The Role of Quorum Sensing in Phage Lifecycle Decision: A Switch Between Lytic and Lysogenic Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
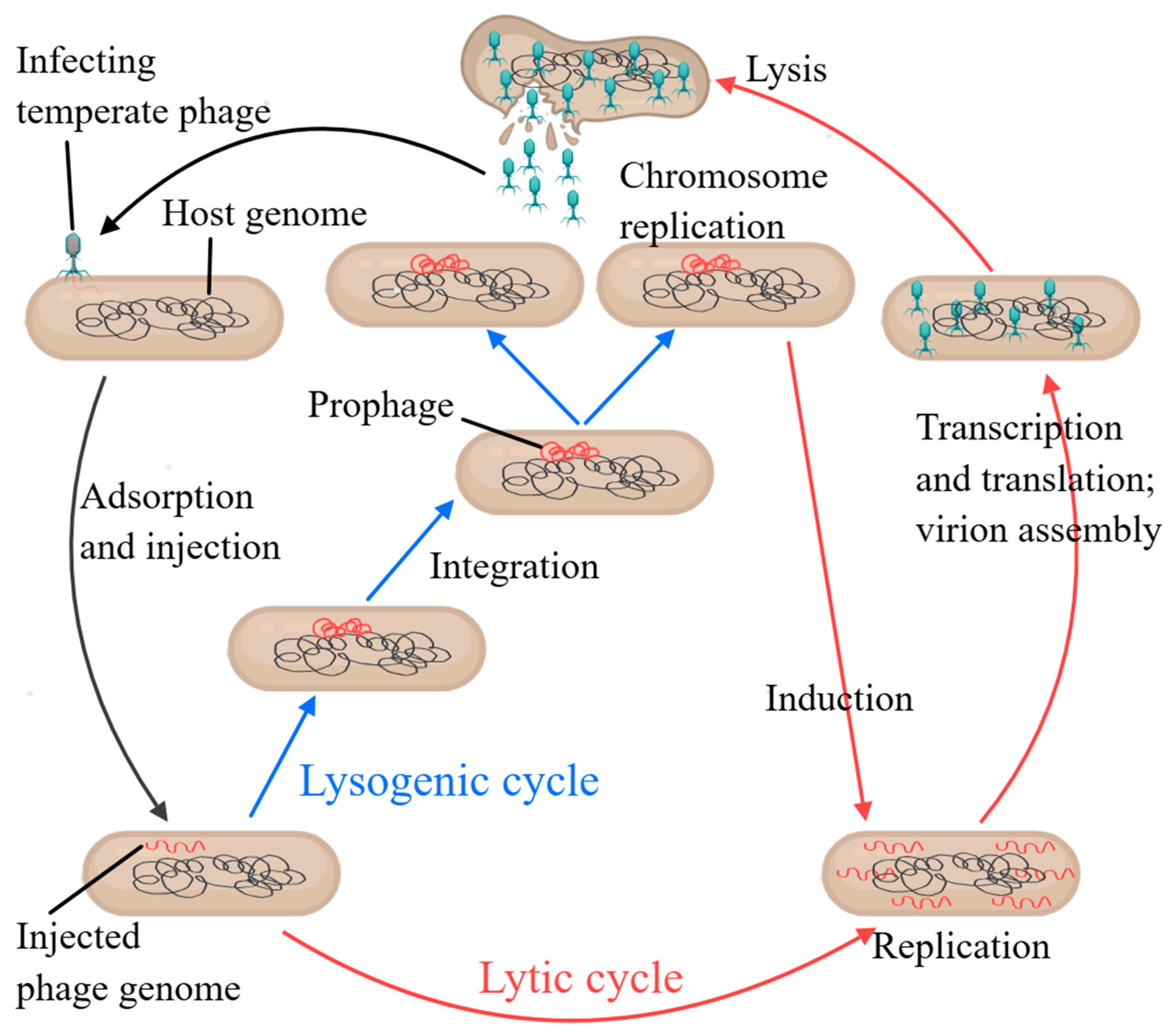
1.1. Definition and Classification of Phages
1.2. Introduction of Quorum Sensing
2. Quorum Sensing in the Interaction Between Phages and Hosts
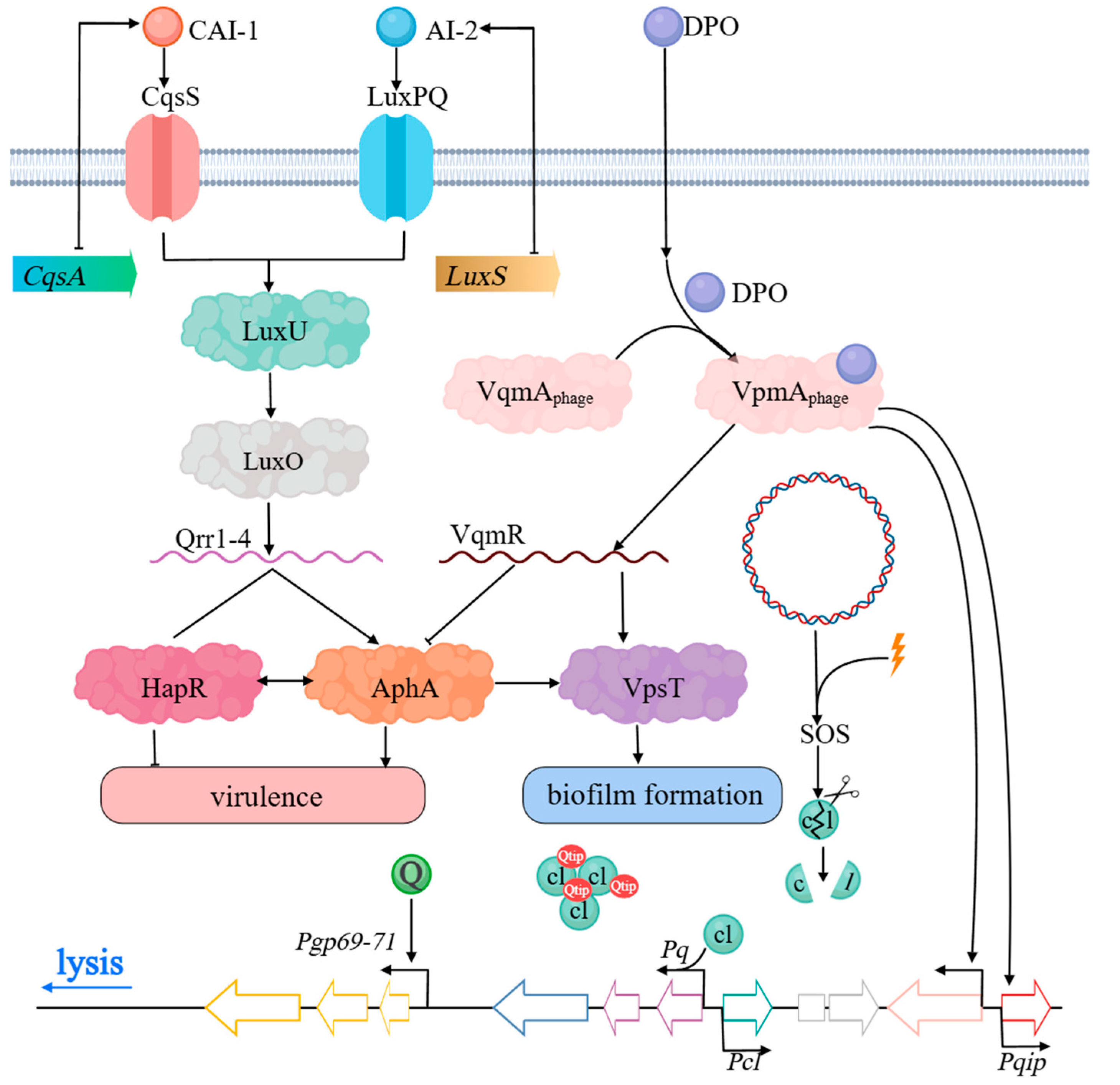
2.1. Information Transfer Between Phage and Host
2.2. Utilization of QS and QQ Receptor Homologs by Phages
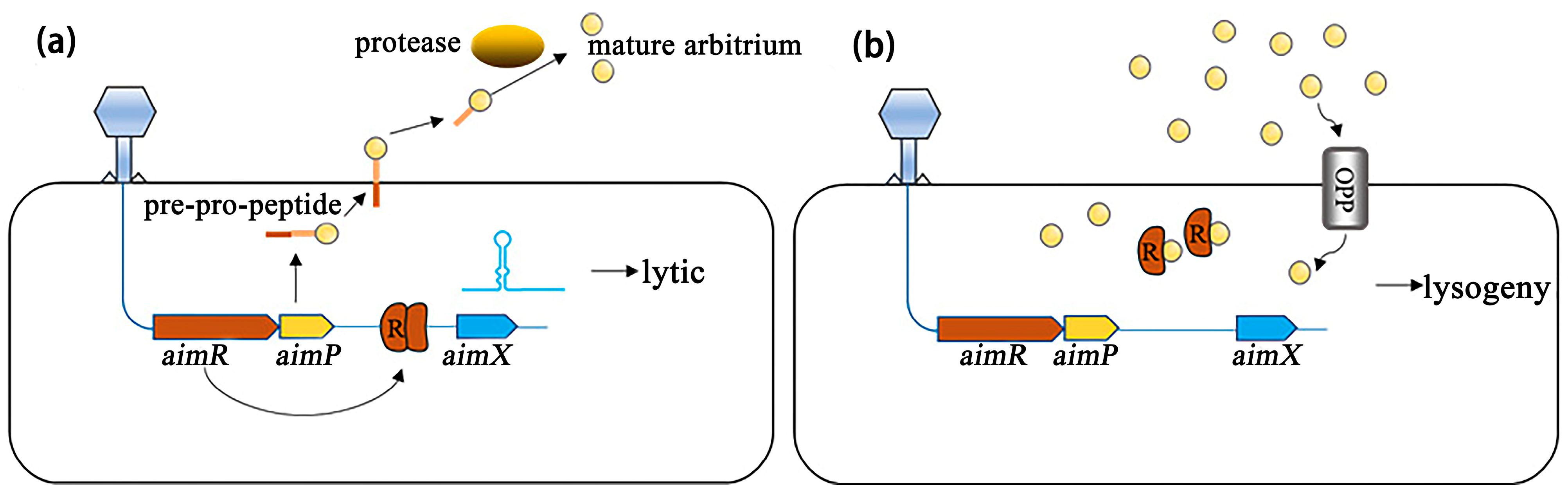
2.3. Arbitrium System: A New Phage–Phage Communication System
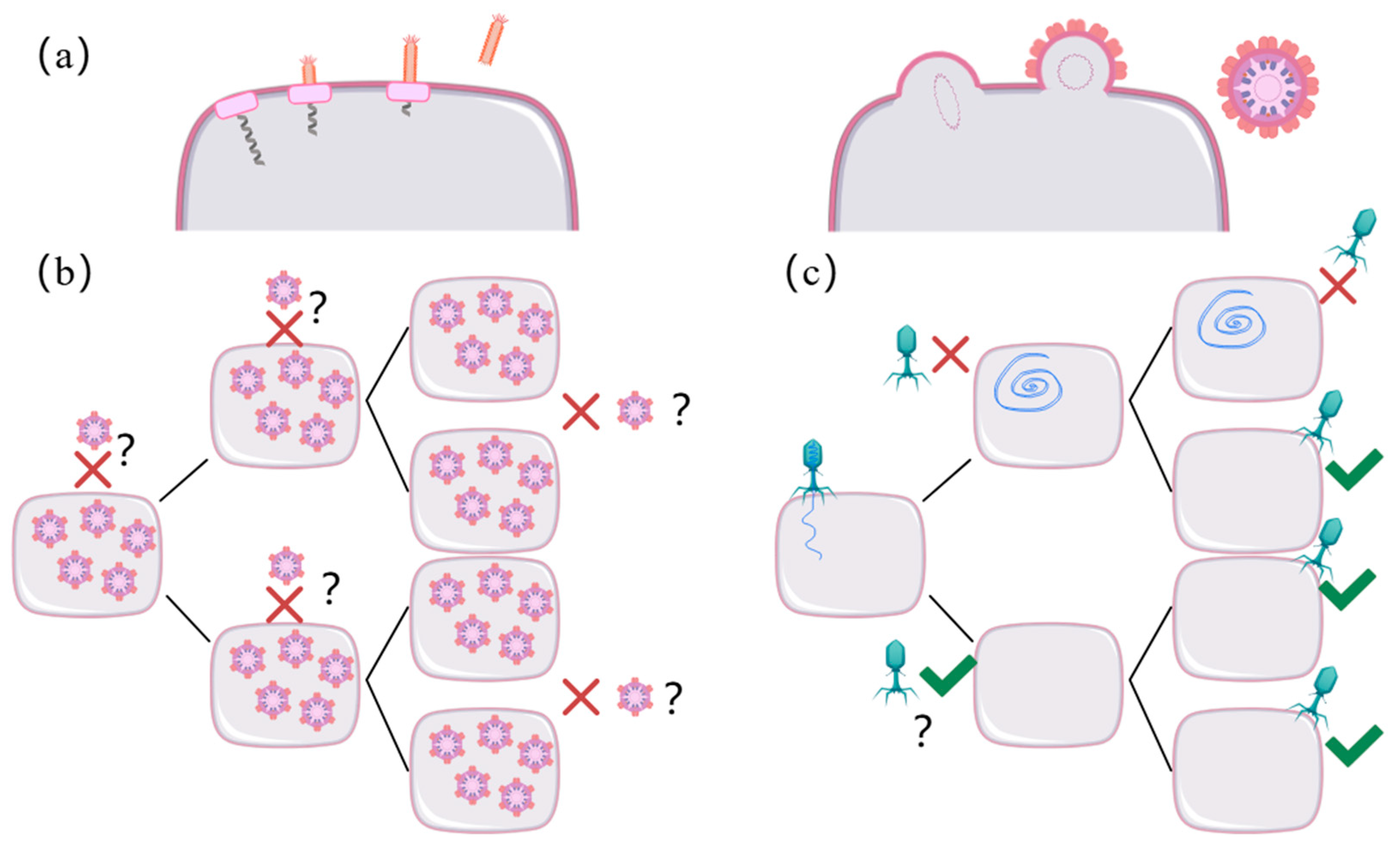
2.4. Specificity and Evolutionary Dynamics of QS in Phage–Host Interactions
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.R.; Fan, H.H.; Tong, Y.G. Unveil the Secret of the Bacteria and Phage Arms Race. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrangou, R.; Fremaux, C.; Deveau, H.; Richards, M.; Boyaval, P.; Moineau, S.; Romero, D.A.; Horvath, P. CRISPR provides acquired resistance against viruses in prokaryotes. Science 2007, 315, 1709–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoux, M.; Laub, M.T. Toxin-Antitoxin Systems as Phage Defense Elements. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 76, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, A.G.; Lindsay, J.A.; Read, T.D. Determinants of Phage Host Range in Staphylococcus Species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00209-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivam, S.; Li, G.L.; Lucia-Sanz, A.; Weitz, J.S. Timescales modulate optimal lysis-lysogeny decision switches and near-term phage reproduction. Virus Evol. 2022, 8, veac037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shotland, Y.; Shifrin, A.; Ziv, T.; Teff, D.; Koby, S.; Kobiler, O.; Oppenheim, A.B. Proteolysis of bacteriophage λ CII by Escherichia coli FtsH (HflB). J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3111–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Mi, J.H.; He, Y.L.; Xuan, G.H.; Wang, J.X.; Li, M.Z.; Tong, Y.G. Quorum sensing inhibits phage infection by regulating biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa PAO1. J. Virol. 2024, 16, e01872-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loenen, W.A.M.; Dryden, D.T.F.; Raleigh, E.A.; Wilson, G.G.; Murray, N.E. Highlights of the DNA cutters: A short history of the restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.A.; McKenzie, R.E.; Fagerlund, R.D.; Kieper, S.N.; Fineran, P.C.; Brouns, S.J.J. CRISPR-Cas: Adapting to change. Science 2017, 356, aal5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoux, M.; Srikant, S.; Teodoro, G.I.C.; Zhang, T.; Littlehale, M.L.; Boron, S.; Badiee, M.; Leung, A.K.L.; Sorek, R.; Laub, M.T. The DarTG toxin-antitoxin system provides phage defence by ADP-ribosylating viral DNA. Nat. Microbiol 2022, 7, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapot-Chartier, M.-P. Interactions of the cell-wall glycopolymers of lactic acid bacteria with their bacteriophages. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobiler, O.; Rokney, A.; Friedman, N.; Court, D.L.; Stavans, J.; Oppenheim, A.B. Quantitative kinetic analysis of the bacteriophage λ genetic network. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4470–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, M.; Wegrzyn, G. Pseudolysogeny. In Advances in Virus Research; Lobocka, M., Szybalski, W.T., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; Volume 82, pp. 339–349. [Google Scholar]
