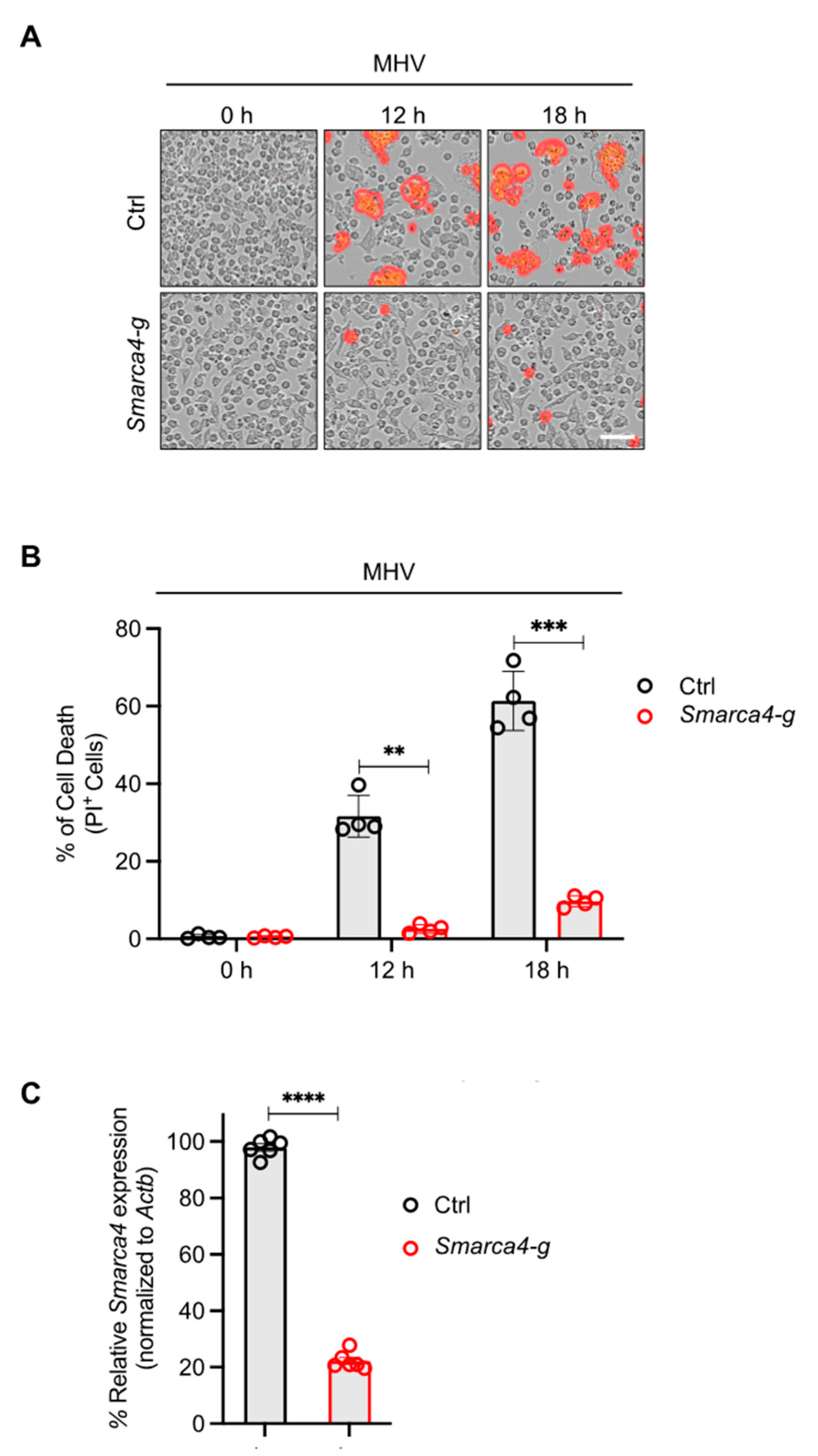
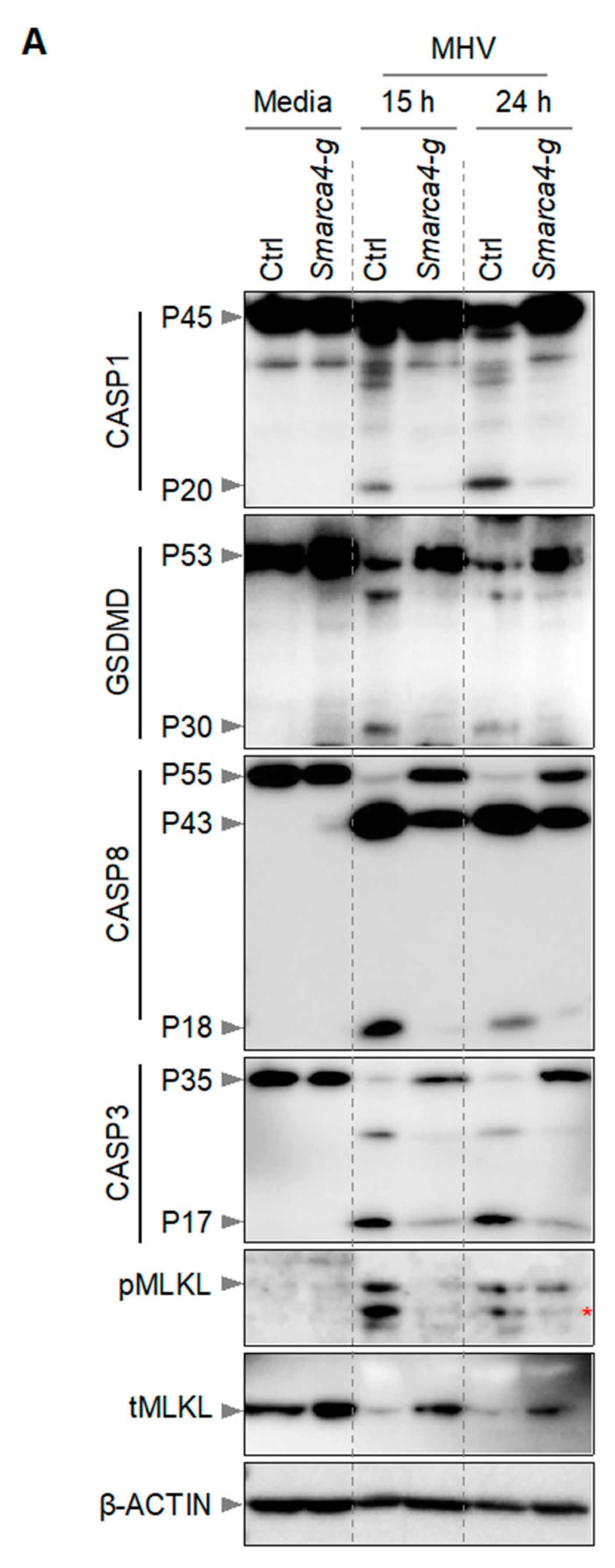
3.2. SMARCA4 Is a Regulator of MHV-Induced Inflammatory Cell Death
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanneganti, T.D. Intracellular innate immune receptors: Life inside the cell. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 297, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Williams, E.P.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Karki, R.; Banoth, B.; Burton, A.; Webby, R.; Channappanavar, R.; Jonsson, C.B.; Kanneganti, T.D. Impaired NLRP3 inflammasome activation/pyroptosis leads to robust inflammatory cell death via caspase-8/RIPK3 during coronavirus infection. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14040–14052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, M.S.; Kanneganti, T.D. Innate immunity: The first line of defense against SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Made, C.I.; Simons, A.; Schuurs-Hoeijmakers, J.; van den Heuvel, G.; Mantere, T.; Kersten, S.; van Deuren, R.C.; Steehouwer, M.; van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Jaeger, M.; et al. Presence of Genetic Variants Among Young Men With Severe COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellinghaus, D.; Degenhardt, F.; Bujanda, L.; Buti, M.; Albillos, A.; Invernizzi, P.; Fernández, J.; Prati, D.; Baselli, G.; Asselta, R.; et al. Genomewide Association Study of Severe COVID-19 with Respiratory Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte-Schrepping, J.; Reusch, N.; Paclik, D.; Baßler, K.; Schlickeiser, S.; Zhang, B.; Krämer, B.; Krammer, T.; Brumhard, S.; Bonaguro, L.; et al. Severe COVID-19 Is Marked by a Dysregulated Myeloid Cell Compartment. Cell 2020, 182, 1419–1440.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, R.L.; Lukassen, S.; Trump, S.; Hennig, B.P.; Wendisch, D.; Pott, F.; Debnath, O.; Thürmann, L.; Kurth, F.; Völker, M.T.; et al. COVID-19 severity correlates with airway epithelium-immune cell interactions identified by single-cell analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, R.; Kanneganti, T.D. The ‘cytokine storm’: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic prospects. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 681–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, R.; Sharma, B.R.; Tuladhar, S.; Williams, E.P.; Zalduondo, L.; Samir, P.; Zheng, M.; Sundaram, B.; Banoth, B.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; et al. Synergism of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma Triggers Inflammatory Cell Death, Tissue Damage, and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cytokine Shock Syndromes. Cell 2021, 184, 149–168.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, Y.; Ramón-Luing, L.A.; Ruiz, A.; García-Martínez, A.; Sánchez-Monciváis, A.; Barreto-Rodríguez, O.; Falfán-Valencia, R.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Medina-Quero, K.; Buendia-Roldan, I.; et al. COVID-19 patients with high TNF/IFN-γ levels show hallmarks of PANoptosis, an inflammatory cell death. Microbes Infect. 2023, 25, 105179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Song, W.; Reheman, H.; Wang, D.; Qu, J.; Li, Y. PANoptosis, an indicator of COVID-19 severity and outcomes. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbae124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, R.; Lee, S.; Mall, R.; Pandian, N.; Wang, Y.; Sharma, B.R.; Malireddi, R.S.; Yang, D.; Trifkovic, S.; Steele, J.A.; et al. ZBP1-dependent inflammatory cell death, PANoptosis, and cytokine storm disrupt IFN therapeutic efficacy during coronavirus infection. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabo6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandeya, A.; Kanneganti, T.D. Therapeutic potential of PANoptosis: Innate sensors, inflammasomes, and RIPKs in PANoptosomes. Trends Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandian, N.; Kanneganti, T.D. PANoptosis: A Unique Innate Immune Inflammatory Cell Death Modality. J. Immunol. 2022, 209, 1625–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Gullett, J.M.; Tweedell, R.E.; Kanneganti, T.D. Innate immune inflammatory cell death: PANoptosis and PANoptosomes in host defense and disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2250235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukens, J.R.; Gurung, P.; Vogel, P.; Johnson, G.R.; Carter, R.A.; McGoldrick, D.J.; Bandi, S.R.; Calabrese, C.R.; Vande Walle, L.; Lamkanfi, M.; et al. Dietary modulation of the microbiome affects autoinflammatory disease. Nature 2014, 516, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullett, J.M.; Tweedell, R.E.; Kanneganti, T.D. It’s All in the PAN: Crosstalk, Plasticity, Redundancies, Switches, and Interconnectedness Encompassed by PANoptosis Underlying the Totality of Cell Death-Associated Biological Effects. Cells 2022, 11, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malireddi, R.K.S.; Kesavardhana, S.; Karki, R.; Kancharana, B.; Burton, A.R.; Kanneganti, T.D. RIPK1 Distinctly Regulates Yersinia-Induced Inflammatory Cell Death, PANoptosis. Immunohorizons 2020, 4, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karki, R.; Sundaram, B.; Sharma, B.R.; Lee, S.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Nguyen, L.N.; Christgen, S.; Zheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Samir, P.; et al. ADAR1 restricts ZBP1-mediated immune response and PANoptosis to promote tumorigenesis. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, B.; Pandian, N.; Mall, R.; Wang, Y.; Sarkar, R.; Kim, H.J.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Karki, R.; Janke, L.J.; Vogel, P.; et al. NLRP12-PANoptosome activates PANoptosis and pathology in response to heme and PAMPs. Cell 2023, 186, 2783–2801.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Karki, R.; Wang, Y.Q.; Nguyen, L.N.; Kalathur, R.C.; Kanneganti, T.D. AIM2 forms a complex with pyrin and ZBP1 to drive PANoptosis and host defence. Nature 2021, 597, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malireddi, R.K.S.; Bynigeri, R.R.; Mall, R.; Connelly, J.P.; Pruett-Miller, S.M.; Kanneganti, T.D. Inflammatory cell death, PANoptosis, screen identifies host factors in coronavirus innate immune response as therapeutic targets. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, S.R.; Navas-Martin, S. Coronavirus pathogenesis and the emerging pathogen severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 635–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth-Cross, J.K.; Bender, S.J.; Weiss, S.R. Murine coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus is recognized by MDA5 and induces type I interferon in brain macrophages/microglia. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9829–9838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schickli, J.H.; Zelus, B.D.; Wentworth, D.E.; Sawicki, S.G.; Holmes, K.V. The murine coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 from persistently infected murine cells exhibits an extended host range. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 9499–9507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joung, J.; Konermann, S.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Platt, R.J.; Brigham, M.D.; Sanjana, N.E.; Zhang, F. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout and transcriptional activation screening. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 828–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Köster, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, C.H.; Xiao, T.; Liu, J.S.; Brown, M.; Liu, X.S. Quality control, modeling, and visualization of CRISPR screens with MAGeCK-VISPR. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, M.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, T.; Chen, C.H.; Wu, A.; Wu, F.; Traugh, N.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; et al. Integrative analysis of pooled CRISPR genetic screens using MAGeCKFlute. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 756–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malireddi, R.K.S.; Gurung, P.; Mavuluri, J.; Dasari, T.K.; Klco, J.M.; Chi, H.; Kanneganti, T.D. TAK1 restricts spontaneous NLRP3 activation and cell death to control myeloid proliferation. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doench, J.G.; Fusi, N.; Sullender, M.; Hegde, M.; Vaimberg, E.W.; Donovan, K.F.; Smith, I.; Tothova, Z.; Wilen, C.; Orchard, R.; et al. Optimized sgRNA design to maximize activity and minimize off-target effects of CRISPR-Cas9. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; She, Y.; Sun, Q.; Shi, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, D.C.; Shao, F. Pore-forming activity and structural autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature 2016, 535, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ruan, J.; Pan, Y.; Magupalli, V.G.; Wu, H.; Lieberman, J. Inflammasome-activated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature 2016, 535, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayagaki, N.; Stowe, I.B.; Lee, B.L.; O‘Rourke, K.; Anderson, K.; Warming, S.; Cuellar, T.; Haley, B.; Roose-Girma, M.; Phung, Q.T.; et al. Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical inflammasome signalling. Nature 2015, 526, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, K.; Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Cai, T.; Wang, F.; Shao, F. Cleavage of GSDMD by inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature 2015, 526, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sborgi, L.; Ruhl, S.; Mulvihill, E.; Pipercevic, J.; Heilig, R.; Stahlberg, H.; Farady, C.J.; Muller, D.J.; Broz, P.; Hiller, S. GSDMD membrane pore formation constitutes the mechanism of pyroptotic cell death. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 1766–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.N.; Kanneganti, T.D. PANoptosis in Viral Infection: The Missing Puzzle Piece in the Cell Death Field. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Ma, Z.; Xie, J.; Li, W.; Su, L.; Zhang, G.; Xu, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, W. The role of cell death in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riegler, A.N.; Benson, P.; Long, K.; Leal, S.M., Jr. Differential activation of programmed cell death in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuriakose, T.; Man, S.M.; Malireddi, R.K.; Karki, R.; Kesavardhana, S.; Place, D.E.; Neale, G.; Vogel, P.; Kanneganti, T.D. ZBP1/DAI is an innate sensor of influenza virus triggering the NLRP3 inflammasome and programmed cell death pathways. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.H.; Karki, R.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Mall, R.; Sarkar, R.; Sharma, B.R.; Klein, J.; Berns, H.; Pisharath, H.; Pruett-Miller, S.M.; et al. NINJ1 mediates inflammatory cell death, PANoptosis, and lethality during infection conditions and heat stress. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malireddi, R.K.S.; Gurung, P.; Kesavardhana, S.; Samir, P.; Burton, A.; Mummareddy, H.; Vogel, P.; Pelletier, S.; Burgula, S.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Innate immune priming in the absence of TAK1 drives RIPK1 kinase activity–independent pyroptosis, apoptosis, necroptosis, and inflammatory disease. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20191644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malireddi, R.K.S.; Karki, R.; Sundaram, B.; Kancharana, B.; Lee, S.; Samir, P.; Kanneganti, T.D. Inflammatory Cell Death, PANoptosis, Mediated by Cytokines in Diverse Cancer Lineages Inhibits Tumor Growth. Immunohorizons 2021, 5, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christgen, S.; Zheng, M.; Kesavardhana, S.; Karki, R.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Banoth, B.; Place, D.E.; Briard, B.; Sharma, B.R.; Tuladhar, S.; et al. Identification of the PANoptosome: A Molecular Platform Triggering Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis (PANoptosis). Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Karki, R.; Vogel, P.; Kanneganti, T.D. Caspase-6 Is a Key Regulator of Innate Immunity, Inflammasome Activation, and Host Defense. Cell 2020, 181, 674–687 e613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, B.; Pandian, N.; Kim, H.J.; Abdelaal, H.M.; Mall, R.; Indari, O.; Sarkar, R.; Tweedell, R.E.; Alonzo, E.Q.; Klein, J.; et al. NLRC5 senses NAD+ depletion, forming a PANoptosome and driving PANoptosis and inflammation. Cell 2024, 187, 4061–4077.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Mears, J.R.; Shakib, L.; Beynor, J.I.; Shanaj, S.; Korsunsky, I.; Nathan, A.; Donlin, L.T.; Raychaudhuri, S. IFN- γ and TNF- α drive a CXCL10 + CCL2 + macrophage phenotype expanded in severe COVID-19 and other diseases with tissue inflammation. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euskirchen, G.M.; Auerbach, R.K.; Davidov, E.; Gianoulis, T.A.; Zhong, G.; Rozowsky, J.; Bhardwaj, N.; Gerstein, M.B.; Snyder, M. Diverse roles and interactions of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex revealed using global approaches. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotter, K.W.; Archer, T.K. The BRG1 transcriptional coregulator. Nucl. Recept. Signal 2008, 6, e004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, P.D.; Pogany, J. The dependence of viral RNA replication on co-opted host factors. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 10, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Alfajaro, M.M.; DeWeirdt, P.C.; Hanna, R.E.; Lu-Culligan, W.J.; Cai, W.L.; Strine, M.S.; Zhang, S.M.; Graziano, V.R.; Schmitz, C.O.; et al. Genome-wide CRISPR Screens Reveal Host Factors Critical for SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Cell 2021, 184, 76–91.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Patil, A.; Collings, C.K.; Alfajaro, M.M.; Liang, Y.; Cai, W.L.; Strine, M.S.; Filler, R.B.; DeWeirdt, P.C.; Hanna, R.E.; et al. Pharmacological disruption of mSWI/SNF complex activity restricts SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebendenne, A.; Roy, P.; Bonaventure, B.; Chaves Valadão, A.L.; Desmarets, L.; Arnaud-Arnould, M.; Rouillé, Y.; Tauziet, M.; Giovannini, D.; Touhami, J.; et al. Bidirectional genome-wide CRISPR screens reveal host factors regulating SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV and seasonal HCoVs. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1090–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Moore, M.J.; Vasilieva, N.; Sui, J.; Wong, S.K.; Berne, M.A.; Somasundaran, M.; Sullivan, J.L.; Luzuriaga, K.; Greenough, T.C.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature 2003, 426, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Ge, J.; Yu, J.; Shan, S.; Zhou, H.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor. Nature 2020, 581, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaux, C.A.; Rolain, J.M.; Raoult, D. ACE2 receptor polymorphism: Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2020, 53, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.K.; Jiang, G.S.; Holmes, K.V. Receptor for mouse hepatitis virus is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen family of glycoproteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5533–5536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malireddi, R.K.S.; Kanneganti, T.-D. Chromatin Regulator SMARCA4 Is Essential for MHV-Induced Inflammatory Cell Death, PANoptosis. Viruses 2024, 16, 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081261
Malireddi RKS, Kanneganti T-D. Chromatin Regulator SMARCA4 Is Essential for MHV-Induced Inflammatory Cell Death, PANoptosis. Viruses. 2024; 16(8):1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081261
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalireddi, R. K. Subbarao, and Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti. 2024. "Chromatin Regulator SMARCA4 Is Essential for MHV-Induced Inflammatory Cell Death, PANoptosis" Viruses 16, no. 8: 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081261
APA StyleMalireddi, R. K. S., & Kanneganti, T.-D. (2024). Chromatin Regulator SMARCA4 Is Essential for MHV-Induced Inflammatory Cell Death, PANoptosis. Viruses, 16(8), 1261. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16081261