- Suttle, C.A. Marine viruses—Major players in the global ecosystem. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurwitz, B.L.; Hallam, S.J.; Sullivan, M.B. Metabolic reprogramming by viruses in the sunlit and dark ocean. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.L.; Zhang, C.J.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, L.B.; Tang, B.; Wei, Y.L. Isolation and characterization of glacier VMY22, a novel lytic cold-active bacteriophage of Bacillus cereus. Virol. Sin. 2015, 30, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, Z.; Abedon, S.T. Diversity of phage infection types and associated terminology: The problem with ‘Lytic or lysogenic’. Fems Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363, fnw047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Court, D.L.; Oppertheim, A.B.; Adhya, S.L. A new look at bacteriophage λ genetic networks. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatina, A.; Tal, N.; Sorek, R. Abortive Infection: Bacterial Suicide as an Antiviral Immune Strategy. In Annual Review of Virology; Enquist, L., Ed.; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2020; Volume 7, pp. 371–384. [Google Scholar]
- Brady, A.; Felipe-Ruiz, A.; del Sol, F.G.; Marina, A.; Quiles-Puchalt, N.; Penadés, J.R. Molecular Basis of Lysis-Lysogeny Decisions in Gram-Positive Phages. In Annual Review of Microbiology; Gottesman, S., Ed.; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2021; Volume 75, pp. 563–581. [Google Scholar]
- Casjens, S.R.; Hendrix, R.W. Bacteriophage lambda: Early pioneer and still relevant. Virology 2015, 479, 310–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L.T. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.M.; Koskella, B.; Lin, H.C. Phage therapy: An alternative to antibiotics in the age of multi-drug resistance. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 8, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Q.Y.; Trinh, J.T.; Zeng, L.Y. High-resolution studies of lysis-lysogeny decision-making in bacteriophage lambda. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 3343–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranquet, C.; Toussaint, A.; de Jong, H.; Maenhaut-Michel, G.; Geiselmann, J. Control of bacteriophage Mu lysogenic repression. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, K.; Parua, P.K.; Datta, A.B.; Parrack, P. Escherichia coli HflK and HflC can individually inhibit the HflB (FtsH)-mediated proteolysis of λCII in vitro. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 501, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheim, A.B.; Kobiler, O.; Stavans, J.; Court, D.L.; Adhya, S. Switches in bacteriophage lambda development. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2005, 39, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lewis, D.E.A.; Adhya, S. The Developmental Switch in Bacteriophage λ: A Critical Role of the Cro Protein. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Dai, J.J.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, Y.; Tang, F. Mechanisms of interactions between bacteria and bacteriophage mediate by quorum sensing systems. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 2299–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaSarre, B.; Federle, M.J. Exploiting Quorum Sensing To Confuse Bacterial Pathogens. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 73–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Sánchez, I.; Magos-Castro, M.; Guarneros, G. Transcriptional analysis in bacteriophage Fc02 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa revealed two overlapping genes with exclusion activity. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1027380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veses-Garcia, M.; Liu, X.; Rigden, D.J.; Kenny, J.G.; McCarthy, A.J.; Allison, H.E. Transcriptomic Analysis of Shiga-Toxigenic Bacteriophage Carriage Reveals a Profound Regulatory Effect on Acid Resistance in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 8118–8125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundarram, A.; Britton, B.C.; Liu, J.; Desiree, K.; Ogas, R.; Lemaster, P.; Navarrete, B.; Nowakowski, H.; Harrod, M.K.; Marks, D.; et al. Lytic Capacity Survey of Commercial Listeria Phage Against Listeria spp. with Varied Genotypic and Phenotypic Characteristics. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taj, M.K.; Ling, J.X.; Bing, L.L.; Qi, Z.; Taj, I.; Hassani, T.M.; Samreen, Z.; Yunlin, W. Effect of dilution, temperature and pH on the lysis activity of T4 phage against E. coli BL21. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2014, 24, 1252–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, R.; Soberón, N.; Escobedo, S.; Suárez, J.E. Bacteriophage induction versus vaginal homeostasis: Role of H2O2 in the selection of Lactobacillus defective prophages. Int. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Liu, P.; Wu, T.; Guo, S. Genitic information and biological characteristics of mycobacteriophage Chy5. Chin. J. Zoonoses 2020, 36, 462–468. [Google Scholar]
- Ameh, E.M.; Tyrrel, S.; Harris, J.A.; Pawlett, M.; Orlova, E.V.; Ignatiou, A.; Nocker, A. Lysis Performance of Bacteriophages with Different Plaque Sizes and Comparison of Lysis Kinetics After Simultaneous and Sequential Phage Addition. Phage 2020, 1, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, A.; Pardessus, J.; L’Hostis, G.; Fevre, C.; Barc, C.; Dalloneau, E.; Jouan, Y.; Bodier-Montagutelli, E.; Perez, Y.; Thorey, C.; et al. Inhaled bacteriophage therapy in a porcine model of pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa during mechanical ventilation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 3829–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igler, C.; Abedon, S.T. Commentary: A Host-Produced Quorum-Sensing Autoinducer Controls a Phage Lysis-Lysogeny Decision. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingmer, H.; Gerlach, D.; Wolz, C. Temperate Phages of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.W.; Putonti, C. UPΦ phages, a new group of filamentous phages found in several members of Enterobacteriales. Virus Evol. 2020, 6, veaa030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mäntynen, S.; Laanto, E.; Oksanen, H.M.; Poranen, M.M.; Díaz-Muñoz, S.L. Black box of phage-bacterium interactions: Exploring alternative phage infection strategies. Open Biol 2021, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenens, W.; Makumi, A.; Govers, S.K.; Lavigne, R.; Aertsen, A. Viral Transmission Dynamics at Single-Cell Resolution Reveal Transiently Immune Subpopulations Caused by a Carrier State Association. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, J.; Lyons, T.; Heras, V.L.; Recio, M.V.; Gahan, C.G.M.; O’Sullivan, T.P. Investigation of halogenated furanones as inhibitors of quorum sensing-regulated bioluminescence in Vibrio harveyi. Future Med. Chem. 2023, 15, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.T.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, Y.Z.; Zhu, X.; Pan, J.Y. Regulatory Mechanisms and Promising Applications of Quorum Sensing-Inhibiting Agents in Control of Bacterial Biofilm Formation. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 589640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.Y.; Zuo, J.; Wang, H.K.; Grenier, D.; Yi, L.; Wang, Y. Contribution of quorum sensing to virulence and antibiotic resistance in zoonotic bacteria. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 59, 107965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Feng, T.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.H. The Mechanisms and Applications of Quorum Sensing (QS) and Quorum Quenching (QQ). J. Ocean Univ. 2019, 18, 1427–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erez, Z.; Steinberger-Levy, I.; Shamir, M.; Doron, S.; Stokar-Avihail, A.; Peleg, Y.; Melamed, S.; Leavitt, A.; Savidor, A.; Albeck, S.; et al. Communication between viruses guides lysis-lysogeny decisions. Nature 2017, 541, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard-Varona, C.; Hargreaves, K.R.; Abedon, S.T.; Sullivan, M.B. Lysogeny in nature: Mechanisms, impact and ecology of temperate phages. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, C.; Li, Y.Y.; Lopez, P.; Bapteste, E. Beyond arbitrium: Identification of a second communication system in Bacillus phage phi3T that may regulate host defense mechanisms. ISME J. 2021, 15, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, D.; Roy, K.; Williamson, K.E.; Srinivasiah, S.; Wommack, K.E.; Radosevich, M. Acyl-Homoserine Lactones Can Induce Virus Production in Lysogenic Bacteria: An Alternative Paradigm for Prophage Induction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7142–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.-E. Inhibition of N-acyl-homoserine Lactone Quorum Sensing; University of Aberdeen: Aberdeen, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby, M.L.; Hogg, G.D.; Assaad, M.R.; Williamson, K.E. Seasonal trends in lysogeny in an Appalachian oak-hickory forest soil. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e01408-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azimi, S.; Klementiev, A.D.; Whiteley, M.; Diggle, S.P. Bacterial Quorum Sensing During Infection. In Annual Review of Microbiology; Gottesman, S., Ed.; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2020; Volume 74, pp. 201–219. [Google Scholar]
- Coolahan, M.; Whalen, K.E. A review of quorum-sensing and its role in mediating interkingdom interactions in the ocean. Commun. Biol. 2025, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taj, M.K.; Bing, L.L.; Qi, Z.; Ling, J.X.; Taj, I.; Hassani, T.M.; Samreen, Z.; Mangle, A.; Wei, Y.L. Quorum Sensing Molecules Acyl-Homoserine Lactones and Indole Effect on T4 Bacteriophage Production and Lysis Activity. Pak. Vet. J. 2014, 34, 397–399. [Google Scholar]
- Laganenka, L.; Sander, T.; Lagonenko, A.; Chen, Y.; Link, H.; Sourjik, V. Quorum Sensing and Metabolic State of the Host Control Lysogeny-Lysis Switch of Bacteriophage T1. mBio 2019, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossmann, F.S.; Racek, T.; Wobser, D.; Puchalka, J.; Rabener, E.M.; Reiger, M.; Hendrickx, A.P.A.; Diederich, A.K.; Jung, K.; Klein, C.; et al. Phage-mediated Dispersal of Biofilm and Distribution of Bacterial Virulence Genes Is Induced by Quorum Sensing. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyland-Kroghsbo, N.M.; Mærkedahl, R.B.; Lo Svenningsen, S. A Quorum-Sensing-Induced Bacteriophage Defense Mechanism. mBio 2013, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.Y.; Li, T.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, E.H.; Li, W.B.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, H.Y. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of N-Acyl-Homoserine Lactone Analogs of Quorum Sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 948687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.G.; Taylor, V.L.; Bona, D.; Tsao, Y.; Stanley, S.Y.; Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; McCallum, M.; Bondy-Denomy, J.; Howell, P.L.; Nodwell, J.R.; et al. A phage-encoded anti-activator inhibits quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 571–583.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheriff, E.K.; Salvato, F.; Andersen, S.E.; Chatterjee, A.; Kleiner, M.; Duerkop, B.A. Enterococcal quorum-controlled protease alters phage infection. FEMS Microbes 2024, 5, xtae022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, B.K.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing controls biofilm formation in Vibrio cholerae. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.M.; Hansen, M.F.; de Carvalho, L.N.; Roder, H.L.; Burmolle, M.; Middelboe, M.; Svenningsen, S.L. High cell densities favor lysogeny: Induction of an H20 prophage is repressed by quorum sensing and enhances biofilm formation in Vibrio anguillarum. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1731–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croxatto, A.; Pride, J.; Hardman, A.; Williams, P.; Cámara, M.; Milton, D.L. A distinctive dual-channel quorum-sensing system operates in Vibrio anguillarum. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauritzen, J.J.; Sondberg, E.; Kalatzis, P.G.; Roager, L.; Gram, L.; Svenningsen, S.L.; Middelboe, M. Strain-specific quorum-sensing responses determine virulence properties in Vibrio anguillarum. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 25, 1344–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.M.; Lo Svenningsen, S.; Middelboe, M. Quorum Sensing Determines the Choice of Antiphage Defense Strategy in Vibrio anguillarum. mbio 2015, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bru, J.L.; Rawson, B.; Trinh, C.; Whiteson, K.; Hoyland-Kroghsbo, N.M.; Siryaporn, A. PQS Produced by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa Stress Response Repels Swarms Away from Bacteriophage and Antibiotics. J. Bacteriol. 2019, 201, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broniewski, J.M.; Chisnall, M.A.W.; Hoyland-Kroghsbo, N.M.; Buckling, A.; Westra, E.R. The effect of Quorum sensing inhibitors on the evolution of CRISPR-based phage immunity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, P.; Diggle, S.P.; Friman, V.P. Bacterial cell-to-cell signaling promotes the evolution of resistance to parasitic bacteriophages. Ecol. Evol. 2017, 7, 1936–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyland-Kroghsbo, N.M.; Bassler, B.L. Phage Infection Restores PQS Signaling and Enhances Growth of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasI Quorum-Sensing Mutant. J. Bacteriol. 2022, 204, e00557-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, H.; Zimmermann-Kogadeeva, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Sauer, U.; De Smet, J.; Muchez, L.; Lissens, M.; Staes, I.; Voet, M.; Wagemans, J.; et al. Metabolic reprogramming of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by phage-based quorum sensing modulation. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartzkopf, C.M.; Robinson, A.J.; Ellenbecker, M.; Faith, D.R.; Schmidt, A.K.; Brooks, D.M.; Lewerke, L.; Voronina, E.; Dandekar, A.A.; Secor, P.R. Tripartite interactions between filamentous Pf4 bacteriophage, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and bacterivorous nematodes. PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1010925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Zhang, L.H. The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.Y.; Sun, Q.H.; Yang, B.X.; Pan, X.W.; He, Y.; Yang, H.J. Quorum sensing influences phage infection efficiency via affecting cell population and physiological state. J. Basic Microbiol. 2017, 57, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavigne, R.; Lecoutere, E.; Wagemans, J.; Cenens, W.; Aertsen, A.; Schoofs, L.; Landuyt, B.; Paeshuyse, J.; Scheer, M.; Schobert, M.; et al. A Multifaceted Study of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Shutdown by Virulent Podovirus LUZ19. mbio 2013, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friman, V.P.; Ghoul, M.; Molin, S.; Johansen, H.K.; Buckling, A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa adaptation to lungs of cystic fibrosis patients leads to lowered resistance to phage and protist enemies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silpe, J.E.; Bassler, B.L. A Host-Produced Quorum-Sensing Autoinducer Controls a Phage Lysis-Lysogeny Decision. Cell 2019, 176, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kessel, J.C.; Mukherjee, S. Another battle won in the phage-host arms race: Pseudomonas phage blocks quorum sensing regulator LasR. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.P.; He, J.X.; Rahme, L.G. Mutation analysis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa mvfR and pqsABCDE gene promoters demonstrates complex quorum-sensing circuitry. Microbiology 2006, 152, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, G.H.; Lin, H.; Tan, L.; Zhao, G.; Wang, J.X. Quorum Sensing Promotes Phage Infection in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. mbio 2022, 13, e03174-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ho, J.M.L.; Shis, D.L.; Gupta, C.; Long, J.; Wagner, D.S.; Ott, W.; Josic, K.; Bennett, M.R. Tuning the dynamic range of bacterial promoters regulated by ligand-inducible transcription factors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrow, J.M., 3rd; Hudson, L.L.; Wells, G.; Coleman, J.P.; Pesci, E.C. CysB Negatively Affects the Transcription of pqsR and Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal Production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 1988–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Silpe, J.E.; Schramma, K.R.; Cong, J.P.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R.; Bassler, B.L. A Vibrio cholerae autoinducer-receptor pair that controls biofilm formation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silpe, J.E.; Bassler, B.L. Phage-Encoded LuxR-Type Receptors Responsive to Host-Produced Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Autoinducers. mbio 2019, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Zhi, S.X.; Yang, N.; Yang, W.S. Understanding the mechanism of asymmetric gene regulation determined by the VqmA of vibriophage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 558, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silpe, J.E.; Bridges, A.A.; Huang, X.L.; Coronado, D.R.; Duddy, O.P.; Bassler, B.L. Separating Functions of the Phage-Encoded Quorum-Sensing-Activated Antirepressor Qtip. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 27, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.A.; Hawver, L.A.; Ng, W.L. Parallel quorum sensing signaling pathways in Vibrio cholerae. Curr. Genet. 2016, 62, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watve, S.; Barrasso, K.; Jung, S.R.A.; Davis, K.J.; Hawver, L.A.; Khataokar, A.; Palaganas, R.G.; Neiditch, M.B.; Perez, L.J.; Ng, W.L. Parallel quorum-sensing system in Vibrio cholerae prevents signal interference inside the host. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hargreaves, K.R.; Kropinski, A.M.; Clokie, M.R.J. What Does the Talking? Quorum Sensing Signalling Genes Discovered in a Bacteriophage Genome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e0085131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duddy, O.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum Sensing Across Bacterial and Viral Domains. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggers, C.H.; Gray, C.M.; Preisig, A.M.; Glenn, D.M.; Pereira, J.; Ayers, R.W.; Alshahrani, M.; Acabbo, C.; Becker, M.R.; Bruenn, K.N.; et al. Phage-mediated horizontal gene transfer of both prophage and heterologous DNA by φBB-1, a bacteriophage of Borrelia burgdorferi. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftw107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- León-Félix, J.; Villicaña, C. The Impact of Quorum Sensing on the Modulation of Phage-Host Interactions. J. Bacteriol. 2021, 203, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.; Parmar, P.; Rao, P.; Goswami, D.; Saraf, M. Twin Peaks: Presenting the Antagonistic Molecular Interplay of Curcumin with LasR and LuxR Quorum Sensing Pathways. Curr. Microbiol. 2020, 77, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamanikandan, S.; Srinivasan, P. Exploring the selectivity of auto-inducer complex with LuxR using molecular docking, mutational studies and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1131, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, C.; Caumont-Sarcos, A.; Comeau, A.M.; Krisch, H.M. Isolation and genomic characterization of the first phage infecting Iodobacteria: φPLPE, a myovirus having a novel set of features. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, C.; Muras, A.; Romero, M.; López, M.; Tomás, M.; Otero, A. Multiple Quorum Quenching Enzymes Are Active in the Nosocomial Pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC17978. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dela Ahator, S.; Sagar, S.; Zhu, M.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, L.H. Nutrient Availability and Phage Exposure Alter the Quorum-Sensing and CRISPR-Cas-Controlled Population Dynamics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mSystems 2022, 7, e00092-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, K.; Zhang, J.; Zou, T.T.; Liu, Z. AimR Adopts Preexisting Dimer Conformations for Specific Target Recognition in Lysis-Lysogeny Decisions of Bacillus Phage phi3T. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Caballero, S.; Chmielowska, C.; Quiles-Puchalt, N.; Brady, A.; del Sol, F.G.; Mancheño-Bonillo, J.; Felipe-Ruiz, A.; Meijer, W.J.J.; Penadés, J.R.; Marina, A. Antagonistic interactions between phage and host factors control arbitrium lysis-lysogeny decision. Nat. Microbiol 2024, 9, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdugo-Fuentes, A.; Gastélum, G.; Rocha, J.; de la Torre, M. Multiple and Overlapping Functions of Quorum Sensing Proteins for Cell Specialization in Bacillus Species. J. Bacteriol. 2020, 202, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Sol, F.G.; Penadés, J.R.; Marina, A. Deciphering the Molecular Mechanism Underpinning Phage Arbitrium Communication Systems. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiditch, M.B.; Capodagli, G.C.; Prehna, G.; Federle, M.J. Genetic and Structural Analyses of RRNPP Intercellular Peptide Signaling of Gram-Positive Bacteria. In Annual Review of Genetics; Bonini, N.M., Ed.; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2017; Volume 51, pp. 311–333. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, C.; Xiong, J.; Gu, Y.J.; Yin, K.; Wang, J.J.; Hu, Y.H.; Zhou, D.; Fu, X.H.; Qi, S.Q.; Zhu, X.F.; et al. Structural and functional insights into the regulation of the lysis-lysogeny decision in viral communities. Nat. Microbiol 2018, 3, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunny, G.M.; Berntsson, R.P.A. Enterococcal Sex Pheromones: Evolutionary Pathways to Complex, Two-Signal Systems. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guan, Z.Y.; Pei, K.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Yin, P.; Peng, D.H.; Zou, T.T. Structural basis of the arbitrium peptide-AimR communication system in the phage lysis-lysogeny decision. Nat. Microbiol 2018, 3, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokar-Avihail, A.; Tal, N.; Erez, Z.; Lopatina, A.; Sorek, R. Widespread Utilization of Peptide Communication in Phages Infecting Soil and Pathogenic Bacteria. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 746–755.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.Y.; Pei, K.; Wang, J.; Cui, Y.Q.; Zhu, X.; Su, X.; Zhou, Y.B.; Zhang, D.L.; Tang, C.; Yin, P.; et al. Structural insights into DNA recognition by AimR of the arbitrium communication system in the SPbeta phage. Cell Discov. 2019, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Sol, F.G.; Quiles-Puchalt, N.; Brady, A.; Penadés, J.R.; Marina, A. Insights into the mechanism of action of the arbitrium communication system in SPbeta phages. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.B.; Kang, R.; Yu, T.; Jiang, X.J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.P.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.L. Cinnamaldehyde Targets the LytTR DNA-Binding Domain of the Response Regulator AgrA to Attenuate Biofilm Formation of Listeria monocytogenes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00300-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, J.B.; Lion, S.; Buckling, A.; Westra, E.R.; Gandon, S. Regulation of prophage induction and lysogenization by phage communication systems. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, 5046–5051.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abedon, S.T. Look Who’s Talking: T-Even Phage Lysis Inhibition, the Granddaddy of Virus-Virus Intercellular Communication Research. Viruses 2019, 11, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.B.; Liu, J.H.; Liu, C.J.; Yang, A.D.; Qiao, J.J. Quorum sensing for population-level control of bacteria and potential therapeutic applications. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1319–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laganenka, L.; Sourjik, V. Bacterial Quorum Sensing Signals at the Interdomain Interface. Isr. J. Chem. 2023, 63, e202200080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, C.M.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. In Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2005; Volume 21, pp. 319–346. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.B.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55, 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silpe, J.E.; Duddy, O.P.; Bassler, B.L. Natural and synthetic inhibitors of a phage-encoded quorum-sensing receptor affect phage-host dynamics in mixed bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2217813119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housby, J.N.; Mann, N.H. Phage therapy. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Yadav, A. Synthetic phage and its application in phage therapy. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2023, 200, 61–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, Z.C.; Mao, Z.Z.; Tang, M.R.; Chen, H.C.; Qian, C.R.; Zeng, W.L.; Zhou, T.L.; Wu, Q. Quorum sensing gene lasR promotes phage vB_Pae_PLY infection in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, D.P.; Melo, L.D.R.; Azeredo, J. Understanding the Complex Phage-Host Interactions in Biofilm Communities. In Annual Review of Virology; Enquist, L.W., Ed.; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2021; Volume 8, pp. 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Coughlan, L.M.; Briandet, R.; Cotter, P.D. Biofilms in Food Processing Environments: Challenges and Opportunities. In Annual Review of Food Science and Technology; Doyle, M.P., McClements, D.J., Eds.; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2019; Volume 10, pp. 173–195. [Google Scholar]
- Chevallereau, A.; Pons, B.J.; van Houte, S.; Westra, E.R. Interactions between bacterial and phage communities in natural environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, Y. The Role of Quorum Sensing in Phage Lifecycle Decision: A Switch Between Lytic and Lysogenic Pathways. Viruses 2025, 17, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030317
Shang J, Wang K, Zhou Q, Wei Y. The Role of Quorum Sensing in Phage Lifecycle Decision: A Switch Between Lytic and Lysogenic Pathways. Viruses. 2025; 17(3):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030317
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Junjie, Kehan Wang, Qian Zhou, and Yunlin Wei. 2025. "The Role of Quorum Sensing in Phage Lifecycle Decision: A Switch Between Lytic and Lysogenic Pathways" Viruses 17, no. 3: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030317
APA StyleShang, J., Wang, K., Zhou, Q., & Wei, Y. (2025). The Role of Quorum Sensing in Phage Lifecycle Decision: A Switch Between Lytic and Lysogenic Pathways. Viruses, 17(3), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17030317






